- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Pathology of respiration. (Subject 15) презентация
Содержание
- 1. Pathology of respiration. (Subject 15)
- 2. Respiratory failure Lungs are unable to
- 3. Respiratory failure classification Type 1 – hypoxia
- 4. Reasons of respiratory failure Disturbances of
- 5. Reasons of respiratory failure Extra-lungs disturbances of:
- 6. Disturbances of alveolar ventilation OBSTRUCTIVE RESTRICTIVE
- 7. Obstructive lung disorders Obstruction of the
- 8. Restrictive lung diseases Disturbances of lung’s
- 9. Restrictive lung diseases Extrapulmonary reasons: Changes in
- 10. Disorders of perfusion Hyperperfusion Local
- 11. Disorders of perfusion Hypoperfusion heart pathology (heart
- 12. Mismatching of ventilation and perfusion Ventilation/perfusion ratio
- 13. Diffusion impairment ↑ distance for diffusion
- 14. Manifestations of respiratory failure Hypoxemia
- 15. Hypoxemia Manifestations impairment of mental performance and
- 16. Hypercapnia Manifestations ↓ pH and respiratory
- 17. Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) Causes
- 18. ARDS pathogenesis and clinics Injury and
- 19. ARDS clinical manifestation rapid onset, 12 to
- 20. Pulmonary edema cardiogenic (left-sided heart failure)
- 21. Non-cardiogenic pulmonary edema alveolar walls
- 22. Pulmonary edema symptoms Acute difficult breathing
- 23. Pulmonary edema symptoms Chronic pulmonary edema: nocturia
- 24. Short breath (dyspnea) violation of frequency,
- 25. Dyspnea classification According to pathogenesis Cerebral dyspnoea
- 26. Dyspnea classification Due to dyspnea character: Hyperpnea
- 27. Dyspnoe mechanisms Humoral – increase of pCO2
- 28. Cerebral dyspnea Excitation of respiratory centre
- 29. Cheyne-Stokes respiration failure of the respiratory
