- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Consumer buying behavior презентация
Содержание
- 1. Consumer buying behavior
- 2. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights
- 3. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights
- 4. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights
- 5. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights
- 6. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights
- 7. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights
- 8. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights
- 9. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights
- 10. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights
- 11. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights
- 12. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights
- 13. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights
- 14. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights
- 15. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights
- 16. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights
- 17. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights
- 18. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights
- 19. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights
- 20. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights
- 21. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights
- 22. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights
- 23. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights
- 24. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights
- 25. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights
- 26. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights
- 27. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights
- 28. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights
- 29. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights
- 30. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights
- 31. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights
- 32. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights
- 33. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights
- 34. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights
- 35. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 9 |
- 36. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 9 |
- 37. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights
- 38. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights
- 39. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights
- 40. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights
- 41. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights
- 42. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights
- 43. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights
- 44. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights
- 45. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights
- 46. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights
Слайд 2Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
9 |
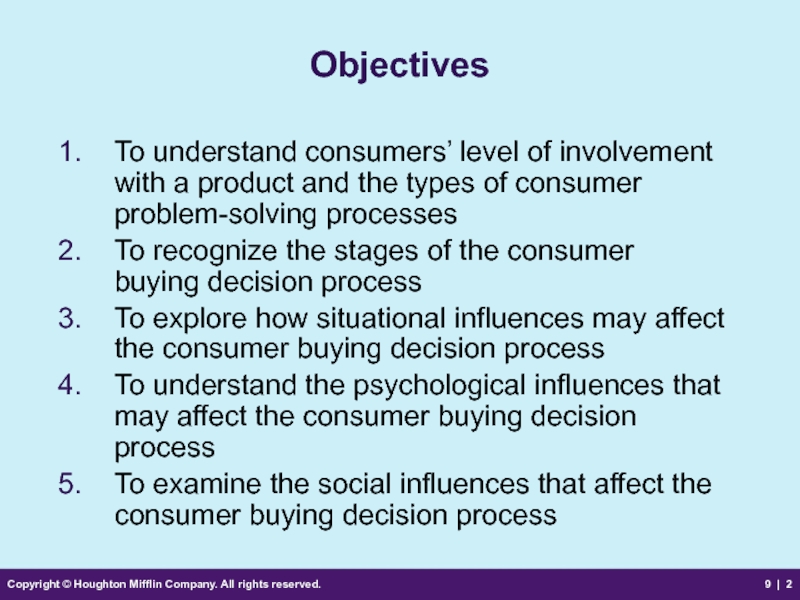
Objectives
To understand
To recognize the stages of the consumer buying decision process
To explore how situational influences may affect the consumer buying decision process
To understand the psychological influences that may affect the consumer buying decision process
To examine the social influences that affect the consumer buying decision process
Слайд 3Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
9 |
Chapter Outline
Level
Consumer Buying Decision Process
Situational Influences on the Buying Decision Process
Psychological Influences on the Buying Decision Process
Social Influences on the Buying Decision Process
Слайд 4Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
9 |
Introduction: Key
Buying Behavior
The decision processes and acts of people involved in buying and using products
