- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Drug allergy: the mechanisms of development, symptoms, diagnostics, and treatment. Measures preventing the drug allergy презентация
Содержание
- 1. Drug allergy: the mechanisms of development, symptoms, diagnostics, and treatment. Measures preventing the drug allergy
- 2. Adverse Drug Reactions (ADRs) include all unintended
- 3. Unpredictable reactions: ● Drug Intolerance
- 4. A. Humoral Type: Type I (Anaphylactic) reactions
- 5. B. Cell Mediated: Type IV (Delayed hypersensitivity)
- 6. The antigen reacts with reaginic IgE antibodies,
- 7. DRUG ALLERGY The most dangerous type of
- 8. Allergic Anamnesis Ignoring Analgin,
- 9. The various subtypes of T lymphocytes
- 10. The spectrum of drug allergic reactions and
- 11. Atopic allergy and targets for therapy Allergen
- 12. Aspirin and other NSAIDs are reported to
- 13. Cyclo-oxygenase (COX) and Lipoxygenase (LO) are
- 14. ANTIALLERGIC DRUGS 1. Drugs Stabilizing Mast Cell
- 15. GLUCOCORTICOIDS (GCs) 1. Short-acting: Hydrocortisone acetate
- 16. Mechanism of Action of Glucocorticoids Steroid hormones
- 17. Action of GCs on mediators of inflammatory
- 18. Adverse effects of GCs: Cushing’s syndrome:
- 19. Cromolyn sodium (caps. 20 mg for inhalation)
- 20. Ketotifen (tab. 1 mg), a cromolyn analog,
- 21. H1-Receptors: Exocrine excretion => ?Nasal
- 23. H1-Receptor Antagonists I GENERATION (SEDATIVE): Dimedrol
- 24. Pharmacodynamics of antihistamine H1 blockers ⮞
- 25. Dimedrol (Diphenhydramine)-Tab 0.05 g, amp 1%-1 ml
- 26. Terfenadine (Claritin)-. ● blocks cardiac K+
- 27. Sympathomimetics: Adrenaline h/ch - 0.1% sol. 0.3-0,5-1
- 28. Drugs used to treat Delayed Type Hypersensitivity
- 29. Drugs used to treat Delayed
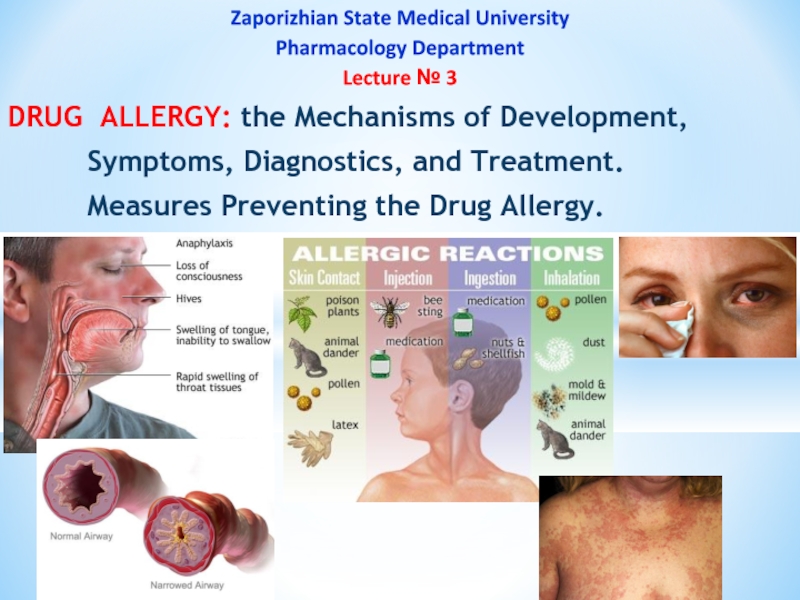
Слайд 1Zaporizhian State Medical University
Pharmacology Department
Lecture № 3
DRUG ALLERGY: the Mechanisms of
Symptoms, Diagnostics, and Treatment.
Measures Preventing the Drug Allergy.
Слайд 2Adverse Drug Reactions (ADRs) include all unintended pharmacologic effects of a
● Therapeutic Failures,
● Intentional Overdosage,
● Abuse of the Drug, or
● Errors in Administration.
