- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Myelodysplastic Syndromes презентация
Содержание
- 1. Myelodysplastic Syndromes
- 2. MDS • Clonal stem cell disorders •
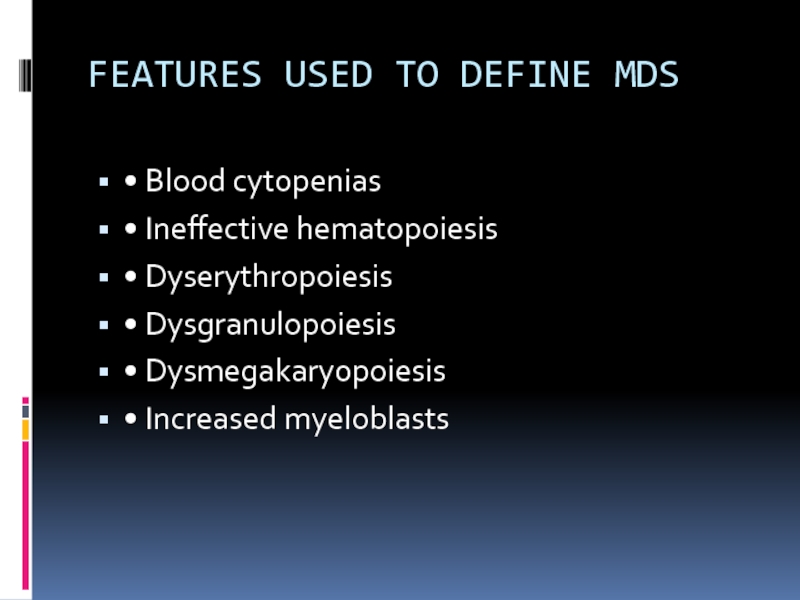
- 3. FEATURES USED TO DEFINE MDS •
- 7. FAB CLASSIFICATION OF MDS • Refractory
- 8. WHO CLASSIFICATION OF MDS • Refractory anemia
- 9. MAJOR CHANGES IN WHO CLASSIFICATION OF
- 10. REFRACTORY ANEMIA (RA) • Only erythroid lineage
- 12. REFRACTORY CYTOPENIA WITH MULTILINEAGE DYSPLASIA (RCMD)
- 16. MDS WITH ISOLATED del(5q) • Refractory
- 17. REFRACTORY ANEMIA WITH EXCESS BLASTS (RAEB) •
- 18. REFRACTORY ANEMIA WITH EXCESS BLASTS (RAEB)
- 19. MYELODYSPLASTIC SYNDROME UNCLASSIFIABLE (MDS-U) •
- 20. MYELODYSPLASTIC SYNDROME WITH INCREASED MARROW
- 22. HYPOCELLULAR MDS • Cellularity of marrow
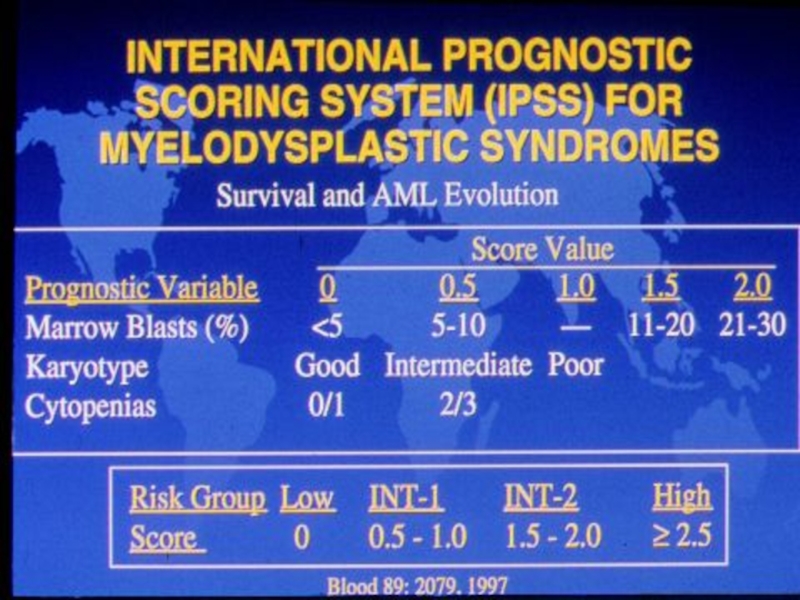
- 23. PROGNOSTIC INDICATORS IN MDS • Age
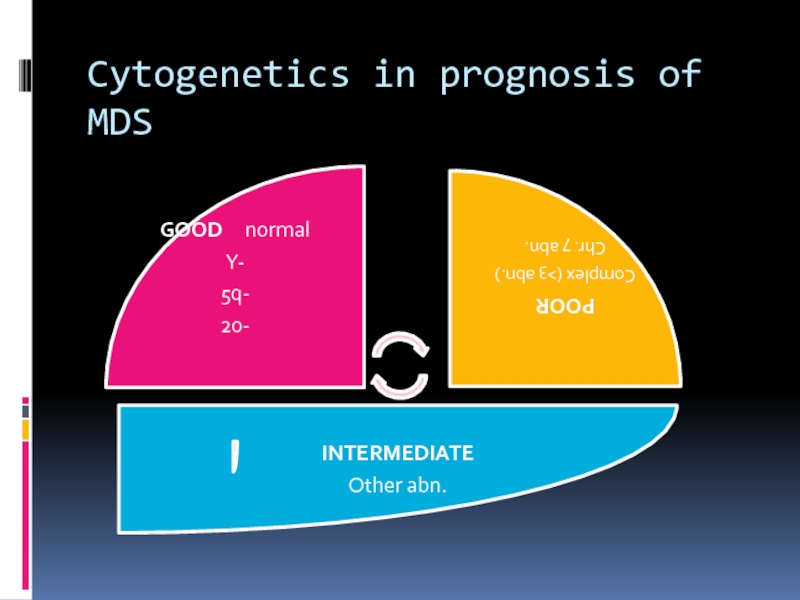
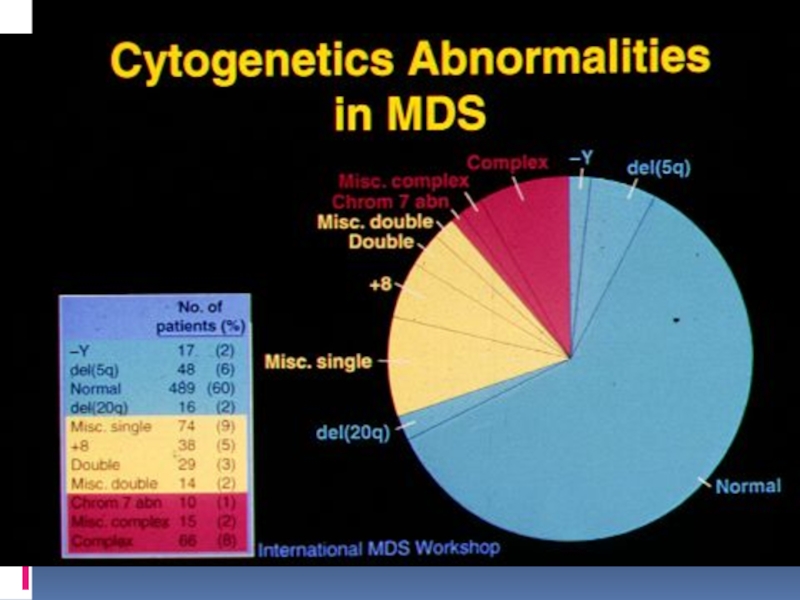
- 24. Cytogenetics in prognosis of MDS
- 25. DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS OF MDS • Non-neoplastic
- 26. PROBLEM AREAS IN THE DISTINCTION OF
- 27. DISTINCTION OF MDS FROM CHRONIC MYELOPROLIFERATIVE DISORDERS
- 28. WHO CLASSIFICATION OF MYELODYSPLASTIC/ MYELOPROLIFERATIVE DISEASE
- 29. CHRONIC MYELOMONOCYTIC LEUKEMIA • Bridges MDS
- 30. ATYPICAL CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKEMIA (aCML)
