- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Contract Risk Management for Engineering Contractors презентация
Содержание
- 1. Contract Risk Management for Engineering Contractors
- 2. © BARRY ORR Pre-Contract Introduction Trends in
- 3. © BARRY ORR Reasons for Developing a
- 4. © BARRY ORR Trends in the Transference
- 5. © BARRY ORR Risk Assessment Identification of
- 6. © BARRY ORR Pre-contract Errors No structured
- 7. © BARRY ORR TO BID OR NOT
- 8. © BARRY ORR Sales Strategy Reasons for
- 9. © BARRY ORR Sales Strategy (Cont.) Agents
- 10. © BARRY ORR Pre-contract Errors No structured
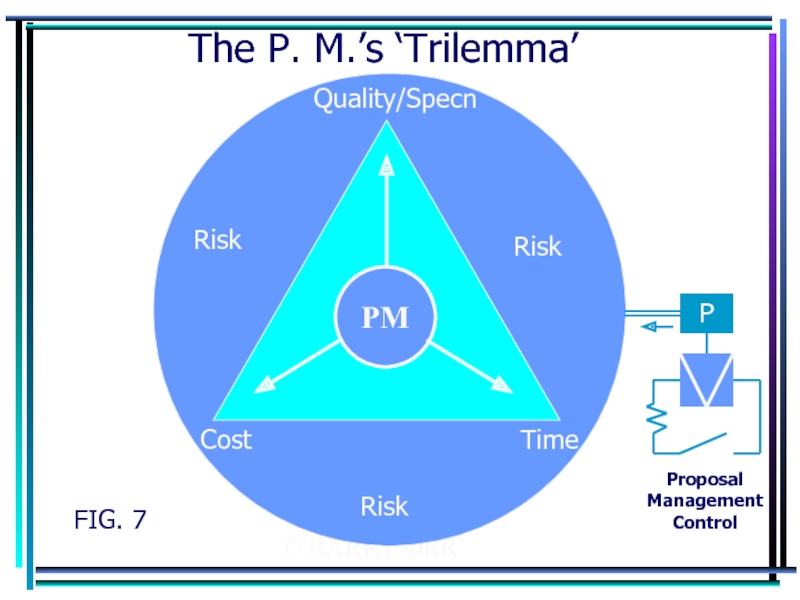
- 11. © BARRY ORR The P. M.’s ‘Trilemma’ FIG. 7
- 12. © BARRY ORR Pre-contract Errors No structured
- 13. © BARRY ORR Some reasons why we
- 14. © BARRY ORR Essential elements of CRMP
- 15. © BARRY ORR CRMP IS NOT ANTI-SELL
- 16. © BARRY ORR Tender Approval Procedure Tender
- 17. © BARRY ORR Essentials of our Risk
- 18. © BARRY ORR What is a fair
- 19. © BARRY ORR Areas Addressed in our
- 20. © BARRY ORR
- 21. © BARRY ORR
- 22. © BARRY ORR
- 23. © BARRY ORR
- 24. © BARRY ORR
- 25. © BARRY ORR Corrected Risk Provision Calculation
- 26. © BARRY ORR The Negotiation One leader
- 27. © BARRY ORR Re-allocation of Risk Longer
- 28. Contract Risk Management for Engineering Contractors Part 2: Post-contract
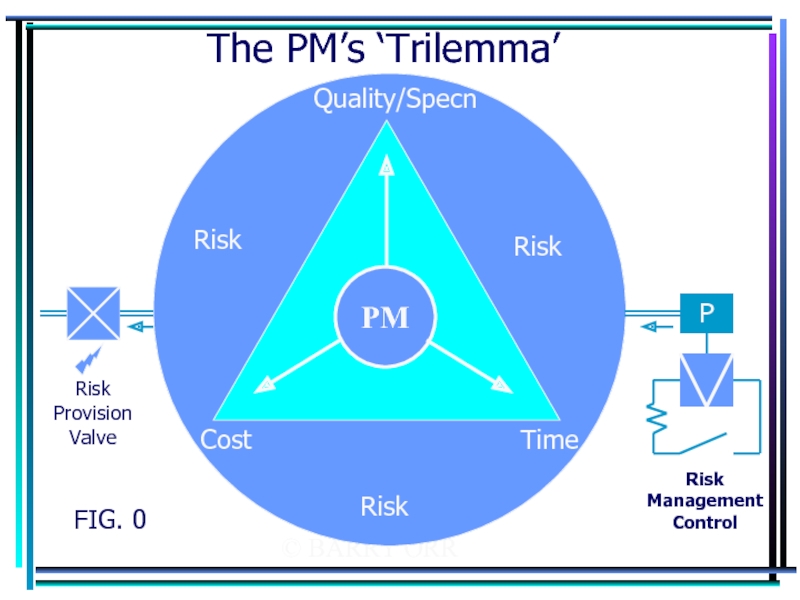
- 29. © BARRY ORR The PM’s ‘Trilemma’ FIG. 0
- 30. © BARRY ORR Post-contract Errors Inadequate attention
- 31. © BARRY ORR Contract Start-up Meeting Internal
- 32. © BARRY ORR Contract Start-up Meeting Internal
- 33. © BARRY ORR Contract Start-up Meeting With
- 34. © BARRY ORR Post-contract Errors Inadequate attention
- 35. © BARRY ORR Risk management – Key
- 36. © BARRY ORR Essential Elements of a
- 37. © BARRY ORR Contract Administration Full time
- 38. © BARRY ORR Control of Quality Quality
- 39. © BARRY ORR Safety and Operability Reviews
- 40. © BARRY ORR HAZOP Study Reviews Review
- 41. © BARRY ORR Contract Reporting (Part 1)
- 42. © BARRY ORR Contract Reporting (Part 2)
- 43. © BARRY ORR Contract Reporting (Part 3)
- 44. © BARRY ORR Principal objectives of a
- 45. © BARRY ORR Contract Audit Principles Impartial
- 46. © BARRY ORR Preparations for Audit Develop
- 47. © BARRY ORR Audit Execution - Presale
