- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Sexually transmitted bacterial diseases презентация
Содержание
- 1. Sexually transmitted bacterial diseases
- 2. PLAN Morphology Culture Antigenic structure Virulence factors
- 3. A 28-year-old hair dresser complained of
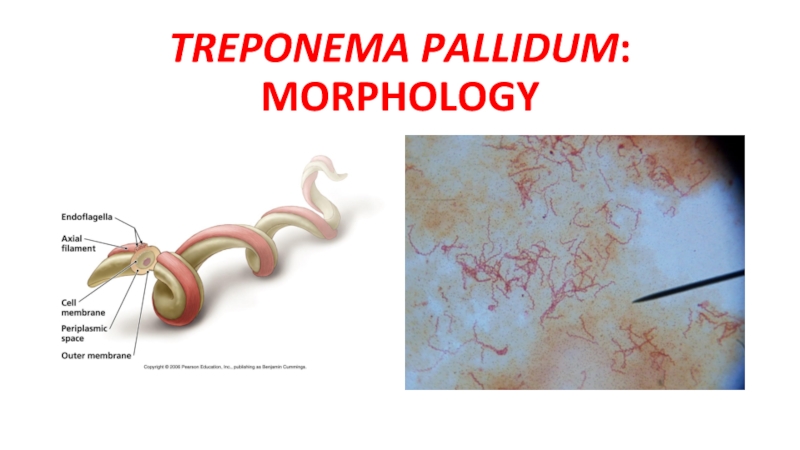
- 4. TREPONEMA PALLIDUM: MORPHOLOGY
- 5. TREPONEMA PALLIDUM : ANTIGENIC STRUCTURE Cardiolipin antigen
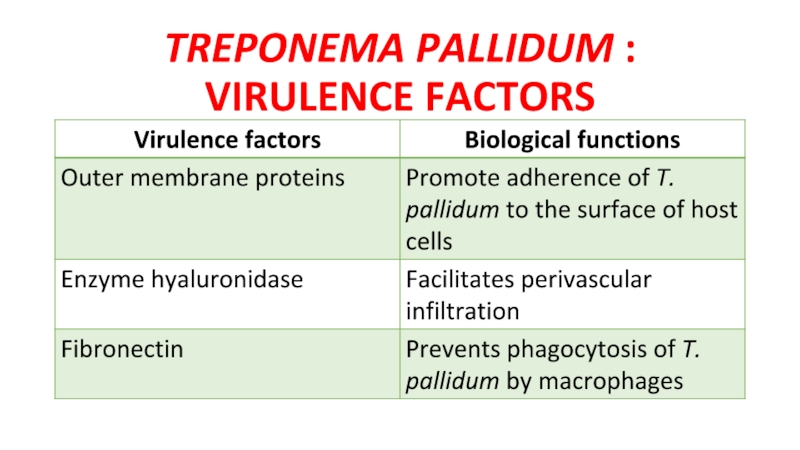
- 6. TREPONEMA PALLIDUM : VIRULENCE FACTORS
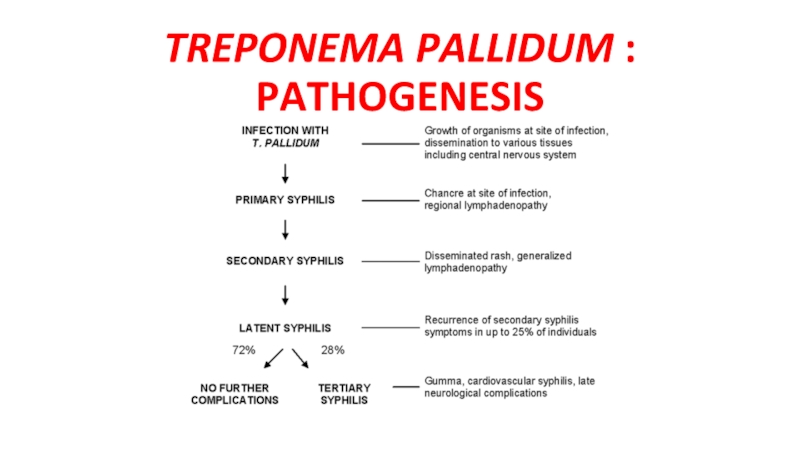
- 7. TREPONEMA PALLIDUM : PATHOGENESIS
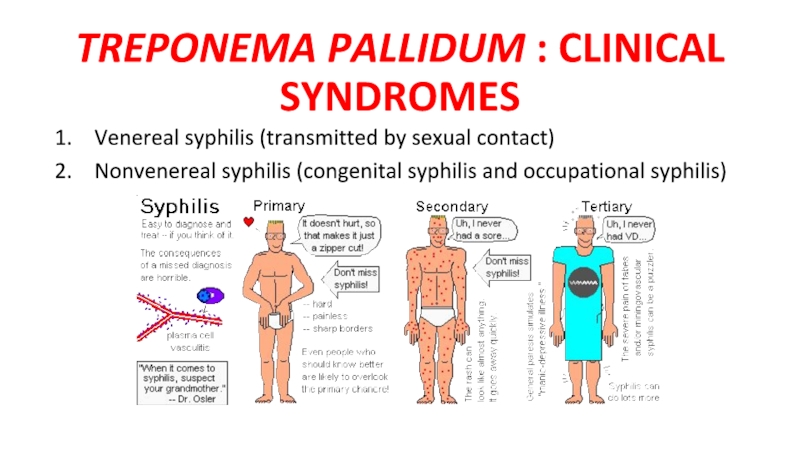
- 8. TREPONEMA PALLIDUM : CLINICAL SYNDROMES Venereal syphilis
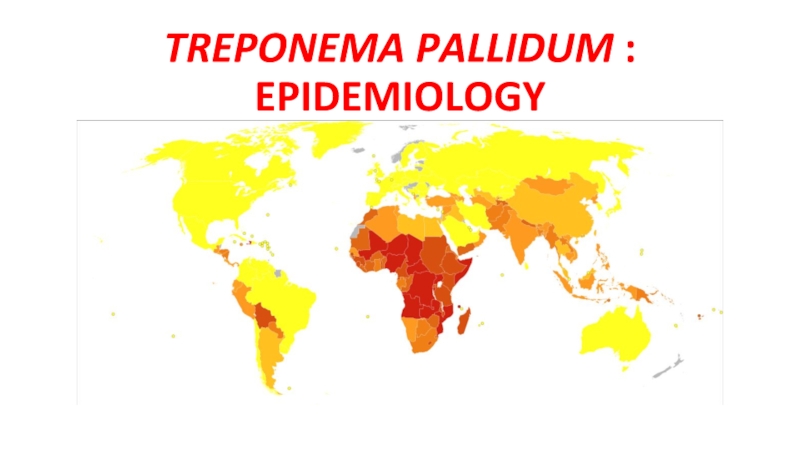
- 9. TREPONEMA PALLIDUM : EPIDEMIOLOGY
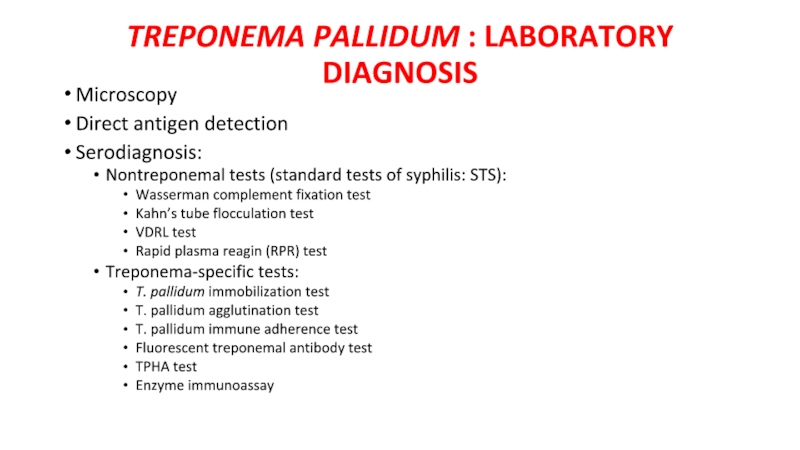
- 10. TREPONEMA PALLIDUM : LABORATORY DIAGNOSIS Microscopy Direct