- 30. Bioth's respirations cluster respiration. damage to
- 31. Kussmaul breathing The cause of Kussmaul
- 32. Agonal respiration shallow, irregular inspirations followed
- 33. Other dyspnea types Lungs dyspnea Embolism
- 34. Asphyxia a condition of severe deficiency
- 35. Asphyxia causes Physical obstruction of air flow
- 36. Asphyxia stages 1st stage - ↑ frequency
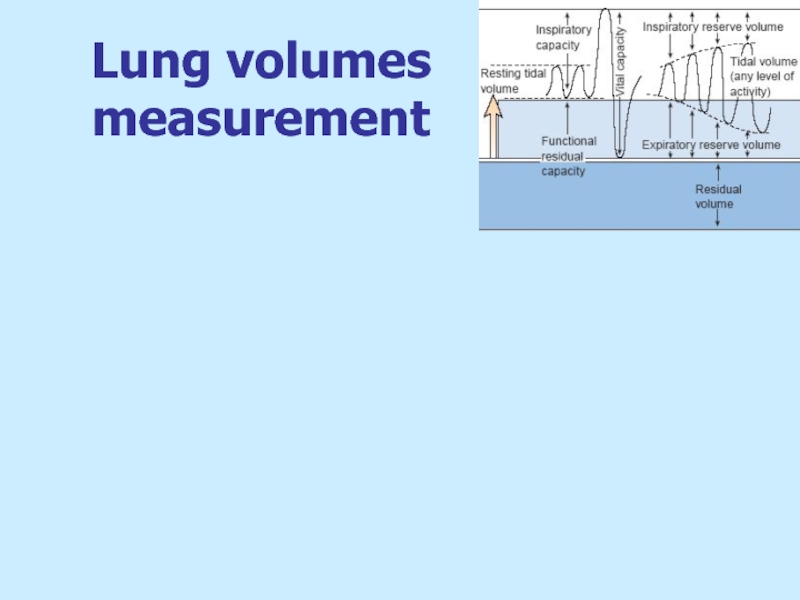
- 37. Lung volumes measurement
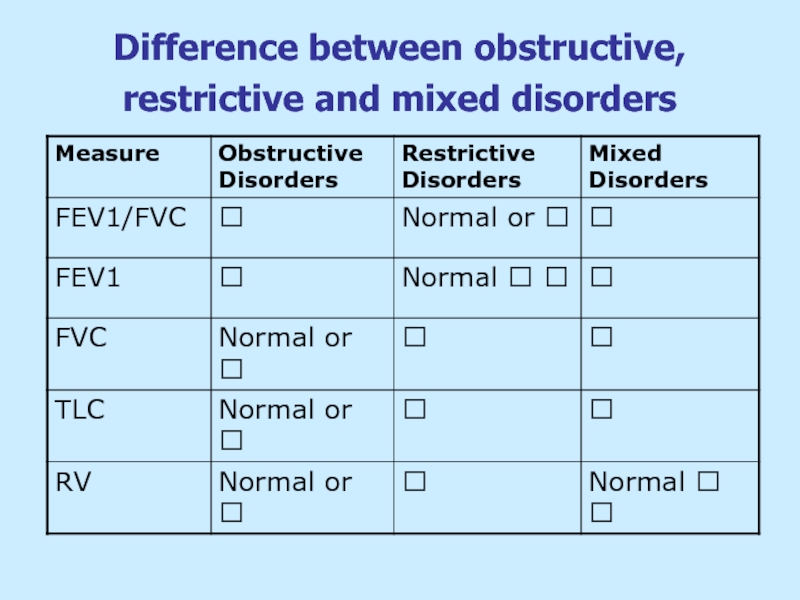
- 38. Difference between obstructive, restrictive and mixed disorders
Слайд 2Respiratory failure
Lungs are unable to provide:
an adequate supply of
and/or to remove CO2 efficiently
In arterial blood: pO2 - 95 - 100 mm Hg pCO2 - 43 - 46 mm Hg
Classification:
Acute failure – minutes to hours (bronchial asthma attack, acute pneumonia).
Subacute –days to weeks (pneumonia, bronchitis).
Chronic – months to years (emphysema of lungs, disseminated lung fibrosis).
Слайд 3Respiratory failure classification
Type 1 – hypoxia without hypercapnia
low oxygen in
ventilation/perfusion mismatch
pnemonia, lung edema
gases diffusion disturbances
Type 2 – hypoxia with hypercapnia
reduced breathing effort;
increased resistance to breathing (asthma);
? in the area of the lung that is not available for gas exchange (COPD,emphysema).
Слайд 4Reasons of respiratory failure
Disturbances of lungs function
ventilation,
perfusion,
alveolar
gases diffusion through alveolar-capillary membrane.
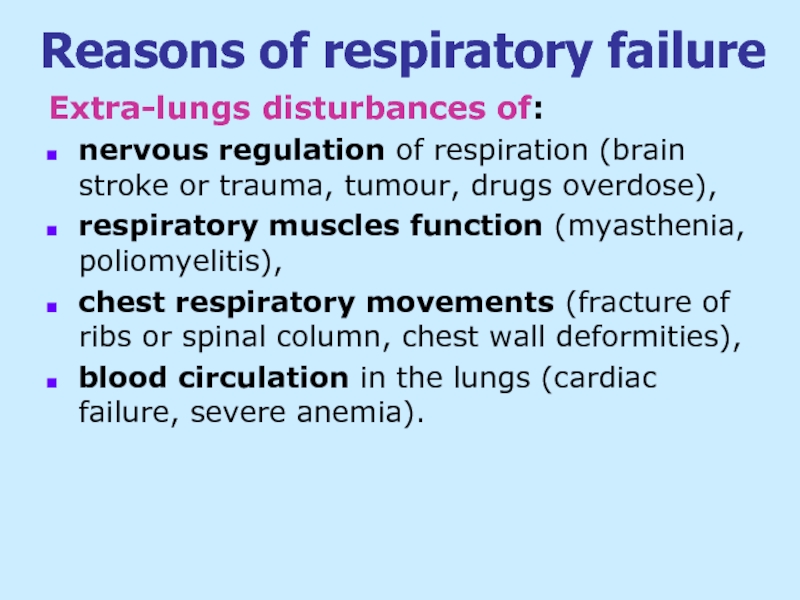
Слайд 5Reasons of respiratory failure
Extra-lungs disturbances of:
nervous regulation of respiration (brain stroke
respiratory muscles function (myasthenia, poliomyelitis),
chest respiratory movements (fracture of ribs or spinal column, chest wall deformities),
blood circulation in the lungs (cardiac failure, severe anemia).