- 48. © BARRY ORR Audit Execution – Start-up
- 49. © BARRY ORR Audit Execution – Contract
- 50. © BARRY ORR Contract Close-out and final
- 51. © BARRY ORR The contractors 12-point plan
Слайд 1Contract Risk Management for Engineering Contractors
J. Barry Orr MBE
BEng (Hons), CEng,
Слайд 2© BARRY ORR
Pre-Contract
Introduction
Trends in the Transference of Risk
Principal causes of loss
Essential
FIG. 1
Слайд 3© BARRY ORR
Reasons for Developing a Comprehensive CRMP
Risk management is a
Clients were transferring more risk to contractors
Some risks were not being identified early enough
The result was profit erosion after the point of sale
Project managers were blamed for profit erosion
‘Disaster’ contracts were endangering the company
FIG. 2
Слайд 4© BARRY ORR
Trends in the Transference of Risk
Tighter prices for the
Lump sum fixed prices were normal
Technical change is accelerating – innovation
Plant performance tests more onerous
Trends towards re-vamping existing plants
Novelty of client, country, culture, language, applicable law
Clients becoming more commercially skilled
Contract terms becoming more onerous
Clients want predictability of cost, time, performance and return on investment
FIG. 3
Слайд 5© BARRY ORR
Risk Assessment
Identification of risks
Response
Rejection
Amelioration
Transference
Acceptance
Analysis of accepted risks
Provisions/contingencies for accepted
FIG. 4
Слайд 6© BARRY ORR
Pre-contract Errors
No structured objective enquiry acceptance procedure
Inadequate quality of
Inadequate priority in staffing the proposal team
Inadequate involvement of senior management
Inexperienced proposal management
No structured tender approval procedure
Inadequate/inappropriate contract conditions
Failure to control the negotiation
FIG. 5
Слайд 7© BARRY ORR
TO BID OR NOT TO BID
Are sufficient resources available?
Has
Are the ITB conditions compatible with the CRMP?
What are the chances of success?
Does client relationship demand that we bid?
FIG. 6
The above questions are addressed at the Enquiry Acceptance Meeting
Слайд 8© BARRY ORR
Sales Strategy
Reasons for bidding
The winning features of the bid
Importance
Project execution strategy
Commercial and financial aspects
Strategic alliances and the reasons for these
Government involvement
Client contacts
FIG. 6(a)
Слайд 9© BARRY ORR
Sales Strategy (Cont.)