- 31. JUVENILE MYELOMONOCYTIC LEUKEMIA (JMML) • Synonymous
- 32. MONOSOMY 7 SYNDROME • Anemia and leukocytosis
- 33. OTHER MORPHOLOGIC FINDINGS IN MDS •
- 34. MDS/MPD, UNCLASSIFIABLE • Features of MDS
- 35. Treatment Supportive care – blood products, infections
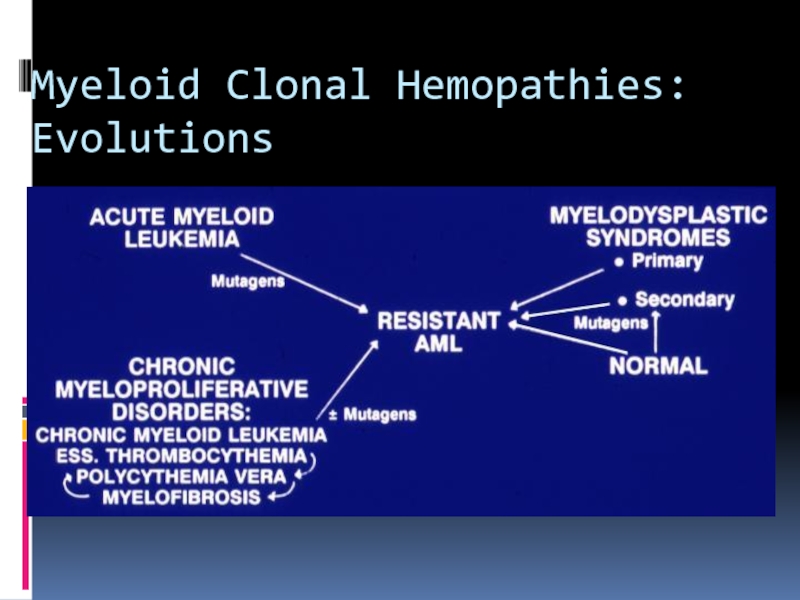
- 36. Myeloid Clonal Hemopathies: Evolutions
- 42. Survival Based on WPSS Malcovati et
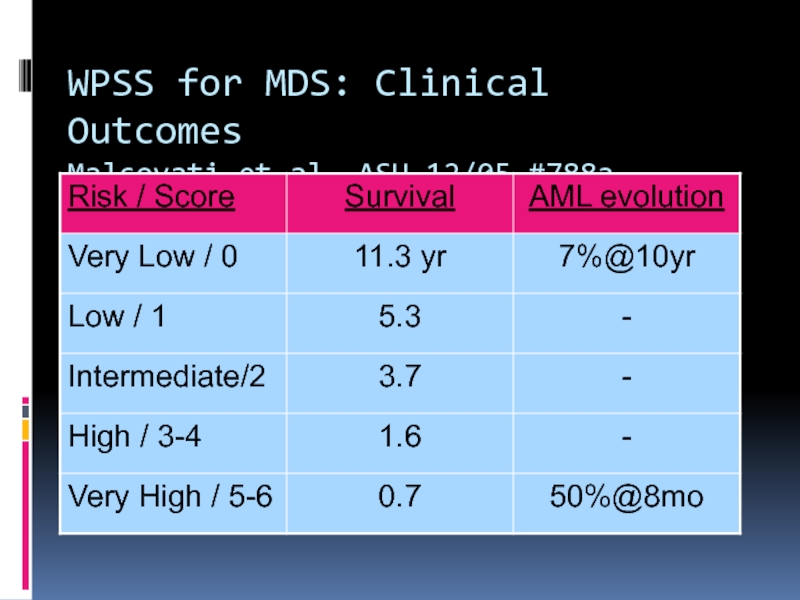
- 43. WPSS for MDS: Clinical Outcomes Malcovati et al, ASH 12/05 #788a
- 44. THANK YOU
Слайд 2MDS
• Clonal stem cell disorders
• Maturation defects
• Ineffective hematopoiesis
• Blood cytopenias
•
Risk of transformation to AML
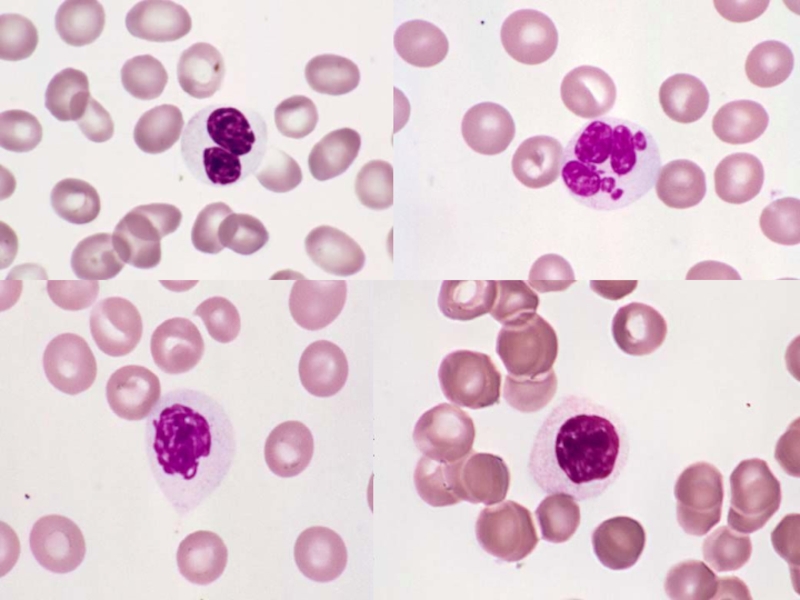
Слайд 3FEATURES USED TO DEFINE MDS
• Blood cytopenias
• Ineffective hematopoiesis
• Dyserythropoiesis
• Dysgranulopoiesis
•
Dysmegakaryopoiesis
• Increased myeloblasts
• Increased myeloblasts
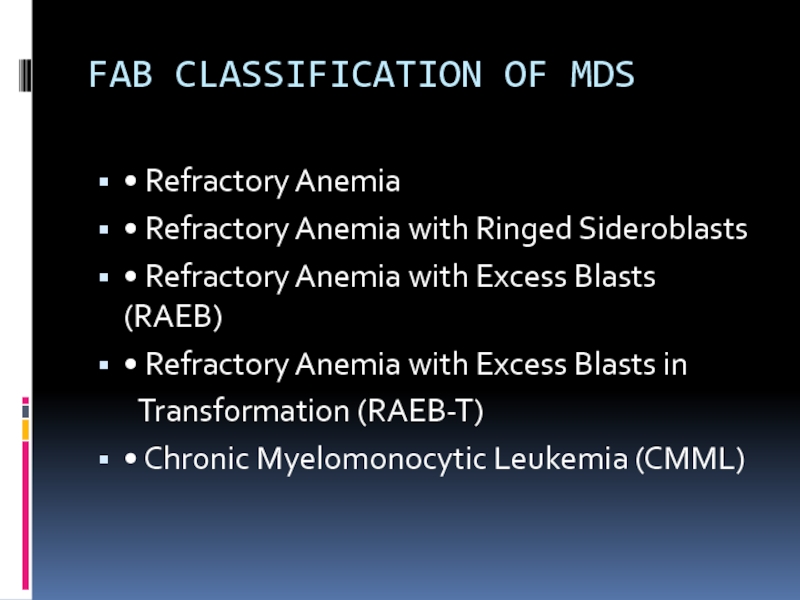
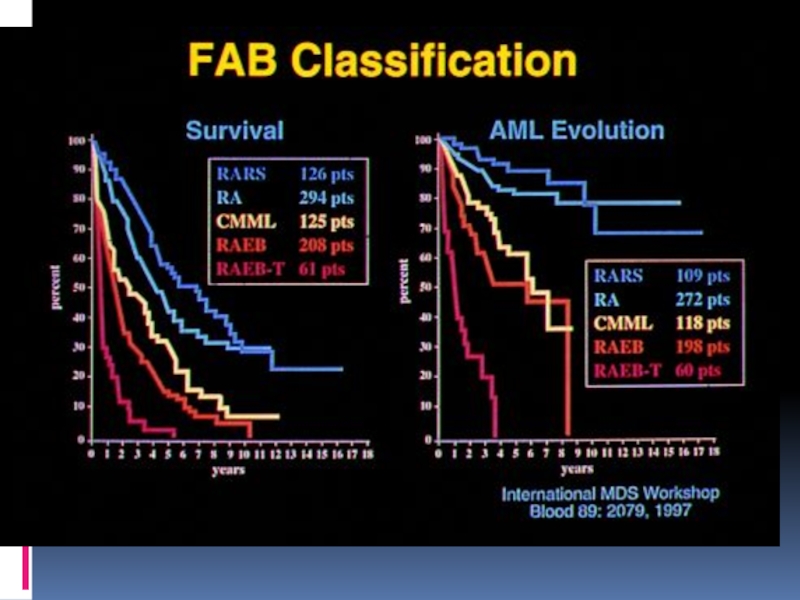
Слайд 7FAB CLASSIFICATION OF MDS
• Refractory Anemia
• Refractory Anemia with Ringed Sideroblasts
•
Refractory Anemia with Excess Blasts (RAEB)
• Refractory Anemia with Excess Blasts in
Transformation (RAEB-T)
• Chronic Myelomonocytic Leukemia (CMML)
• Refractory Anemia with Excess Blasts in
Transformation (RAEB-T)
• Chronic Myelomonocytic Leukemia (CMML)
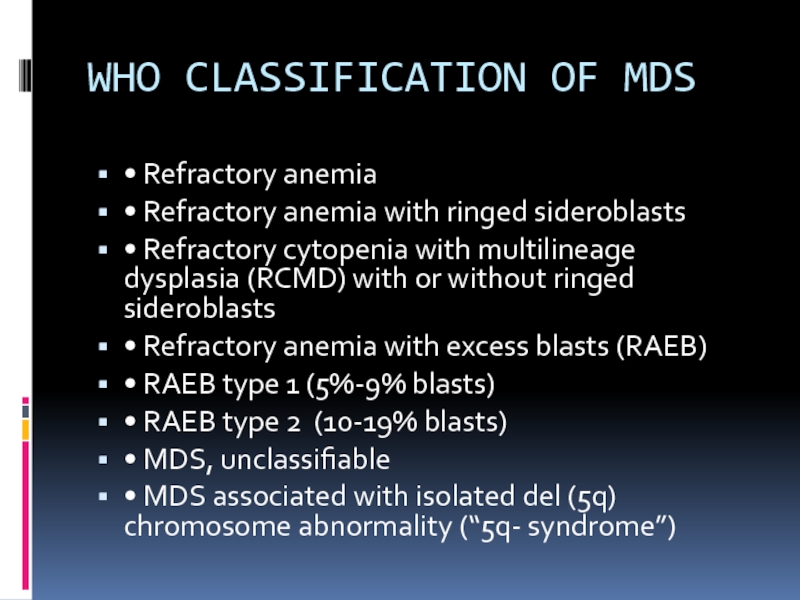
Слайд 8WHO CLASSIFICATION OF MDS
