Kathleen Tozer, MD
- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Introductory/ Neuroimaging: What you need to know at 3 am And some cool stuff презентация
Содержание
- 1. Introductory/ Neuroimaging: What you need to know at 3 am And some cool stuff
- 2. Outline Choosing a study Normal anatomy Trauma Ischemic stroke Aneurysm
- 3. Outline Choosing a study Normal anatomy Trauma Ischemic stroke Aneurysm
- 4. Which study? Acute change For acute mental
- 5. Which study? Vascular CTA: Neck: Aortic arch
- 6. Regarding contrast: Iodinated contrast: GFR > 60:
- 7. Regarding contrast: Gadolinium contrast: GFR > 60:
- 8. Hounsfield Units (HU) CT density scale: Air
- 9. Outline Choosing a study Normal anatomy Trauma Ischemic stroke Aneurysm
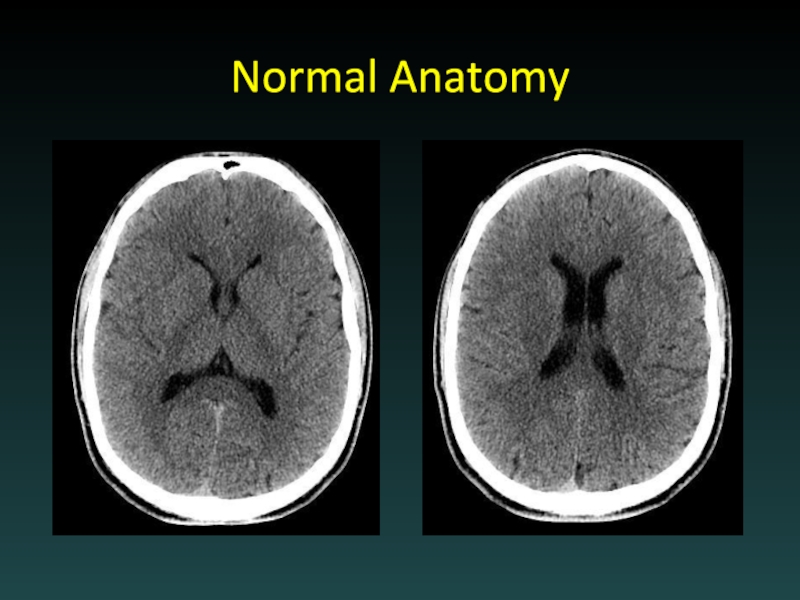
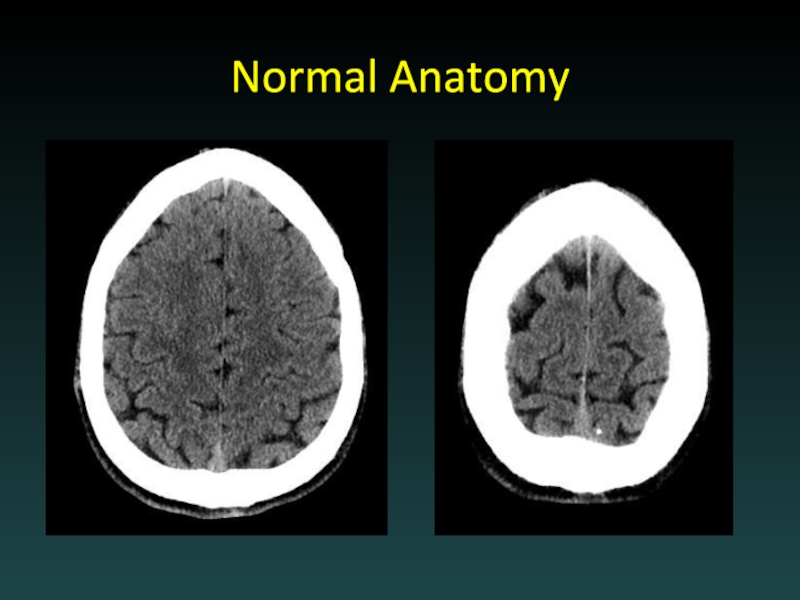
- 10. Normal Anatomy
- 11. Normal Anatomy
- 12. Normal Anatomy
