- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Opportunistic Enterobacteriaceae презентация
Содержание
- 2. Opportunistic Enterobacteriaceae
- 3. OPPORTUNISTIC INFECTIONS OF ENTEROBACTERIACEAE GRAM NEGATIVE SEPSIS
- 4. OPPORTUNISTIC INFECTIONS (cont.) GRAM NEGATIVE SEPSIS Life-threatening
- 5. OPPORTUNISTIC INFECTIONS (cont.) URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS Usually
- 6. OPPORTUNISTIC INFECTIONS (cont.) ABDOMINAL SEPSIS Caused by
- 7. OPPORTUNISTIC INFECTIONS (cont.) SPONTANEOUS BACTERIAL PERITONITIS Usually
- 8. Common Virulence Factors Endotoxin Capsule Antigenic phase
- 9. Fever Leukopenia (reduced #
- 10. See Handout on Enterobacteriaceae General Information
- 11. Summary of Escherichia coli Infections
- 12. Summary of Escherichia coli Infections (cont.)
- 13. Gastroenteritis Caused by E. coli
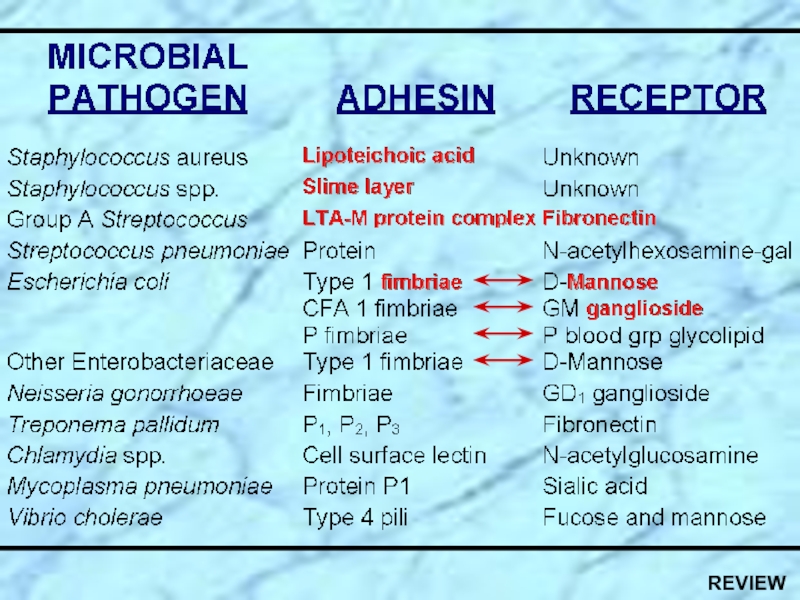
- 14. Specialized Virulence Factors Associated with E. coli
