- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Background of the lecture презентация
Содержание
- 1. Background of the lecture
- 2. Я вас приветствую! You are Welcome I am a toddler!
- 3. Propedutics pediatrics (Basic clinical pediatrics)
- 5. The Child is not reduced copy of adult person!
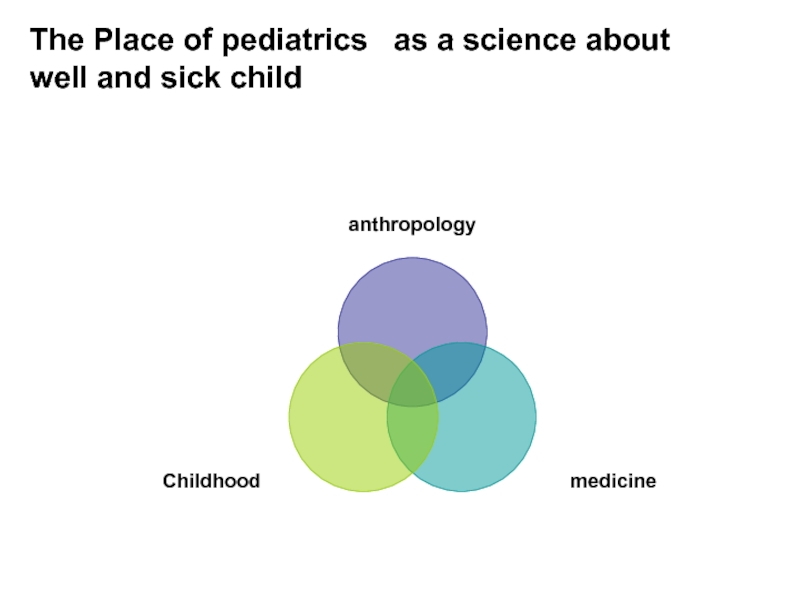
- 6. Study areas of the propedeutics of pediatrics
- 7. The Practical physician in everyday work has
- 8. Childhood Periods
- 9. From the moment of the baby conception
- 10. The embrional period begins with the 1-st
- 11. The child born at 22 - 38
- 12. During the first 16 weeks of pregnancy
- 13. Critical periods of intrauterinal development.
- 14. Critical periods of intrauterinal development.
- 15. Perinatal pediod of development includes the
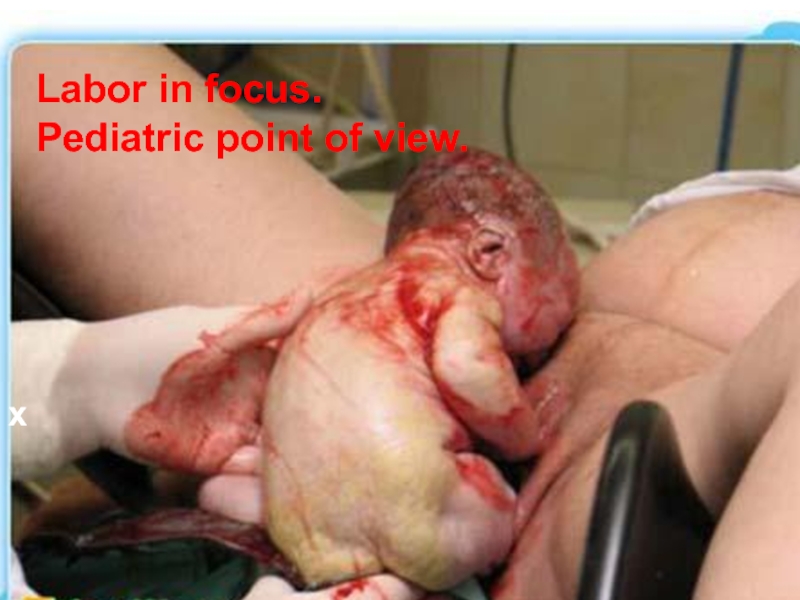
- 16. х Labor in focus. Pediatric point of view.
- 17. In spite of progress of humanity, the