ADRs are categorized into:
Type A: predictable (75%) – dose dependent, related to the known pharmacologic actions of the drug, and occur in otherwise healthy individuals
Type B: unpredictable (25%) reactions - generally dose independent, unrelated to the actions of
the drug, and occur
only in SUSCEPTIBLE INDIVIDUALS.
Слайд 3Unpredictable reactions:
● Drug Intolerance
● Drug Idiosyncrasy
● Drug
● Pseudoallergic Reactions.
Drug allergy is a non-predictable immunologically mediated ADR to a pharmaceutical and/or formulation agent in a sensitized person.
Drug allergy differs from drug toxicity in many ways:
● The lesion produced by allergy is lower in incidence
● It is unpredictable;
● Prior exposure to the drug may cause sensitization;
● The lesion is dose independent and rash, fever,
eosinophilia and blood dyscrasias can occur.
Слайд 4A. Humoral Type:
Type I (Anaphylactic) reactions - Immediate hypersensitivity reactions are
Urticaria, Itching, Subepidermal Necrolysis – Lyell's syndrome, Angioedema, Asthma, Rhinitis, Anaphylactic Shock.
Type II (Cytolytic) reactions are mediated by IgG or IgM:
Blood Transfusion Reactions, Haemolytic Disease of Newborns, Autoimmune Haemolytic Anemia, Thrombocytopenia, Agranulocytosis, Aplastic Anaemia, Haemolysis, Organ Damage (the liver, kidney, muscle), Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Some Drug Reactions.
Type III (Retarded) reactions are mediated by circulating antibodies (predominantly mopping antibody, IgG):
Serum sickness - symptoms develop within 7-10 days and include Urticaria, Lymphadenopathy, Myalgia, Arthralgia, Fever,
Polyarthritis Nodosa, Stevens-Johnson syndrome.
Systemic lupus erythematosus is an autoimmune disorder that may be induced by Hydralazine, Novocainamide, Isoniazid and other drugs.
Слайд 5B. Cell Mediated:
Type IV (Delayed hypersensitivity) reactions:
several hours or days
are cell-mediated through production of sensitized
T-lymphocytes carrying receptors for the antigen.
On contact with antigen these T cells produce limphokines which attract granulocytes and generate an inflammatory response, e.g., contact dermatitis, some rashes, fever, photosensitization.
Слайд 6The antigen reacts with reaginic IgE antibodies, bound to the surface
●Those that ⭡Vascular Permeability and contract smooth muscles: Histamine, PAF, SRS-A, Bradykinin.
●Those that are chemotactic for or activate other pro-inflammatory cells: Leukotriene B4,
Eosinophil and Neutrophil Chemotactic Factors.
●Those that modulate the release of other mediators: Bradykinin, PAF, Prostaglandins.
●Those which cause termination of the immune inflammatory response.
Слайд 7DRUG ALLERGY
The most dangerous type of ADRs.
45% reports of AR/SE of
900 reports of allergic reactions on drugs
(36% reports of AR/SE of drugs) in Ukraine
during 1996-2008.
Latent forms of hypersensitivity to drugs –
in 10-15% world population and
20% healthy people (according to WHO).
Слайд 8
Allergic Anamnesis Ignoring
Analgin, Aspirin, Ampicillin were administered in patients with
Severe allergic reactions were observed –
Anaphylactic Shock, Quincke‘s edema, Toxic Dermatitis.
Allergic reacitons on Flemoxin and Grunamox in patients with drug allergy to Amoxicillin
Allergic reacitons on Solpadein the active substance of which is Paracetamole.
The main reason of manifestation – absence of knowledge of numerous trade names of
Generic Drugs containing the Same Active Agents.
Слайд 9The various subtypes of T lymphocytes
(Cytotoxic, Helper and Suppressor) and
They regulate Humoral Immunity, B lymphocyte function.
T-cells carrying CD4+ antigen are responsible for
the HELPER function and the delayed hypersensitivity.
Th1 cells enhance CMI but inhibit Humoral Immunity.
Th2 cells have the opposite effect.
T-cells carrying CD8+ antigen are mainly responsible
for the CYTOTOXIC and SUPPRESSOR functions.