Consumer Buying Behavior
Buying behavior of people
who purchase products for
personal use and not for
business purposes
Слайд 5Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
9 |
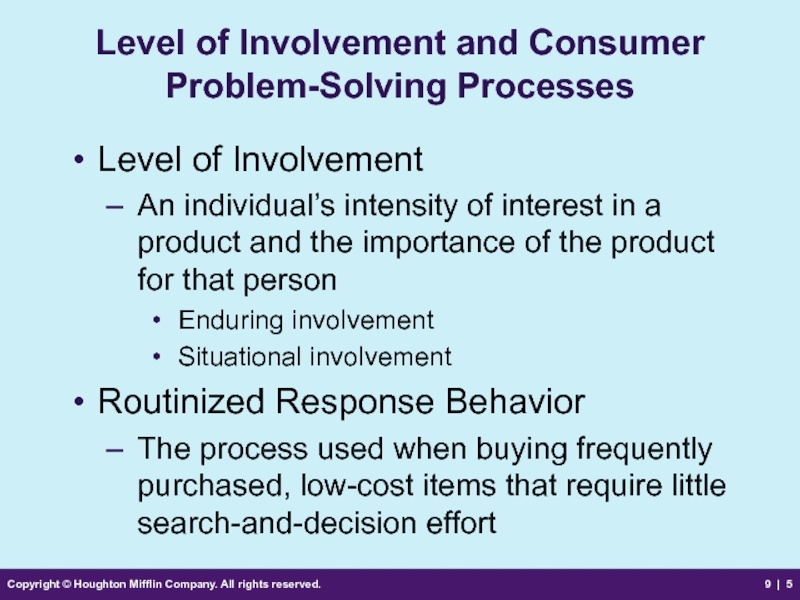
Level of
Level of Involvement
An individual’s intensity of interest in a product and the importance of the product for that person
Enduring involvement
Situational involvement
Routinized Response Behavior
The process used when buying frequently purchased, low-cost items that require little search-and-decision effort
Слайд 6Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
9 |
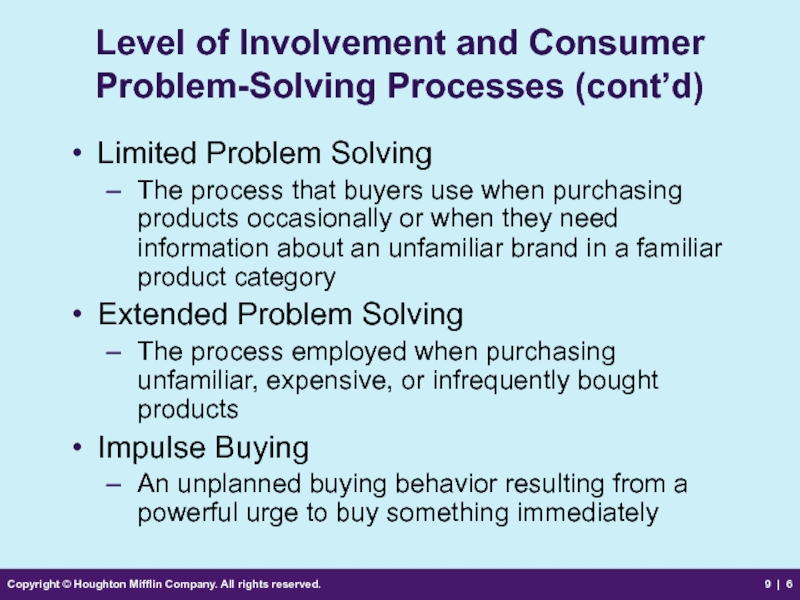
Level of
Limited Problem Solving
The process that buyers use when purchasing products occasionally or when they need information about an unfamiliar brand in a familiar product category
Extended Problem Solving
The process employed when purchasing unfamiliar, expensive, or infrequently bought products
Impulse Buying
An unplanned buying behavior resulting from a powerful urge to buy something immediately
Слайд 7Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
9 |
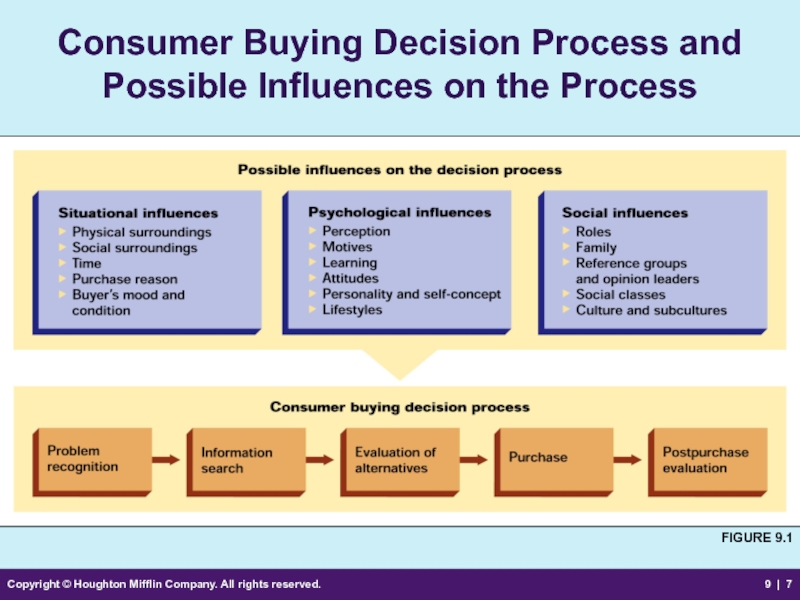
Consumer Buying
FIGURE 9.1
Слайд 8Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
9 |
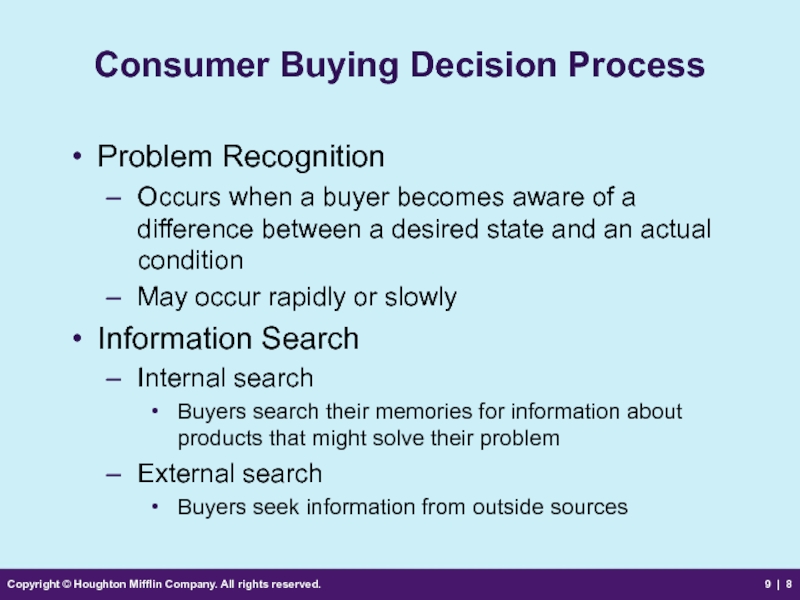
Consumer Buying
Problem Recognition
Occurs when a buyer becomes aware of a difference between a desired state and an actual condition
May occur rapidly or slowly
Information Search
Internal search
Buyers search their memories for information about products that might solve their problem
External search
Buyers seek information from outside sources
Слайд 9Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
9 |
This Visine
Courtesy of Pfizer, Inc.
Слайд 10Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
9 |
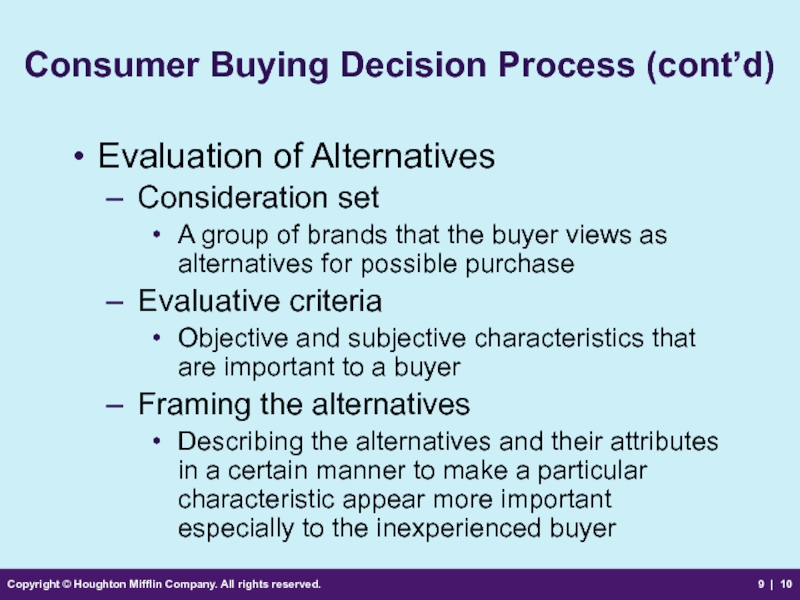
Consumer Buying
Evaluation of Alternatives
Consideration set
