- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
The State of Healthcare in South East Asia презентация
Содержание
- 2. CONTENTS A Snapshot of Healthcare in the
- 3. Healthcare in South East Asia is going
- 4. A SNAPSHOT OF THE REGION The
- 5. ASEAN TOTAL HEALTHCARE SPEND – OVER
- 6. ASEAN TOTAL HEALTHCARE SPEND AS %
- 7. ASEAN GOVERNMENT HEALTHCARE SPEND % OF
- 8. ASEAN SPEND PER CAPITA Data from World
- 9. INDONESIA There has been considerable investor
- 10. PHILIPPINES Investments, especially in public-private
- 11. MALAYSIA Malaysia has increased its 2013
- 12. SINGAPORE An aging population and a
- 13. The Big Healthcare Themes for 2014
- 14. The Big Healthcare Themes for 2014 The
- 15. Private Healthcare Growth Private healthcare growth is
- 16. The Increasing Relevance of ASEAN ASEAN is
- 17. The ASEAN Economic Community (AEC) The ASEAN
- 18. THE REGIONAL COMPREHENSIVE ECONOMIC PARTNERSHIP (RCEP) The
- 19. The Increasing Relevance of ASEAN As
- 20. The Increasing Relevance of ASEAN The HSSWG
- 21. The Increasing Relevance of ASEAN As ASEAN
- 22. Bigger and Better Public Health Provision Across
- 23. A focus on growing ‘new’ health threats
- 24. A focus on growing ‘new’ health threats
- 25. HIV/AIDS According to the UNDP, Indonesia faces
- 26. HIV/AIDS Although HIV/AIDS is a growing concern,
- 27. Medical Tourism Medical tourism is Big Business
- 28. Healthcare Across ASEAN
- 29. INDONESIA Small budgets and underinvestment have
- 30. SJSN AND THE INTRODUCTION OF BPJS (A
- 31. THAILAND Healthcare in Thailand can generally be
- 32. THAILAND 2014 AND BEYOND Despite its healthcare
- 33. PHILIPPINES The Filipino healthcare system can generally
- 34. The private sector, which is much larger
- 35. MALAYSIA Malaysia has a very high level
- 36. VIETNAM Healthcare in Vietnam can generally be
- 37. SINGAPORE Despite the relatively low level of
- 38. BRUNEI Brunei has a very good public
- 39. MYANMAR, CAMBODIA, LAOS Healthcare in these three
- 40. Appendix: Digital Healthcare Across ASEAN
- 41. 3,784,644,400 43% 57% Total Asian
- 42. Digital health is growing in South
- 43. Telehealth Systems Therapeutic & Diagnostic Medical Devices
- 44. INDONESIA IT and digital technologies are already
- 45. PHILIPPINES The digital landscape in the Philippines
- 46. THAILAND Successive Thai governments have aimed to
- 47. MALAYSIA For digital healthcare providers, big opportunities;
- 48. VIETNAM In Vietnam, digital healthcare is
- 49. BRUNEI The Government of Brunei aims to
- 50. Appendix: Thoughts for Pharma
- 51. Pharma Market – South Asia Region US$
- 52. Drugs Spend And Market Size Source: World
- 53. Stephen Lock Edelman Indonesia Stephen.Lock@edelman.com THANK YOU
Слайд 2CONTENTS
A Snapshot of Healthcare in the Region
The Big Healthcare Themes for
Healthcare Across ASEAN: Country Overviews
Appendix: Digital Healthcare Across ASEAN
Appendix: Thoughts for Pharma
Слайд 3Healthcare in South East Asia is going through a period of
Rapid economic growth
Rapid population growth
Increasing affluence and demand for better, and in some cases, private healthcare
Public healthcare sector reform and broadening
The introduction of ‘new’ growing healthcare challenges…
Healthcare in South East Asia
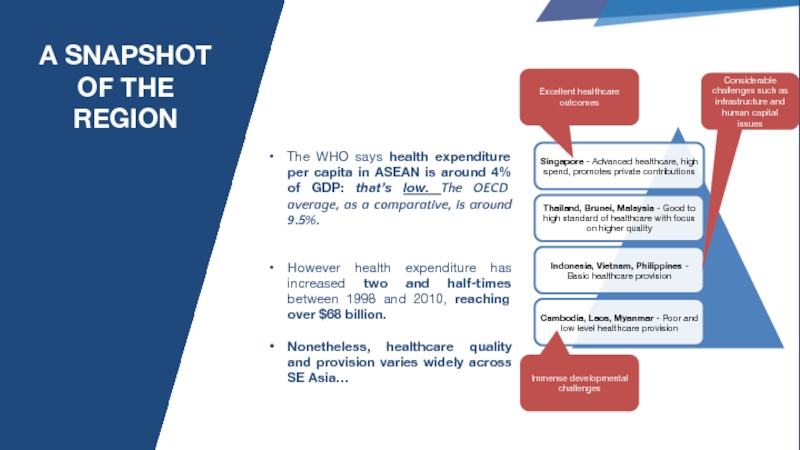
Слайд 4A SNAPSHOT OF THE REGION
The WHO says health expenditure per capita
However health expenditure has increased two and half-times between 1998 and 2010, reaching over $68 billion.
