skin and venereal diseases
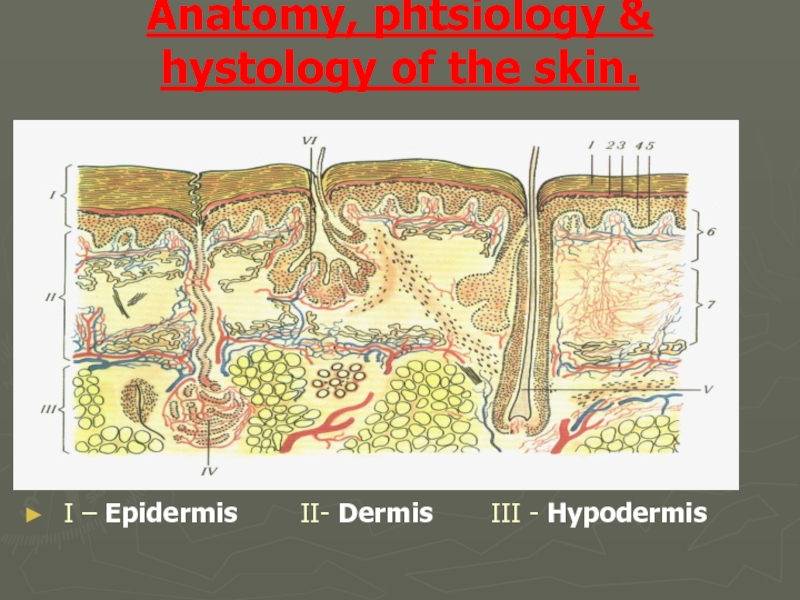
Anatomy, phtsiology & hystology of the skin.
Primary & secondary morphological elements
Zaporozhye 2016
- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Anatomy, phtsiology & hystology of the skin презентация
Содержание
- 1. Anatomy, phtsiology & hystology of the skin
- 2. The Skin Hypodermis (subcutaneous fatty
- 3. Anatomy, phtsiology & hystology of the skin.
- 4. Epidermis Stratum basale - Germinatinne layer Stratum
- 5. Epidermis 1.Stratum basale (germinative layer) Keratinoblastis (1
