- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Cardiac arrhythmias презентация
Содержание
- 1. Cardiac arrhythmias
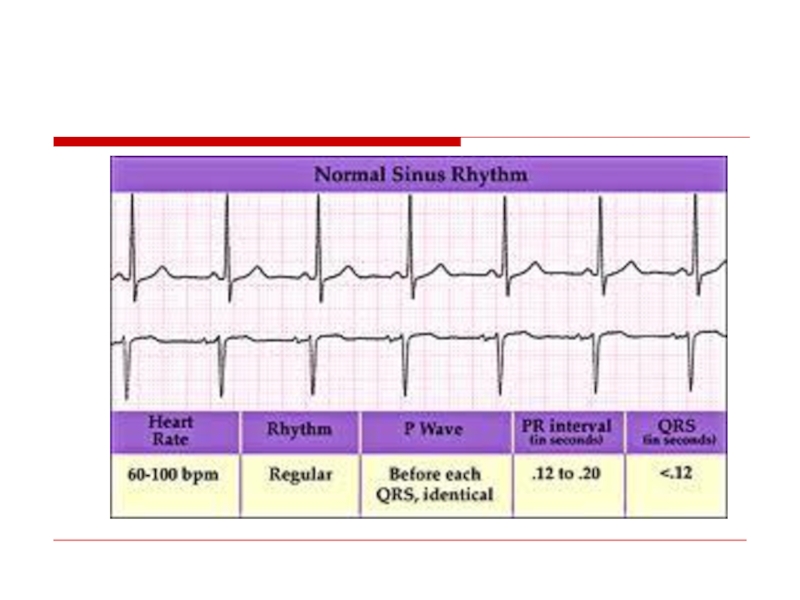
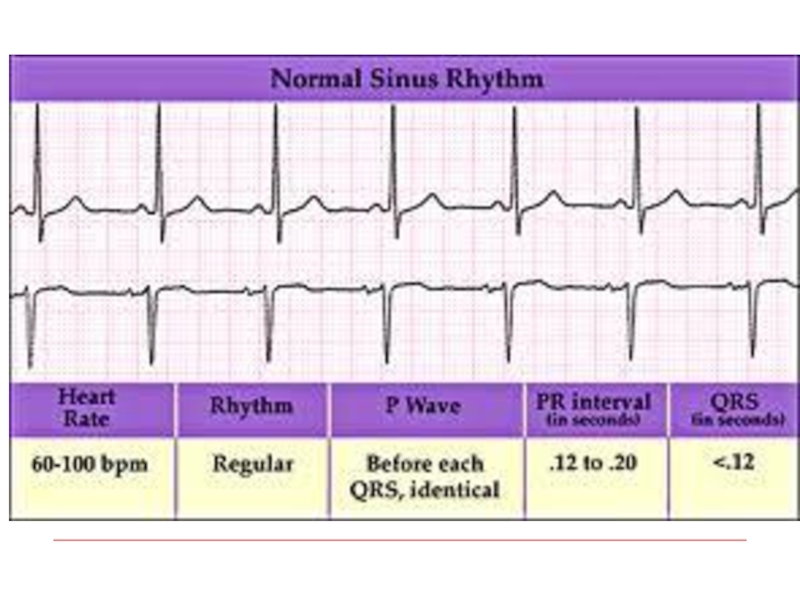
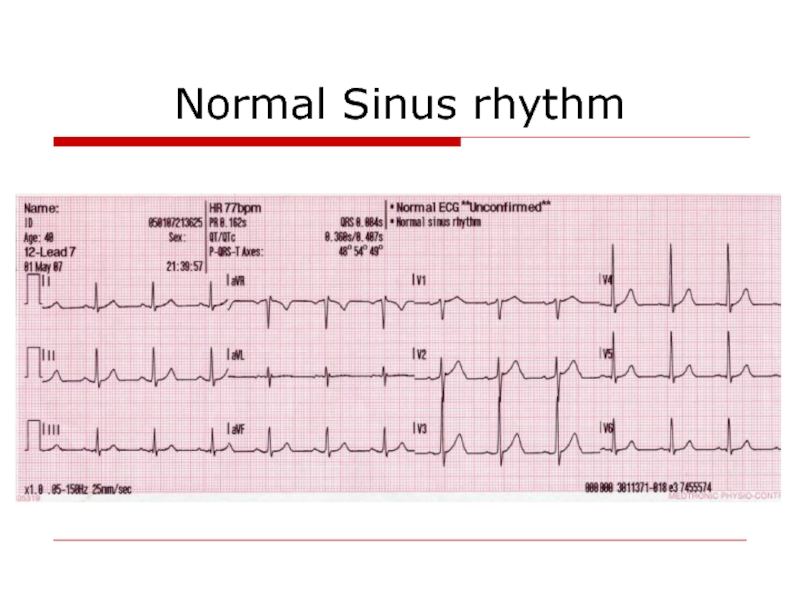
- 9. Normal Sinus rhythm
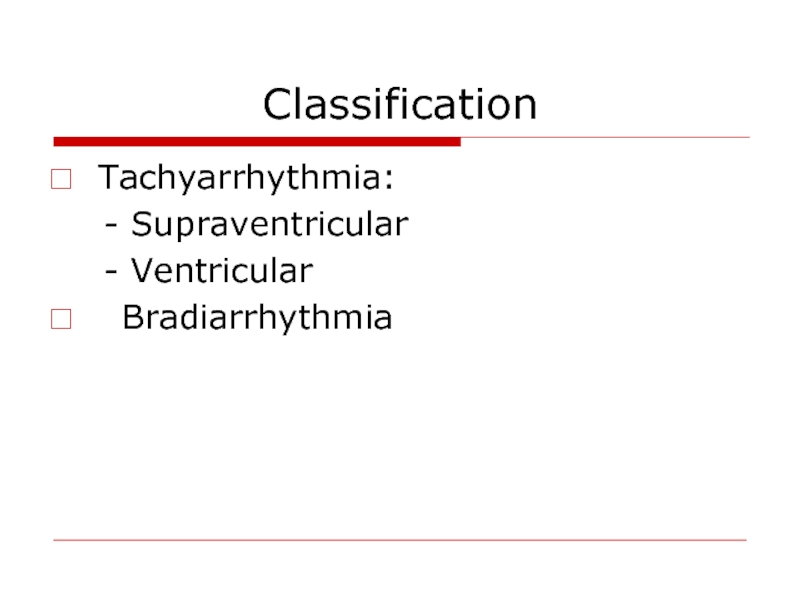
- 10. Classification Tachyarrhythmia: - Supraventricular
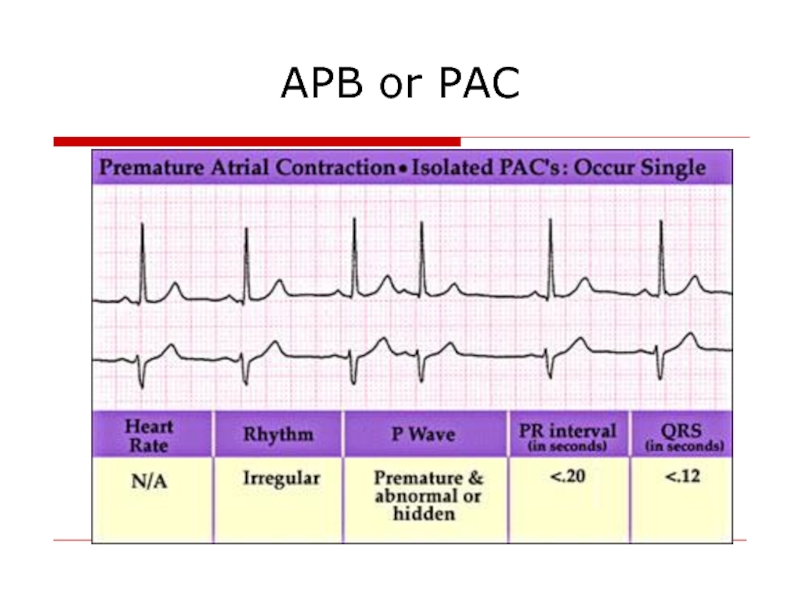
- 11. APB or PAC
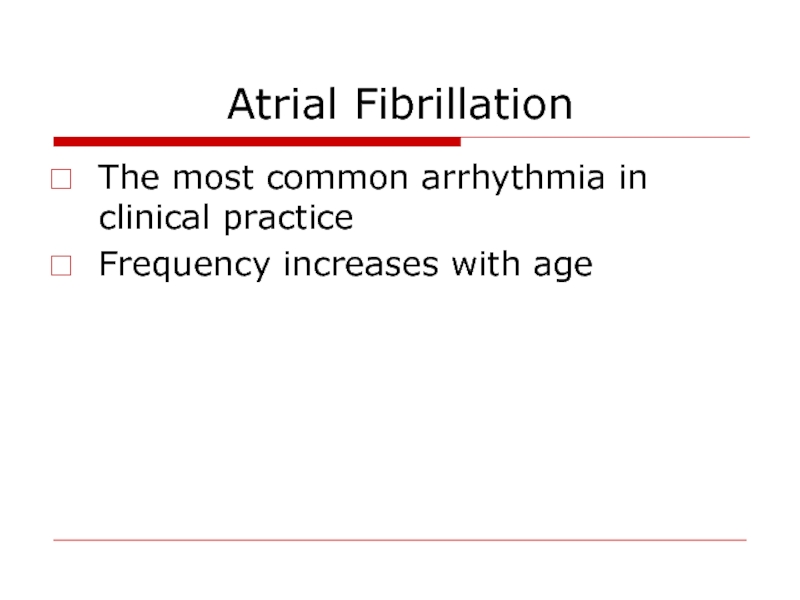
- 12. Atrial Fibrillation The most common arrhythmia in clinical practice Frequency increases with age
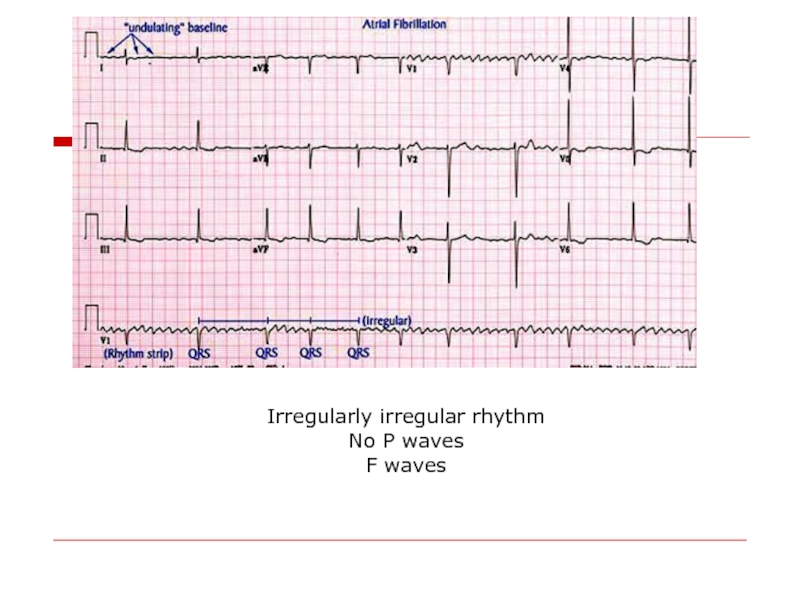
- 13. Irregularly irregular rhythm No P waves F waves
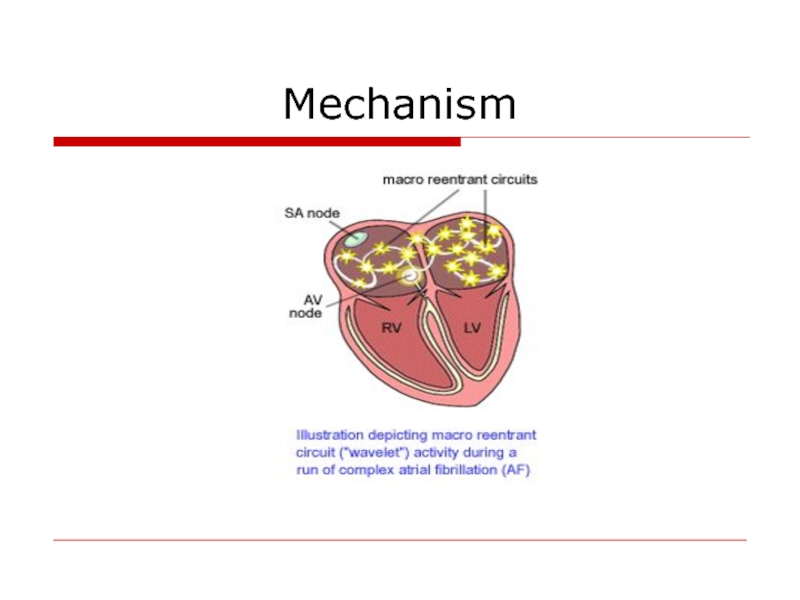
- 14. Mechanism
- 15. Most common causes Valvular heart disease: (MS,MR)
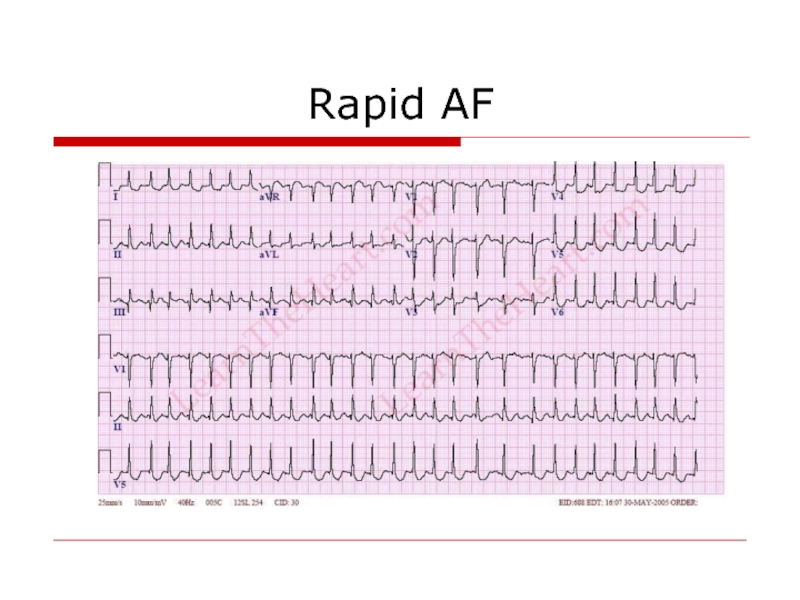
- 16. Rapid AF
- 17. Consequences of Atrial Fibrillation Hemodynamic loss of
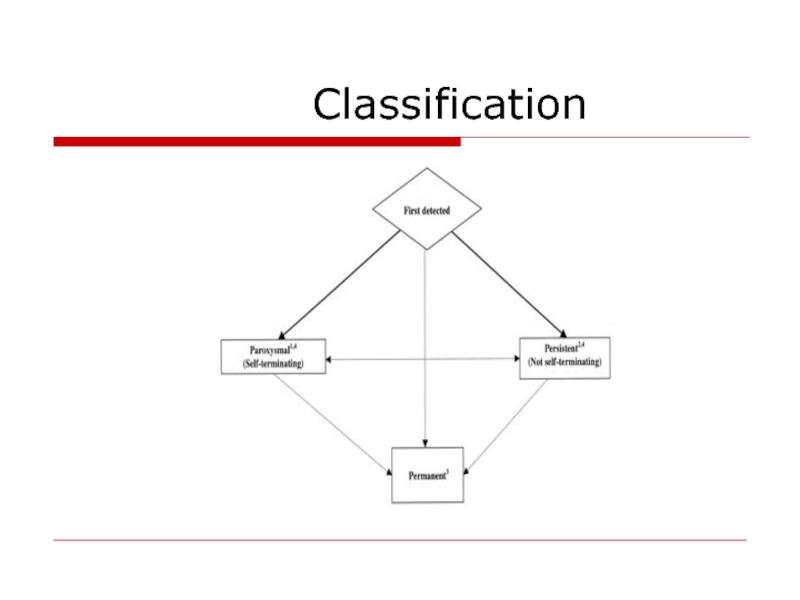
- 18. Classification
- 19. Treatment options 1. Rhythm control – restoration
- 20. Williams Classification of Antyarrhythmic Drugs Class I-
- 21. IB : Do not reduce
- 22. Class II – beta blockers Class
- 23. Cardioversion Pharmacological Propafenon Amiodaron Flecainide
- 24. Cardioversion Electric In acute
- 25. Predictors of successful cardioverson Short AF duration
- 26. Maintenance of sinus rhythm Propafenon Amiodaron Dronedaron Sotalol Flecainide
- 29. Rate Control Acute setting – IV