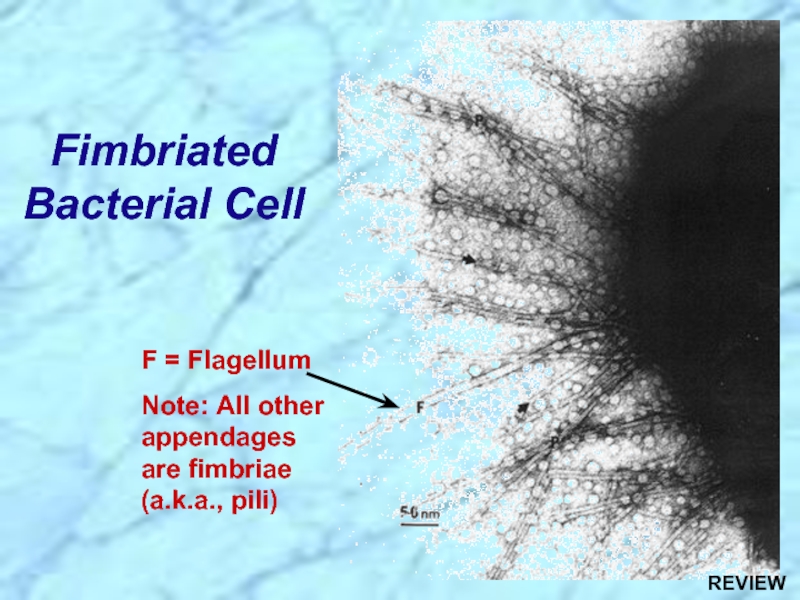
- 15. Fimbriated Bacterial Cell F = Flagellum Note: All other appendages are fimbriae (a.k.a., pili)
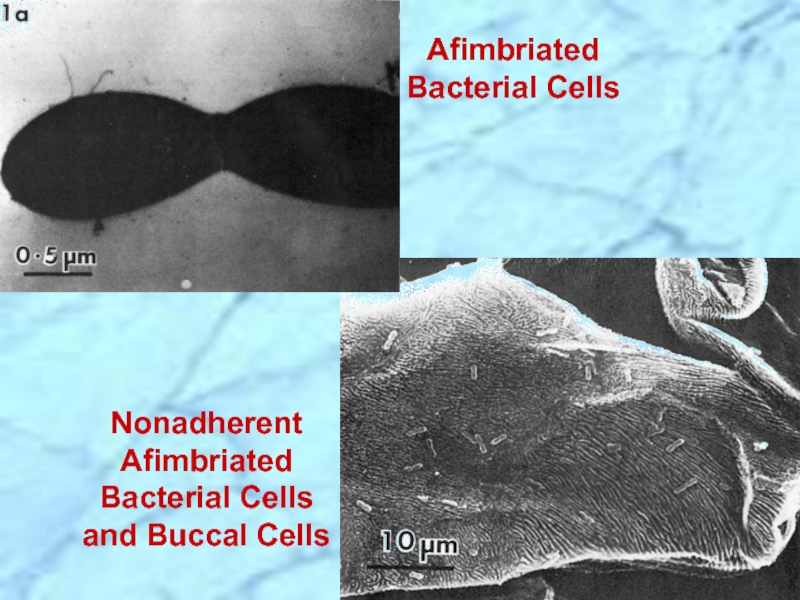
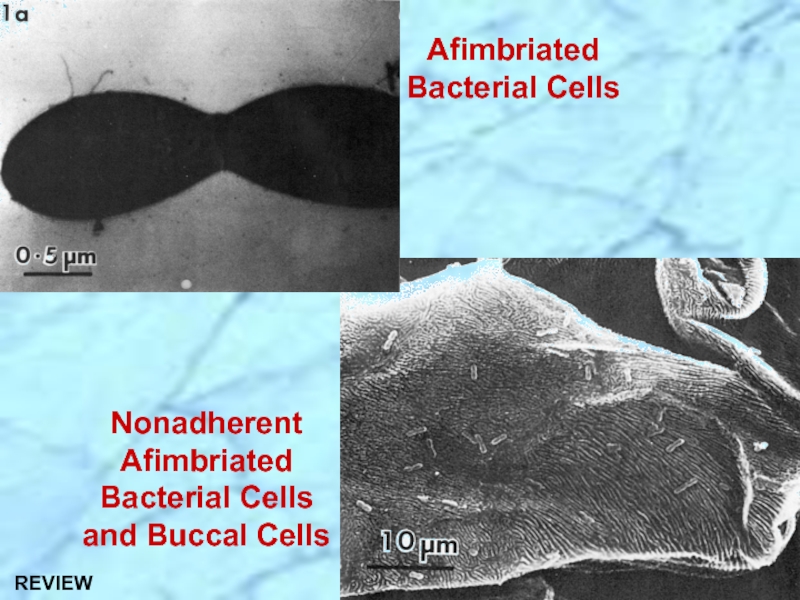
- 16. Afimbriated Bacterial Cells Nonadherent Afimbriated Bacterial Cells and Buccal Cells
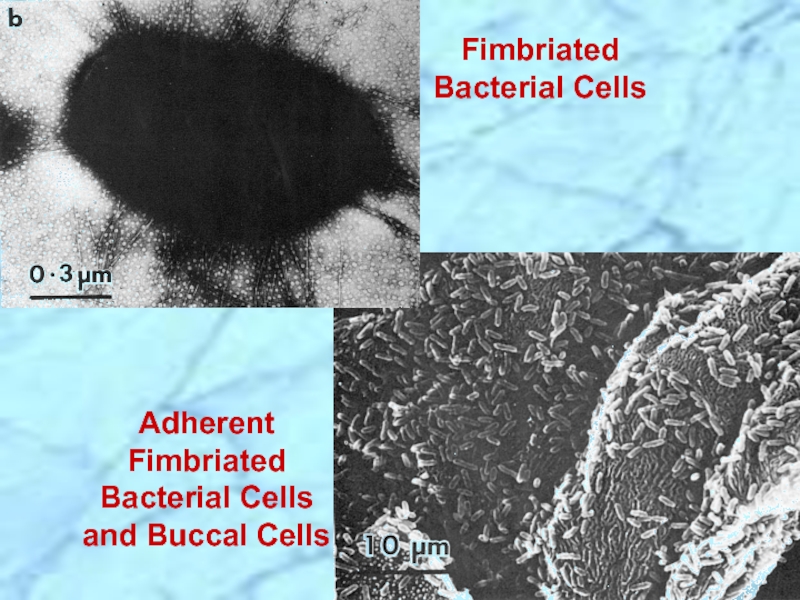
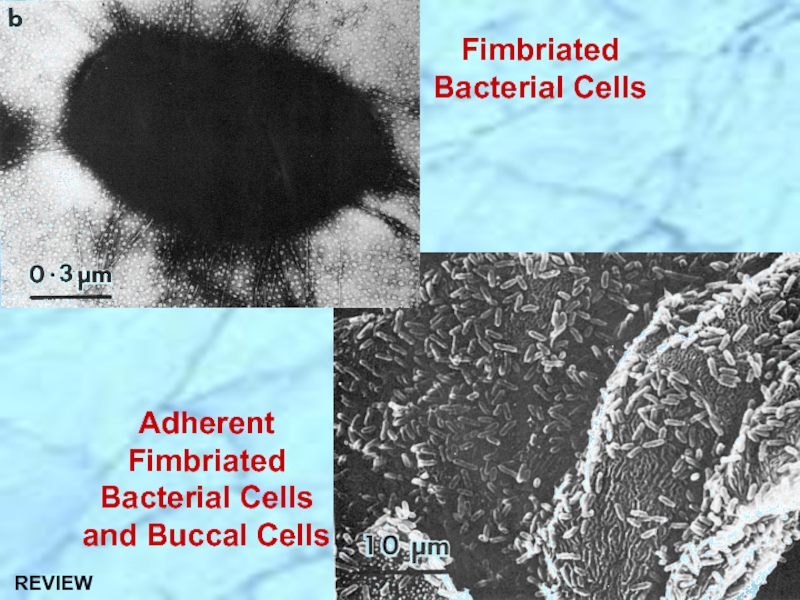
- 17. Adherent Fimbriated Bacterial Cells and Buccal Cells Fimbriated Bacterial Cells
- 19. (ETEC) (EHEC)
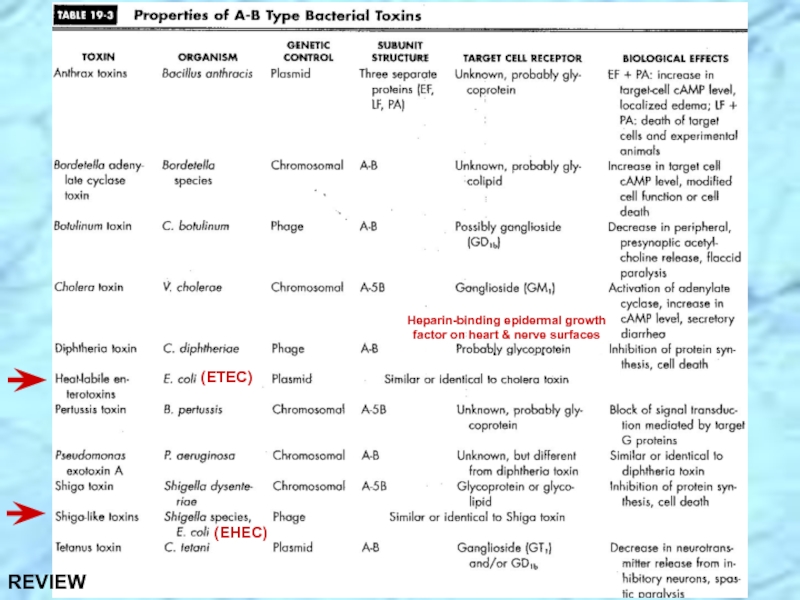
- 21. REVIEW
- 22. OPPORTUNISTIC INFECTIONS OF ENTEROBACTERIACEAE GRAM NEGATIVE SEPSIS
- 23. Common Virulence Factors Endotoxin Capsule Antigenic phase
- 24. REVIEW See Handout on Enterobacteriaceae General Information
- 25. Fever Leukopenia (reduced #
- 26. Summary of Escherichia coli Infections REVIEW
- 27. Summary of Escherichia coli Infections (cont.) REVIEW
