- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Acute myeloid leukemia презентация
Содержание
- 1. Acute myeloid leukemia
- 2. What is an Acute Myeloid Leukemia ?
- 3. ETIOLOGY Environment: irradiation, chemotherapeutic agents, organic
- 5. AML Aggressive disease with an acute
- 6. Leukemia
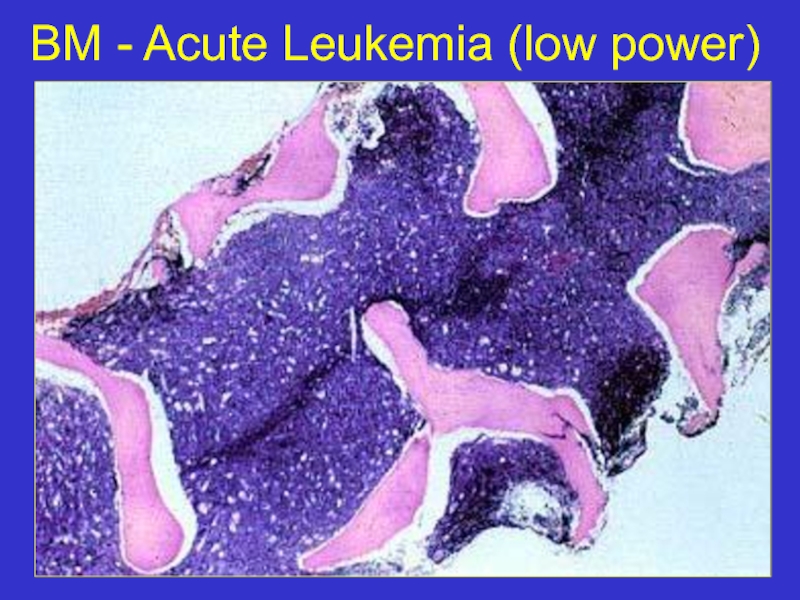
- 7. BM - Acute Leukemia (low power)
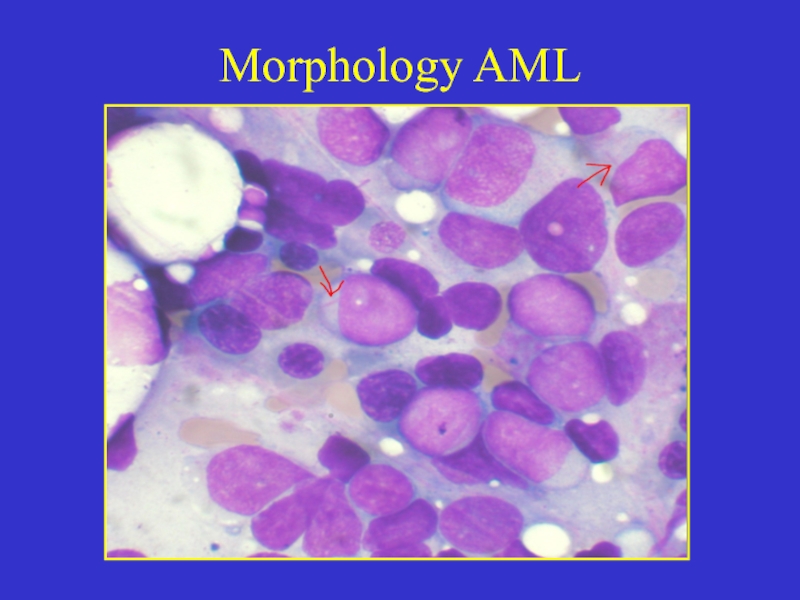
- 8. Morphology AML
- 9. Pathophysiology Radiation
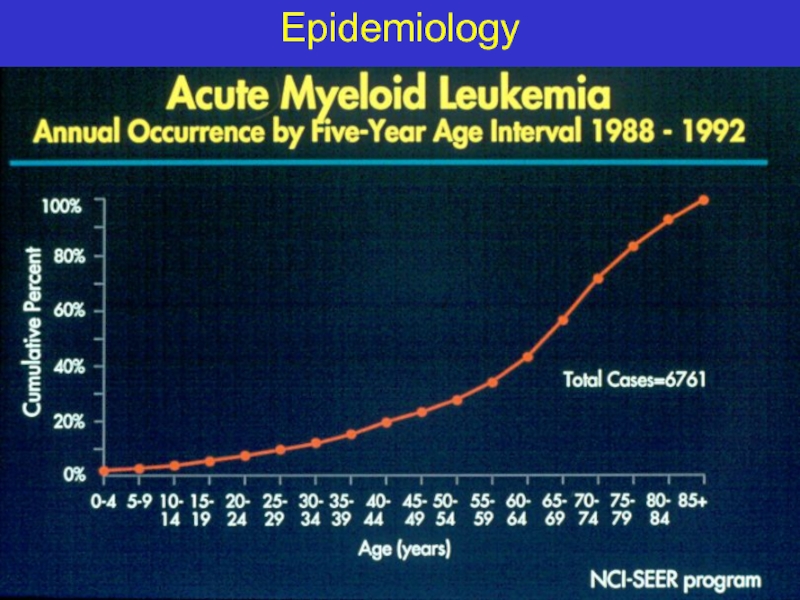
- 10. Epidemiology
- 11. Predisposing factors Environmental