- 6. Epidermis 2. Stratum spinosum (pricle-cell layer) Dendritic
- 7. Epidermis 4. Stratum lucidum (lucid layer)
- 8. Dermis (the true skin)
- 9. Dermis (the true skin) True homogeneous
- 10. Dermis (the true skin) Cells structure
- 11. Protective (barrier) functions of the skin
- 12. Protective (barrier) functions of the skin
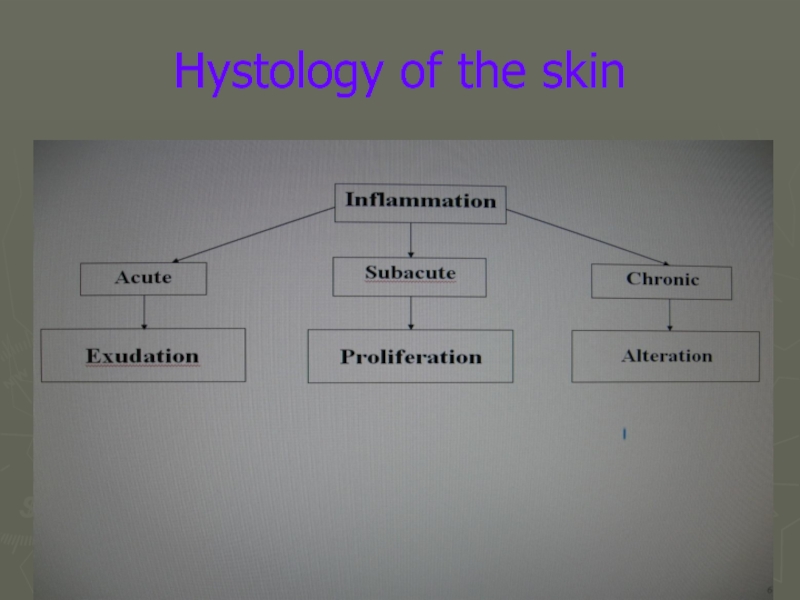
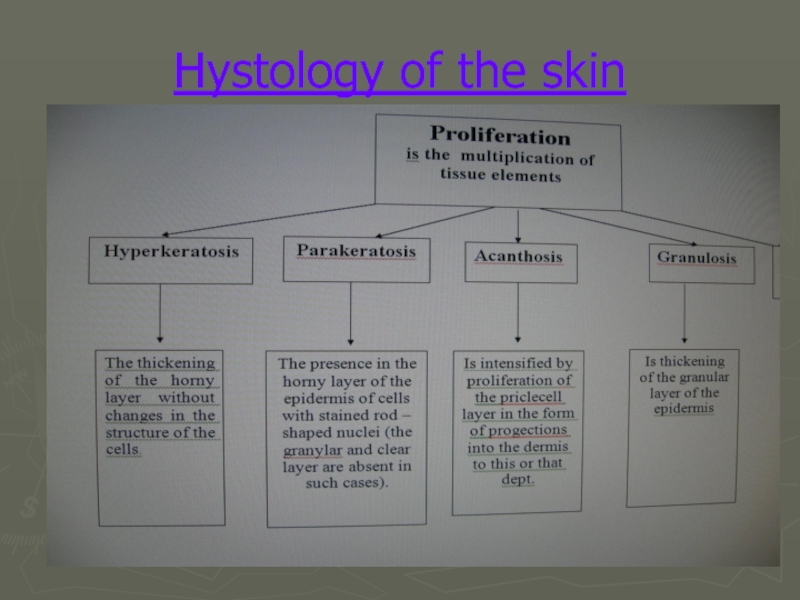
- 13. Hystology of the skin
- 14. Hystology of the skin
- 15. Hystology of the skin
- 16. Hystology of the skin