- 28. Gastroenteritis Caused by E. coli REVIEW
- 29. Fimbriated Bacterial Cell F = Flagellum
- 30. Afimbriated Bacterial Cells Nonadherent Afimbriated Bacterial Cells and Buccal Cells REVIEW
- 31. Adherent Fimbriated Bacterial Cells and Buccal Cells Fimbriated Bacterial Cells REVIEW
- 32. REVIEW
- 33. (ETEC) (EHEC) REVIEW
Слайд 3OPPORTUNISTIC INFECTIONS OF ENTEROBACTERIACEAE
GRAM NEGATIVE SEPSIS
URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS
PNEUMONIA
ABDOMINAL
MENINGITIS
SPONTANEOUS BACTERIAL PERITONITIS
ENDOCARDITIS
Слайд 4OPPORTUNISTIC INFECTIONS (cont.)
GRAM NEGATIVE SEPSIS
Life-threatening
Usually nosocomial
Commonly caused by E. coli
Early Phase (REVERSIBLE)
Decreased arterial resistance; Increased cardiac output
Kinins (protein vasodilators & mediators of inflammation) in plasma due to tissue damage, endotoxin, AG-AB complexes
Second Phase (REVERSIBLE)
Increased arterial resistance; Decreased cardiac output
Third Phase (IRREVERSIBLE)
Vascular collapse with organ failure
Endotoxin induced DIC, hemorrhage and death
Слайд 5OPPORTUNISTIC INFECTIONS (cont.)
URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS
Usually ascending infection, not hematogenous route
Greatest incidence
Incidence increases with age in males
Most commonly caused by E. coli
Diagnosis by microscopic & cultural exam of urine
Obtain urine by catheter through urethra into bladder, clean catch midstream (CCMS) or suprapubic tap
PNEUMONIA
Nosocomial; Spread by personnel and equipment
Frequently caused by K. pneumoniae
Often in middle-aged males who abuse alcohol
Difficult to diagnose due to commensals in sputum
Слайд 6OPPORTUNISTIC INFECTIONS (cont.)
ABDOMINAL SEPSIS
Caused by flora of the GI tract
Infections usually
MENINGITIS
Usually nosocomial
Frequently caused by E. coli
Diagnosis by microscopic & cultural exam of CSF
Слайд 7OPPORTUNISTIC INFECTIONS (cont.)