- 13. Normal Anatomy
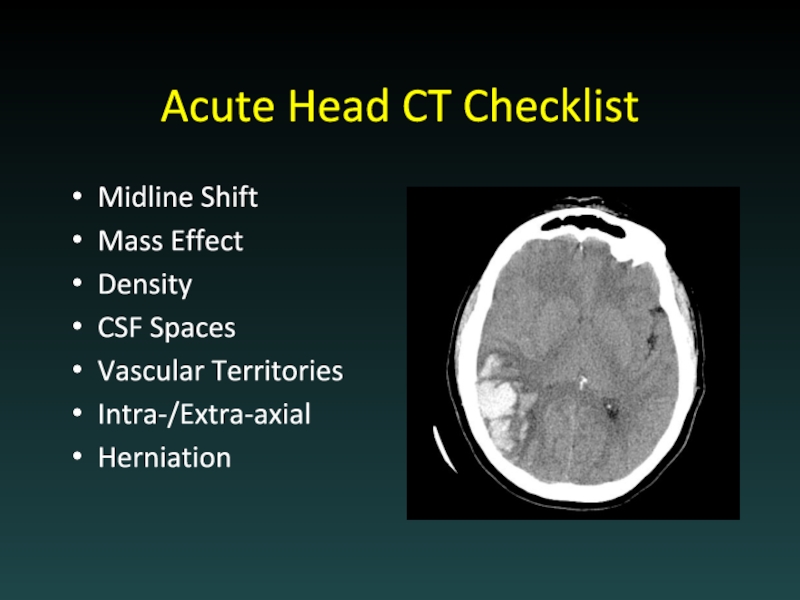
- 14. Acute Head CT Checklist Midline Shift Mass Effect Density CSF Spaces Vascular Territories Intra-/Extra-axial Herniation
- 15. Outline Choosing a study Normal anatomy Trauma Ischemic stroke Aneurysm
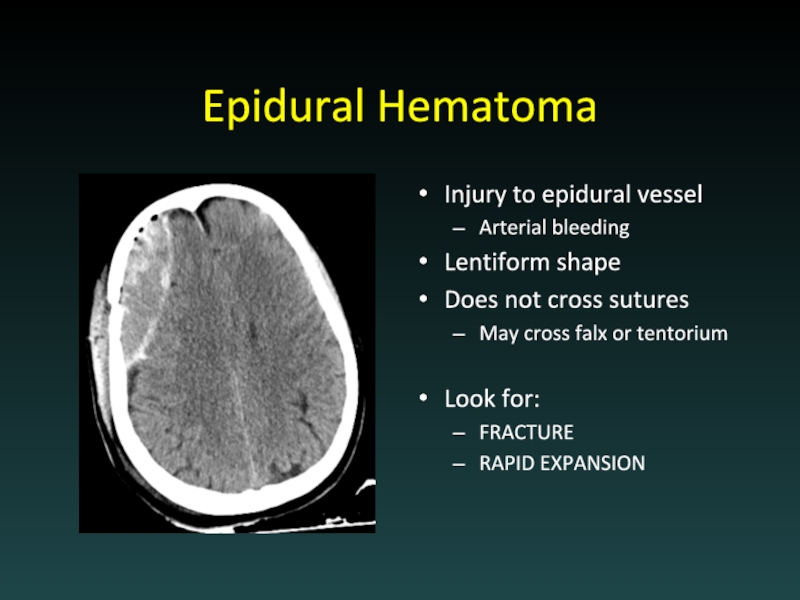
- 17. Epidural Hematoma Injury to epidural vessel Arterial
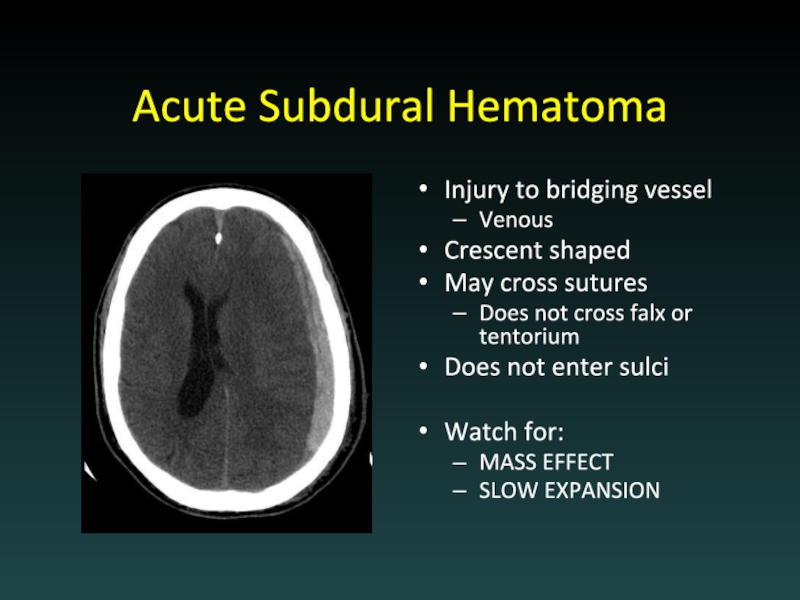
- 19. Acute Subdural Hematoma Injury to bridging vessel
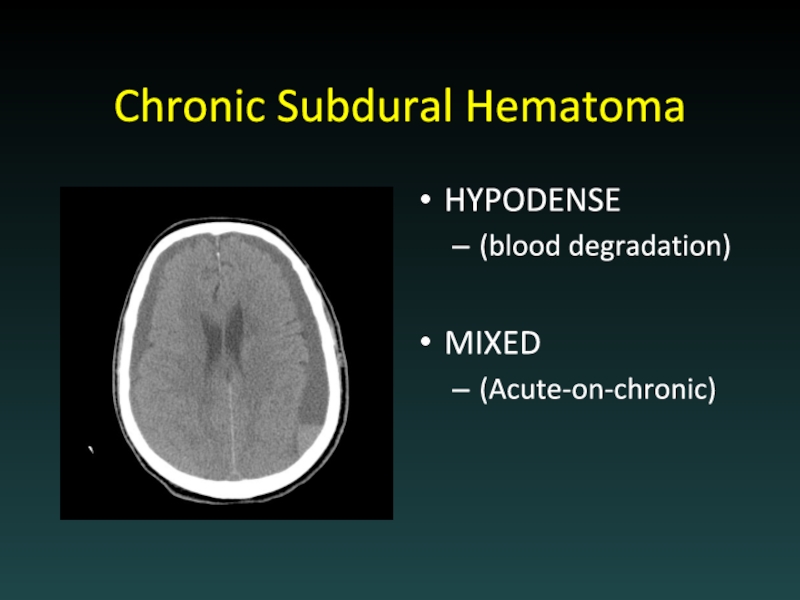
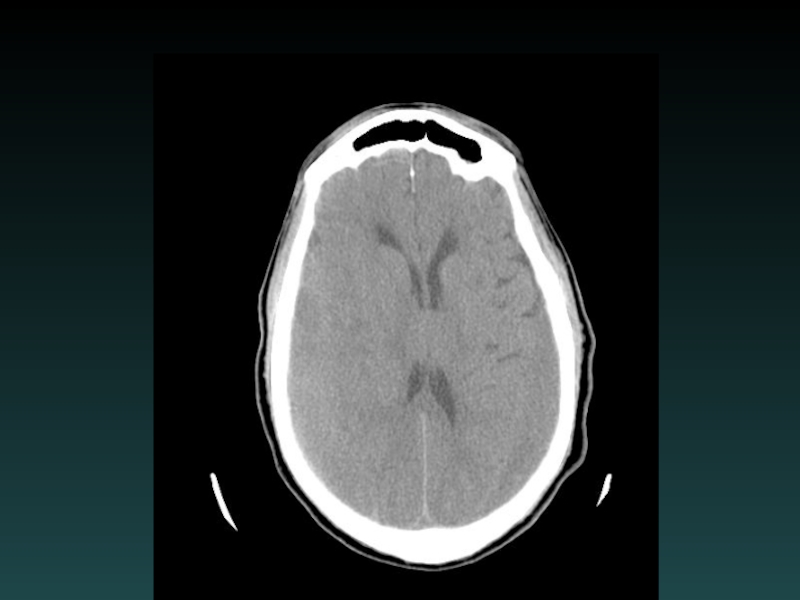
- 21. Chronic Subdural Hematoma HYPODENSE (blood degradation) MIXED (Acute-on-chronic)
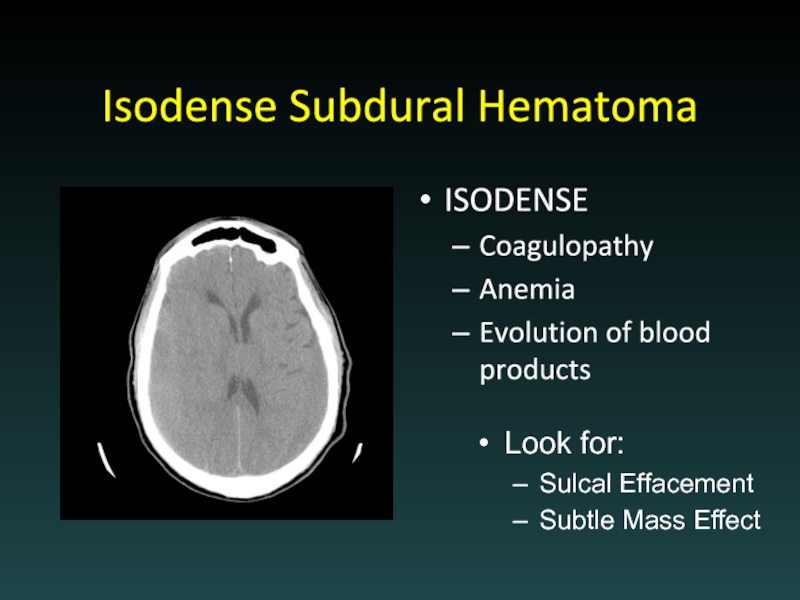
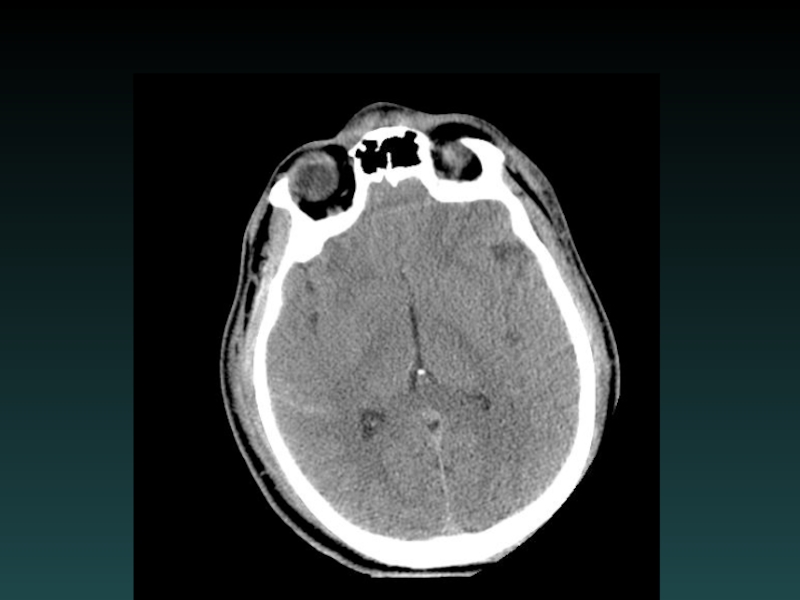
- 23. Isodense Subdural Hematoma ISODENSE Coagulopathy Anemia Evolution
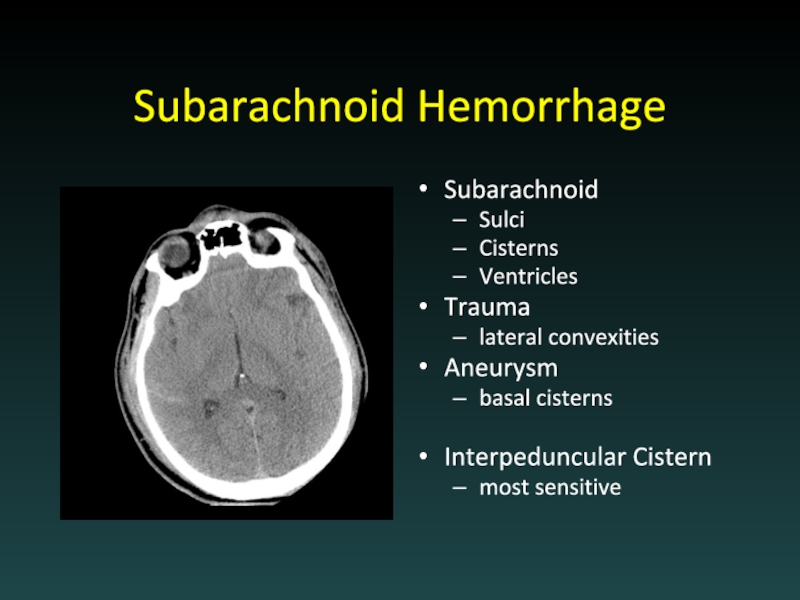
- 25. Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Subarachnoid Sulci Cisterns