- 31. – Severe symptoms due to AF –
- 32. Rate Control as First-Line Choice Consider
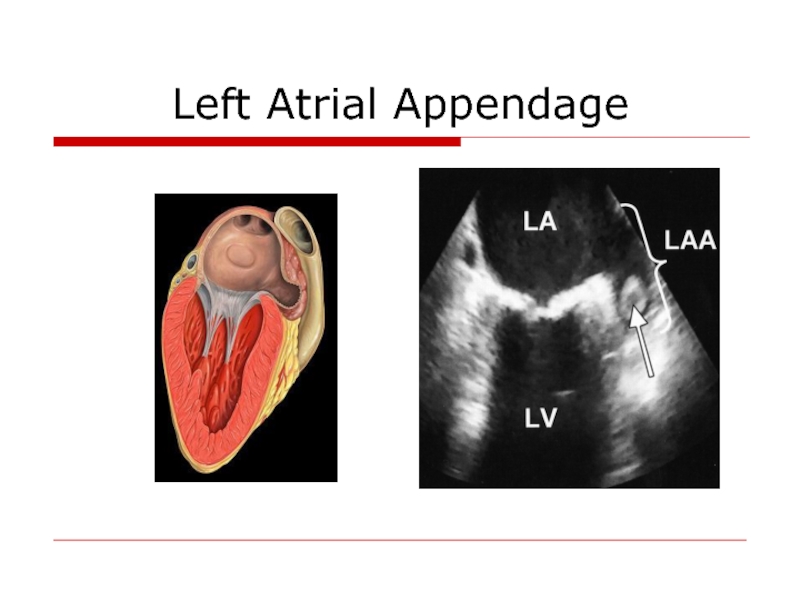
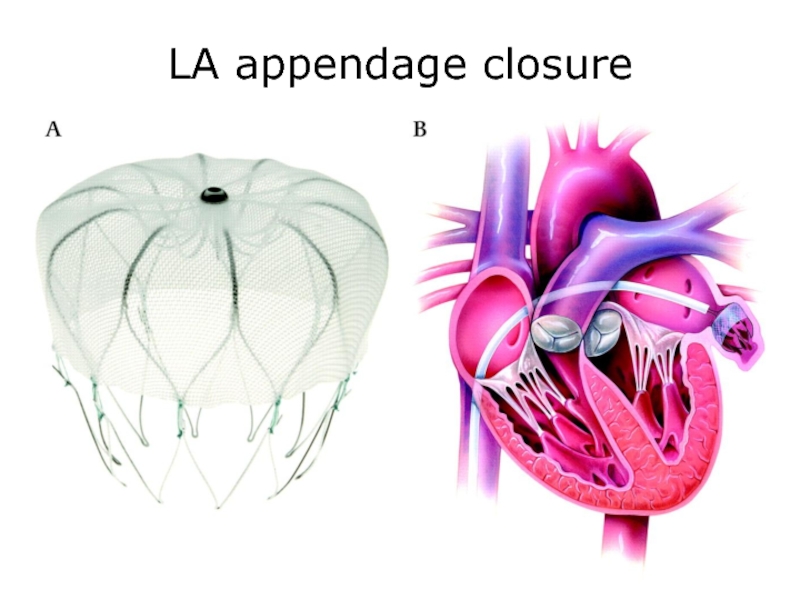
- 33. Left Atrial Appendage
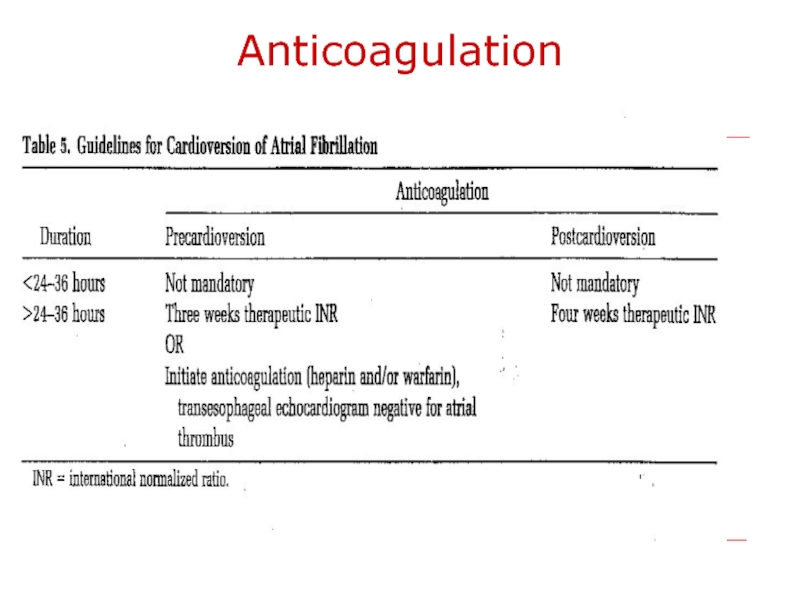
- 34. Anticoagulation
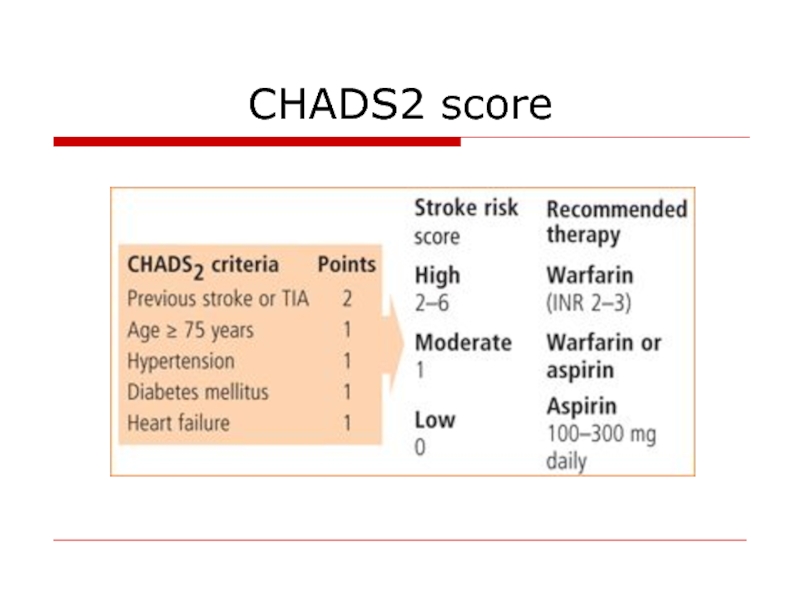
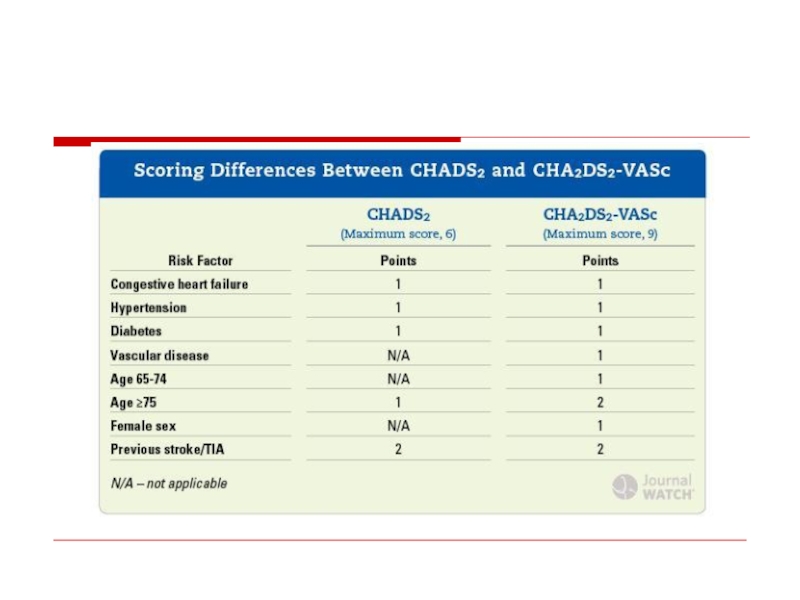
- 35. CHADS2 score
- 37. Novel Oral Anticoagulants Dabigatran (Pradaxa)- direct oral
- 38. Invasive AF treatment
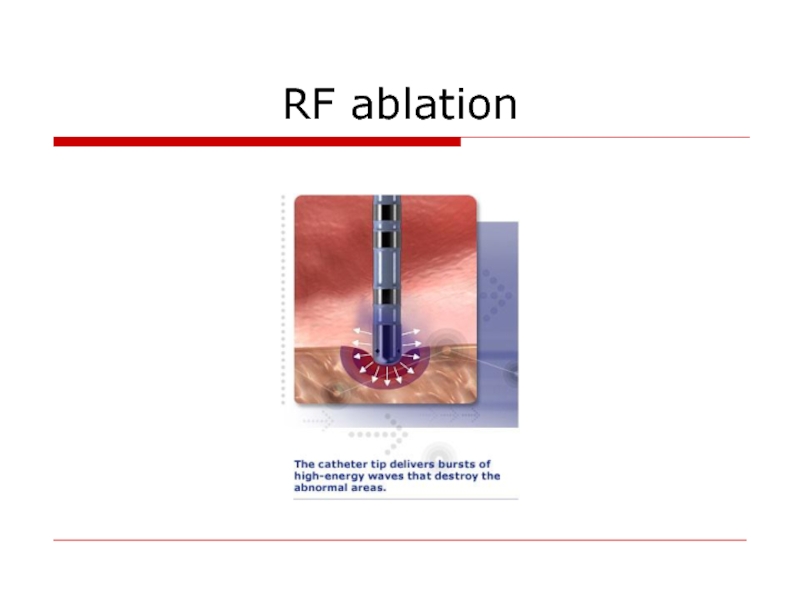
- 39. RF ablation
- 40. Invasive AF management Rate control
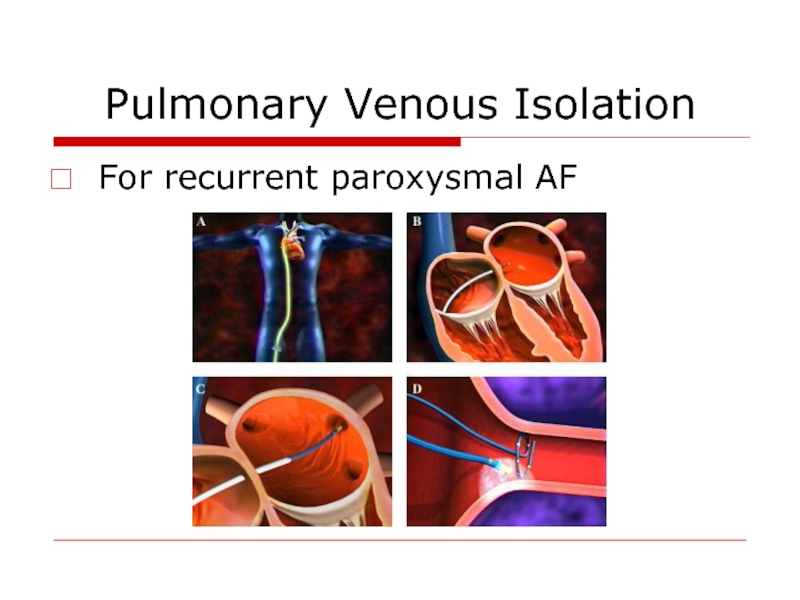
- 41. Pulmonary Venous Isolation For recurrent paroxysmal AF
- 42. Cox-Maze Procedure Left Atrial Isolation (1980) Corridor
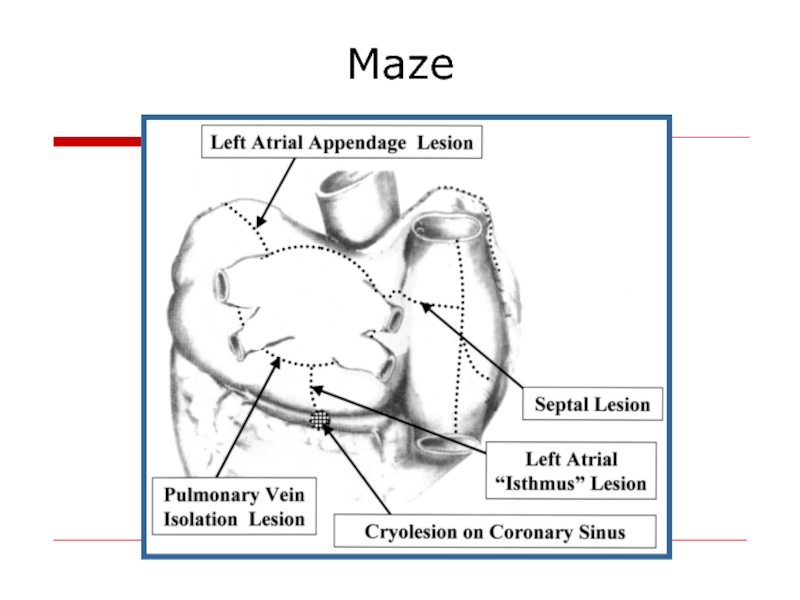
- 43. Maze
- 44. LA appendage closure
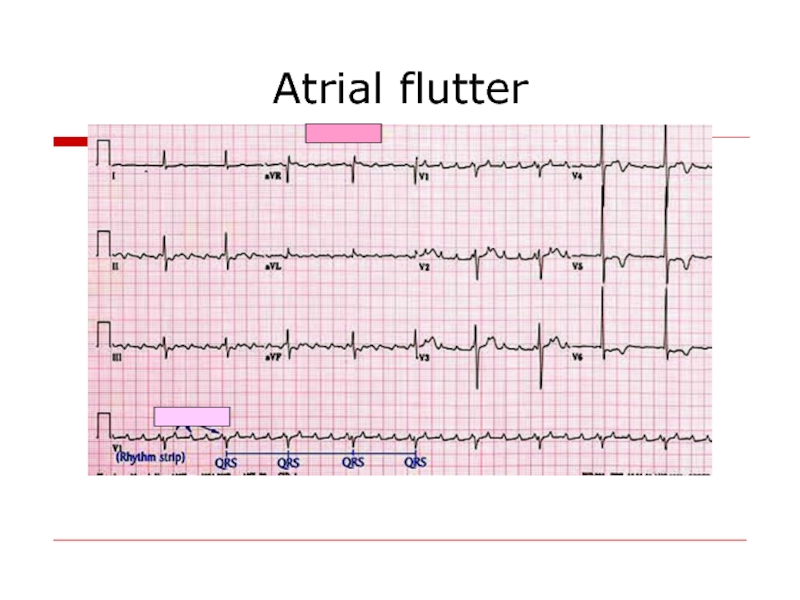
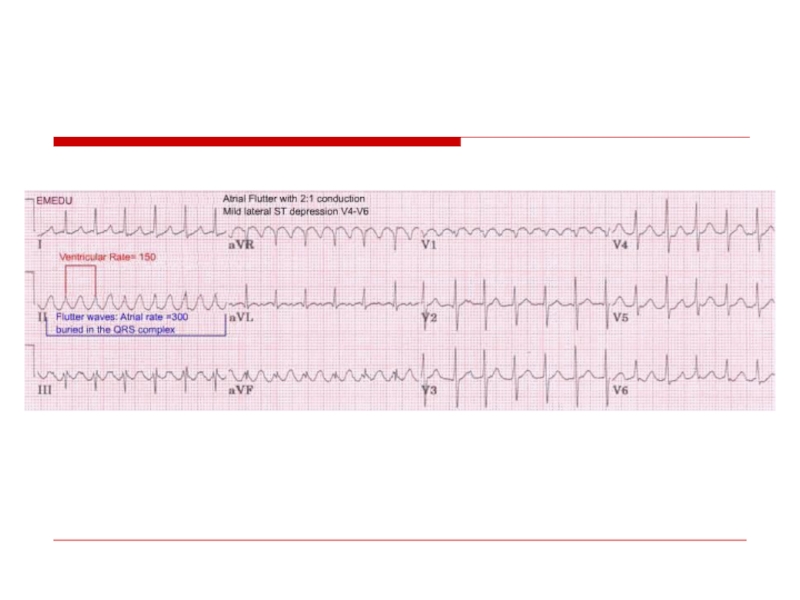
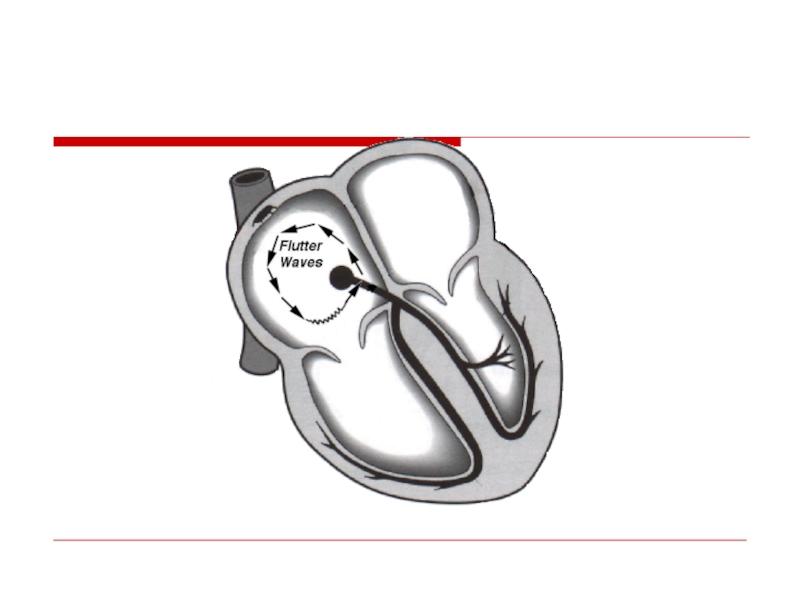
- 45. Atrial flutter
- 48. Management Electric Cardioversion Slowing Ventricular rate
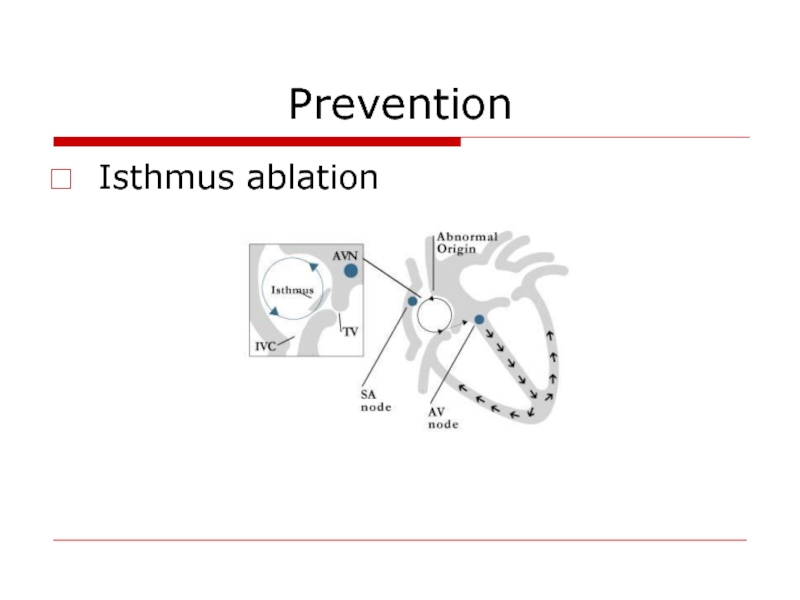
- 49. Prevention Isthmus ablation
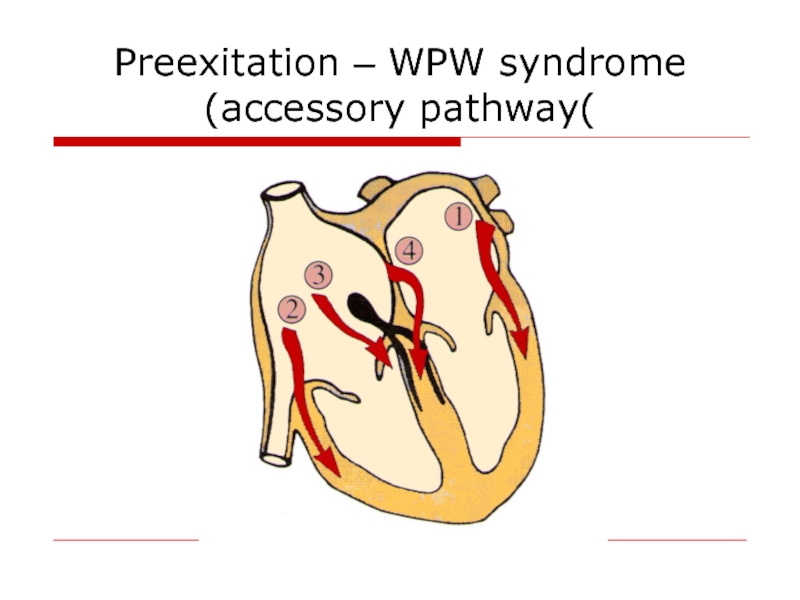
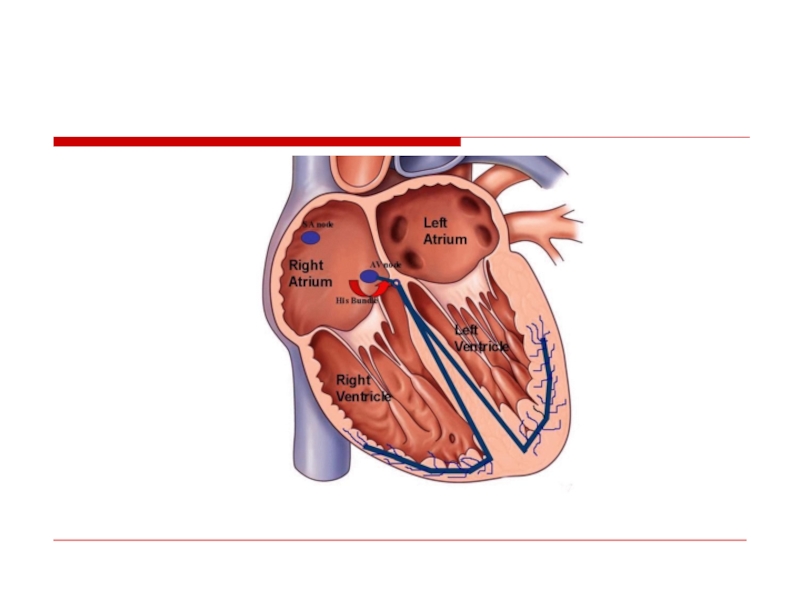
- 50. Preexitation – WPW syndrome (accessory pathway(
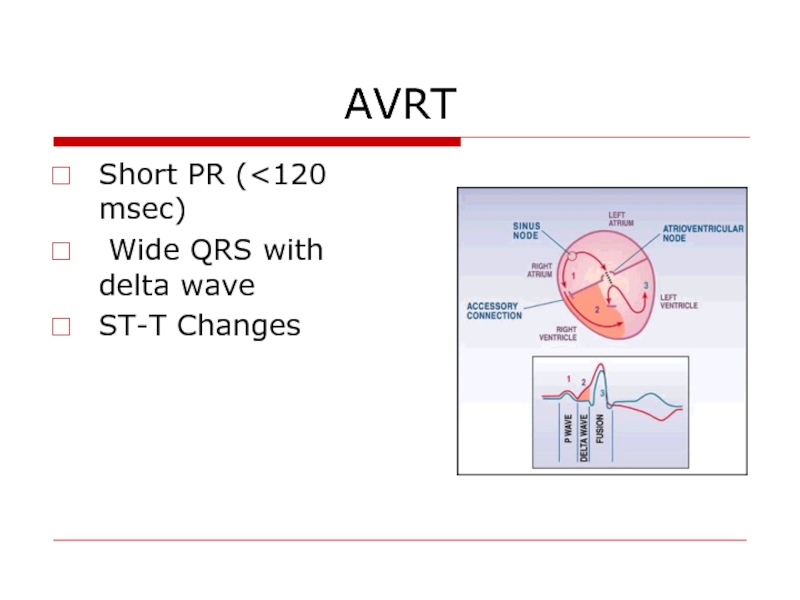
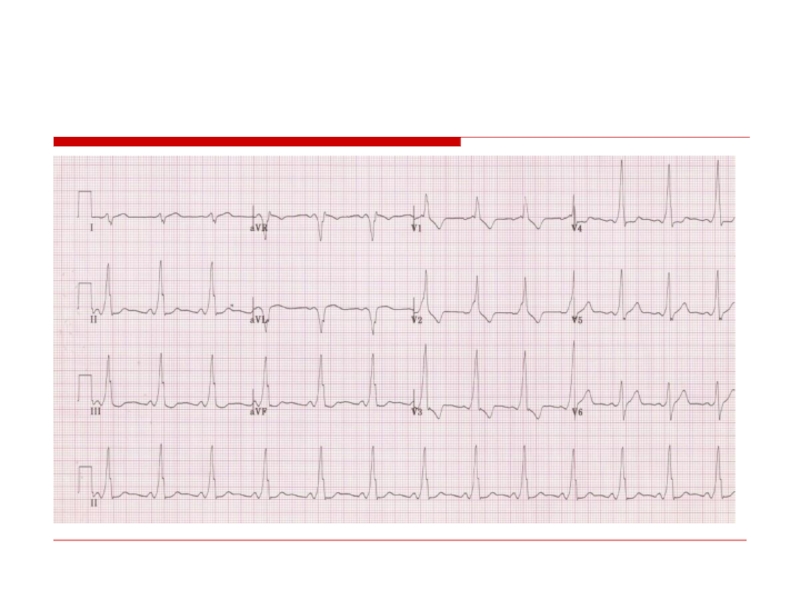
- 51. AVRT Short PR (
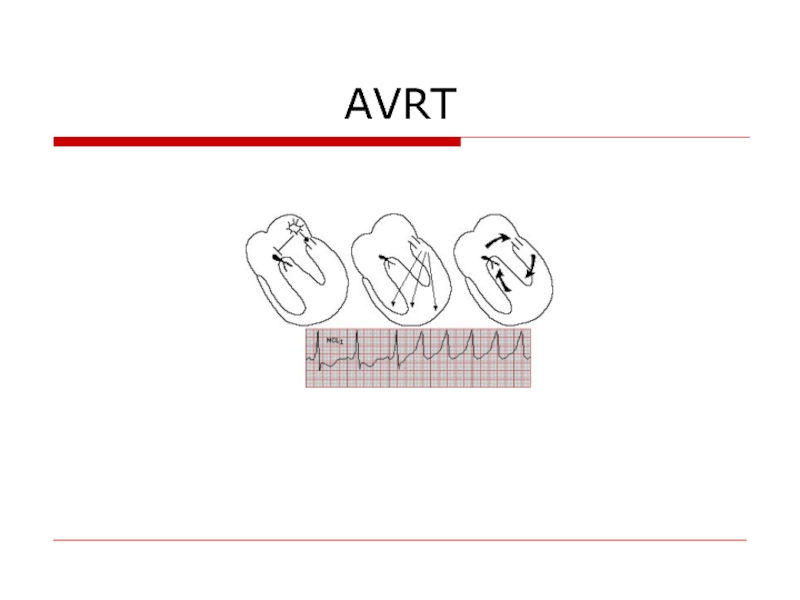
- 53. AVRT
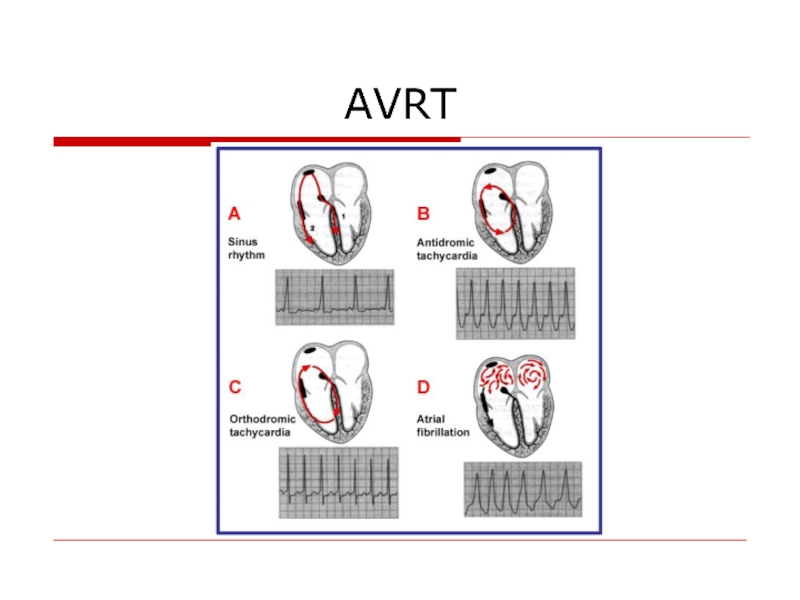
