- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Cardiovascular disease In pregnancy презентация
Содержание
- 1. Cardiovascular disease In pregnancy
- 2. Cardiac Diseases Rheumatic heart disease Congenital heart
- 3. Physiological Consideration with Heart Disease In Pregnancy
- 4. cont… Later
- 5. cont… Heart:
- 6. conti….
- 7. Diagnosis of Heart Disease Some clinical indicators
- 8. Clinical findings
- 9. Diagnostic studies Electrocardiography
- 10. Echocardiography:
- 11. Clinical clssification
- 12. Preconceptional counseling Maternal mortality
- 13. cont… Life
- 14. Risks for Maternal Mortality Caused by Various
- 15. Group 2 – Moderate Risk
- 16. Group 3 – Major Risk
- 17. Management In assuring
- 18. Management Four concepts that
- 19. Management of Class 1 & 2 General
- 20. management cont…..
- 21. Management cont….. Labor and
- 22. * fluid balance and
- 23. puerperium
- 24. Management of class 3&4 ؟ whether
- 25. Most common lesions: _Rheumatic
- 26. Peripartum cardiomyopathy : this
- 27. Prognosis :
Слайд 1Cardiovascular Disease In Pregnancy
It is a relatively common in women of
Maternal mortality related to heart disease has decreased remarkably over the past 50 years (from 5.6 to 0.3/100 000 live birth)
Heart disease are still the second most common non obstetrical cause of maternal mortality.
Слайд 2Cardiac Diseases
Rheumatic heart disease
Congenital heart disease
Hypertensive heart disease
Coronary
Thyroid
Syphilitic
Kyphoscoliotic cardiac disease
Idiopathic
Corpulmonale
Constrictive pericarditis
Heart block
Isolated myocarditis
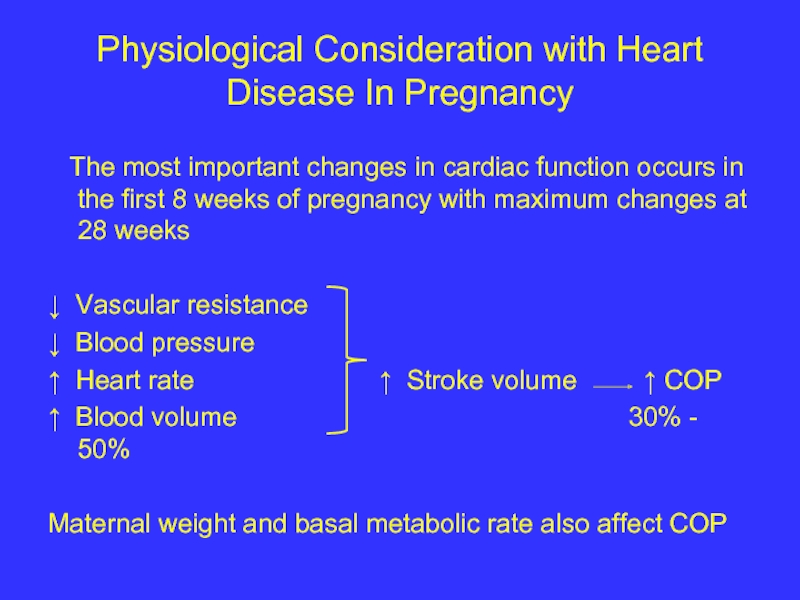
Слайд 3Physiological Consideration with Heart Disease In Pregnancy
The most important
↓ Vascular resistance
↓ Blood pressure
↑ Heart rate ↑ Stroke volume ↑ COP
↑ Blood volume 30% - 50%
Maternal weight and basal metabolic rate also affect COP
Слайд 4
cont…
Later in pregnancy COP is higher when
During labor COP increase moderately in the first stage of labor and appreciably greater in the second stage
COP also increase in the immediate post partum period
Слайд 5
cont…
Heart:
The heart is displaced upward and
Resting pulse increase by about 10 bpm
There is some changes in the cardiac sounds include:
An exaggerated splitting of the first heart sound with increase loudness of both components, no definite changes in the aortic and pulmonary elements of the second sound, and aloud easily heard third sound
Слайд 6
conti….
Systolic murmur is heard in 90 %
Soft diastolic murmur transiently in 20 %
Continuous murmur arising from the breast vasculature in10 % of cases
Слайд 7Diagnosis of Heart Disease
Some clinical indicators of heart disease during
Pregnancy
Progressive dyspnea or orthopnea
Nocturnal cough
Hemoptysis
Syncope
Chest pain
Слайд 8
Clinical findings
Clubbing of fingers
persistent neck vein distension
Systolic murmur grade 3/6 or greater
Diastolic murmur
Cardiomegaly
Persistent arrhythmia
Persistent split-second sound
Criteria for pulmonary hypertension
Слайд 9Diagnostic studies
Electrocardiography
An average 15 – degree left
ECG , and mild ST changes may be seen in the
inferior leads, Atrial and ventricular premature
contractions are relatively frequent
Chest x – ray:
Heart silhouette normally is larger in pregnancy,
however gross cardiomegaly can be excluded
Слайд 10
Echocardiography:
Normal changes include :
Significantly increase left atrial size and left
ventricular outflow cross sectional area.