Agents
Counter trade
Competition
Contractor’s weaknesses and strengths
Proposal documentation
Pricing
Tender evaluation
Visits to client pre-tender
FIG. 6(b)
Слайд 10© BARRY ORR
Pre-contract Errors
No structured objective enquiry acceptance procedure
Inadequate quality of
Inadequate priority in staffing the proposal team
Inadequate involvement of senior management
Inexperienced proposal management
No structured tender approval procedure
Inadequate/inappropriate contract conditions
Failure to control the negotiation
FIG. 5
Слайд 12© BARRY ORR
Pre-contract Errors
No structured objective enquiry acceptance procedure
Inadequate quality of
Inadequate priority in staffing the proposal team
Inadequate involvement of senior management
Inexperienced proposal management
No structured tender approval procedure
Inadequate/inappropriate contract conditions
Failure to control the negotiation
FIG. 5
Слайд 13© BARRY ORR
Some reasons why we take bad contracts
We do not
The effects of novelty in all its forms
The ability to justify a ‘thin’ estimate
Self delusion in avoiding under recovery/redundancies
Occasional technical weakness of our selling position
Inconsistencies/conflict in the contract documentation
The dangers in the ‘thrill of the chase’
The many other potential risks in a particular contract
FIG. 8
Слайд 14© BARRY ORR
Essential elements of CRMP – Pre-contract
Enquiry acceptance procedure
Tender approval
Risk assessment and analysis
Contract start-up procedures
Contract control procedures for time, cost, quality/specification
Contract review and reporting procedures
Staff training and development
Contract auditing system
Contract close-out reports
FIG. 9
Слайд 15© BARRY ORR
CRMP
IS NOT ANTI-SELL
IT IS INTENDED TO ENSURE:
OBJECTIVITY
CONSISTENCY
HONESTY
And
TO AVOID SELF-DELUSION
FIG.
Слайд 16© BARRY ORR
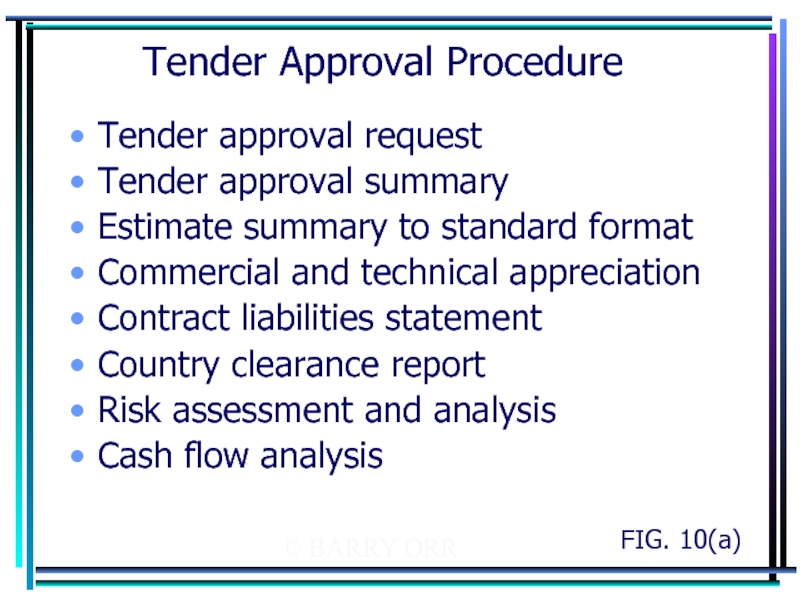
Tender Approval Procedure
Tender approval request
Tender approval summary
Estimate summary to
Commercial and technical appreciation
Contract liabilities statement
Country clearance report
Risk assessment and analysis
Cash flow analysis
FIG. 10(a)
Слайд 17© BARRY ORR
Essentials of our Risk Analysis
Based on collective experience of
Maximum experience should be assembled
Participants need a common thought process – standardisation
Complete in one session