SPONTANEOUS BACTERIAL PERITONITIS
Usually in patients with liver ailments
Commonly caused
ENDOCARDITIS
Vascular endocardial surface inflammation
Mostly caused by Gram-positive cocci, but 1-3% caused by aerobic Gram-negative rods
Diagnosis by blood culture
Difficult to treat; Treatment is of long duration
Слайд 8Common Virulence Factors
Endotoxin
Capsule
Antigenic phase variation
Sequestration of growth factors
Resistance to serum killing
Antimicrobial
Factors Associated with Specific Pathogens
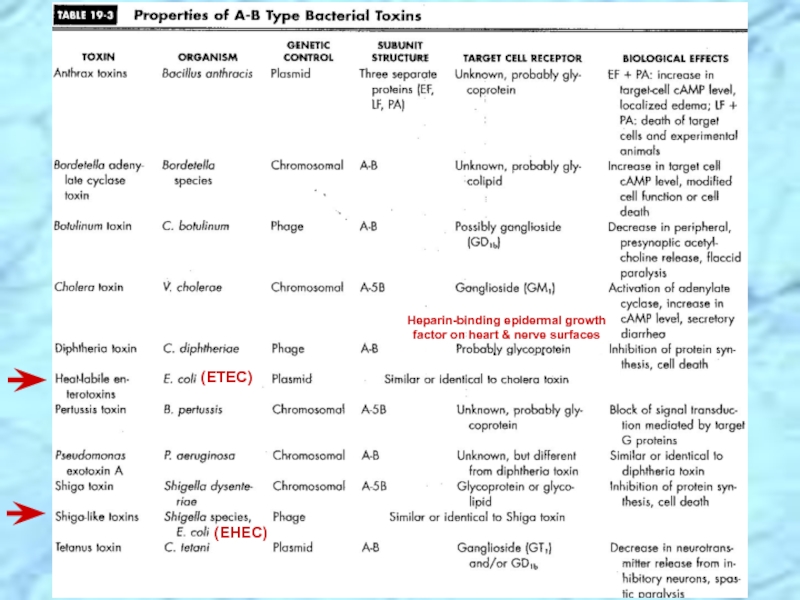
Exotoxin production
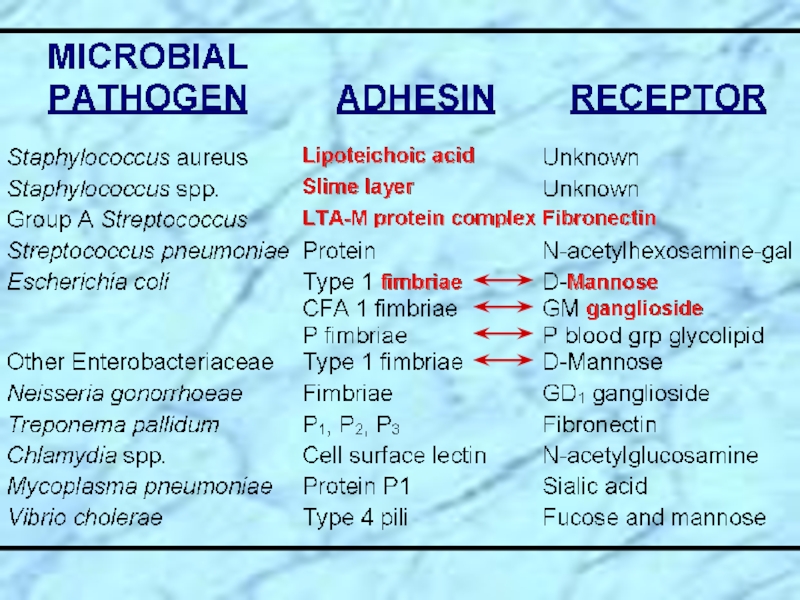
Expression of adhesion factors
Intracellular survival and multiplication
Virulence Factors Associated with Enterobacteriaceae
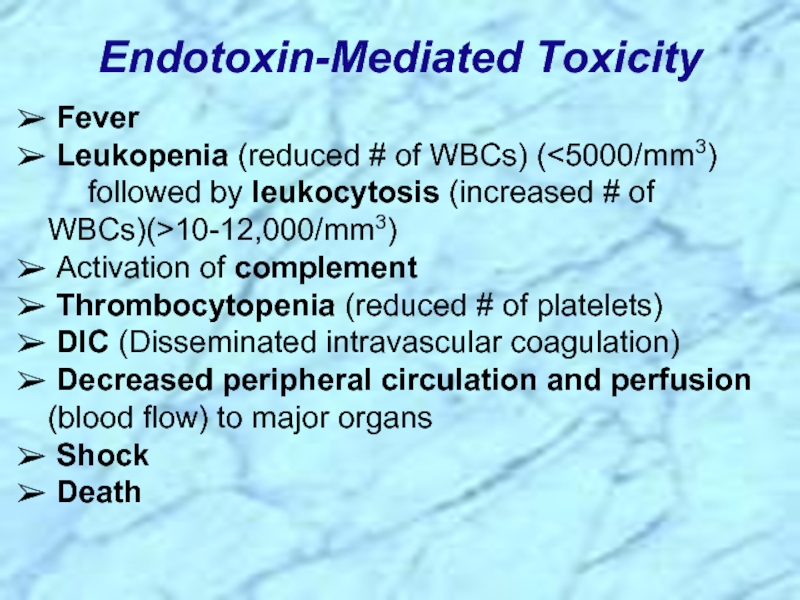