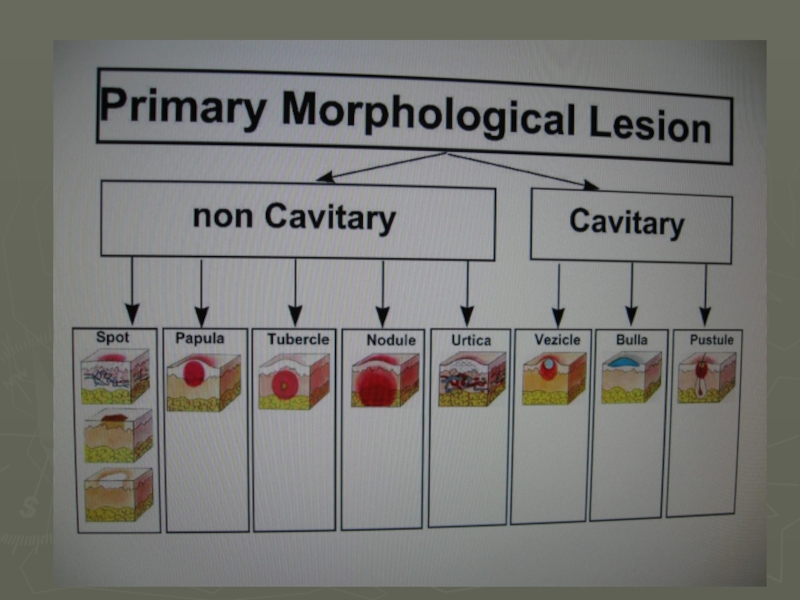
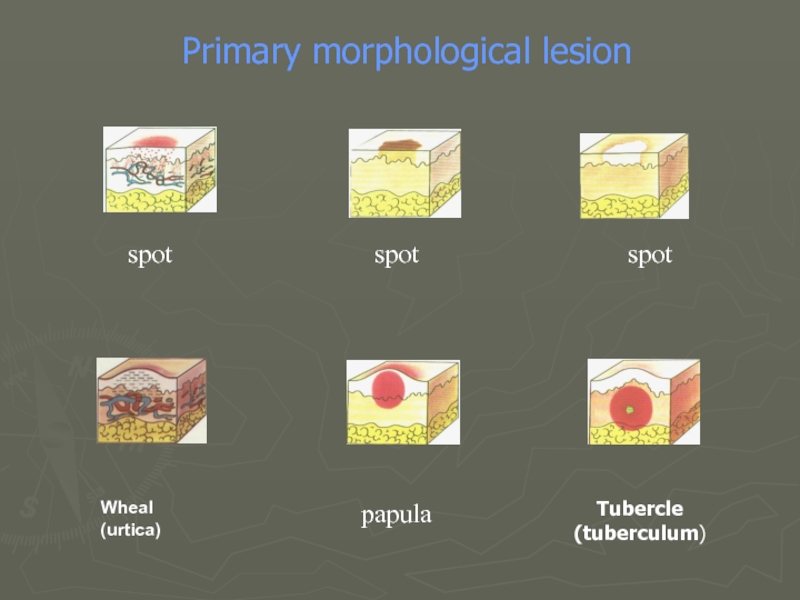
- 19. spot spot spot Tubercle (tuberculum) Wheal (urtica) Primary morphological lesion papula
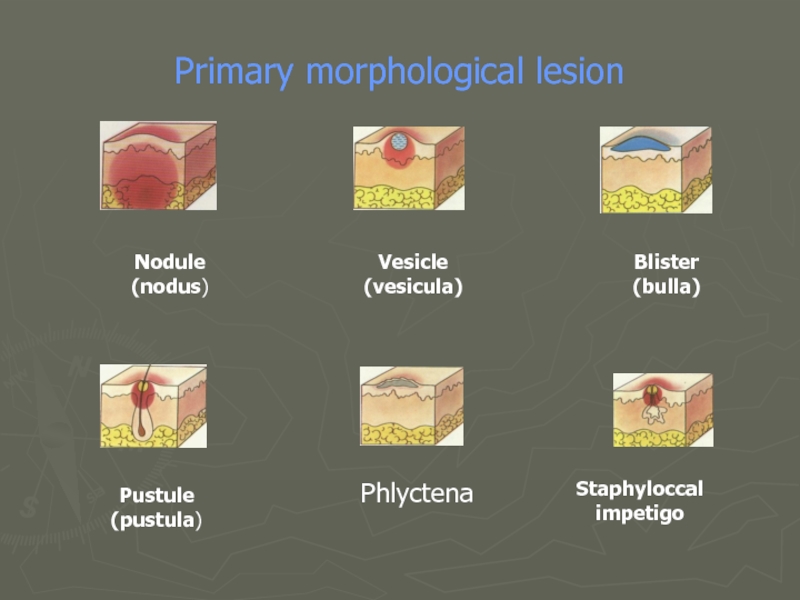
- 20. Primary morphological lesion Pustule (pustula) Phlyctena Staphyloccal impetigo Nodule (nodus) Vesicle (vesicula) Blister (bulla)
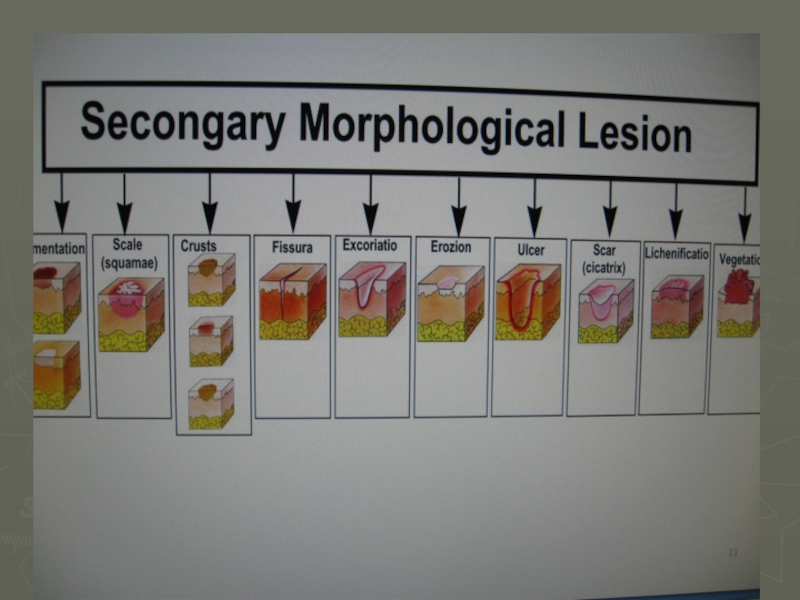
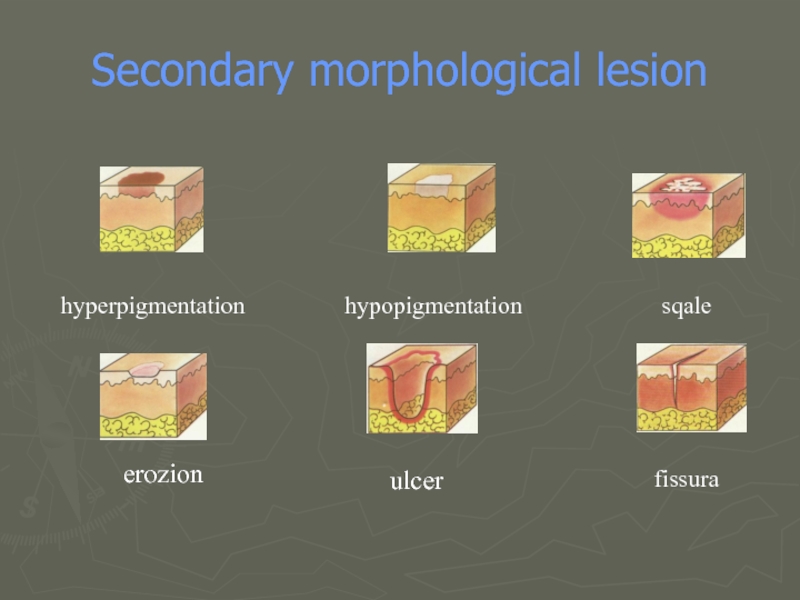
- 21. Secondary morphological lesion hyperpigmentation hypopigmentation sqale erozion ulcer fissura