• Refractory anemia
• Refractory anemia with ringed sideroblasts
•
Refractory cytopenia with multilineage dysplasia (RCMD) with or without ringed sideroblasts
• Refractory anemia with excess blasts (RAEB)
• RAEB type 1 (5%-9% blasts)
• RAEB type 2 (10-19% blasts)
• MDS, unclassifiable
• MDS associated with isolated del (5q) chromosome abnormality (“5q- syndrome”)
• Refractory anemia with excess blasts (RAEB)
• RAEB type 1 (5%-9% blasts)
• RAEB type 2 (10-19% blasts)
• MDS, unclassifiable
• MDS associated with isolated del (5q) chromosome abnormality (“5q- syndrome”)
Слайд 9
MAJOR CHANGES IN WHO
CLASSIFICATION OF MDS
• Blast count for a diagnosis
of AML is reduced from 30% to 20%
• RAEB-T is eliminated
• Refractory cytopenia with multilineage dysplasia (RCMD) is added
• 5q- syndrome is added
• CMML is incorporated into a bridging MDS-MPD classification
• RAEB-T is eliminated
• Refractory cytopenia with multilineage dysplasia (RCMD) is added
• 5q- syndrome is added
• CMML is incorporated into a bridging MDS-MPD classification
Слайд 10REFRACTORY ANEMIA (RA)
• Only erythroid lineage involved
• Normocytic or macrocytic anemia
•
Reticulocytopenia
• Usually normal or ↑RBC precursors
• Variable dyserythropoiesis
• <5% blasts in BM, none in blood
• Usually normal or ↑RBC precursors
• Variable dyserythropoiesis
• <5% blasts in BM, none in blood
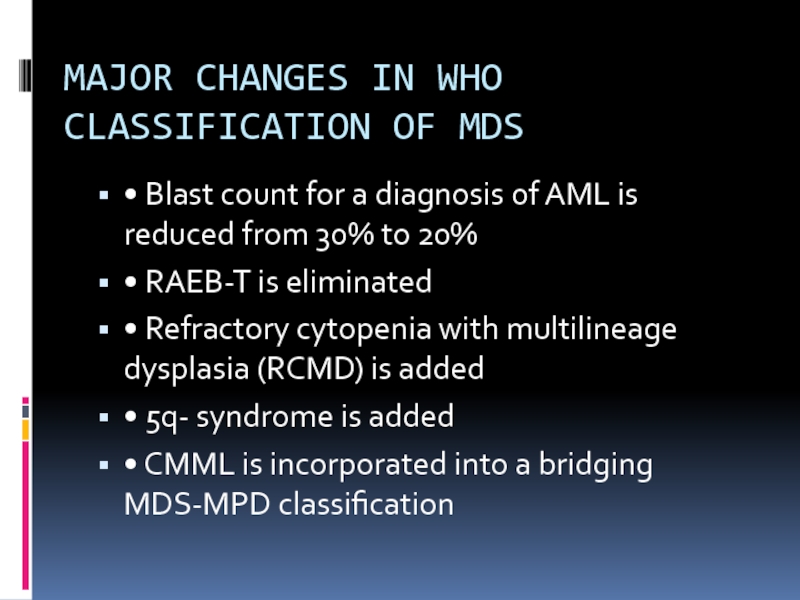