- 12. Clinical symptoms of Acute Leukemia Bone marrow
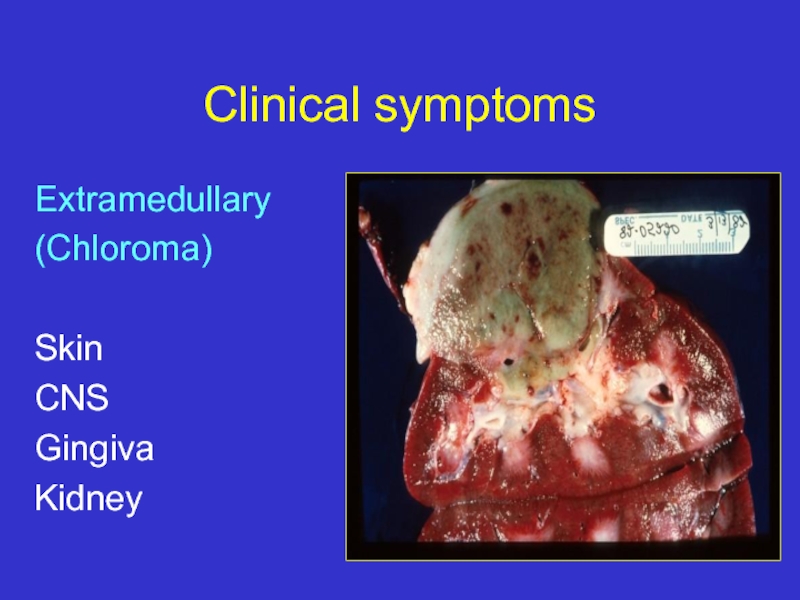
- 13. Clinical symptoms Extramedullary (Chloroma)
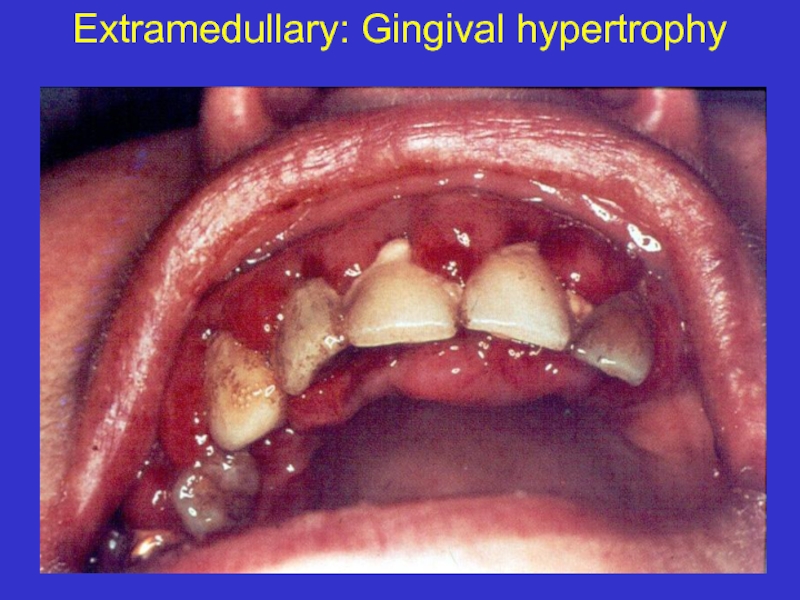
- 14. Extramedullary: Gingival hypertrophy
- 15. Clinical symptomes DIC
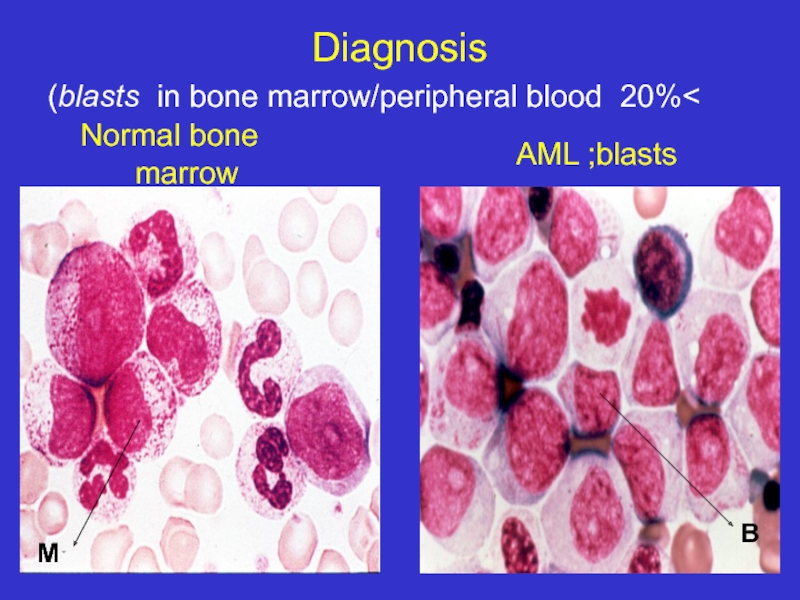
- 16. Diagnosis >20% blasts in bone
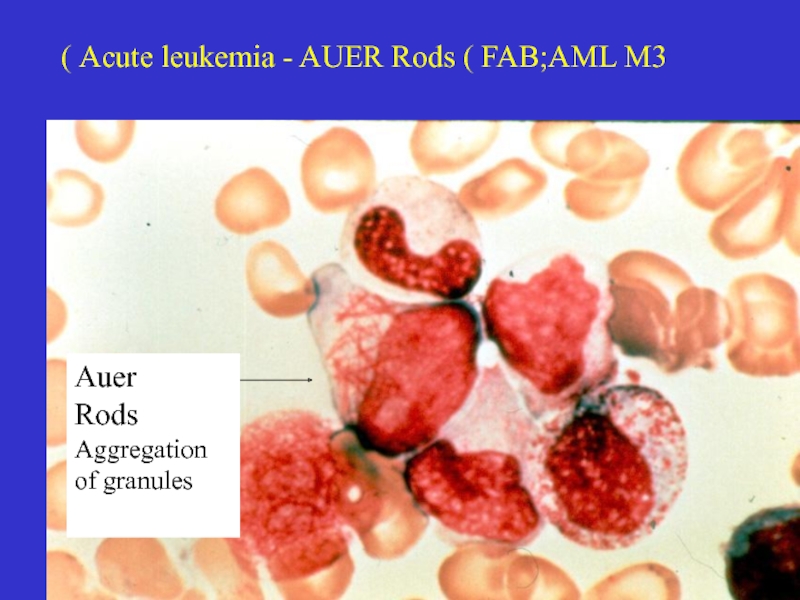
- 17. Acute leukemia - AUER Rods ( FAB;AML
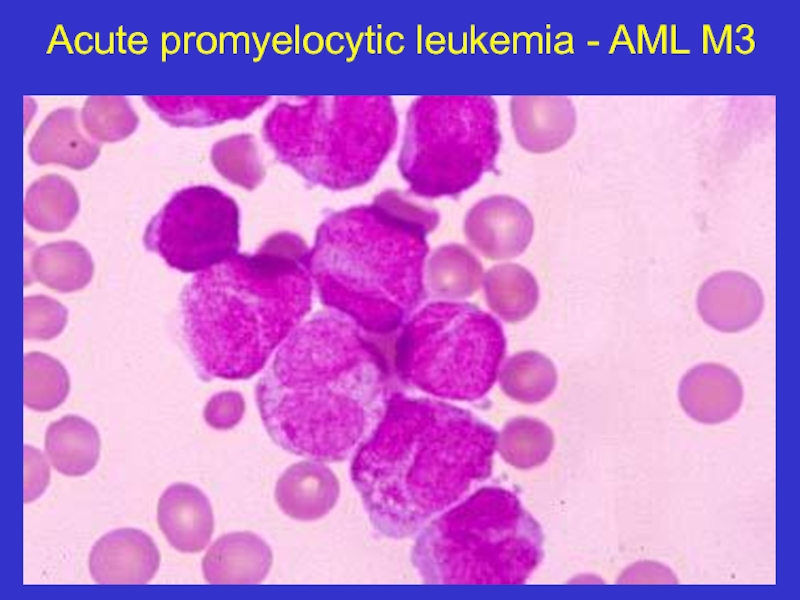
- 18. Acute promyelocytic leukemia - AML M3
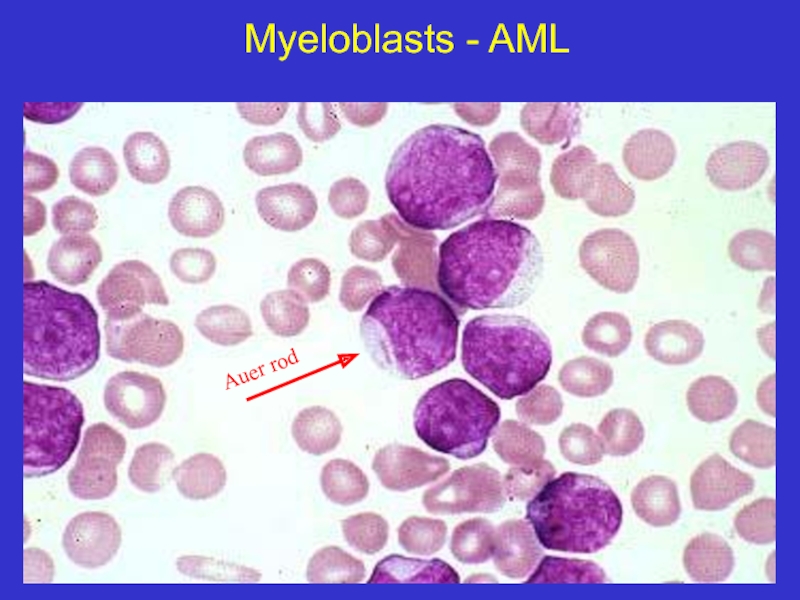
- 19. Myeloblasts - AML Auer rod