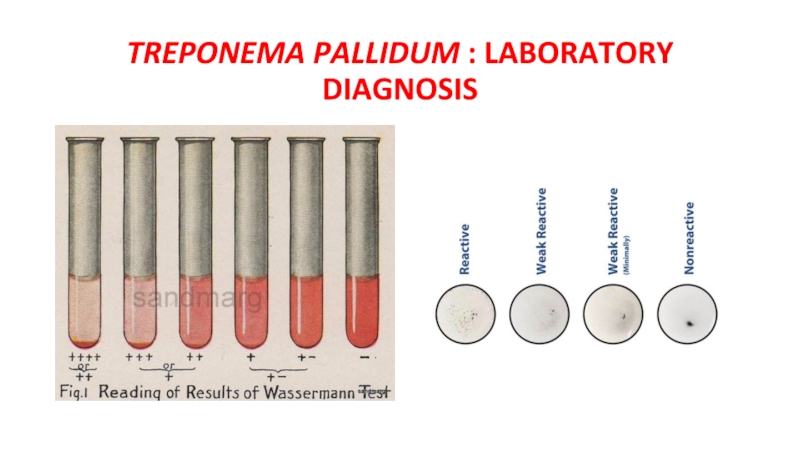
- 11. TREPONEMA PALLIDUM : LABORATORY DIAGNOSIS
- 12. A 6-year-old boy attended the Ophthalmology
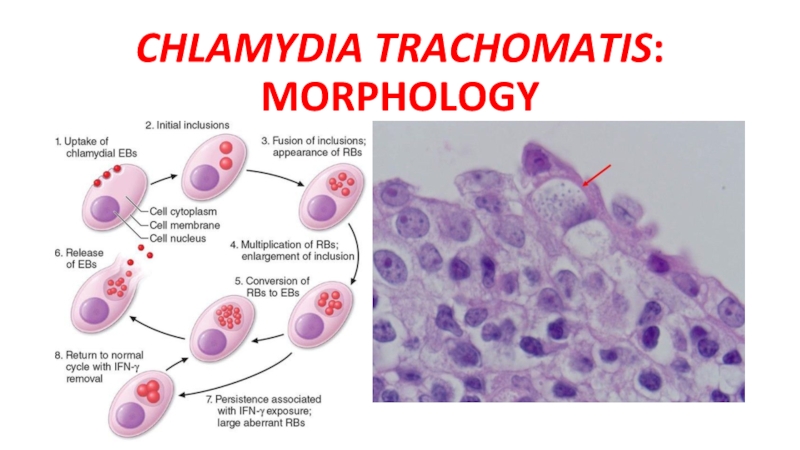
- 13. CHLAMYDIA TRACHOMATIS: MORPHOLOGY
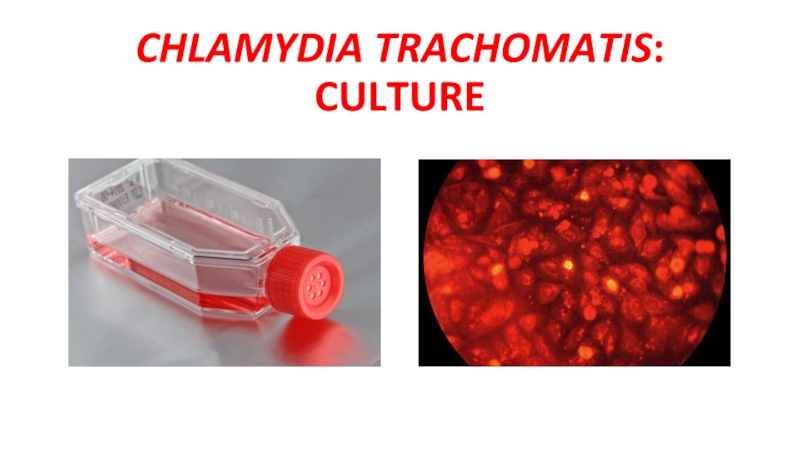
- 14. CHLAMYDIA TRACHOMATIS: CULTURE
- 15. CHLAMYDIA TRACHOMATIS: ANTIGENIC STRUCTURE Genus-specific antigen Species-specific
- 16. CHLAMYDIA TRACHOMATIS: VIRULENCE FACTORS The ability to
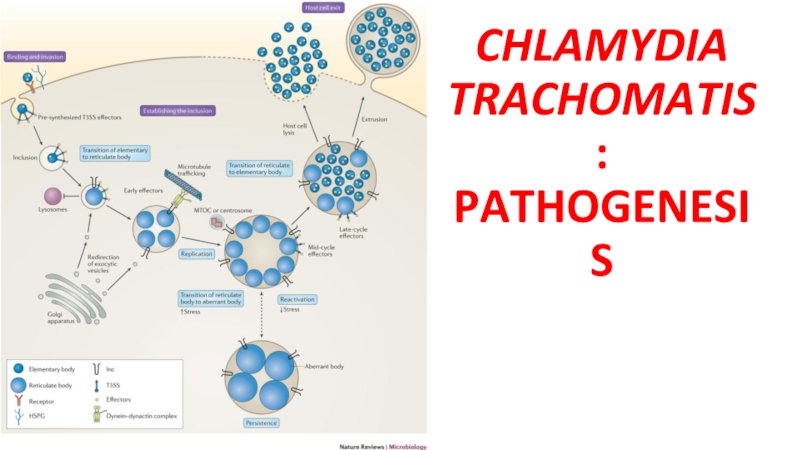
- 17. CHLAMYDIA TRACHOMATIS: PATHOGENESIS
- 18. CHLAMYDIA TRACHOMATIS: CLINICAL SYNDROMES Lymphogranuloma venereum Ocular
- 19. CHLAMYDIA TRACHOMATIS: CLINICAL SYNDROMES
- 20. CHLAMYDIA TRACHOMATIS: LABORATORY DIAGNOSIS Microscopy Culture Antigen detection Serodiagnosis Frei’s skin test
- 21. A 22-year-old female complained of lower
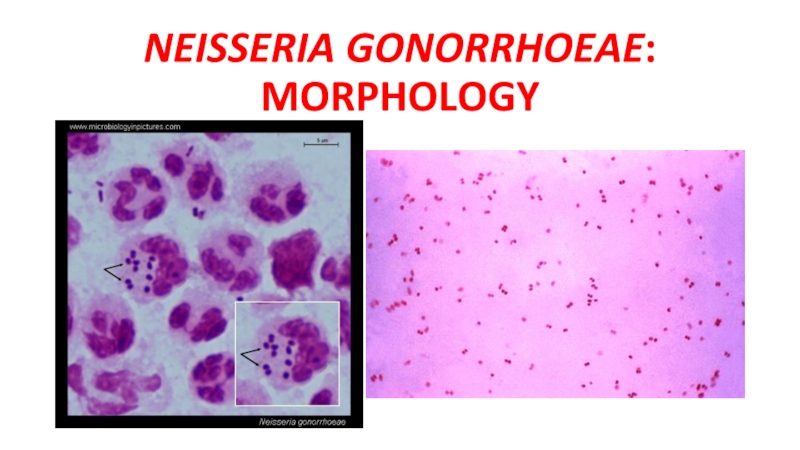