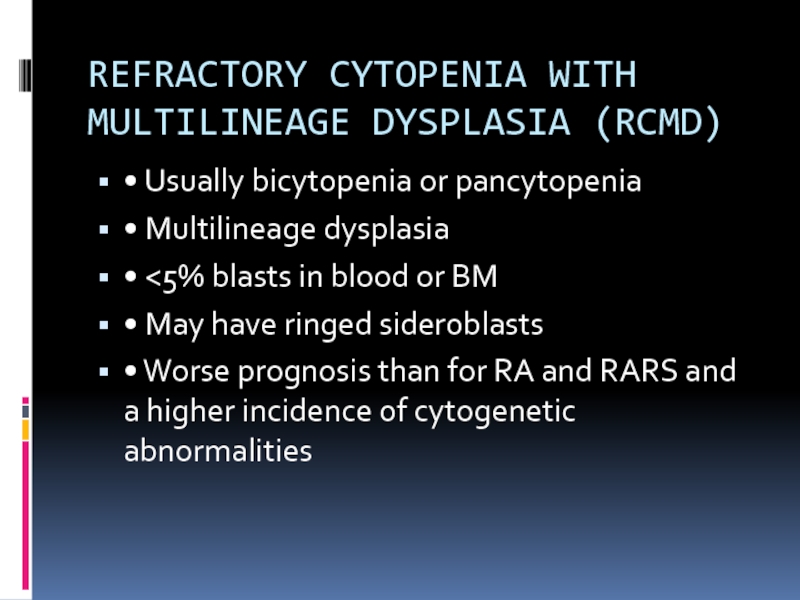
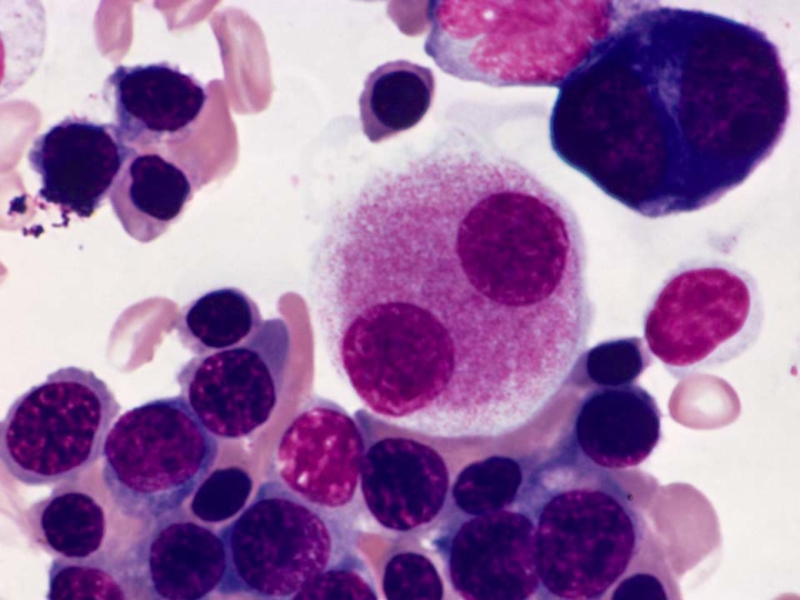
Слайд 12REFRACTORY CYTOPENIA WITH
MULTILINEAGE DYSPLASIA (RCMD)
• Usually bicytopenia or pancytopenia
• Multilineage dysplasia
•
<5% blasts in blood or BM
• May have ringed sideroblasts
• Worse prognosis than for RA and RARS and a higher incidence of cytogenetic abnormalities
• May have ringed sideroblasts
• Worse prognosis than for RA and RARS and a higher incidence of cytogenetic abnormalities
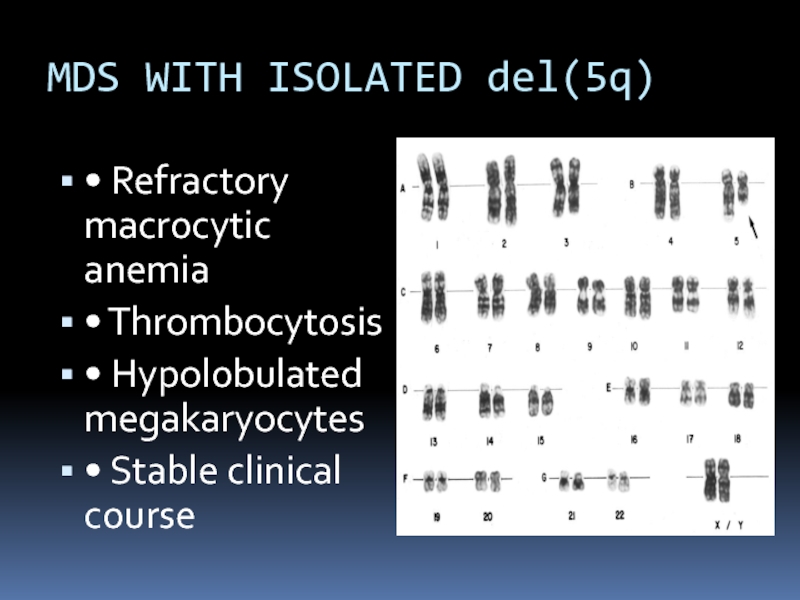
Слайд 16MDS WITH ISOLATED del(5q)
• Refractory macrocytic anemia
• Thrombocytosis
• Hypolobulated megakaryocytes
• Stable
clinical course
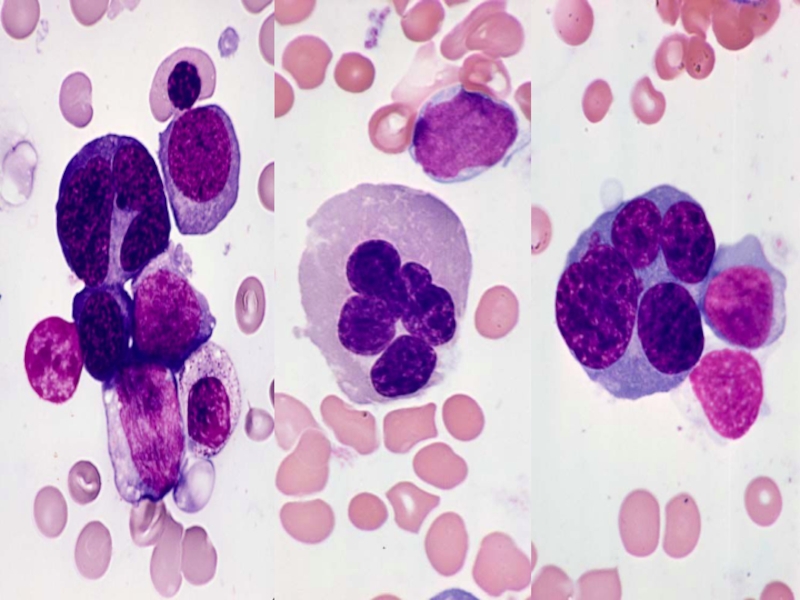
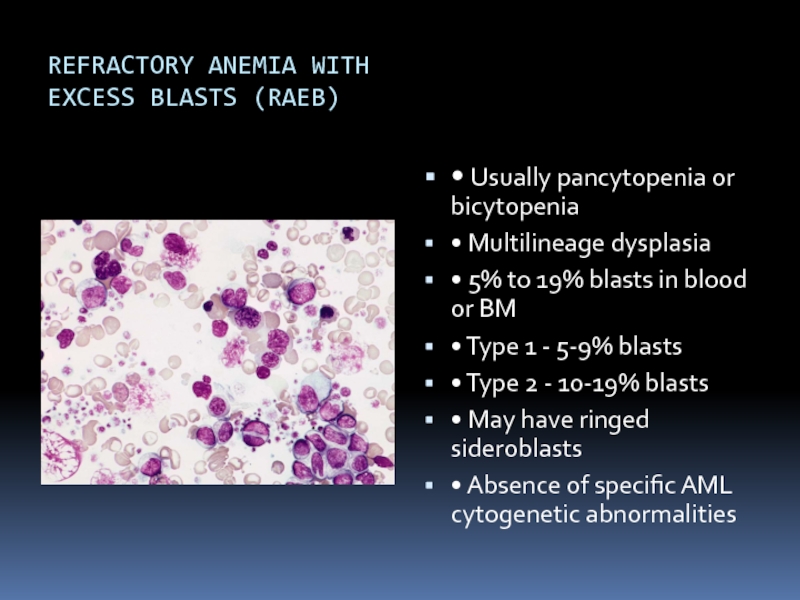
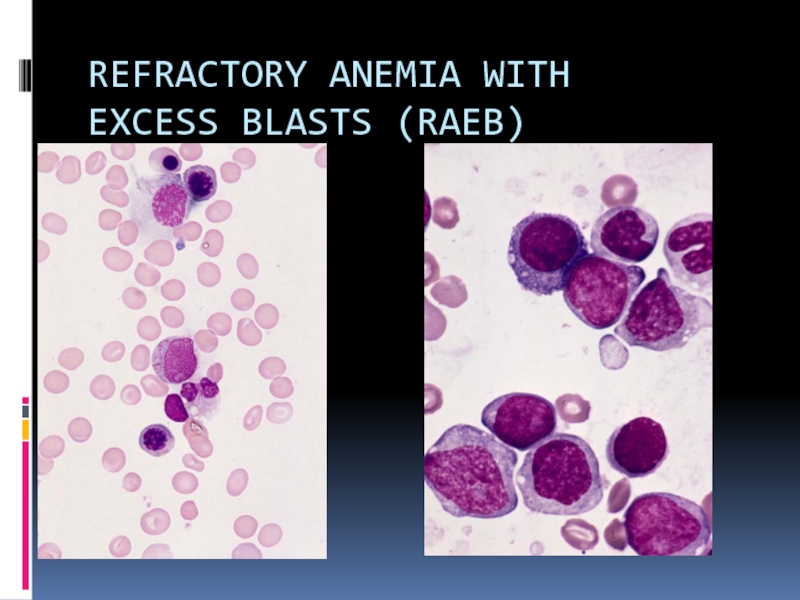
Слайд 17REFRACTORY ANEMIA WITH
EXCESS BLASTS (RAEB)
• Usually pancytopenia or bicytopenia
• Multilineage dysplasia
•
5% to 19% blasts in blood or BM
• Type 1 - 5-9% blasts
• Type 2 - 10-19% blasts
• May have ringed sideroblasts
• Absence of specific AML cytogenetic abnormalities
• Type 1 - 5-9% blasts
• Type 2 - 10-19% blasts
• May have ringed sideroblasts
• Absence of specific AML cytogenetic abnormalities
Слайд 19
MYELODYSPLASTIC SYNDROME
UNCLASSIFIABLE (MDS-U)
• Cytopenias
• No or rare blasts in blood
• Unilineage
dysplasia
• <5% marrow blasts
• No Auer rods
• <5% marrow blasts
• No Auer rods
Слайд 20
