- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Viral hepatitis презентация
Содержание
- 1. Viral hepatitis
- 2. Viral hepatitis is a group of etiologically
- 3. The problem of viral hepatitis remains the
- 4. At present following viruses, causing viral hepatitis
- 5. LIVER DISEASE CATEGORIES
- 8. Causes of Acute Hepatitis
- 9. Causes of Chronic Hepatitis Abbreviations: NAFLD:
- 10. Clinical Stages Incubation Period - the time
- 11. Human Hepatitis Viruses Human Hepatitis Viruses
- 12. Clinical Spectrum Subclinical Infection – serologic and
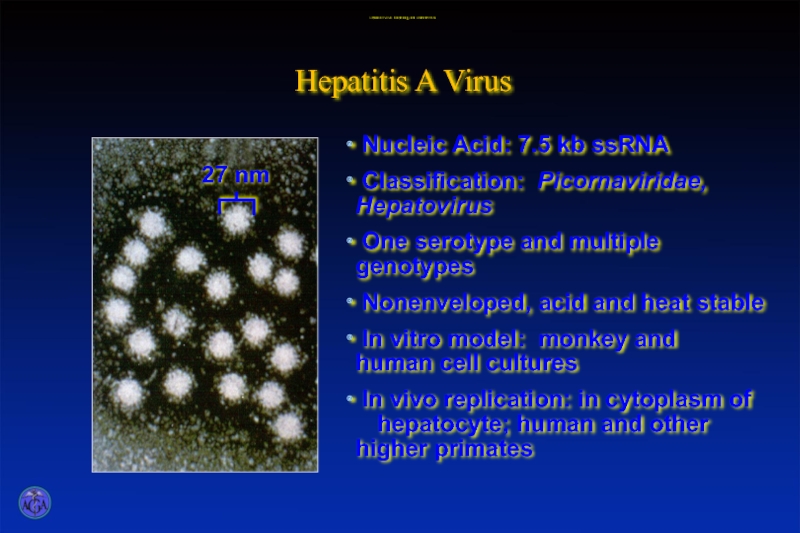
- 13. Hepatitis A Virus Hepatitis A Virus: Morphology and Characteristics
- 14. Hepatitis A Virus
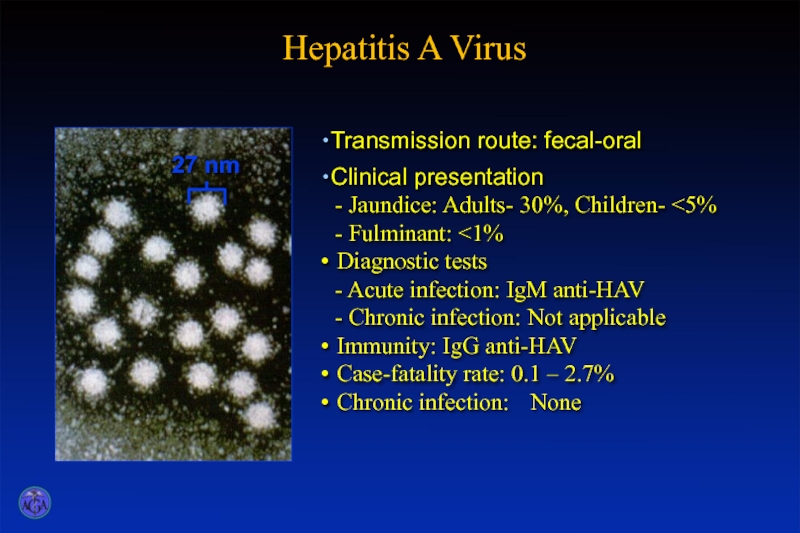
- 15. Hepatitis A Virus
- 16. Epidemiology 1. Transmission: fecal-oral a)
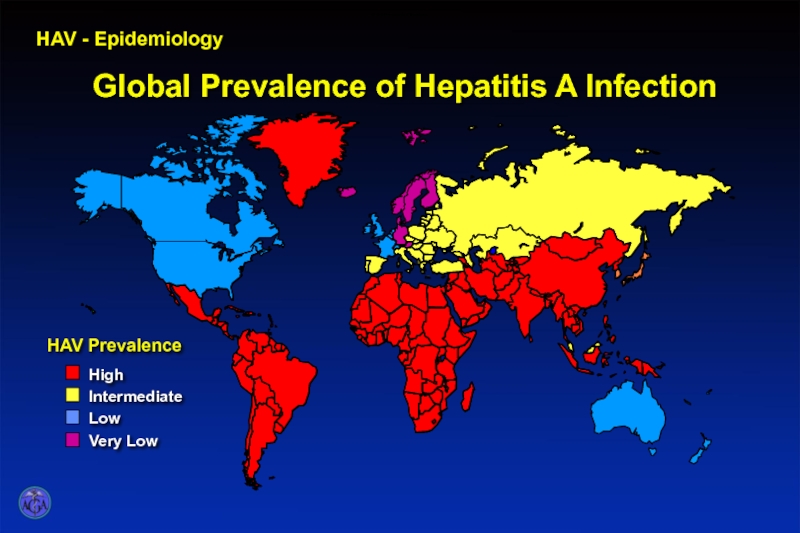
- 17. HAV - Epidemiology Global Prevalence of Hepatitis A
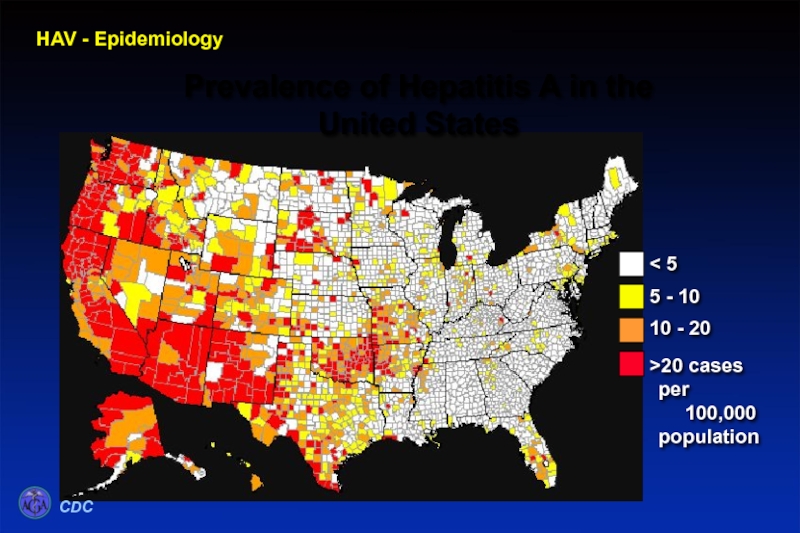
- 18. HAV - Epidemiology Prevalence of
- 19. Routes of Hepatitis A Transmission HAV - Epidemiology
- 20. Typical Serologic Course of Acute Hepatitis A
- 21. Age-specific Incidence of Hepatitis A HAV