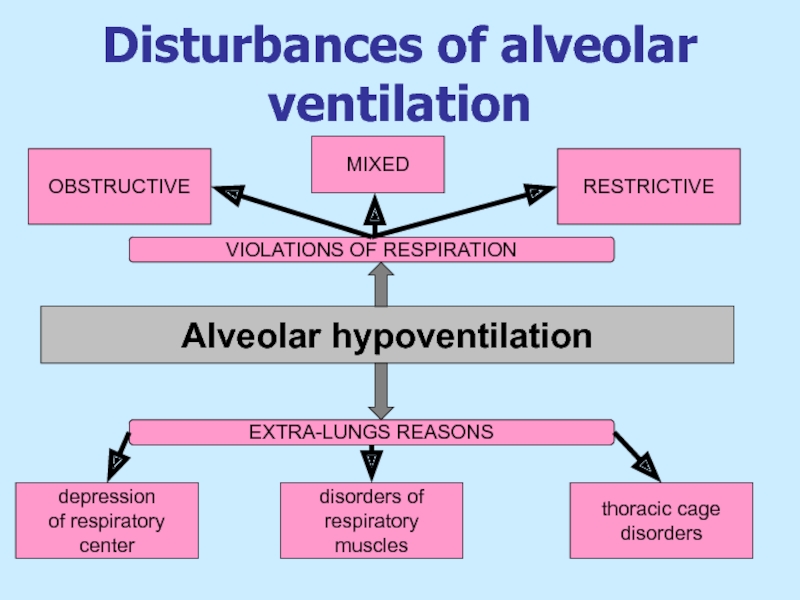
Слайд 6Disturbances of alveolar ventilation
OBSTRUCTIVE
RESTRICTIVE
depression
of respiratory center
disorders of
respiratory
thoracic cage
disorders
VIOLATIONS OF RESPIRATION
EXTRA-LUNGS REASONS
Alveolar hypoventilation
MIXED
Слайд 7Obstructive lung disorders
Obstruction of the upper respiratory ways:
embolism (foreign
compression (tumour),
spasm of larynx (neurogenous, inflammatory).
Decreased permeability of the lower respiratory ways:
increased bronchial muscles tonus (bronchospasm),
embolism of bronchi:
edema of bronchial mucous membranes
hypersecretion of mucus by bronchial glands (inflammation, asthma).
Violation of bronchi flexibility
lungs emphysema.
Слайд 8Restrictive lung diseases
Disturbances of lung’s expansion
Pulmonary reasons:
? area of lung
? elasticity of lung tissue (pneumosclerosis, lung fibrosis, sarcoidosis)
Alveolar or interstitial lung edema
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS).
Deficiency of surfactant (premature infants)
Слайд 9Restrictive lung diseases
Extrapulmonary reasons:
Changes in pleura and mediastinum (exudative pleurisy, pneumothorax,
Changes of thorax and respiratory muscles (deformation of thorax, paralysis of diaphragm).
Changes of abdominal cavity organs (hepatomegaly, ascites).
Слайд 10Disorders of perfusion
Hyperperfusion
Local - pneumonia.
Total - stress reaction
Erythrocytes have less time for normal gas exchange ?hypoxemia.
