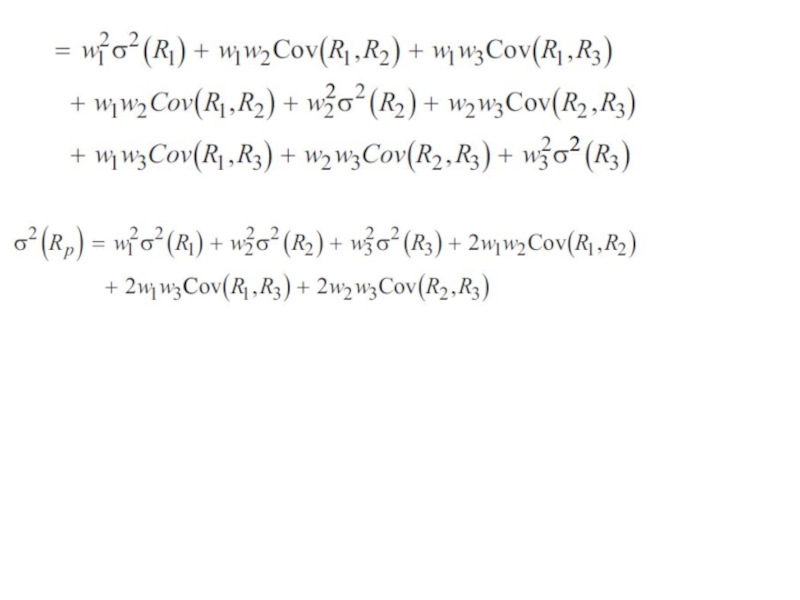- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Probability Concepts презентация
Содержание
- 1. Probability Concepts
- 2. Definition of Probability Probability is a
- 3. Probability Stated as Odds Odds for E
- 4. Unconditional and conditional probability The probability in
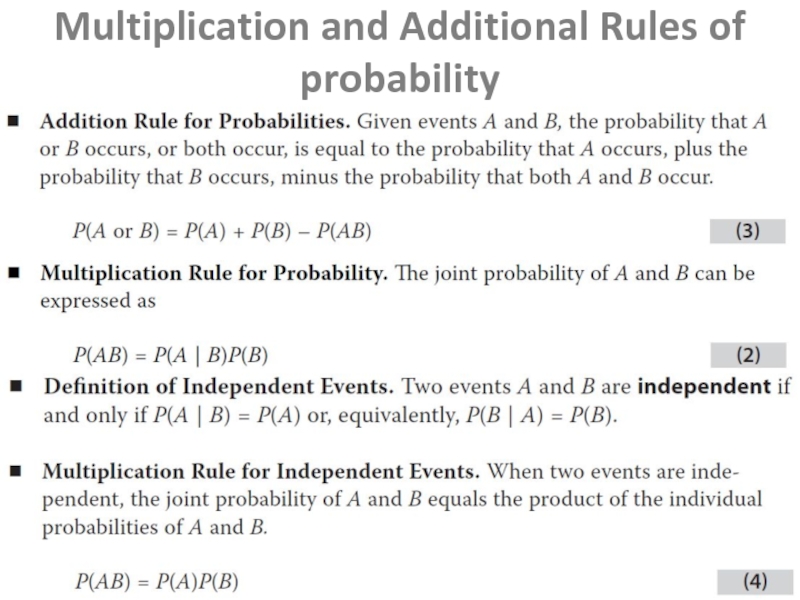
- 5. Multiplication and Additional Rules of probability
- 6. The Total Probability Rule
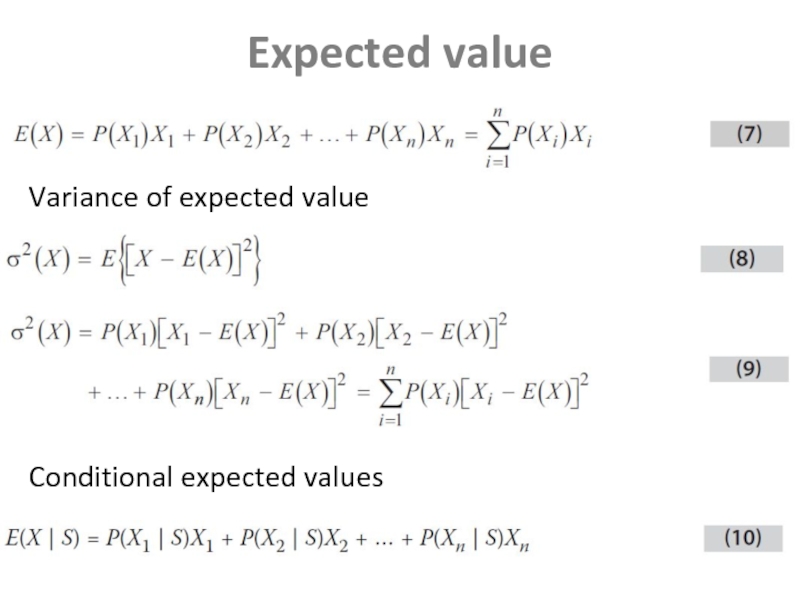
- 7. Expected value Variance of expected value Conditional expected values
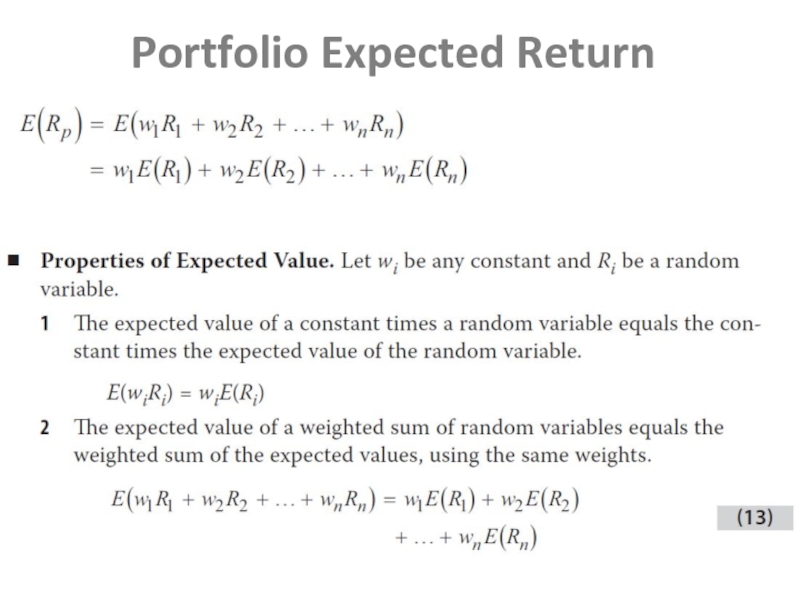
- 8. Portfolio Expected Return
- 11. Covariance and Correlation Covariance is a measure
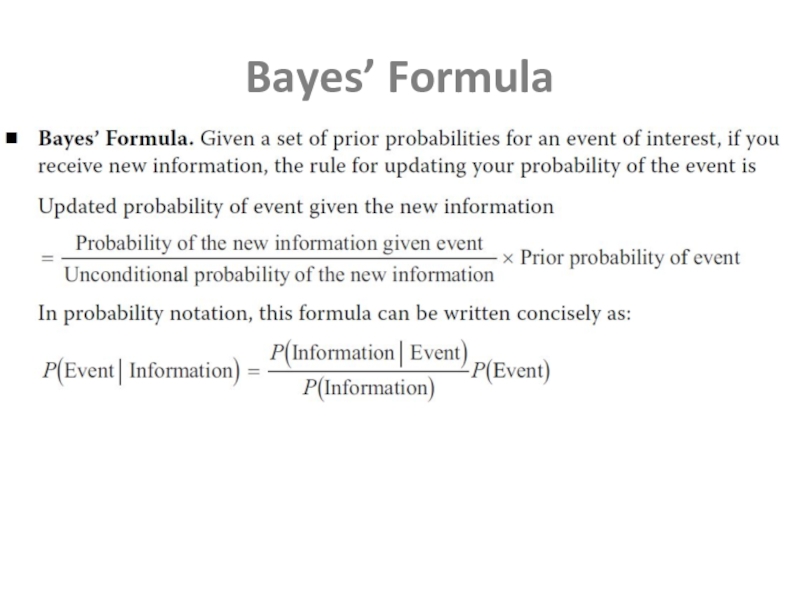
- 12. Bayes’ Formula
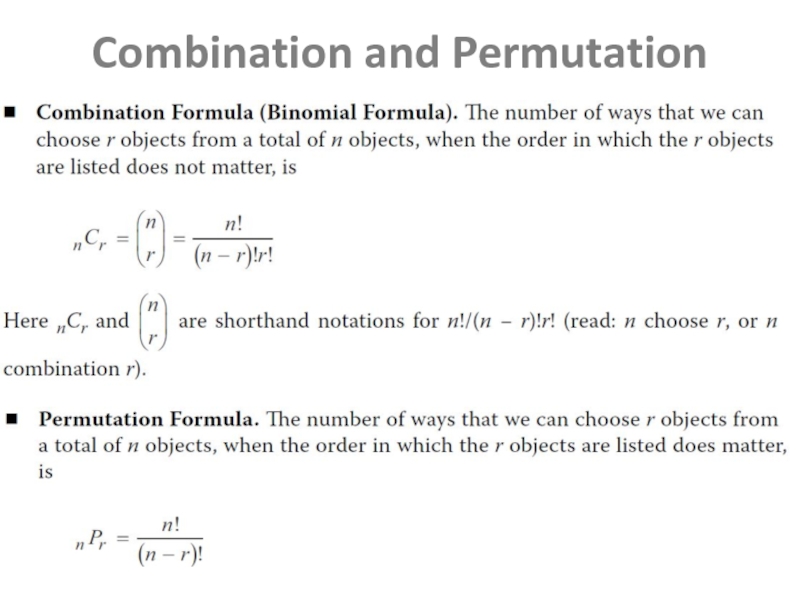
- 13. Principles of Counting
- 14. Combination and Permutation
Слайд 2Definition of Probability
Probability is a number between 0 and 1