MYELODYSPLASTIC SYNDROME
WITH INCREASED MARROW
FIBROSIS
• Pancytopenia
• Trilineage dysplasia
• Bone marrow fibrosis
• ↑and
dysplastic megakaryocytes
• No splenomegaly
• ? poor survival
• No splenomegaly
• ? poor survival
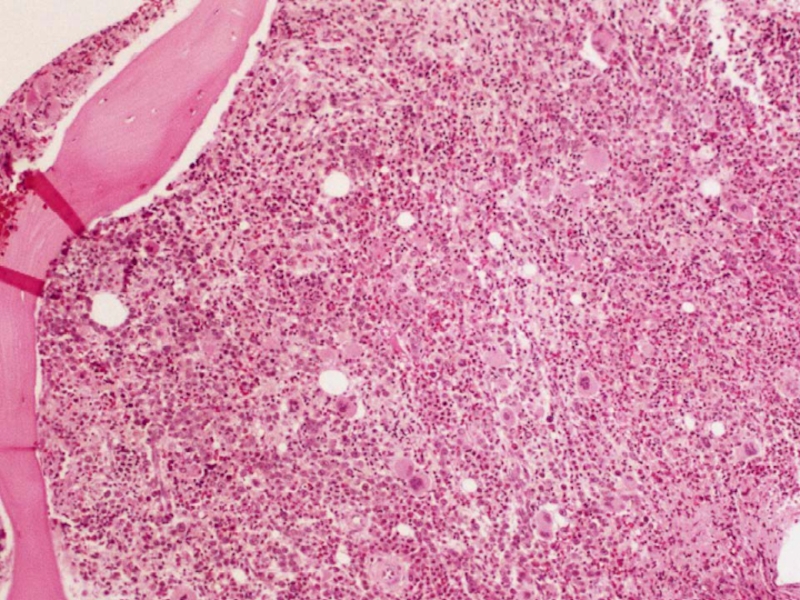
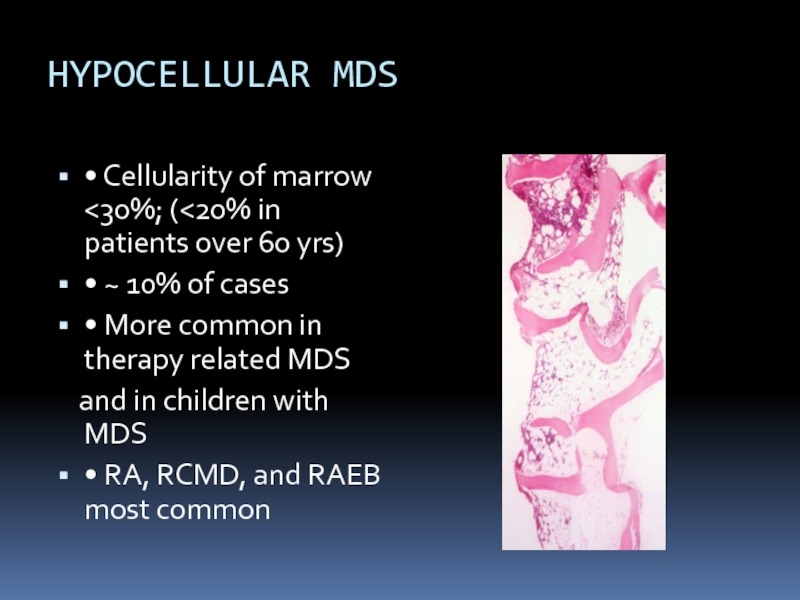
Слайд 22HYPOCELLULAR MDS
• Cellularity of marrow
yrs)
• ~ 10% of cases
• More common in therapy related MDS
and in children with MDS
• RA, RCMD, and RAEB most common
• ~ 10% of cases
• More common in therapy related MDS
and in children with MDS
• RA, RCMD, and RAEB most common
Слайд 23PROGNOSTIC INDICATORS IN
MDS
• Age
• Gender
• Bone marrow blast %
• # of
cytopenias
• Cytogenetics
• Cytogenetics
Слайд 25DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS OF MDS
• Non-neoplastic causes of myelodysplasia
• Megaloblastic changes
• Toxic
agents, i.e., heavy metals, acute alcohol intoxication
• Drug effects
• Congenital dyserythropoietic anemia
• Chronic infectious disease
• Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS)
• Drug effects
• Congenital dyserythropoietic anemia
• Chronic infectious disease
• Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS)
• Neoplastic Diseases
• Chronic myeloproliferative disease
• Acute myeloid leukemia
Слайд 26
PROBLEM AREAS IN THE
DISTINCTION OF MDS AND AML
• Borderline blast counts
•
Cases with >50% erythroid precursors