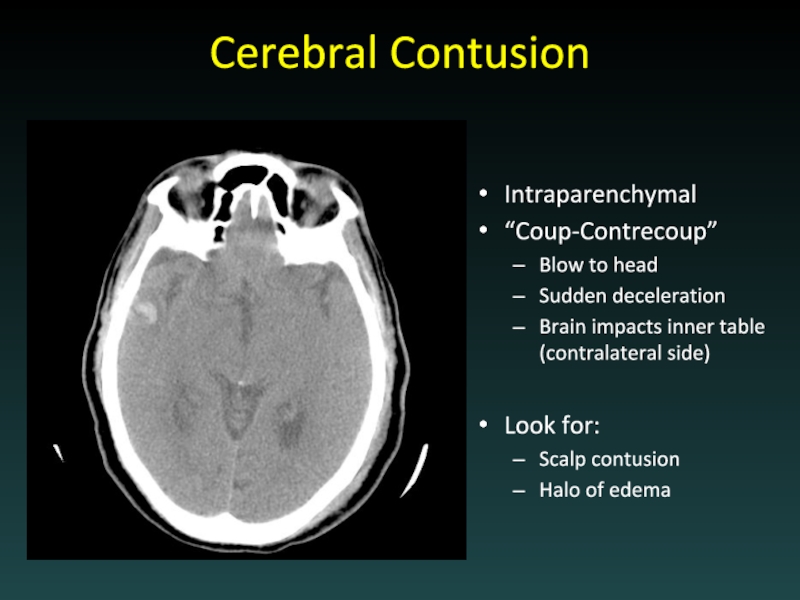
- 27. Cerebral Contusion Intraparenchymal “Coup-Contrecoup” Blow to head
- 29. Subcortical Injury Shear-Strain forces Penetrating vessels Axonal
- 30. MRI: Diffuse Axonal Injury
- 33. Diffuse Cerebral Edema Grey-white interface often obscured
- 34. Outline Choosing a study Normal anatomy Trauma Ischemic stroke Aneurysm
- 35. Stroke
- 37. Acute Ischemia-Infarction Subtle HYPODENSITY Vascular distribution Loss
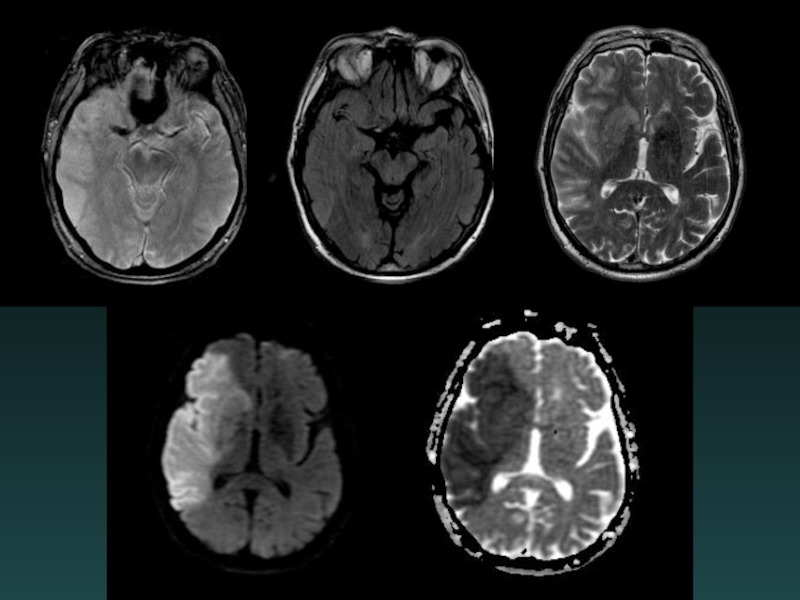
- 38. Diffusion-MRI: Acute Infarct
- 40. Acute facial droop, hemiparesis
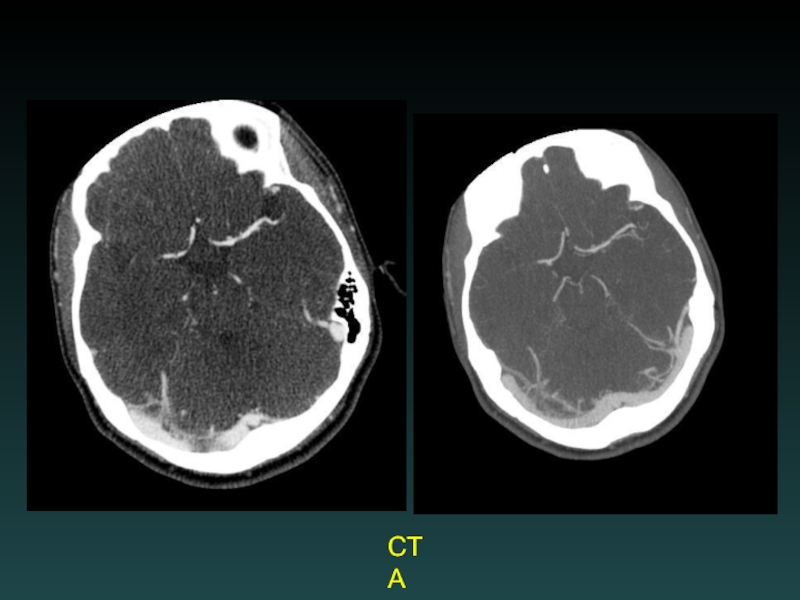
- 42. CTA
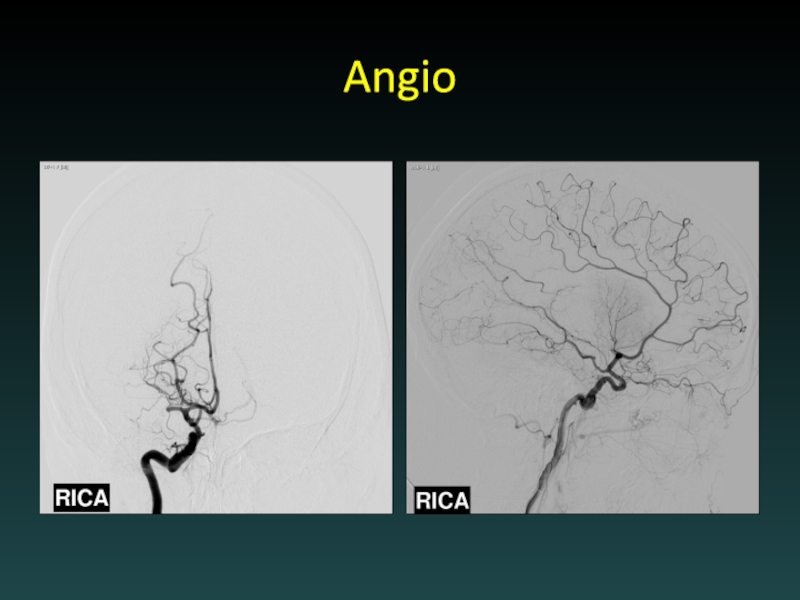
- 43. Angio
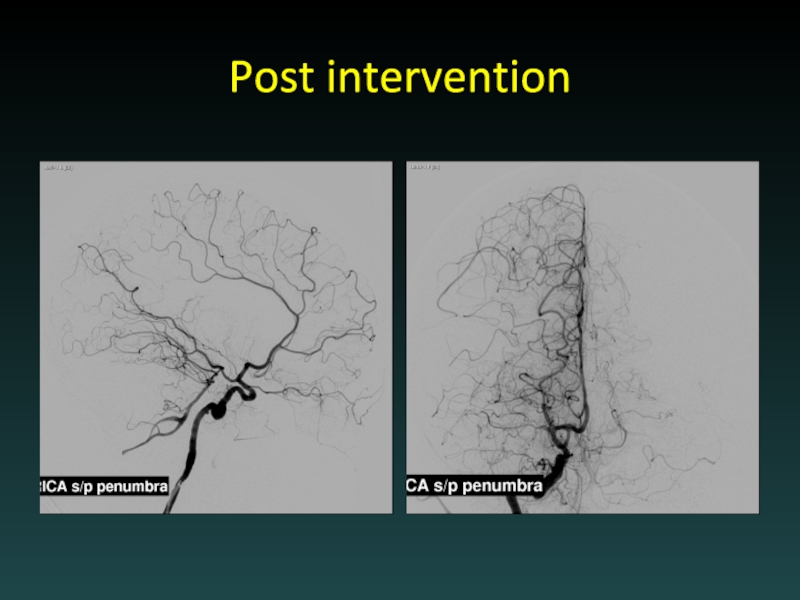
- 44. Post intervention
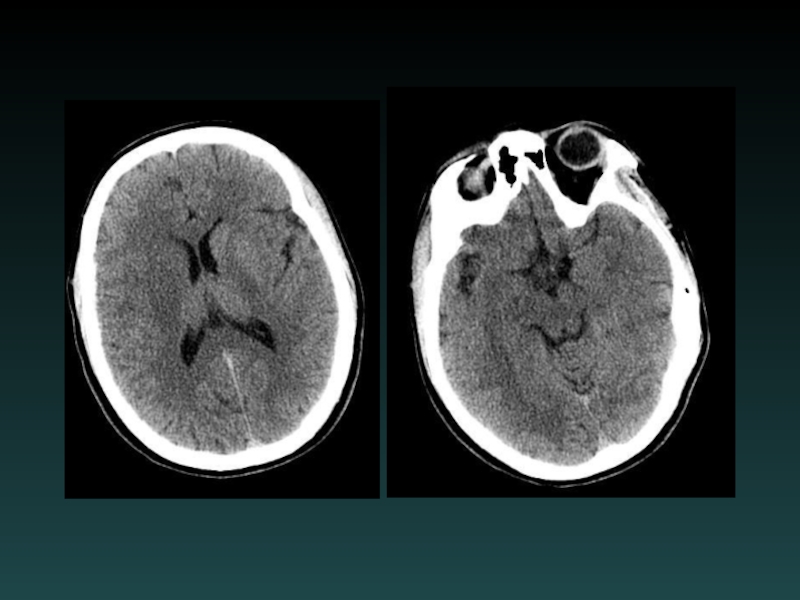
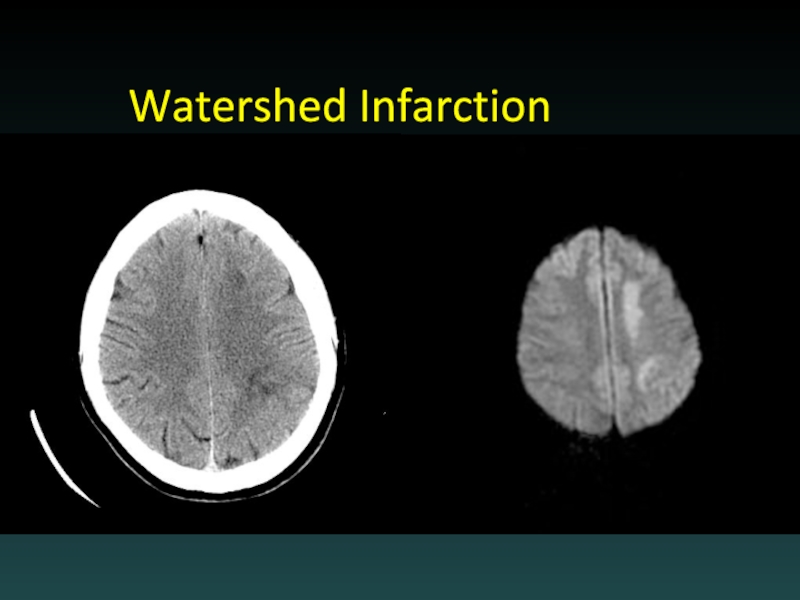
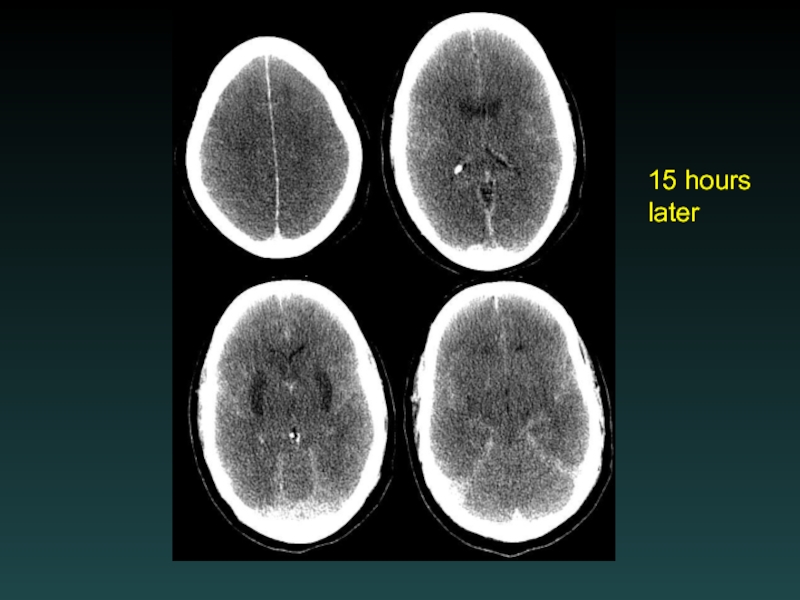
- 45. Watershed Infarction