Address maximum number of elements of the estimate
Set a standard acceptable level of probability of breaking even
Simple and quick to operate and adjust
Market situation must not affect it
FIG. 11
Слайд 18© BARRY ORR
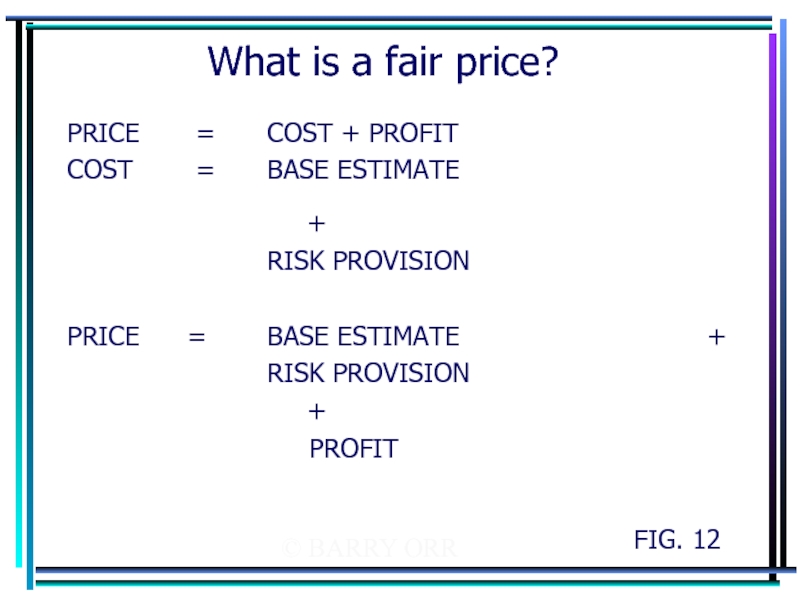
What is a fair price?
PRICE = COST + PROFIT
COST
+
RISK PROVISION
PRICE = BASE ESTIMATE +
RISK PROVISION
+
PROFIT
FIG. 12
Слайд 19© BARRY ORR
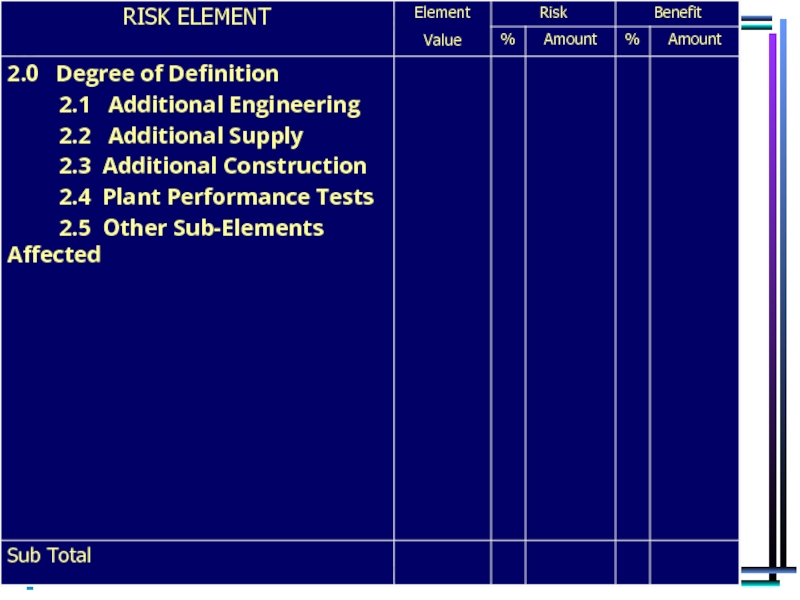
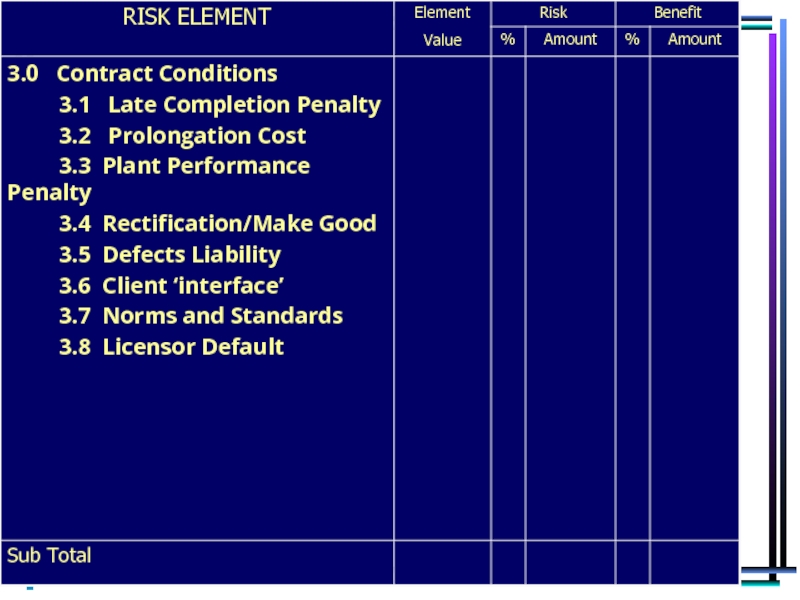
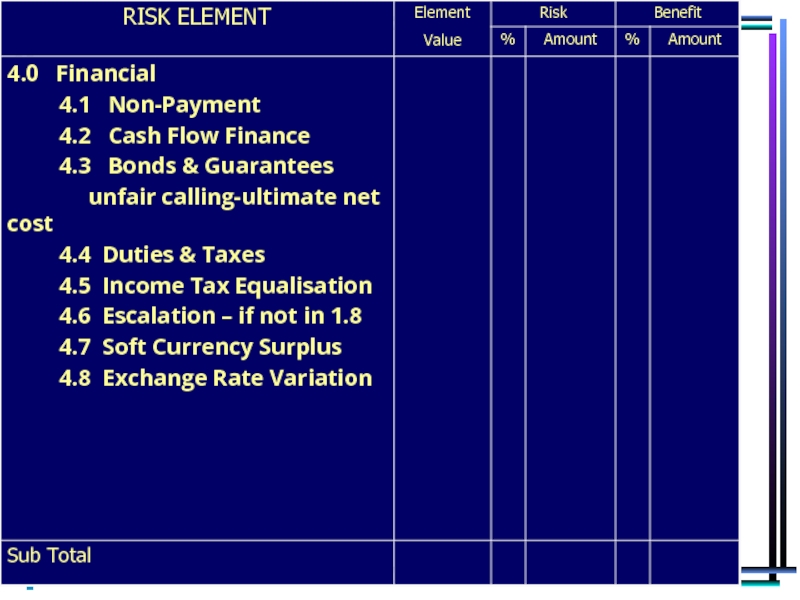
Areas Addressed in our Risk Analysis
Estimating accuracy – all
Degree of definition – impact on activities
Contract conditions – risk areas
Financial risks in contract execution
Siteworks risks – if not covered above
FIG. 13
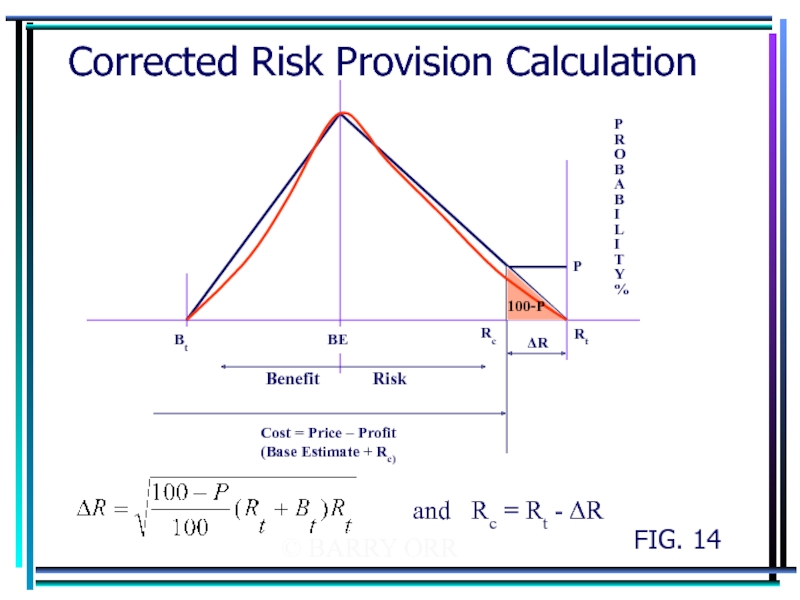
Слайд 26© BARRY ORR
The Negotiation
One leader and decision-maker and small team
Prepare and
Retain the support of vendors and subcontractors
Share the ‘pain of concessions’
Continually update the risk analysis
Negotiate reallocation of risk
Data base for evaluation of scope changes
Achieve a fair/acceptable deal or walk away
Seek reapproval before settling
FIG. 15
Слайд 27© BARRY ORR
Re-allocation of Risk
Longer project schedule
Relax plant performance criteria
Reduce liquidated
Reduce defects liability period
Early freeze date for basic engineering
Apply international design standards
Client to provide insurance cover
Improve terms of payment
Relax bonds and guarantees
Client responsibility for duties and taxes
Client accepts tender-to-contract exchange rate risk
FIG. 16
Слайд 30© BARRY ORR
Post-contract Errors
Inadequate attention to contract start-up
Inexperienced Project Management
Inadequate authority
Inadequate control procedures
Inadequate reporting and forecasting
Inadequate Risk Management strategies
Poor Contract Administration
Inadequate Involvement of Senior Management
FIG. 1
Слайд 31© BARRY ORR
Contract Start-up Meeting
Internal 1
Background to the project
The sales process:
Enquiry
Development of the proposal
Assumed contract execution strategy
The as-sold estimate
The contract programme
Tender acceptance documentation
Finally negotiated scope and responsibilities
Details of contract documentation
Client personnel and relationships
Third parties involved
Meeting led by Chief Sales executive