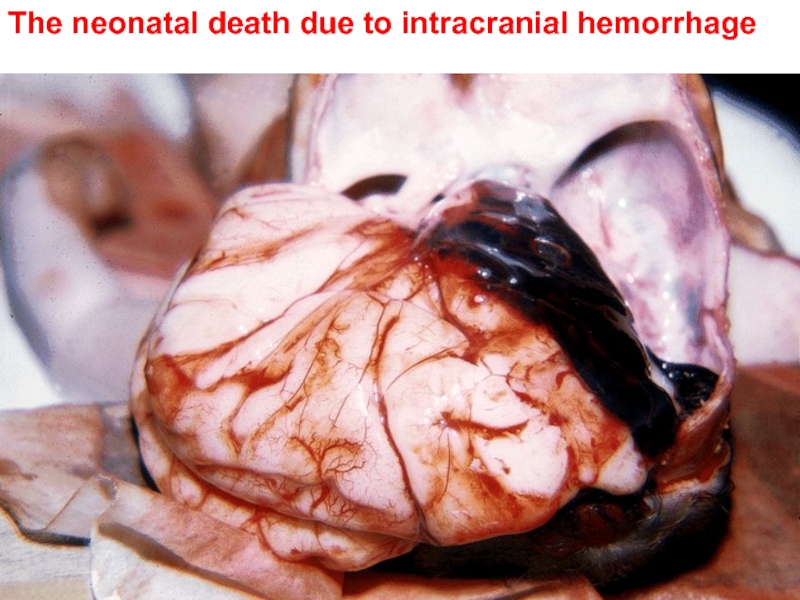
- 18. The neonatal death due to intracranial hemorrhage
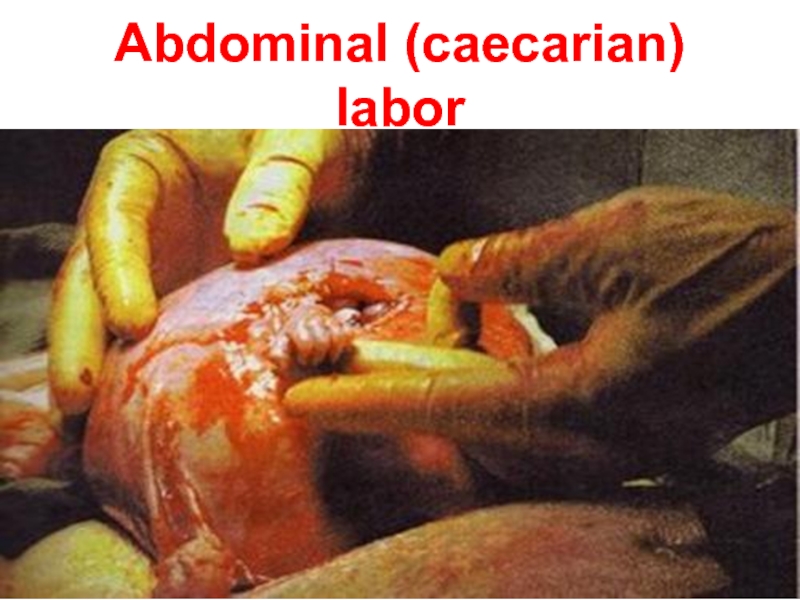
- 19. Abdominal (caecarian) labor
- 20. Extrauterinal (postnatal) period of life
- 22. First examination of the newborn. All children
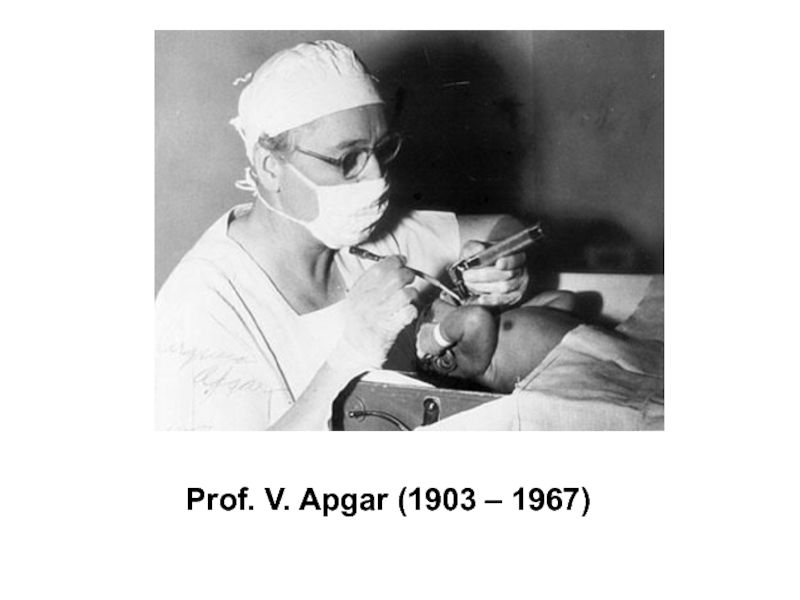
- 23. Prof. V. Apgar (1903 – 1967)
- 25. Neonatal Asphyxia Quick estimation using Аpgar score
- 26. Apgar score and asphyxia 7 –
- 29. Preterm babies There are 4 degrees
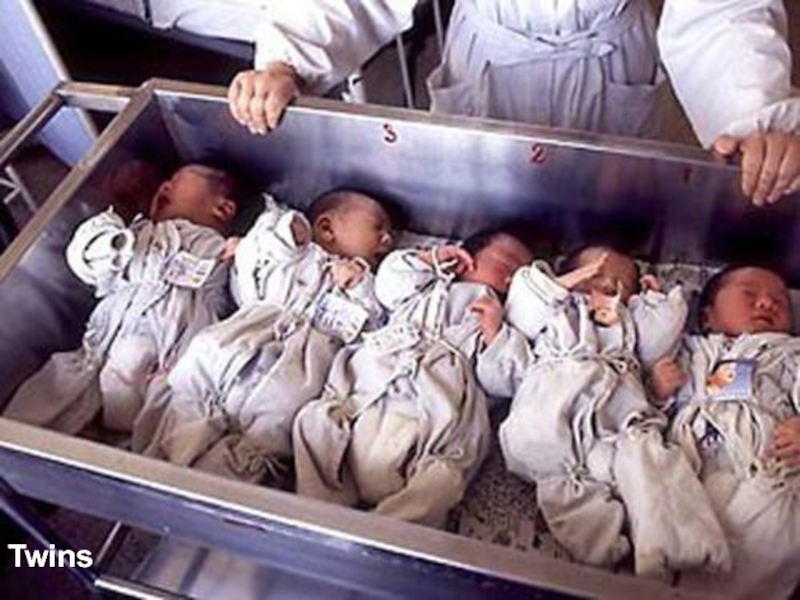
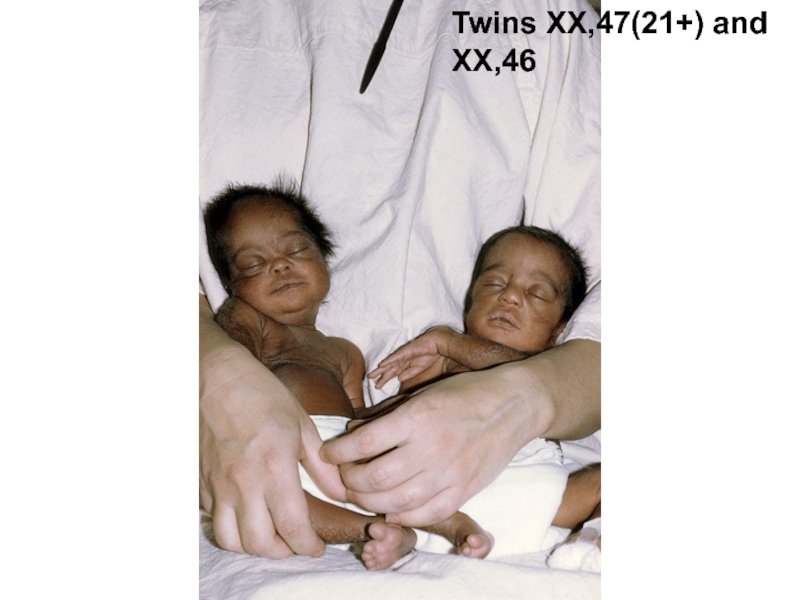
- 30. Twins
- 31. Fetal immaturity If a child
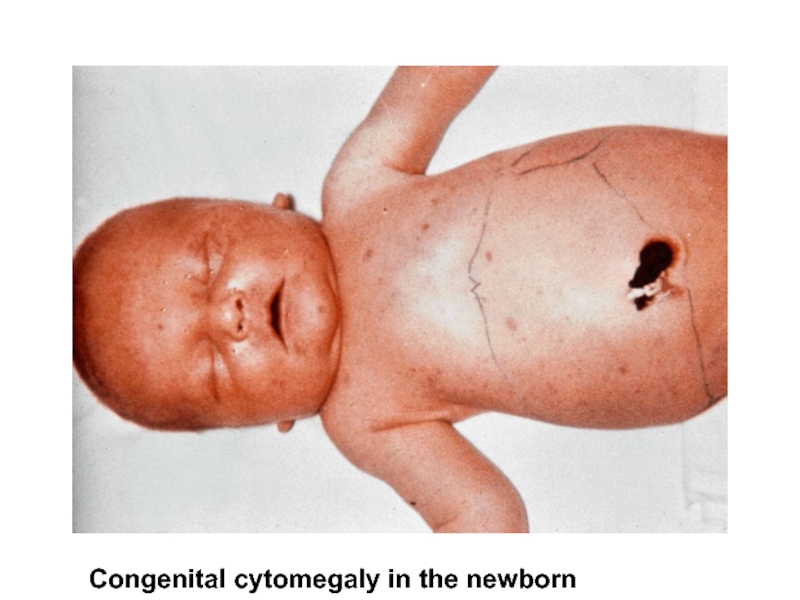
- 33. Congenital cytomegaly in the newborn
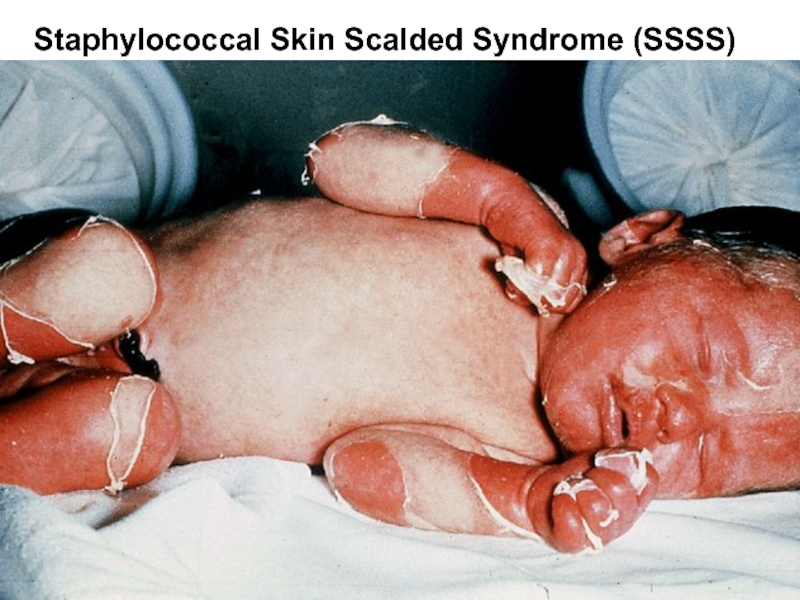
- 34. Staphylococcal Skin Scalded Syndrome (SSSS)
- 35. Twins XX,47(21+) and ХХ,46
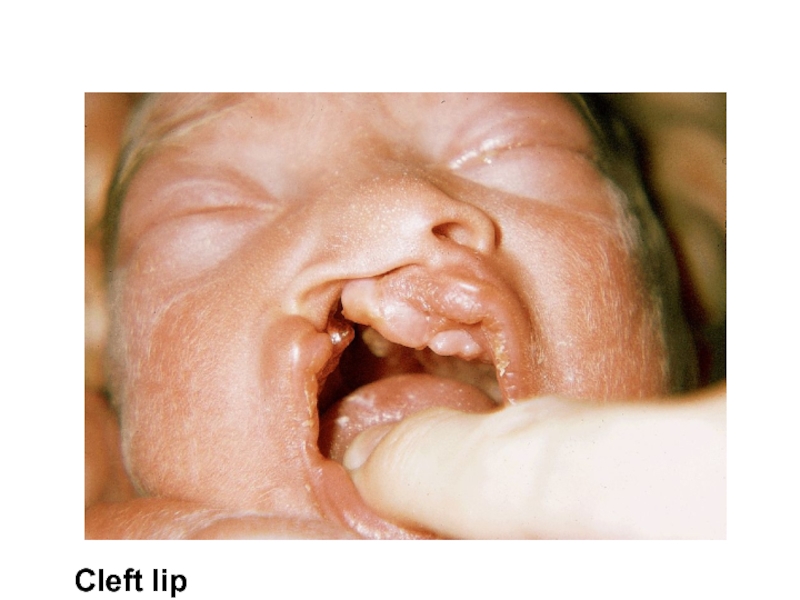
- 36. Cleft lip
- 37. The CNS condition of newborn
- 38. The deep long sleeping is common in