The diffusion of CO2– not altered.
Type 1 respiratory failure
Слайд 11Disorders of perfusion
Hypoperfusion
heart pathology (heart failure, valvular disorders)
vessels pathology (atherosclerosis,
Pathogenetic mechanisms:
low cardiac output
opening of shunts between arteries and veins of pulmonary circulation
obstruction of lung vessels
Type 1 respiratory failure
Слайд 12Mismatching of ventilation and perfusion
Ventilation/perfusion ratio differs in lungs physiologically
Reason of
Problems with ventilation
Collapsed airways (emphysema)
Bronchoconstriction (COPD, asthma)
Inflammation (bronchitis, pneumonia)
Lung diseases (fibrosis, pulmonary vascular congestion)
Low oxygen in alveoli ↓ perfusion
Carbon dioxide is increased
Type 2 respiratory failure
Слайд 13Diffusion impairment
↑ distance for diffusion (lung edema, inflammation, fibrous changes).
↓
Type 1 respiratory failure
Слайд 14Manifestations
of respiratory failure
Hypoxemia - pO2 < 50 mm Hg
Hypercapnia - pCO2 >50 mm Hg.
Hypoxemia Manifestations.
resulting from impaired function of vital centers
resulting from activation of compensatory mechanisms
Слайд 15Hypoxemia Manifestations
impairment of mental performance and behavior
peripheral vasoconstriction
diaphoresis (sweating)
central or peripheral cyanosis
↑ blood pressure
↑ heart rate, hyperventilation
Слайд 16Hypercapnia Manifestations
↓ pH and respiratory acidosis
compensated by renal bicarbonate retention
vasodilating effect of CO2 :
increase in cerebral blood flow and cerebral spinal fluid pressure (headache);
hyperemic conjunctivae;
warm and flushed skin.
Nervous system effects of CO2 -progressive somnolence, disorientation, coma.
Слайд 17Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS)
Causes
aspiration of gastric contents, toxic
trauma (with or without fat emboli),
sepsis
acute pancreatitis
pneumonia, alveolar bleedings
reactions to drugs and toxins.
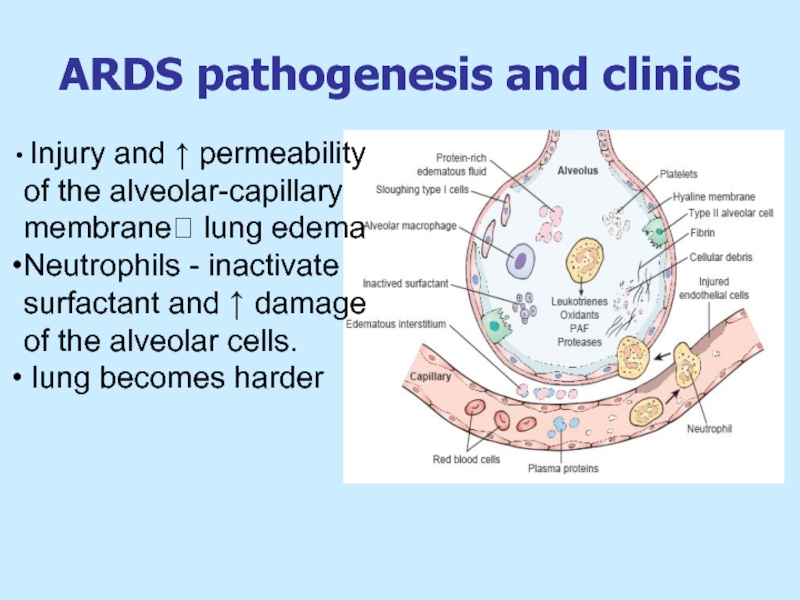
Слайд 18ARDS pathogenesis and clinics
Injury and ↑ permeability of the alveolar-capillary
Neutrophils - inactivate surfactant and ↑ damage of the alveolar cells.