that describes the chance that a stated event will occur.
An event is a specified set of outcomes of a random variable.
Mutually exclusive events can occur only one at a time. Exhaustive events cover or contain all possible outcomes.
The two defining properties of a probability are, first, that 0 ≤ P(E) ≤ 1 where P(E) denotes the probability of an event E), and second, that the sum of the probabilities of any set of mutually exclusive and exhaustive events equals 1.
A probability estimated from data as a relative frequency of occurrence is an empirical probability. A probability drawing on personal or subjective judgment is a subjective probability. A probability obtained based on logical analysis is an a priori probability.
An event is a specified set of outcomes of a random variable.
Mutually exclusive events can occur only one at a time. Exhaustive events cover or contain all possible outcomes.
The two defining properties of a probability are, first, that 0 ≤ P(E) ≤ 1 where P(E) denotes the probability of an event E), and second, that the sum of the probabilities of any set of mutually exclusive and exhaustive events equals 1.
A probability estimated from data as a relative frequency of occurrence is an empirical probability. A probability drawing on personal or subjective judgment is a subjective probability. A probability obtained based on logical analysis is an a priori probability.
Слайд 3Probability Stated as Odds
Odds for E = P(E)/[1 − P(E)]. The
odds for E are the probability of E divided by 1 minus the probability of E. Given odds for E of “a to b,” the implied probability of E is a/(a + b).
In the example, the statement that the odds for the company’s EPS for FY2014 beating $0.69 are 1 to 7 means that the speaker believes the probability of the event is 1/(1 + 7) = 1/8 = 0.125.