- 22. NEISSERIA GONORRHOEAE: MORPHOLOGY
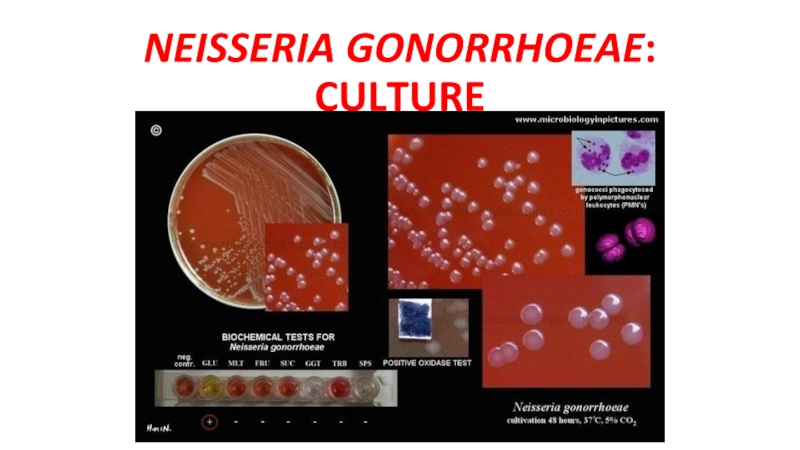
- 23. NEISSERIA GONORRHOEAE: CULTURE
- 24. NEISSERIA GONORRHOEAE: VIRULENCE FACTORS
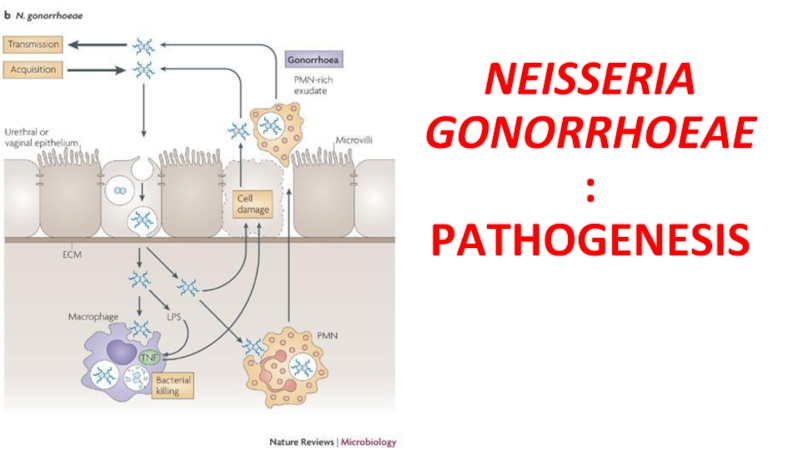
- 25. NEISSERIA GONORRHOEAE: PATHOGENESIS
- 26. NEISSERIA GONORRHOEAE: CLINICAL SYNDROMES gonorrhea, disseminated
- 27. NEISSERIA GONORRHOEAE: LABORATORY DIAGNOSIS Microscopy Culture Antigen detection SerodiagnosiS
- 28. NEISSERIA GONORRHOEAE: CLINICAL SYNDROMES gonorrhea, disseminated
- 29. NEISSERIA GONORRHOEAE: LABORATORY DIAGNOSIS Microscopy Culture Antigen detection SerodiagnosiS
Слайд 2PLAN
Morphology
Culture
Antigenic structure
Virulence factors
Pathogenesis
Immunity
Clinical syndromes
Epidemiology
Laboratory diagnosis
Treatment
Prevention
Слайд 3
A 28-year-old hair dresser complained of a painless small ulcer on
