- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Anticoagulant, Antiagregant Therapy презентация
Содержание
- 1. Anticoagulant, Antiagregant Therapy
- 2. Overview Indications Heparin/heparin like drugs and their complications Warfarin New anticoagulant drugs
- 3. Indications of Anticoagulant Therapy Treatment and Prevention
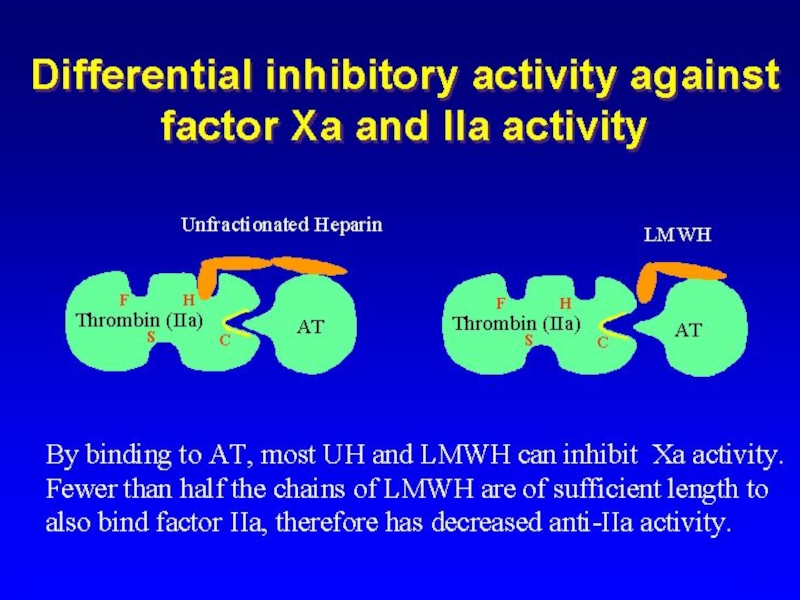
- 4. Standard Heparin Heterogenous mixture of polysaccharide chains
- 5. Enhances Antithrombin Activity
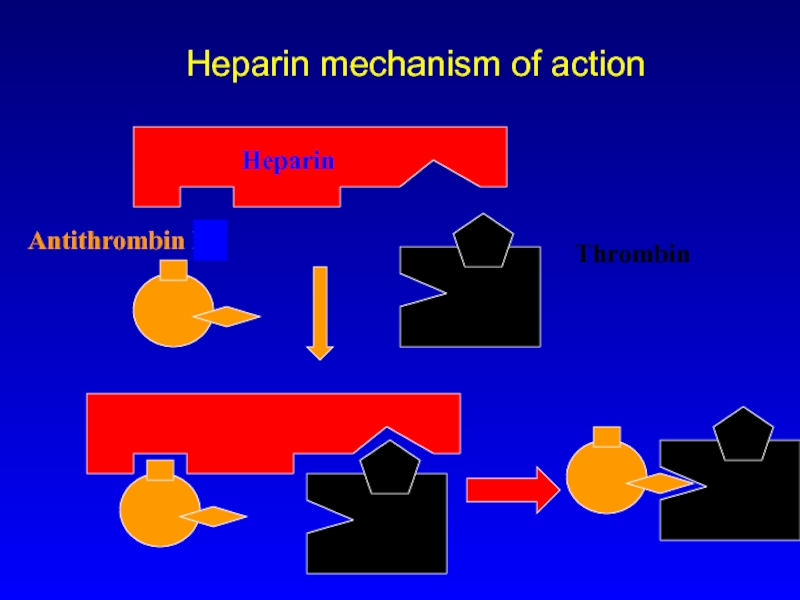
- 6. Heparin mechanism of action Heparin Antithrombin III Thrombin
- 7. Monitoring Heparin Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time (APTT)
- 8. Low Molecular Weight Heparin Changed management of
- 13. Complications of Heparin Haemorrhage Heparin-induced thrombocytopaenia (HIT) Osteoporosis (long-term only)
- 14. Vitamin K Synthesis of Functional Coagulation Factors
- 15. Warfarin Synthesis of Non Functional Coagulation Factors
- 17. Enhances Antithrombin Activity Warfarin
- 18. Warfarin: Major Adverse Effect—Haemorrhage Factors that may
