- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Cardiogenic shock презентация
Содержание
- 1. Cardiogenic shock
- 2. Definitions of shock Severe hemodynamic impairment which
- 3. Signs of hypoperfusion -
- 4. Cardiogenic shock Hemodynamic criteria -
- 5. Pathogenesis of shock Inadequate
- 6. Types of shock Hypovolemic Traumatic Cardiogenic Septic Neurogenic Hypoadrenal
- 7. SHOCK Cold, clammy extremities Warm,bounding
- 8. Causes of cardiogenic shock Acute myocardial infarction
- 9. Etiology of cardiogenic shock in SHOCK
- 10. Cardiogenic shock due to RV failure Acute
- 11. Cardiogenic shock due to RV failure Reduction
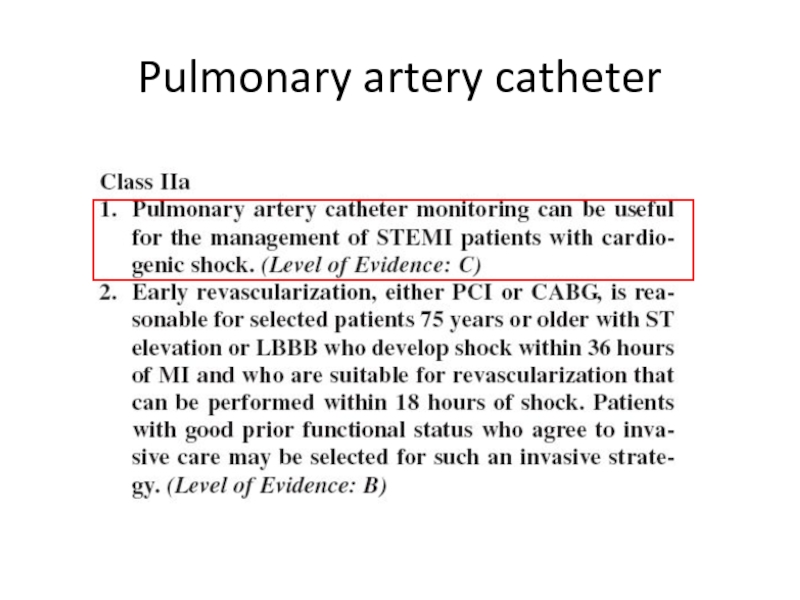
- 12. Hemodynamic monitoring
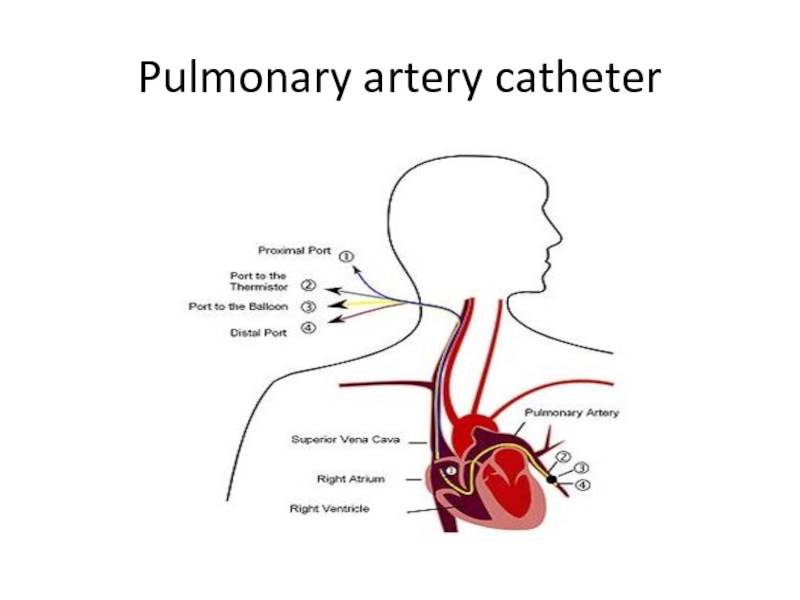
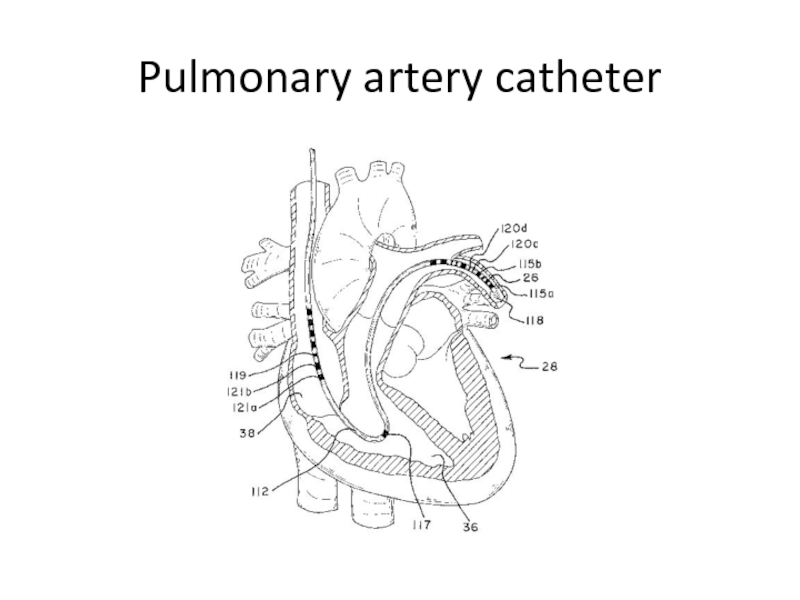