Nonetheless, healthcare quality and provision varies widely across SE Asia…
Excellent healthcare outcomes
Immense developmental challenges
Considerable challenges such as infrastructure and human capital issues
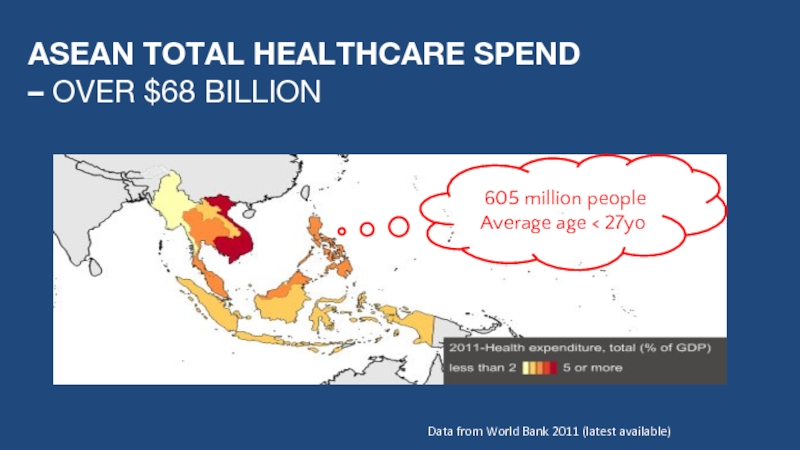
Слайд 5ASEAN TOTAL HEALTHCARE SPEND
– OVER $68 BILLION
Data from World Bank
605 million people
Average age < 27yo
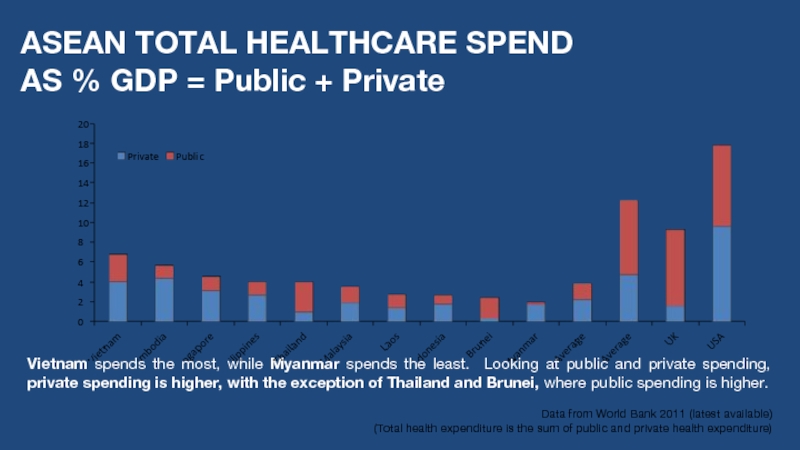
Слайд 6ASEAN TOTAL HEALTHCARE SPEND AS % GDP = Public + Private
Vietnam spends the most, while Myanmar spends the least. Looking at public and private spending, private spending is higher, with the exception of Thailand and Brunei, where public spending is higher.