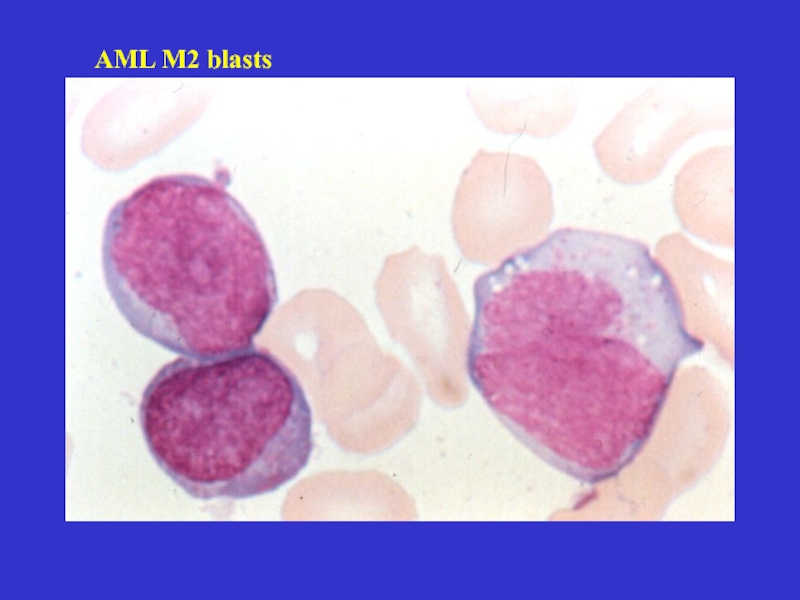
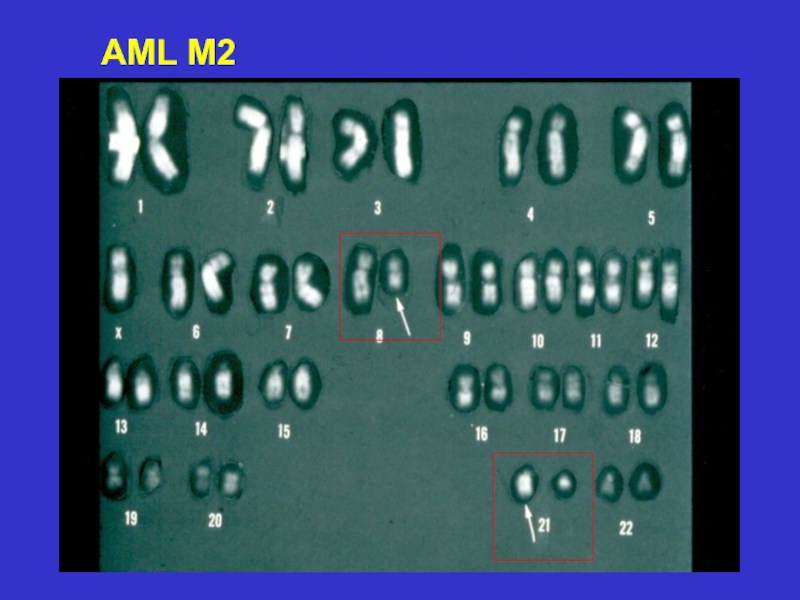
- 20. AML M2 blasts
- 21. French American British (FAB) classification
- 22. AML – WHO classification AML with recurrent
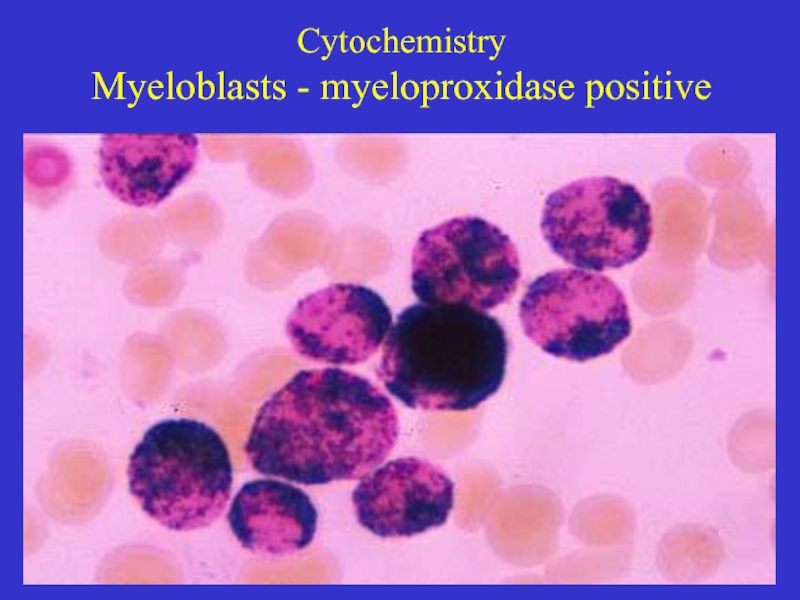
- 23. Cytochemistry Myeloblasts - myeloproxidase positive
- 24. Diagnosis Diagnosis :>20% blasts in BM
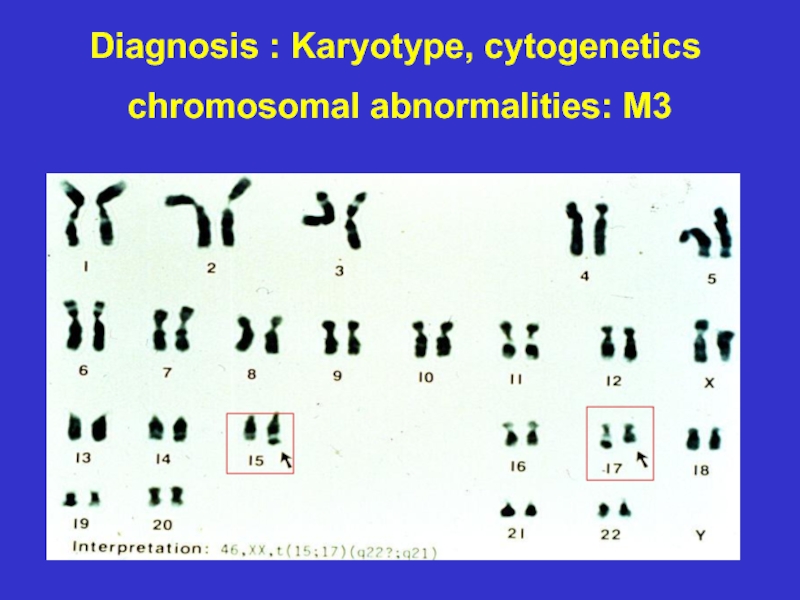
- 25. Diagnosis : Karyotype, cytogenetics chromosomal abnormalities: M3
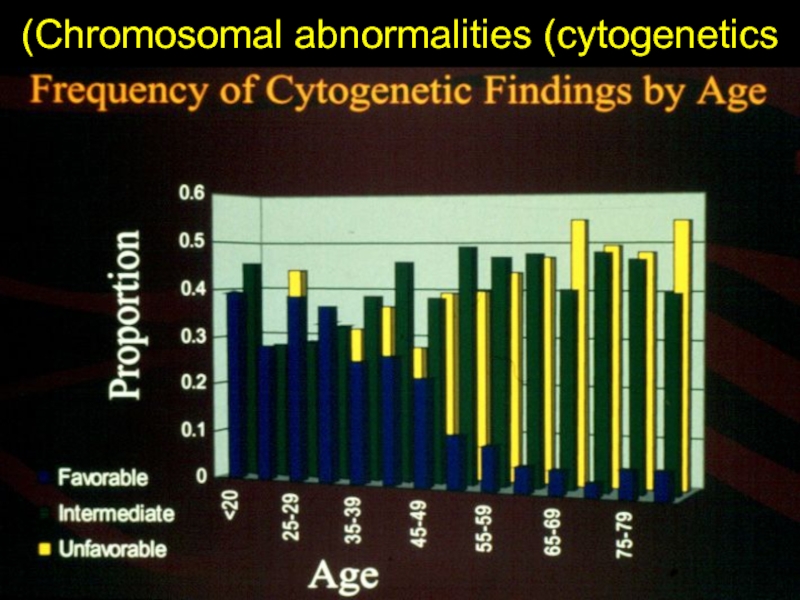
- 27. Chromosomal abnormalities (cytogenetics)