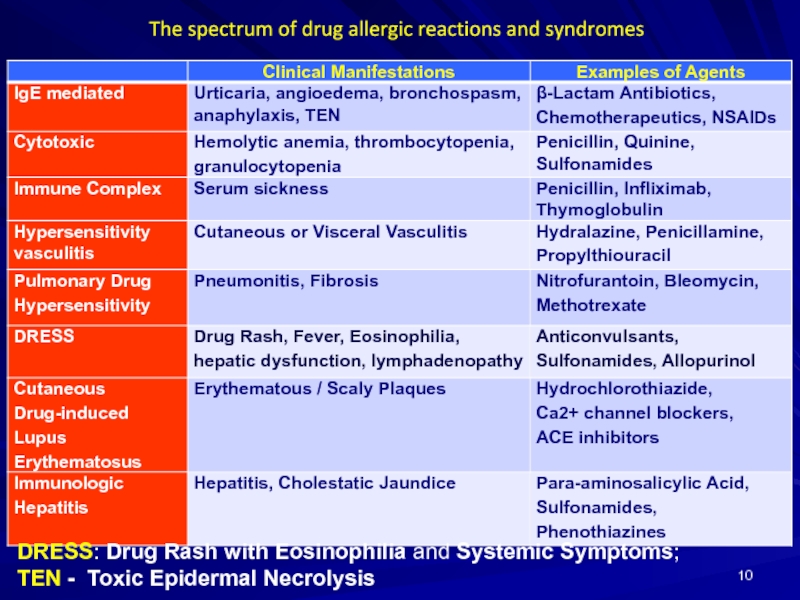
Слайд 10The spectrum of drug allergic reactions and syndromes
DRESS: Drug Rash with
TEN - Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis
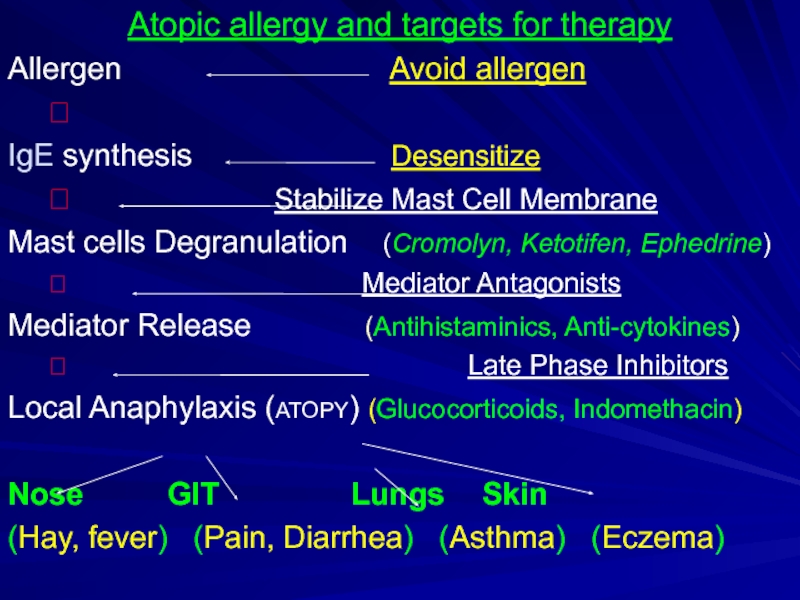
Слайд 11Atopic allergy and targets for therapy
Allergen
?
IgE synthesis Desensitize
? Stabilize Mast Cell Membrane
Mast cells Degranulation (Cromolyn, Ketotifen, Ephedrine)
? Mediator Antagonists
Mediator Release (Antihistaminics, Anti-cytokines)
? Late Phase Inhibitors
Local Anaphylaxis (ATOPY) (Glucocorticoids, Indomethacin)
Nose GIT Lungs Skin
(Hay, fever) (Pain, Diarrhea) (Asthma) (Eczema)
Слайд 12Aspirin and other NSAIDs are reported to account for 21-25% of
Intake of:
- Analgin
- Diclophenac
- Ketanov
- Baralgetas
produced severe Bronchoobstructive Syndrome in
patients with Aspirin Asthma.
Aspirin-induced asthma refers to the development of acute bronchoconstriction, profuse rhinorrhea and
skin flushing in asthmatic individuals following
the ingestion of aspirin.
Слайд 13Cyclo-oxygenase (COX) and Lipoxygenase (LO) are
2 main pathways of the
The COX pathway converts Arachidonic Acid to Prostaglandins, Prostacyclin and Thromboxane A.
Attacks of asthma precipitated by Aspirin like drugs are due to the inhibition of COX in airways of the sensitive patients:
the Bronchoconstrictor PgF at the expense of
the Bronchodilator PgE2 due to altered COX response.