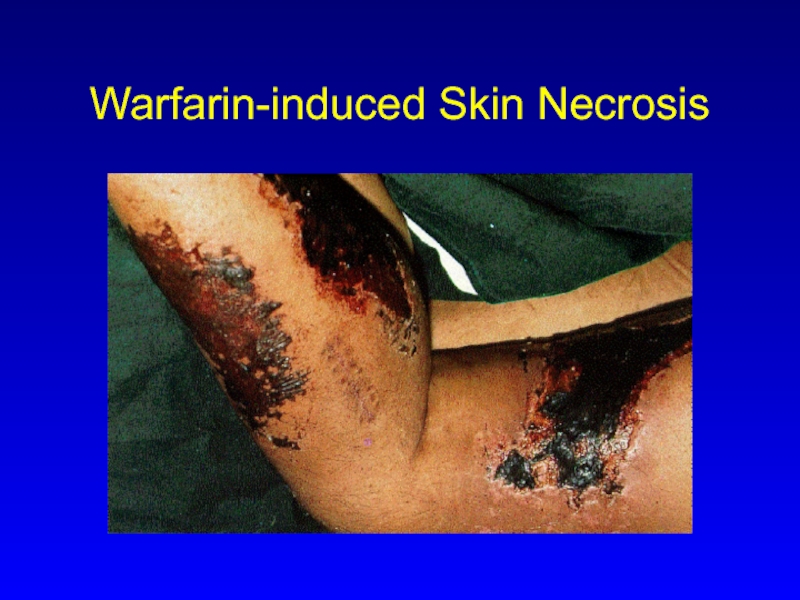
- 19. Warfarin-induced Skin Necrosis
- 20. Prothrombin Time (PT) Historically, a most reliable
- 21. Changing over from Heparin to Warfarin May
- 22. Warfarin: Dosing & Monitoring Start low
- 23. Relative Contraindications to Warfarin Therapy Situations where
- 24. Reversing action of warfarin Plasma Rapid but
- 25. New Anticoagulation Drugs Direct Thrombin Inhibitors PO:
- 26. Synthetic Pentasaccharide E.g Fondaparinux (Arixtra®) Synthetic, single
- 27. Dabigatran (Pradaxa®) Two doses available. Twice
- 28. Rivaroxaban (Xarelto®); Apixaban (Eliquis®) Once/ twice daily
- 29. Enhances Antithrombin Activity Dabigatran Rivaroxaban Apixaban Edoxaban
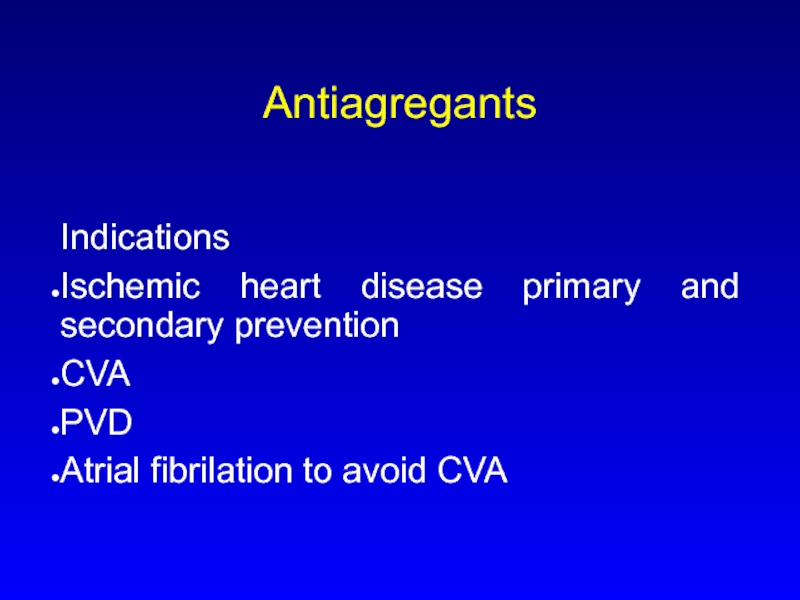
- 30. Antiagregants Indications Ischemic heart disease primary and
- 31. Aspirin COX-2 inhibitor side effects: gastritis, gastric ulcer Allergy Thrombocytopenia
- 32. Clopidrogel (Plavix®) AD receptor inhibitor Side effects: Bleeding Thrombocytopenia allergy