- 54. AVRT
- 55. Treatment Acute treatment: Wide complex
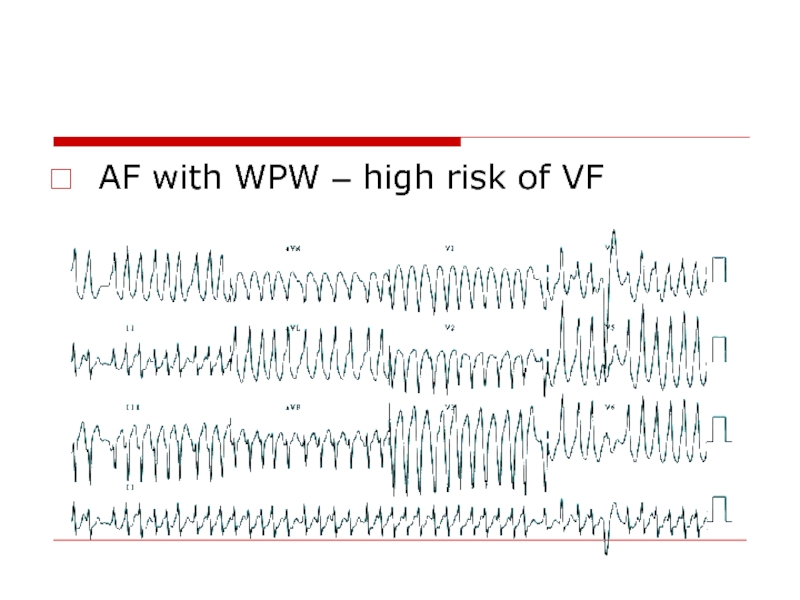
- 56. AF with WPW – high risk of VF
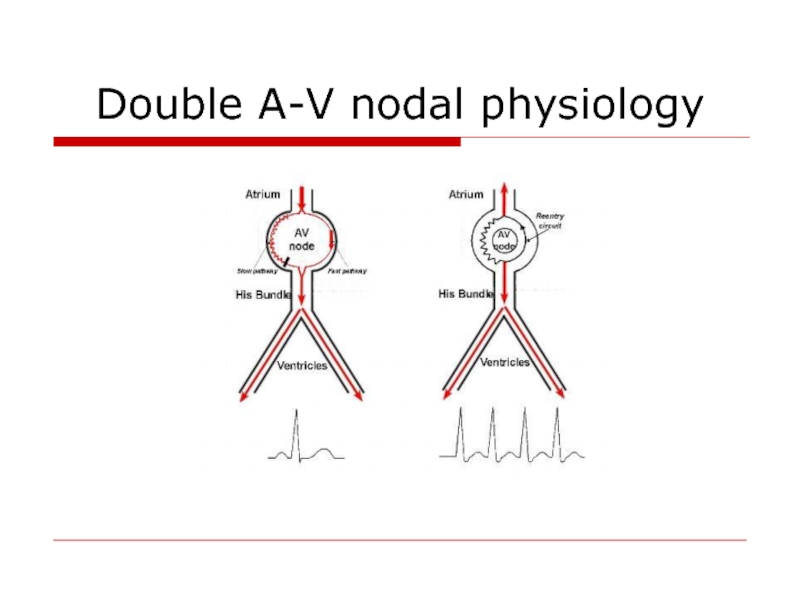
- 57. Double A-V nodal physiology
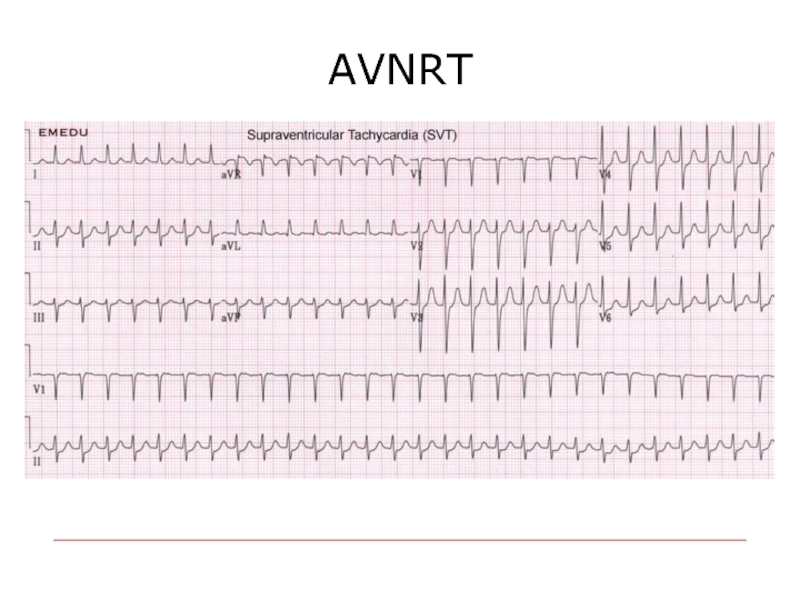
- 59. AVNRT
- 60. Management of narrow complex SVT If unstable
- 61. Preventive treatment Drugs EPS
- 62. Ventricular Arrhythmias
- 63. Ventricular premature beats Ventricular premature complexes
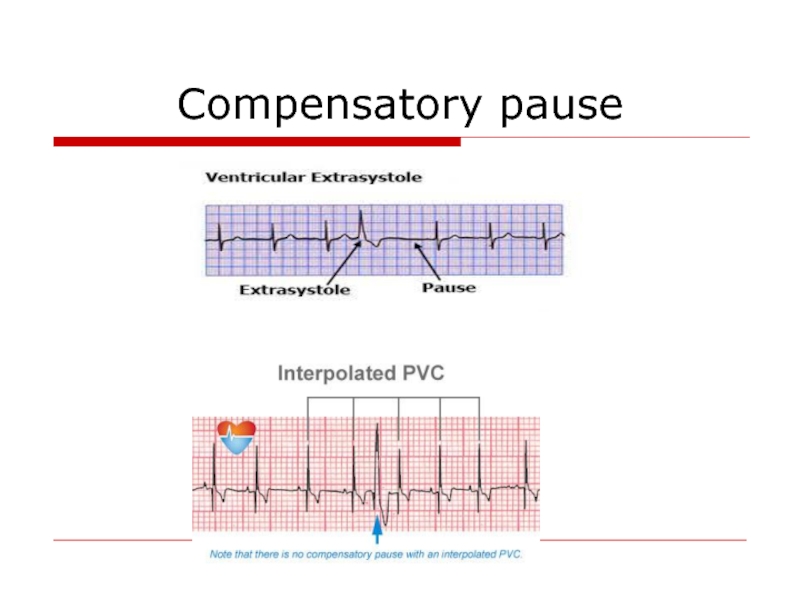
- 64. Compensatory pause
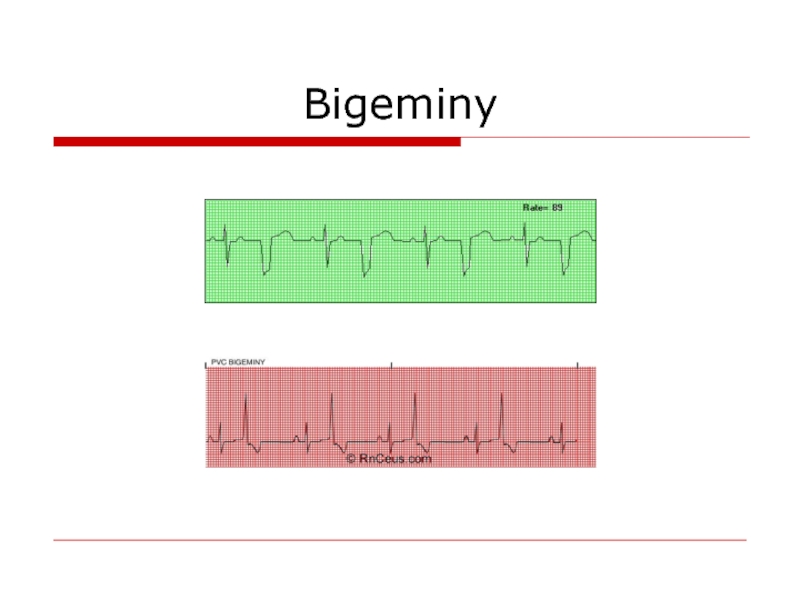
- 65. Bigeminy
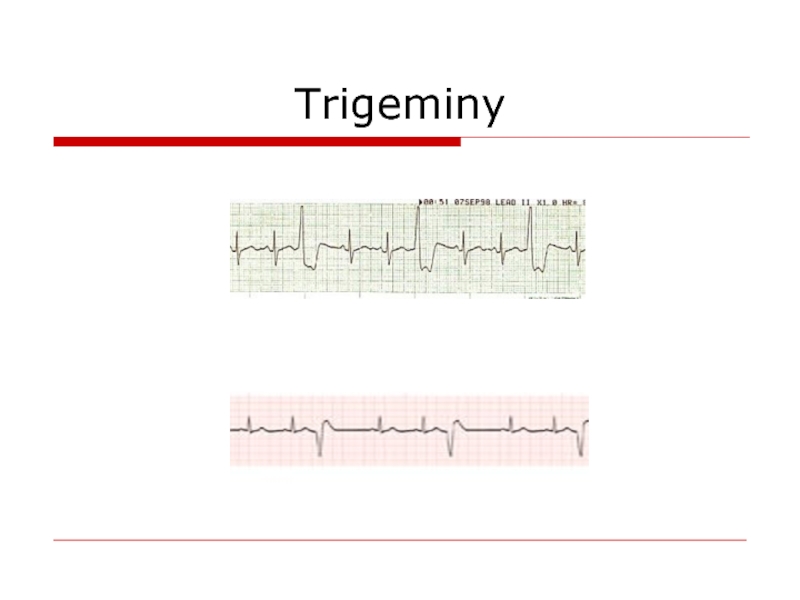
- 66. Trigeminy
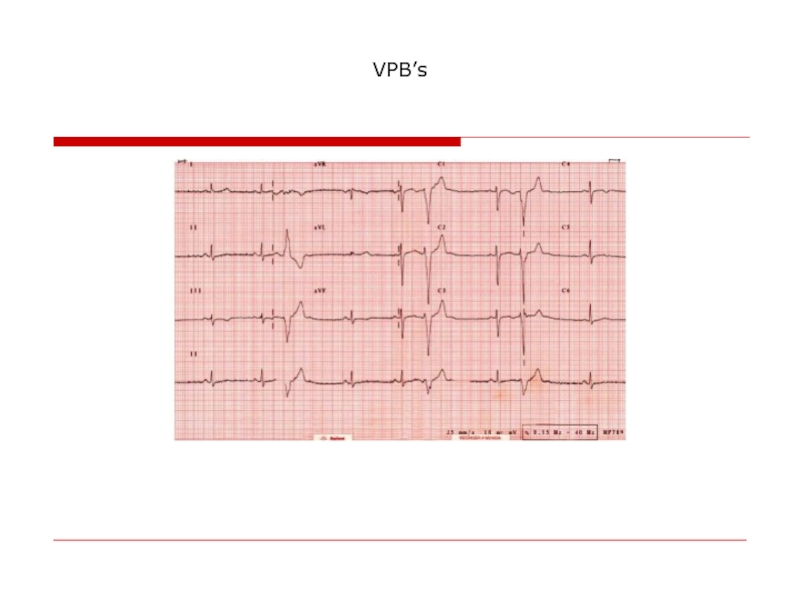
- 67. VPB’s
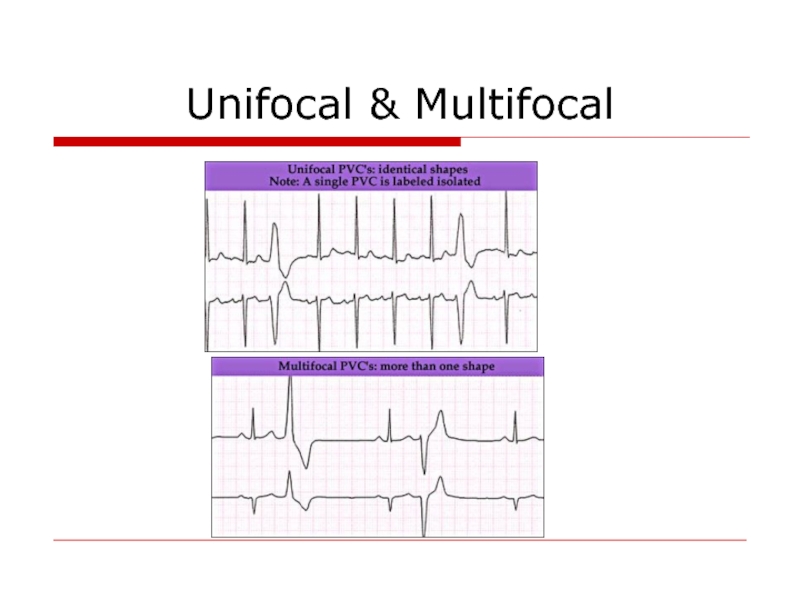
- 68. Unifocal & Multifocal
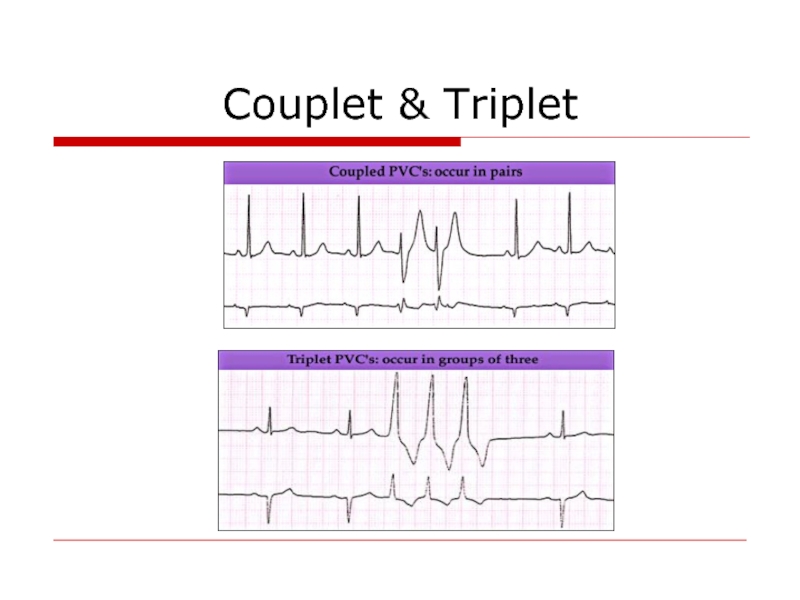
- 69. Couplet & Triplet
- 70. Causes LV false tendons, infection
- 71. Complex Ventricular Arrhythmia Nonsustained
- 72. Definition: Ventricular tachycardia consist of at least
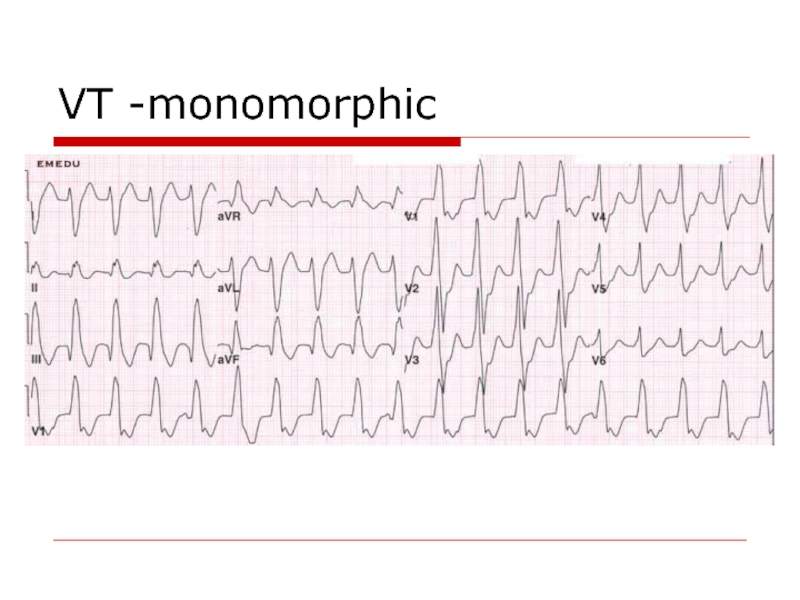
- 73. VT -monomorphic
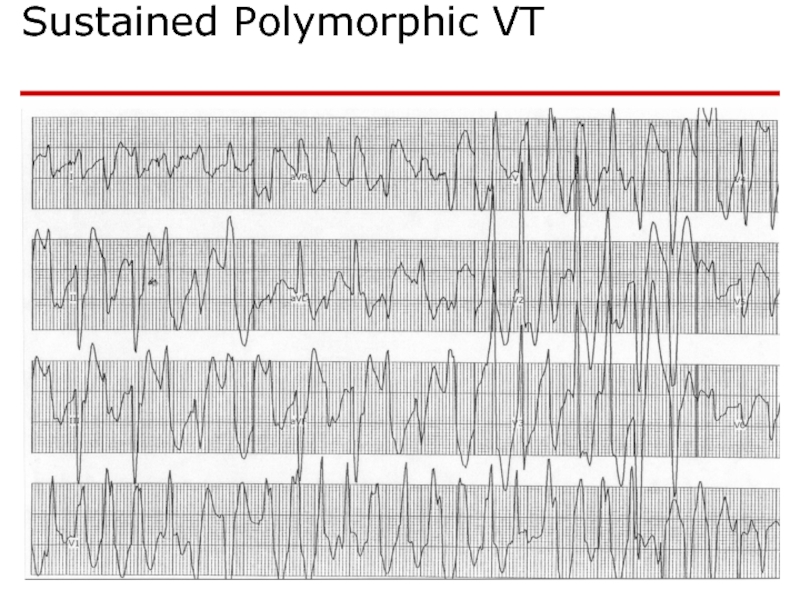
- 74. Sustained Polymorphic VT
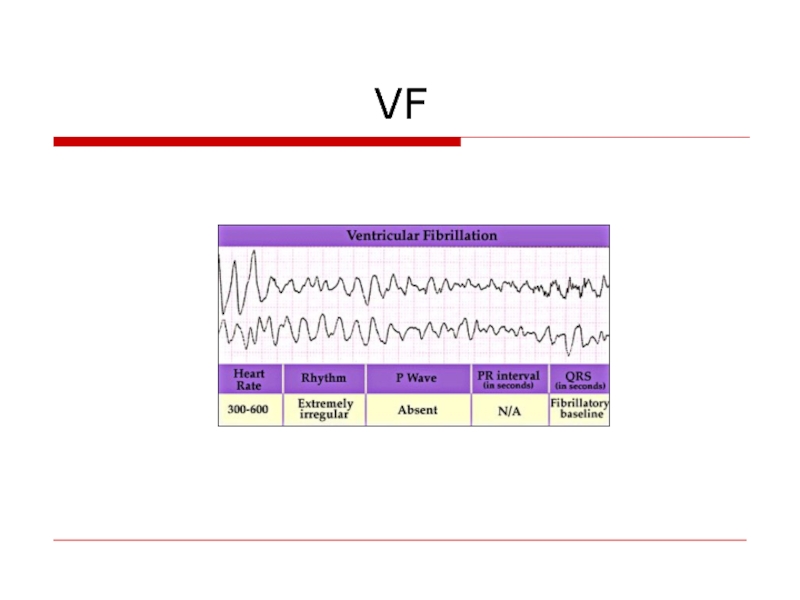
- 75. VF
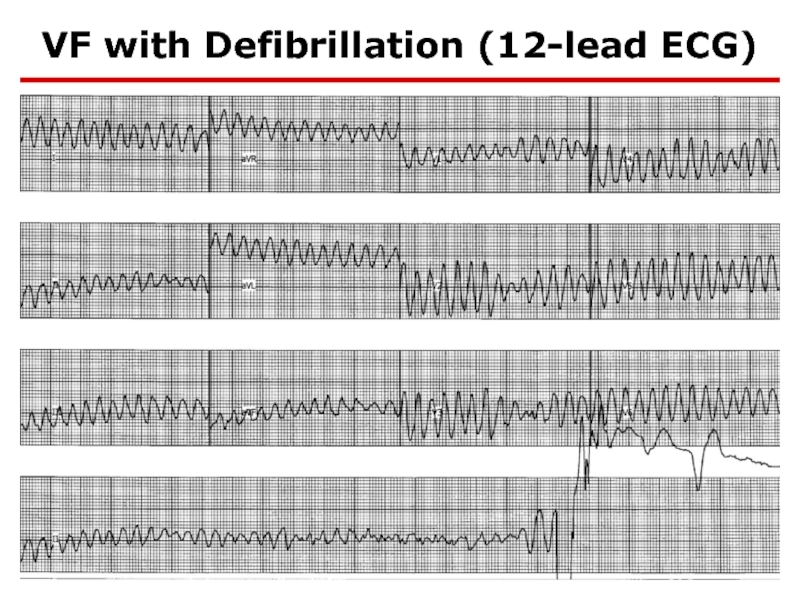
- 76. VF with Defibrillation (12-lead ECG)
- 77. Causes Chronic coronary heart disease
- 78. Ventricular fibrillation - 62.4% Bradyarrhythmias (including advanced
- 79. VA management Acute Chronic (secondary prevention)