The LO Pathway converts Arachidonic Acid to
Leukotriene A4 (LT A4) further hydroxylated to LT B4.
LT B4 is a potent chemotactic agent.
The Sulphidopeptide Leukotrienes LT C4, LT D4 and LT E4 are constrictors of the smooth muscle of the airway
Aspirin-induced asthma may relate to the inhibition of COX, resulting in the "shunting" of Arachidonic Acid cascade to the 5- Lipoxygenase pathway.
Слайд 14ANTIALLERGIC DRUGS
1. Drugs Stabilizing Mast Cell Membrane:
Glucocorticoids: Prednisolone, Hydrocortisone
Antihistamine H1
a Mast cell stabilizer: Cromolyn
β-adrenomimetics: Adrenaline, Ephedrine
Methylxanthines: Euphylline (Aminophylline)
2. Antihistamine H1 agents: Dimedrol, Diprazine, Loratadine
3. Agents eliminating generalized symptoms of immediate allergic reactions:
Adrenomimetics: Adrenaline
Methylxanthines: Euphylline, Theophylline
Ca2+ preparations: Calcium chloride, Ca2+ gluconate
4. Agents decreasing tissue damage: Glucocorticoids
Слайд 15GLUCOCORTICOIDS (GCs)
1. Short-acting: Hydrocortisone acetate
2. Intermediate-acting:
Prednisolone
Triamcinolone
3. Long-acting: Betametasone,
Dexametasone
OINTMENTS for local use - Fluorine-containing:
Synaflan, Flumethasone
AEROSOLS or POWDERS FOR INHALATIONS: Beclometasone
Fluticasone
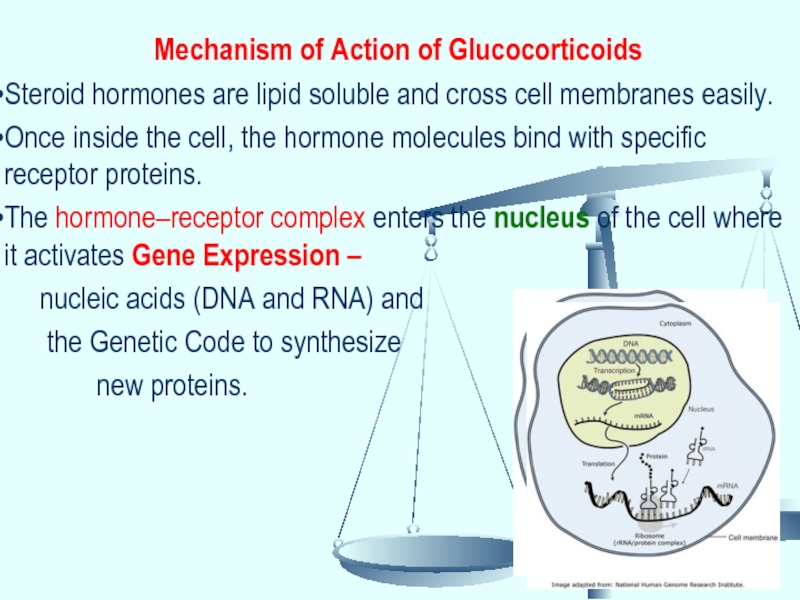
Слайд 16Mechanism of Action of Glucocorticoids
Steroid hormones are lipid soluble and cross
Once inside the cell, the hormone molecules bind with specific receptor proteins.
The hormone–receptor complex enters the nucleus of the cell where it activates Gene Expression –
nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) and
the Genetic Code to synthesize
new proteins.
Слайд 17Action of GCs on mediators of inflammatory
and immune response:
GCs change
? Production of prostanoids owing to
Decreased Expression of COX-2
? Generation of cytokines –
IL 1-6, IL-8, TNF-α and cell adhesion factor – through inhibition of transcription of
the relevant genes
? Complement components in the plasma
? Generation of induced NO
? Histamine release from basophils
? IgG production.