Odds against E = [1 − P(E)]/P(E), the reciprocal of odds for E. Given odds against E of “a to b,” the implied probability of E is b/(a+ b).
The statement that the odds against the company’s EPS for FY2014 beating $0.69 are 15 to 1 is consistent with a belief that the probability of the event is 1/(1 + 15) = 1/16 = 0.0625.
In the example, the statement that the odds for the company’s EPS for FY2014 beating $0.69 are 1 to 7 means that the speaker believes the probability of the event is 1/(1 + 7) = 1/8 = 0.125.
Odds against E = [1 − P(E)]/P(E), the reciprocal of odds for E. Given odds against E of “a to b,” the implied probability of E is b/(a+ b).
The statement that the odds against the company’s EPS for FY2014 beating $0.69 are 15 to 1 is consistent with a belief that the probability of the event is 1/(1 + 15) = 1/16 = 0.0625.
Слайд 4Unconditional and conditional probability
The probability in answer to the straightforward question
“What is the probability of this event A?” is an unconditional probability, denoted P(A). Unconditional probability is also frequently referred to as marginal probability.
Contrast the question “What is the probability of A?” with the question “What is the probability of A, given that B has occurred?” The probability in answer to this last question is a conditional probability, denoted P(A | B) (read: “the probability of A given B”).
Contrast the question “What is the probability of A?” with the question “What is the probability of A, given that B has occurred?” The probability in answer to this last question is a conditional probability, denoted P(A | B) (read: “the probability of A given B”).
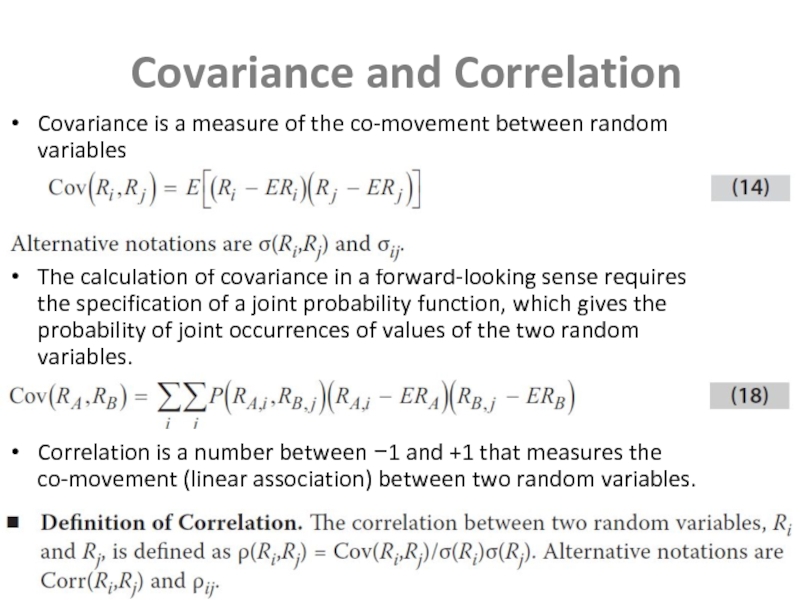
Слайд 11Covariance and Correlation
Covariance is a measure of the co-movement between random
variables
The calculation of covariance in a forward-looking sense requires the specification of a joint probability function, which gives the probability of joint occurrences of values of the two random variables.
Correlation is a number between −1 and +1 that measures the co-movement (linear association) between two random variables.
The calculation of covariance in a forward-looking sense requires the specification of a joint probability function, which gives the probability of joint occurrences of values of the two random variables.
Correlation is a number between −1 and +1 that measures the co-movement (linear association) between two random variables.


![Probability Stated as OddsOdds for E = P(E)/[1 − P(E)]. The odds for E are](/img/tmb/4/357898/bd559be4d128cc57cd37eed052e0fcd9-800x.jpg)