lung becomes harder
Слайд 19ARDS clinical manifestation
rapid onset, 12 to 18 hours after initial event
↑
signs of respiratory failure
diffuse bilateral consolidation of the lung tissue
marked hypoxemia
multiple organ failure (kidneys, GIT, CNS, and cardiovascular system)
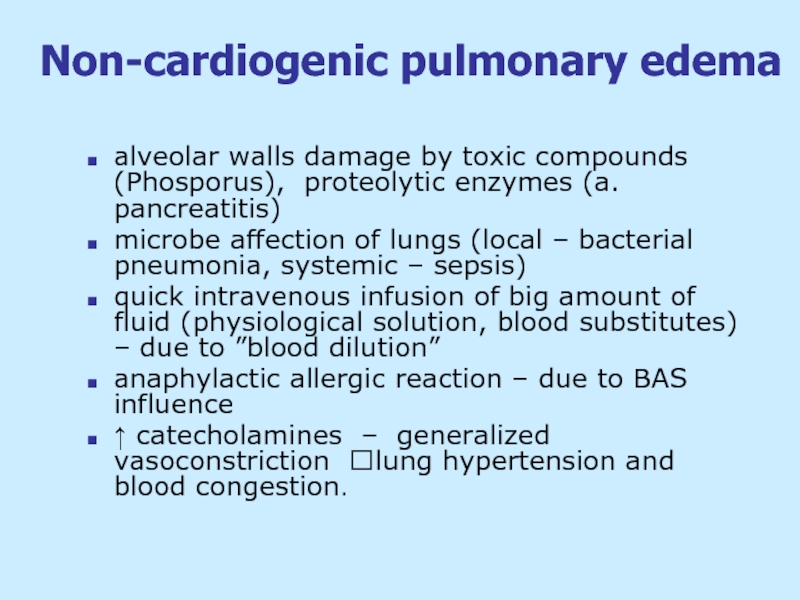
Слайд 21Non-cardiogenic pulmonary edema
alveolar walls damage by toxic compounds (Phosporus), proteolytic
microbe affection of lungs (local – bacterial pneumonia, systemic – sepsis)
quick intravenous infusion of big amount of fluid (physiological solution, blood substitutes) – due to ”blood dilution”
anaphylactic allergic reaction – due to BAS influence
↑ catecholamines – generalized vasoconstriction ?lung hypertension and blood congestion.
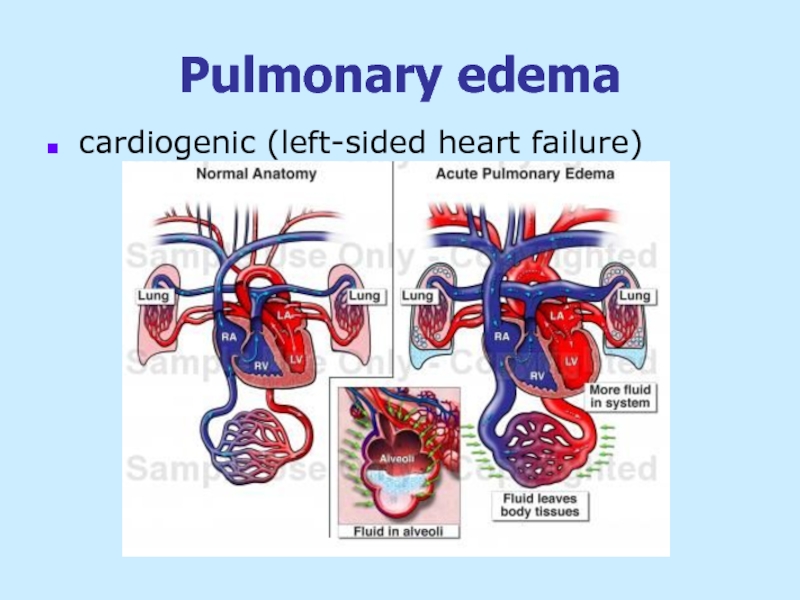
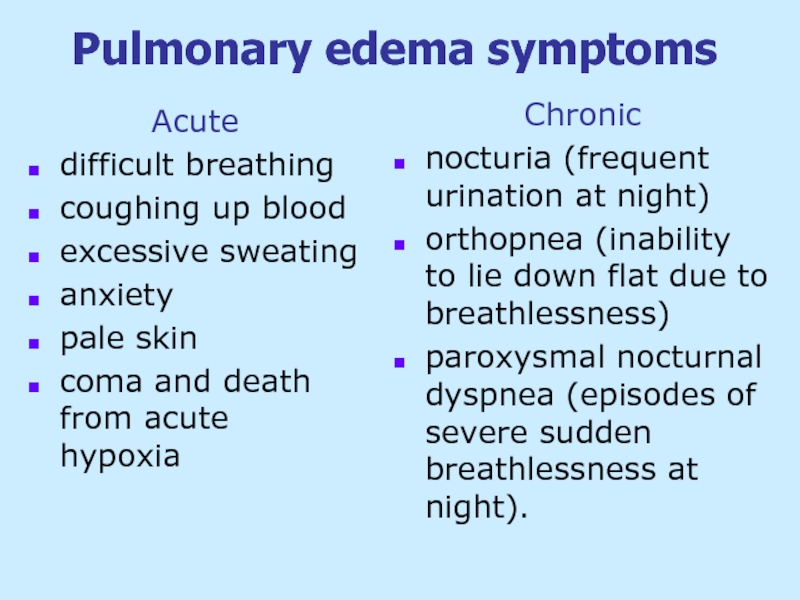
Слайд 22Pulmonary edema symptoms
Acute
difficult breathing
coughing up blood
excessive sweating
anxiety
pale
coma and death from acute hypoxia
Chronic
nocturia (frequent urination at night)
orthopnea (inability to lie down flat due to breathlessness)
paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea (episodes of severe sudden breathlessness at night).
Слайд 23Pulmonary edema symptoms
Chronic pulmonary edema:
nocturia (frequent urination at night),
ankle edema
orthopnea (inability to lie down flat due to breathlessness)
paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea (episodes of severe sudden breathlessness at night).
Слайд 24Short breath (dyspnea)
violation of frequency, depth, rhythm of breath
changes
“air hunger”
Слайд 25Dyspnea classification
According to pathogenesis
Cerebral dyspnoea (central) - violation of respiratory center
Lung dyspnoea– diseases of lungs, bronchi, pleura.
Cardiac dyspnoea - heart diseases with cardiac failure.
Hematic dyspnoea - ↓ in blood oxygen capacity (anaemia), acidosis.
Слайд 26Dyspnea classification
Due to dyspnea character:
Hyperpnea
Tachypnea
Bradypnea
Apnoea
Due to altered phase of respiration:
Inspiratory dyspnea
Expiratory dyspnea
Mixed dyspnoea
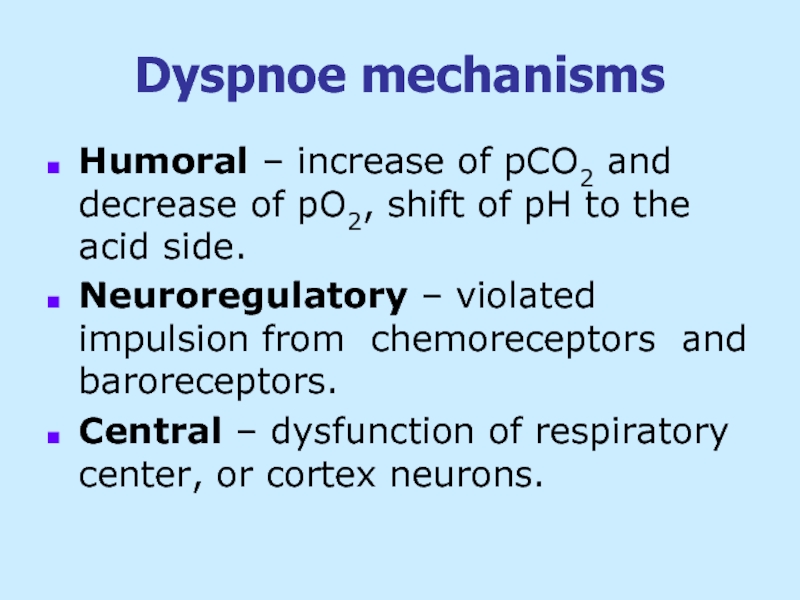
Слайд 27Dyspnoe mechanisms
Humoral – increase of pCO2 and decrease of pO2, shift
Neuroregulatory – violated impulsion from chemoreceptors and baroreceptors.