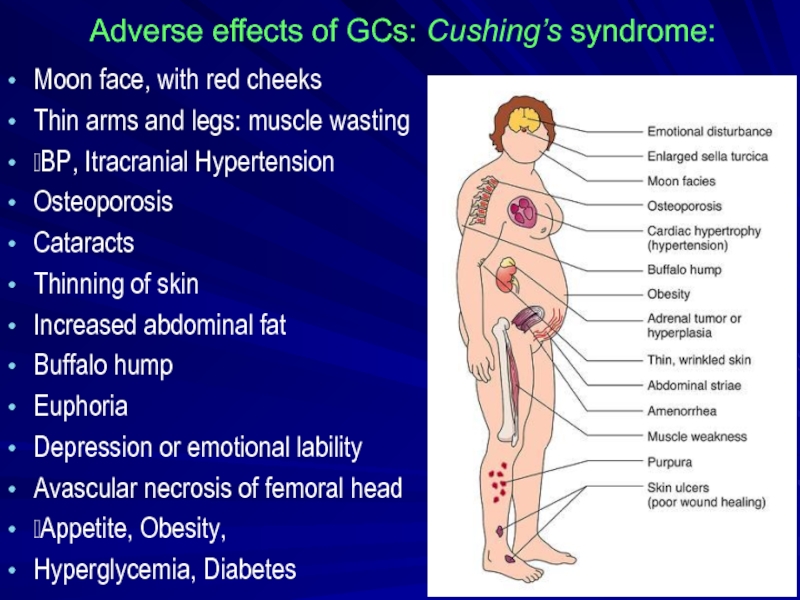
Слайд 18Adverse effects of GCs: Cushing’s syndrome:
Moon face, with red cheeks
Thin
?BP, Itracranial Hypertension
Osteoporosis
Cataracts
Thinning of skin
Increased abdominal fat
Buffalo hump
Euphoria
Depression or emotional lability
Avascular necrosis of femoral head
?Appetite, Obesity,
Hyperglycemia, Diabetes
Слайд 19Cromolyn sodium (caps. 20 mg for inhalation) and
Nedocromil (aerosol: 2
They stabilize the mast cell membrane and inhibit release of the mediators of Type I allergic reaction, including: histamine and Slow Reacting Substance of Anaphylaxis (SRS-A) from sensitized must cells.
Pretreatment with cromolyn blocks allergen-induced and exercise-induced bronchoconstriction by acting on inflammatory cells such as eosinophils.
Слайд 20Ketotifen (tab. 1 mg), a cromolyn analog, is an antihistaminic (H1)
● It inhibits stimulation of immunogenic and inflammatory cells (mast cells, macrophages, eosinophils, lymphocytes, neutrophils) and mediator release.
● It is believed to inhibit airway inflammation induced by
platelet activating factor (PAF).
Ketotifen prevents bronchial asthma attacks.
● It also produces relief in patients with rhinitis, atopic dermatitis, conjunctivitis, urticaria, food allergy, migraine
Adverse effects: sedation, dry mouth, dizziness, nausea,
weight gain.
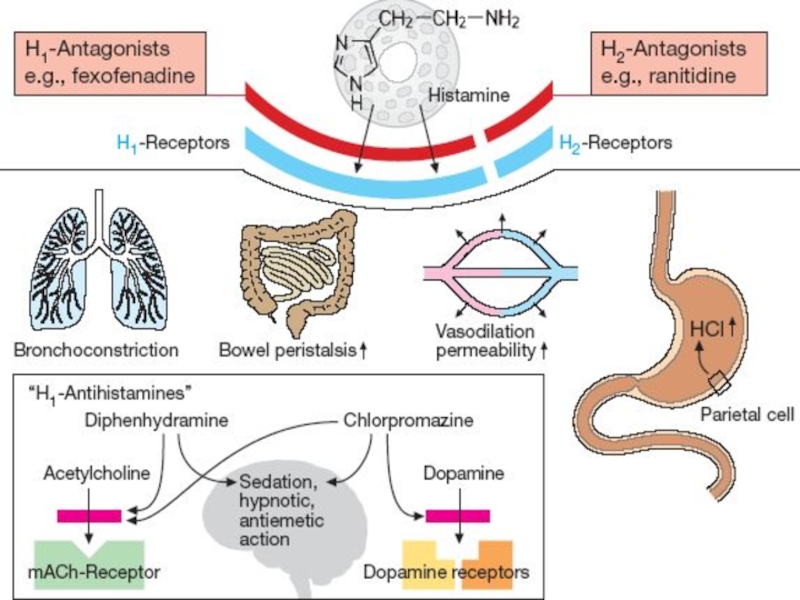
Слайд 21H1-Receptors:
Exocrine excretion => ?Nasal and Bronchial mucus
Intestinal smooth muscle contraction =>
cramps and diarrhea
Sensory nerve endings: itch and pain
H2-Receptors:
Stomach: Stimulation of Gastric Hydrochloric Acid Secretion
H1- and H2-Receptors:
Cardiovascular system: ?BP and ?HR