- 39. CNS. Neonetal responses (Newborn's Reflexes )
- 40. Oral responses. Suckling – it is
- 41. Spinal group of automatic responses in newborns
- 42. Grasping reflex. How does it work: If
- 43. Grasping reflex from the soles
- 44. Babinsky reflex. Stimulation the lateral sole from
- 45. "Crawling" reflex. How does it work?: If
- 46. Stepping reflex How it
- 47. Postural reflexes Tonic neck reflex
- 48. Transitory states in neonatal
- 49. The syndrom just right now been born
- 50. Transitory hyperventilation, gasps, apnoe. The
- 51. Common transitory neonatal states. Physiological (primary)
- 52. Physiological jaundice in newborns
- 53. So-called sexual crisis in newborns or mastopathy
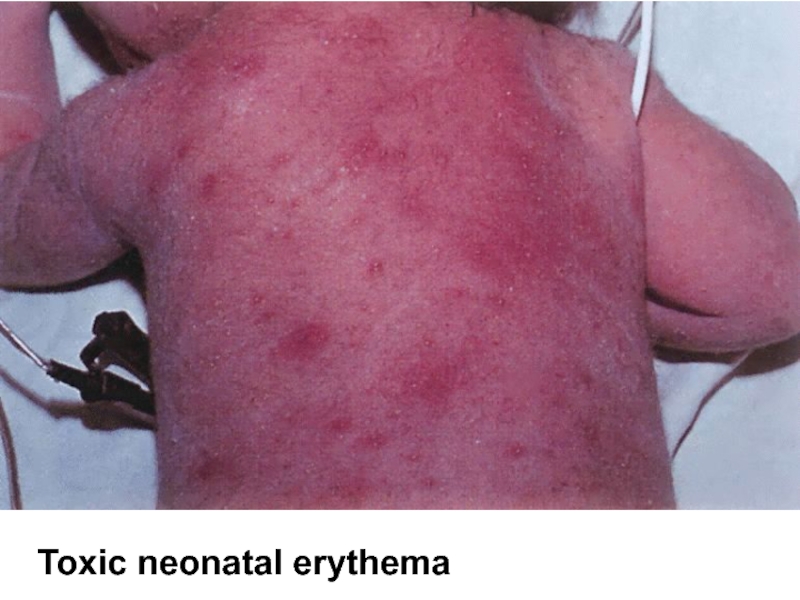
- 55. Toxic neonatal erythema
- 56. Neonatal primary care As a rule in
- 57. Suction of the mucus and fluids from
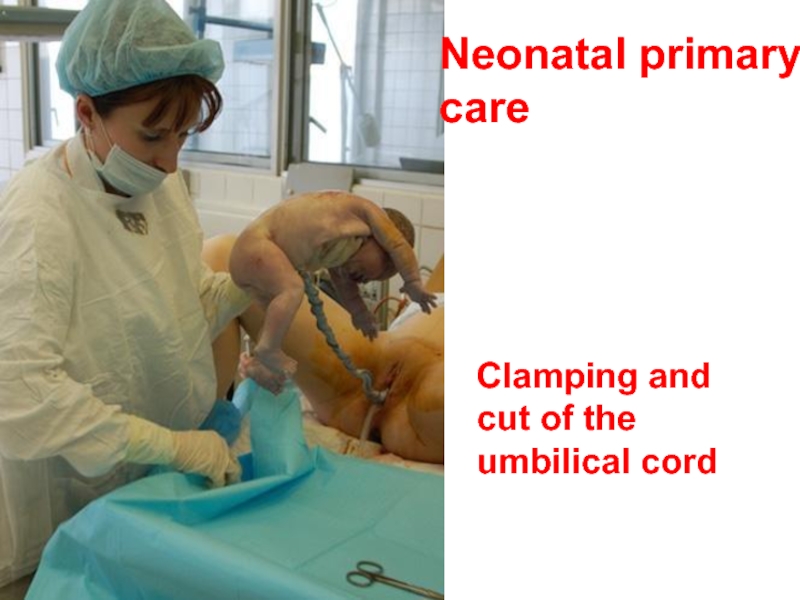
- 58. Neonatal primary care Clamping and cut of the umbilical cord