Data from World Bank 2011 (latest available)
(Total health expenditure is the sum of public and private health expenditure)
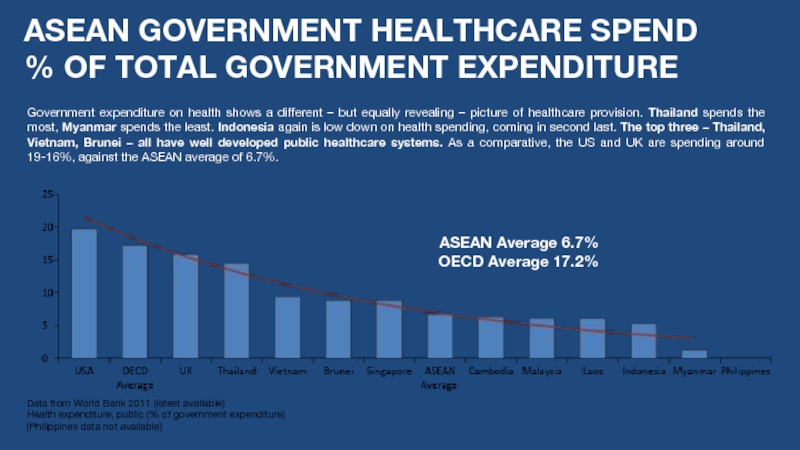
Слайд 7ASEAN GOVERNMENT HEALTHCARE SPEND
% OF TOTAL GOVERNMENT EXPENDITURE
Data from World
Health expenditure, public (% of government expenditure)
(Philippines data not available)
Government expenditure on health shows a different – but equally revealing – picture of healthcare provision. Thailand spends the most, Myanmar spends the least. Indonesia again is low down on health spending, coming in second last. The top three – Thailand, Vietnam, Brunei – all have well developed public healthcare systems. As a comparative, the US and UK are spending around 19-16%, against the ASEAN average of 6.7%.
ASEAN Average 6.7%
OECD Average 17.2%
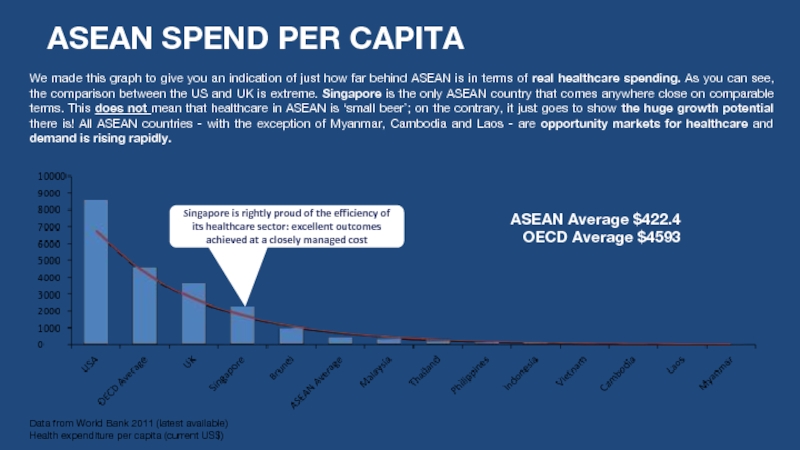
Слайд 8ASEAN SPEND PER CAPITA
Data from World Bank 2011 (latest available)
Health expenditure
ASEAN Average $422.4
OECD Average $4593
We made this graph to give you an indication of just how far behind ASEAN is in terms of real healthcare spending. As you can see, the comparison between the US and UK is extreme. Singapore is the only ASEAN country that comes anywhere close on comparable terms. This does not mean that healthcare in ASEAN is ‘small beer’; on the contrary, it just goes to show the huge growth potential there is! All ASEAN countries - with the exception of Myanmar, Cambodia and Laos - are opportunity markets for healthcare and demand is rising rapidly.
Singapore is rightly proud of the efficiency of its healthcare sector: excellent outcomes achieved at a closely managed cost
Слайд 9INDONESIA
There has been considerable investor interest in Indonesia’s healthcare space, including
The Indonesian government has tried to encourage more private sector involvement in the health sector. The Negative Investment List currently stipulates that foreign investors may now own up to 67% (65% previously) in healthcare related businesses. Ownership in the pharmaceutical sector is capped at 75%. It should be noted however that Indonesia still places limits of foreign ownership and rights.