Central – dysfunction of respiratory center, or cortex neurons.
Слайд 28Cerebral dyspnea
Excitation of respiratory centre - frequent deep respiration.
Inhibition
Periodic breathing appears at brain affections by:
trauma
stroke
tumour
inflammation
endogenous and exogenous intoxications
Слайд 29Cheyne-Stokes respiration
failure of the respiratory center
bigger concentrations of CO2
causes: strokes, head injuries or brain tumors, congestive heart failure, morphine administration.
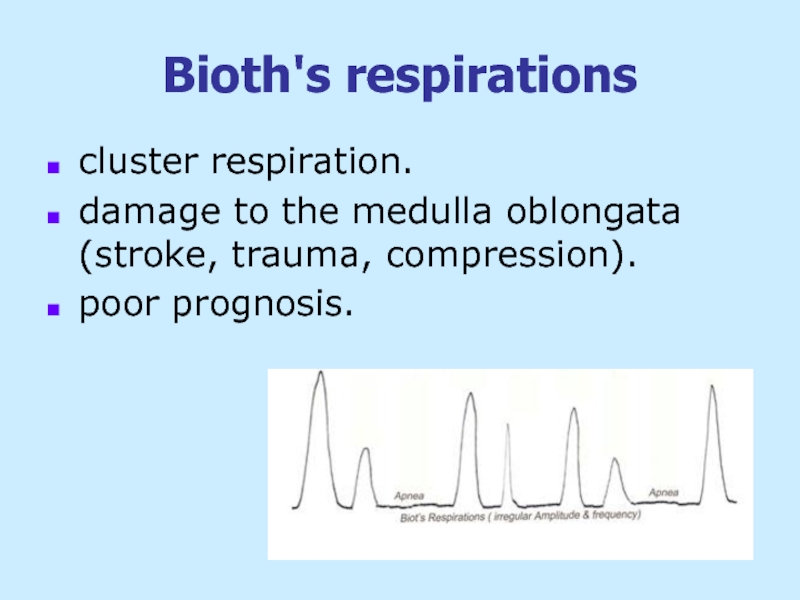
Слайд 30Bioth's respirations
cluster respiration.
damage to the medulla oblongata (stroke, trauma, compression).
poor prognosis.
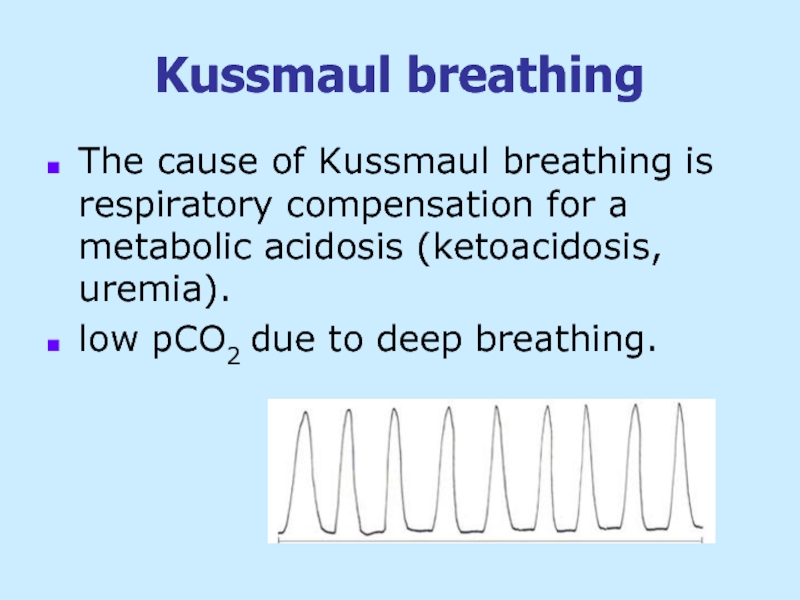
Слайд 31Kussmaul breathing
The cause of Kussmaul breathing is respiratory compensation for
low pCO2 due to deep breathing.