- 80. Sustained VT Hemodynamically stable: -
- 81. Polymorphic VT Polymorphic VT with long QT
- 83. Chronic Management (secondary prevention) Evaluation
- 84. Treatment of the underlying disease Revascularisation Valve surgery CHD repair
- 85. ♥ Electrolytes: Mg & K
- 86. Antiarrhytmic drugs Antiarrhythmic drugs (except for BB)
- 87. Invasive treatment AICD EPS with ablation Surgical ablation
- 88. AICD for primary prevention of SCD 1.Post
- 89. Long QT syndrome Congenital (family) Acquired:
- 91. Long QT syndrome treatment Acute 1.Remove
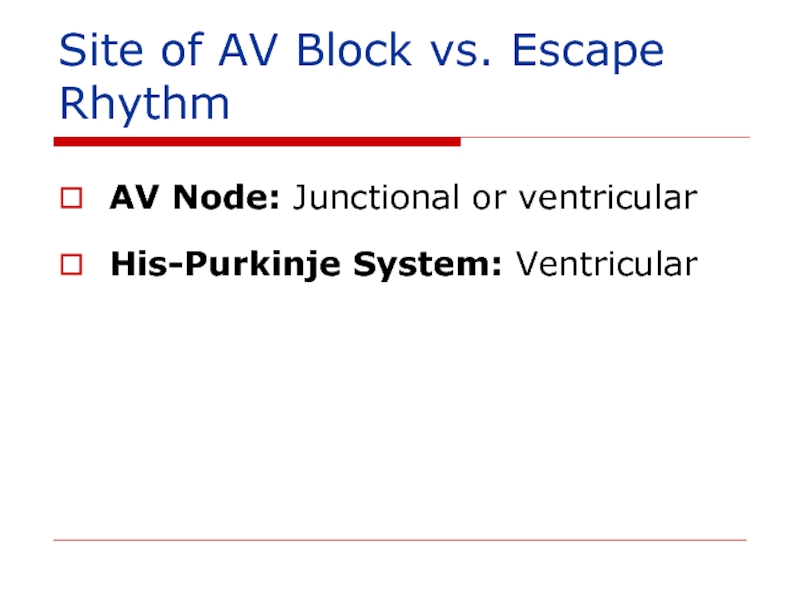
- 92. Long QT syndrome treatment Chronic – for
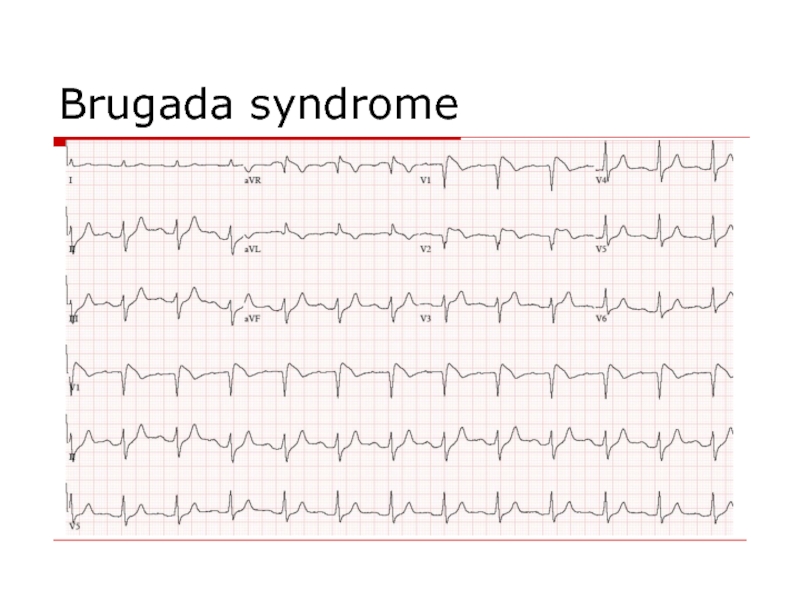
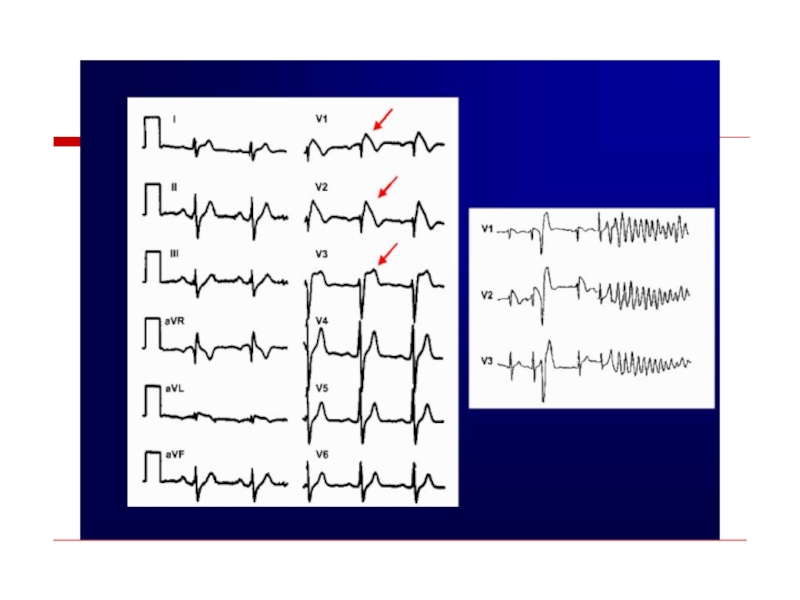
- 94. Brugada syndrome
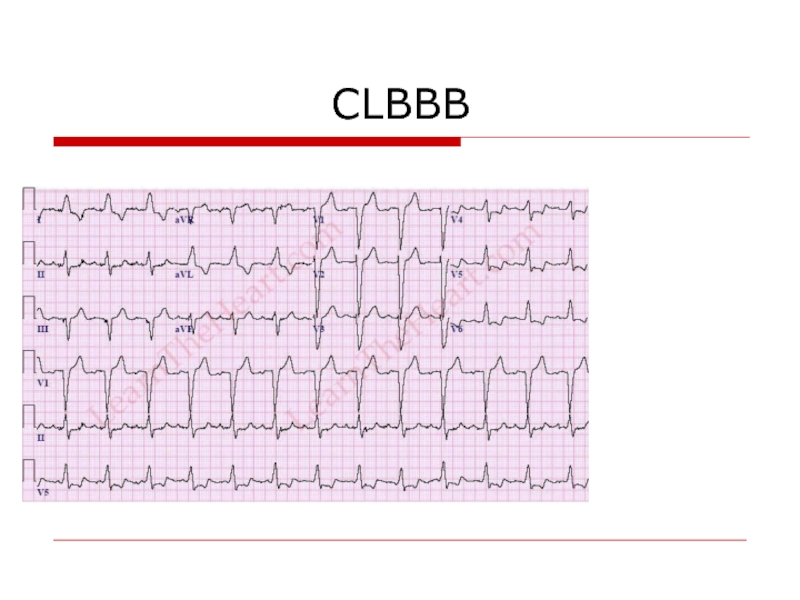
- 97. CLBBB
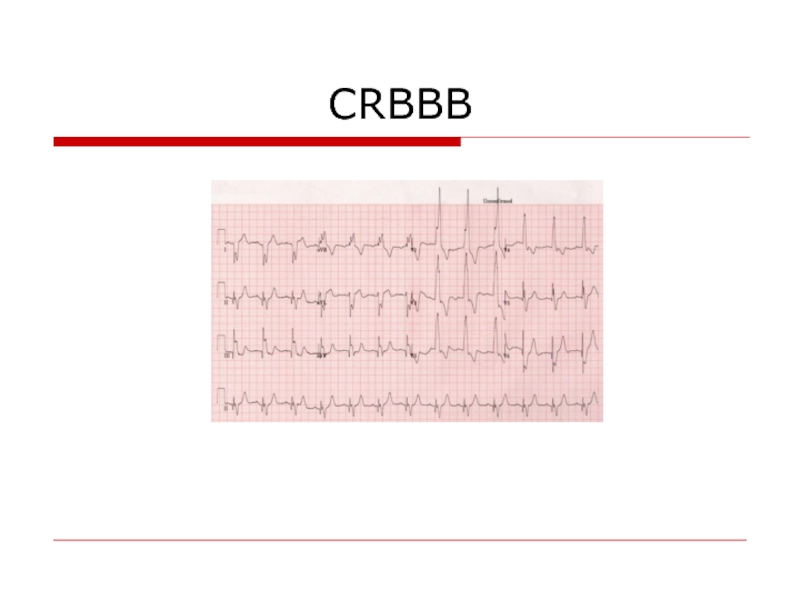
- 98. CRBBB
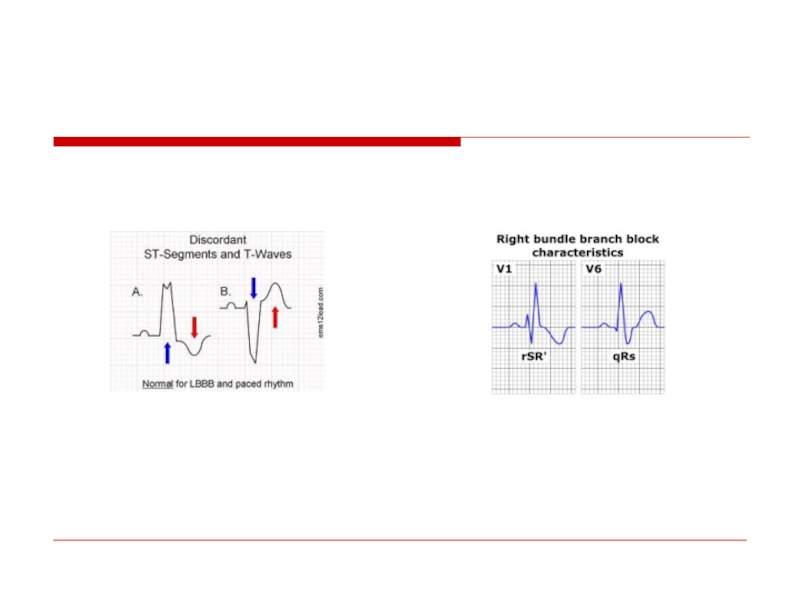
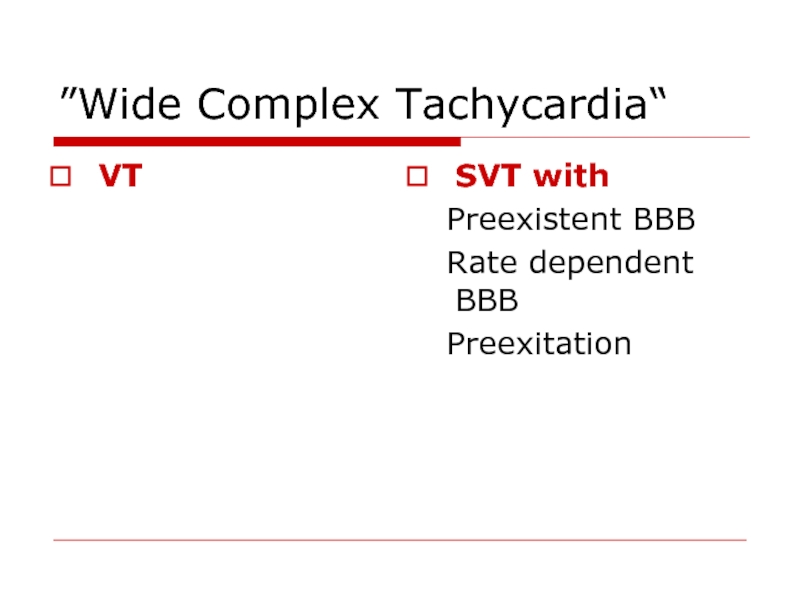
- 100. “Wide Complex Tachycardia” VT SVT with
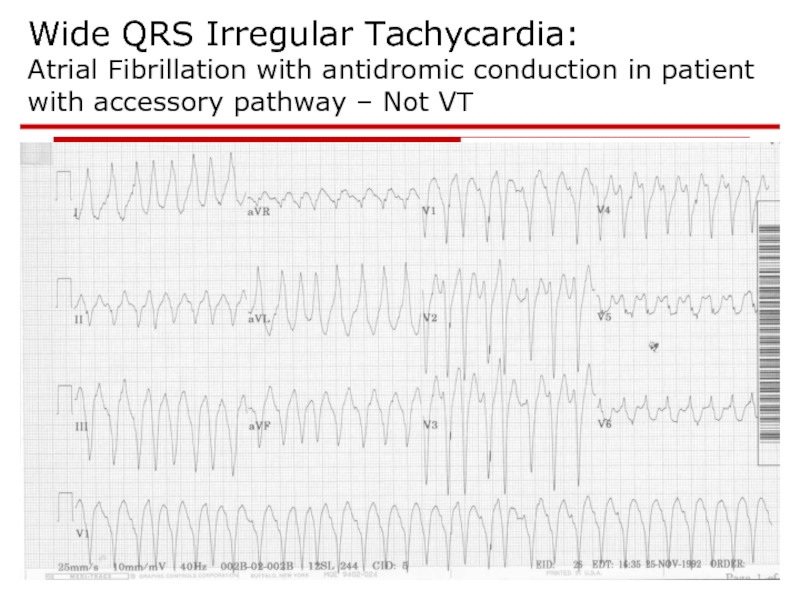
- 102. Wide QRS Irregular Tachycardia: Atrial Fibrillation with
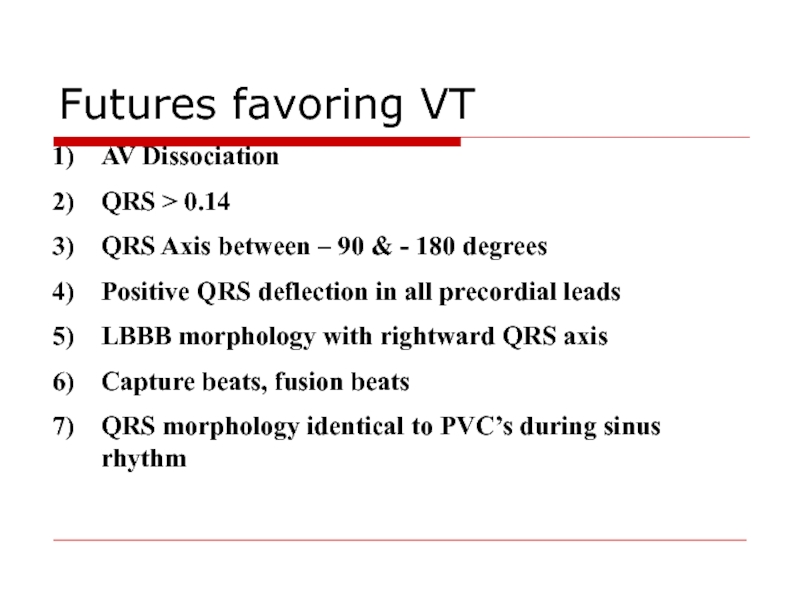
- 103. AV Dissociation QRS > 0.14 QRS Axis
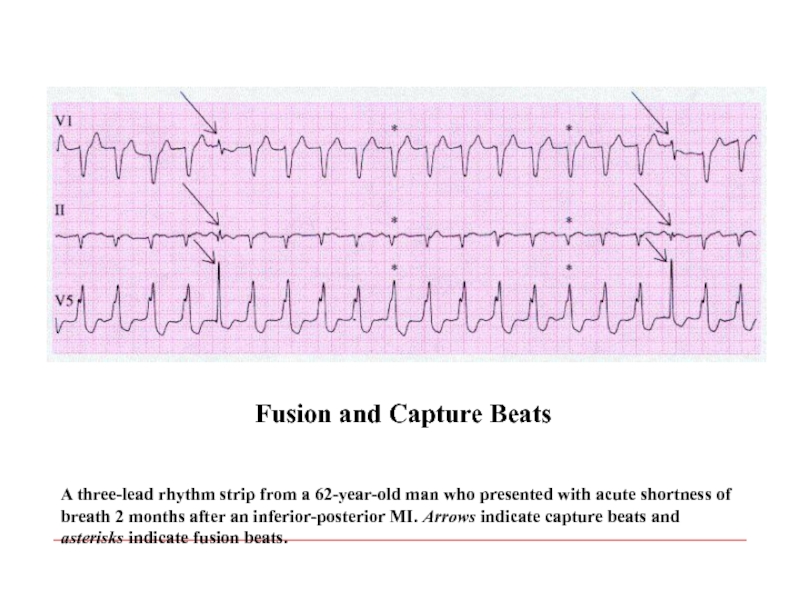
- 104. A three-lead rhythm strip from a 62-year-old
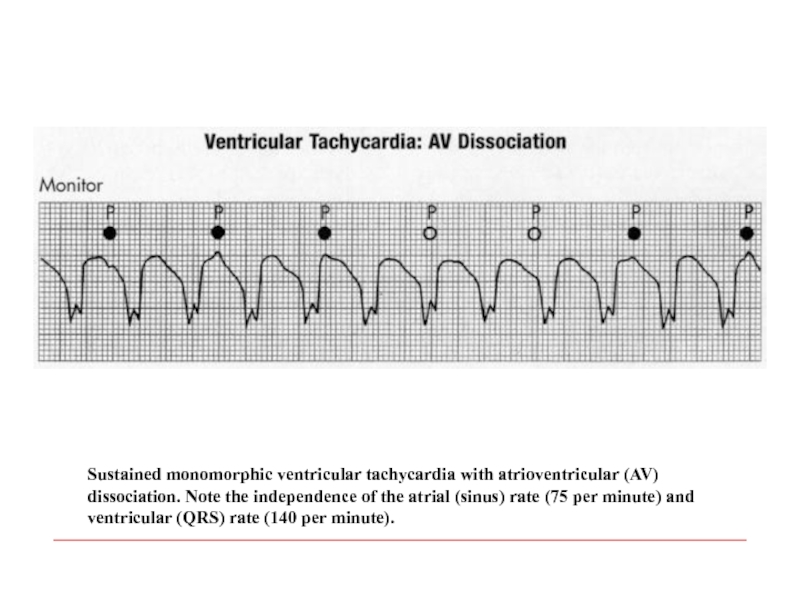
- 105. Sustained monomorphic ventricular tachycardia with atrioventricular (AV)
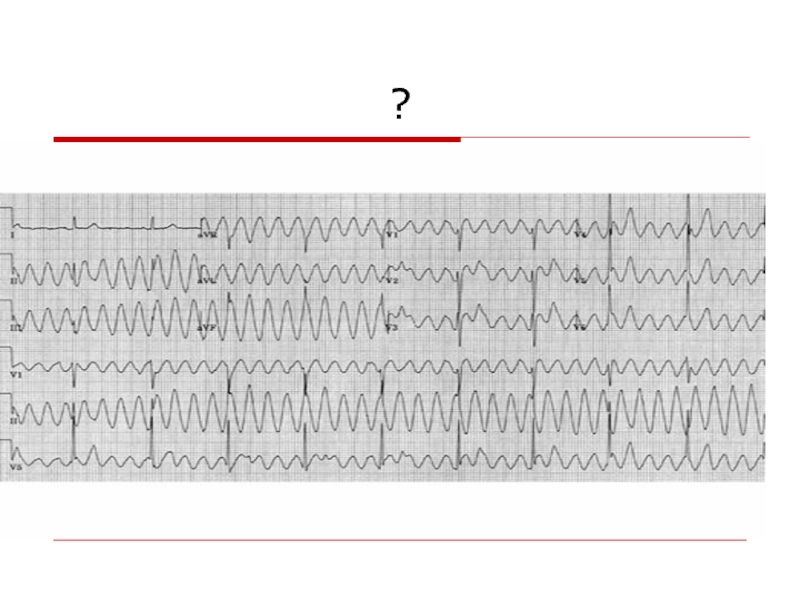
- 106. ?