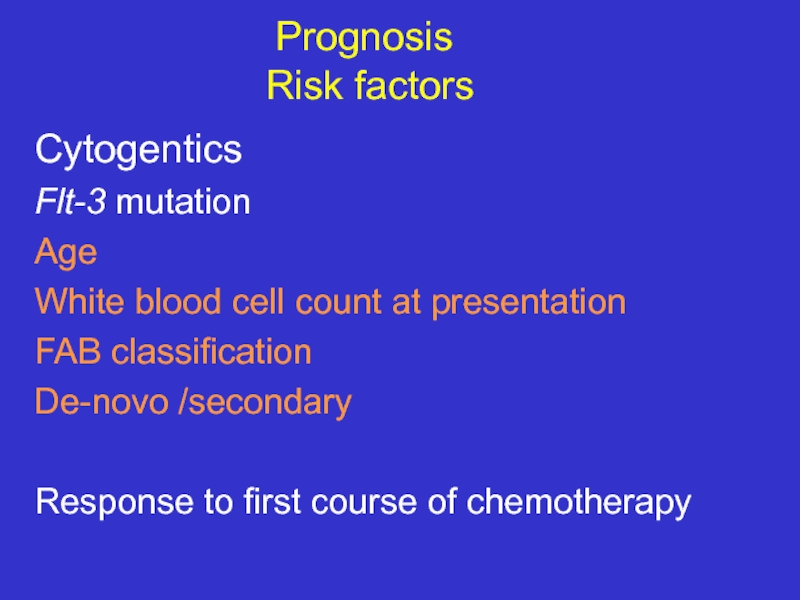
- 28. Prognosis Risk factors Cytogentics
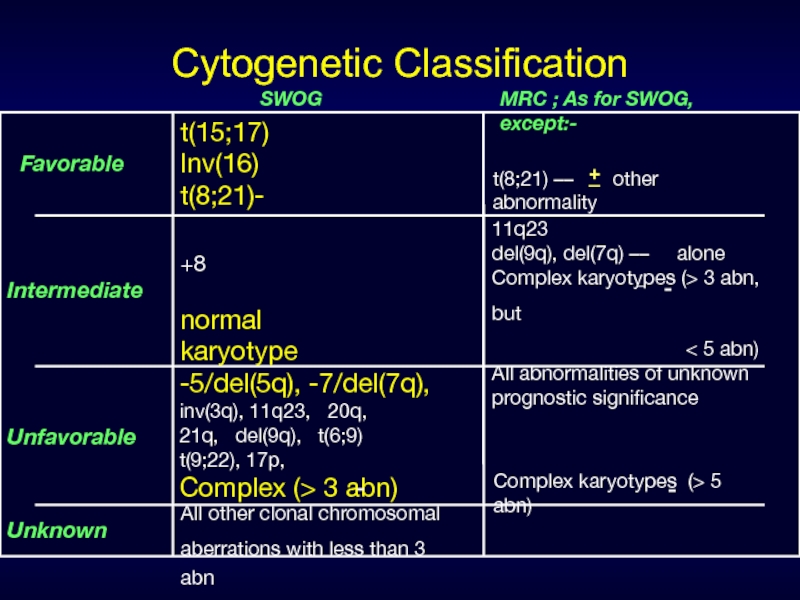
- 29. Cytogenetic Classification Favorable Intermediate SWOG
- 30. 0 50 25 75 100 0 1
- 31. Treatment
- 32. Treatment of acute leukemia (I) Supportive
- 33. Treatment in the Younger AML Patient
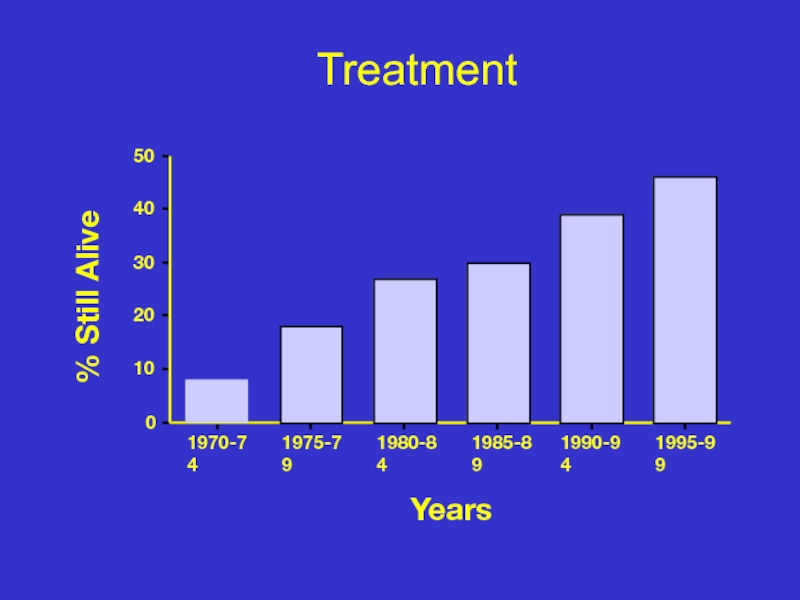
- 34. Outcome at 5 years
- 35. So how to choose which therapy to
- 36. 0 0% 20% 40% Unfavorable
- 37. What is the best treatment? Who should
- 38. AML in Elderly patients(>60 years) The majority
- 39. Future directions Identify new prognostic factors