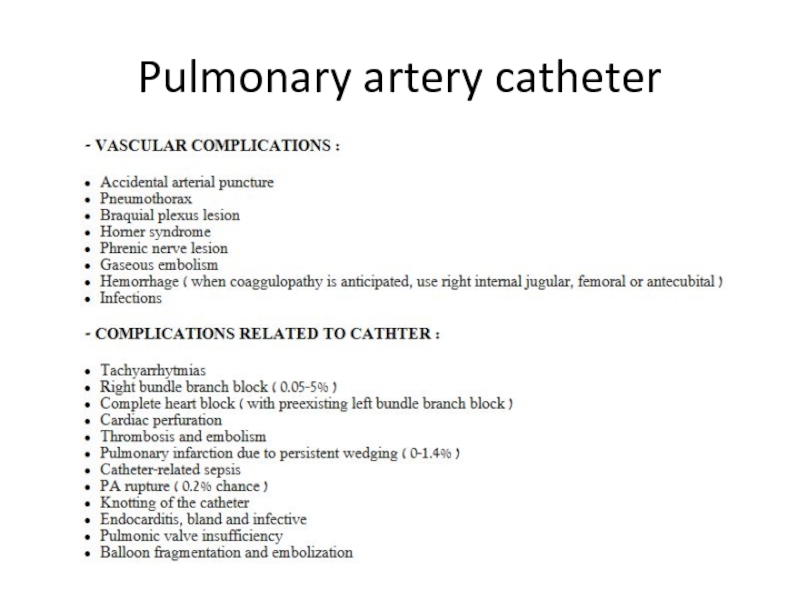
- 13. Pulmonary artery catheter
- 14. Pulmonary artery catheter
- 15. Pulmonary artery catheter
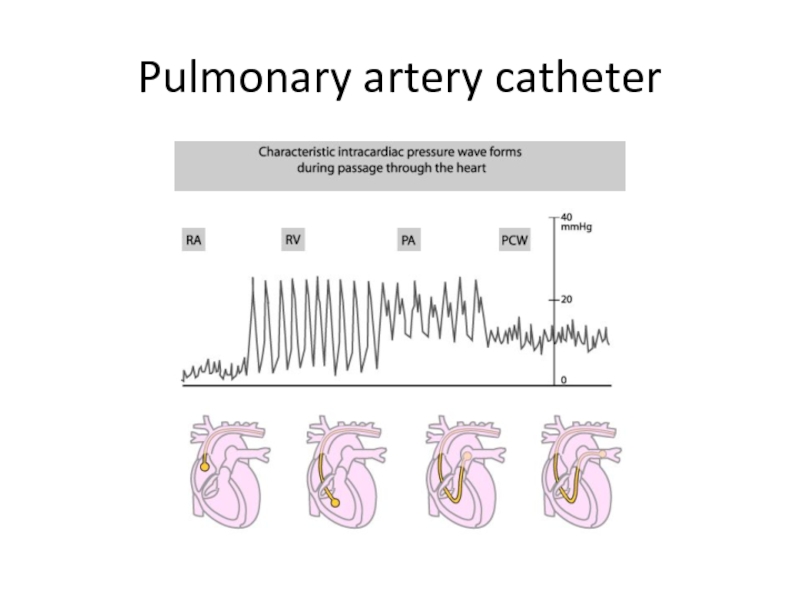
- 16. Pulmonary artery catheter
- 17. Pulmonary artery catheter
- 18. Pulmonary artery catheter
- 19. Pulmonary artery catheter
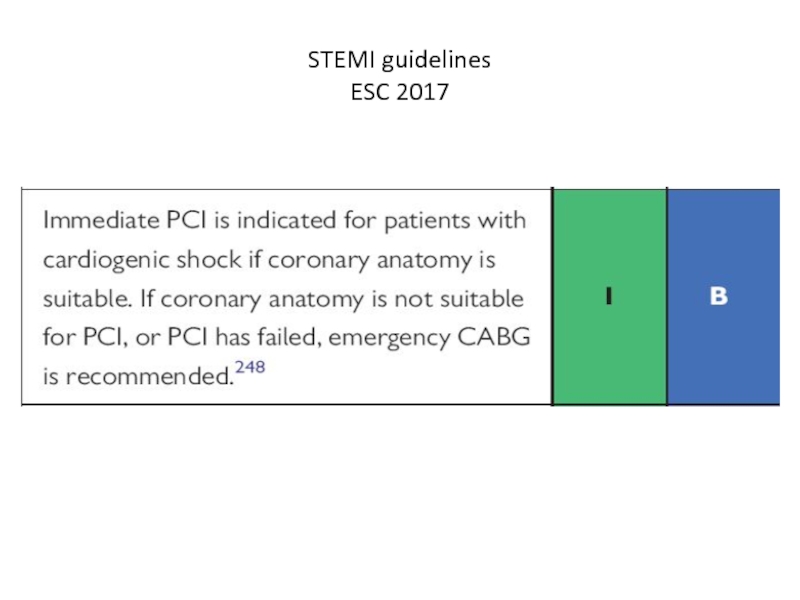
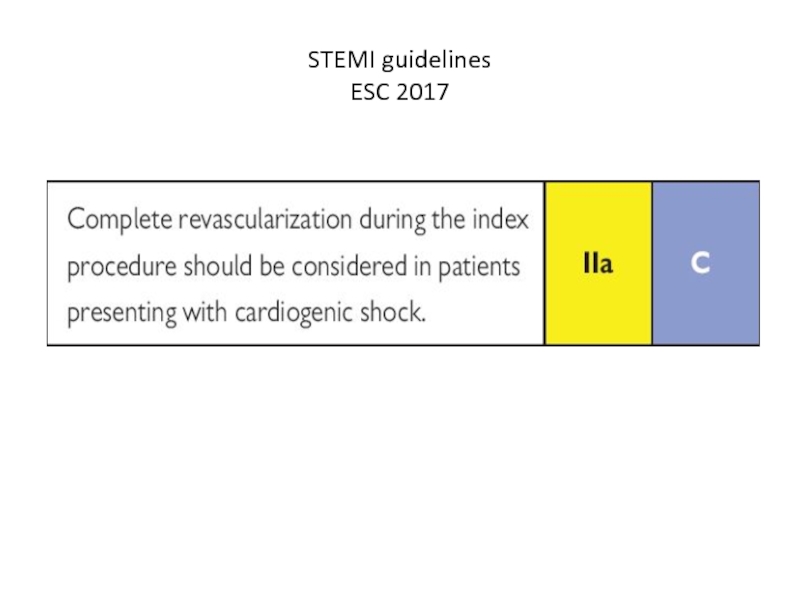
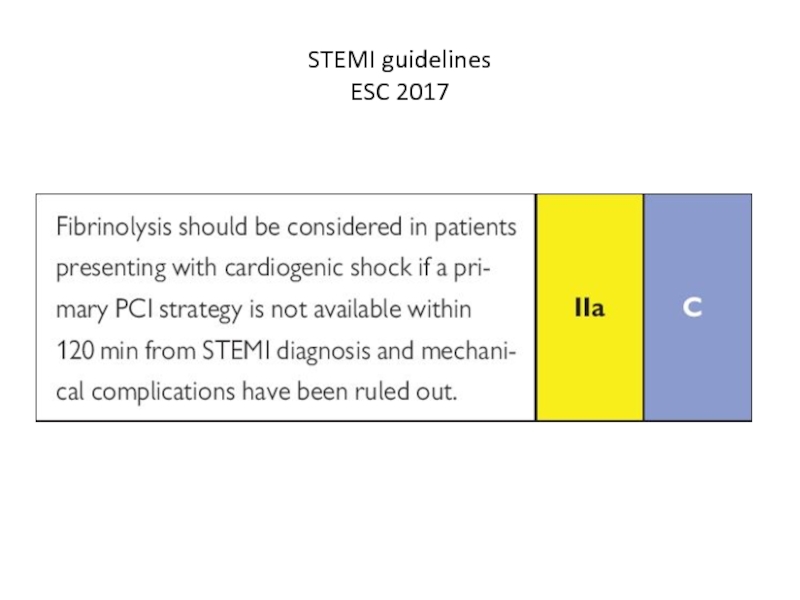
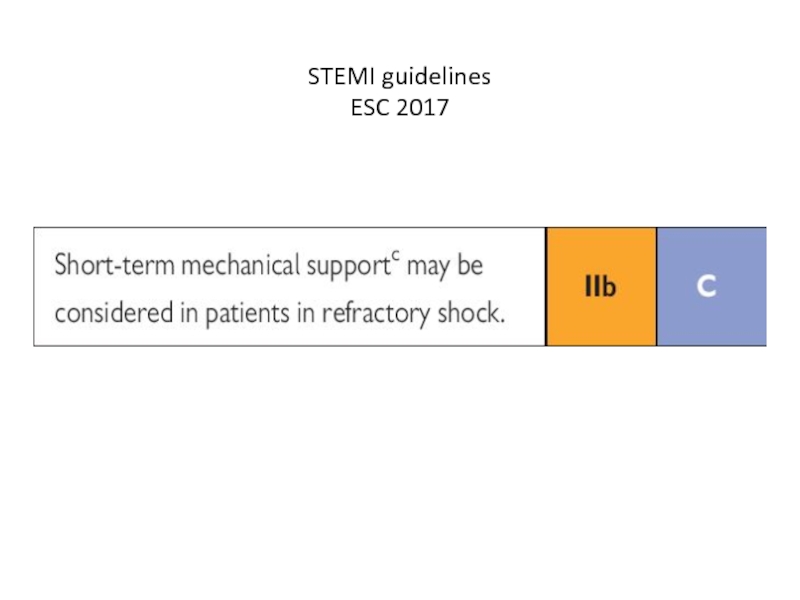
- 20. STEMI guidelines ESC 2017
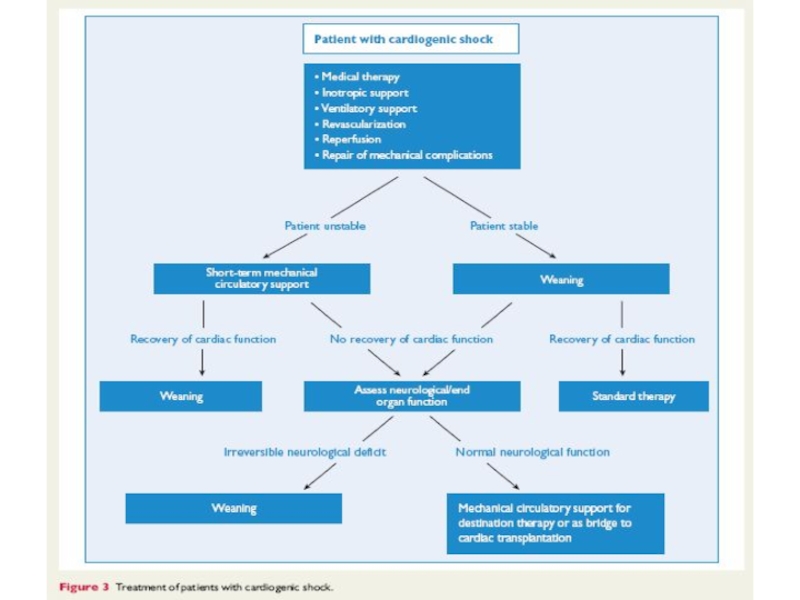
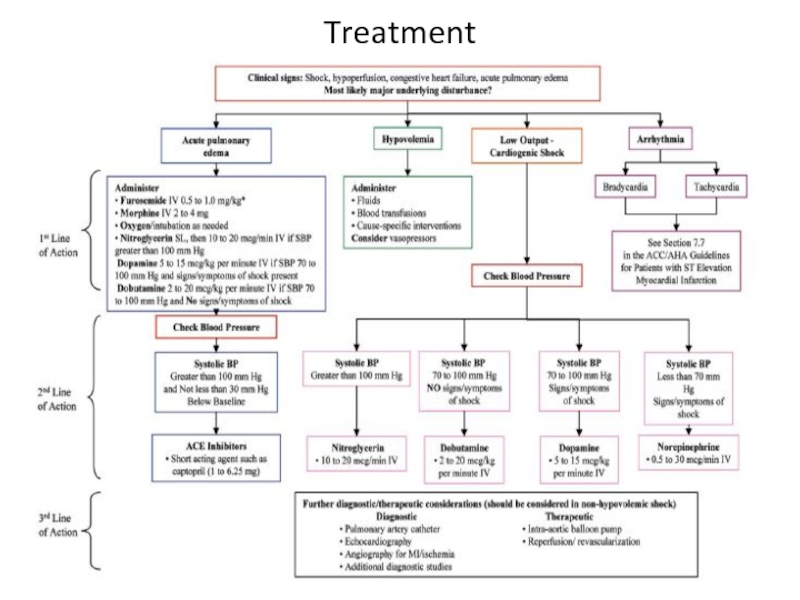
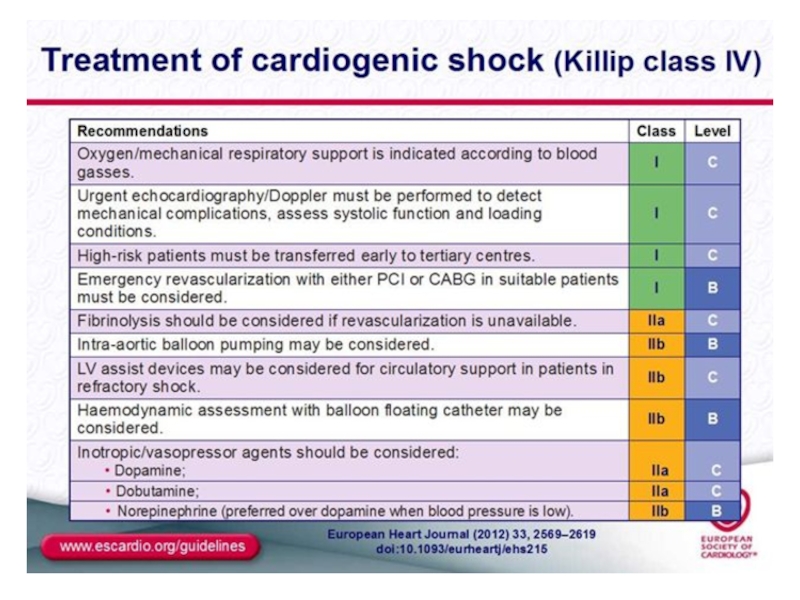
- 21. Treatment of cardiogenic shock
- 22. Inotropes IABP Early revascularization (PCI or
- 27. STEMI guidelines ESC 2017