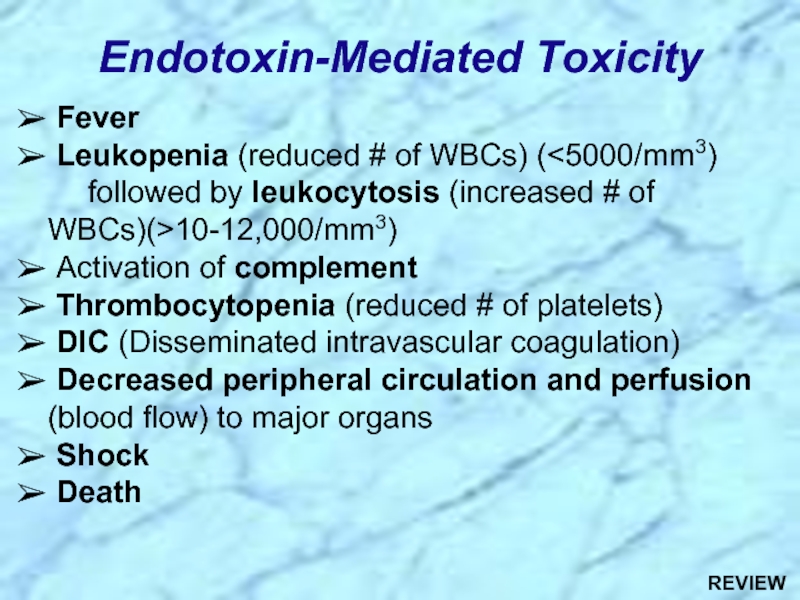
Слайд 9 Fever
Leukopenia (reduced # of WBCs) (
Activation of complement
Thrombocytopenia (reduced # of platelets)
DIC (Disseminated intravascular coagulation)
Decreased peripheral circulation and perfusion (blood flow) to major organs
Shock
Death
Endotoxin-Mediated Toxicity
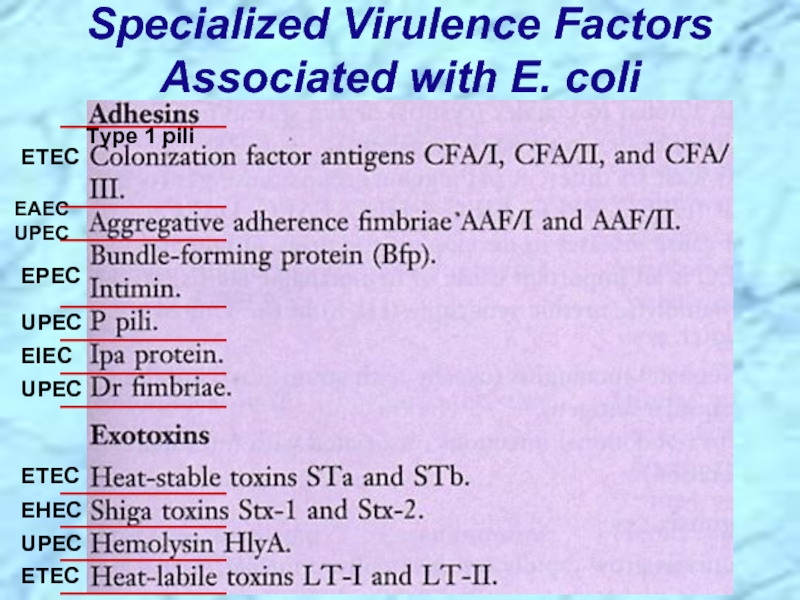
Слайд 14Specialized Virulence Factors Associated with E. coli
EAEC UPEC
EPEC
ETEC
Type 1
UPEC
UPEC
EIEC
ETEC
ETEC
EHEC
UPEC
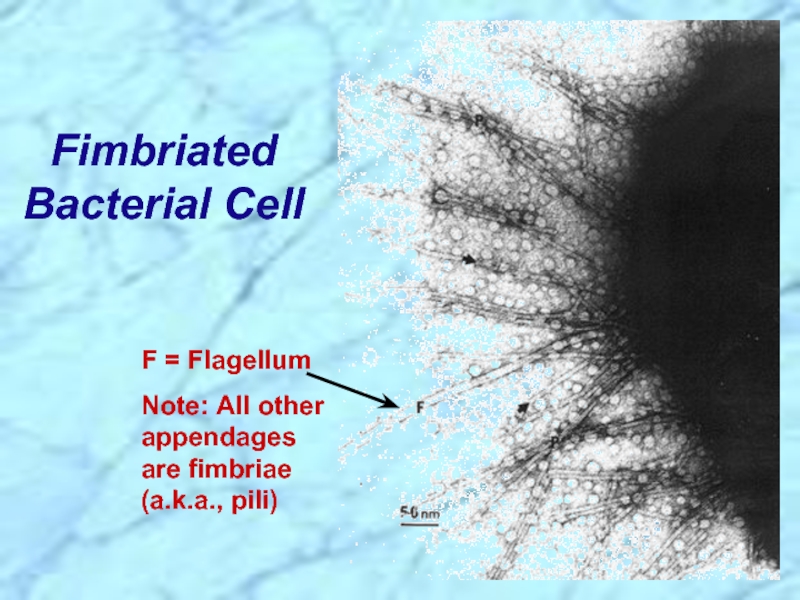
Слайд 15Fimbriated Bacterial Cell
F = Flagellum
Note: All other appendages are fimbriae
Слайд 22OPPORTUNISTIC INFECTIONS OF ENTEROBACTERIACEAE
GRAM NEGATIVE SEPSIS
URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS
PNEUMONIA
ABDOMINAL
MENINGITIS
SPONTANEOUS BACTERIAL PERITONITIS
ENDOCARDITIS
REVIEW
Слайд 23Common Virulence Factors
Endotoxin
Capsule
Antigenic phase variation
Sequestration of growth factors
Resistance to serum killing
Antimicrobial
Factors Associated with Specific Pathogens
Exotoxin production
Expression of adhesion factors
Intracellular survival and multiplication
Virulence Factors Associated with Enterobacteriaceae
REVIEW
Слайд 25 Fever
Leukopenia (reduced # of WBCs) (
Activation of complement
Thrombocytopenia (reduced # of platelets)
DIC (Disseminated intravascular coagulation)
Decreased peripheral circulation and perfusion (blood flow) to major organs
Shock
Death
Endotoxin-Mediated Toxicity
REVIEW
Слайд 29Fimbriated Bacterial Cell
F = Flagellum
Note: All other appendages are fimbriae
REVIEW