- 40. Summary The majority of patients still
- 41. Suggested Reading Hoffbrand Hematology Williams Hematology Harrison’s
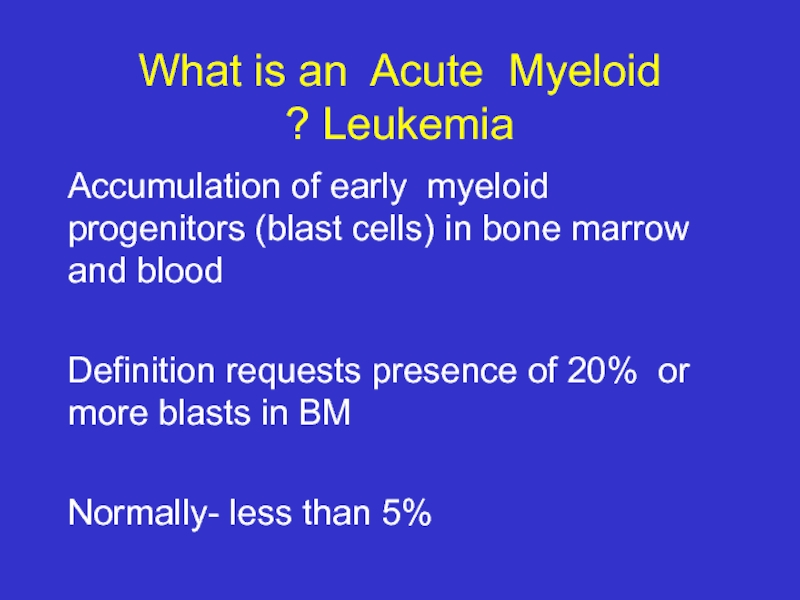
Слайд 2What is an Acute Myeloid Leukemia ?
Accumulation of early myeloid progenitors
Definition requests presence of 20% or more blasts in BM
Normally- less than 5%
Слайд 3ETIOLOGY
Environment: irradiation, chemotherapeutic agents, organic solvents – benzene etc.
Genetic diseases:
Acquired disorders: Aplastic Anemia, PNH
MOST OF THE CASES APPEAR WITH NO APPARENT RISK FACTORS!!!