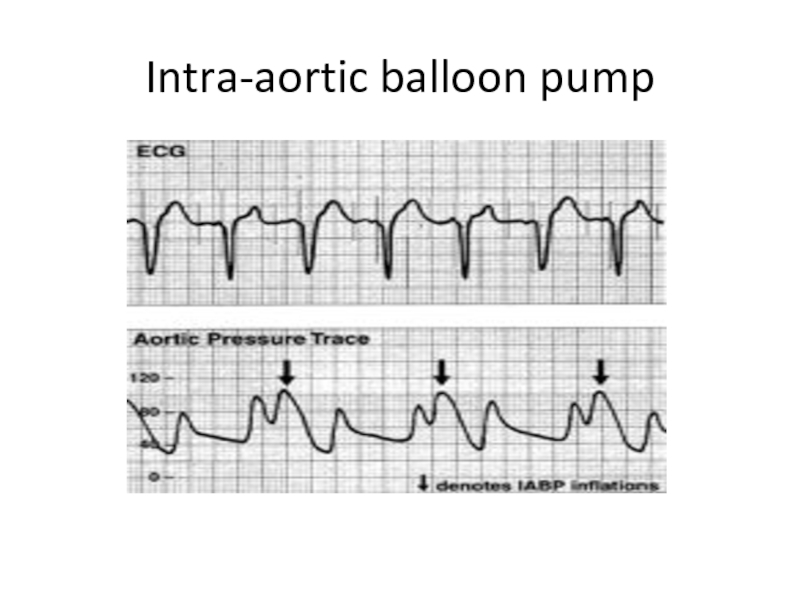
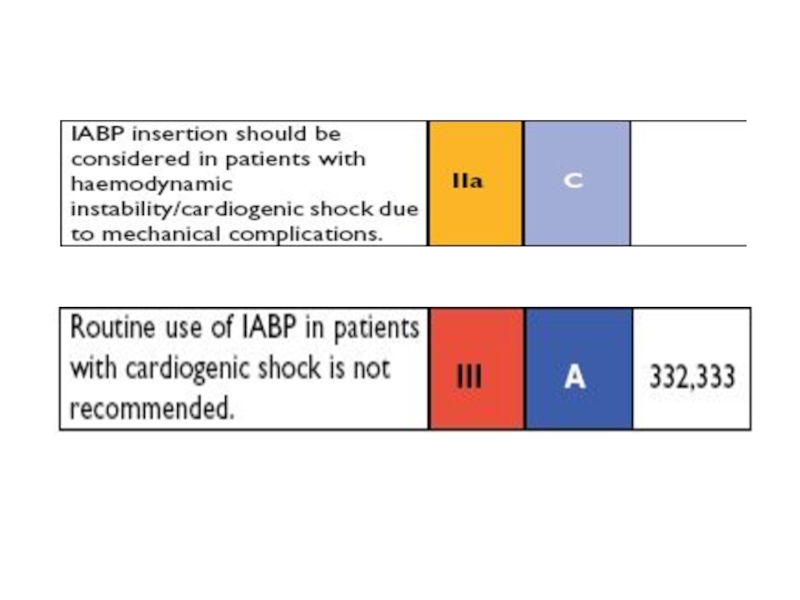
- 28. Intra-aortic balloon pump (IABP)
- 29. Intra-aortic balloon pump
- 30. Intra-aortic balloon pump Contraindications Absolute
- 31. Intra-aortic balloon pump
- 32. Intra-aortic balloon
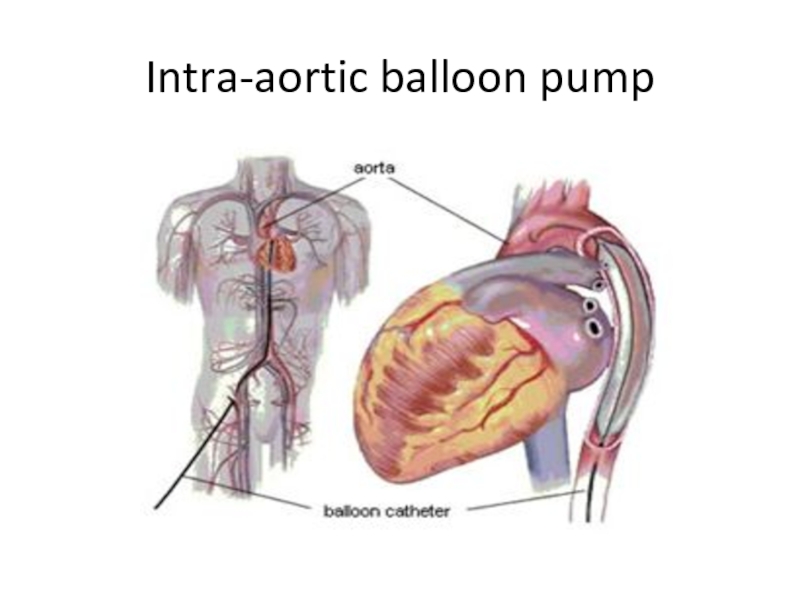
- 33. Intra-aortic balloon pump
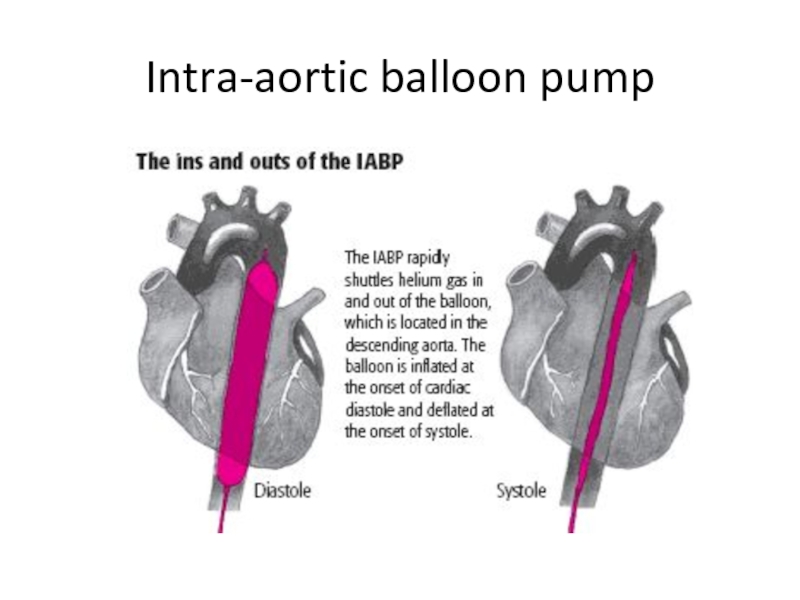
- 34. Intra-aortic balloon pump
- 35. Intra-aortic balloon pump
- 36. Intra-aortic balloon pump
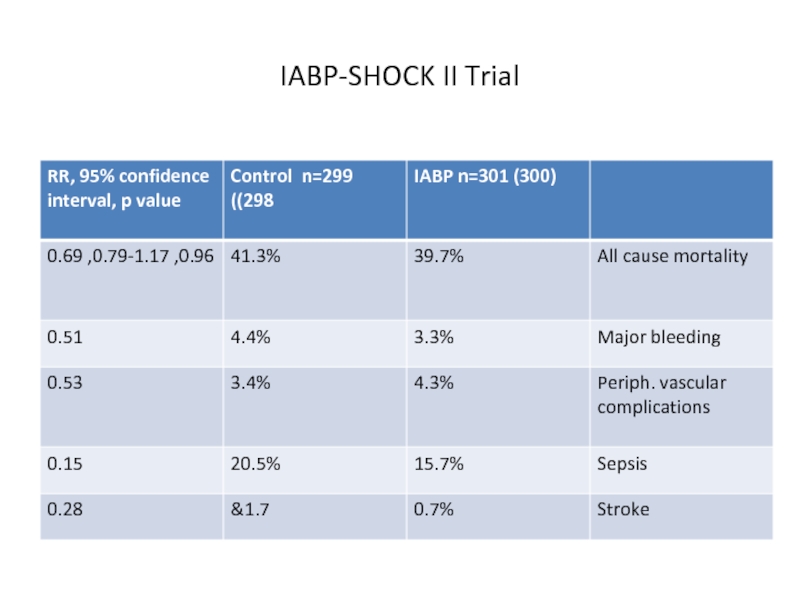
- 37. IABP-SHOCK II Trial
- 38. IABP-SHOCK II Trial
- 39. IABP-SHOCK II Trial: conclusions
- 40. STEMI guidelines ESC 2017
- 41. Early revascularization
- 42. SHOCK trial Early revascularization in
- 43. SHOCK trial Shock criteria
- 44. SHOCK trial Timing