• Cases with criteria of MDS with a cytogenetic abnormalities specific for AML
(Rosati S, Anastasi J, Vardiman J. Sem Hematol 23:
• Cases with criteria of MDS with a cytogenetic abnormalities specific for AML
(Rosati S, Anastasi J, Vardiman J. Sem Hematol 23:
Слайд 27DISTINCTION OF MDS FROM
CHRONIC MYELOPROLIFERATIVE
DISORDERS
MDS
CMPD
Cytopenias
Ineffective hematopoiesis
Dysplasia
No splenomegaly
Normal or elevated blood counts
Effective
hematopoiesis
No dysplasia
Splenomegaly
No dysplasia
Splenomegaly
Слайд 28WHO CLASSIFICATION OF
MYELODYSPLASTIC/
MYELOPROLIFERATIVE DISEASE
• Chronic Myelomonocytic Leukemia (CMML)
• Atypical Chronic Myeloid
Leukemia (aCML)
• Juvenile Myelomonocytic Leukemia (JMML)
• Myelodysplastic/Myeloprolilferative Disease,
Unclassifiable
• Juvenile Myelomonocytic Leukemia (JMML)
• Myelodysplastic/Myeloprolilferative Disease,
Unclassifiable
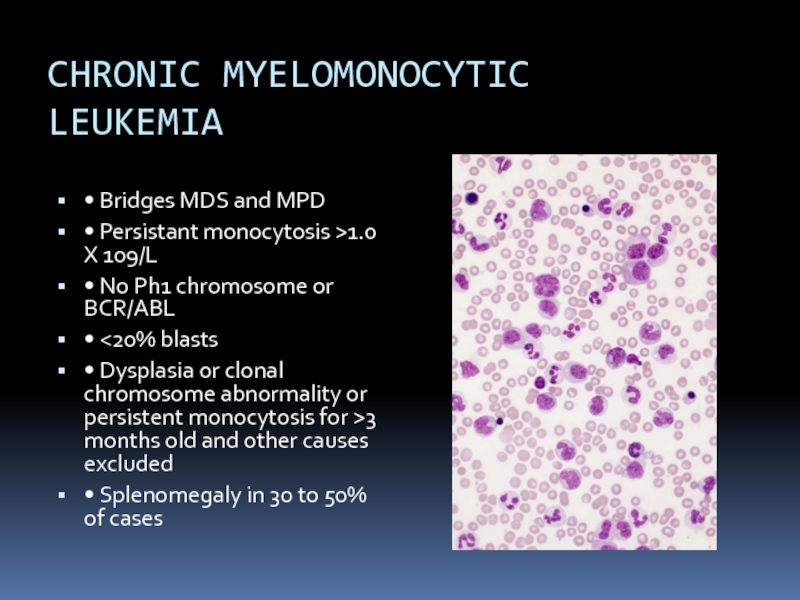
Слайд 29CHRONIC MYELOMONOCYTIC
LEUKEMIA
• Bridges MDS and MPD
• Persistant monocytosis >1.0 X 109/L
•
No Ph1 chromosome or BCR/ABL
• <20% blasts
• Dysplasia or clonal chromosome abnormality or persistent monocytosis for >3 months old and other causes excluded
• Splenomegaly in 30 to 50% of cases
• <20% blasts
• Dysplasia or clonal chromosome abnormality or persistent monocytosis for >3 months old and other causes excluded
• Splenomegaly in 30 to 50% of cases
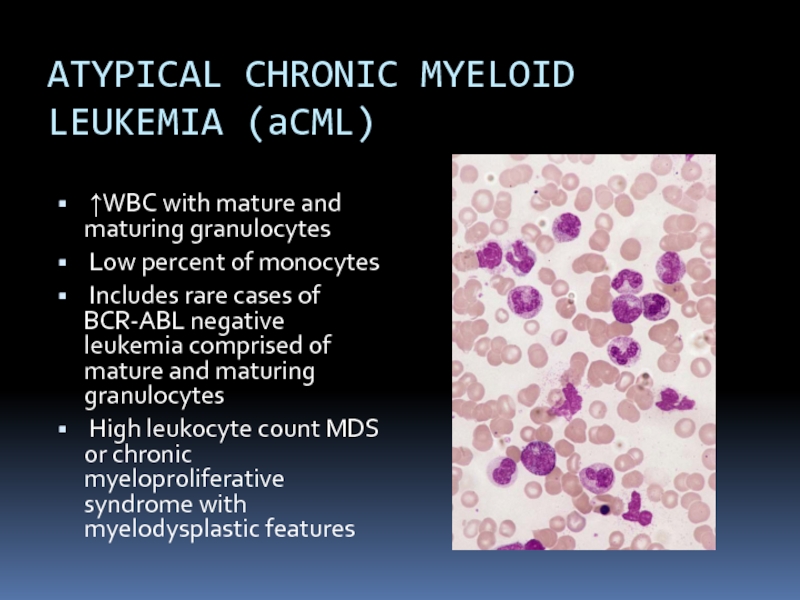