- 33. New antiplatelet agents AD receptor inhibitor: Prasugrel Ticagrelor Elinogrel
Слайд 1Anticoagulant, Antiagregant Therapy
Dr Inna Tzoran
Thrombosis and Hemostasis Unit
Rambam Madical Center
Слайд 2Overview
Indications
Heparin/heparin like drugs and their complications
Warfarin
New anticoagulant drugs
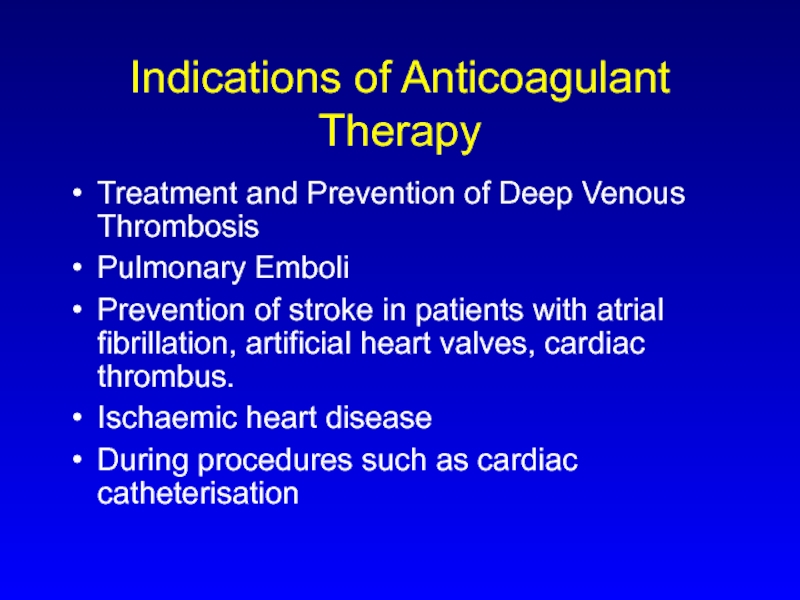
Слайд 3Indications of Anticoagulant Therapy
Treatment and Prevention of Deep Venous Thrombosis
Pulmonary Emboli
Prevention
of stroke in patients with atrial fibrillation, artificial heart valves, cardiac thrombus.
Ischaemic heart disease
During procedures such as cardiac catheterisation
Ischaemic heart disease
During procedures such as cardiac catheterisation
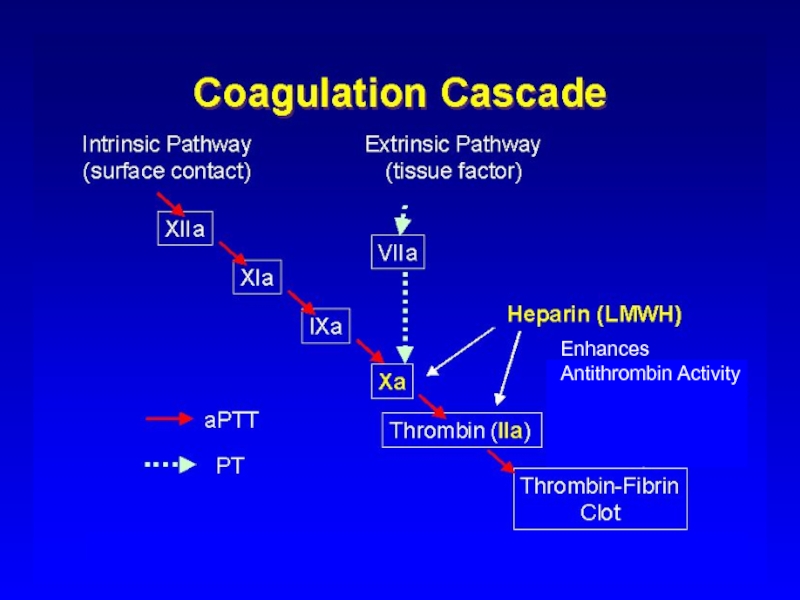
Слайд 4Standard Heparin
Heterogenous mixture of polysaccharide chains
MW 3k to 30k
Active in
vitro and in vivo
Administration - parenteral- Do not inject IM - only IV or deep s.c.
Half-life 1 - 2 hrs - monitor APTT
Adverse effect - haemorrhage - antidote - protamine sulphate
Administration - parenteral- Do not inject IM - only IV or deep s.c.