A group of brands that the buyer views as alternatives for possible purchase
Evaluative criteria
Objective and subjective characteristics that are important to a buyer
Framing the alternatives
Describing the alternatives and their attributes in a certain manner to make a particular characteristic appear more important especially to the inexperienced buyer
Слайд 11Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
9 |
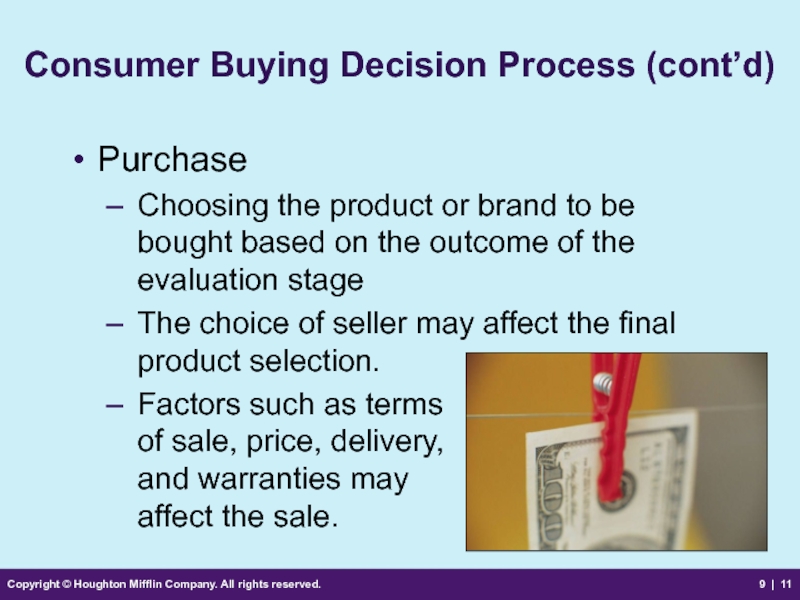
Consumer Buying
Purchase
Choosing the product or brand to be bought based on the outcome of the evaluation stage
The choice of seller may affect the final product selection.
Factors such as terms
of sale, price, delivery,
and warranties may
affect the sale.
Слайд 12Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
9 |
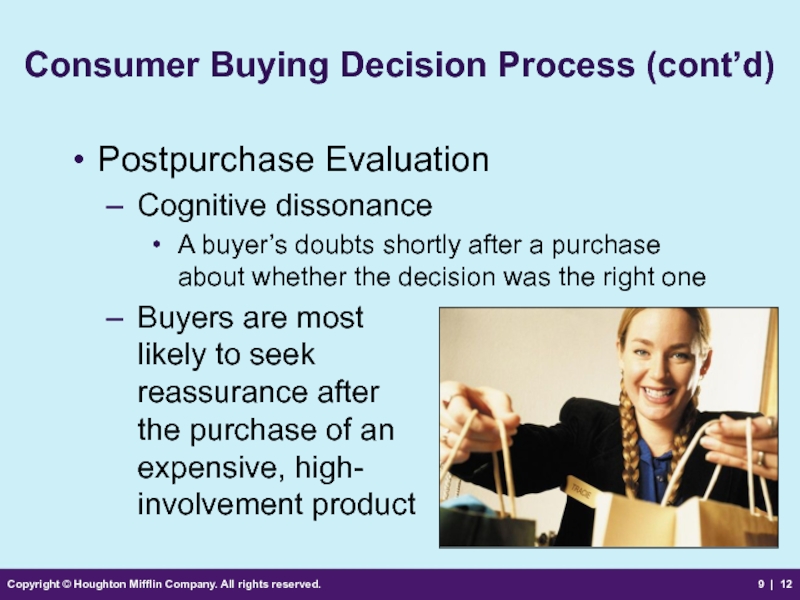
Consumer Buying
Postpurchase Evaluation
Cognitive dissonance
A buyer’s doubts shortly after a purchase about whether the decision was the right one
Buyers are most
likely to seek
reassurance after
the purchase of an
expensive, high-
involvement product
Слайд 13Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
9 |
What Part
© The Procter & Gamble Company. Used by permission.
Слайд 14Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
9 |
On Which
Courtesy of NAPA Online.
Слайд 15Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
9 |
Class Exercise
In
A recent college graduate reads Consumer Reports to compare automobile ratings.
On the first day of class, a student finds out that a programmable calculator is needed for the course, but she doesn’t own one.
After purchasing an evening gown, a woman decides that it is not quite appropriate for her special occasion.
Слайд 16Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
9 |
Class Exercise
A
A teenager compares numerous compact disc players and narrows the choice down to two players.
While on the way to work, a person’s automobile stalls and will not start again.