- 22. Clinical Features of Hepatitis A Transmission
- 23. Clinical Features of Hepatitis A Jaundice Adults-30% Children-
- 24. Hepatitis E Virus Hepatitis E Virus: Morphology and Characteristics
- 25. Hepatitis E Epidemiology
- 26. Hepatitis E Epidemiology
- 27. Hepatitis E Clinical Characteristics
- 28. Clinical Features of Hepatitis E Transmission
- 29. Hepatitis E Course of Acute Infection
- 30. Clinical Features of Hepatitis E Fulminant
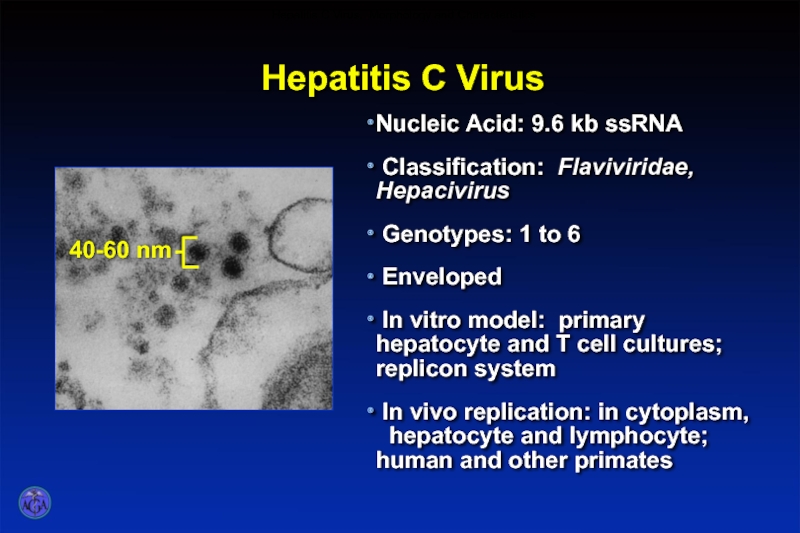
- 31. Hepatitis C Virus Hepatitis C Virus: Morphology and Characteristics
- 32. Prevalence HCV - Epidemiology Alter MJ et
- 33. HCV - Epidemiology Terrault NA, Hepatology 2002
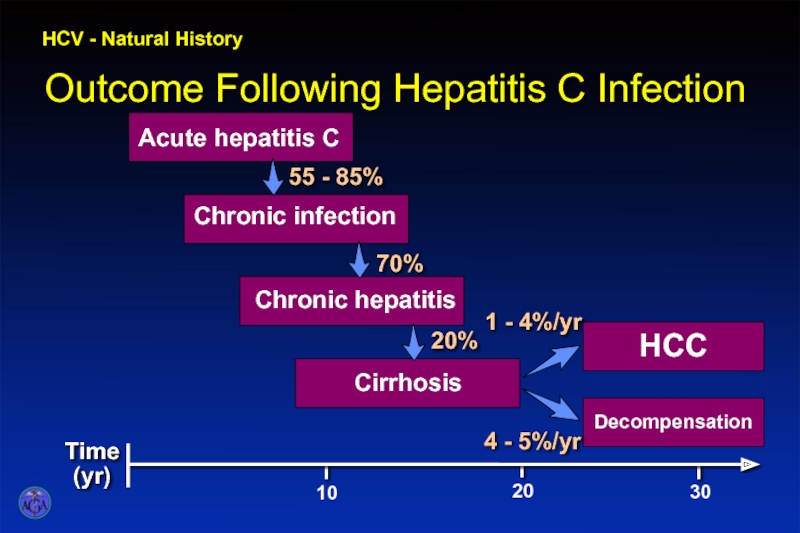
- 34. HCV - Natural History Outcome Following Hepatitis C Infection
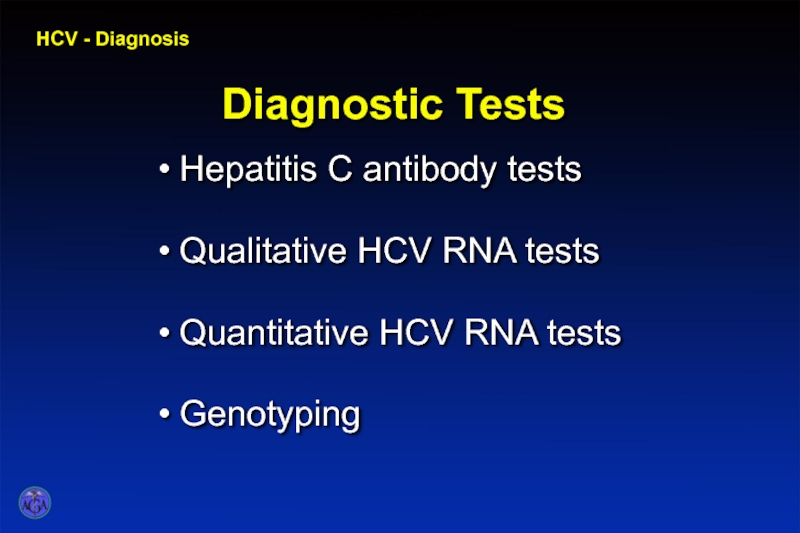
- 35. HCV - Diagnosis Diagnostic Tests
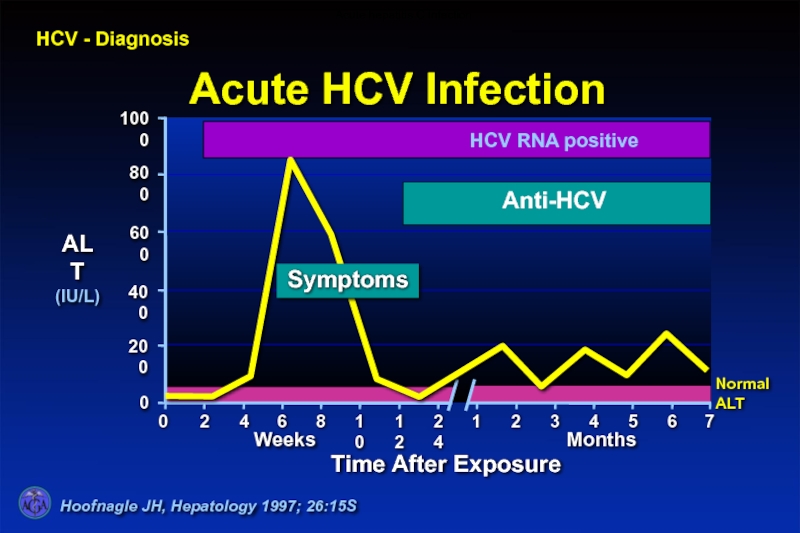
- 36. Hoofnagle JH, Hepatology 1997; 26:15S HCV - Diagnosis Acute hepatitis C infection
- 37. HCV - Diagnosis Antibody tests for hepatitis C
- 38. HCV - Diagnosis Qualitative tests for HCV RNA