Слайд 32Agonal respiration
shallow, irregular inspirations followed by irregular pauses.
gasping, labored
Causes
cerebral ischemia
extreme hypoxia or anoxia
Слайд 33Other dyspnea types
Lungs dyspnea
Embolism or narrowing of upper respiratory ways
bronchial asthma (expiratory dyspnoea)
pneumonia, pleurisy
Cardiac dyspnea
cardiac failure, heart valves pathology
Hematic dyspnea
anemia
metHb formation (CO poisoning).
Слайд 34Asphyxia
a condition of severe deficiency of oxygen supply with severe
Causes:
Insufficient environmental oxygen:
Inhalation of non-oxygen gases (helium, CO2 fire).
Loss of aircraft cabin pressure;
Exposure to a vacuum.
Слайд 35Asphyxia causes
Physical obstruction of air flow
Compressive asphyxia
Drowning (water or other
Choking due to object in the airways or inhalation of vomit.
Narrowing of the airways (anaphylaxis, asthma).
Disturbances of respiration
CO inhalation.
Pulmonary agents (phosgene),blood agents (cyanide).
Drug overdose.
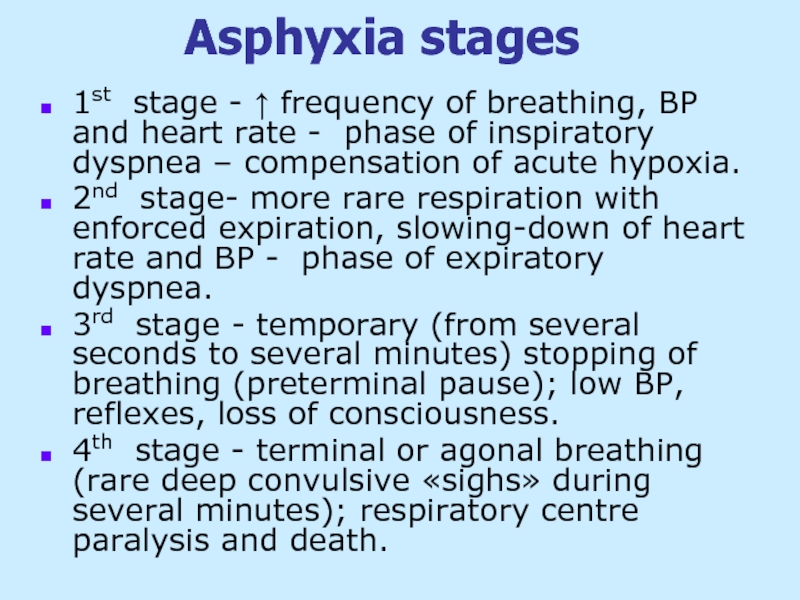
Слайд 36Asphyxia stages
1st stage - ↑ frequency of breathing, BP and heart
2nd stage- more rare respiration with enforced expiration, slowing-down of heart rate and BP - phase of expiratory dyspnea.
3rd stage - temporary (from several seconds to several minutes) stopping of breathing (preterminal pause); low BP, reflexes, loss of consciousness.
4th stage - terminal or agonal breathing (rare deep convulsive «sighs» during several minutes); respiratory centre paralysis and death.