At an open-house party, a guest realizes that the host already owns the gift he plans to give.
A person receives a sample package of laundry detergent in the mail and uses it to wash a load of clothes.
Слайд 17Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
9 |
Situational Influences
Situational Influences
Factors that can influence a buyer’s purchase decision and may cause the buyer to shorten, lengthen, or terminate the process.
Situational Factors
Physical surroundings
Social surroundings
Time perspective
Reason for purchase
Buyer’s momentary mood
and condition
Слайд 18Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
9 |
Psychological Influences
Psychological Influences
Factors that in part determine people’s general behavior, thus influencing their behavior as consumers
Perception
The process of selecting,
organizing, and
interpreting information
inputs to produce
meaning
Слайд 19Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
9 |
Psychological Influences
Selective Exposure
The process of selecting inputs to be exposed to our awareness while ignoring others
Selective Distortion
An individual’s changing or twisting of information when it is inconsistent with personal feelings or beliefs
Selective Retention
Remembering information inputs that support personal feelings and beliefs and forgetting inputs that do not
Слайд 20Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
9 |
Psychological Influences
Perceptual Organization
Organizing and integrating new information with what is already stored in memory.
Closure occurs when
a person mentally fills
in missing elements in
a pattern or statement
Слайд 21Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
9 |
Psychological Influences
Interpretation
The assignment of meaning to what has been organized based on what is expected or what is familiar
Attempts by marketers to influence interpretation can fail because
consumers block out seller’s information.
consumers interpret seller’s information differently than intended.
consumers discard information that is inconsistent with prior beliefs.
Слайд 22Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
9 |
Psychological Influences
Motives
An internal energizing force that directs a person’s behavior toward satisfying needs or achieving goals
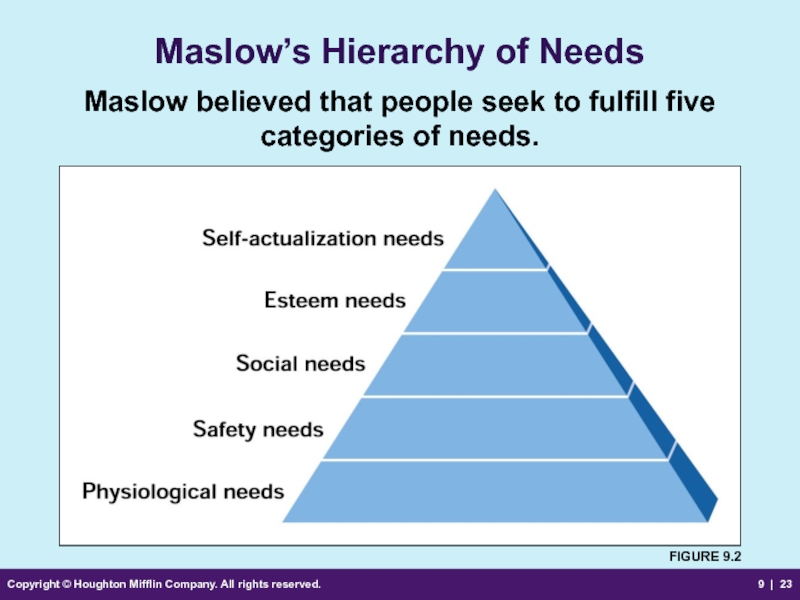
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
The five levels of needs that humans are motivated to seek and satisfy, from least to most important are
Physiological needs—food, water, sex, clothing, shelter
Safety needs—security, freedom
Social needs—love, affection, belonging
Esteem needs—respect, recognition, self-worth
Self-actualization needs—personal growth needs
Слайд 23Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
9 |
Maslow’s Hierarchy
Maslow believed that people seek to fulfill five categories of needs.
FIGURE 9.2
Слайд 24Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
9 |
Psychological Influences
Learning
Changes in an individual’s thought processes and behavior caused by information and experience
Behaviors that produce satisfying consequences are likely to be repeated.
Consumers learn about products by
experiencing the products personally.
gaining additional product knowledge from seller-provided information.
indirect information from other purchasers/users.