Skin:
‘Triple Response’ – Wheal formation, Reddening, Flare
Слайд 23H1-Receptor Antagonists
I GENERATION (SEDATIVE):
Dimedrol (Diphenhydramine)
Diprazine (Promethazine)
Suprastine (Chloropyramine)
Diazoline
Tavegyl (Clemastin)
II GENERATION
Loratadine (Claritin)
Terfenadine
Astemizole
Phencarol (Quifenadine)
III GENERATION (ACTIVE METABOLITES):
Telfast (Fexofenadine)
Zirtek (Cetirizine)
Слайд 24Pharmacodynamics of antihistamine H1 blockers
⮞ Block the actions of histamine
antagonism at the H1-receptor
⮞ Antagonist effects at other receptors:
⮞ M - Cholinoceptors
⮞ α1 - Adrenoreceptors
⮞ 5-Hydrohytryptamine (5-HT) receptors
Diprazin ⮞ Dimedrol ⮞ Suprastin ⮞ Diazolin
Слайд 25Dimedrol (Diphenhydramine)-Tab 0.05 g, amp 1%-1 ml
competes to H1 receptors
the bronchi, GIT, uterus, and large blood vessels.
By binding to receptors, suppresses histamine-induced allergic symptoms, even though it does not prevent its release.
Central antimuscarinic actions is responsible for antivertigo, antiemetic, and antidyskinetic action.
Clinical uses:
⮞ Allergy symptoms
⮞ Motion sickness
⮞ Parkinson’s disease
⮞ Nonproductive cough
⮞ Insomnia
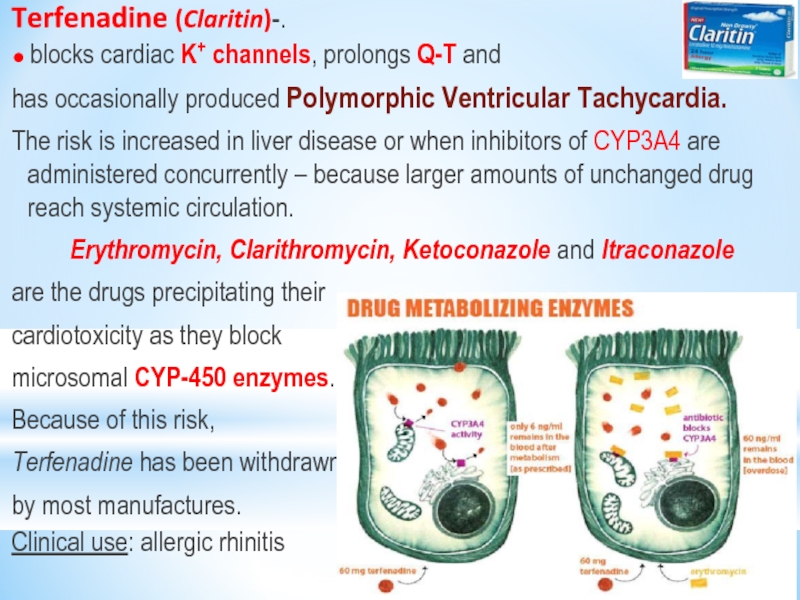
Слайд 26Terfenadine (Claritin)-.
● blocks cardiac K+ channels, prolongs Q-T and
has
The risk is increased in liver disease or when inhibitors of CYP3A4 are administered concurrently – because larger amounts of unchanged drug reach systemic circulation.
Erythromycin, Clarithromycin, Ketoconazole and Itraconazole
are the drugs precipitating their
cardiotoxicity as they block
microsomal CYP-450 enzymes.
Because of this risk,
Terfenadine has been withdrawn
by most manufactures.