- 39. Clinical Features of Hepatitis C Transmission
- 40. Clinical Features of Hepatitis C Jaundice 5
- 41. 42 nm 22 nm Nucleic Acid: 3.2
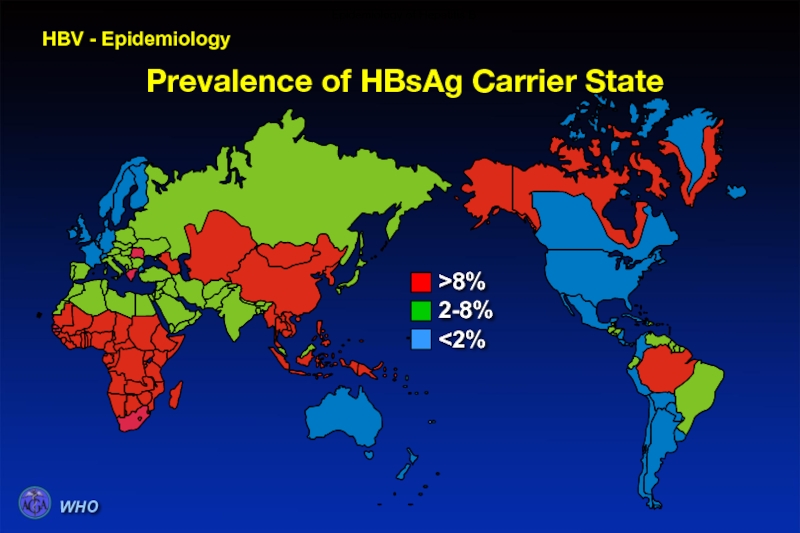
- 42. HBV - Epidemiology Prevalence of HBsAg Carrier State WHO Epidemiology of Hepatitis B
- 43. HBV - Epidemiology Risk factors for hepatitis B infection
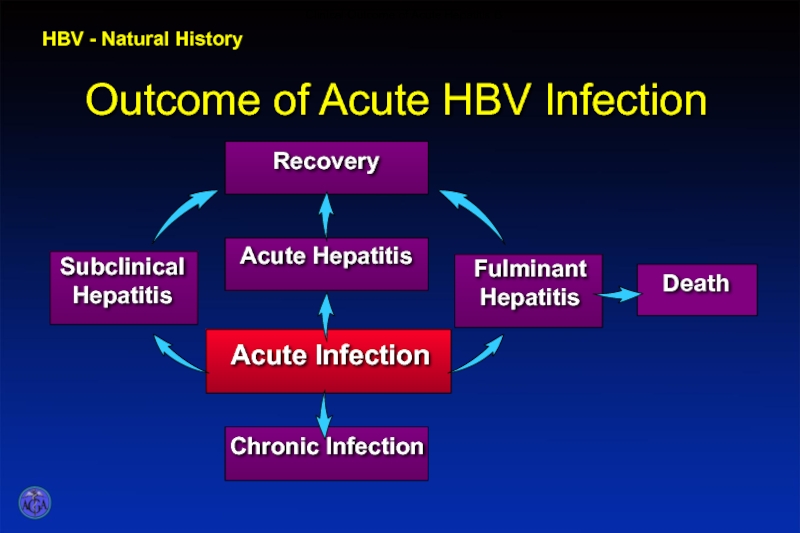
- 44. HBV - Natural History Clinical Outcome of Acute Hepatitis B
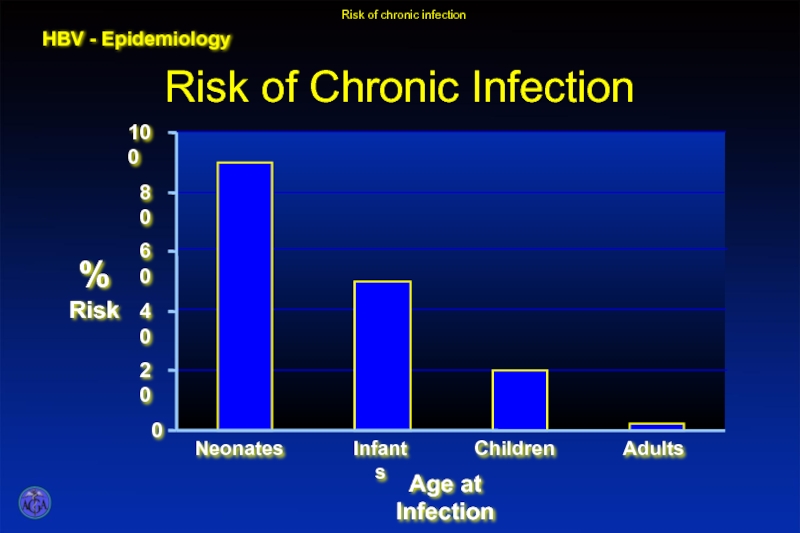
- 45. HBV - Epidemiology Risk of chronic infection
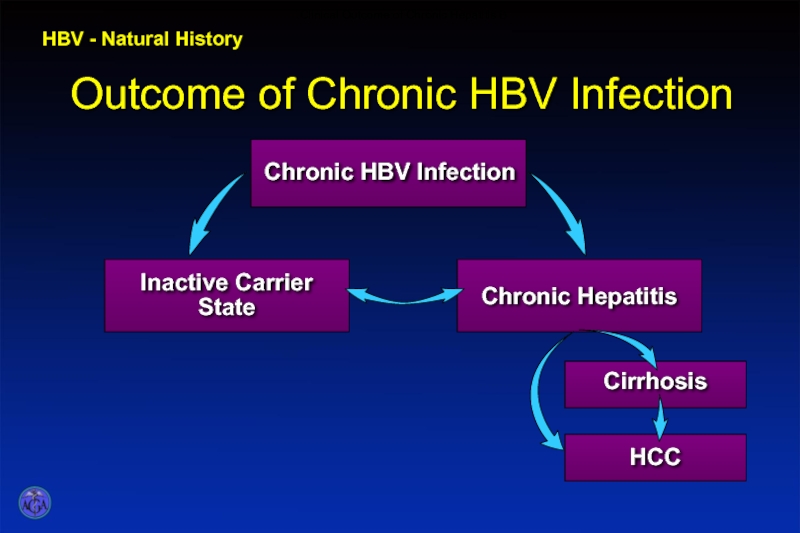
- 46. Outcome of Chronic HBV Infection HBV - Natural History Clinical Outcome of Chronic Hepatitis B
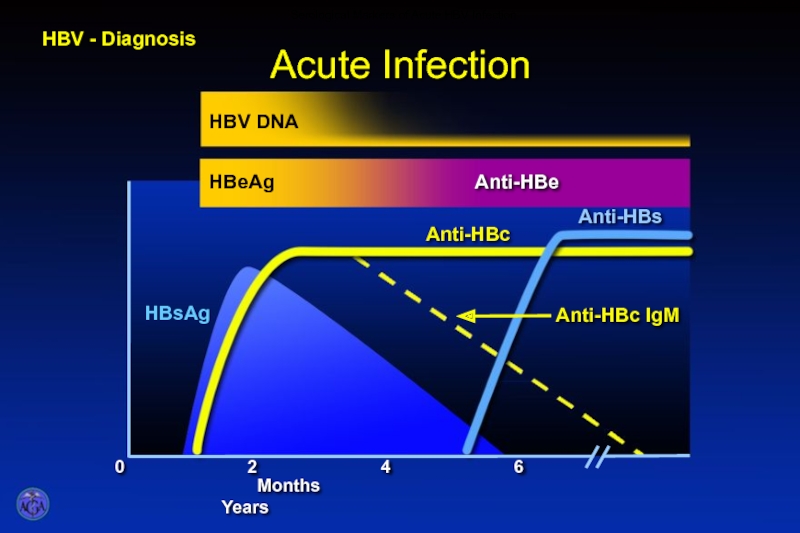
- 47. HBV - Diagnosis Serological Markers of Acute HBV Infection
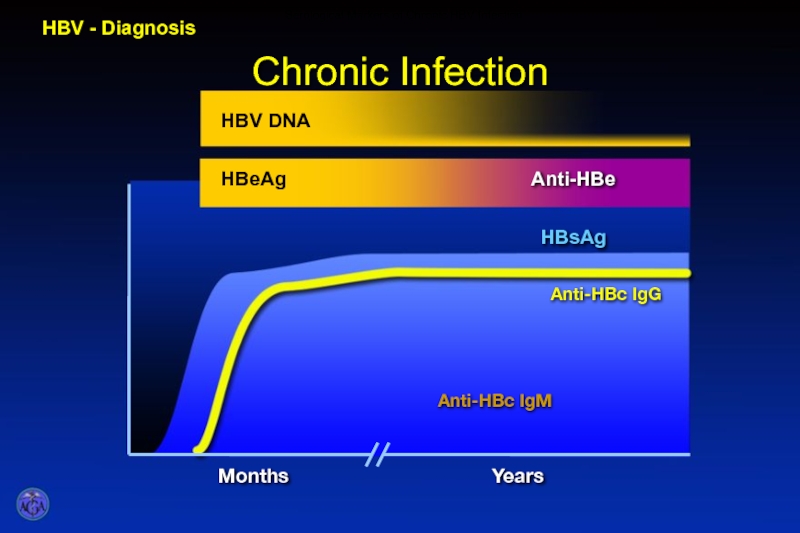
- 48. Chronic Infection HBV - Diagnosis Serological Markers of Chronic HBV Infection
- 49. HBV - Diagnosis Clinical Significance of Serological Markers for HBV Infection
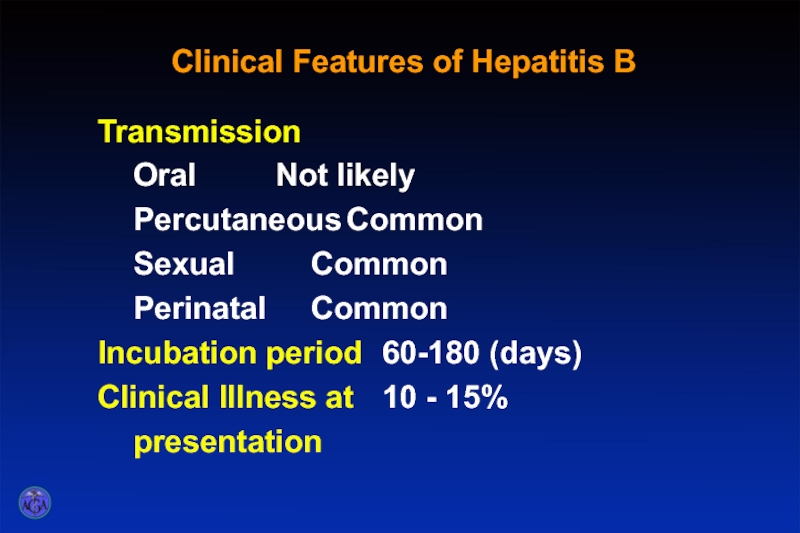
- 50. Clinical Features of Hepatitis B Transmission
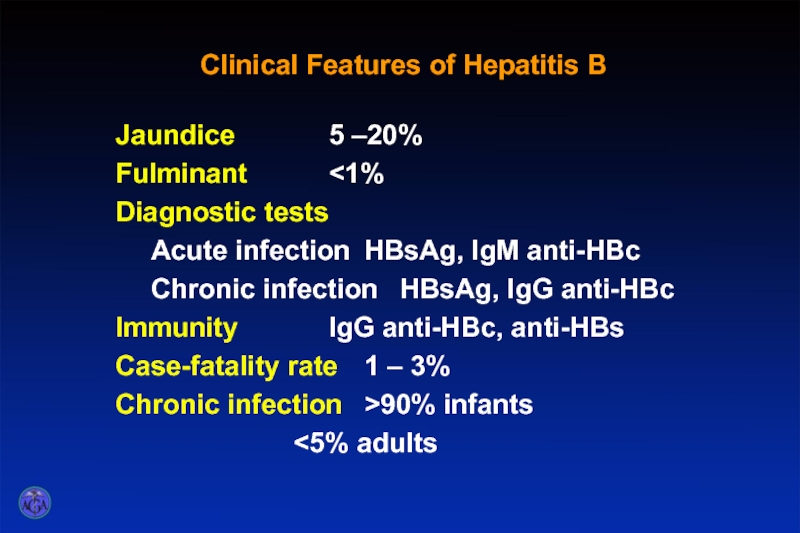