Half-life 1 - 2 hrs - monitor APTT
Adverse effect - haemorrhage - antidote - protamine sulphate
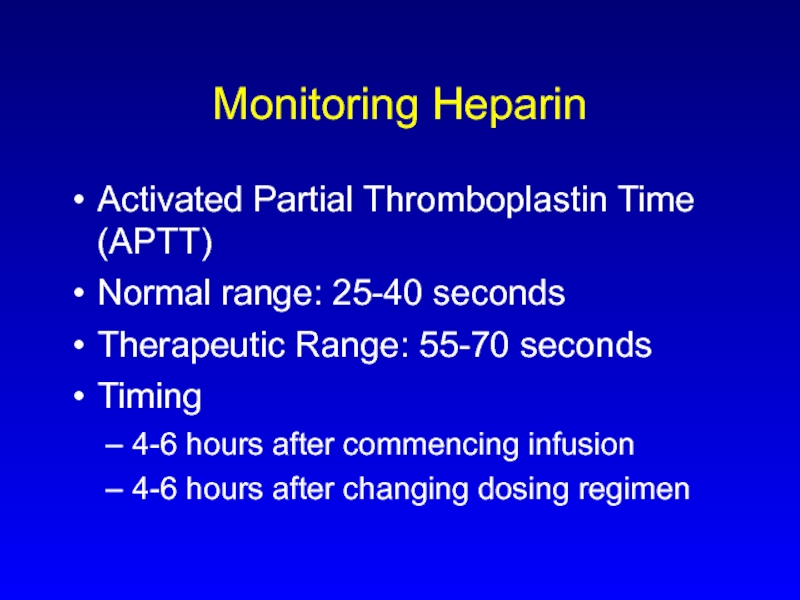
Слайд 7Monitoring Heparin
Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time (APTT)
Normal range: 25-40 seconds
Therapeutic Range: 55-70 seconds
Timing
4-6 hours after commencing infusion
4-6 hours after changing dosing regimen
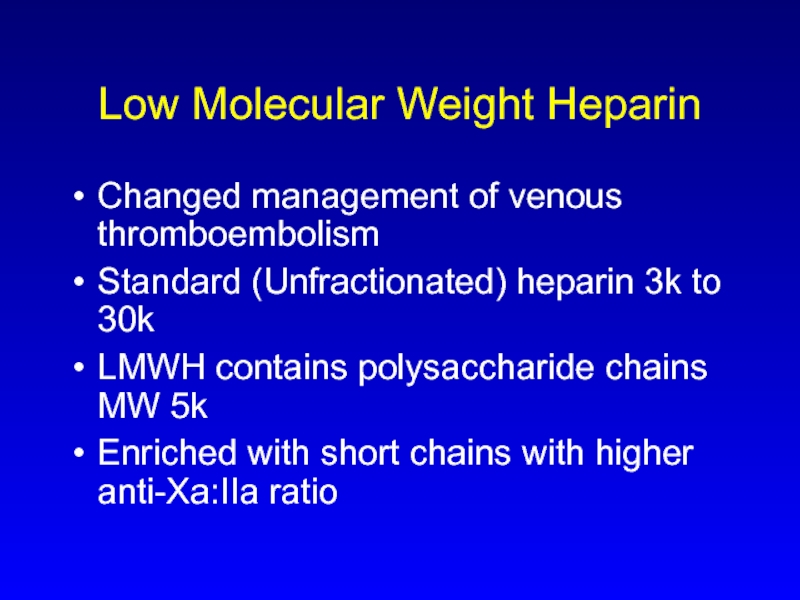
Слайд 8Low Molecular Weight Heparin
Changed management of venous thromboembolism
Standard (Unfractionated) heparin 3k
to 30k
LMWH contains polysaccharide chains MW 5k
Enriched with short chains with higher anti-Xa:IIa ratio
LMWH contains polysaccharide chains MW 5k
Enriched with short chains with higher anti-Xa:IIa ratio
Слайд 13Complications of Heparin
Haemorrhage
Heparin-induced thrombocytopaenia (HIT)
Osteoporosis (long-term only)
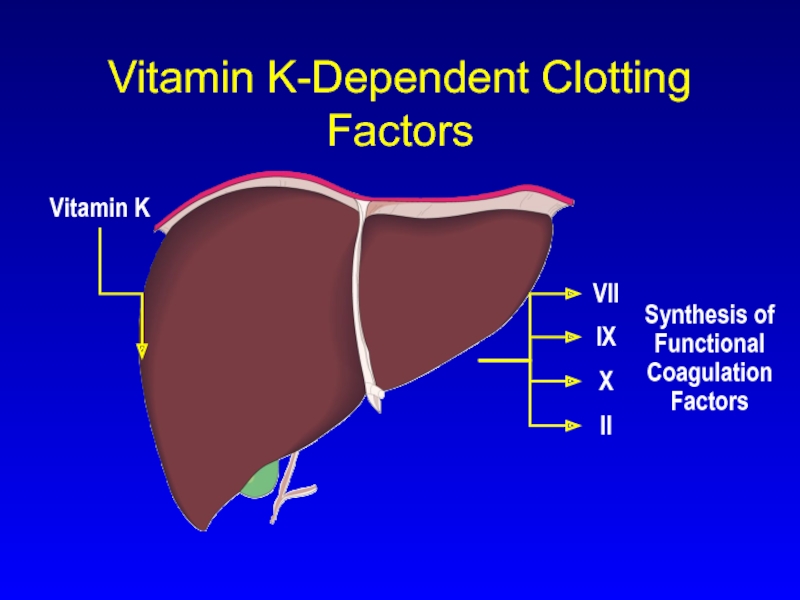
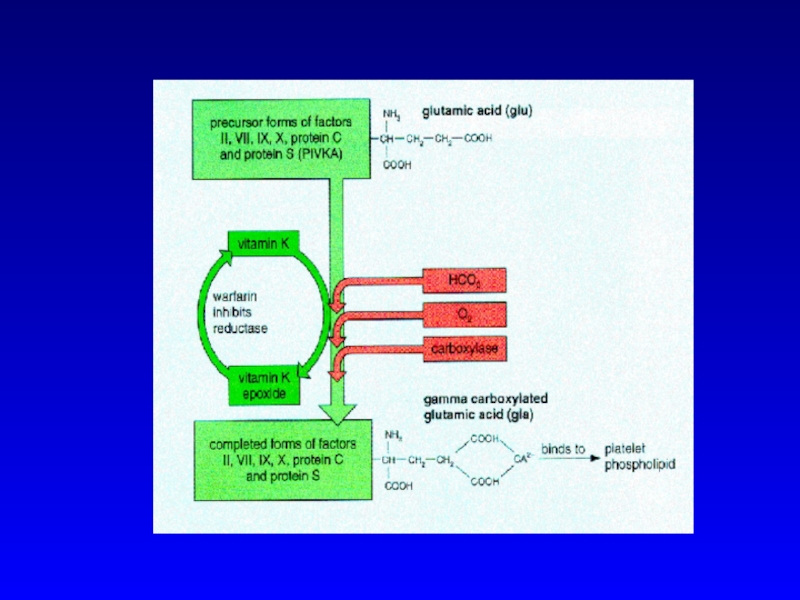
Слайд 14Vitamin K
Synthesis of Functional Coagulation Factors
VII
IX
X
II
Vitamin K-Dependent Clotting Factors
