- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Global Health Risks. Health Statistics and Informatics презентация
Содержание
- 1. Global Health Risks. Health Statistics and Informatics
- 2. Global health is the health of the
- 3. Respiratory infections HIV/AIDS Malaria
- 4. Respiratory infections Infections of the
- 5. HIV/AIDS Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is
- 6. Malaria Malaria is an infectious disease caused
- 7. Nutrition In 2010, about 104 million children
Слайд 2Global health is the health of the population in a global
context.
Often problems are highlighted that go beyond national borders or have a global political and economic impact.
And the problems are as follows:
Слайд 4
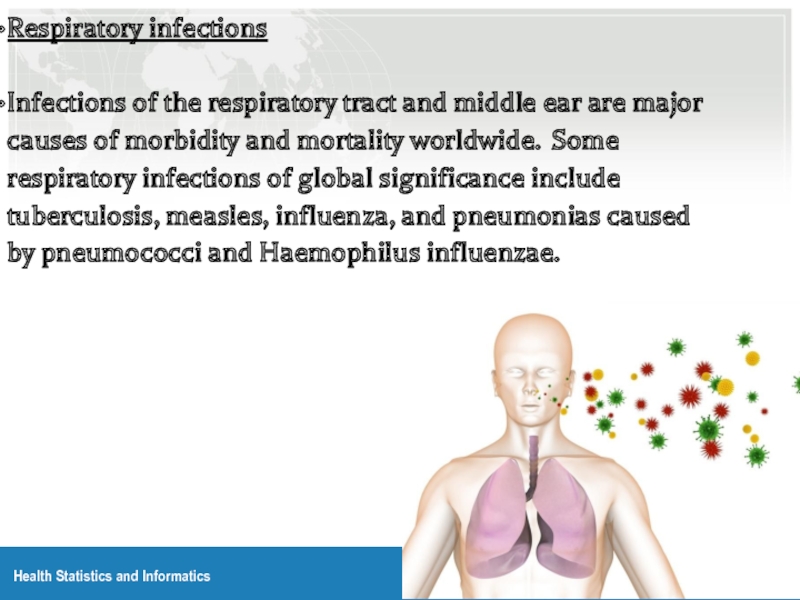
Respiratory infections
Infections of the respiratory tract and middle ear are major
causes of morbidity and mortality worldwide. Some respiratory infections of global significance include tuberculosis, measles, influenza, and pneumonias caused by pneumococci and Haemophilus influenzae.
Слайд 5HIV/AIDS
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is transmitted through unclean needles, blood transfusions,
and from mother to child during birth or lactation. Globally, HIV is primarily spread through blood intercourse. The infection damages the immune system, leading to acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) and eventually, death.
Слайд 6Malaria
Malaria is an infectious disease caused by mosquitoes caused by parasites
of the genus Plasmodium. Symptoms may include fever, headaches, chills, and nausea. Every year in the world there are about 500 million cases of malaria, most often among children and pregnant women in the region.
Слайд 7Nutrition
In 2010, about 104 million children were underweight, and malnutrition contributes
about a third of the deaths of children around the world. Malnutrition worsens the immune system by increasing the incidence, severity and duration of infections (including measles, pneumonia , and diarrhea). Infection can also contribute to malnutrition