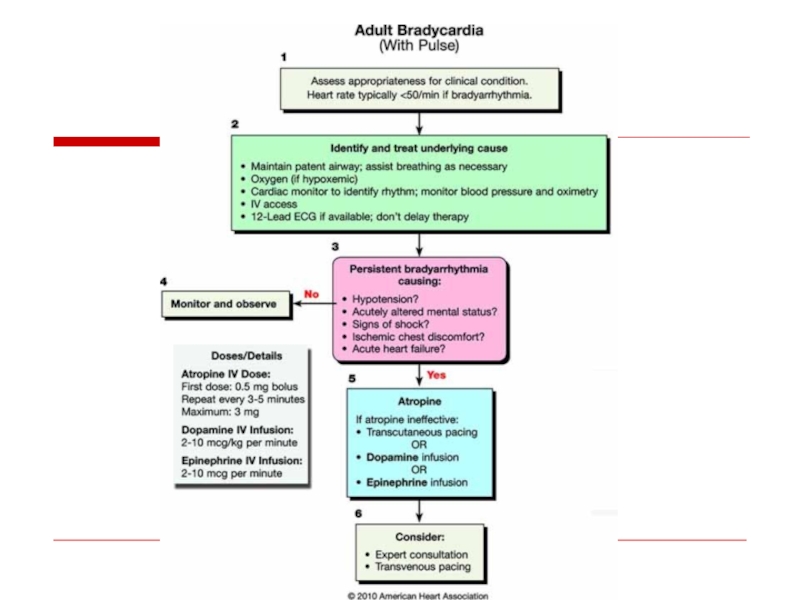
- 108. Atrioventricular Conduction Disturbances and Bradyarrhythmias
- 109. Sites of Disturbances in Impulse Formation
- 111. AV Block
- 112. AV Block - Definitions First Degree:
- 113. First Degree
- 115. Second Degree AV Block - Type I
- 116. II Block P P
- 117. II
- 118. II P P P P P P
- 119. Second Degree AV Block - Type II
- 120. II P P P P P P
- 121. EKG/Clinical Clues* to site of 2:1 Second
- 122. II P P P P P P
- 123. Site of AV Block vs. Escape Rhythm AV Node: Junctional or ventricular His-Purkinje System: Ventricular
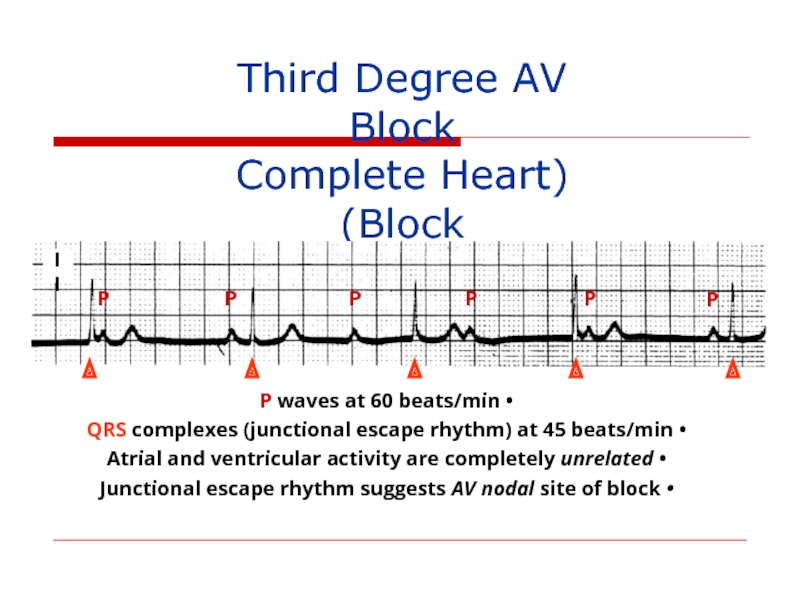
- 125. Third Degree AV Block (Complete Heart
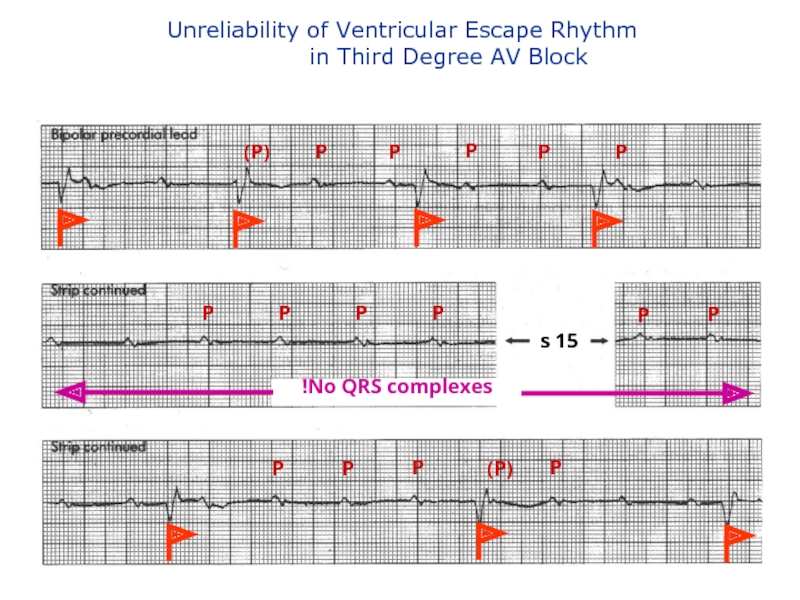
- 126. Unreliability of Ventricular Escape Rhythm
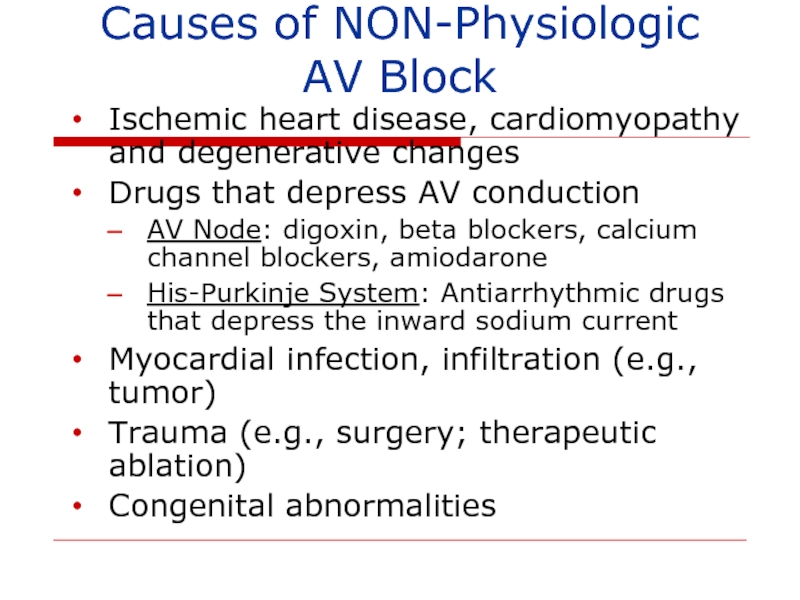
- 129. Causes of NON-Physiologic AV Block Ischemic heart
- 130. Sinus Bradyarrhythmias
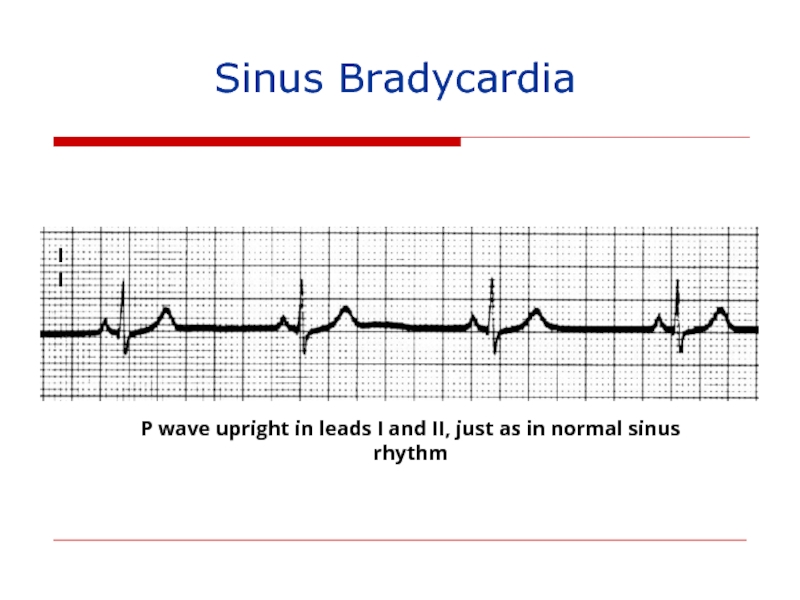
- 131. Sinus Bradycardia II P wave upright in
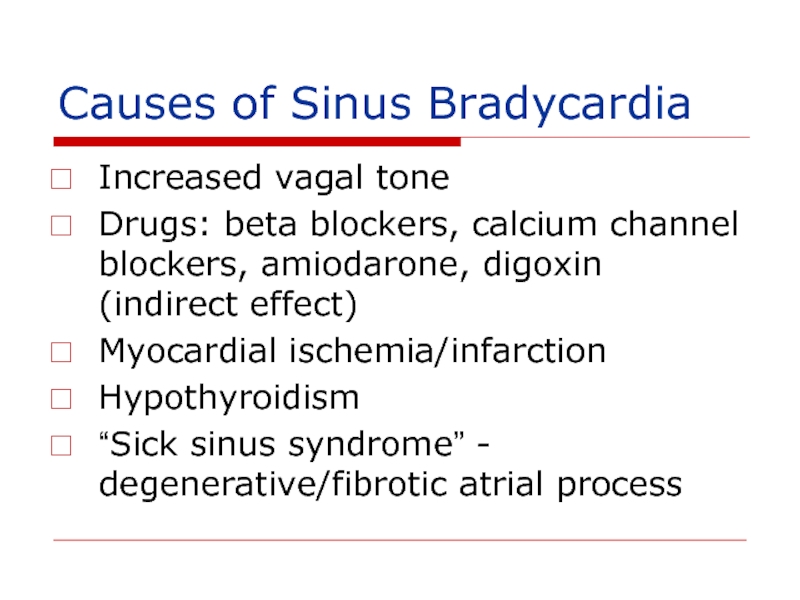
- 132. Causes of Sinus Bradycardia Increased vagal tone
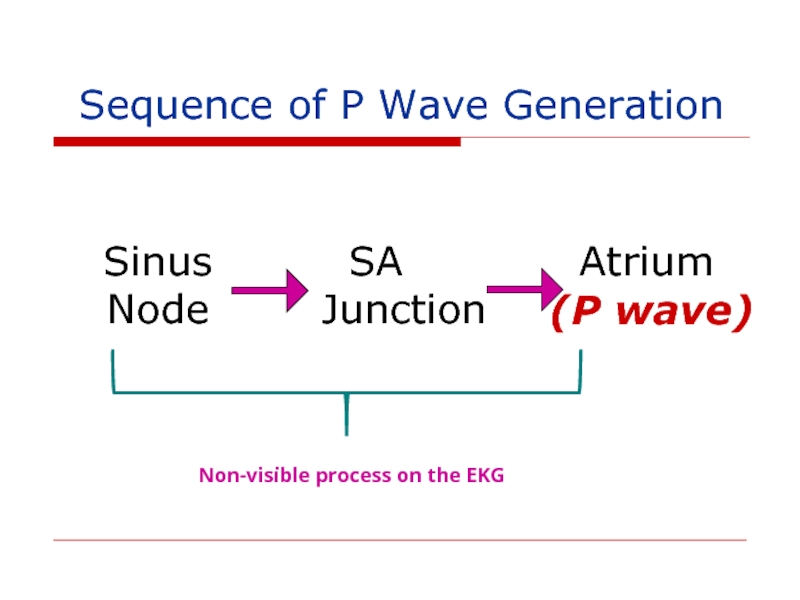
- 133. Sequence of P Wave Generation Sinus
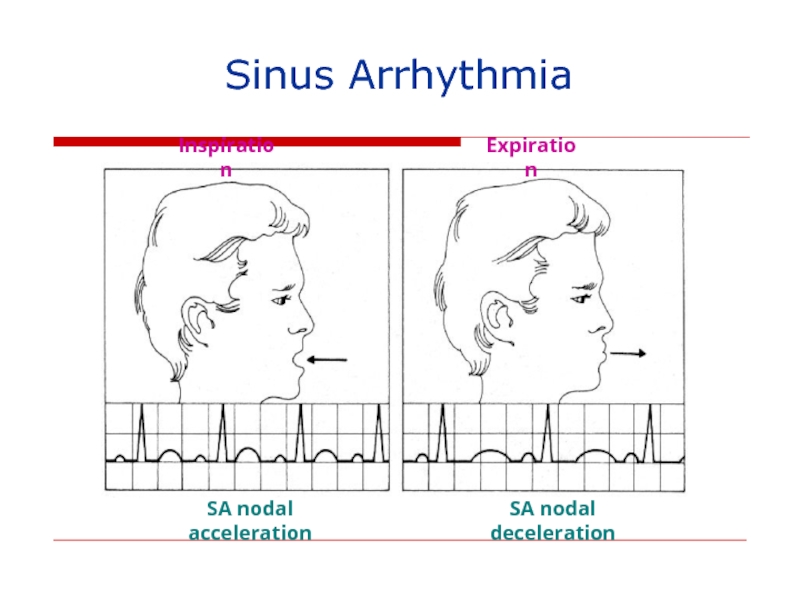
- 134. Inspiration Expiration SA nodal acceleration SA nodal deceleration Sinus Arrhythmia
- 135. Sinoatrial (SA) Exit Block - Definitions First
- 136. Second Degree SA Exit Block - Type
- 137. Second Degree SA Exit Block - Type
- 138. X 2X
- 139. P P P’ P’
- 140. Tachycardia-Bradycardia (Form of
- 141. Sinus Arrest → Asystole Sinus rhythm
- 142. Causes of SA Exit Block and Sinus
- 143. Sick Sinus Syndrome (1) persistent spontaneous sinus
Слайд 12Atrial Fibrillation
The most common arrhythmia in clinical practice
Frequency increases with age
Слайд 15Most common causes
Valvular heart disease: (MS,MR)
LV hypertrophy (HTN, other cause)
Cardiomyopathy
Thyrotoxicosis
Alcohol (“holiday
Atrial septal defect
Lone AF (structurally normal heart)
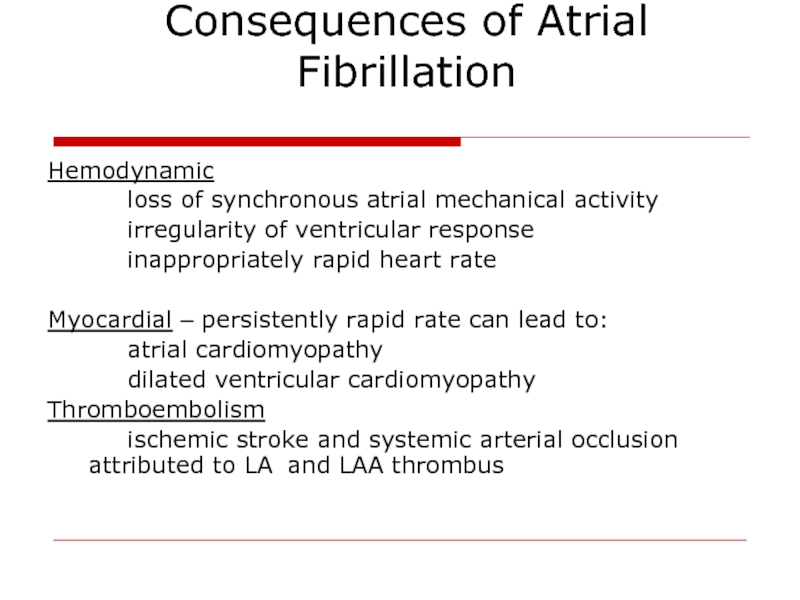
Слайд 17Consequences of Atrial Fibrillation
Hemodynamic
loss of synchronous atrial mechanical activity
irregularity of ventricular
inappropriately rapid heart rate
Myocardial – persistently rapid rate can lead to:
atrial cardiomyopathy
dilated ventricular cardiomyopathy
Thromboembolism
ischemic stroke and systemic arterial occlusion attributed to LA and LAA thrombus
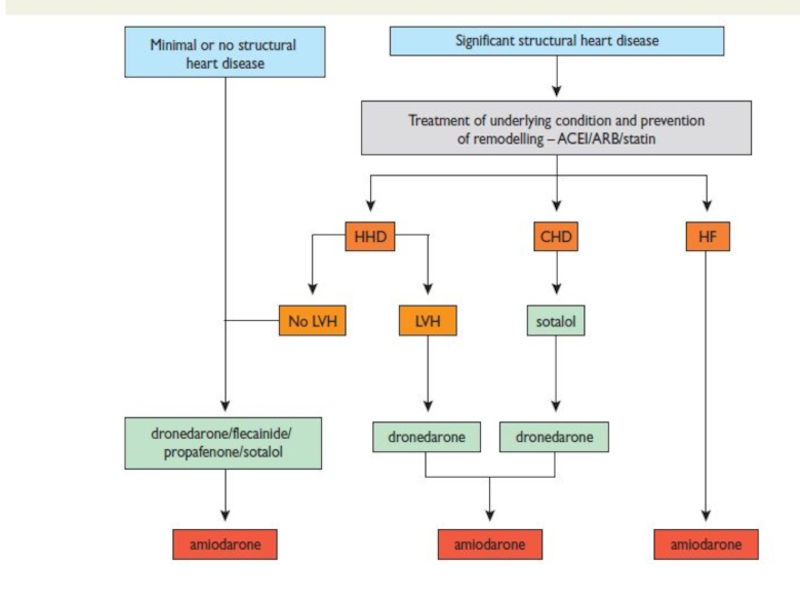
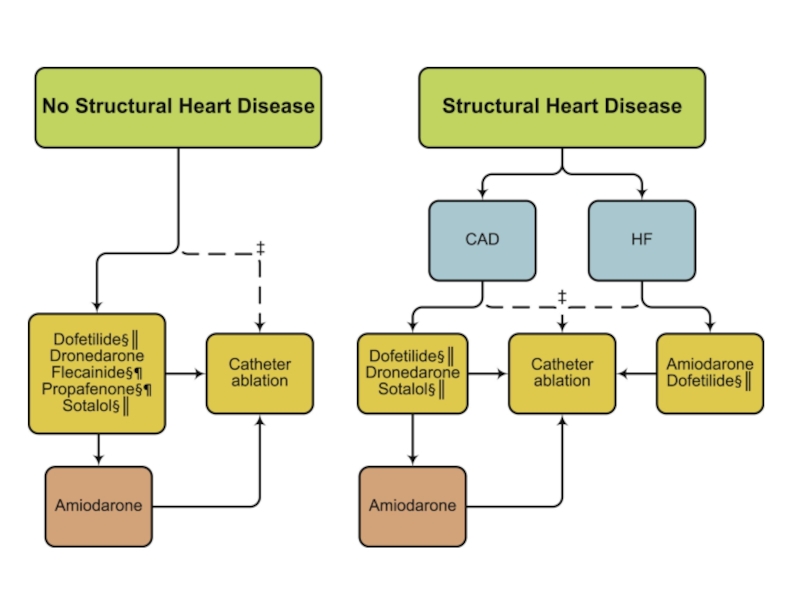
Слайд 19Treatment options
1. Rhythm control – restoration and maintenance of sinus rhythm
2.
Prevention of Thromboembolysm !
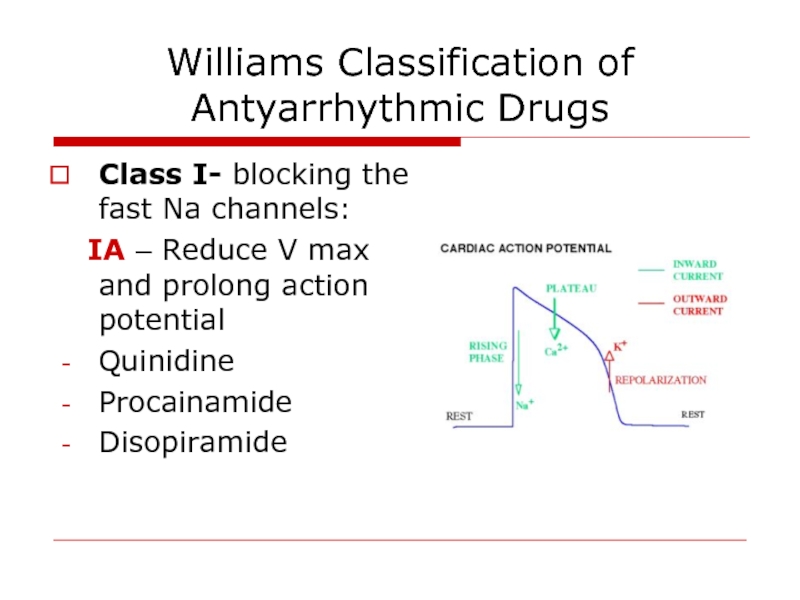
Слайд 20Williams Classification of Antyarrhythmic Drugs
Class I- blocking the fast Na channels:
Quinidine
Procainamide
Disopiramide
Слайд 21
IB : Do not reduce V max and shorten action
Lidocaine
Phenytoin
Mexiletine
IC: Reduce V max
Flecainide
Propafenon
Слайд 22
Class II – beta blockers
Class III – K channel blockers
- Sotalol
- Bretylium
Class IV – Ca channel blockers
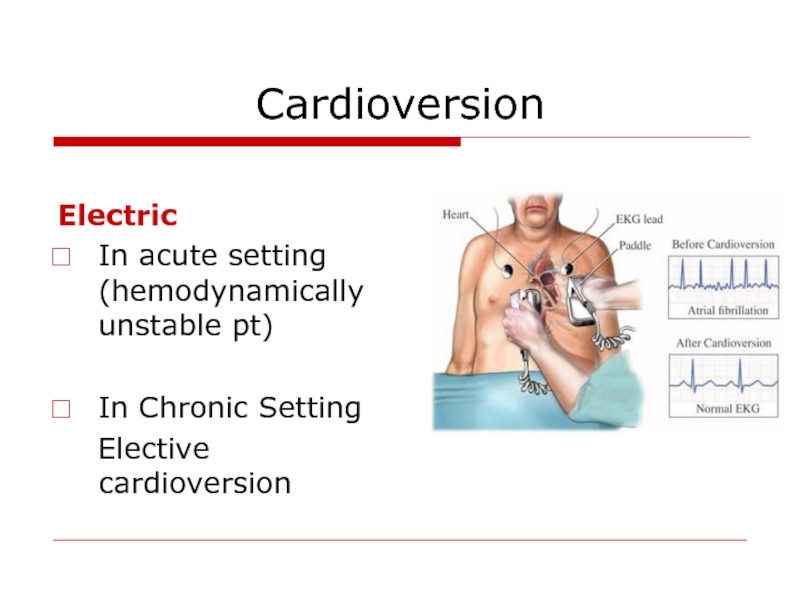
Слайд 24Cardioversion
Electric
In acute setting (hemodynamically unstable pt)
In Chronic
Elective cardioversion
Слайд 25Predictors of successful cardioverson
Short AF duration
Young age
Normal atrial size