Private investors are taking more interest in Indonesian healthcare. Blackstone, Bain Capital, and Dubai's Abraaj Capital, among others, have all been looking to break into the Indonesian healthcare sector by acquiring a percentage of private Indonesian healthcare operator Siloam, according to Reuters.
Siloam is the major hospital chain in Indonesia, but there are also a number of other private providers
POINTS OF INTEREST FOR HEALTHCARE INVESTORS LOOKING AT ASEAN
Слайд 10PHILIPPINES
Investments, especially in public-private partnerships (PPPs), are big in the
The government opened for bidding the construction of a 700-bed capacity specialty tertiary hospital earlier this year. The project is estimated to cost US$ 135 million.
Large private healthcare investments are also taking place; Makati Medical Centre, one of the leading hospitals in the Philippines, is investing heavily in new laboratories for the diagnosis and treatment of diseases…
POINTS OF INTEREST FOR HEALTHCARE INVESTORS LOOKING AT ASEAN
THAILAND
Thailand has a well-developed healthcare sector.
Private investment is increasing rapidly as demand for good quality provision grows as government provision falls behind in quality.
Bangkok Dusit Medical Services, the largest private hospital operator in Thailand, has invested in highly profitable non-core medical businesses…
Слайд 11MALAYSIA
Malaysia has increased its 2013 budget by 15% for healthcare to
For digital healthcare providers, big opportunities; from 2010-2014 the government is making a push to expand the use of IT in medical care, health education and health services system management. It is pushing “telemedicine” which allows for virtual medical consultation and training.
There has been an issue with telemedicine ‘take-up’ however; despite this private sector demand is strong…
POINTS OF INTEREST FOR HEALTHCARE INVESTORS LOOKING AT ASEAN
VIETNAM
An increase in demand for private healthcare in Vietnam is boosting investments. The government is offering generous incentives to foreign investors in the health sector: foreign healthcare backers enjoy a corporate income tax rate of 10%, tax exemption over the first four years of a project and a 50% subsequent tax break in the following years.
Last year, VinMec, the country’s largest and first hotel-like hospital was built, featuring five-star hotel standards, 25 VIP rooms, and two presidential suites.
The Triple Eye Infrastructure Corporation is awaiting government permissions to invest over $160 million in building a 200-bed international hospital.
The Chandler Corporation, has also made a move on Vietnam's largest private hospital group, Hoan My Medical Corporation, putting in $99 million to acquire an 80% stake…
Слайд 12SINGAPORE
An aging population and a focus on improving healthcare is driving
The country’s recent health policy was laid out in the ‘Healthcare 2020 Masterplan’…
Changes starting in 2014 include a new payment scheme introduced by the government that will cover more patients, more conditions and more treatments. In particular, there will be more support for the elderly and for low income families.
Singapore plans to add 3,700 hospital beds and recruit 20,000 more healthcare workers. Two more general hospitals, four community hospitals, and six polyclinics will open by 2020.
POINTS OF INTEREST FOR HEALTHCARE INVESTORS LOOKING AT ASEAN
BRUNEI
Brunei is small but rich! Investment remains high in its well funded healthcare sector.
Parkway Pantai, one of Asia's largest private healthcare providers, is in a joint venture with the Brunei Investment Agency to manage a 21-bed specialty cardiac center…
Слайд 14The Big Healthcare Themes for 2014
The year 2014 will be an
Some of the main issues will be:
The continued opening up of the private healthcare market and the embrace of the Public-Private Partnership (PPP) mechanism
The increasing relevance of ASEAN
A greater demand for better and wider provision from the public sector
More focus on growing but largely ignored health problems
Слайд 15Private Healthcare Growth
Private healthcare growth is continuing to grow at a
In Indonesia, the government has moved in recent years to encourage more private sector involvement and revised the Negative Investment List to allow for more private sector investment.
In the Philippines too, investments in PPPs are big. The government needs private sector cash to sustain state provision.
In Thailand, private investment is growing at breakneck speed as demand for good quality provision grows and government provision falls behind.