Preliminary handover to Operations
FIG. 2
Слайд 32© BARRY ORR
Contract Start-up Meeting
Internal 2
Introduction of key members of team
Confirmation
P.M.’s view of risk analysis
Strategy for execution and risk management
Responsibilities of each discipline
Cost control budget
Contract programme
Quality plan
Meeting led by Project Manager
Final take-over by Operations
FIG. 3
Слайд 33© BARRY ORR
Contract Start-up Meeting
With Client
As-sold scope
Project administration procedures
Contract variation procedure
Client
Reporting and review meetings
Basic design freeze dates
Client involvement and lines of communication
Training requirements
To set the ground rules for the contract
FIG. 4
Слайд 34© BARRY ORR
Post-contract Errors
Inadequate attention to contract start-up
Inexperienced Project Management
Inadequate authority
Inadequate control procedures
Inadequate reporting and forecasting
Inadequate Risk Management strategies
Poor Contract Administration
Inadequate Involvement of Senior Management
FIG. 1
Слайд 35© BARRY ORR
Risk management – Key Requirements
PM to review risk provision
PM to develop strategies for each area of risk
PM reviews strategies regularly (monthly)
PM repeats risk analysis monthly
Application of QA reduces risk
Operational audits on contracts confirm strategies
FIG. 5
Слайд 36© BARRY ORR
Essential Elements of a CRMP
Enquiry acceptance procedure
Tender approval procedures
Risk
Contract start-up procedures
Contract control procedures for time; cost; quality/specification
Contract review and reporting procedures
Staff training and development
Contract auditing system
Contract close-out reports
FIG. 6
Слайд 37© BARRY ORR
Contract Administration
Full time contract administrator
Detailed records and computerised retrieval
Credit control
Contract variations and change control
Site controls and record keeping
Daily diaries
As-built programmes and drawings
Minutes of meetings
Dated progress photographs
Site instructions and valuations
Weather and lost time records
FIG. 7
Слайд 38© BARRY ORR
Control of Quality
Quality plan should be part of contract
Apply quality assurance – BS5750 (Part 1), ISO 9001
Engineering
Procurement
Construction
Vendors
Subcontractors
Familiarity with quality manual
Apply technical audits to engineering
Implement quality control through inspection