Clinical use: allergic rhinitis
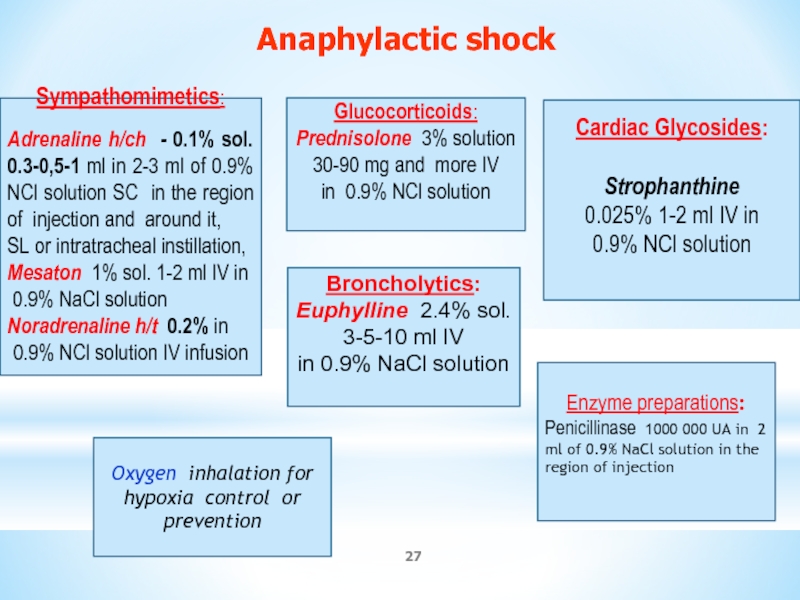
Слайд 27Sympathomimetics:
Adrenaline h/ch - 0.1% sol. 0.3-0,5-1 ml in 2-3 ml of
SL or intratracheal instillation,
Mesaton 1% sol. 1-2 ml IV in
0.9% NaCl solution
Noradrenaline h/t 0.2% in
0.9% NCl solution IV infusion
Glucocorticoids:
Prednisolone 3% solution 30-90 mg and more IV
in 0.9% NCl solution
Broncholytics:
Euphylline 2.4% sol.
3-5-10 ml IV
in 0.9% NaCl solution
Oxygen inhalation for hypoxia control or
prevention
Enzyme preparations:
Penicillinase 1000 000 UA in 2 ml of 0.9% NaCl solution in the region of injection
Cardiac Glycosides:
Strophanthine
0.025% 1-2 ml IV in
0.9% NCl solution
Anaphylactic shock
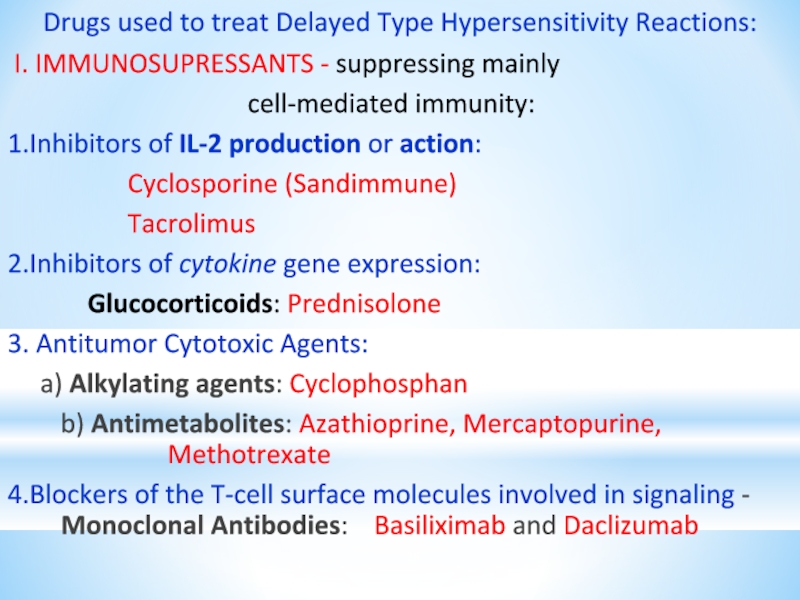
Слайд 28Drugs used to treat Delayed Type Hypersensitivity Reactions:
I. IMMUNOSUPRESSANTS
cell-mediated immunity:
1.Inhibitors of IL-2 production or action:
Cyclosporine (Sandimmune)
Tacrolimus
2.Inhibitors of cytokine gene expression:
Glucocorticoids: Prednisolone
3. Antitumor Cytotoxic Agents:
a) Alkylating agents: Cyclophosphan
b) Antimetabolites: Azathioprine, Mercaptopurine, Methotrexate
4.Blockers of the T-cell surface molecules involved in signaling - Monoclonal Antibodies: Basiliximab and Daclizumab
Слайд 29
Drugs used to treat
Delayed Type Hypersensitivity Reactions:
II. Drugs decreasing
1. Glucocorticoids
2. NSAIDs