the penis during the last 2 weeks. When asked, he said he had repeated sexual relation with a female sexual worker approximately many months back. On examination, the pus exudate from the smear did not reveal any Treponema. Serum sample was found to be positive for syphilis by the VDRL test. ELISA for HIV was negative
Слайд 5TREPONEMA PALLIDUM : ANTIGENIC STRUCTURE
Cardiolipin antigen
T. pallidum group-specific antigen
T.
pallidum species-specific antigen
Слайд 8TREPONEMA PALLIDUM : CLINICAL SYNDROMES
Venereal syphilis (transmitted by sexual contact)
Nonvenereal syphilis
(congenital syphilis and occupational syphilis)
Слайд 10TREPONEMA PALLIDUM : LABORATORY DIAGNOSIS
Microscopy
Direct antigen detection
Serodiagnosis:
Nontreponemal tests (standard tests of
syphilis: STS):
Wasserman complement fixation test
Kahn’s tube flocculation test
VDRL test
Rapid plasma reagin (RPR) test
Treponema-specific tests:
T. pallidum immobilization test
T. pallidum agglutination test
T. pallidum immune adherence test
Fluorescent treponemal antibody test
TPHA test
Enzyme immunoassay
Wasserman complement fixation test
Kahn’s tube flocculation test
VDRL test
Rapid plasma reagin (RPR) test
Treponema-specific tests:
T. pallidum immobilization test
T. pallidum agglutination test
T. pallidum immune adherence test
Fluorescent treponemal antibody test
TPHA test
Enzyme immunoassay
Слайд 12
A 6-year-old boy attended the Ophthalmology OPD with symptoms of conjunctivitis
of the right eye. Examination showed follicular hypertrophy with diffuse inflammation that had affected the entire conjunctiva along with pannus formation. Iodine staining of conjunctival scrapings demonstrated inclusion bodies of Chlamydia trachomatis. The condition was diagnosed as trachoma.