Слайд 5AML
Aggressive disease with an acute onset
Can occur De Novo
following a known leukomogemic trigger (radiation, chemotherapy, diseases):
Secondary AML
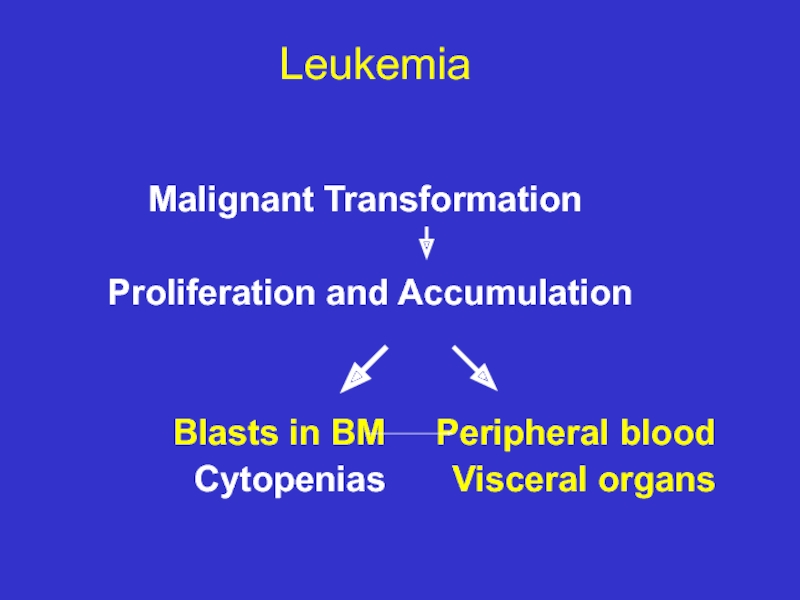
Слайд 6 Leukemia
Malignant Transformation
Proliferation and Accumulation
Visceral organs Cytopenias
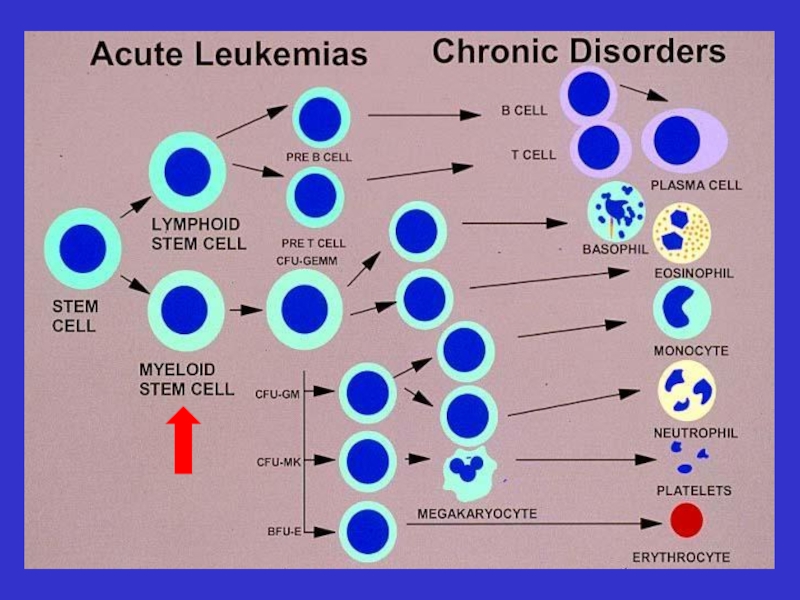
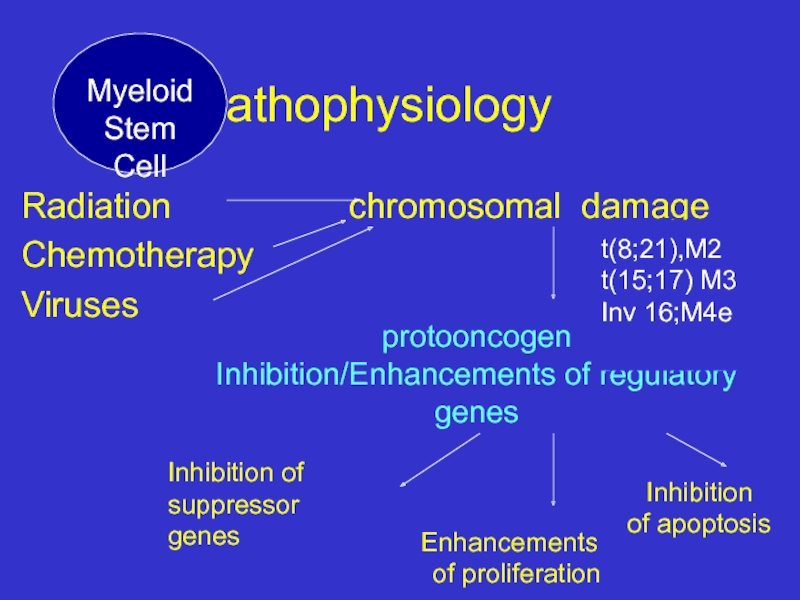
Слайд 9 Pathophysiology
Radiation
Chemotherapy
Viruses
protooncogen
Inhibition/Enhancements of regulatory genes
Inhibition of
suppressor genes
Enhancements
of proliferation
t(8;21),M2
t(15;17) M3
Inv 16;M4e
Inhibition
of apoptosis
Myeloid
Stem Cell
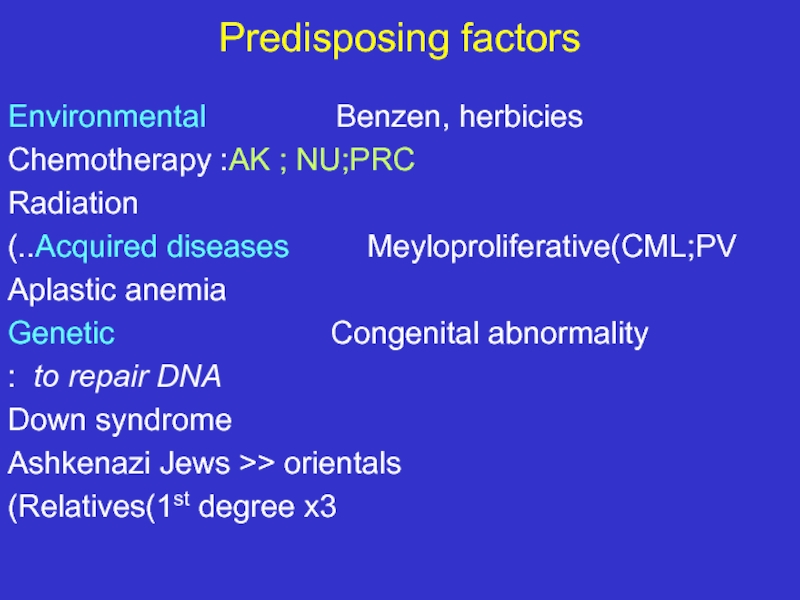
Слайд 11Predisposing factors
Environmental Benzen,
Chemotherapy :AK ; NU;PRC
Radiation
Acquired diseases Meyloproliferative(CML;PV..)