Слайд 25Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
9 |
Psychological Influences
Attitudes
An individual’s enduring evaluation of, feelings about, and behavioral tendencies toward an object or idea
Attitudinal Components
Cognitive
Knowledge and information about the object or idea
Affective
Feelings and emotions toward the object or idea
Behavioral
Individual’s action regarding the object or idea
Слайд 26Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
9 |
Psychological Influences
Attitude Scale
A means of measuring consumer attitudes by gauging the intensity of individuals’ reactions to adjectives, phrases, or sentences about an object
Слайд 27Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
9 |
Psychological Influences
Personality and Self-Concept
Personality
A set of internal traits and distinct behavioral tendencies that result in consistent patterns of behavior in certain situations
Self-concept (self-image)
Perception or view of oneself
Lifestyles
Lifestyle
An individual’s pattern of living expressed through activities, interests, and opinions
Слайд 28Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
9 |
Social Influences
Social Influences
The forces other people exert on one’s buying behavior
Role
Actions and activities that a person in a particular position is supposed to perform based on expectations of the individual and surrounding persons
Multiple role-expectation sets affect behavior.
Roles influence both general and buying behaviors.
Слайд 29Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
9 |
Social Influences
Family Influences
Consumer socialization
The process through which a
person acquires the knowledge
and skills to function as a
consumer
Family decision-making processes
Autonomic—equally shared decision-making
Husband-dominant—husband makes decisions
Wife-dominant—wife makes decisions
Syncratic—decisions made jointly
Слайд 30Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
9 |
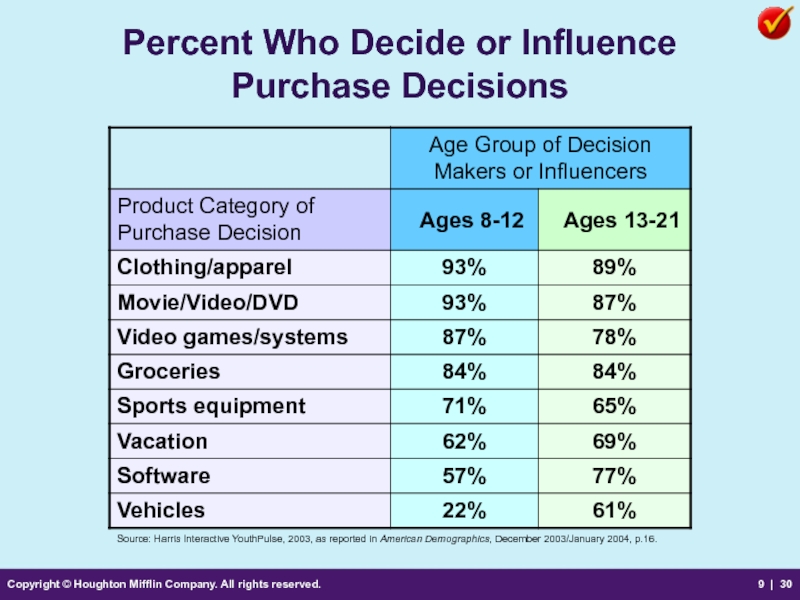
Percent Who
Source: Harris Interactive YouthPulse, 2003, as reported in American Demographics, December 2003/January 2004, p.16.
Слайд 31Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
9 |
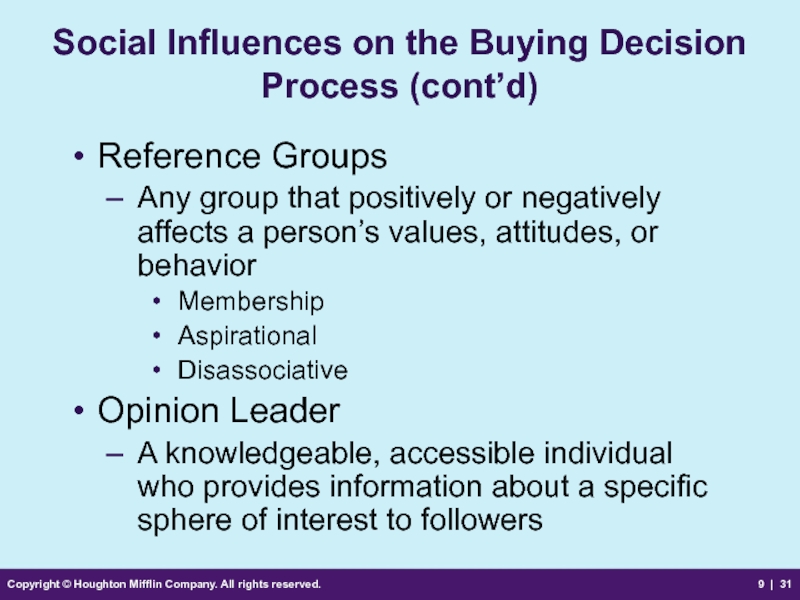
Social Influences
Reference Groups
Any group that positively or negatively affects a person’s values, attitudes, or behavior
Membership
Aspirational
Disassociative
Opinion Leader
A knowledgeable, accessible individual who provides information about a specific sphere of interest to followers
Слайд 32Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
9 |
How Do
For each of the products below, indicate whether one’s reference group would influence one’s decision to buy the product in general, the type of product within the category, and/or the brand decision. Use more than one X when appropriate.