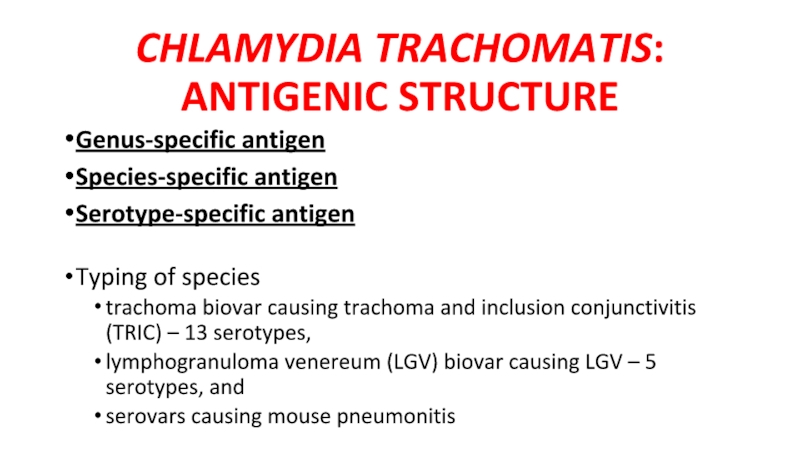
Слайд 15CHLAMYDIA TRACHOMATIS: ANTIGENIC STRUCTURE
Genus-specific antigen
Species-specific antigen
Serotype-specific antigen
Typing of species
trachoma biovar causing
trachoma and inclusion conjunctivitis (TRIC) – 13 serotypes,
lymphogranuloma venereum (LGV) biovar causing LGV – 5 serotypes, and
serovars causing mouse pneumonitis
lymphogranuloma venereum (LGV) biovar causing LGV – 5 serotypes, and
serovars causing mouse pneumonitis
Слайд 16CHLAMYDIA TRACHOMATIS: VIRULENCE FACTORS
The ability to multiply intracellularly in the infected
cell is the key mechanism of virulence of C. trachomatis.
The bacteria prevent fusion of phagolysosome with cellular liposomes, thereby preventing intracellular killing of the bacteria by the host cell.
Repeated infections caused by C. trachomatis contribute to pathology seen in the infected eye in trachoma.
The bacteria prevent fusion of phagolysosome with cellular liposomes, thereby preventing intracellular killing of the bacteria by the host cell.
Repeated infections caused by C. trachomatis contribute to pathology seen in the infected eye in trachoma.
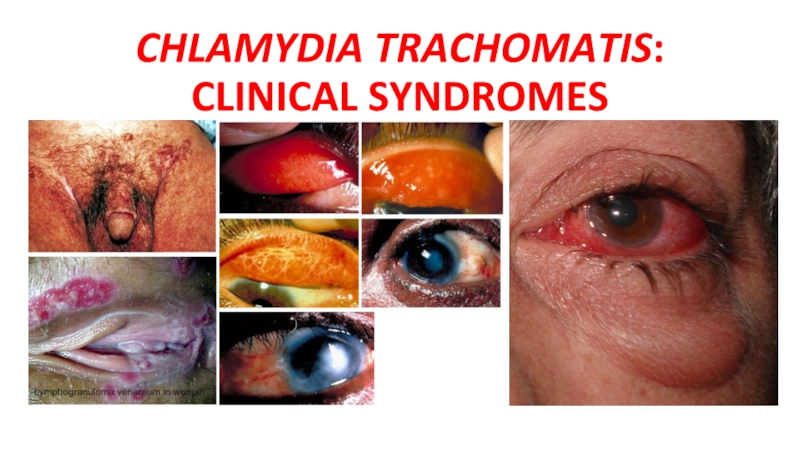
Слайд 18CHLAMYDIA TRACHOMATIS: CLINICAL SYNDROMES
Lymphogranuloma venereum
Ocular LGV
Trachoma
Adult inclusion conjunctivitis
Neonatal conjunctivitis
Infant pneumonia
Urogenital infections
Слайд 20CHLAMYDIA TRACHOMATIS: LABORATORY DIAGNOSIS
Microscopy
Culture
Antigen detection
Serodiagnosis
Frei’s skin test
Слайд 21
A 22-year-old female complained of lower abdominal pain on and off
for the last 3 months. She complained of a feeling of heaviness in the pelvis and pain during sexual intercourse. On examination, a tender mass was found to the right side during examination. Gram staining of cervical swab showed plenty of pus cells and a few Gram-negative cocci. She gave a history of allergy to penicillins.
Слайд 26NEISSERIA GONORRHOEAE: CLINICAL SYNDROMES
gonorrhea,
disseminated gonococcal infections (DGI),
ophthalmia neonatorum, and
other gonococcal diseases
Слайд 28NEISSERIA GONORRHOEAE: CLINICAL SYNDROMES
gonorrhea,
disseminated gonococcal infections (DGI),
ophthalmia neonatorum, and
other gonococcal diseases