No organic heart
Слайд 29Rate Control
Acute setting – IV
- Esmolol
- Metoprolol
- Dilthiazem
- Digoxin (HF)
Chronic setting – PO (the same drugs)
Слайд 31– Severe symptoms due to AF
– Patients with CHF
– Younger patients
–
– First episode of AF
Attempt Rhythm Control First
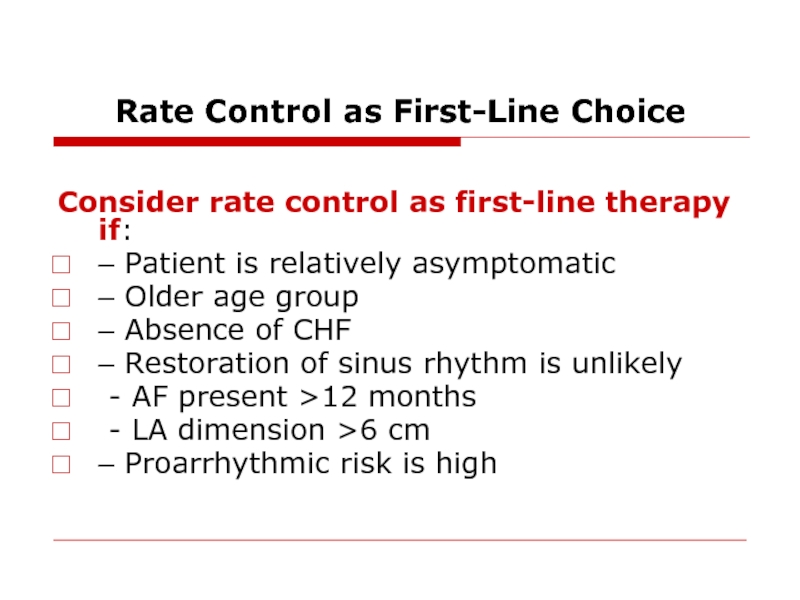
Слайд 32Rate Control as First-Line Choice
Consider rate control as first-line therapy if:
–
– Older age group
– Absence of CHF
– Restoration of sinus rhythm is unlikely
- AF present >12 months
- LA dimension >6 cm
– Proarrhythmic risk is high
Слайд 37Novel Oral Anticoagulants
Dabigatran (Pradaxa)- direct oral thrombin inhibitor
Rivaroxaban (Xarelto)– direct oral
Apixaban (Eliquis) - direct oral factor Xa inhibitor
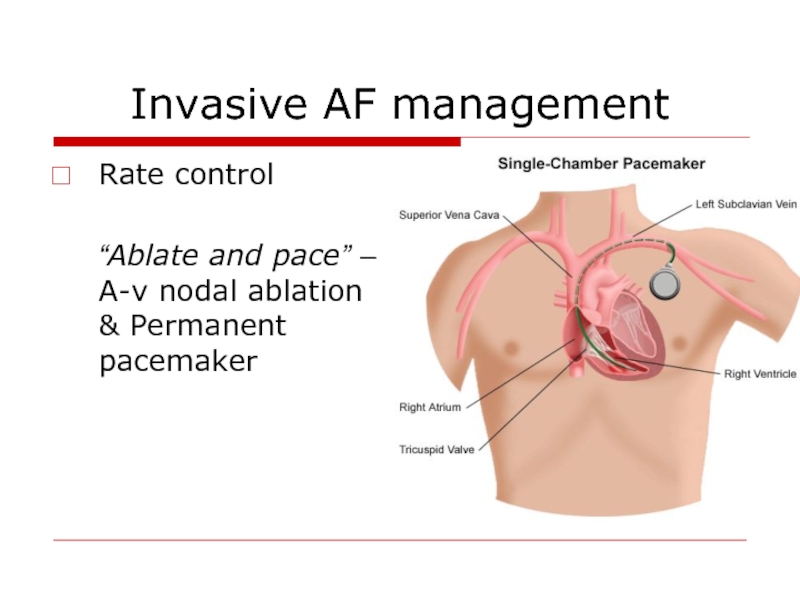
Слайд 40Invasive AF management
Rate control
“Ablate and pace” – A-v
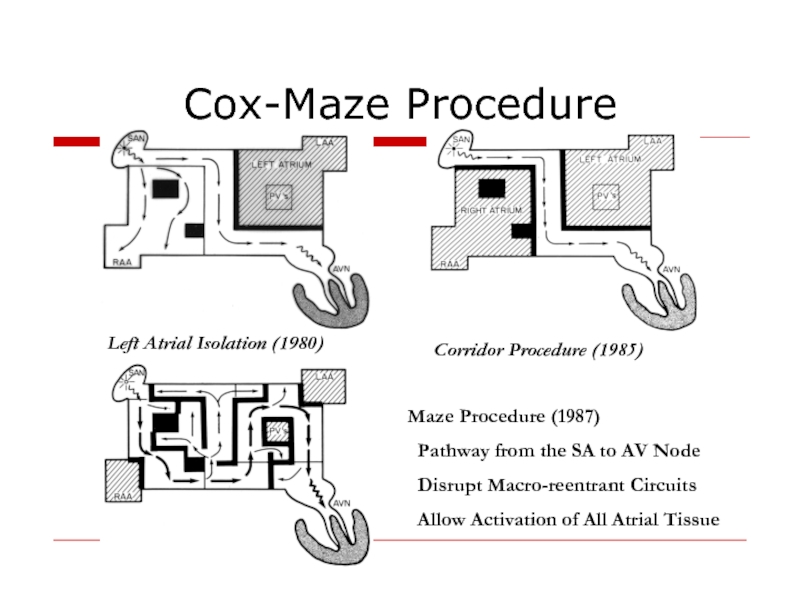
Слайд 42Cox-Maze Procedure
Left Atrial Isolation (1980)
Corridor Procedure (1985)
Maze Procedure (1987)
Pathway from
Disrupt Macro-reentrant Circuits
Allow Activation of All Atrial Tissue
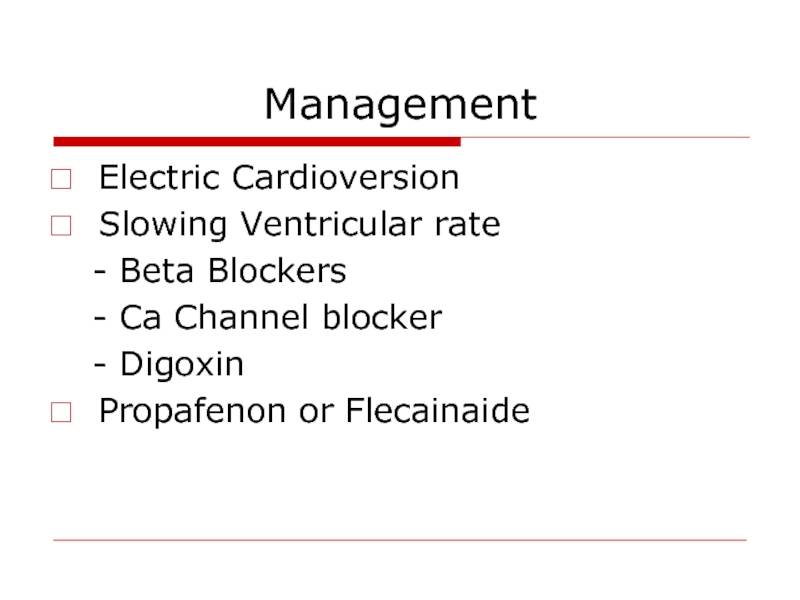
Слайд 48Management
Electric Cardioversion
Slowing Ventricular rate
- Beta Blockers
- Ca
- Digoxin
Propafenon or Flecainaide
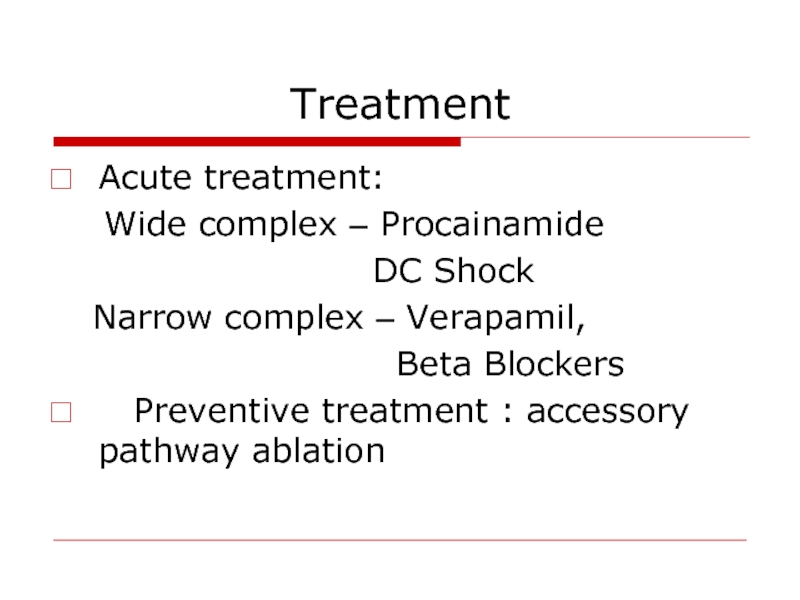
Слайд 55Treatment
Acute treatment:
Wide complex – Procainamide
Narrow complex – Verapamil,
Beta Blockers
Preventive treatment : accessory pathway ablation
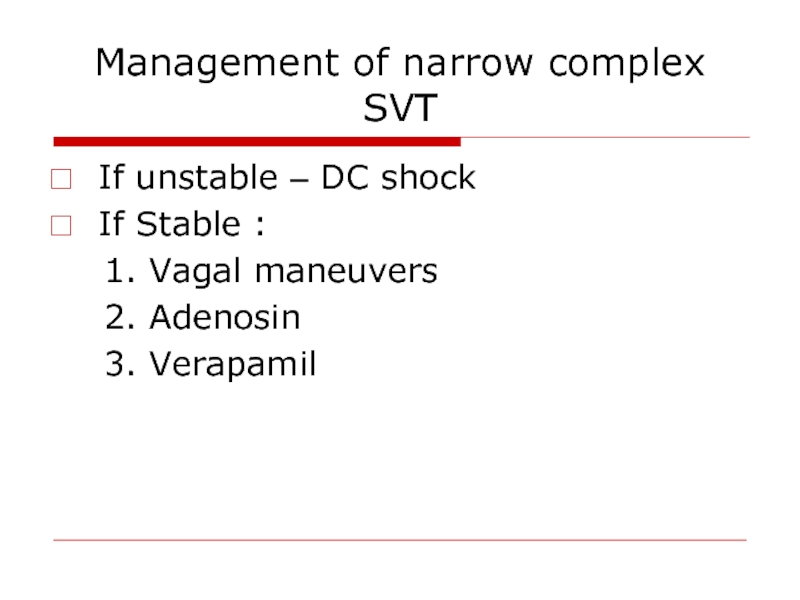
Слайд 60Management of narrow complex SVT
If unstable – DC shock
If Stable :
2. Adenosin
3. Verapamil
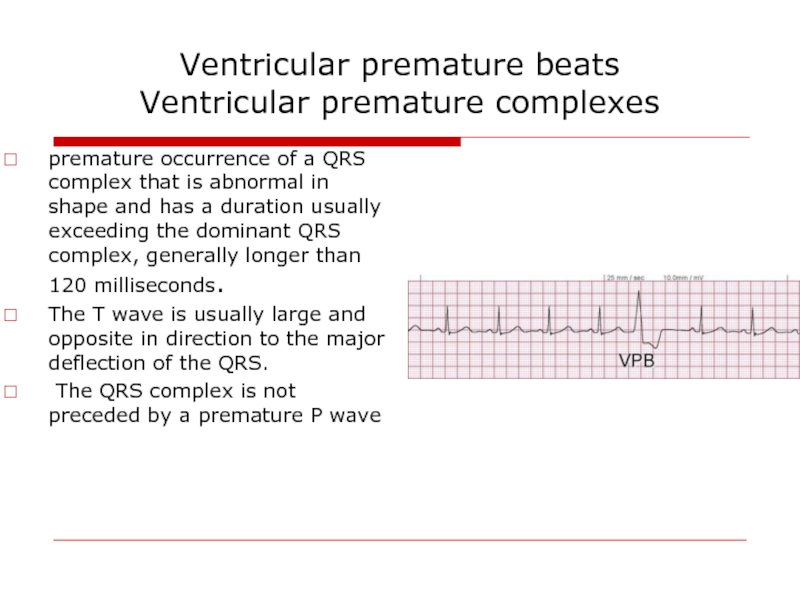
Слайд 63Ventricular premature beats
Ventricular premature complexes
premature occurrence of a QRS complex
The T wave is usually large and opposite in direction to the major deflection of the QRS.
The QRS complex is not preceded by a premature P wave
Слайд 70Causes
LV false tendons,
infection
in ischemic or inflamed myocardium,
hypoxia,
Anesthesiaor
Medications
electrolyte imbalance,
tension states,
myocardial stretch,
excessive use of tobacco, caffeine, or alcohol.
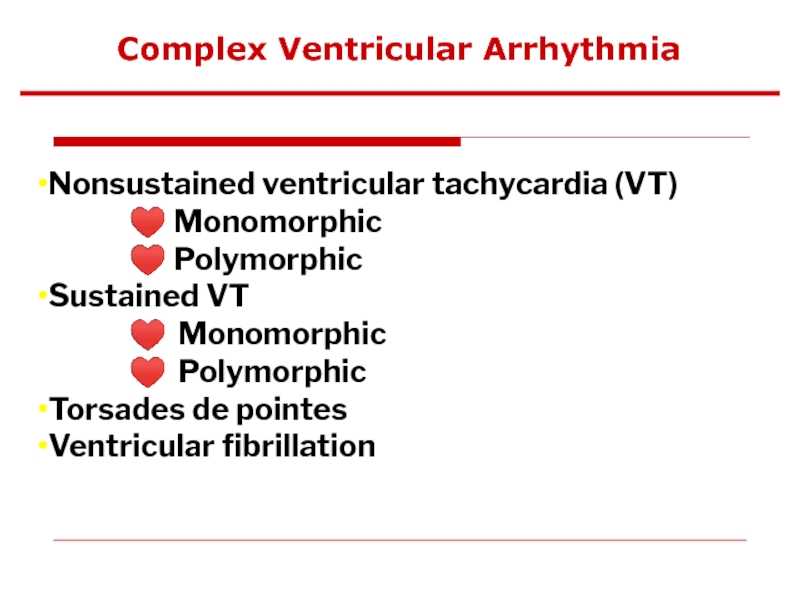
Слайд 71Complex Ventricular Arrhythmia
Nonsustained ventricular tachycardia (VT)
♥ Monomorphic
♥ Polymorphic
Sustained VT
♥ Monomorphic
♥ Polymorphic
Torsades
Ventricular fibrillation
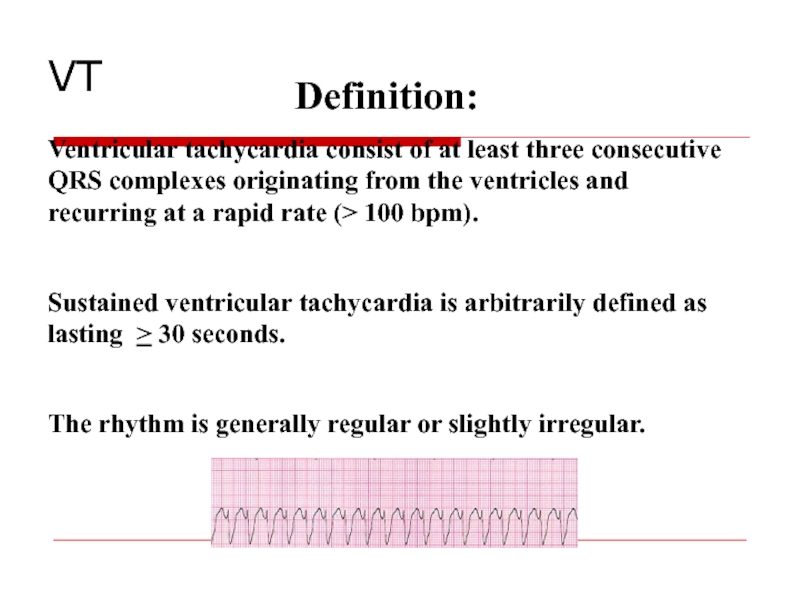
Слайд 72Definition:
Ventricular tachycardia consist of at least three consecutive QRS complexes originating
Sustained ventricular tachycardia is arbitrarily defined as lasting > 30 seconds.
The rhythm is generally regular or slightly irregular.
VT
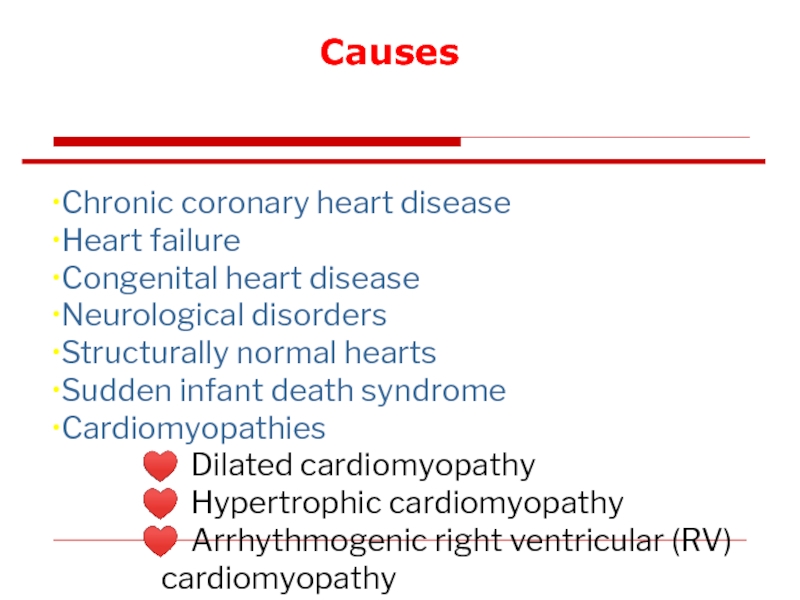
Слайд 77Causes
Chronic coronary heart disease
Heart failure
Congenital heart disease
Neurological disorders
Structurally normal hearts
Sudden infant
Cardiomyopathies
♥ Dilated cardiomyopathy
♥ Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
♥ Arrhythmogenic right ventricular (RV)
cardiomyopathy
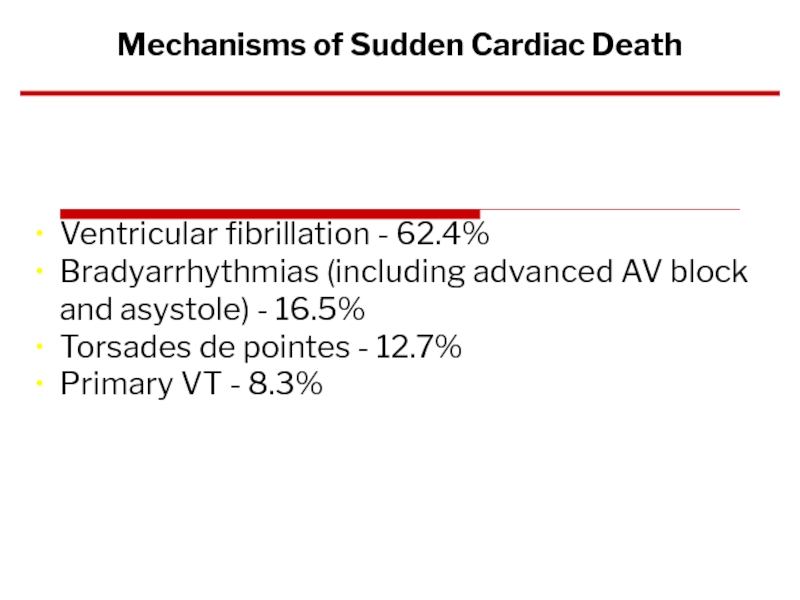
Слайд 78Ventricular fibrillation - 62.4%
Bradyarrhythmias (including advanced AV block and asystole) -
Torsades de pointes - 12.7%
Primary VT - 8.3%
Mechanisms of Sudden Cardiac Death
Bayes de Luna et al. Am Heart J 1989;117:151–9.