- 48. 15 hours later
- 49. Anoxic brain injury Loss of Gray-White Progresses with worsening edema PseudoSAH Hydrocephalus Cisterns compressed
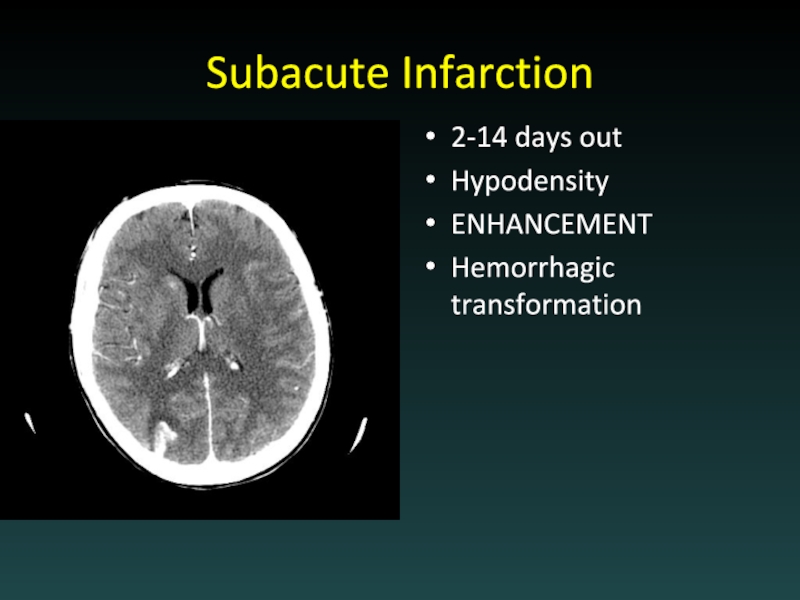
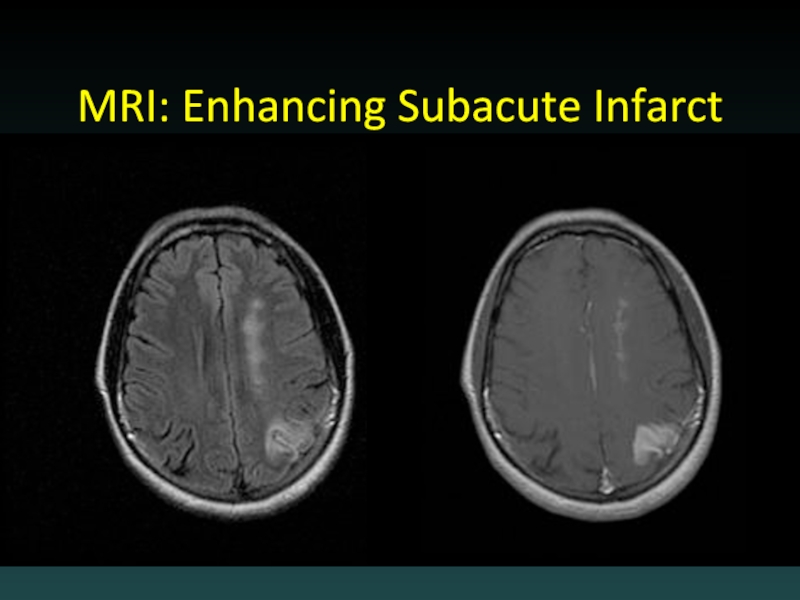
- 50. Subacute Infarction 2-14 days out Hypodensity ENHANCEMENT Hemorrhagic transformation
- 51. MRI: Enhancing Subacute Infarct
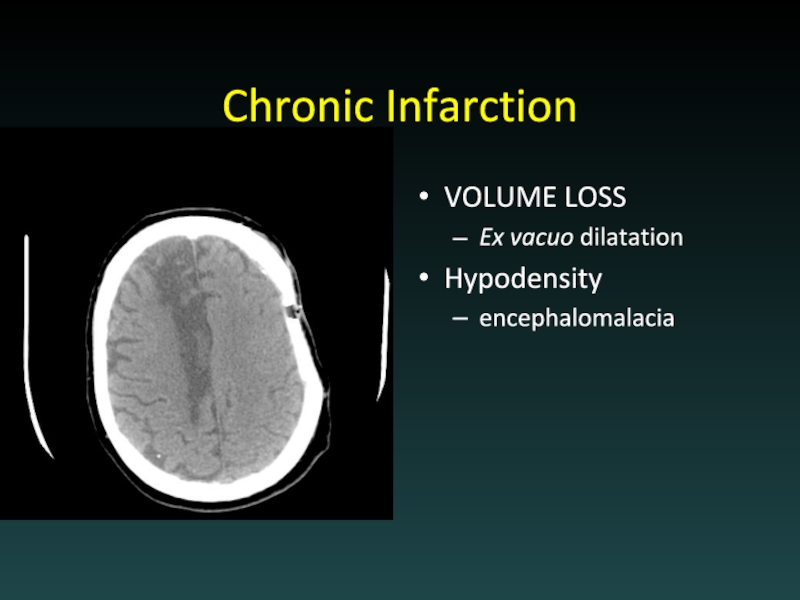
- 52. Chronic Infarction VOLUME LOSS Ex vacuo dilatation Hypodensity encephalomalacia
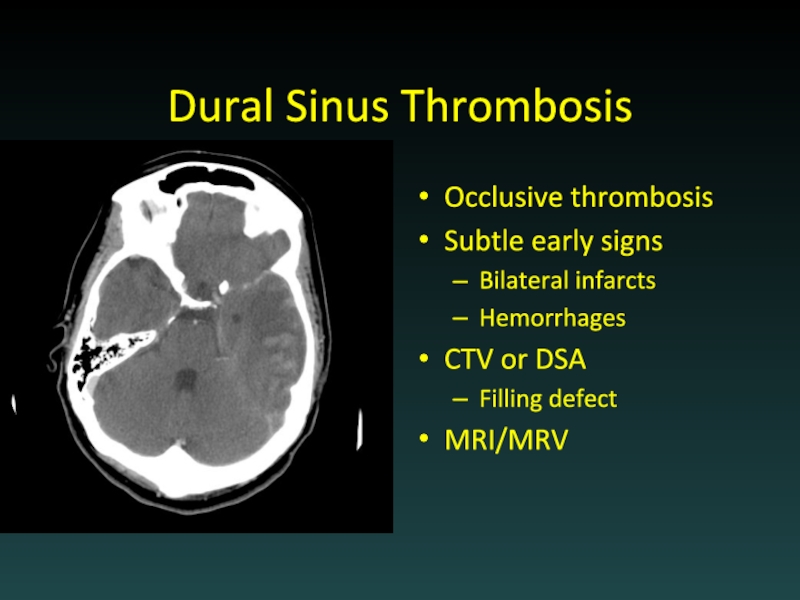
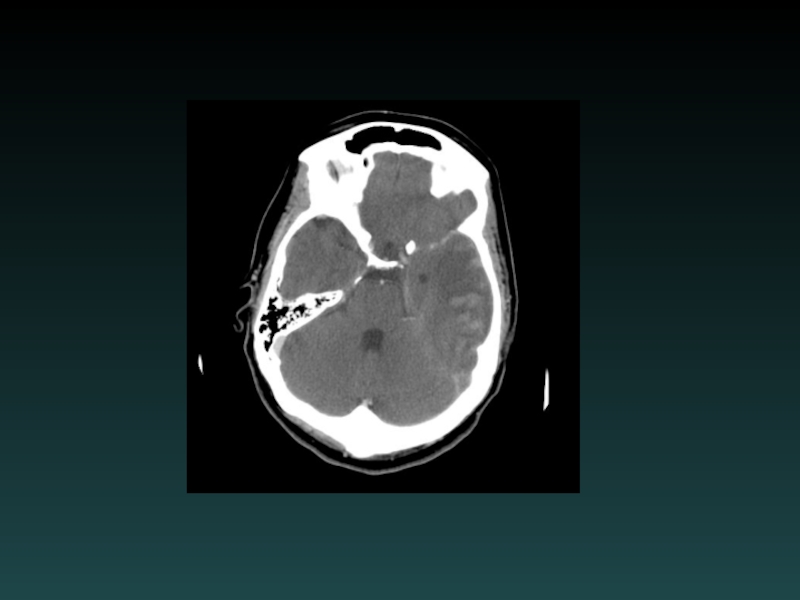
- 53. Dural Sinus Thrombosis Occlusive thrombosis Subtle early
- 55. Outline Choosing a study Normal anatomy Trauma Ischemic stroke Aneurysm
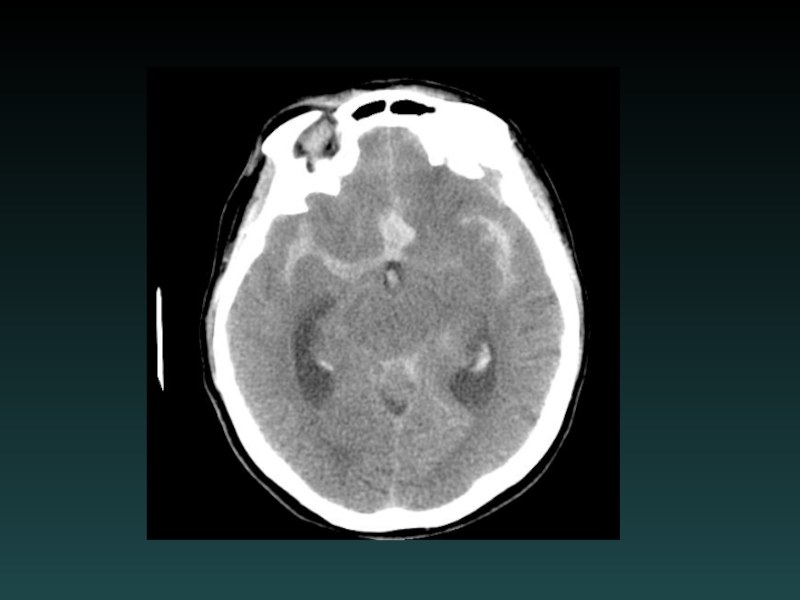
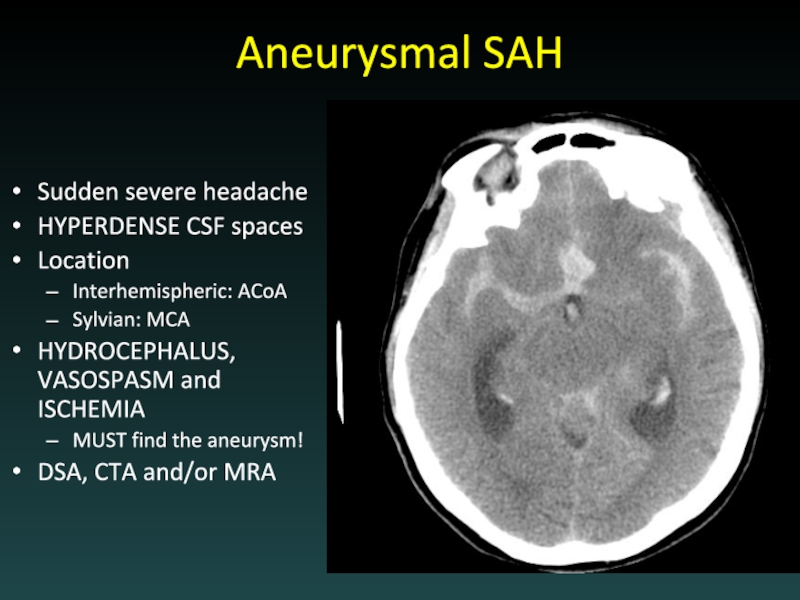
- 57. Aneurysmal SAH Sudden severe headache HYPERDENSE CSF
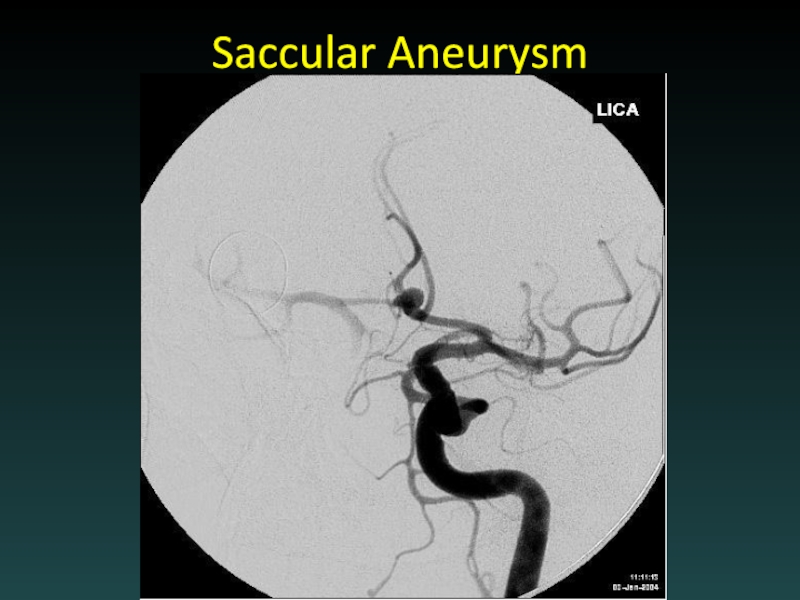
- 58. Saccular Aneurysm