- 59. Clamping and cut of the
- 60. The Humid newborn is quickly coolling!
- 61. Gonoblenorrhea (gonococcal conjunctivitis) prevention
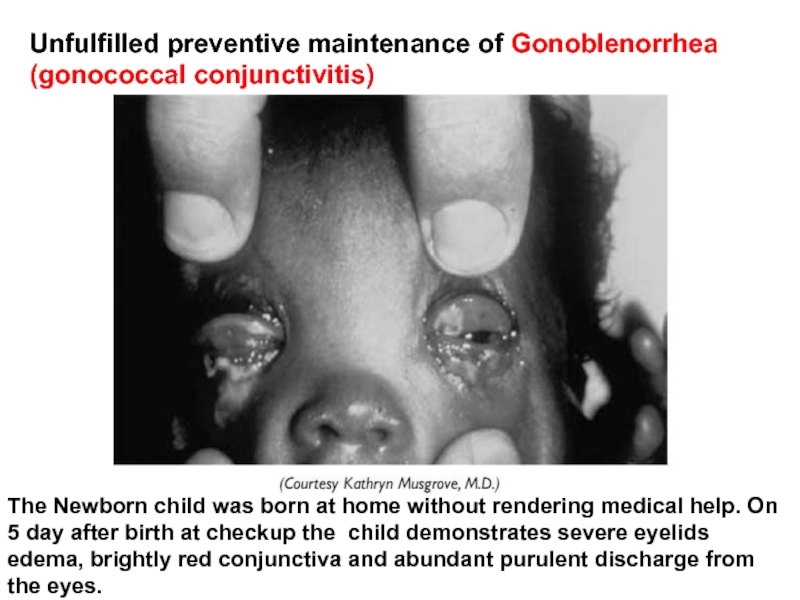
- 62. Unfulfilled preventive maintenance of Gonoblenorrhea (gonococcal conjunctivitis)
- 63. We Congratulate you. The first
- 64. Consolidation Haw long does the human gestation
Слайд 1Background of the lecture
Propedutics pediatrics
(Basic clinical pediatrics). Introduction
Childhood Periods
Extrauterinal
Labor, pediatric aspects
Newborns. First examination, CNS estimation. Common transitory states, Neonatal primary care
Слайд 6Study areas of the propedeutics of pediatrics
The physical, psychic and
The anatomical and physiological particularities of internal organs and their systems in children according the age. The Methods of the clinical study. The Semiotics the most important symptoms and syndroms in pediatrics.