Aplastic anemia
Genetic Congenital abnormality
to repair DNA :
Down syndrome
Ashkenazi Jews >> orientals
Relatives(1st degree x3)
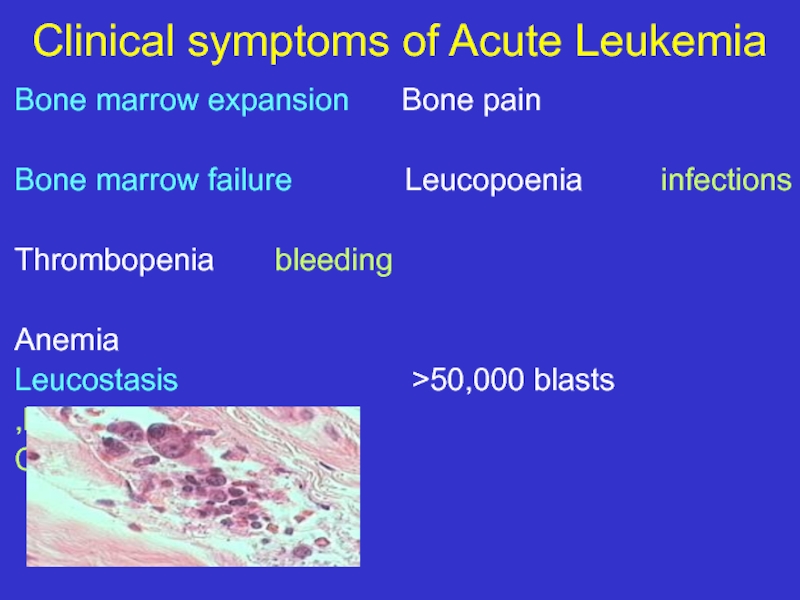
Слайд 12Clinical symptoms of Acute Leukemia
Bone marrow expansion Bone pain
Bone
Thrombopenia bleeding
Anemia
Leucostasis >50,000 blasts
Dispnea,
CNS
Слайд 15Clinical symptomes
DIC
Bleeding Thrombosis
Metabolic Hyperuricemia Tumor lysis syndrome
K, phosphor, Ca
Uric Acid
Слайд 21French American British (FAB) classification
-Based on morphology and
-Divides patients into 7 AML subtypes
-A morphological rather than biological classification
-Correlation between morphological and biological characteristics may exist , but not always
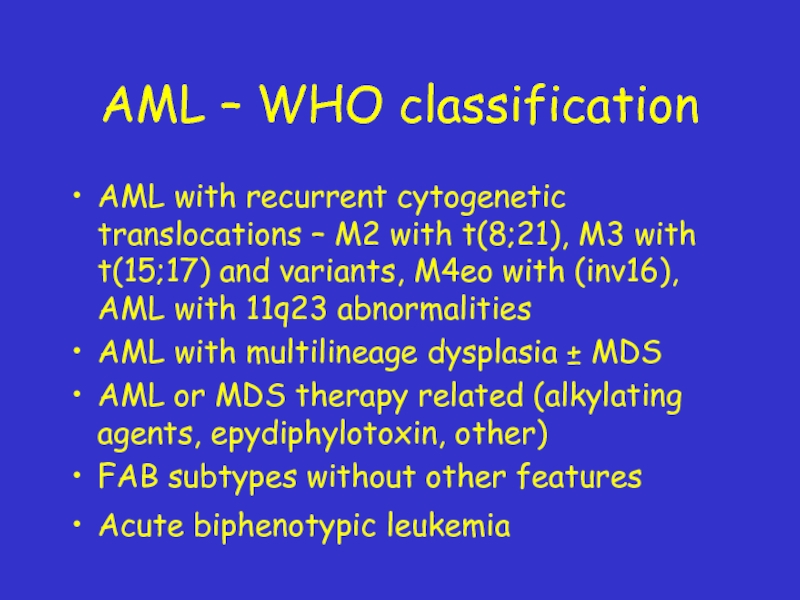
Слайд 22AML – WHO classification
AML with recurrent cytogenetic translocations – M2 with
AML with multilineage dysplasia ± MDS
AML or MDS therapy related (alkylating agents, epydiphylotoxin, other)
FAB subtypes without other features
Acute biphenotypic leukemia
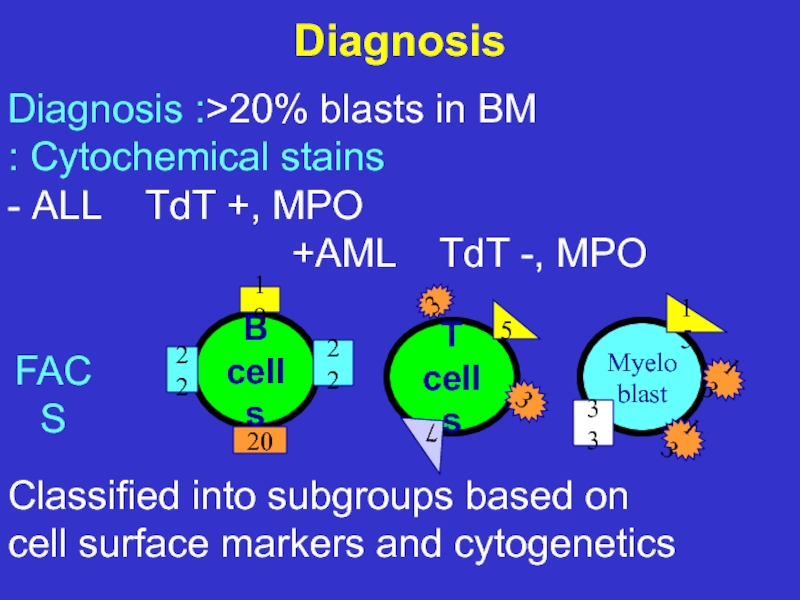
Слайд 24Diagnosis
Diagnosis :>20% blasts in BM
Cytochemical stains :
ALL
AML TdT -, MPO+
Classified into subgroups based on
cell surface markers and cytogenetics
B cells
T cells
19
22
20
22
3
3
5
7
Myeloblast
15
13
13
33
FACS
Слайд 28 Prognosis
Risk factors
Cytogentics
Flt-3 mutation
Age
White blood cell count at presentation
FAB
De-novo /secondary
Response to first course of chemotherapy
Слайд 29
Cytogenetic Classification
Favorable
Intermediate
SWOG
Unfavorable
Unknown
MRC ; As for SWOG, except:-
t(15;17)
Inv(16)
t(8;21)-
t(8;21) ––
+8
normal karyotype
11q23
del(9q), del(7q) –– alone
Complex karyotypes (> 3 abn, but
< 5 abn)
All abnormalities of unknown
prognostic significance
All other clonal chromosomal
aberrations with less than 3 abn
-5/del(5q), -7/del(7q),
inv(3q), 11q23, 20q,
21q, del(9q), t(6;9)
t(9;22), 17p,
Complex (> 3 abn)
Complex karyotypes (> 5 abn)
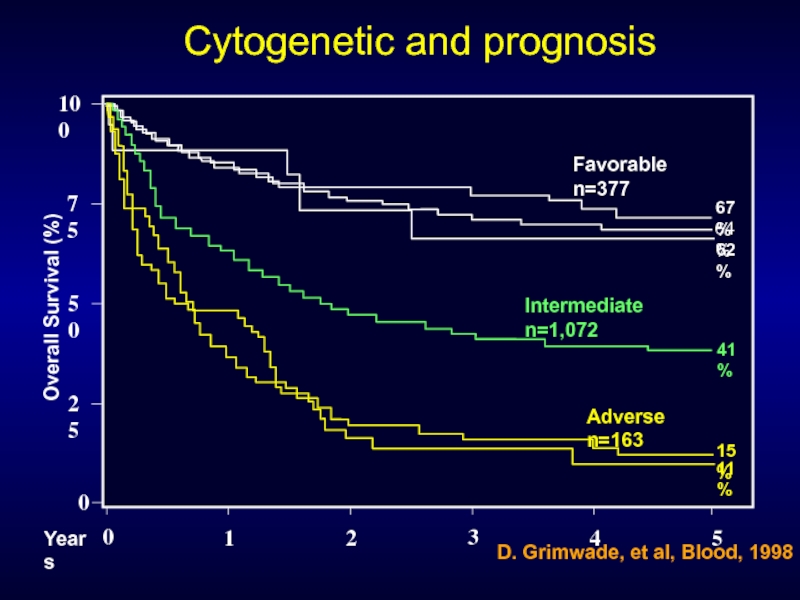
Слайд 300
50
25
75
100
0
1
Overall Survival (%)
Years
2
3
4
5
67%
64%
62%
41%
15%
11%
Favorable n=377