- 45. SHOCK trial Exclusion criteria
- 46. SHOCK trial End points primary
- 47. SHOCK trial Results
- 48. SHOCK trial
- 49. SHOCK trial 1 year survival Early
- 50. SHOCK trial
- 51. Early revascularization and long-term survival in cardiogenic
- 52. STEMI guidelines 2004 Cardiogenic shock
- 53. ACCF/AHA STEMI GL 2013
- 54. STEMI guidelines ESC 2017
- 55. STEMI guidelines ESC 2017
- 56. STEMI guidelines ESC 2017
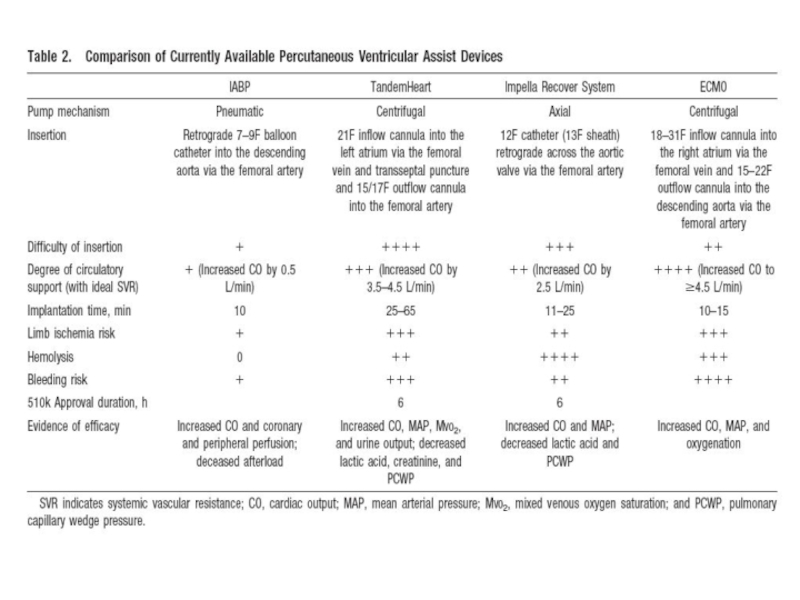
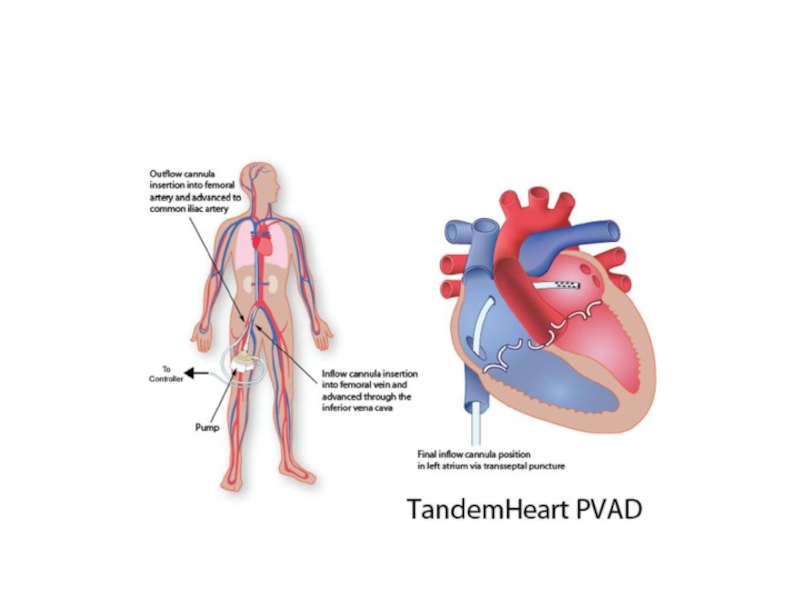
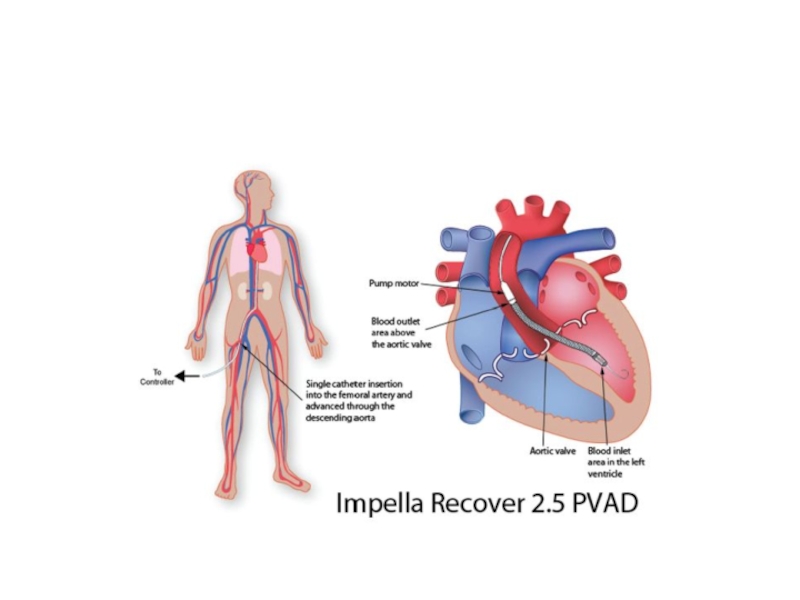
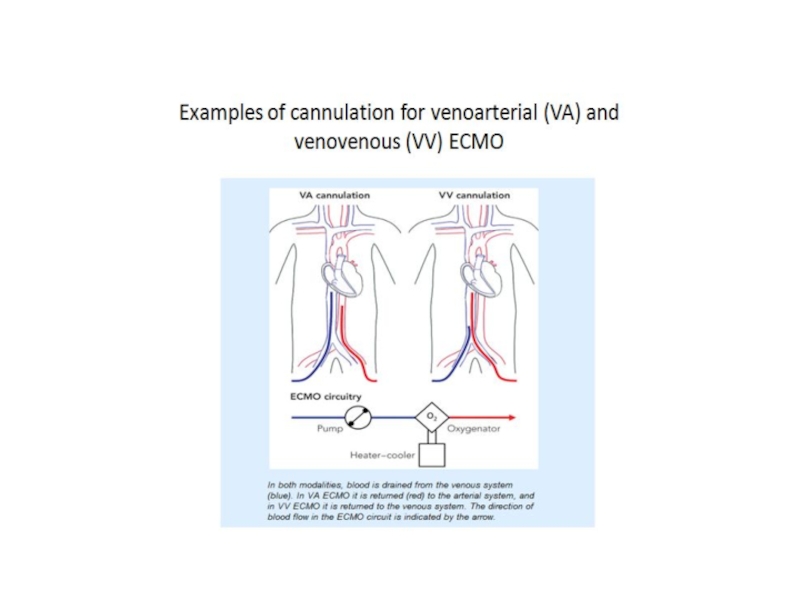
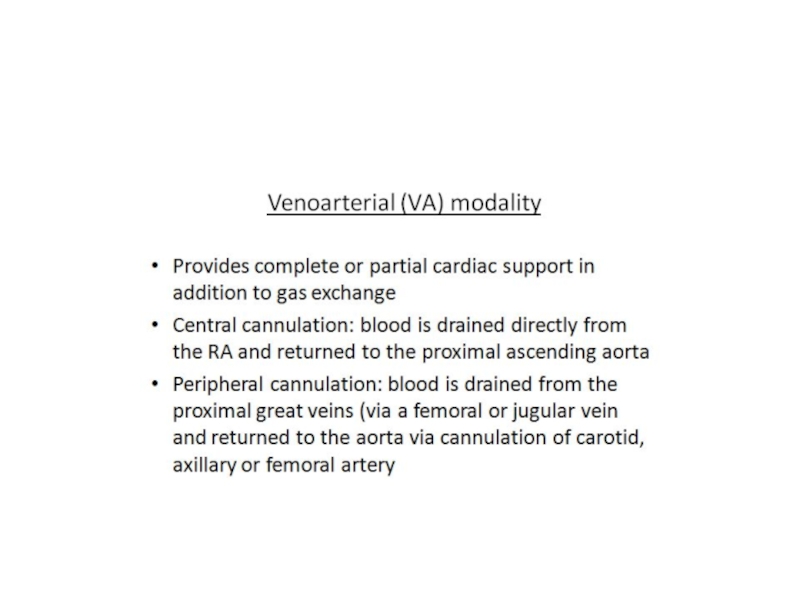
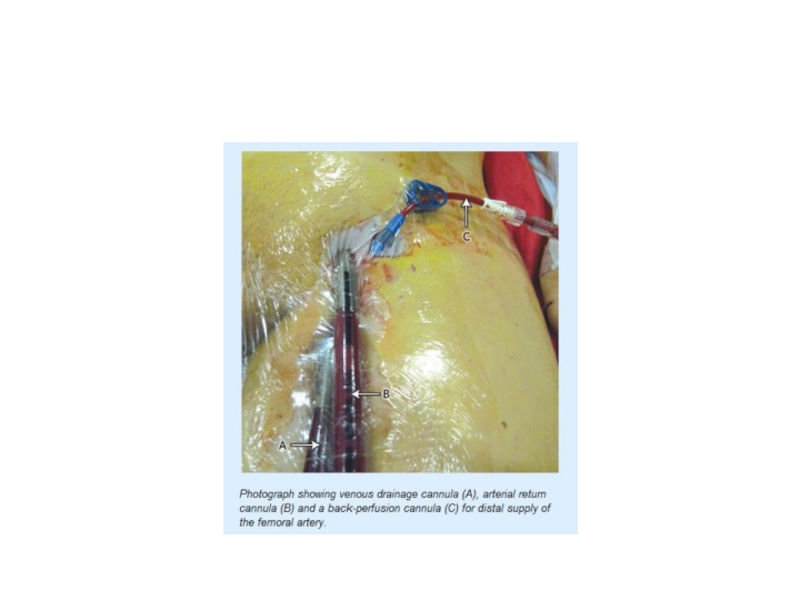
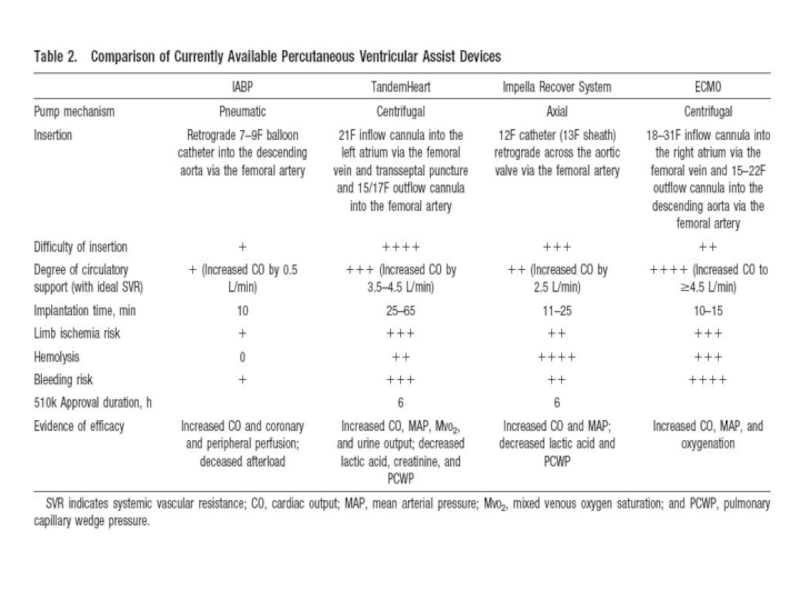
- 57. Percutaneous ventricular assist devices