Nursing (feeding) and common looking after
Emergency care in typical situations
Слайд 7The Practical physician in everyday work has to be alongside with
Слайд 9From the moment of the baby conception till adult condition achievement
Слайд 10The embrional period begins with the 1-st day after conception and
The fetogenesis begins since 9 weeks and ends approximately on 40-th week of the full pregnancy. In this period the differentiation and maturation of the body organ systems happen following by development, maturation and aging of placenta.
Intrauterinal period of the human development
Слайд 11The child born at 22 - 38 weeks of pregnancy and
Children been born after 42 weeks of pregnancy and later must be classified as a postterms.
Слайд 12During the first 16 weeks of pregnancy the fetal growing and
Within the following 16 weeks, (since 17 till 32 weeks of gestation) the rate of cellular multiplication begins gradually to decrease. At this time gradually the processes of the cellular size increasing take power. It is so called combined hyperplasia and hypertrophy phase of the intrauterinal development.
Within 7 weeks of gestation (since 33 till 40 weeks of pregnancy) in fetal development the cellular hypertrophy dominates setting fetal growth (fetal cellular hypertrophy phase). As a rule the fetus accumulates subcutaneous fat in consequence of the adipocytes hypertrophy.
Слайд 13Critical periods of intrauterinal development.
Forming of organs (organogenesis) in embryogenesis
Слайд 14Critical periods of intrauterinal development.
Now it is agreed to select
The First critical period is a time of the fertilized egg into the womb implantation. Its mistakes lead the embrio to death and spontaneous abortion.
The Second critical period can happen in time of placenta development, begins at 3-st week of pregnancy and lasts till 11-12 weeks of pregnancy.
The Third critical period corresponds to the time of internal organs systemogenesis. For all organs the proper sensitive periods exist. Some times the organogenesis does not finish with delivery and continues within the early childhood.
Слайд 15 Perinatal pediod of development includes the time since 22 weeks of
The neonatal and infantile mortality rates is closely connected with the happening perinatal abnormalities.
Слайд 17In spite of progress of humanity, the biological essence of person
Слайд 20Extrauterinal (postnatal) period of life
Labor
Neonatal (newborn, till 28 days)
Infants (1
Toddlers (1 – 3 yr)
Preschoolers (3 -7 yr)
Early school children (7 – 12 yr)
Late schoolers (12 – 18 yr)
Teens (10 – 18 yr)
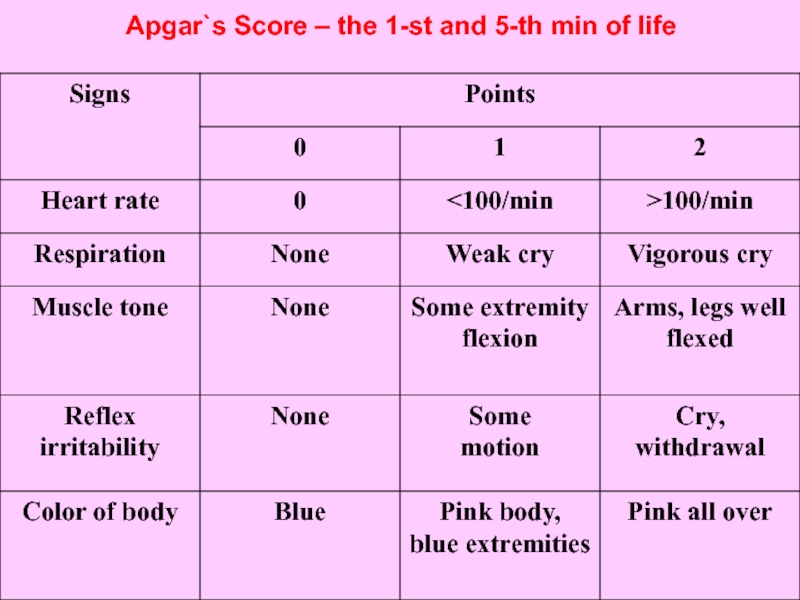
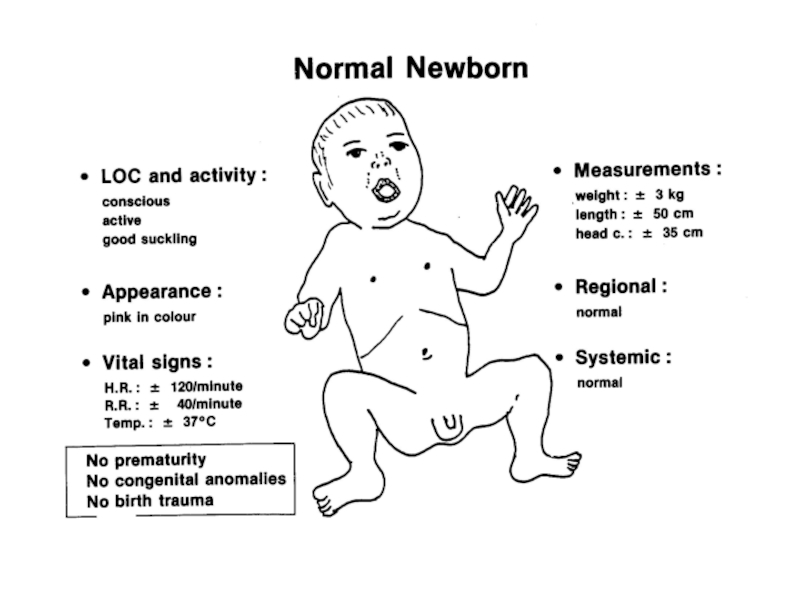
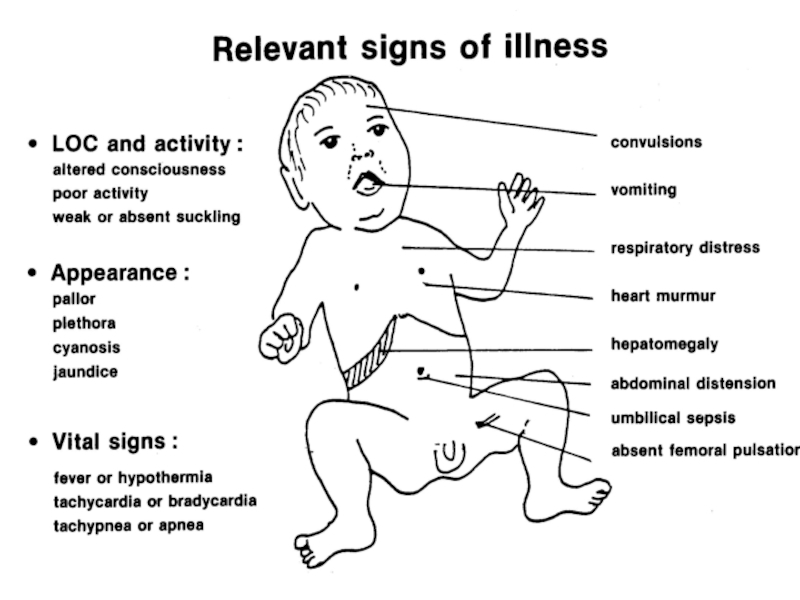
Слайд 22First examination of the newborn.