Type of Product
Product Within the Brand
Product Decision Category Decision
Soft drink
Bar soap
Telephone
Jeans
Car
Sweatshirt with
college name
DVD player
Bathroom tissue
Слайд 33Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
9 |
Debate Issue
Is
Слайд 34Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
9 |
Social Influences
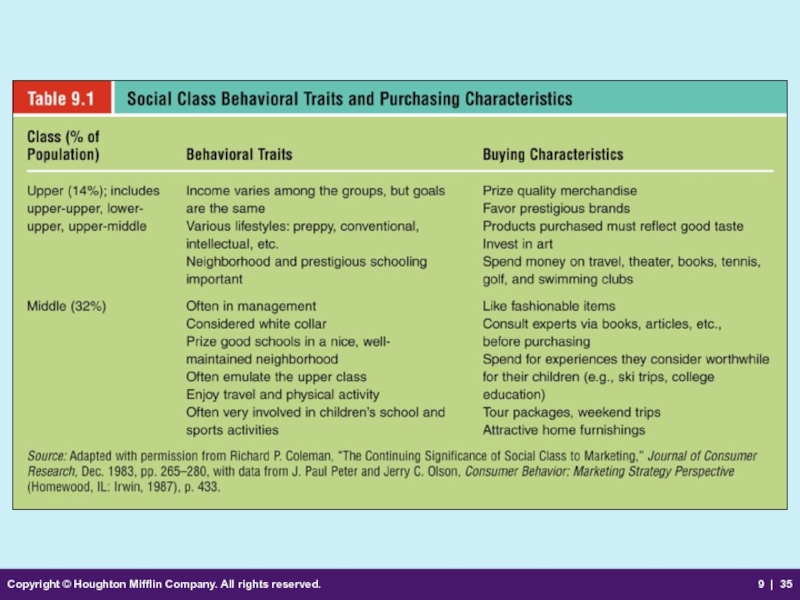
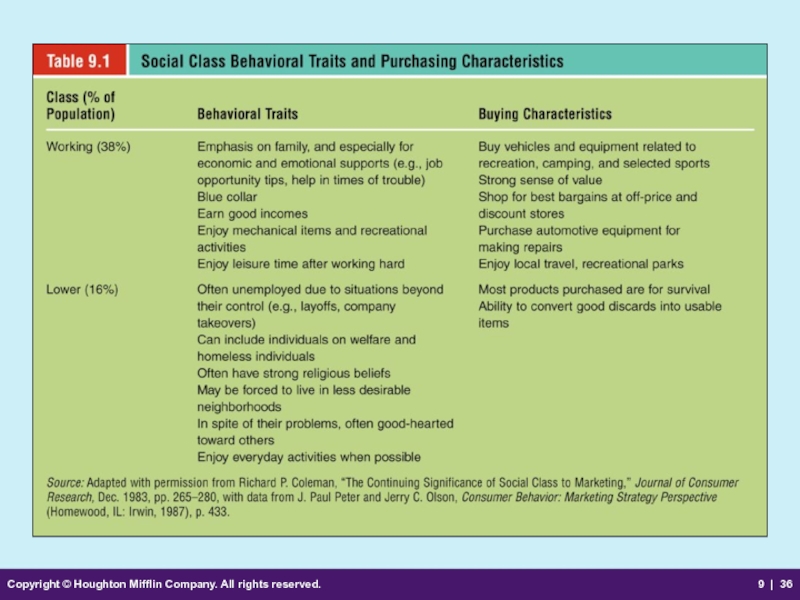
Social Class
An open group of individuals with similar social rank
Individuals in the same social class
develop and assume common behavioral patterns.
have similar attitudes, values, language patterns, and possessions.