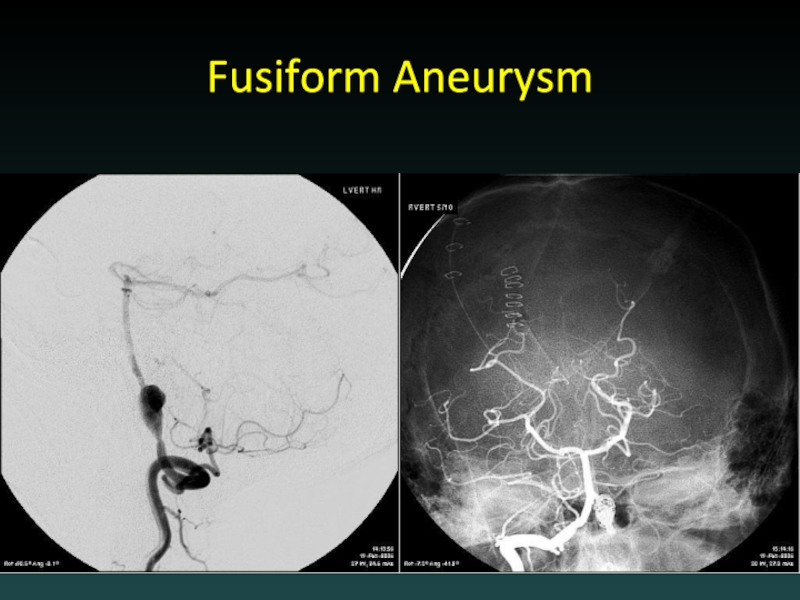
- 59. Fusiform Aneurysm
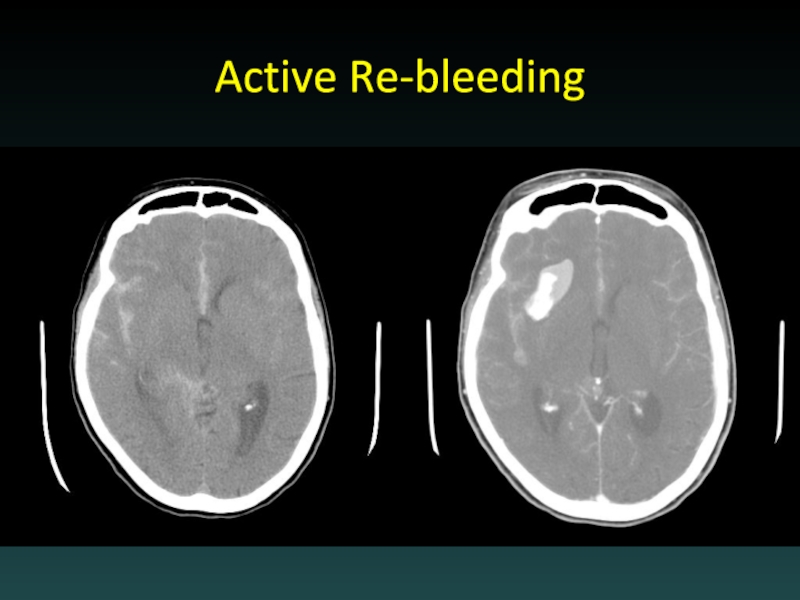
- 60. Active Re-bleeding
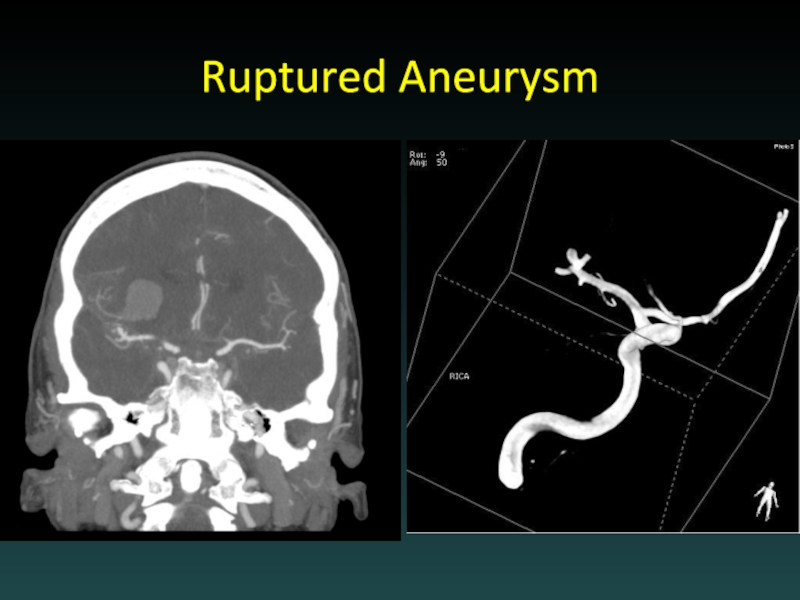
- 61. Ruptured Aneurysm
- 63. Intracerebral Hemorrhage Hypertension Most common Characteristic Locations
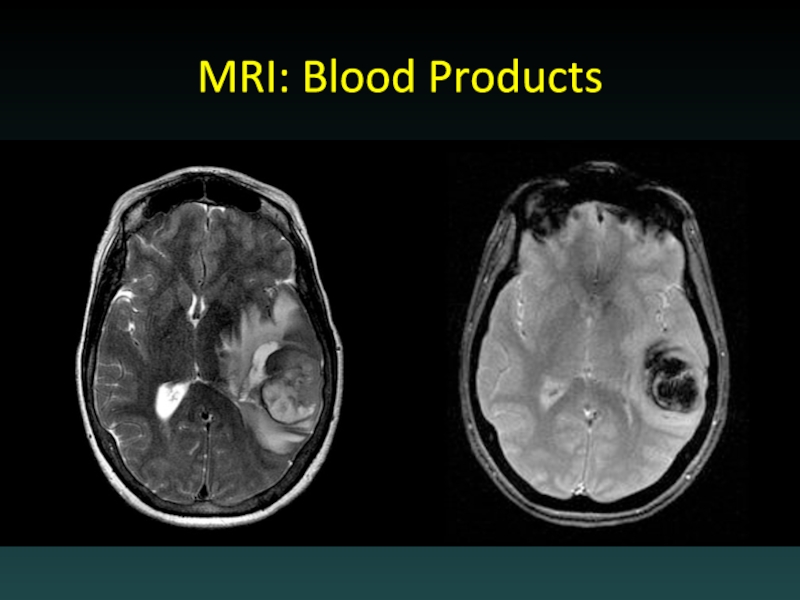
- 64. MRI: Blood Products
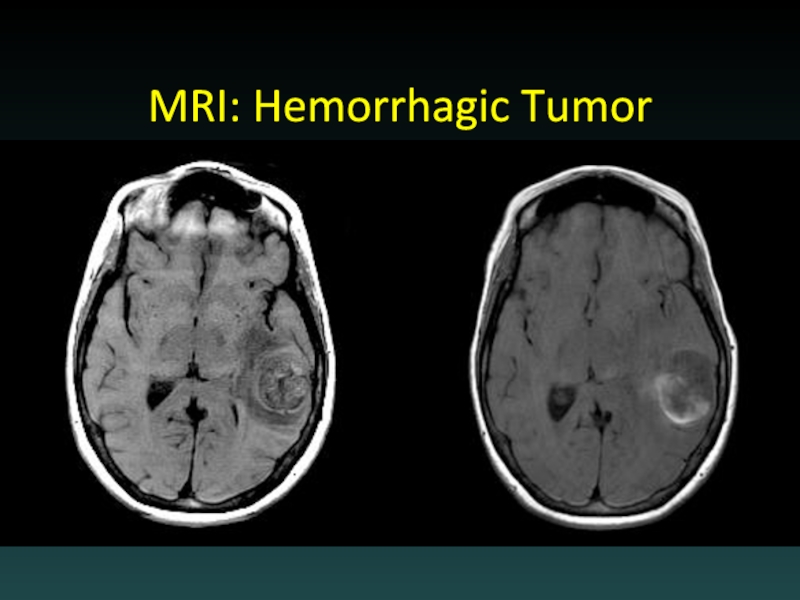
- 65. MRI: Hemorrhagic Tumor
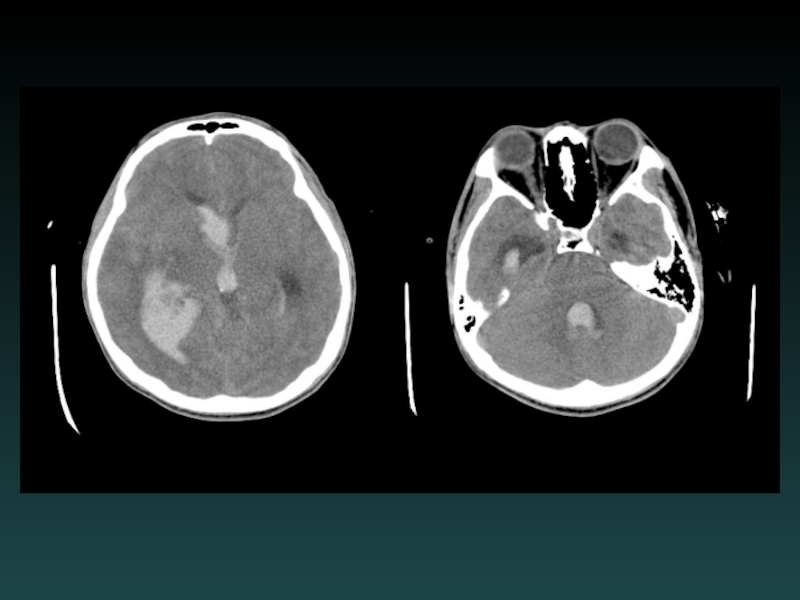
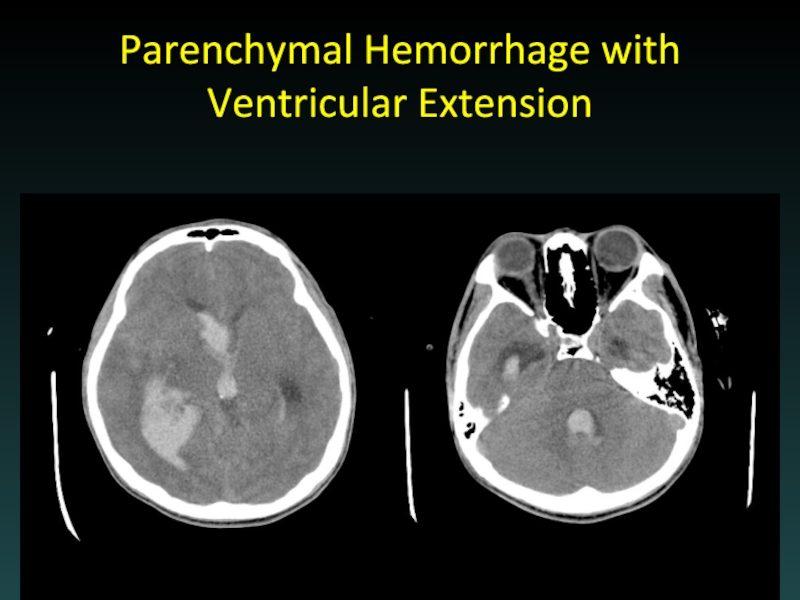
- 67. Parenchymal Hemorrhage with Ventricular Extension
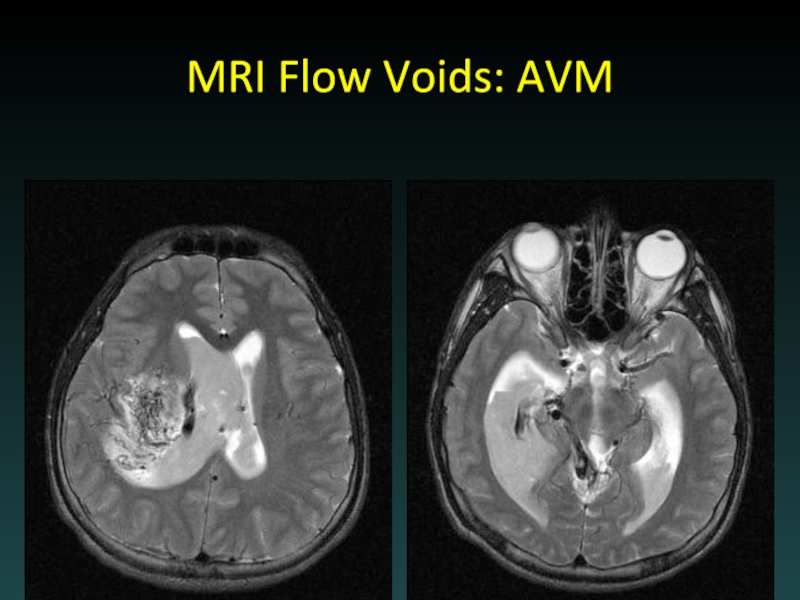
- 68. MRI Flow Voids: AVM
Слайд 1Introductory Neuroimaging: What you need to know at 3 am And some
cool stuff. . .
Слайд 4Which study? Acute change
For acute mental status change, first study is
ALWAYS noncontrast head CT
Brain MR:
Stroke protocol (noncontrast)
ICH protocol (with contrast)
Tumor protocol (with contrast)
Brain MR:
Stroke protocol (noncontrast)
ICH protocol (with contrast)
Tumor protocol (with contrast)
Слайд 5Which study? Vascular
CTA:
Neck: Aortic arch through Circle of Willis.
Head: Circle
of Willis only
MRA:
Brain: noncontrast
Neck: without and with contrast.
MRA:
Brain: noncontrast
Neck: without and with contrast.
Слайд 6Regarding contrast:
Iodinated contrast:
GFR > 60:
in the clear
GFR < 60:
If
acute, tread cautiously, especially if <30
Hydration, mucomyst, Sodium bicarb protocol
Decrease dose, Visipaque
ESRD:
Coordinate with hemodialysis
Hydration, mucomyst, Sodium bicarb protocol
Decrease dose, Visipaque
ESRD:
Coordinate with hemodialysis
Слайд 7Regarding contrast:
Gadolinium contrast:
GFR > 60:
in the clear
GFR 30-60:
weigh risks.
Consider noncontrast study first.
Multihance
GFR < 30:
CONTRAINDICATED due to risk of NSF (nephrogenic systemic fibrosis).