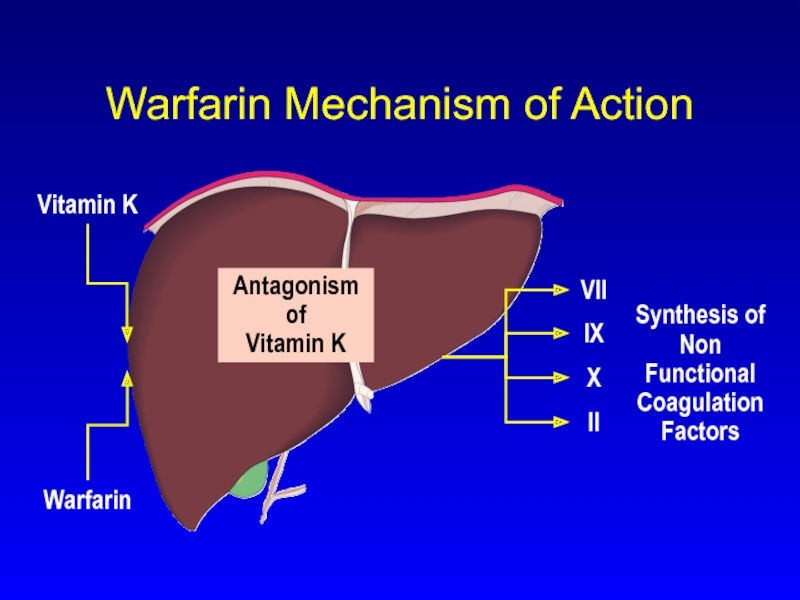
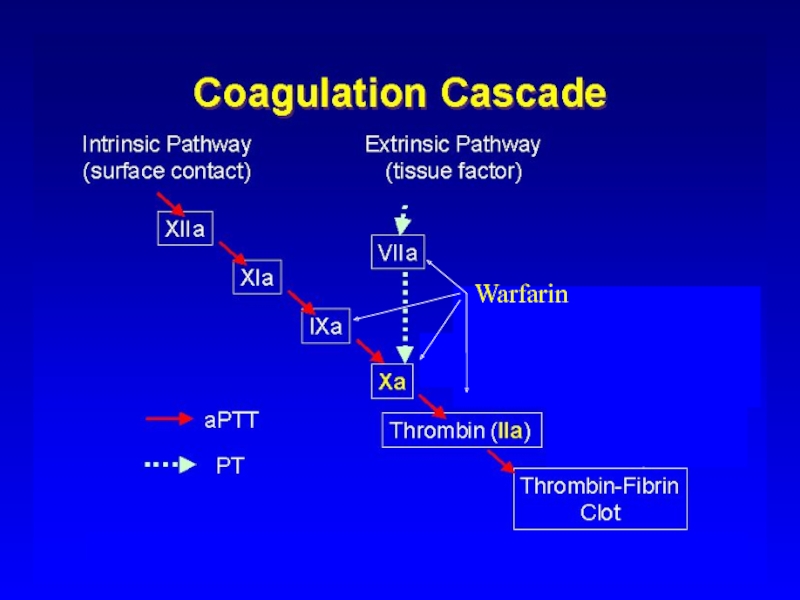
Слайд 15Warfarin
Synthesis of Non Functional Coagulation Factors
Antagonism
of
Vitamin K
Warfarin Mechanism of Action
Vitamin K
VII
IX
X
II
Слайд 18Warfarin: Major Adverse Effect—Haemorrhage
Factors that may influence bleeding risk:
Intensity of anticoagulation
Concomitant
clinical disorders
Concomitant use of other medications
Quality of management
Concomitant use of other medications
Quality of management
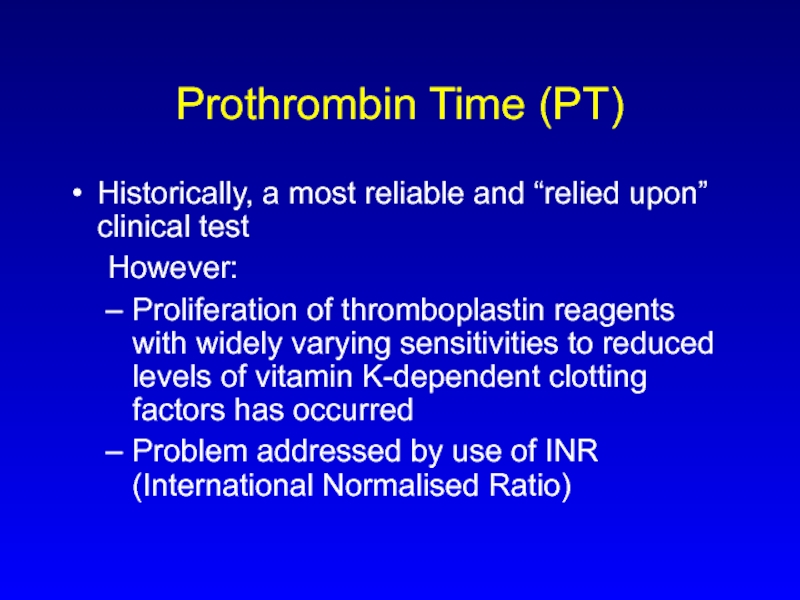
Слайд 20Prothrombin Time (PT)
Historically, a most reliable and “relied upon” clinical test
However:
Proliferation
of thromboplastin reagents with widely varying sensitivities to reduced levels of vitamin K-dependent clotting factors has occurred
Problem addressed by use of INR (International Normalised Ratio)
Problem addressed by use of INR (International Normalised Ratio)
Слайд 21Changing over from Heparin to Warfarin
May begin concomitantly with heparin therapy
Heparin