All children are examined using the Apgar
According to the assessment of their intensity appearance they are given 0, 1 or 2 points agreeably. Healthy new-born usually demonstrates 8 - 10 points in the first minute of his life and has 9 - 10 points by the Apgar score fifth minutes later.
Слайд 25Neonatal Asphyxia
Quick estimation using Аpgar score ables to diagnose one of
Asphyxia is an absence of natural breathing. The respiratory deficiency in asphyxia can be seen in the presence of heartbeats and must be revealed immediately after the labor. The development of asphyxia as a rule is a result of antenatal deep hypoxia which damages a breathing regulatory center and can be a result of the premature placenta detachment, umbilical cord rupture or its compression because of the tight knot etc.
Слайд 26Apgar score and asphyxia
7 – 6 points – mild asphyxia
5
3 - 1 – severe, life threatening
In asphyxic children with low index of Аpgar score on 1-th and 5-th minutes and especially after 2 hours of treatment it is necessary to expect the development of severe neurological disease like cerebral palsy.
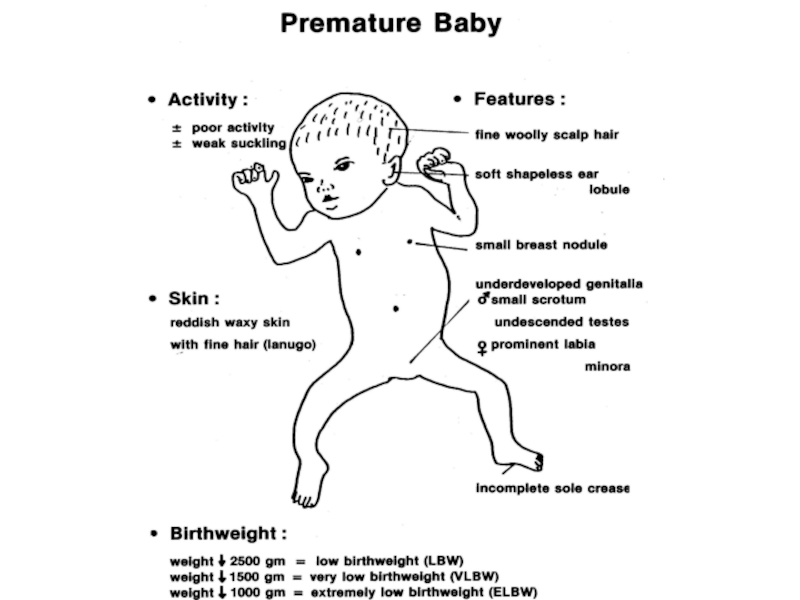
Слайд 29Preterm babies
There are 4 degrees of prematurity according to the
1st degree of prematurity is the most prognostic well. It is characterized by the term of antenatal development less than 34-38 weeks and by the weight of body from 2000 to 2500 grams.
2nd degree - 32 - 34 weeks, mass from 1500 to 2000 grams.
3rd degree - 30 - 32 weeks, mass from 1000 to 1500 grams.
4th degree is the most severe premature state with extremely low weight. The term of antenatal development lasts less than 30 weeks. The weight corresponds to 1 kg and less.
Слайд 31Fetal immaturity
If a child been born in term or nearly in
Слайд 37 The CNS condition of newborn is the prime estimation
Слайд 38The deep long sleeping is common in newborn and lasts usually
Слайд 40Oral responses.