Try noncontrast.
Consult radiology for alternative studies.
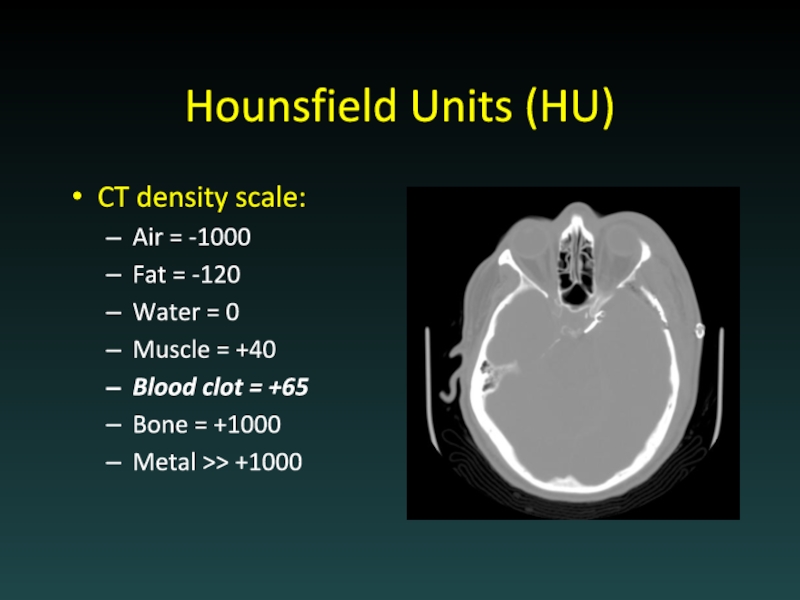
Слайд 8Hounsfield Units (HU)
CT density scale:
Air = -1000
Fat = -120
Water = 0
Muscle
= +40
Blood clot = +65
Bone = +1000
Metal >> +1000
Blood clot = +65
Bone = +1000
Metal >> +1000
Слайд 14Acute Head CT Checklist
Midline Shift
Mass Effect
Density
CSF Spaces
Vascular Territories
Intra-/Extra-axial
Herniation
Слайд 17Epidural Hematoma
Injury to epidural vessel
Arterial bleeding
Lentiform shape
Does not cross sutures
May cross
falx or tentorium
Look for:
FRACTURE
RAPID EXPANSION
Look for:
FRACTURE
RAPID EXPANSION
Слайд 19Acute Subdural Hematoma
Injury to bridging vessel
Venous
Crescent shaped
May cross sutures
Does not cross
falx or tentorium
Does not enter sulci
Watch for:
MASS EFFECT
SLOW EXPANSION
Does not enter sulci
Watch for:
MASS EFFECT
SLOW EXPANSION
Слайд 23Isodense Subdural Hematoma
ISODENSE
Coagulopathy
Anemia
Evolution of blood products
Look for:
Sulcal Effacement
Subtle Mass Effect
Слайд 25Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
Subarachnoid
Sulci
Cisterns
Ventricles
Trauma
lateral convexities
Aneurysm
basal cisterns
Interpeduncular Cistern
most sensitive
Слайд 27Cerebral Contusion
Intraparenchymal
“Coup-Contrecoup”
Blow to head
Sudden deceleration
Brain impacts inner table (contralateral side)
Look
for:
Scalp contusion
Halo of edema
Scalp contusion
Halo of edema
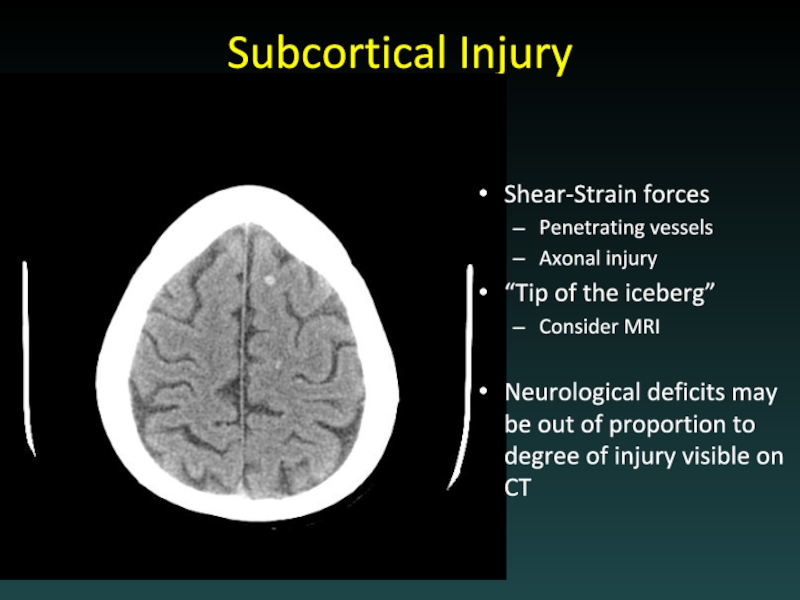
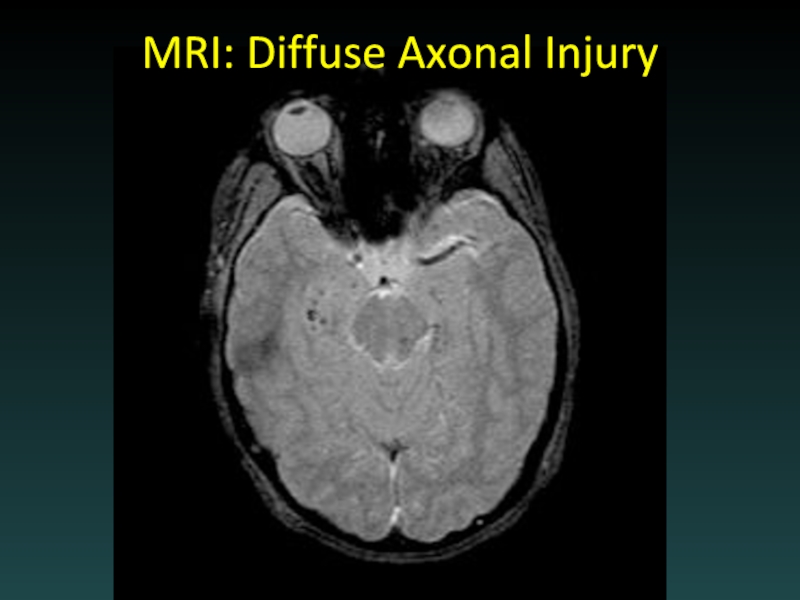
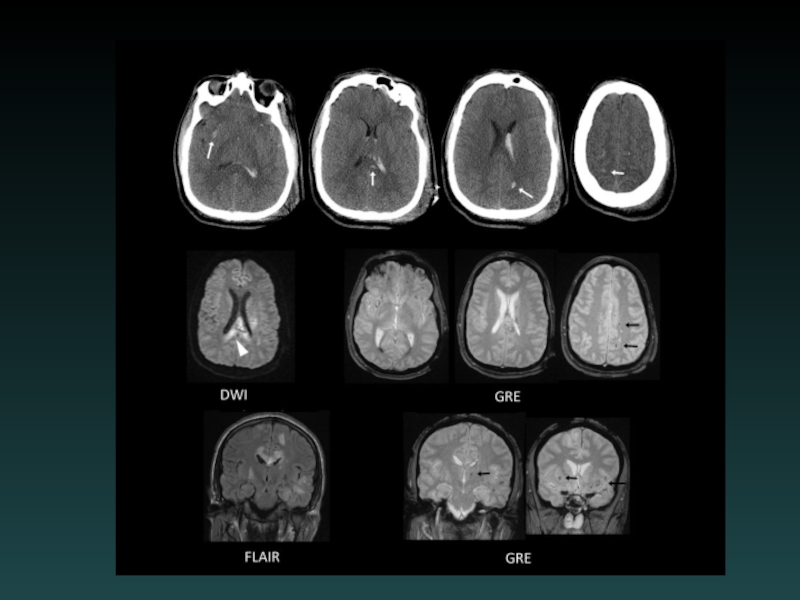
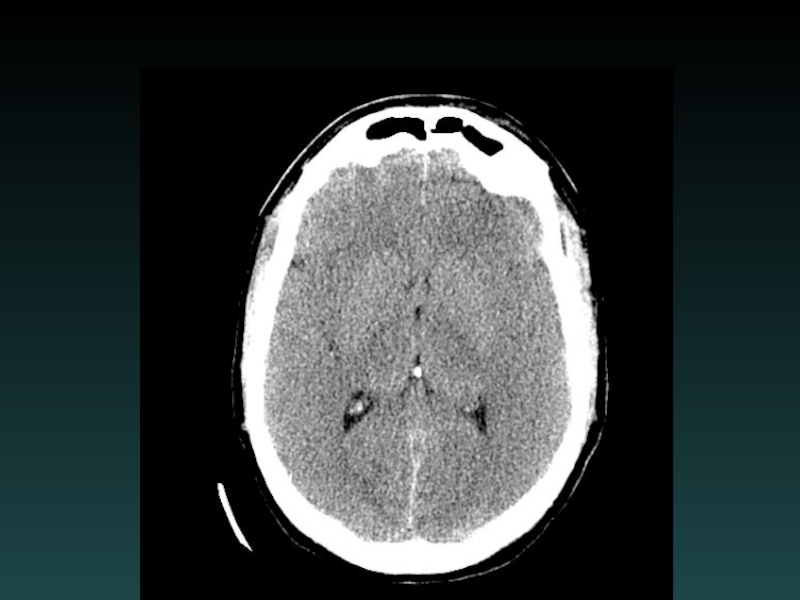
Слайд 29Subcortical Injury
Shear-Strain forces
Penetrating vessels
Axonal injury