- 51. Clinical Features of Hepatitis B Jaundice 5 –20% Fulminant 90% infants
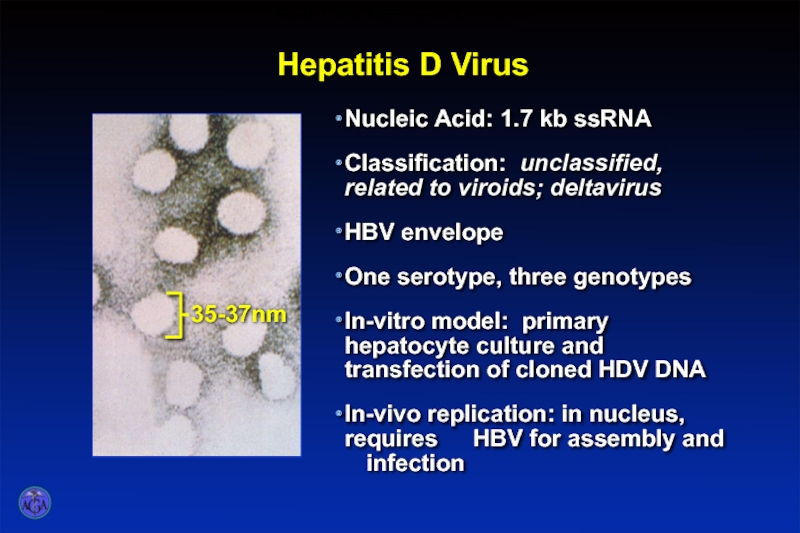
- 52. Hepatitis D Virus Hepatitis D Virus: Morphology and Characteristics
- 53. Pattern Distribution Modes of transmission Endemic Mediterranean Intra-familial Middle East Sexual Central
- 54. HDV Modes of HDV infection
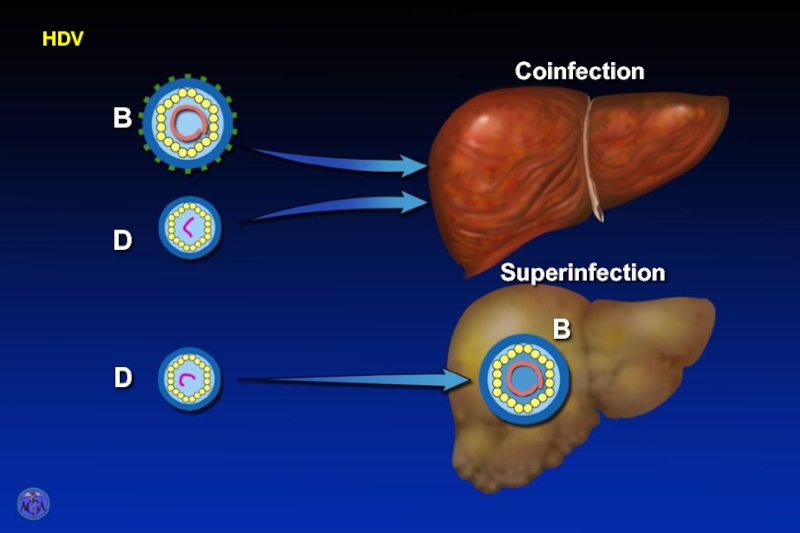
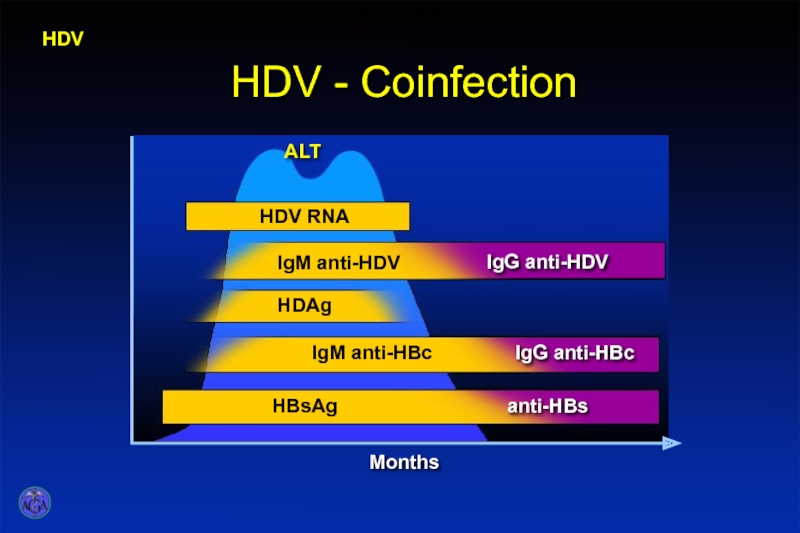
- 55. HDV - Coinfection HDV HDV Co-infection
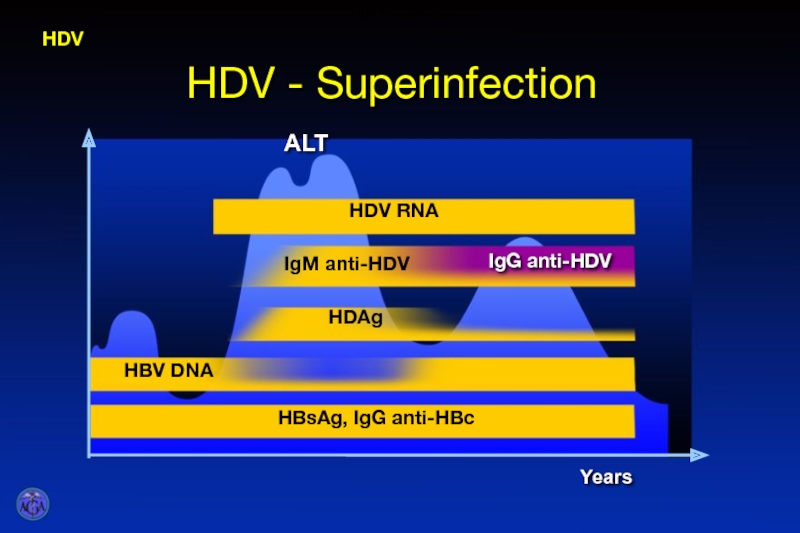
- 56. HDV - Superinfection HDV HDV Superinfection
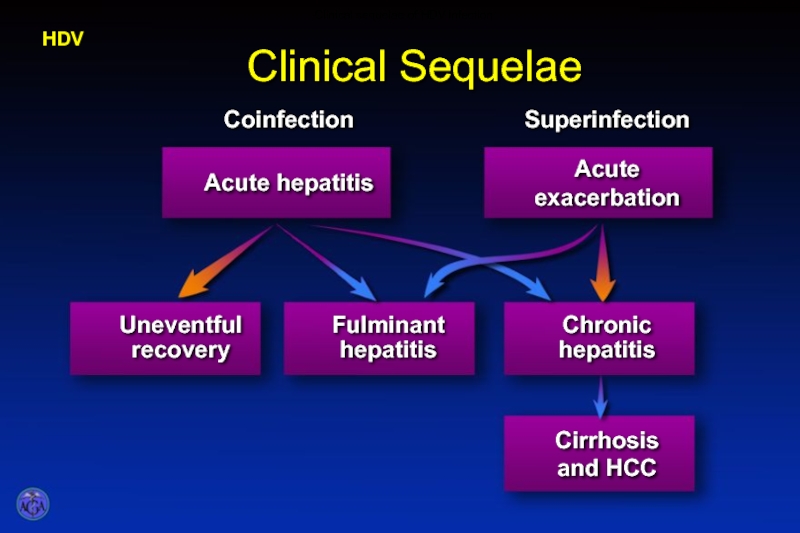
- 57. Clinical Sequelae HDV Clinical sequelae of HDV infection
- 58. Clinical Features of Hepatitis D Transmission
- 59. Clinical Features of Hepatitis D Jaundice Unknown
- 60. Hepatitis E Hepatitis E vs. Hepatitis A
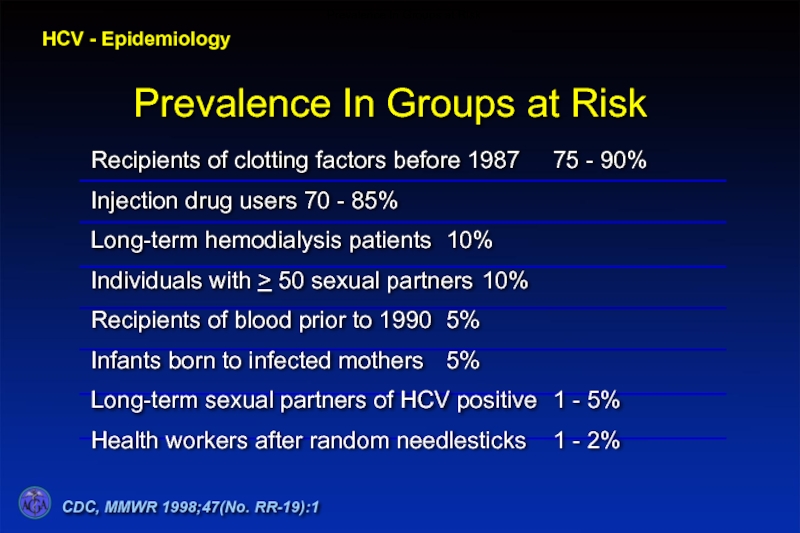
- 61. HCV - Epidemiology CDC, MMWR 1998;47(No. RR-19):1 Prevalence In Groups at Risk
- 62. Indications in Adults Sexual and household contacts
- 63. HBV - Vaccine CDC and WHO Vaccination of selected high-risk groups in adults
Слайд 2Viral hepatitis is a group of etiologically heterogenic diseases which are