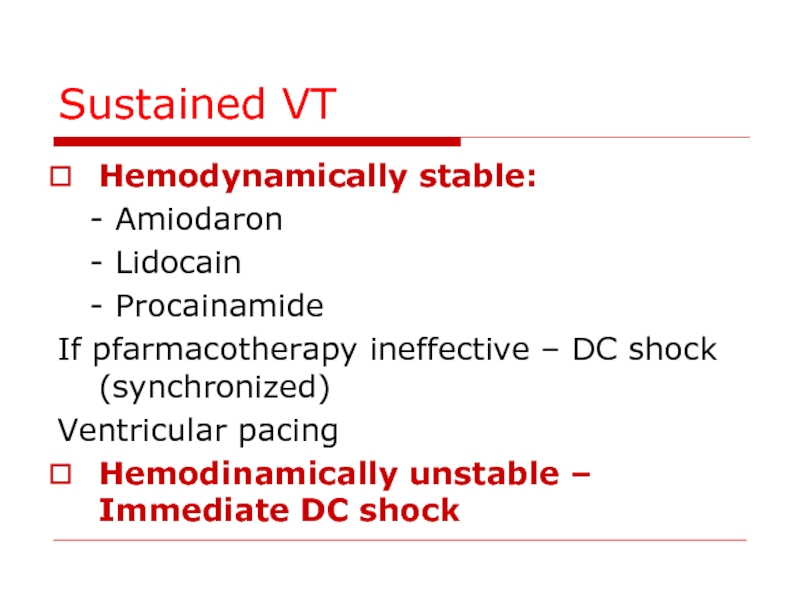
Слайд 80Sustained VT
Hemodynamically stable:
- Amiodaron
- Lidocain
-
If pfarmacotherapy ineffective – DC shock (synchronized)
Ventricular pacing
Hemodinamically unstable – Immediate DC shock
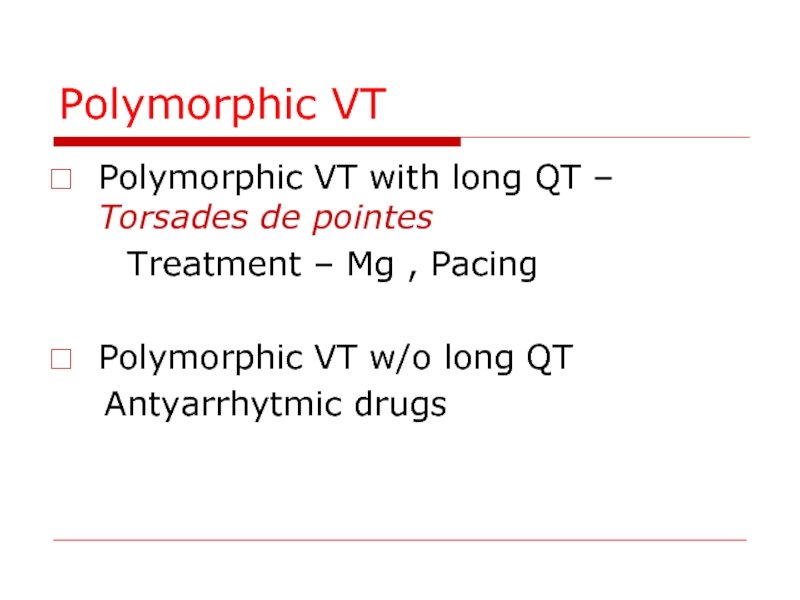
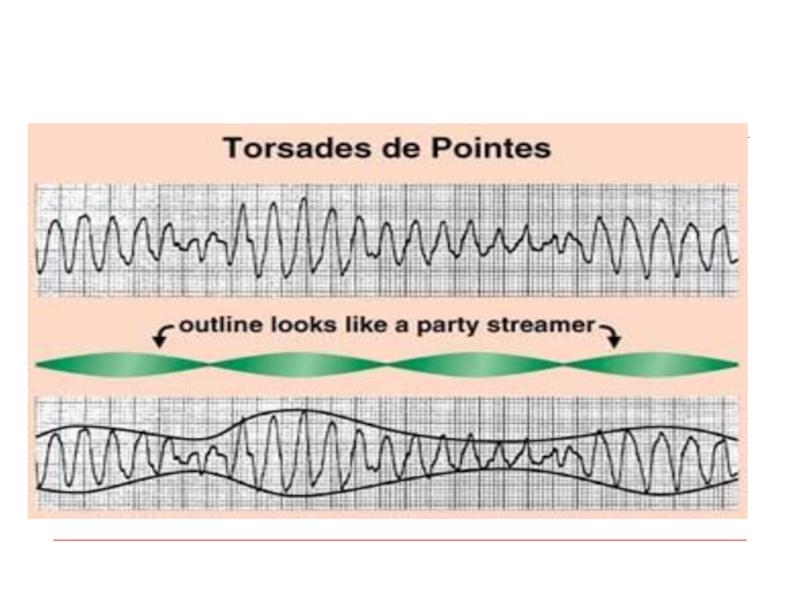
Слайд 81Polymorphic VT
Polymorphic VT with long QT – Torsades de pointes
Polymorphic VT w/o long QT
Antyarrhytmic drugs
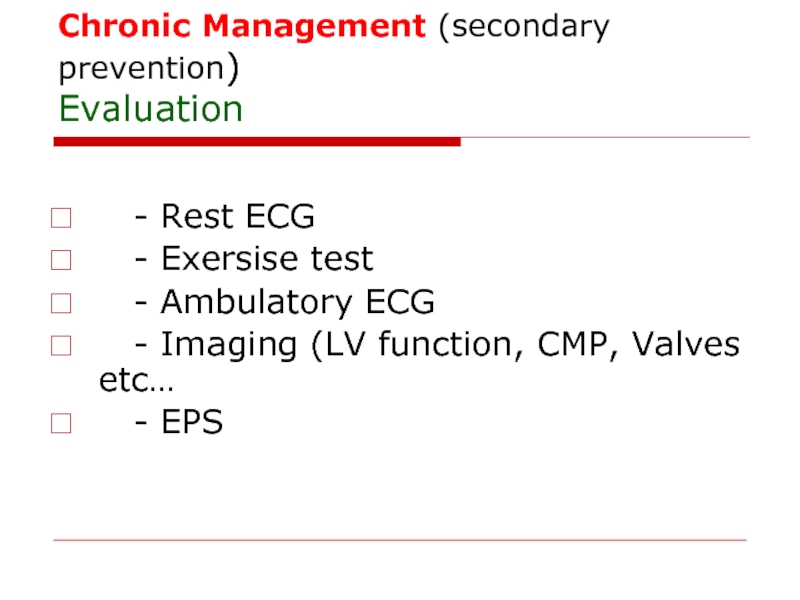
Слайд 83Chronic Management (secondary prevention)
Evaluation
- Rest ECG
- Exersise
- Ambulatory ECG
- Imaging (LV function, CMP, Valves etc…
- EPS
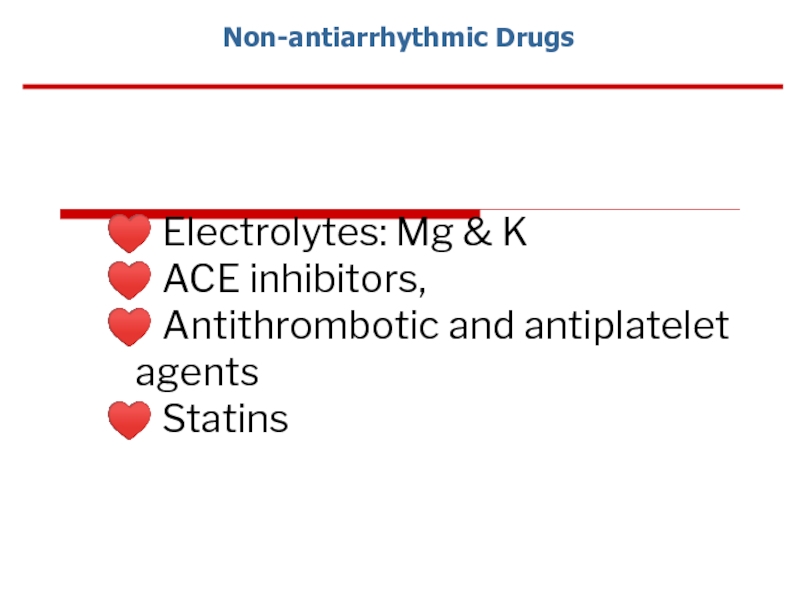
Слайд 85
♥ Electrolytes: Mg & K
♥ ACE inhibitors,
♥ Antithrombotic and antiplatelet
♥ Statins
Non-antiarrhythmic Drugs
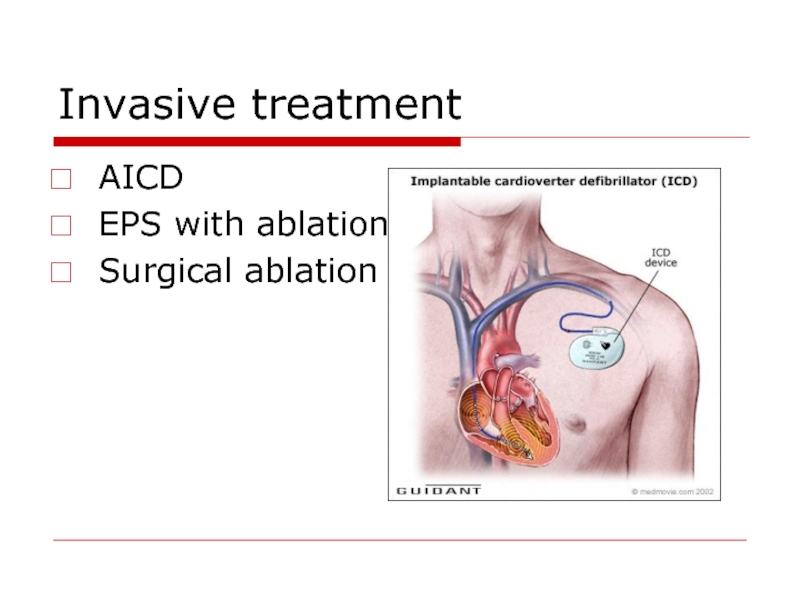
Слайд 86Antiarrhytmic drugs
Antiarrhythmic drugs (except for BB) should not be used as
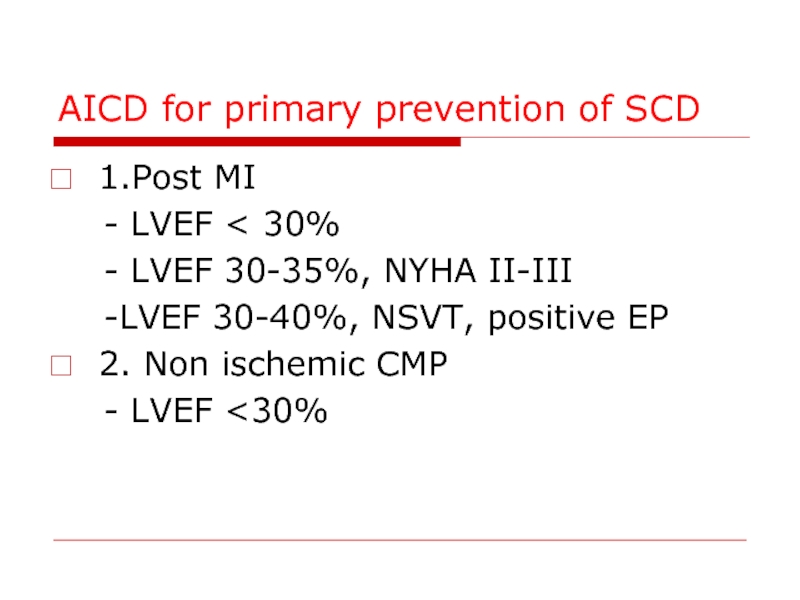
Слайд 88AICD for primary prevention of SCD
1.Post MI
- LVEF
- LVEF 30-35%, NYHA II-III
-LVEF 30-40%, NSVT, positive EP
2. Non ischemic CMP
- LVEF <30%
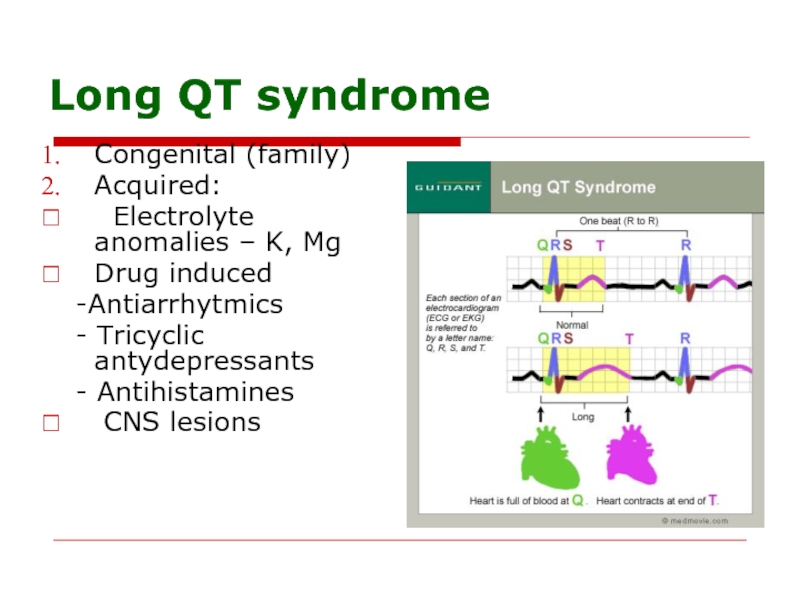
Слайд 89Long QT syndrome
Congenital (family)
Acquired:
Electrolyte anomalies – K, Mg
Drug induced
- Tricyclic antydepressants
- Antihistamines
CNS lesions
Слайд 91Long QT syndrome treatment
Acute
1.Remove the precipitating factor
2. Mg IV
3. Pacing
4.
5. IB antiarrhythmic
Слайд 102Wide QRS Irregular Tachycardia: Atrial Fibrillation with antidromic conduction in patient with
Слайд 103AV Dissociation
QRS > 0.14
QRS Axis between – 90 & - 180
Positive QRS deflection in all precordial leads
LBBB morphology with rightward QRS axis
Capture beats, fusion beats
QRS morphology identical to PVC’s during sinus rhythm
Futures favoring VT
Слайд 104A three-lead rhythm strip from a 62-year-old man who presented with
Fusion and Capture Beats
Слайд 105Sustained monomorphic ventricular tachycardia with atrioventricular (AV) dissociation. Note the independence
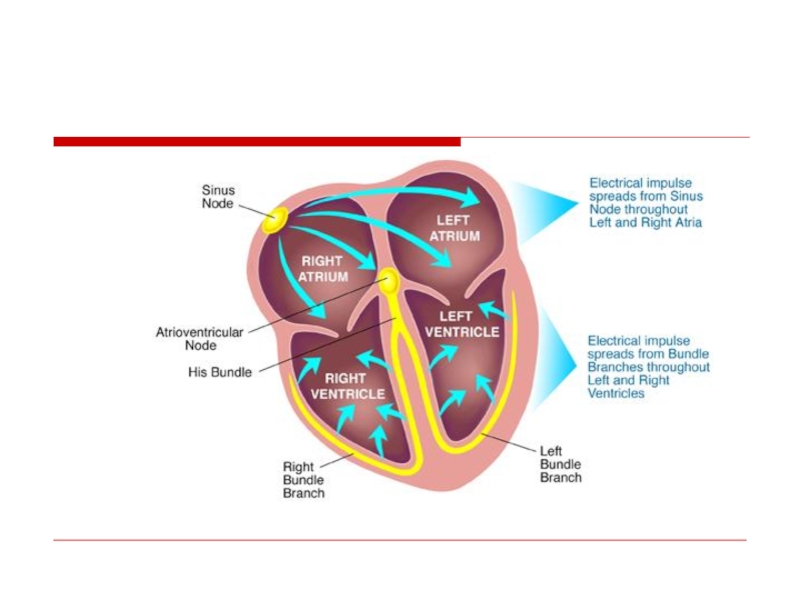
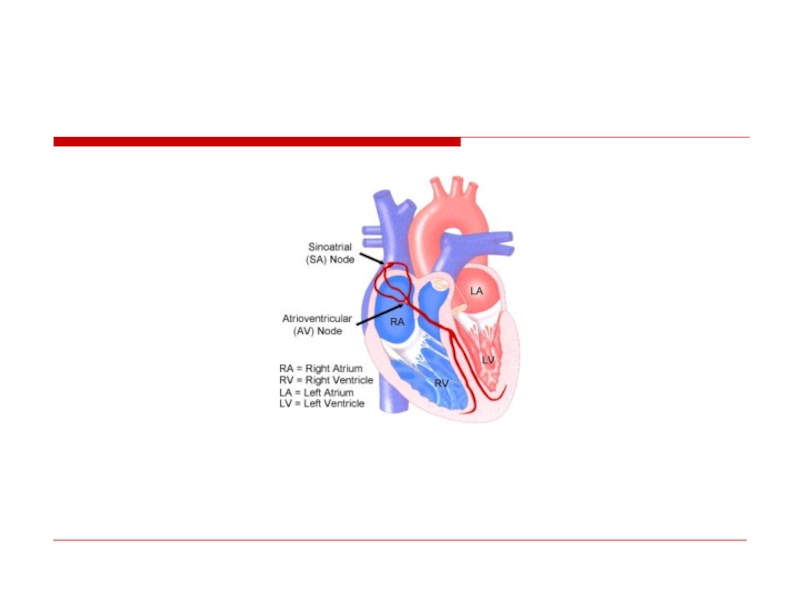
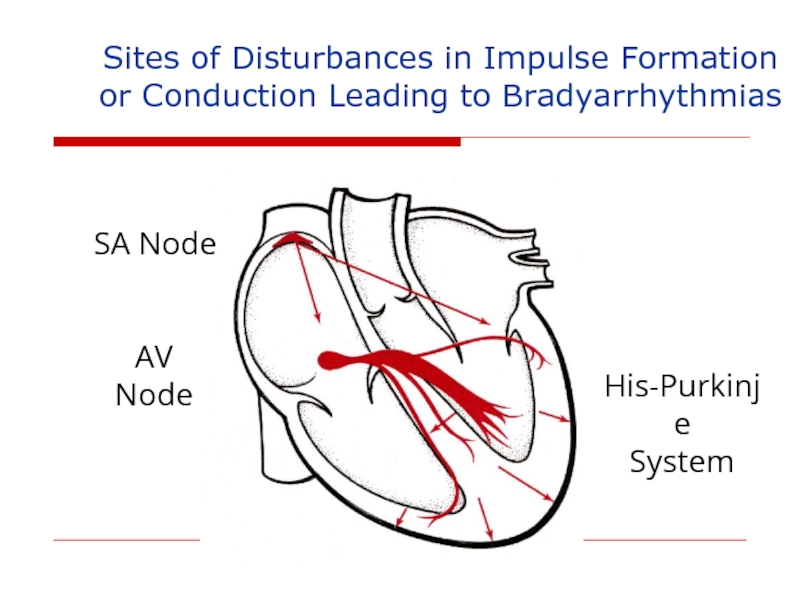
Слайд 109Sites of Disturbances in Impulse Formation
or Conduction Leading to Bradyarrhythmias
SA
AV Node
His-Purkinje
System
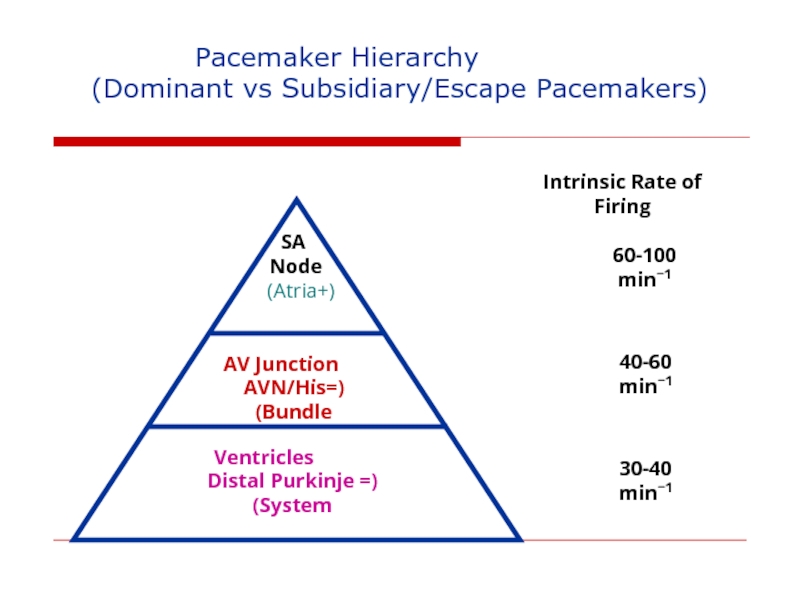
Слайд 110
Pacemaker
(Dominant vs Subsidiary/Escape Pacemakers)
SA
Node
(+Atria)
AV Junction
(=AVN/His Bundle)
Ventricles
(= Distal Purkinje System)
Intrinsic Rate of Firing
60-100 min−1
40-60 min−1
30-40 min−1
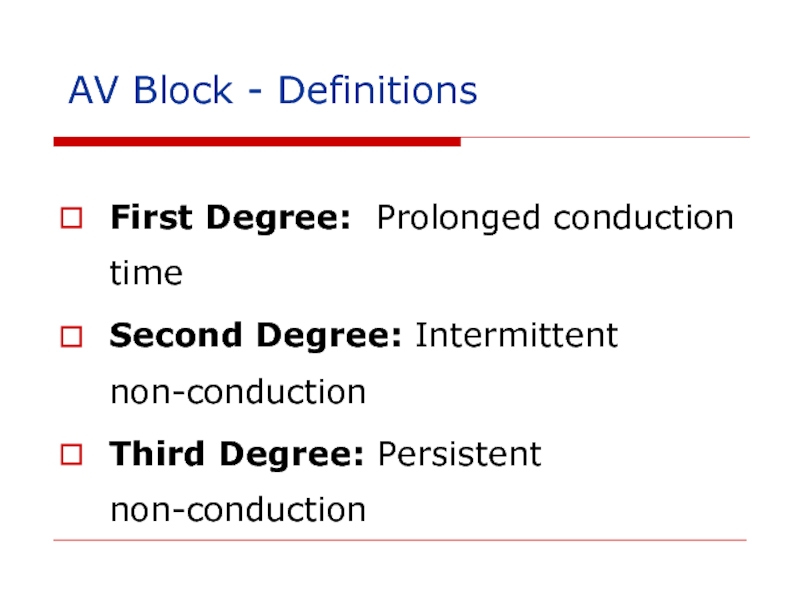
Слайд 112AV Block - Definitions
First Degree: Prolonged conduction time
Second Degree: Intermittent non-conduction
Third
Слайд 113 First Degree AV Block
II
P
P
P
.36
Site of delay most commonly the AV node,
but may be localized to the His-Purkinje system
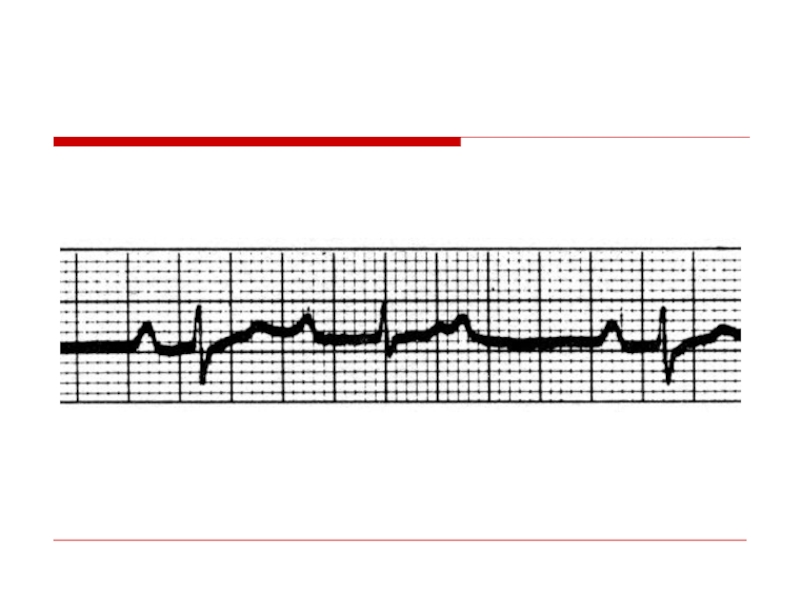
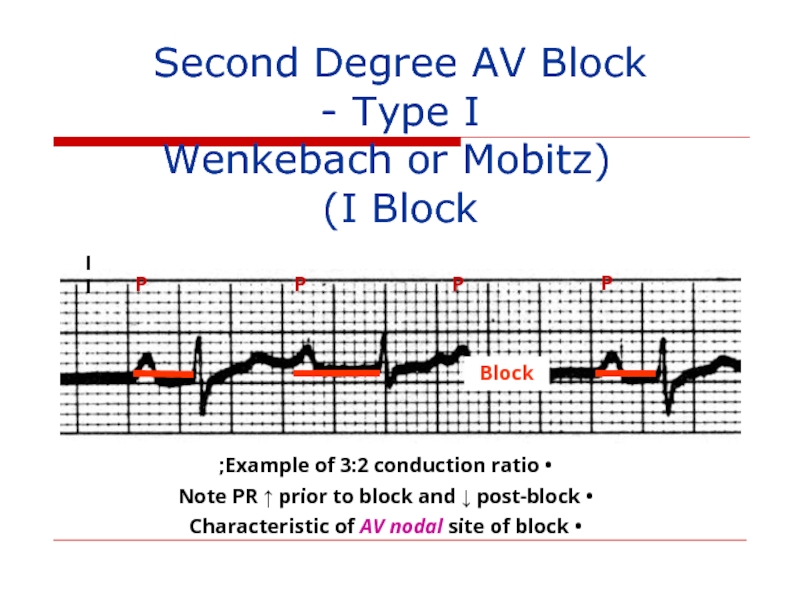
Слайд 115Second Degree AV Block - Type I
(Wenkebach or Mobitz I
P
P
P
P
Block
II
Example of 3:2 conduction ratio;
Note PR ↑ prior to block and ↓ post-block
Characteristic of AV nodal site of block
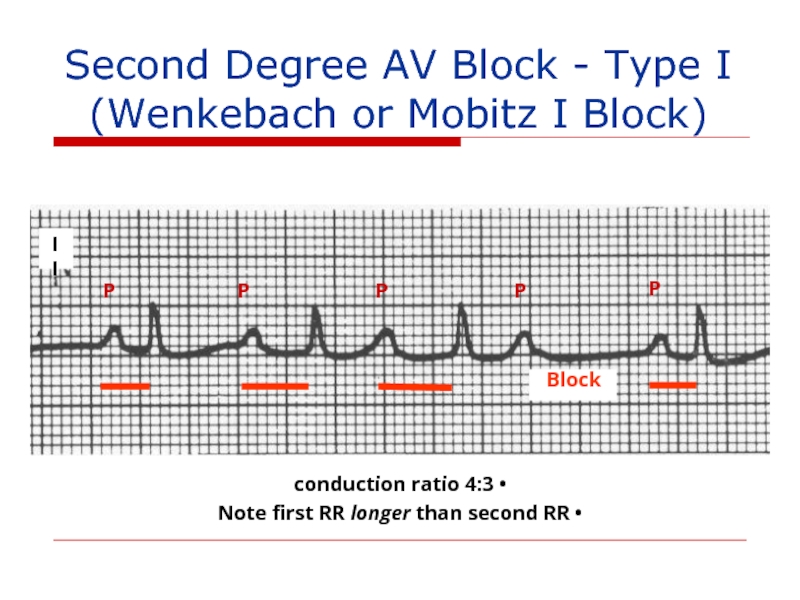
Слайд 116
II
Block
P
P
P
P
P
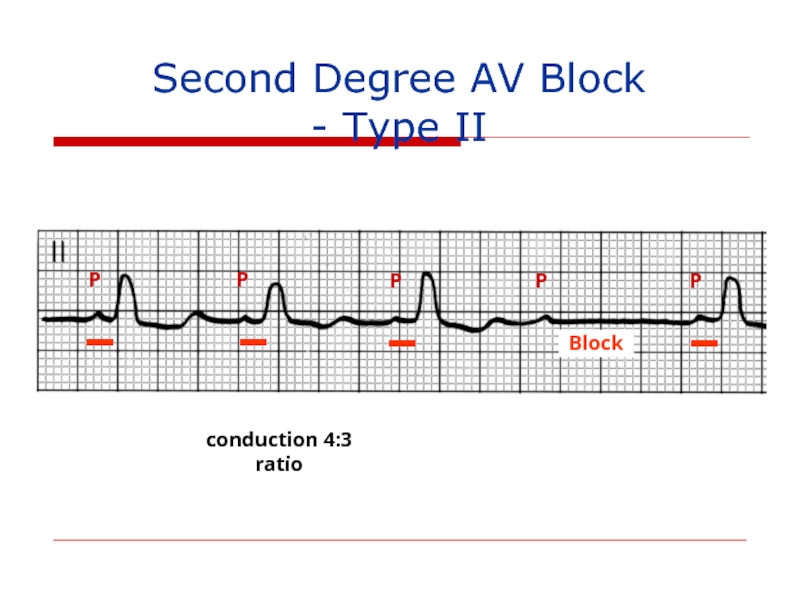
4:3 conduction ratio
Note first RR longer than second RR
Second
(Wenkebach or Mobitz I Block)
Слайд 118II
P
P
P
P
P
P
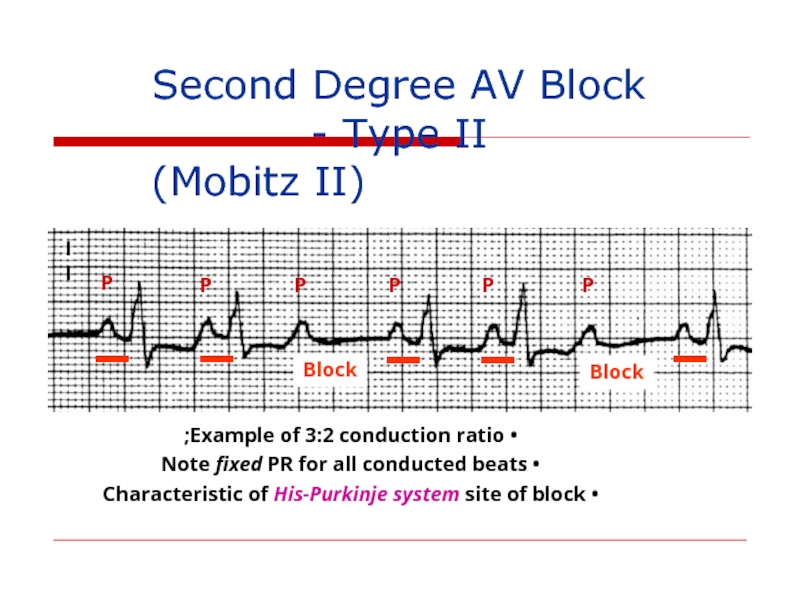
Second Degree AV Block - Type II
Example of 3:2 conduction ratio;
Note fixed PR for all conducted beats
Characteristic of His-Purkinje system site of block
Block
Block
Слайд 120II
P
P
P
P
P
P
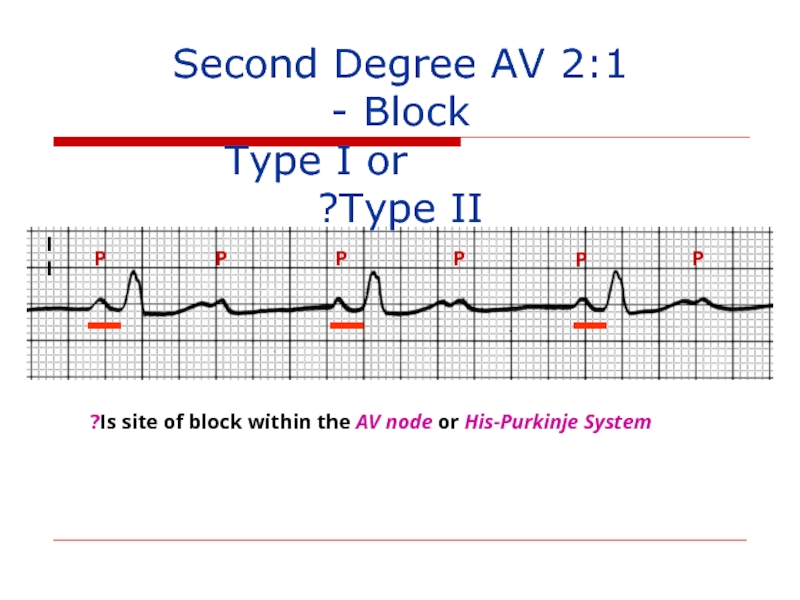
2:1 Second Degree AV Block -
Is site of block within the AV node or His-Purkinje System?