- 69. STEMI guidelines ESC 2017
- 70. Thank you for attention
- 71. Back up slides
- 73. Treatment
Слайд 1Cardiogenic shock
Dr. Michael Kapeliovich, MD, PhD
Director Emergency Cardiology Service
Deputy Director ICCU
9.2017
Слайд 2Definitions of shock
Severe hemodynamic impairment which causes hypoperfusion of vital organs
Clinical
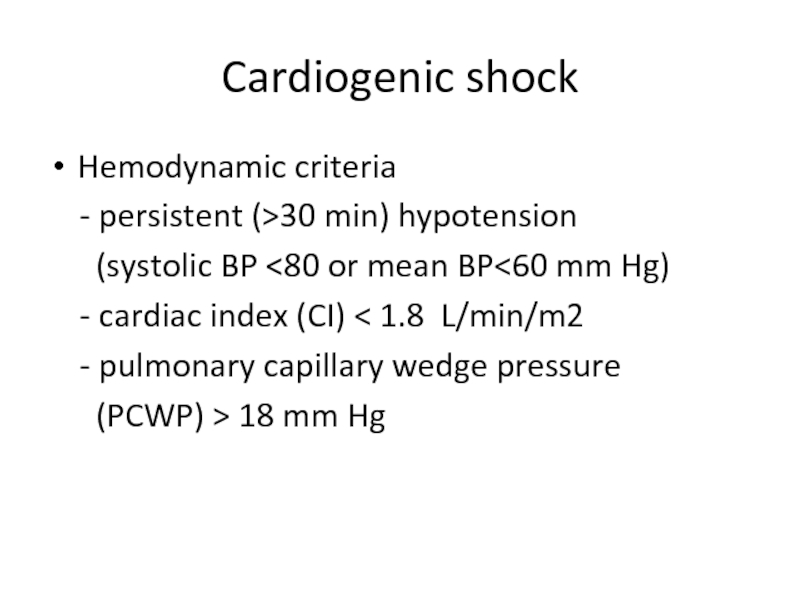
Слайд 4Cardiogenic shock
Hemodynamic criteria
- persistent (>30 min) hypotension
- cardiac index (CI) < 1.8 L/min/m2
- pulmonary capillary wedge pressure
(PCWP) > 18 mm Hg
Слайд 5
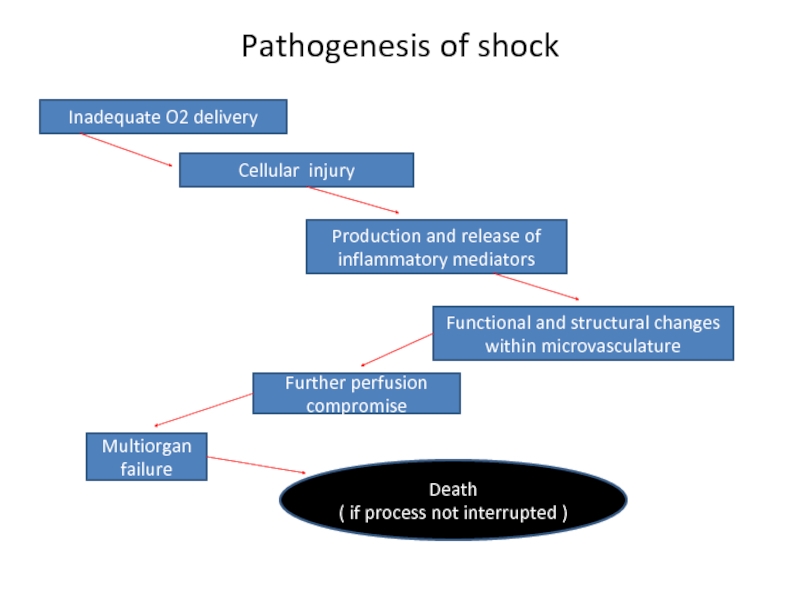
Pathogenesis of shock
Inadequate O2 delivery
Cellular injury
Production and release of inflammatory mediators
Functional
Further perfusion compromise
Multiorgan failure
Death