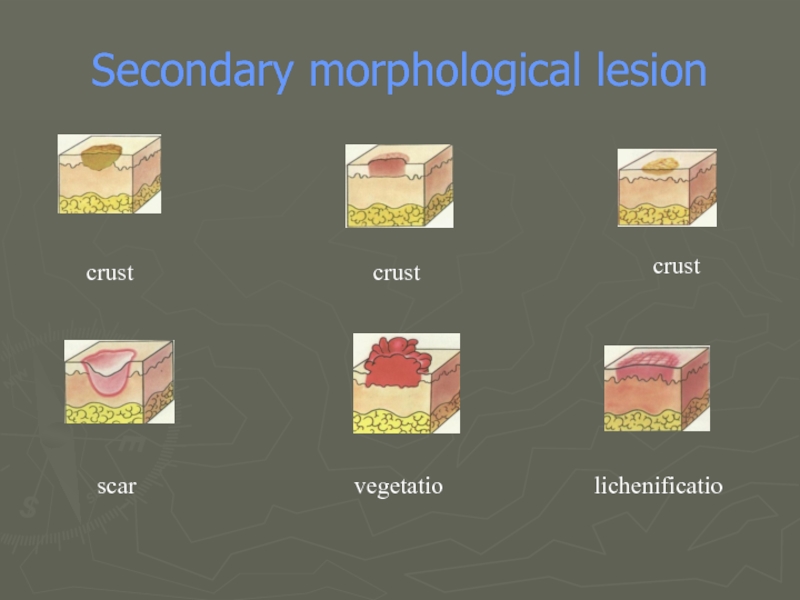
- 22. Secondary morphological lesion crust crust crust scar vegetatio lichenificatio
- 23. Thank you for attention
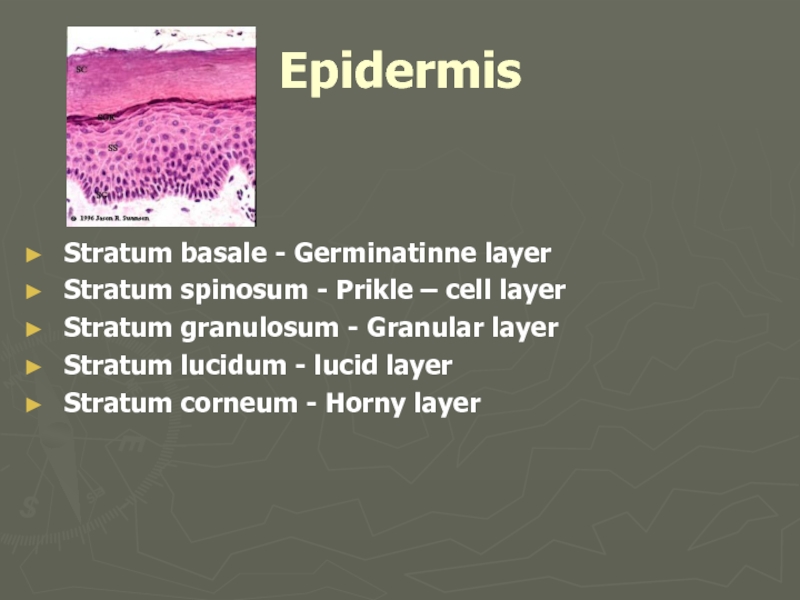
Слайд 4Epidermis
Stratum basale - Germinatinne layer
Stratum spinosum - Prikle – cell layer
Stratum
granulosum - Granular layer
Stratum lucidum - lucid layer
Stratum corneum - Horny layer
Stratum lucidum - lucid layer
Stratum corneum - Horny layer
Слайд 5Epidermis
1.Stratum basale (germinative layer)
Keratinoblastis (1 layer, like a polisade).