Influences many major life decisions
Influences shopping patterns and spending habits
Слайд 37Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
9 |
Social Influences
Culture
The accumulated values, knowledge, beliefs, customs, objects, and concepts of a society
Culture influences buying behavior.
Cultural changes affect product development, promotion, distribution, and pricing.
Subcultures
Groups of individuals whose characteristic values and behavior patterns are similar and differ from those of the surrounding culture
African American • Hispanic • Asian American
Слайд 38Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
9 |
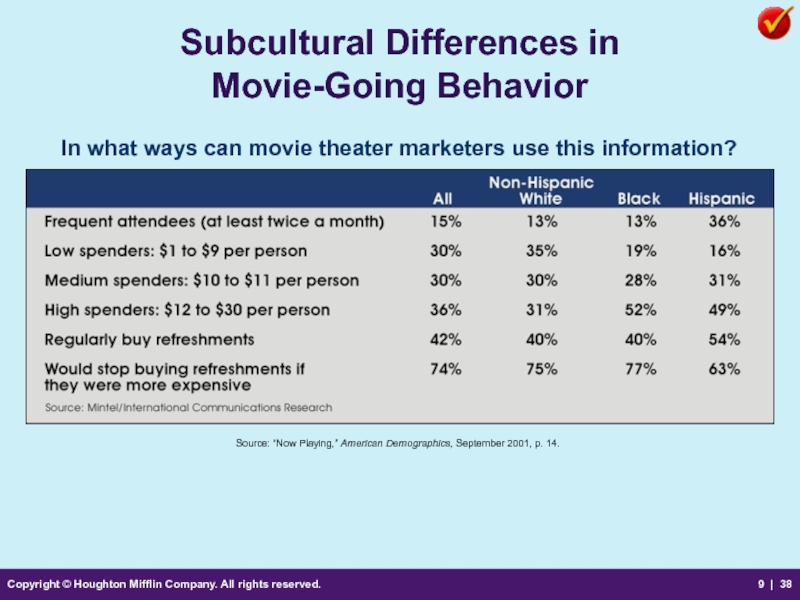
Subcultural Differences
In what ways can movie theater marketers use this information?
Source: “Now Playing,” American Demographics, September 2001, p. 14.
Слайд 39Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
9 |
Class Exercise
Imagine
Your role as a student, family member, employee, church member, or fraternity or sorority member.
Identification with a positive reference group. Disassociation from a negative reference group.
Слайд 40Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
9 |
Class Exercise
Membership within a particular social class. Aspirations to be in a different social class.
Cultural values that accept or reject certain types of behavior. Gender roles: expectations of how men and women should act.
Membership in a subculture based on geography, age, or ethnic background.
Knowing how these factors affect your consumption behavior, how can marketers adjust their marketing mixes to meet your needs?
Слайд 41Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
9 |
Net Sights
Consumerworld.org
Слайд 42Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
9 |
After reviewing
Understand the level of involvement and types of consumer problem-solving processes
Recognize the stages of the consumer buying decision process
Know how situational influences may affect the consumer buying decision process
Understand the psychological influences that may affect the consumer buying decision process
Be familiar with social influences that affect the consumer buying decision process
Слайд 43Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
9 |
Chapter Quiz
Which
Products purchased frequently
Products to be purchased in the future
Products that are purchased routinely
Expensive products
Products purchased as a result of social influences
Слайд 44Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
9 |
Chapter Quiz
When in their information search, consumers focus on communication with friends and relatives, they are utilizing ____________ sources.
internal
personal
marketer-dominated
direct
organizational
Слайд 45Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
9 |
Chapter Quiz
Selective exposure refers to
targeting only certain parts of the total market.
admitting only certain inputs into consciousness.
the circumstances or conditions that exist when a consumer is making a purchase decision.
the process of selecting, organizing, and interpreting information inputs to produce meaning.
remembering inputs that support personal feelings and beliefs and forgetting those that do not.
Слайд 46Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
9 |
Chapter Quiz
Which of the following is the fastest growing, most affluent subculture in the United States?
African Americans
Hispanics
Asian Americans
Native Americans
Italian Americans