According to the route of transmission hepatitis can be enteral (A,E) and parenteral (B,C,D). The viral hepatitis type F and G is still studied.
Слайд 3The problem of viral hepatitis remains the urgent, as these diseases
Viral hepatitis is a most frequent cause of chronic hepatitis and liver cirrhosis. In some patients viral hepatitis may have lethal outcome.
Слайд 4At present following viruses, causing viral hepatitis are known:
virus of
virus of hepatitis B (VHB);
virus of hepatitis E (VHE);
virus of hepatitis D (VHD), associated with VHB;
virus of hepatitis C (VHC).
Search for new viruses causing viral hepatitis continues.
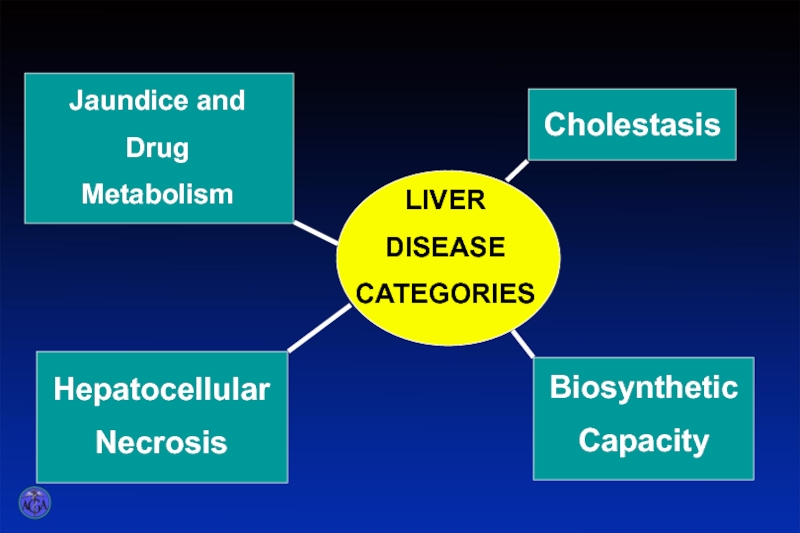
Слайд 5
LIVER
DISEASE
CATEGORIES
Jaundice and
Drug
Metabolism
Cholestasis
Biosynthetic
Capacity
Hepatocellular
Necrosis
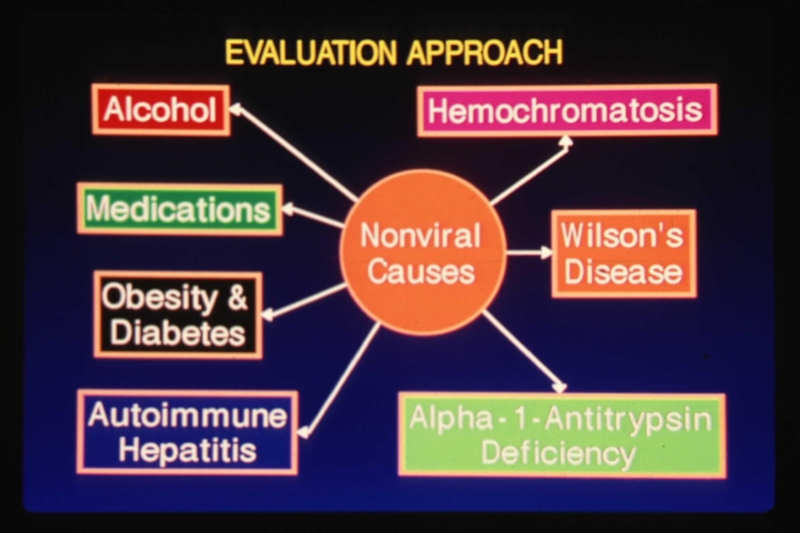
Слайд 9Causes of Chronic Hepatitis
Abbreviations:
NAFLD: nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; AIH: autoimmune
PSC: primary sclerosing cholangitis, A1AT: alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency, HHC:hereditary hemochromotosis
