- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Darwin’s Theory презентация
Содержание
- 1. Darwin’s Theory
- 2. Charles Robert Darwin Charles Robert Darwin (12
- 3. Darwin published his theory with some
- 4. However, many favoured competing explanations and it was
- 5. The journey on the Beagle The Beagle
- 6. The possibility of working, during the journey
- 7. Thanks to those studies Darwin began detailed
- 8. Darwin’s Work Darwin's work established evolutionary descent
- 9. How Darwin conceived his idea He based
- 10. Direct Observation
- 11. The first evidence is the direct observation.
- 12. To explain the second case, we could talk about the Biston Betularia.
- 13. Biston betularia is a white moth, which
- 14. Why? Because the trees, contaminated by smokes,
- 15. Biogeography The second evidence is biogeography. Darwin
- 16. Fossils
- 17. The third evidence were fossils. During
- 18. Homologous Structures The fourth evidence was the
- 19. An Incompleted Theory Darwin lacked of precision,
- 20. THE END
Слайд 2Charles Robert Darwin
Charles Robert Darwin (12 February 1809 – 19 April
Слайд 3 Darwin published his theory with some evidence for evolution in his
Слайд 4However, many favoured competing explanations and it was not until the emergence
In modified form, Darwin's scientific discovery is the unifying theory of the life sciences, explaining the diversity of life.
Слайд 5The journey on the Beagle
The Beagle was a ship used for
Слайд 6The possibility of working, during the journey directly on the field,
Слайд 7Thanks to those studies Darwin began detailed investigations and in 1838
He was writing up his theory in 1858 when Alfred Russel Wallace sent him an essay which described the same idea, prompting immediate joint publication of both of their theories.
Слайд 8Darwin’s Work
Darwin's work established evolutionary descent with modification as the dominant
In 1871 he examined human evolution and sexual selection in The Descent of Man, and Selection in Relation to Sex, followed by The Expression of the Emotions in Man and Animals.
Слайд 9How Darwin conceived his idea
He based his theory on fourth different
Direct Observation
Biogeography
Fossils
Homologous Structures
Слайд 11The first evidence is the direct observation. The first object of
Слайд 13Biston betularia is a white moth, which lives in Manchester. In
Slowly the white moth was replaced by the black moth.
Слайд 14Why? Because the trees, contaminated by smokes, had become black, and
Слайд 15Biogeography
The second evidence is biogeography. Darwin had noticed that in the
Слайд 17The third evidence were fossils. During his journey on the Beagle,
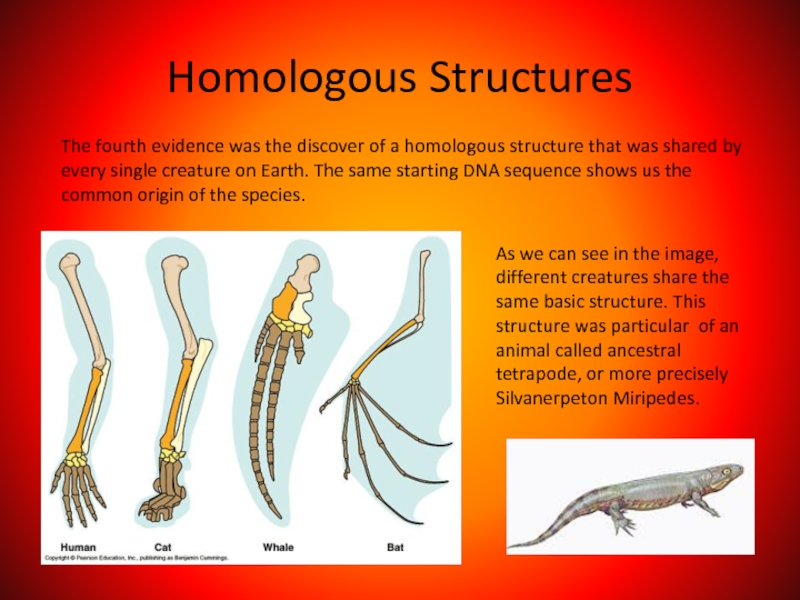
Слайд 18Homologous Structures
The fourth evidence was the discover of a homologous structure
As we can see in the image, different creatures share the same basic structure. This structure was particular of an animal called ancestral tetrapode, or more precisely Silvanerpeton Miripedes.