Suckling – it is the most important reflex in
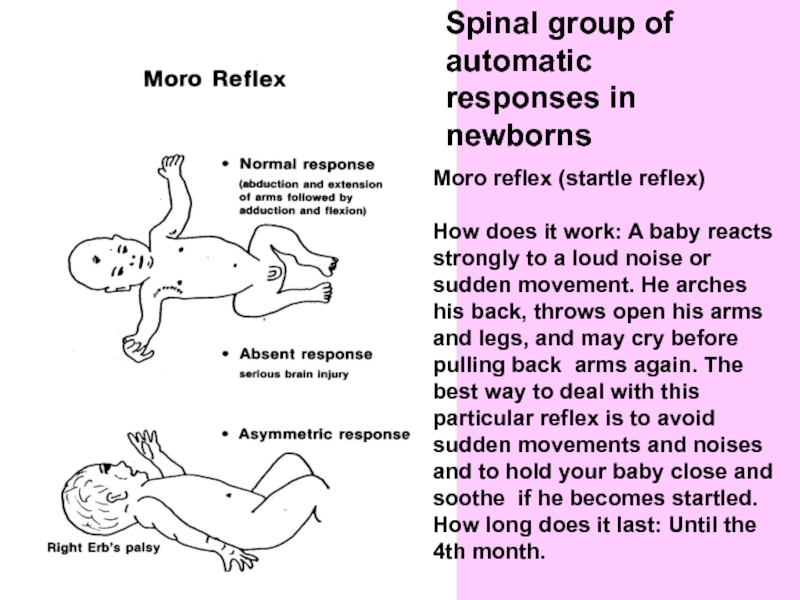
Слайд 41Spinal group of automatic responses in newborns
Moro reflex (startle reflex)
How
Слайд 42Grasping reflex. How does it work: If you touch your baby's
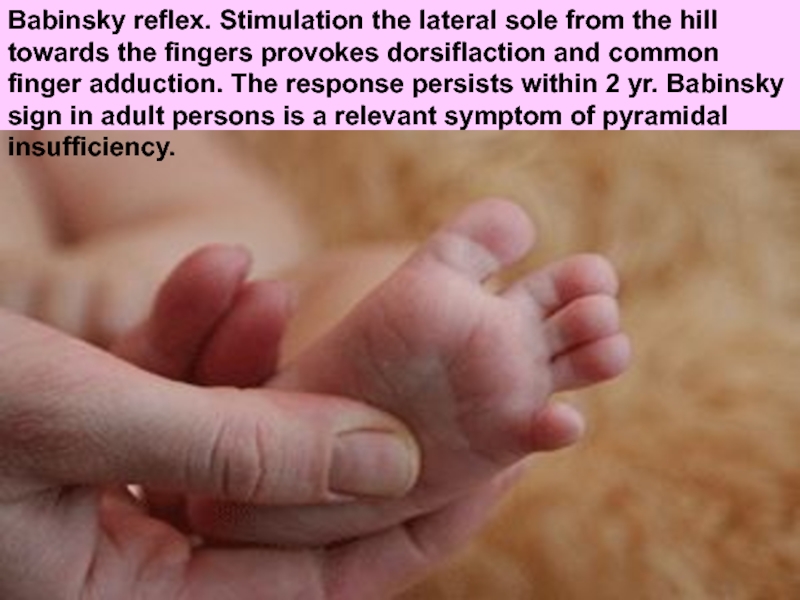
Слайд 44Babinsky reflex. Stimulation the lateral sole from the hill towards the
Слайд 45"Crawling" reflex. How does it work?: If you place a baby
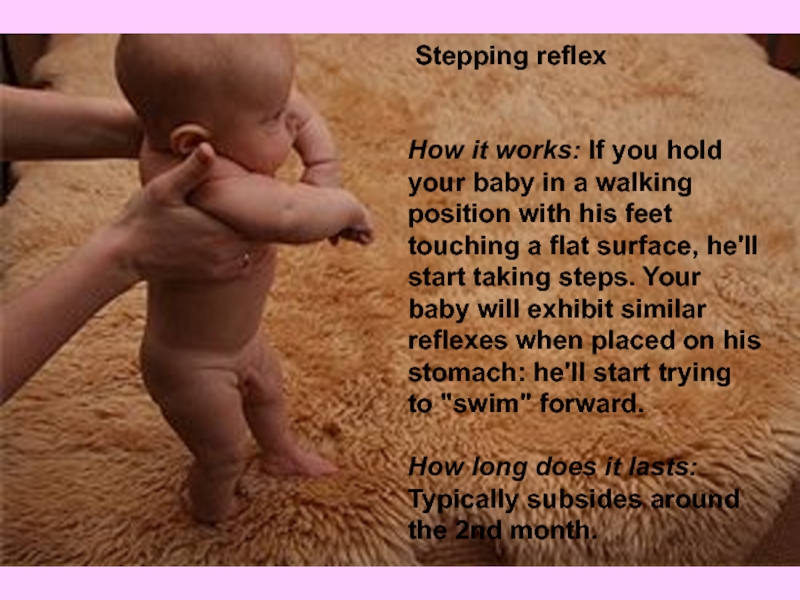
Слайд 46 Stepping reflex
How it works: If you hold your baby in
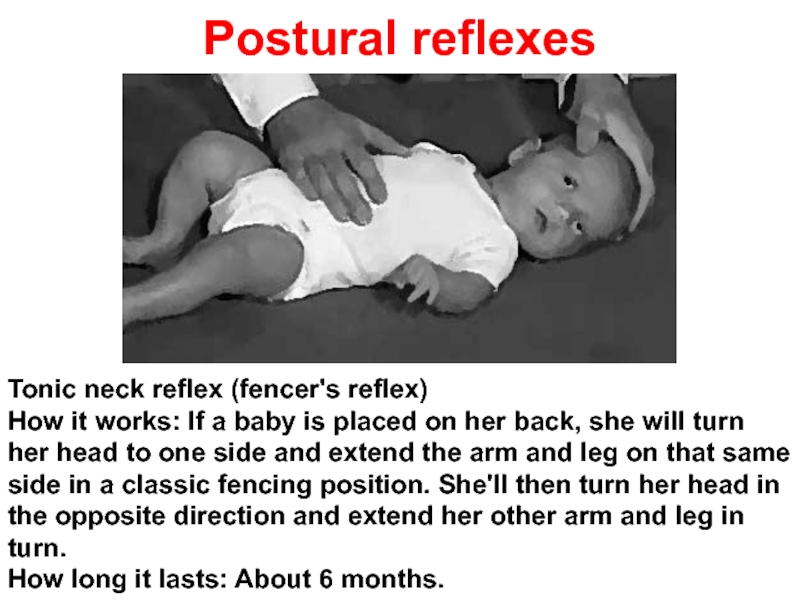
Слайд 47 Postural reflexes
Tonic neck reflex (fencer's reflex)
How it works: If
Слайд 48
Transitory states in neonatal period are reflecting their early
Слайд 49The syndrom just right now been born baby
It is featured
Слайд 50Transitory hyperventilation, gasps, apnoe.
The child after labor should catch first breath-in
The cases of long gasping and apneas lasted more 20 sec., accompanied by cyanosis (pathological apnea) are peculiar to the children with intracranial hemorrhages or pulmonary diseases.
Слайд 51Common transitory neonatal states.
Physiological (primary) body weight loss happens on
Physiological skin redness
Physiological intestinal disfunction
Uric acid crystalluria
Слайд 52Physiological jaundice in newborns
It appears at day 3
In any case the physiologic (benign) jaundice should be distinguished from the neonatal hemolytic disease which can be life threatening condition in affected baby.