Слайд 30ATYPICAL CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKEMIA (aCML)
↑WBC with mature and maturing granulocytes
Low percent of monocytes
Includes rare cases of BCR-ABL negative leukemia comprised of mature and maturing granulocytes
High leukocyte count MDS or chronic myeloproliferative syndrome with myelodysplastic features
Includes rare cases of BCR-ABL negative leukemia comprised of mature and maturing granulocytes
High leukocyte count MDS or chronic myeloproliferative syndrome with myelodysplastic features
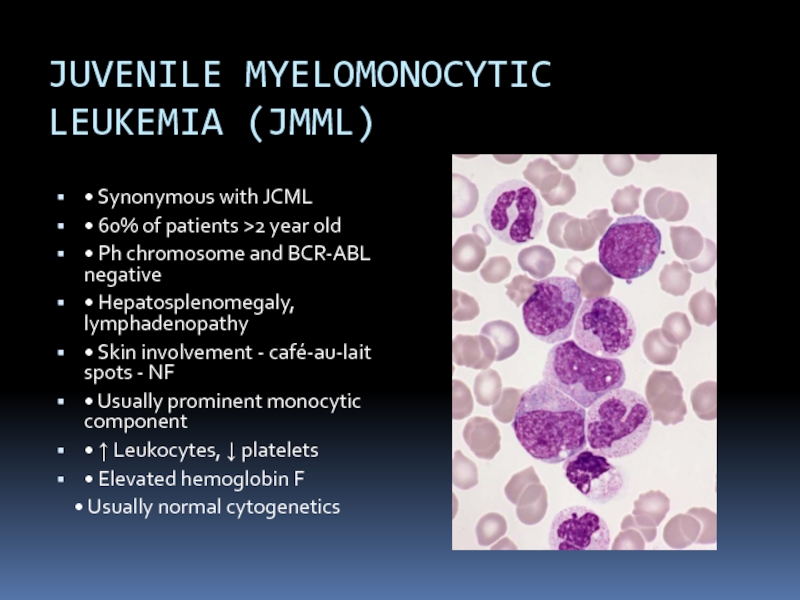
Слайд 31JUVENILE MYELOMONOCYTIC
LEUKEMIA (JMML)
• Synonymous with JCML
• 60% of patients >2 year
old
• Ph chromosome and BCR-ABL negative
• Hepatosplenomegaly, lymphadenopathy
• Skin involvement - café-au-lait spots - NF
• Usually prominent monocytic component
• ↑ Leukocytes, ↓ platelets
• Elevated hemoglobin F
• Usually normal cytogenetics
• Ph chromosome and BCR-ABL negative
• Hepatosplenomegaly, lymphadenopathy
• Skin involvement - café-au-lait spots - NF
• Usually prominent monocytic component
• ↑ Leukocytes, ↓ platelets
• Elevated hemoglobin F
• Usually normal cytogenetics
Слайд 32MONOSOMY 7 SYNDROME
• Anemia and leukocytosis
• Thrombocytopenia in 50%
• Monocytosis
• Defective
neutrophil function with recurrent infections
• Hypercellular BM with ↑ reticulin
• Dysplasia
• Hepatosplenomegaly
• Neurofibromatosis