Melanoblastis (their ratio
is 1:11 to keratinoblastis).
young cells, are devided by mitosis, and form all the structures of epidermis.
Melanin is formed in the melanoblastis and protects the skin from ultraviolet rays.
young cells, are devided by mitosis, and form all the structures of epidermis.
Melanin is formed in the melanoblastis and protects the skin from ultraviolet rays.
Слайд 6Epidermis
2. Stratum spinosum (pricle-cell layer)
Dendritic epidermocytis (5-7 layers)
Langhan’s cells
Hrenstayin’s cells
3. Stratum
granulosum (granular layer)
1-2 layers of elongated cells. There are keratohyalinis granuls in the protoplasm of these cells.
1-2 layers of elongated cells. There are keratohyalinis granuls in the protoplasm of these cells.
Слайд 7Epidermis
4. Stratum lucidum (lucid layer)
These cells contain eleidin. Str. lucidum
contains glycogens, lipoids, fatty acids.
5. Stratum corneum (horny layer)
It is composed of fine, anuclear keratinised elongated cells containing keratin.
5. Stratum corneum (horny layer)
It is composed of fine, anuclear keratinised elongated cells containing keratin.
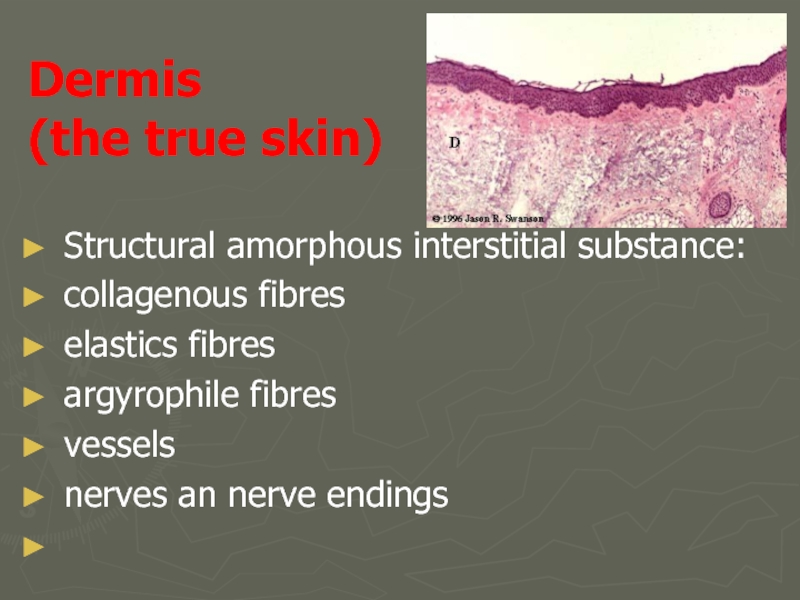
Слайд 8Dermis
(the true skin)
Structural amorphous interstitial substance:
collagenous fibres
elastics fibres
argyrophile fibres
vessels
nerves an
nerve endings
Слайд 9Dermis
(the true skin)
True homogeneous membrane
Lipoids
Mucopolysaccharides (mainly, hyaluronic and chondroitin
– sulfuric acids)
Albuminis
Water
Albuminis
Water
Слайд 10Dermis
(the true skin)
Cells structure
Fibroblasts
Histiocytes
Lymphocytes
Mast cells
Plasma cells
Melanophages
Epithelial appendages of the skin
Слайд 11Protective (barrier) functions of the skin
Protects the organism from the
damaging effect of sun rays
Physiology desquamation
Protect the underlying tissue from drying
Homogeneous tightness of substanal protects from mechanical effects (blows, friction, compression)
Physiology desquamation
Protect the underlying tissue from drying
Homogeneous tightness of substanal protects from mechanical effects (blows, friction, compression)
Слайд 12Protective (barrier) functions of the skin
An acid (pH5.0-6,0) water-lipid mantle
which attenuatus or neutralizis the damaging effect of chemical substances.
Bactericidal properties of sweat (lisocini) and sebum (squaleni)
Immynological function. Skin associated limphoid tissue. Salt
Resistance to electric current
Bactericidal properties of sweat (lisocini) and sebum (squaleni)
Immynological function. Skin associated limphoid tissue. Salt
Resistance to electric current