Intermediate n=1,072
Adverse n=163
D. Grimwade, et al,
Cytogenetic and prognosis
Слайд 32Treatment of acute leukemia (I)
Supportive care :
Hydration
Allopurinol to prevent hyperuricemia
Cytopharesis
Blood products
Patient
History for occupational exposure or exposure
Bone marrow aspiration and biopsy
Bone marrow sample for cytogenetic, FACS, PCR
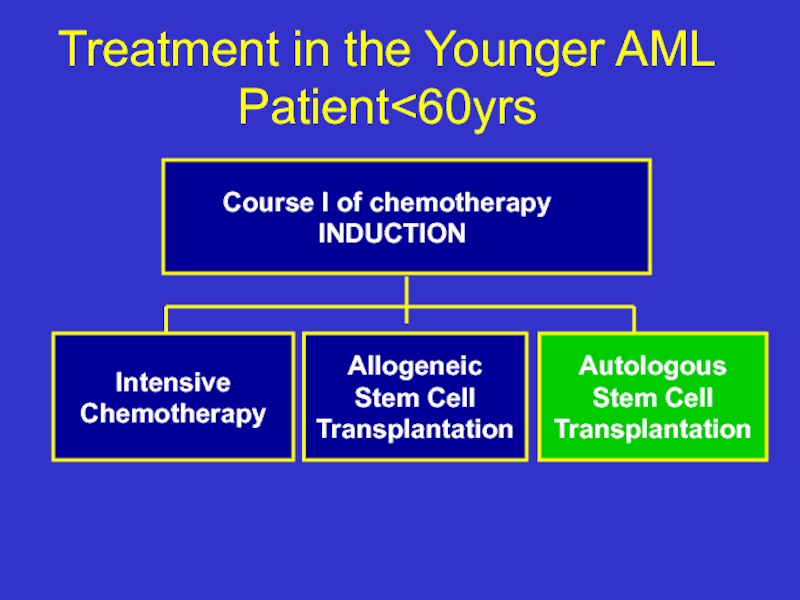
Слайд 33Treatment in the Younger AML Patient
INDUCTION
Intensive
Chemotherapy
Allogeneic
Stem Cell
Transplantation
Autologous
Stem Cell
Transplantation
Слайд 34Outcome at 5 years
Relapse 20-30% 40-60%
Overall survival 50% 50%
TRM 20-30% 5%
Слайд 35So how to choose which therapy to a specific patient?
use
relapse rate and survival
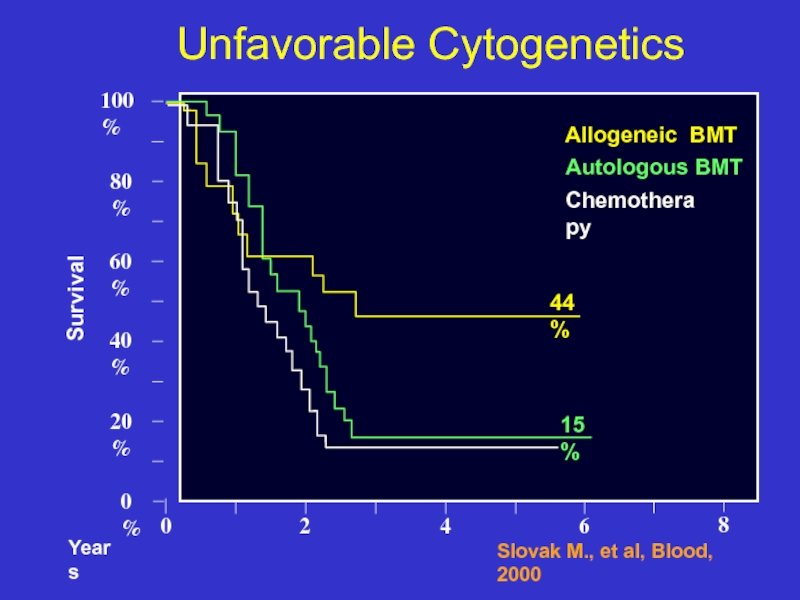
Слайд 360
0%
20%
40%
Unfavorable Cytogenetics
Survival
80%
60%
100%
2
4
6
Slovak M., et al, Blood, 2000
8
Allogeneic BMT
Autologous BMT
Chemotherapy
44%
15%
Years
Слайд 37What is the best treatment?
Who should have a matched related Allo
Who should have an
Auto SCT?
Patients with poor risk
and standard risk younger than 35/40 years in CR1
Patients in CR2 or beyond
Favourable/standard risk patients who relapsed, responded again to chemotherapy and have no matched donor
Patients in CR1 ?
Слайд 38AML in Elderly patients(>60 years)
The majority of the patients are older
Lower remission rate
Higher treatment –related morbidity & mortality
Very poor outcome
higher frequency of poor risk cytogenetics & resistance to chemotherapy
Слайд 39Future directions
Identify new prognostic factors
New therapies : Modulation of drug resistance
Biological, specific treatments:
Monoclonal antibodies
ATRA in APL, t (15;17)
Слайд 40Summary
The majority of patients still die of their disease (significantly
Further improvement is needed:
Better ability to predict patients outcome
Tailoring treatment to patient’s risk factors
Improving therapy & supportive care
New strategies for elderly patients
Слайд 41Suggested Reading
Hoffbrand Hematology
Williams Hematology
Harrison’s Text book of Internal Medicine
תודה