( if process not interrupted )
Слайд 7
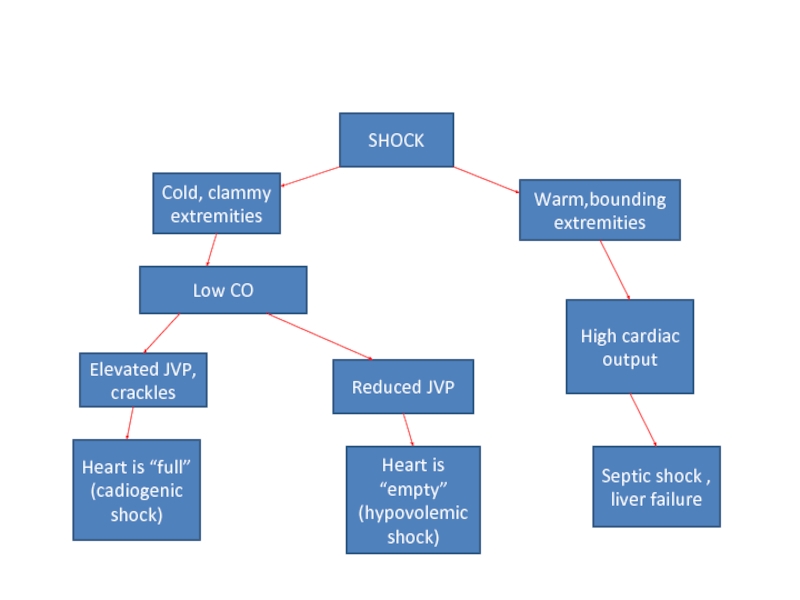
SHOCK
Cold, clammy extremities
Warm,bounding extremities
High cardiac output
Septic shock , liver failure
Elevated JVP,
Reduced JVP
Heart is “empty” (hypovolemic shock)
Low CO
Heart is “full”
(cadiogenic shock)
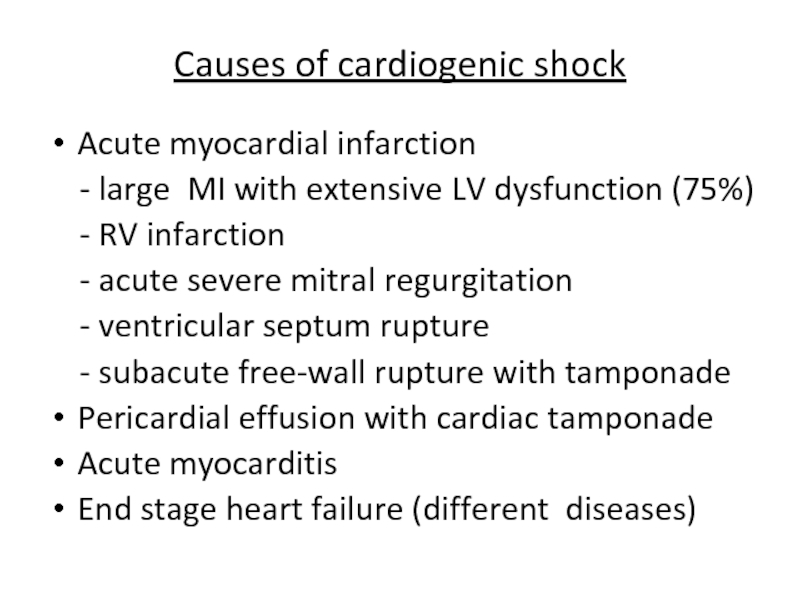
Слайд 8Causes of cardiogenic shock
Acute myocardial infarction
- large MI with
- RV infarction
- acute severe mitral regurgitation
- ventricular septum rupture
- subacute free-wall rupture with tamponade
Pericardial effusion with cardiac tamponade
Acute myocarditis
End stage heart failure (different diseases)
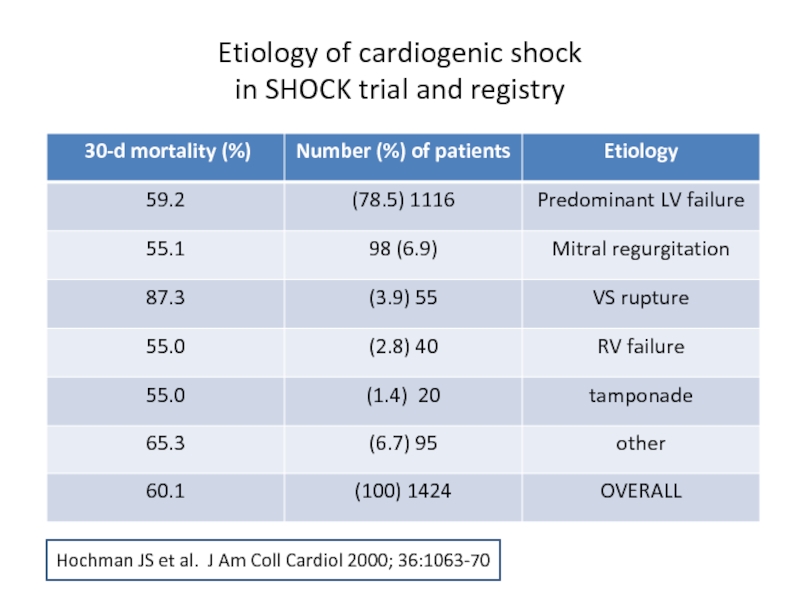
Слайд 9
Etiology of cardiogenic shock
in SHOCK trial and registry
Hochman JS et al.