FIG. 8
Слайд 39© BARRY ORR
Safety and Operability Reviews
HAZOP studies
Qualitative and systematic
Based on PFDs
HAZAN studies
Quantitative
Based on fault tree analysis for major hazards
Engineering safety reviews
Checklist method
Based on protection systems, site plans and area classification
FIG. 9
Слайд 40© BARRY ORR
HAZOP Study Reviews
Review 1
Proposal stage
Safeguards the estimate
Review 2
Soon after
Basic engineering confirmed
Review 3
Major review after basic engineering
Provides sound basis for detail design
Review 4
Prior to AFC stage
Provides sound basis for construction
Review 5
Prior to commissioning
Provides final assurance that plant as built is fit for commissioning
FIG. 10
Слайд 41© BARRY ORR
Contract Reporting (Part 1)
Internal PM’s Monthly Report
Executive Summary
Contract Financial
Progress Summaries – E, P, C1, C2
Claims Analysis
Areas of Concern
Risk Management Strategies
FIG. 11
Слайд 42© BARRY ORR
Contract Reporting (Part 2)
Report to client – lump sum
General description of scope including plant layout
Management summary
Areas of concern
Major events in the period
Schedule review
Commercial review
Engineering/technical review
Procurement/manufacturing review
Construction/commissioning review
FIG. 12
Слайд 43© BARRY ORR
Contract Reporting (Part 3)
Report to client – Management reimbursable
Project Director’s executive summary
Expenditure and commitment reports with ‘S’ curves
Approved budget changes report
Current budget.forecast variation report
Escalation report
Risk provisions review
Cash flow report
Detailed progress for E, P, C1 & C2
Force report
Photographic record of site progress
FIG. 13
Слайд 44© BARRY ORR
Principal objectives of a contract audit
Compliance with the CRMP
Adequacy
Assess risk management strategies
Carry out current risk analysis
Produce cost report and profit forecast
Recommend corrective actions/solutions
FIG. 14
Слайд 45© BARRY ORR
Contract Audit Principles
Impartial and objective
Competent audit team
Authority from Main
Comprehensive scope from enquiry receipt to time now
FIG. 15
Слайд 46© BARRY ORR
Preparations for Audit
Develop standard interrogation procedure
Set up standard format
Follow audit trail from first contact with client to time now
Advise parties in advance of documentation to be available
FIG. 16