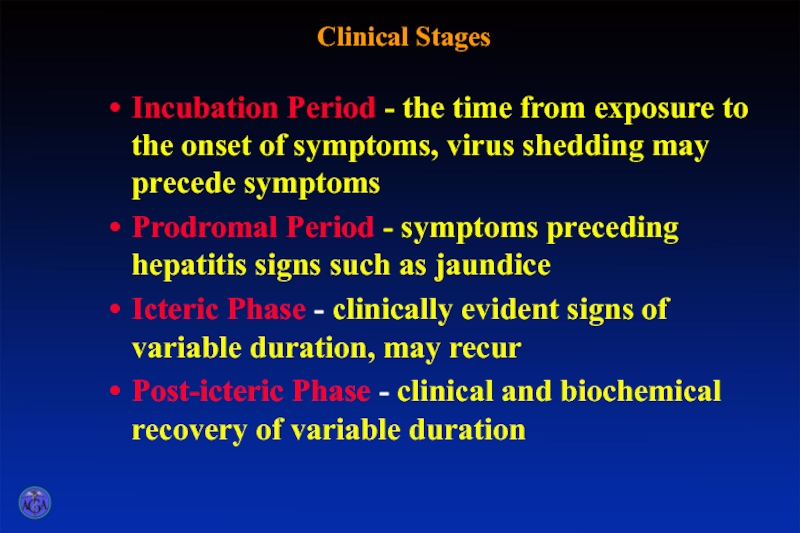
Слайд 10Clinical Stages
Incubation Period - the time from exposure to the onset
Prodromal Period - symptoms preceding hepatitis signs such as jaundice
Icteric Phase - clinically evident signs of variable duration, may recur
Post-icteric Phase - clinical and biochemical recovery of variable duration
Слайд 12Clinical Spectrum
Subclinical Infection – serologic and biochemical evidence
of infection but
Clinical Infection – signs and symptoms of hepatitis,
Acute fulminant – massive necrosis
Acute self-limited – complete recovery
Chronic carrier – usually non-progressive
Chronic active – progressive damage +/- symptoms
Cirrhosis and liver failure
Hepatocellular carcinoma
Слайд 16Epidemiology
1. Transmission: fecal-oral
a) Food-borne or water-borne
b) Raw or
c) Salads or other raw vegetables
2. Can also be transmitted by blood-blood contact, especially associated with IV drug abuse
3. Widespread geographical distribution
4. Often virtually 100% of the population is infected in early childhood, resulting in lasting immunity.
Слайд 18
HAV - Epidemiology
Prevalence of Hepatitis A in the United States
Prevalence of
CDC
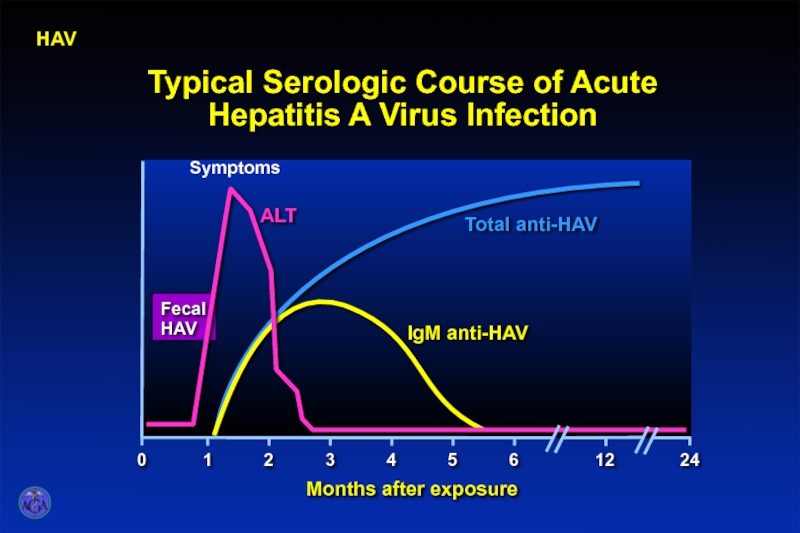
Слайд 20Typical Serologic Course of Acute Hepatitis A Virus Infection
HAV
Serological Course
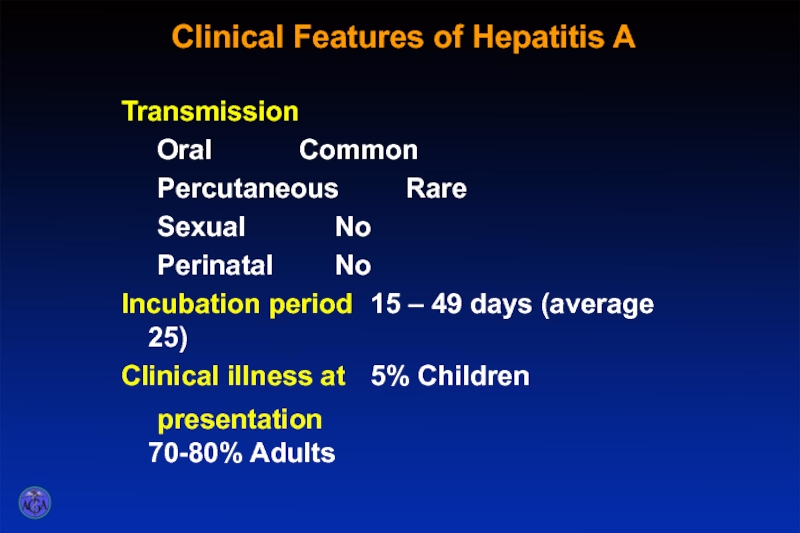
Слайд 22Clinical Features of Hepatitis A
Transmission
Oral Common
Percutaneous Rare
Sexual No
Perinatal No
Incubation period 15 – 49 days (average
Clinical illness at 5% Children
presentation 70-80% Adults
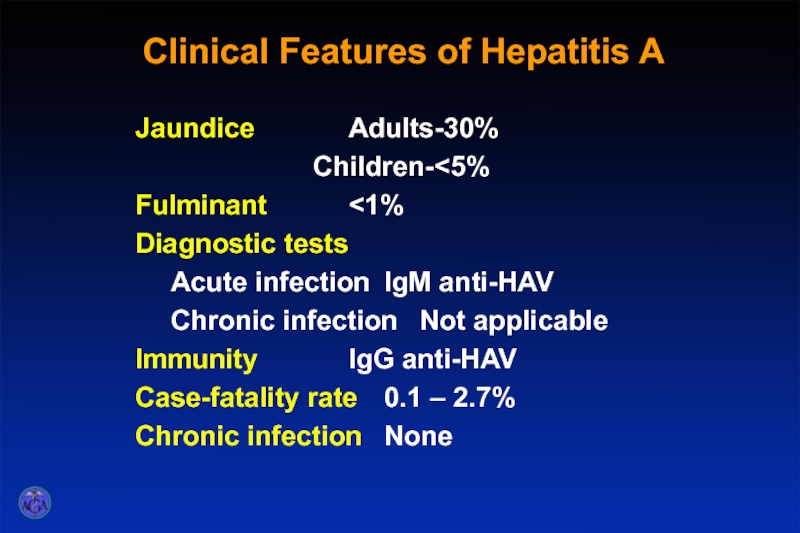
Слайд 23Clinical Features of Hepatitis A
Jaundice Adults-30%
Children-
Case-fatality rate 0.1 – 2.7%
Chronic infection None