should be continued until target INR for two days
When INR reaches desired therapeutic range, discontinue heparin
When INR reaches desired therapeutic range, discontinue heparin
Слайд 22
Warfarin: Dosing & Monitoring
Start low
Initiate 5 mg daily
Educate patient
Stabilise
Titrate to appropriate
INR
Monitor INR frequently (daily then weekly)
Adjust as necessary
Monitor INR regularly (every 1–2 weeks) and adjust
Monitor INR frequently (daily then weekly)
Adjust as necessary
Monitor INR regularly (every 1–2 weeks) and adjust
Слайд 23Relative Contraindications to Warfarin Therapy
Situations where the risk of hemorrhage is
greater than the potential clinical benefits of therapy
Uncontrolled alcohol/drug abuse
Unsupervised dementia/psychosis
Uncontrolled alcohol/drug abuse
Unsupervised dementia/psychosis
Слайд 24Reversing action of warfarin
Plasma
Rapid but short-lasting
Vitamin K
Not rapid, but lasts 1-2
weeks. Do not use if wishing to restart warfarin within next week.
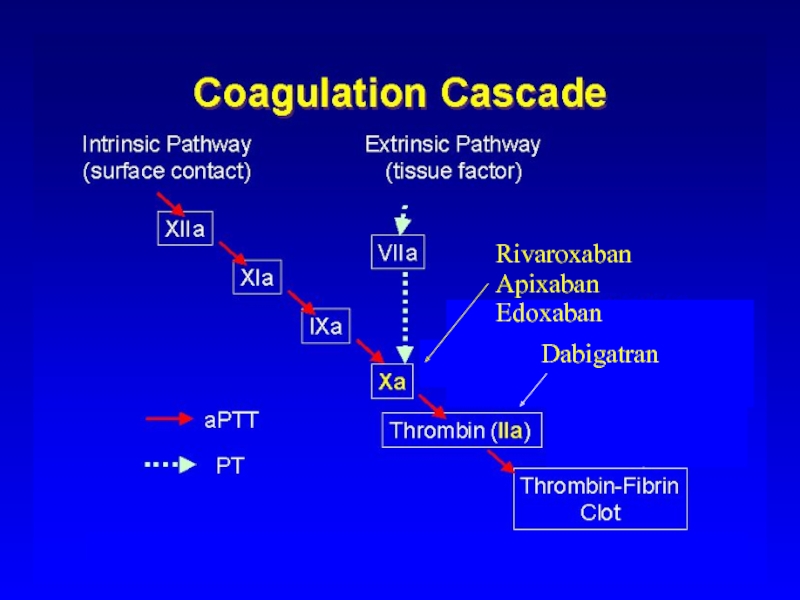
Слайд 25New Anticoagulation Drugs
Direct Thrombin Inhibitors
PO: Dabigatran
IV: hirudin, bivalirudin, and argatroban
Synthetic pentasaccharide
Acivated
Protein C
Tissue Factor Pathway Inhibitor (TFPI)
Factor Xa inhibitor PO: rivaroxaban, apixaban, edoxaban
Tissue Factor Pathway Inhibitor (TFPI)
Factor Xa inhibitor PO: rivaroxaban, apixaban, edoxaban
Слайд 26Synthetic Pentasaccharide
E.g Fondaparinux (Arixtra®)
Synthetic, single molecular entity
Targets Factor Xa
Does not cause
thrombocytopenia
Shown DVT prevention during orthopedic procedures.
Better than LMWH in ischaemic heart disease
Shown DVT prevention during orthopedic procedures.
Better than LMWH in ischaemic heart disease
Слайд 27Dabigatran (Pradaxa®)
Two doses available.
Twice daily treatment.
No monitoring needed.
Recent studies showed
it as good as or even superior to warfarin in atrial fibrillation and VTE treatment.
Слайд 28Rivaroxaban (Xarelto®); Apixaban (Eliquis®)
Once/ twice daily
No dose monitoring needed.
As good as
warfarin in efficacy and superior on safety in AF and VTE treatment