“Tip of the iceberg”
Consider MRI
Neurological deficits may
be out of proportion to degree of injury visible on CT
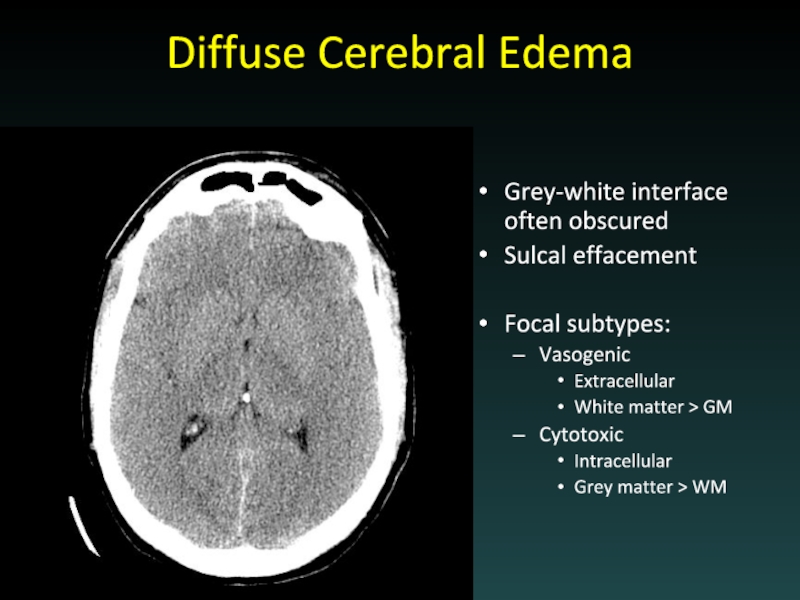
Слайд 33Diffuse Cerebral Edema
Grey-white interface often obscured
Sulcal effacement
Focal subtypes:
Vasogenic
Extracellular
White matter > GM
Cytotoxic
Intracellular
Grey
matter > WM
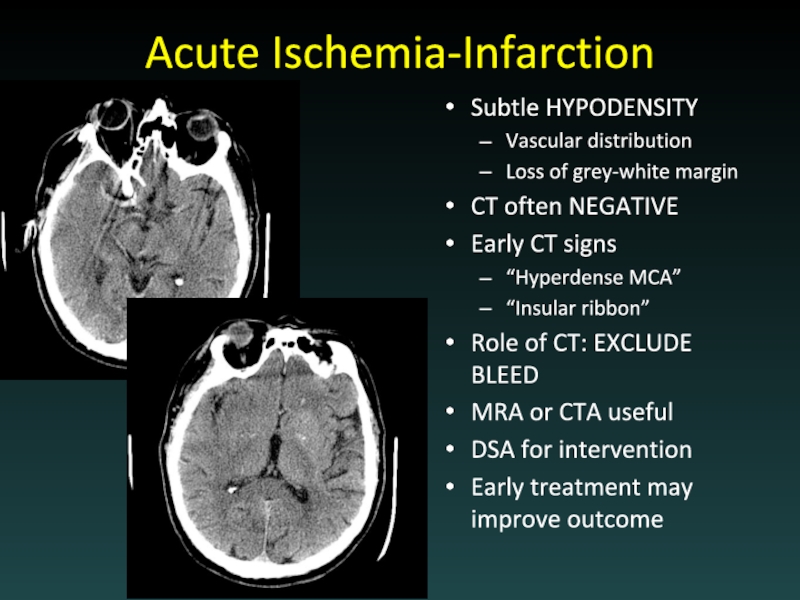
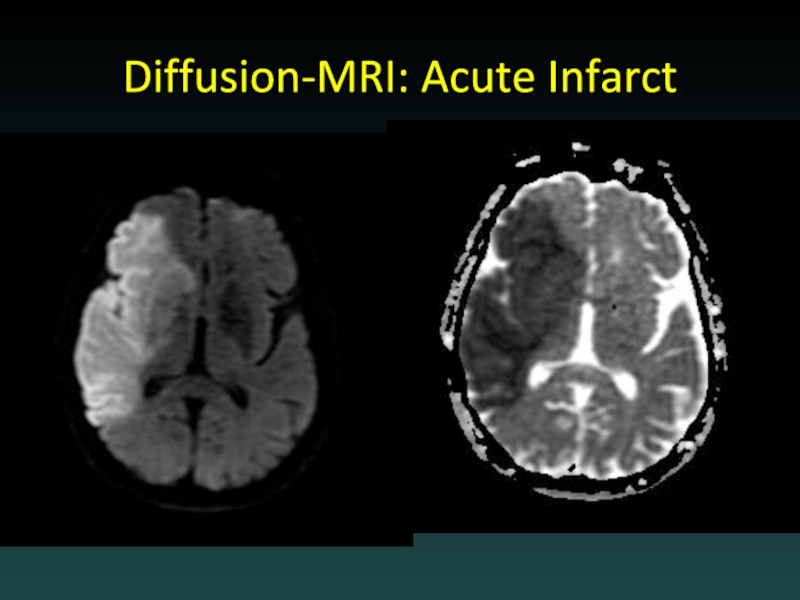
Слайд 37Acute Ischemia-Infarction
Subtle HYPODENSITY
Vascular distribution
Loss of grey-white margin
CT often NEGATIVE
Early CT signs
“Hyperdense
MCA”
“Insular ribbon”
Role of CT: EXCLUDE BLEED
MRA or CTA useful
DSA for intervention
Early treatment may improve outcome
“Insular ribbon”
Role of CT: EXCLUDE BLEED
MRA or CTA useful
DSA for intervention
Early treatment may improve outcome
Слайд 49Anoxic brain injury
Loss of Gray-White
Progresses with worsening edema
PseudoSAH
Hydrocephalus
Cisterns compressed
Слайд 53Dural Sinus Thrombosis
Occlusive thrombosis
Subtle early signs
Bilateral infarcts
Hemorrhages
CTV or DSA
Filling defect
MRI/MRV
Слайд 57Aneurysmal SAH
Sudden severe headache
HYPERDENSE CSF spaces
Location
Interhemispheric: ACoA
Sylvian: MCA
HYDROCEPHALUS, VASOSPASM and ISCHEMIA
MUST
find the aneurysm!
DSA, CTA and/or MRA
DSA, CTA and/or MRA
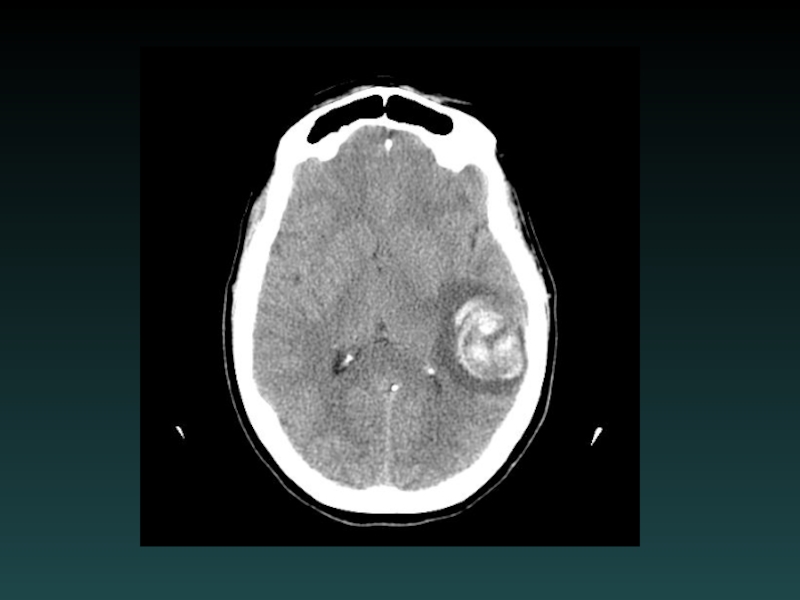
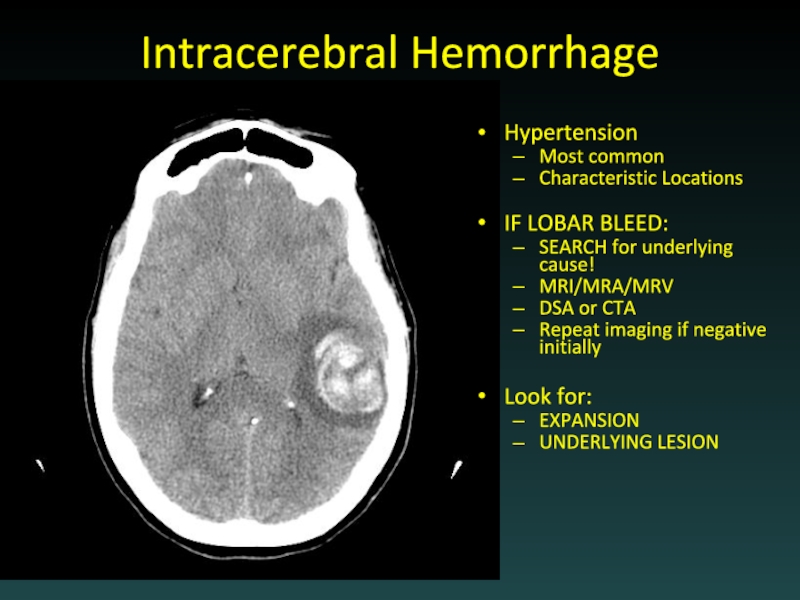
Слайд 63Intracerebral Hemorrhage
Hypertension
Most common
Characteristic Locations
IF LOBAR BLEED:
SEARCH for underlying cause!
MRI/MRA/MRV
DSA or
CTA
Repeat imaging if negative initially
Look for:
EXPANSION
UNDERLYING LESION
Repeat imaging if negative initially
Look for:
EXPANSION
UNDERLYING LESION