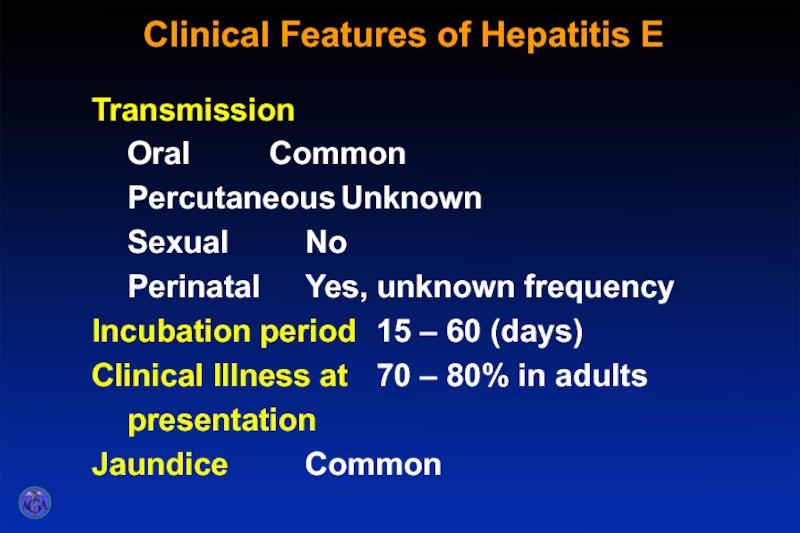
Слайд 28Clinical Features of Hepatitis E
Transmission
Oral Common
Percutaneous Unknown
Sexual No
Perinatal Yes, unknown frequency
Incubation period 15 – 60
Clinical Illness at 70 – 80% in adults
presentation
Jaundice Common
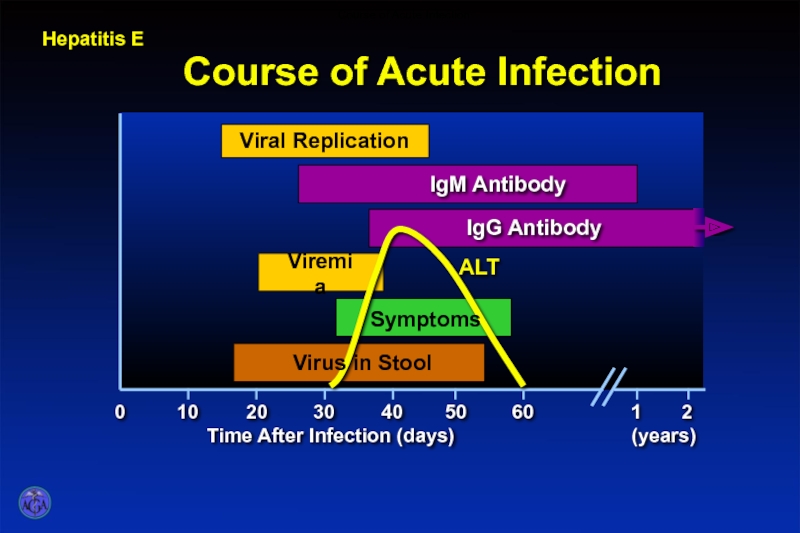
Слайд 30Clinical Features of Hepatitis E
Fulminant
Acute infection IgG anti-HEV (seroconversion)
Chronic infection Not applicable
Immunity Not applicable
Case-fatality rate 0.5 – 4%
1.5 – 21% in pregnant women
Chronic infection None
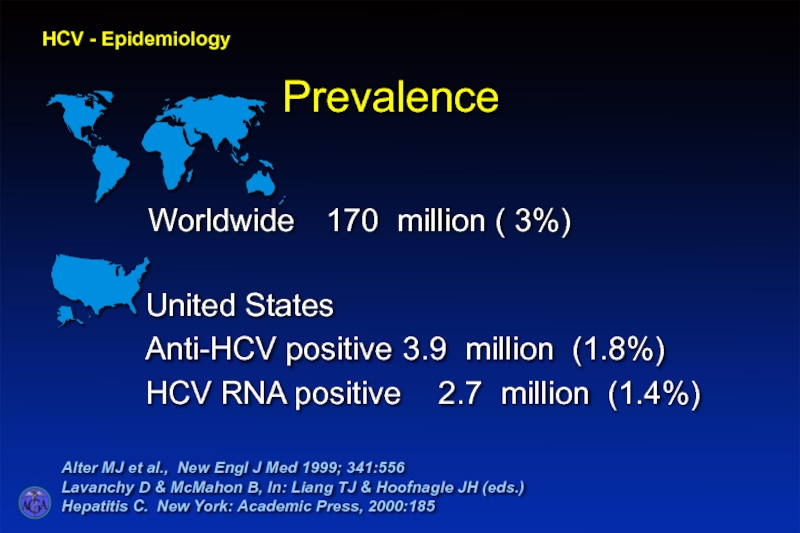
Слайд 32Prevalence
HCV - Epidemiology
Alter MJ et al., New Engl J Med 1999;
Lavanchy D & McMahon B, In: Liang TJ & Hoofnagle JH (eds.)
Hepatitis C. New York: Academic Press, 2000:185
Prevalence
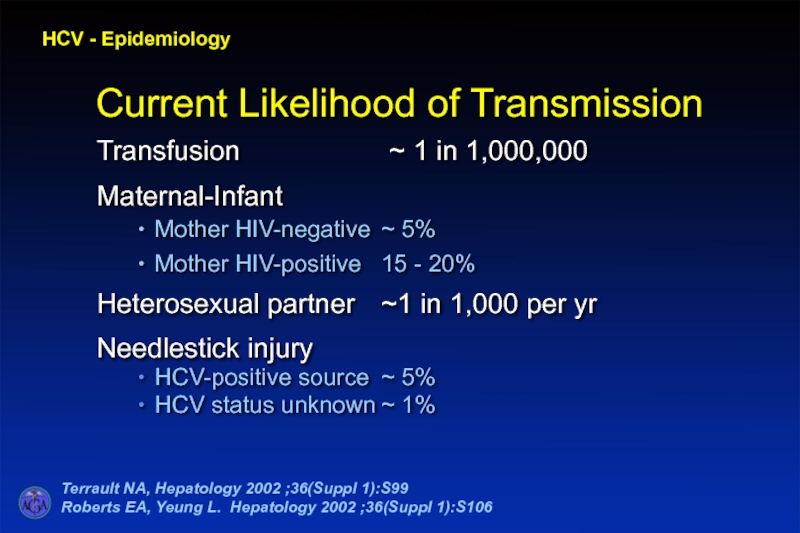
Слайд 33HCV - Epidemiology
Terrault NA, Hepatology 2002 ;36(Suppl 1):S99
Roberts EA, Yeung L.
Current Likelihood of Transmission
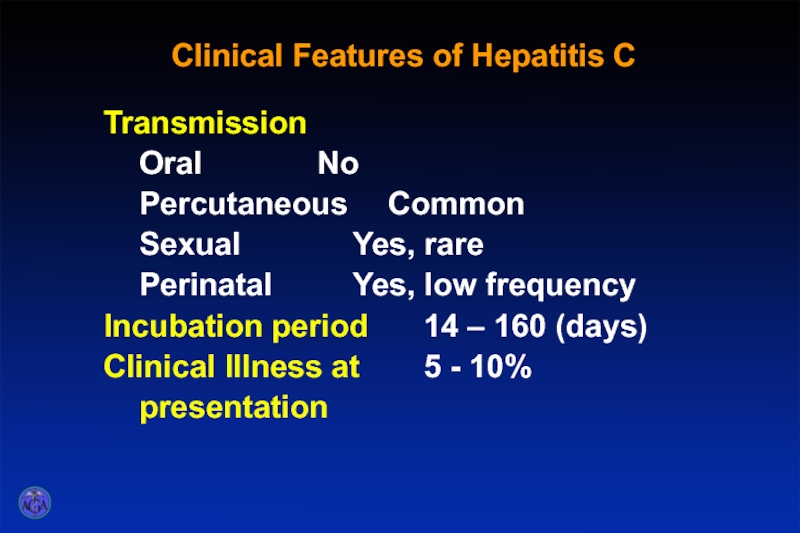
Слайд 39Clinical Features of Hepatitis C
Transmission
Oral No
Percutaneous Common
Sexual Yes, rare
Perinatal Yes, low frequency
Incubation period 14 –
Clinical Illness at 5 - 10%
presentation
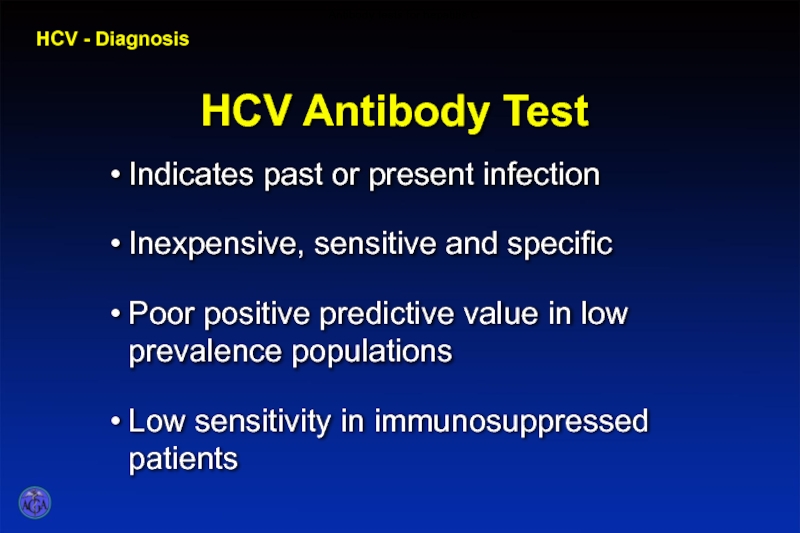
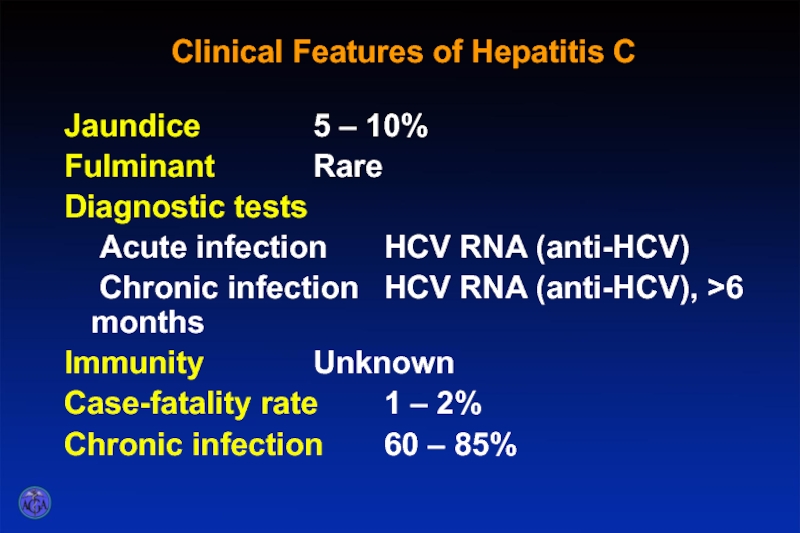
Слайд 40Clinical Features of Hepatitis C
Jaundice 5 – 10%
Fulminant Rare
Diagnostic tests
Acute infection HCV RNA
Chronic infection HCV RNA (anti-HCV), >6 months
Immunity Unknown
Case-fatality rate 1 – 2%
Chronic infection 60 – 85%
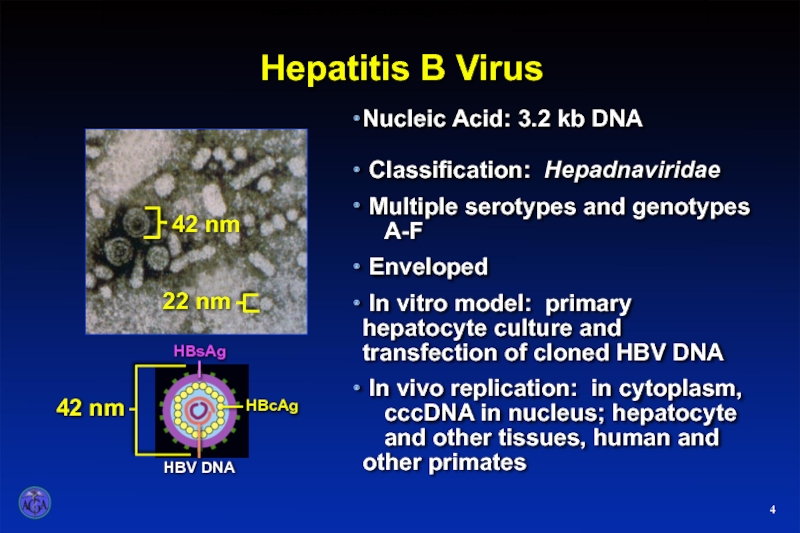
Слайд 4142 nm
22 nm
Nucleic Acid: 3.2 kb DNA
Classification: Hepadnaviridae
Multiple serotypes
Enveloped
In vitro model: primary hepatocyte culture and transfection of cloned HBV DNA