Слайд 11Clinical clssification
The New York Heart
Classification [ NYHA] “ First published in 1928 “
Class 1 : Uncompromised , no limitation of physical
activity
Class 2 : Slightly compromised , slight limitation of
physical activity
Class 3 : Markedly compromised , marked limitation
of physical activity
Class 4 : Severely compromised , inability to perform
any physical activity without discomfort
Слайд 12Preconceptional counseling
Maternal mortality generally varies directly with
However this relationship may change as pregnancy
progresses
Patient with pulmonary hypertension, primary or
secondary are in danger of undergoing decompensation
during pregnancy
Слайд 13
cont…
Life threatening cardiac abnormalities can be reversed
by corrective surgery and subsequent pregnancy is
less dangerous
In other cases fetal consideration predominate, for
example the teratogenic effect of warfarin
Слайд 14Risks for Maternal Mortality Caused by Various Heart Disease
Cardiac Disorder Mortality %
Group 1 – Minimal Risk
Atrial septal defect 0 -1 %
Ventricular septal defect
Patent ductus arteriosus
Pulmonic or tricuspid disease
Fallot tetralogy,corrected
Bioprosthetic valve
Mitral stenosis,NYHA classes 1&2
Слайд 15
Group 2 – Moderate Risk
2A :
Mitral stenosis , NYHA classes 3 & 4
Aortic stenosis
Aortic coarctation without valvar involvement
Fallot tetralogy , uncorrected
Previous myocardial infarction
Marfan syndrome , normal aorta
2B :
Mitral stenosis with atrial fibrillation
Artificial valve
Слайд 16
Group 3 – Major Risk
Pulmonary hypertension
Aortic coarctation with valvar involvement
Marfan syndrome with aortic involvement
NYHA = New York Heart Association.
From the American College of Obstetrics and Gynecologists
(1992a ) , with permission .
Слайд 17Management
In assuring an optimal outcome , management
be a team approach involving ;obstetrician, cardiologist
and anesthesiologist
Risk to patient of : Heart failure, subacute bacterial
endocarditis, and thromboembolic disease will be
identified and minimized
Слайд 18Management
Four concepts that affect management are emphasized
1) the 50% increase in blood volume and COP by the
early 3rd trimester
2) further fluctuation in volume and COP in the
peripartum period
3) a decline in systemic vascular resistance, reaching
a nadir in the 2nd trimester, and then rising to 20%
below normal by late pregnancy
4) hyprcoagulability of special importance in women
requiring anticoagulation in the non pregnant state
Слайд 19Management of Class 1 & 2
General measures:
_ avoid contact with
infection
_ pneumococcal and influenza vaccines are recommended
( patient with valvar heart disease)
_ cigarette smoking is prohibited
_ diet , avoidance of strenuous activity and avoidance of
anemia
Слайд 20
management cont…..
sign’s of heart failure:
» nocturnal cough
» a sudden diminution in ability to carry
out usual duties
» increasing dyspnea on exertion
» attacks of smothering with cough
» hemoptysis, progressive edema and
tachycardia
Слайд 21
Management cont…..
Labor and Delivery :
* vaginal delivery
indication
* relief of pain with intravenous analgesics ,
continuous epidural analgesia is recommended for
most situation , but it’s contraindicated in patient with:
[ Intracardiac shunt , pulmonary hypertension , Aortic stenosis ] ,
to avoid the risk of maternal hypotension
Слайд 22
* fluid balance and antibiotic prophylactic
* semi
* intensive medical management for any sign’s of
impending ventricular failure
[ pulse > 100 , RR > 24 , dyspnea ]
* expedite vaginal delivery
* close monitoring for the 3rd stage of labor
Слайд 23
puerperium
*
and thromboembolism
* delay the procedure of tubal sterilization until
it is obvious that the mother is a febrile, not
anemic and can ambulate without evidence
of distress
* option of contraceptive advise
Слайд 24Management of class 3&4
؟ whether pregnancy should be undertaken
؟
؟ prolonged hospitalization or bed rest
؟ vaginal delivery is preferred
؟ caesarian section delivery should be with the availability of experience anesthetic support in a facility with
experience with complicated cardiac disease
Слайд 25
Most common lesions:
_Rheumatic heart disease
Incidence of rheumatic
countries , It still remain the chief cause of serious mitral
valve disease in women,(3/4thof cases of mitral stenosis)
_Congenital Heart Disease:
many congenital heart lesions appear to be inherited as
polygenic characteristic , 10% of women with congenital
heart disease would give birth to similarly affected infants ,
50 % were concordant for the same anomaly
Слайд 26
Peripartum cardiomyopathy :
this is a diagnosis of exclusion ,
with peripartum heart failure with no apparent etiology,
symptoms of cardiac decompensation appear during
the last weeks of pregnancy or 1 to 6 months postpartum
obstetrical complications such as : preeclampsia, anemia
from blood loss , and infection either contribute or
precipitate heart failure
Слайд 27
Prognosis :
disease depends upon the :
_ functional cardiac capacity
_ other complications that further increase cardiac load
_ quality of medical care provided
_ psychological and socioeconomical factors









![Clinical clssification The New York Heart Association’s Functional Classification [ NYHA]](/img/tmb/2/130760/40d1b8dfcbab89d4b04075071642d367-800x.jpg)





