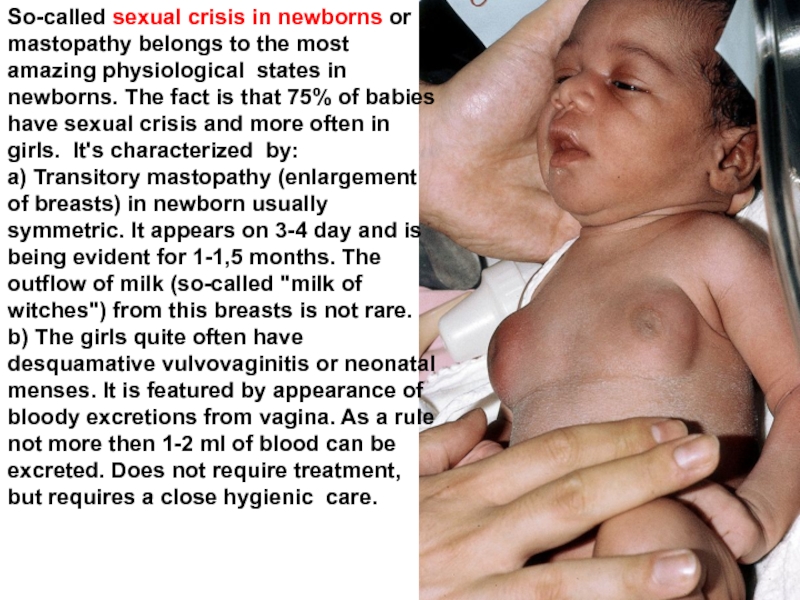
Слайд 53So-called sexual crisis in newborns or mastopathy belongs to the most
a) Transitory mastopathy (enlargement of breasts) in newborn usually symmetric. It appears on 3-4 day and is being evident for 1-1,5 months. The outflow of milk (so-called "milk of witches") from this breasts is not rare.
b) The girls quite often have desquamative vulvovaginitis or neonatal menses. It is featured by appearance of bloody excretions from vagina. As a rule not more then 1-2 ml of blood can be excreted. Does not require treatment, but requires a close hygienic care.
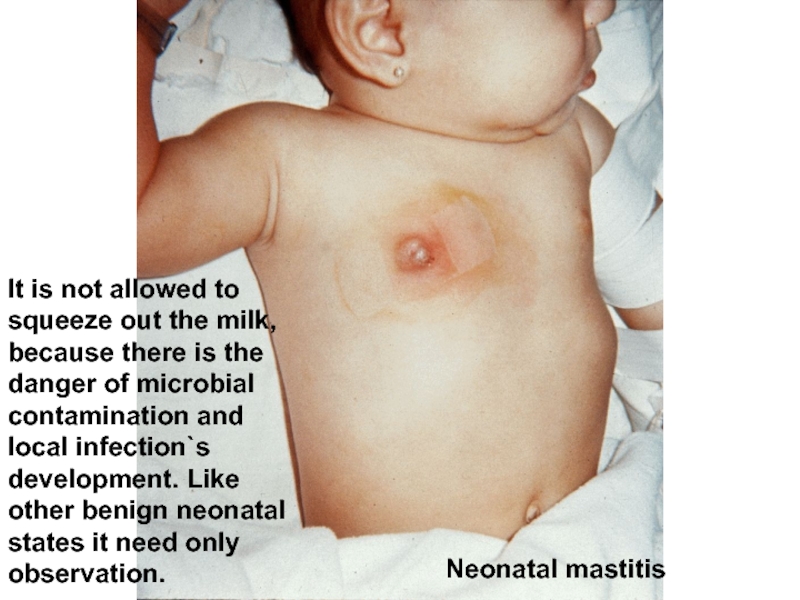
Слайд 54
Neonatal mastitis
It is not allowed to squeeze out the milk, because there is the danger of microbial contamination and local infection`s development. Like other benign neonatal states it need only observation.
Слайд 56Neonatal primary care
As a rule in 90% of all newborns the
But prime measures of care are executed in all cases.
Слайд 57Suction of the mucus and fluids from oral and nasal cavities.
This
Слайд 59
Clamping and cut of the umbilical cord.
The terms of clamping of
a) ordinary or traditional in 1,5 - 2 minutes after the labor in healthy full-term children, usually after the first inspiration and in 1 - 1,5 minutes after in children who has been born prematurely. In case of the late umbilical cord clamping, especially when a newborn is disposed below the cavity of uterus there is the danger of additional placental-fetal hemotransfusion. The surplus volume of blood gets to the fetus. Clinically it can be evident by blood concentration and its high viscosity, by total skin dark blue-red appearance (cyanosis), because of the heightened load on the pumping ability of heart. A physiological jaundice proceeds in children considerably longer.
b) Clamping of the umbilical cord after stopping of its pulsation in children which were born by cesarean section should be done into the practice in more late terms;
c) an umbilical cord cut should be put into the practice in early terms after the birth in condition of very low body weight, in women with fever and in condition when the hemolytic diseases is expected.
In such situation the early umbilical cord cut prevents the penetration of mother's pathogens to the child after the labor and relieves severity of hemolytic or infectious diseases of newborns.
Слайд 60The Humid newborn is quickly coolling!
The separated from the
To warm up!
Слайд 61Gonoblenorrhea (gonococcal conjunctivitis) prevention
It is established by the
Слайд 62Unfulfilled preventive maintenance of Gonoblenorrhea (gonococcal conjunctivitis)
The Newborn child was
Слайд 63 We Congratulate you. The first lecture on pediatrics is over! Apropos…
отработки лекций и индивидуальные консультации производятся на второй академической неделе с 15 до 17.30 по понедельникам в кабинете зав. кафедрой д.м.н., проф. Иванько Олегом Григорьевичем.
Слайд 64Consolidation
Haw long does the human gestation last?
A. 40 min
B. 40 h
C.
D. 40 weeks
E. 4 mo
The most important hereditary response in newborns is:
A. Crying
B. Crawling
C. Cramping
D. Suckling
E. Sleeping