Слайд 10Cardiogenic shock
due to RV failure
Acute dilatation of ischemic RV
Increase in intrapericardial
Decrease in RV systolic pressure and output
Decrease in LV preload
Decrease in LVED dimension and stroke volume
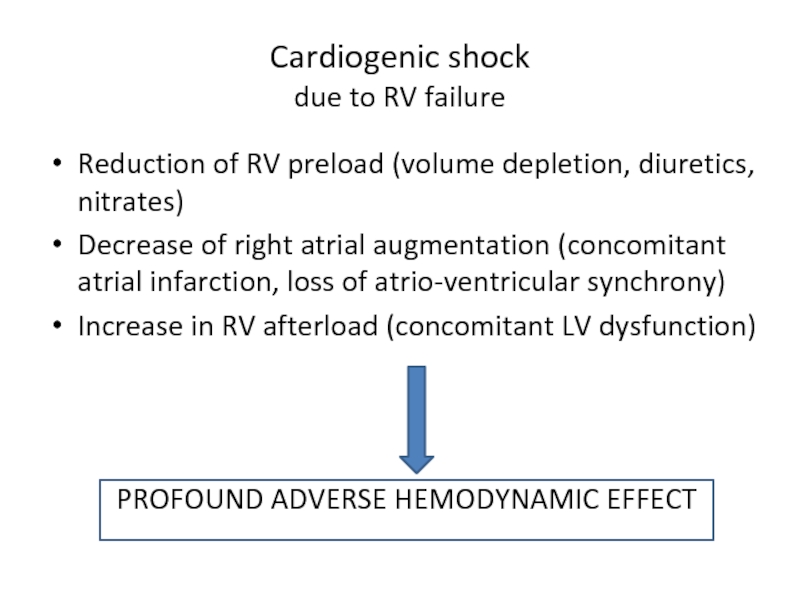
Слайд 11Cardiogenic shock
due to RV failure
Reduction of RV preload (volume depletion, diuretics,
Decrease of right atrial augmentation (concomitant atrial infarction, loss of atrio-ventricular synchrony)
Increase in RV afterload (concomitant LV dysfunction)
PROFOUND ADVERSE HEMODYNAMIC EFFECT
Слайд 22
Inotropes
IABP
Early revascularization (PCI or CABG)
Surgery for mechanical complications
Pericardiocentesis (if tamponade is
Percutaneous ventricular assist devices
Слайд 30
Intra-aortic balloon pump
Contraindications
Absolute
- aortic insufficiensy
- aortic dissection
Relative
- descending thoracic or abdominal aneurysm
- recent groin incision
- morbid obesity
Слайд 39IABP-SHOCK II Trial: conclusions
The use of IAB counterpulsation did
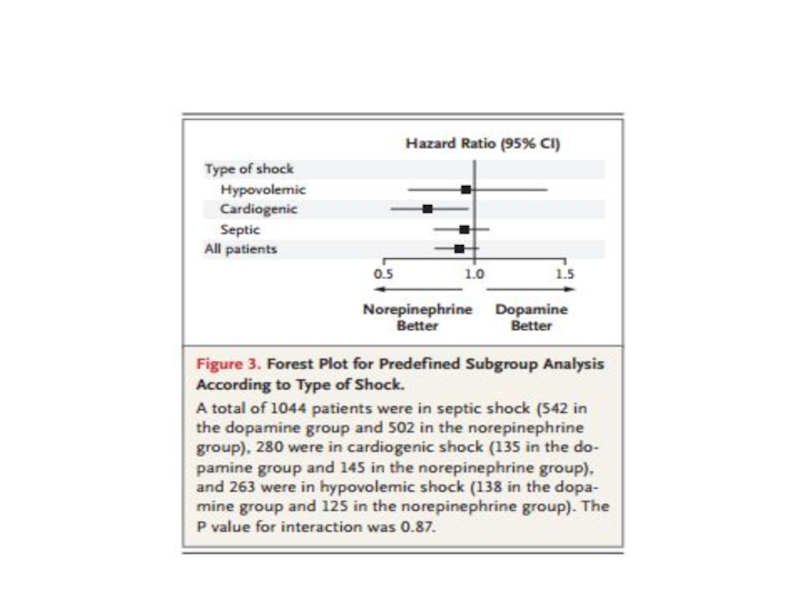
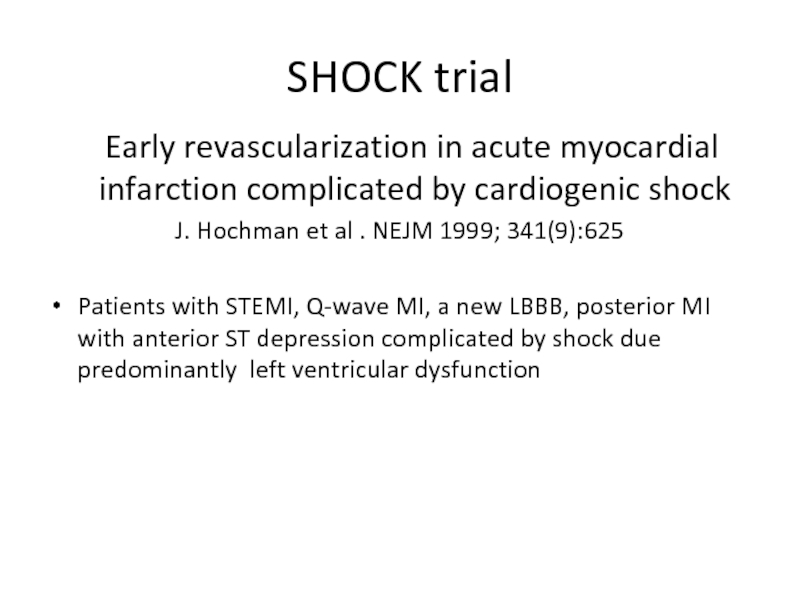
Слайд 42SHOCK trial
Early revascularization in acute myocardial infarction complicated by
J. Hochman et al . NEJM 1999; 341(9):625
Patients with STEMI, Q-wave MI, a new LBBB, posterior MI with anterior ST depression complicated by shock due predominantly left ventricular dysfunction
Слайд 43SHOCK trial
Shock criteria
Clinical :
-
supportive measures to maintain a SBP >90 mm Hg)
- end-organ hypoperfusion (cool extremities or a urine
output < 30 ml/h and heart rate >60 beats per minute)
Hemodynamic:
- CI < 2.2 L/min/m2
- PCWP > 15 mm Hg