In vivo replication: in cytoplasm, cccDNA in nucleus; hepatocyte and other tissues, human and other primates
Hepatitis B Virus
Hepatitis B Virus: Morphology and Characteristics
4
Слайд 46Outcome of Chronic HBV Infection
HBV - Natural History
Clinical Outcome of Chronic
Слайд 50Clinical Features of Hepatitis B
Transmission
Oral Not likely
Percutaneous Common
Sexual Common
Perinatal Common
Incubation period 60-180 (days)
Clinical Illness at 10
presentation
Слайд 51Clinical Features of Hepatitis B
Jaundice 5 –20%
Fulminant
Immunity IgG anti-HBc, anti-HBs
Case-fatality rate 1 – 3%
Chronic infection >90% infants
<5% adults
Слайд 53Pattern Distribution Modes of transmission
Endemic Mediterranean Intra-familial
Middle East Sexual
Central & South
America
Africa
Non-endemic North America Injection drug use
Northern
factor concentrates
HDV
Epidemiologic Patterns
Transmission of hepatitis D virus (HDV)
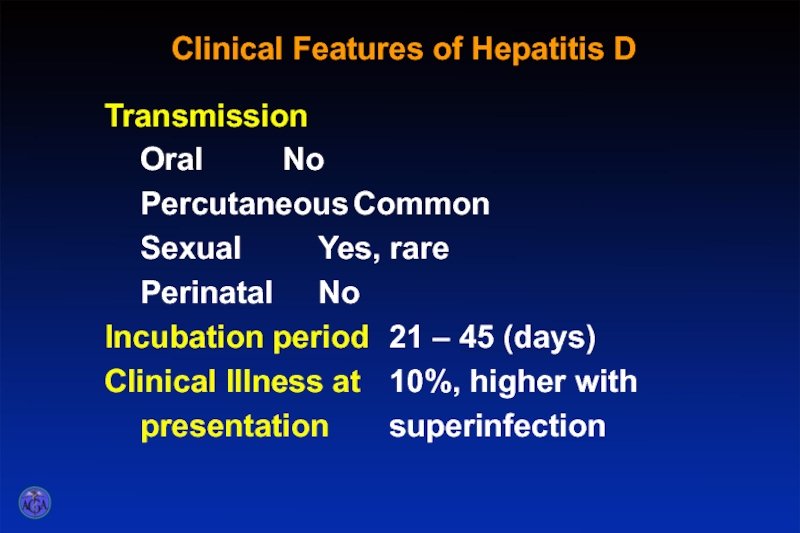
Слайд 58Clinical Features of Hepatitis D
Transmission
Oral No
Percutaneous Common
Sexual Yes, rare
Perinatal No
Incubation period 21 – 45 (days)
Clinical
presentation superinfection
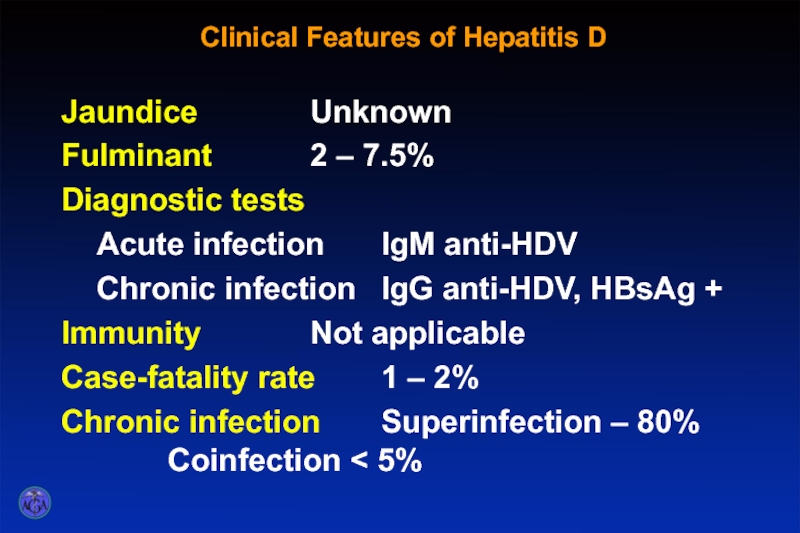
Слайд 59Clinical Features of Hepatitis D
Jaundice Unknown
Fulminant 2 – 7.5%
Diagnostic tests
Acute infection IgM anti-HDV
Chronic
Immunity Not applicable
Case-fatality rate 1 – 2%
Chronic infection Superinfection – 80% Coinfection < 5%
Слайд 62Indications in Adults
Sexual and household contacts of carriers
Sexually active individuals with
Injection drug users
Hemodialysis patients
Recipients of clotting factor concentrates
Families of adoptees from endemic areas
HBV - Vaccine
CDC and WHO
Vaccination of selected high-risk groups in adults