• Hypercellular BM with ↑ reticulin
• Dysplasia
• Hepatosplenomegaly
• Neurofibromatosis
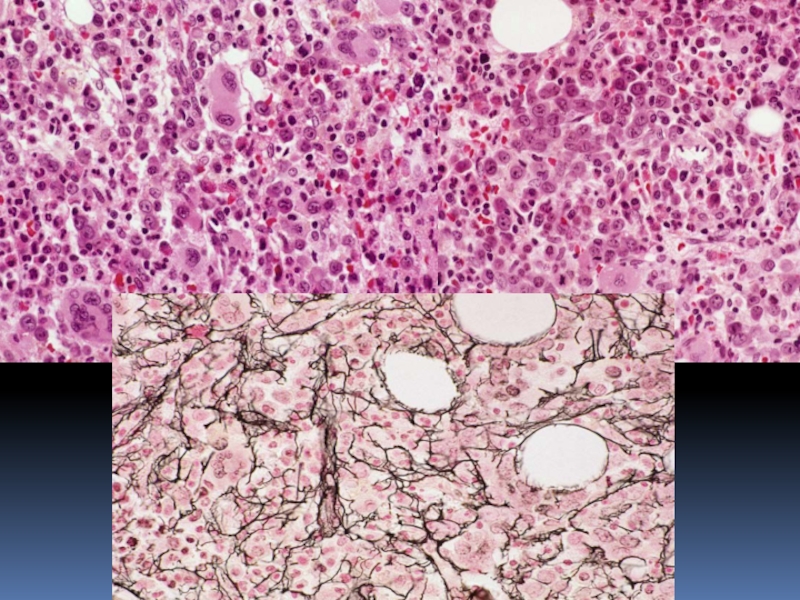
Слайд 33OTHER MORPHOLOGIC
FINDINGS IN MDS
• Changes in marrow cellularity
usually hypercellular
• Increased iron
stores
• Myelofibrosis
• Myelofibrosis
Слайд 34MDS/MPD, UNCLASSIFIABLE
• Features of MDS but with thrombocytosis (>600 X 109/L)
or leukocytosis (>13.0 X 109/L)
• (and) No prior history of MDS or MPD
• (and) No cytogenetic abnormality associated with specific myeloid disorder
• (or) Mixed MDS and MPD features and cannot be assigned to any other category
• (and) No prior history of MDS or MPD
• (and) No cytogenetic abnormality associated with specific myeloid disorder
• (or) Mixed MDS and MPD features and cannot be assigned to any other category
Слайд 35Treatment
Supportive care – blood products, infections etc.
Growth factors – G-CSF, erythropoetin
Hypomethylating
agents – azacitidin, dacogen
Revlimid – 5q-
Allogeneic stem cell transplantation
Revlimid – 5q-
Allogeneic stem cell transplantation
Слайд 42Survival Based on WPSS
Malcovati et al, ASH 05, #788
L et
al. Blood. 2005;106:232a [abstract 788]













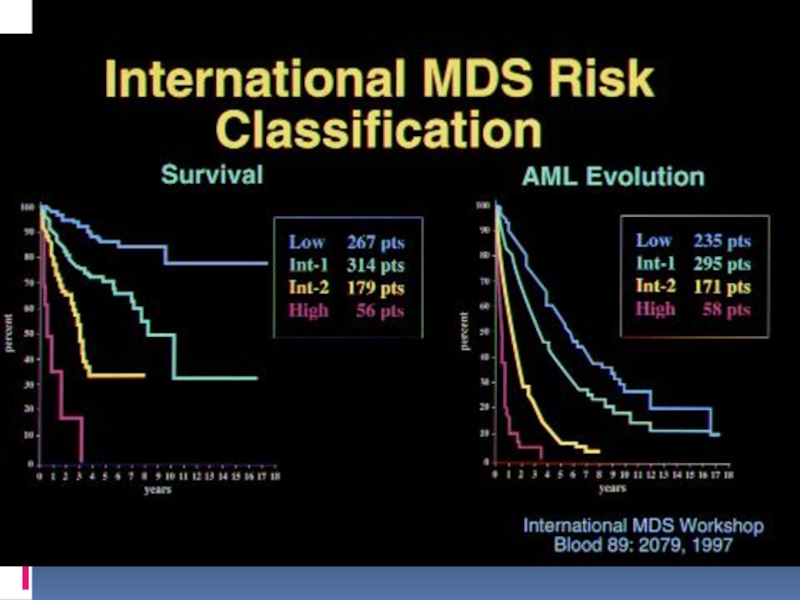
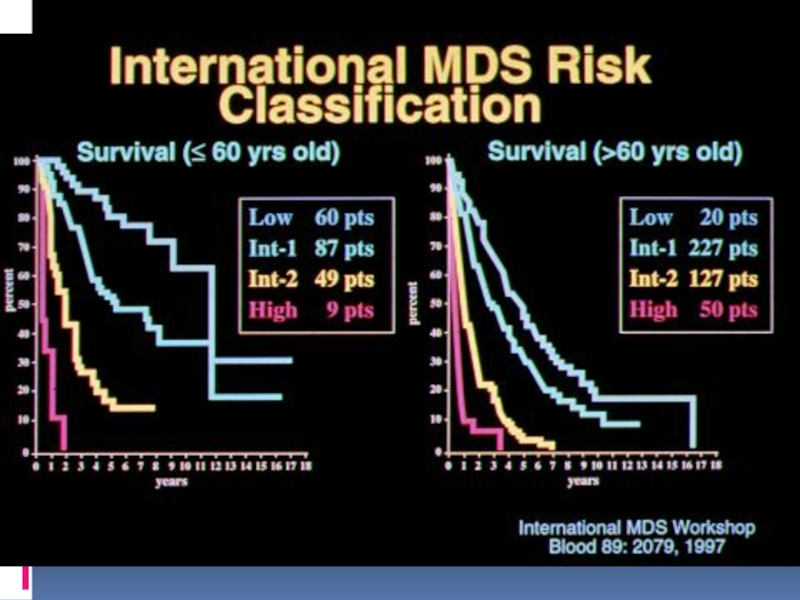
![Survival Based on WPSS Malcovati et al, ASH 05, #788L et al. Blood. 2005;106:232a [abstract 788]](/img/tmb/1/31214/80a3b9fd60b10cd079e98148632fc260-800x.jpg)