Слайд 44SHOCK trial
Timing
- onset of shock within 36
- randomization as soon as possible but no
more than 12 h after Ds of shock
- PCI or CABG as soon as possible and within
6 h of randomization (for patient assigned to
revascularization)
Слайд 45SHOCK trial
Exclusion criteria
- severe systemic illness
- severe valvular disease
- dilated cardiomyopathy
- inability of care givers to gain access for catheterization
- unsuitability for revascularization
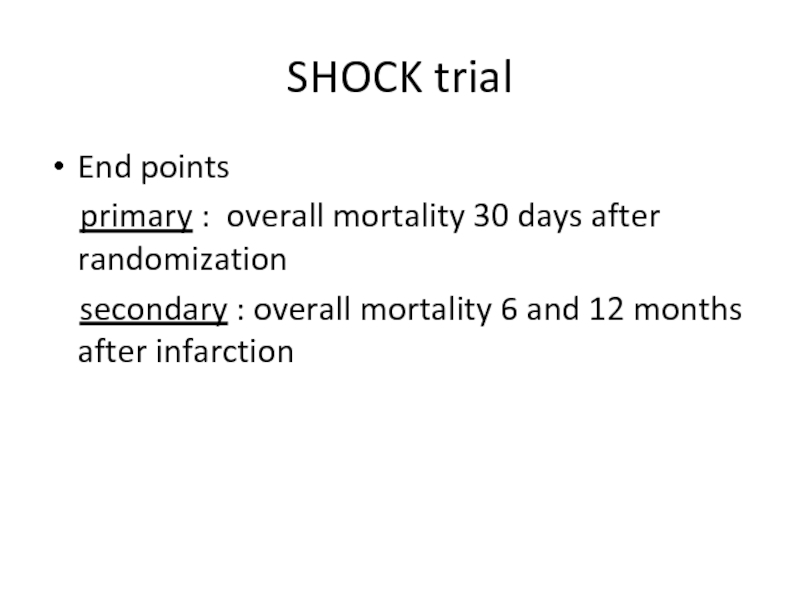
Слайд 46SHOCK trial
End points
primary : overall mortality 30 days after
secondary : overall mortality 6 and 12 months after infarction
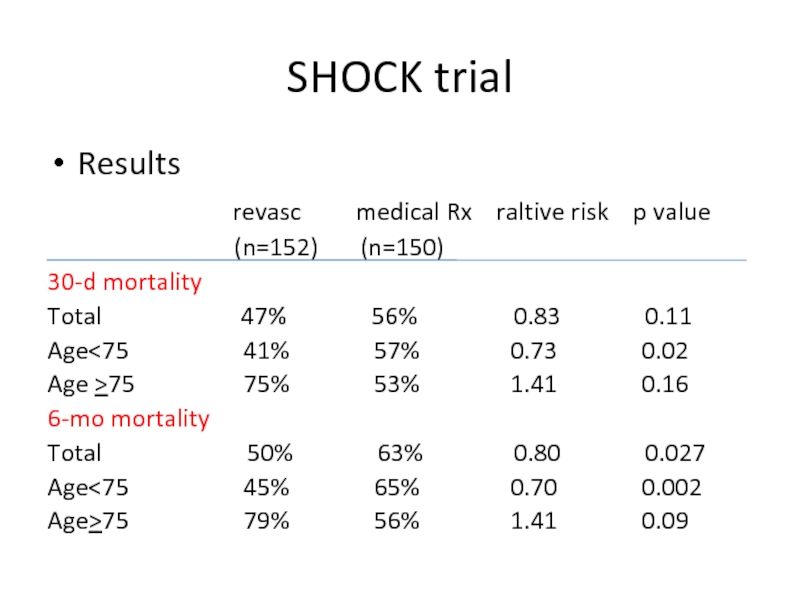
Слайд 47SHOCK trial
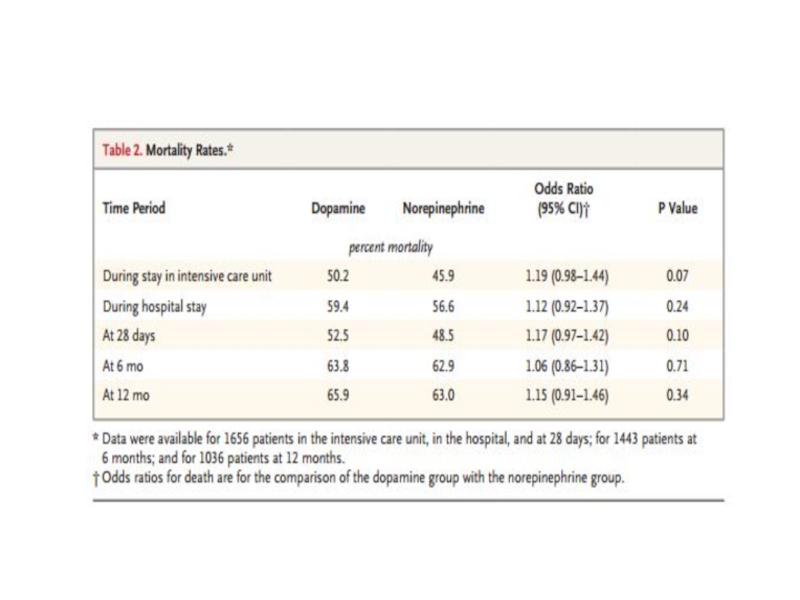
Results
(n=152) (n=150)
30-d mortality
Total 47% 56% 0.83 0.11
Age<75 41% 57% 0.73 0.02
Age >75 75% 53% 1.41 0.16
6-mo mortality
Total 50% 63% 0.80 0.027
Age<75 45% 65% 0.70 0.002
Age>75 79% 56% 1.41 0.09
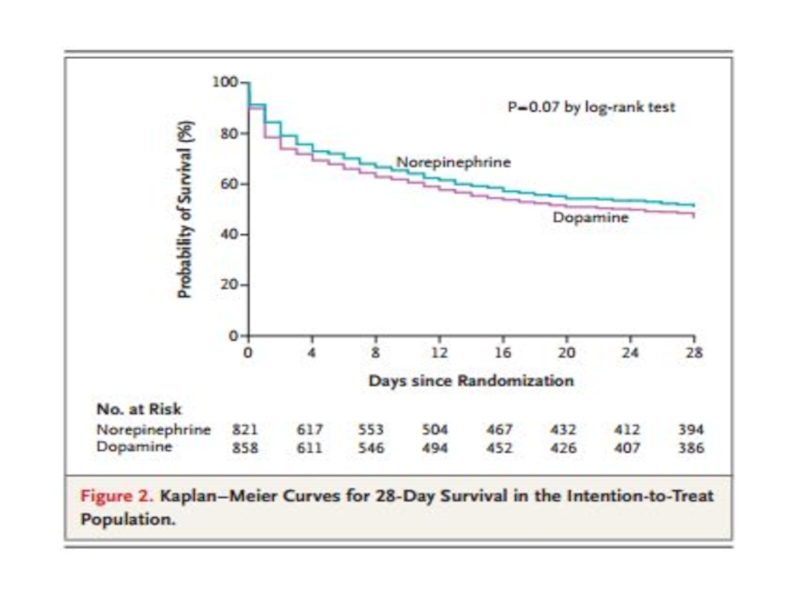
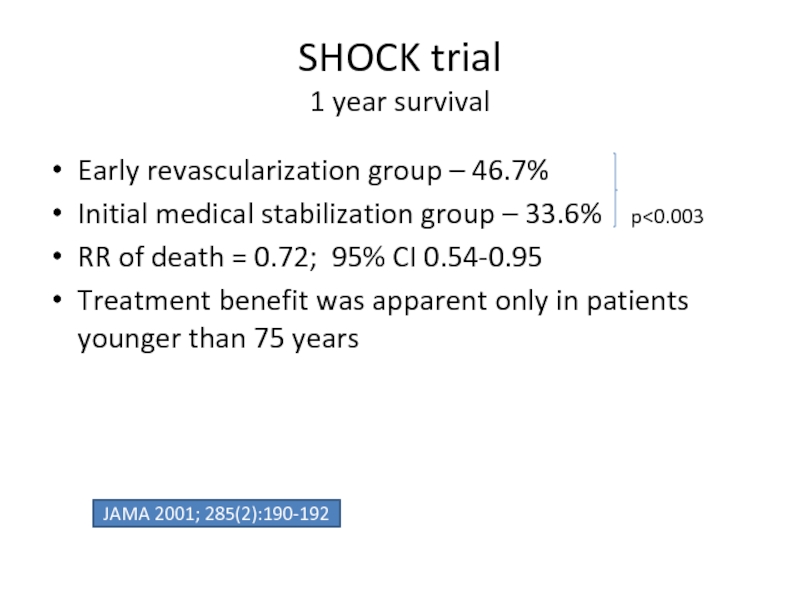
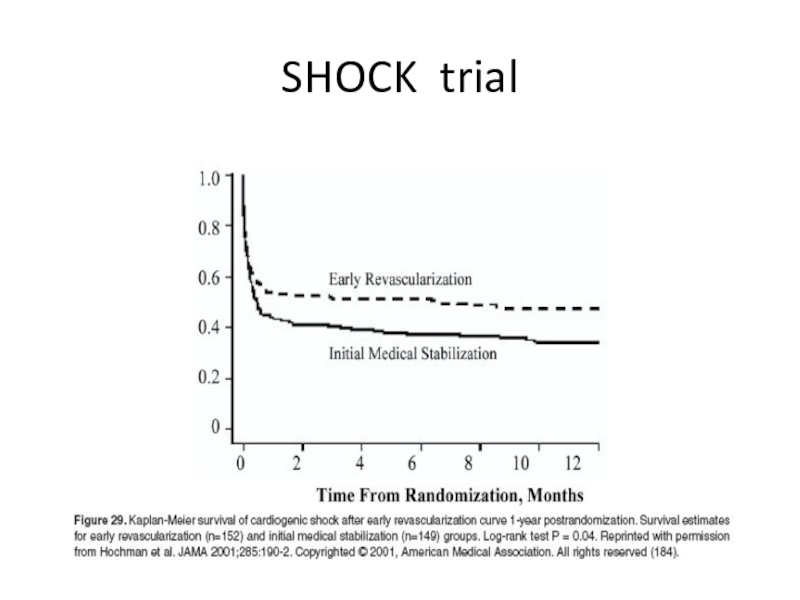
Слайд 49SHOCK trial
1 year survival
Early revascularization group – 46.7%
Initial medical stabilization
RR of death = 0.72; 95% CI 0.54-0.95
Treatment benefit was apparent only in patients younger than 75 years
JAMA 2001; 285(2):190-192
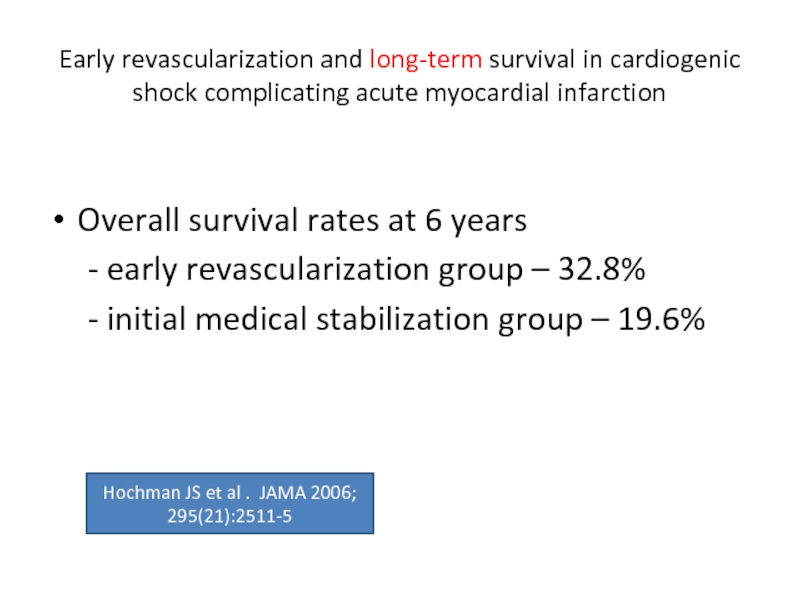
Слайд 51Early revascularization and long-term survival in cardiogenic shock complicating acute myocardial
Overall survival rates at 6 years
- early revascularization group – 32.8%
- initial medical stabilization group – 19.6%
Hochman JS et al . JAMA 2006; 295(21):2511-5