Слайд 121EKG/Clinical Clues* to site of
2:1 Second Degree AV block
QRS narrow
Improves with
Observed in setting of increased vagal tone (e.g., sleep) or AV nodal depressant drugs
QRS wide (BBB patterns)
Unchanged (possibly even precipitated) during exercise
May improve with heart rate slowing during increased vagal tone
Favoring AV Node
Favoring His-Purkinje System
Слайд 122II
P
P
P
P
P
P
P
P
P
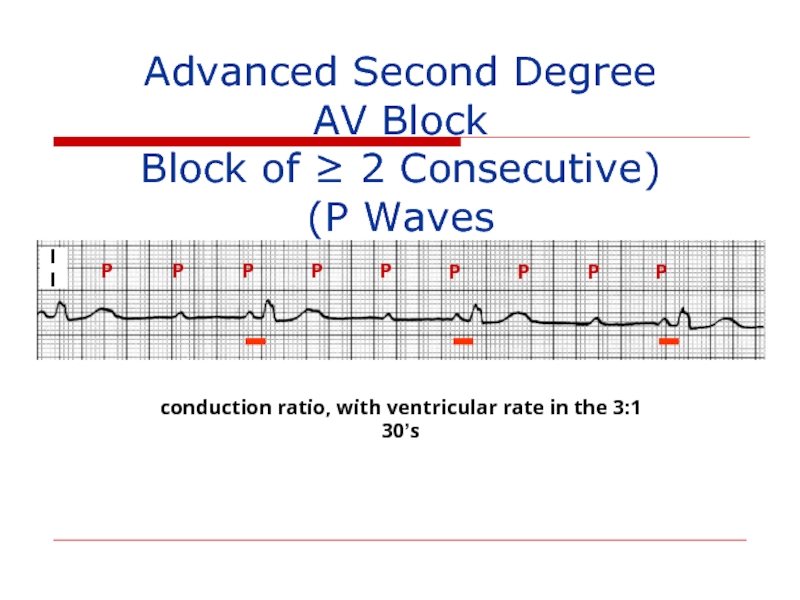
3:1 conduction ratio, with ventricular rate in the 30’s
Advanced Second Degree
(Block of ≥ 2 Consecutive P Waves)
Слайд 123Site of AV Block vs. Escape Rhythm
AV Node: Junctional or ventricular
His-Purkinje
Слайд 125
Third Degree AV Block
(Complete Heart Block)
P
P
P
P
P
P
P waves at 60 beats/min
Atrial and ventricular activity are completely unrelated
Junctional escape rhythm suggests AV nodal site of block
II
Слайд 126Unreliability of Ventricular Escape Rhythm
in
P
P
(P)
P
P
P
P
P
P
P
P
P
No QRS complexes!
P
P
P
(P)
P
15 s
Слайд 129Causes of NON-Physiologic AV Block
Ischemic heart disease, cardiomyopathy and degenerative changes
Drugs
AV Node: digoxin, beta blockers, calcium channel blockers, amiodarone
His-Purkinje System: Antiarrhythmic drugs that depress the inward sodium current
Myocardial infection, infiltration (e.g., tumor)
Trauma (e.g., surgery; therapeutic ablation)
Congenital abnormalities
Слайд 132Causes of Sinus Bradycardia
Increased vagal tone
Drugs: beta blockers, calcium channel blockers,
Myocardial ischemia/infarction
Hypothyroidism
“Sick sinus syndrome” - degenerative/fibrotic atrial process
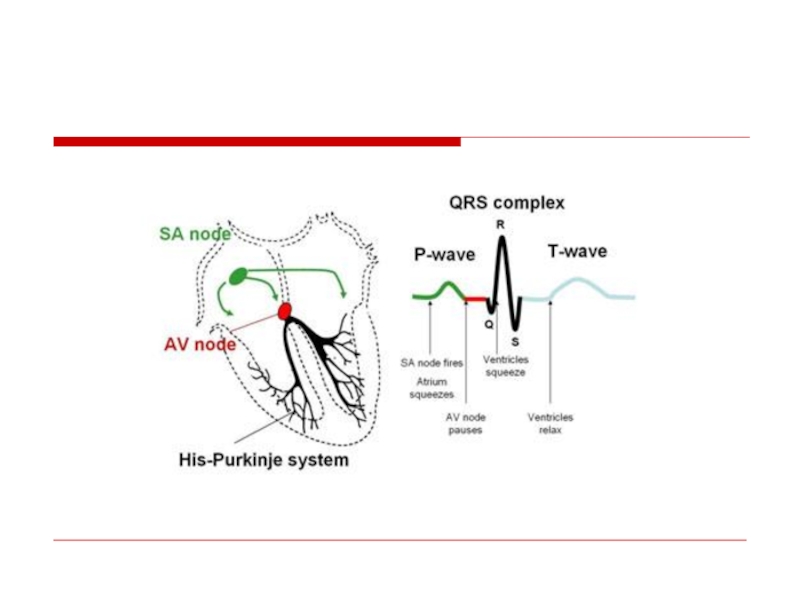
Слайд 133Sequence of P Wave Generation
Sinus
Node
SA
Junction
Atrium
(P wave)
Non-visible process on
Слайд 135Sinoatrial (SA) Exit Block - Definitions
First Degree: Prolonged SA conduction time
Second Degree: Intermittent non-conduction (intermittent absence of P waves)
Third Degree: Persistent non-conduction (complete absence of P waves; escape rhythms only)
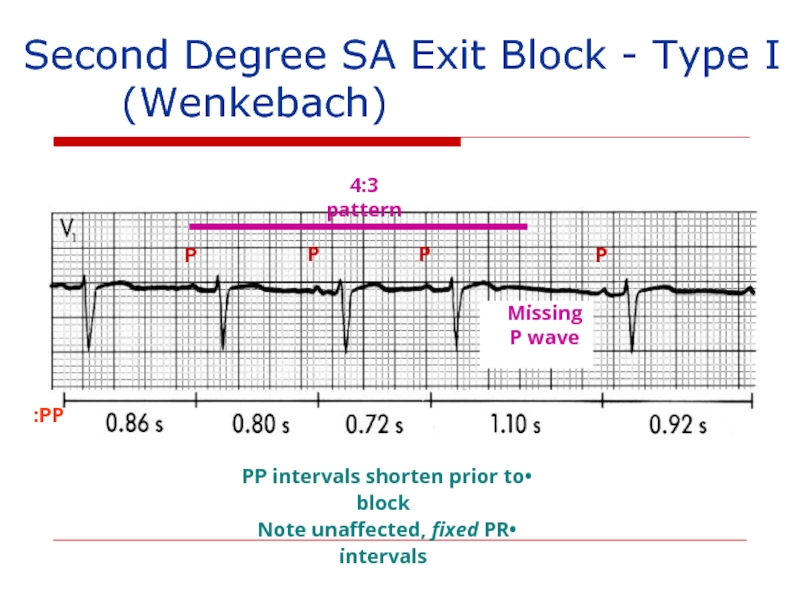
Слайд 136Second Degree SA Exit Block - Type I
P
P
P
P
4:3 pattern
Missing
P wave
PP intervals shorten prior to block
Note unaffected, fixed PR intervals
PP:
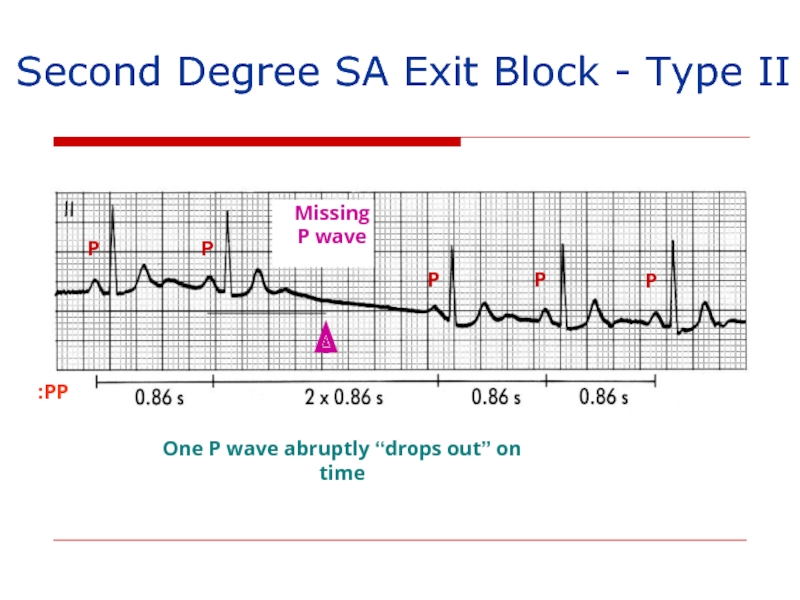
Слайд 137Second Degree SA Exit Block - Type II
PP:
P
P
P
P
P
One P wave abruptly
Missing
P wave
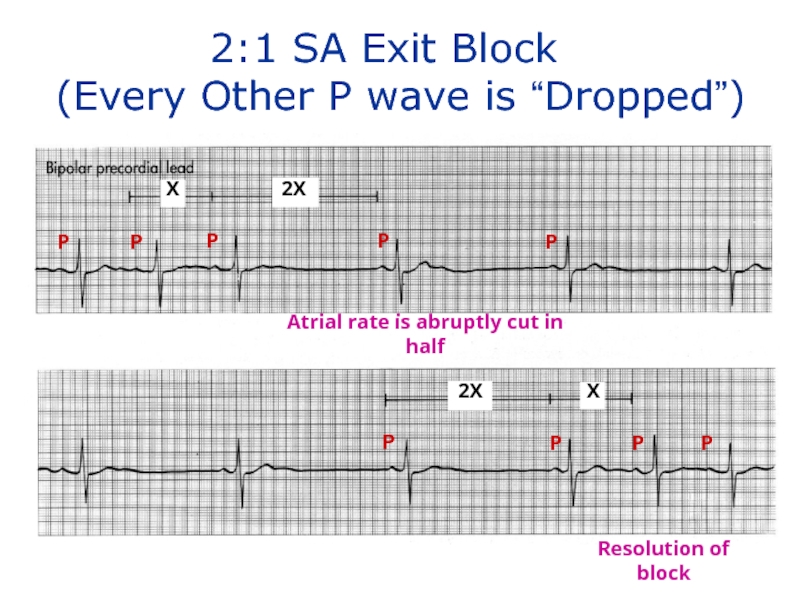
Слайд 138
X
2X
2X
X
P
P
P
P
P
P
P
P
2:1 SA Exit Block
(Every Other
Atrial rate is abruptly cut in half
Resolution of block
P
Слайд 139
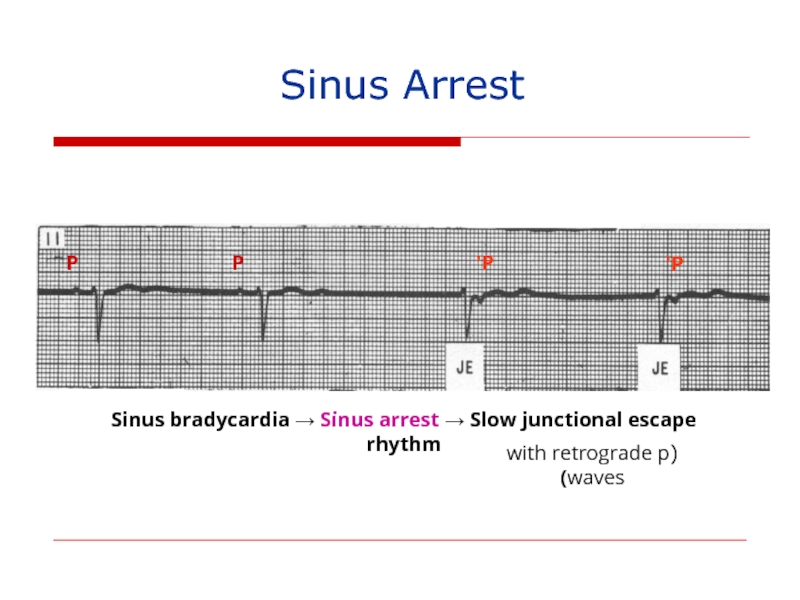
P
P
P’
P’
Sinus bradycardia → Sinus arrest → Slow junctional escape rhythm
(with retrograde
Sinus Arrest
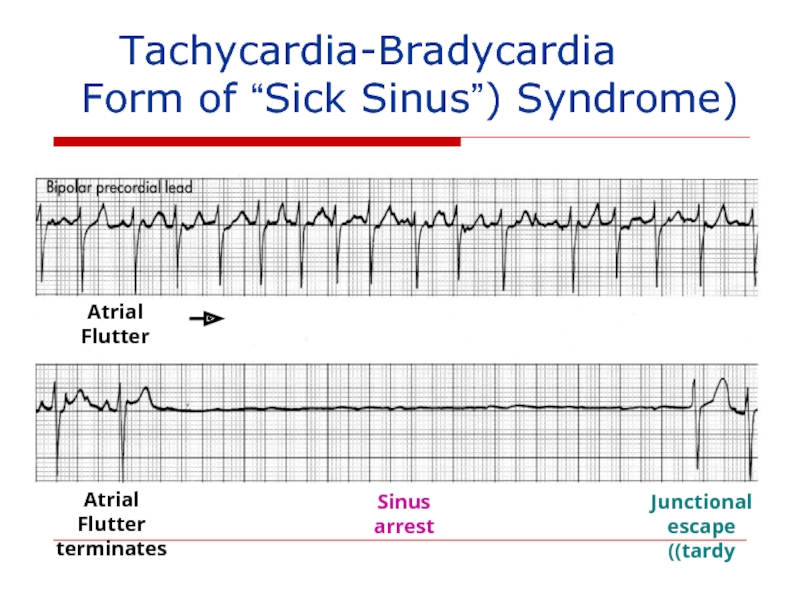
Слайд 140 Tachycardia-Bradycardia
(Form of “Sick Sinus”) Syndrome
Atrial Flutter
Sinus
Junctional
escape (tardy)
Atrial Flutter
terminates
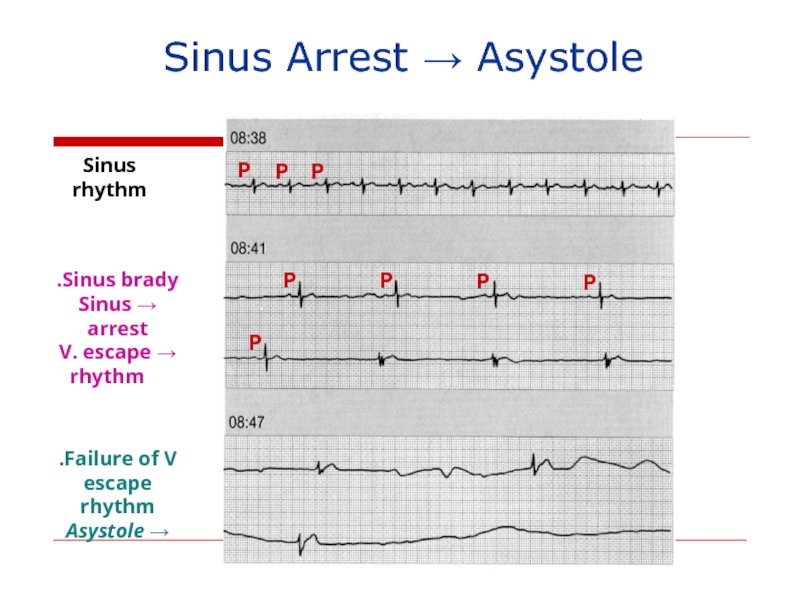
Слайд 141Sinus Arrest → Asystole
Sinus rhythm
Sinus brady.
→ Sinus arrest
→ V. escape
Failure of V.
escape rhythm
→ Asystole
P
P
P
P
P
P
P
P
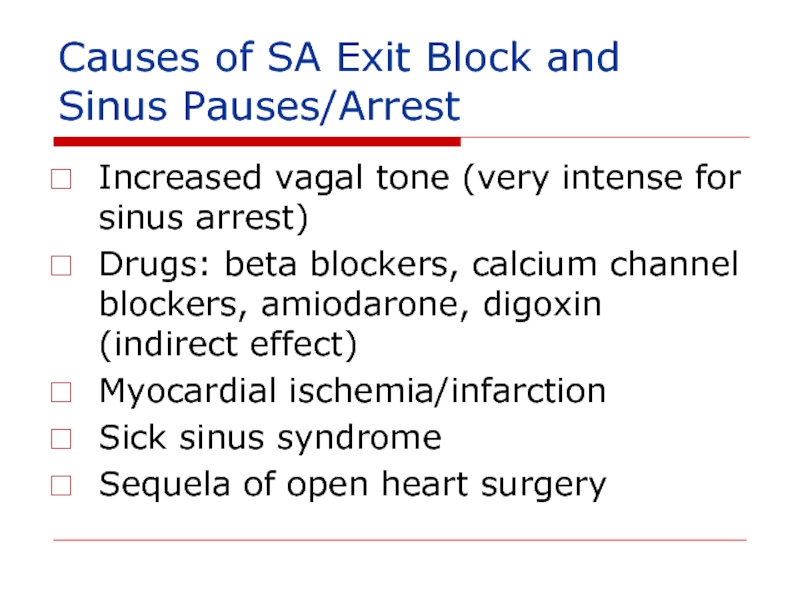
Слайд 142Causes of SA Exit Block and Sinus Pauses/Arrest
Increased vagal tone
Drugs: beta blockers, calcium channel blockers, amiodarone, digoxin (indirect effect)
Myocardial ischemia/infarction
Sick sinus syndrome
Sequela of open heart surgery
Слайд 143Sick Sinus Syndrome
(1) persistent spontaneous sinus bradycardia not caused by drugs
(2) sinus arrest or exit block
(3) combinations of SA and AV conduction disturbances
(4) alternation of paroxysms of rapid regular or irregular atrial tachyarrhythmias and periods of slow atrial and ventricular rates (bradycardia-tachycardia syndrome






















![First Degree AV Block (PR > .20 sec [1 big box])](/img/tmb/5/470469/510e2b2484a1cc910e3706ea85fdb4e7-800x.jpg)