Слайд 47© BARRY ORR
Audit Execution - Presale
Full overview briefing by project manager
Interrogation
Interrogation of proposals
Interrogation of estimating
Check risk analysis presale
Check tender approval submission
Review changes during negotiation
Check final approval
Review commercial contract
FIG. 17
Слайд 48© BARRY ORR
Audit Execution – Start-up
Check handover procedure from proposals to
Review preliminary contract instructions
Review as-sold scope documentation
Review minutes of start-up meeting no.2
Review final contract instructions
Review minutes of start-up meeting with client
Review initial staffing of contract
FIG. 18
Слайд 49© BARRY ORR
Audit Execution – Contract Management
Controls for:
Time
Cost
Quality/specification
Cash management
Site controls –
Control of vendors/subcontractors
Client involvement
Risk identification and management
Contract financial status report – including risk analysis
FIG. 19
Слайд 50© BARRY ORR
Contract Close-out and final actions
Progressive dismantling of task force
Staff
Re-entry to home office organisation
Agree outstanding claims from/on client and subcontractors
Confirm final acceptance by client
Recover bonds and guarantees
Invoice for remaining retentions
Produce final contract financial status report
Write close-out report
FIG. 20
Слайд 51© BARRY ORR
The contractors 12-point plan for project success
Formal enquiry acceptance
Tight proposal management
Comprehensive risk assessment and analysis
Standardised tender approval procedure
Thorough preparation for and discipline during negotiations
Avoid pitfalls with ‘Letter of Intent’. And implement a formal contract start-up procedure
Effective contract administration and application of time/cost/quality controls from Part (1)
Accelerate design whenever possible to create float in the programme
Apply risk management strategies including regular technical, managerial and safety audits and reviews
Site construction requirements to be paramount – locate project manager on site
Thorough preparation for systematic handover to client and expeditious completion of plants/systems performance tests, and monitoring of client operations post handover
Comprehensive close-out of project including obtaining outstanding retention/bonds, settling claims and issuing internal close-out report
FIG. 21