In Vietnam, private healthcare is also on the march. The government is even offering generous incentives to foreign investors in the health sector: foreign healthcare backers enjoy a corporate income tax rate of 10%, tax exemption over the first four years of a project and a 50% subsequent tax break in the following years.
South East Asia truly is going private and there are big opportunities for private healthcare providers and health firms. People with more money are prepared to spend more money on their health.
Слайд 16The Increasing Relevance of ASEAN
ASEAN is becoming more important and relevant
Слайд 17The ASEAN Economic Community (AEC)
The ASEAN Economic Community (AEC) is the
The AEC aims at: (a) a single market and production base, (b) a highly competitive economic region, (c) a region of equitable economic development, and (d) a region fully integrated into the global economy.
Слайд 18THE REGIONAL COMPREHENSIVE ECONOMIC PARTNERSHIP (RCEP)
The Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP)
The 10 ASEAN states plus its FTA partners - Australia, China, India, Japan, South Korea and New Zealand.
A combined GDP of around $17 trillion.
Makes up about 40% of world trade.
16 countries
3 billion people
Слайд 19The Increasing Relevance of ASEAN
As ASEAN becomes more and more relevant,
Through mechanisms such as the Healthcare Services Sectoral Working Group (HSSWG), ASEAN is attempting harmonize health regulations, and regulations regarding some medical products and devices. This has important ramifications for the healthcare industry; understanding and working through ASEAN is increasingly important, as it takes on a larger regional healthcare remit.
Слайд 20The Increasing Relevance of ASEAN
The HSSWG is an important part of
In the future, Mutual Recognition Arrangements (MRAs) on Medical Practioners, Nursing and Dental Practioners could reshape regional healthcare expertise and allow for much more mobility and skill transfers between ASEAN states; likewise with the development of greater equivalences and regional policy streamlining. Many MRAs have already been signed – for example in dentistry and nursing – the issue is streamlining and follow-through at the national legal level on country by country regulations.
ASEAN is and will play a much greater role in shaping regional healthcare in the future.
This is also an important issue to consider in terms of equity. Although opening up of markets could be a boost for the healthcare sector across the region, it also risks exacerbating divides; it is possible that the better-off will be better off still and that less developed systems may fall further behind. Greater mobility may also lead to ‘brain drains’ where highly qualified practioners move to ASEAN countries where higher remuneration is available, increasing capacity and skill gaps.
Слайд 21The Increasing Relevance of ASEAN
As ASEAN pushes forward with regional integration,
This is because ASEAN is aiming to implement a regional system where ASEAN member citizens will be able to receive health services in any country in the region with a similar standard. Medical workers will also eventually be allowed to work in any ASEAN country via the full implementation of MRAs. This means that the demand for doctors and hospital services will increase in countries with good, but affordable healthcare systems.
All these issues will become increasingly important points of focus for the future and in the run-up to 2015.
Слайд 22Bigger and Better Public Health Provision
Across the region, there is a
From the Philippines to Thailand where public ‘universal’ system are already in place, governments are under pressure to provide better health services to those in harder to reach regions – mostly in rural areas.
Indonesia is about to embark on a hugely ambitious program of ‘universal’ healthcare provision via the introduction of basic health insurance coverage through SJSN.
Even in wealthy Singapore, the government is reforming its healthcare insurance policies to focus on increasing affordability, through a reformed MediShield and greater provision for the elderly – with more elderly focused community hospitals planned.
It is not just the private health sector which is growing, but an increasingly growing public sector.
Looking across the other side of the world to Brazil this year, mass protests took place among Brazil’s middle classes at poor public services and provision, including healthcare. What this lesson tells us is that tax-paying middle classes soon demand better services for their hard earned tax payments.
Слайд 23A focus on growing ‘new’ health threats
As ASEAN nations get richer
Over 191 million people are now living with diabetes in the Asia-Pacific according to the International Diabetes Federation (IDF).
Issues such as mental healthcare also need to be addressed. So far the problem is mainly ignored, marginalized - or even worse - stigmatized. As work and lifestyles become more urban and ‘busy’, stress and mental illness is likely to become a growing health problem.
Слайд 24A focus on growing ‘new’ health threats
The other change is that
Despite this shocking statistic, it should be noted that Asia and South East Asia is very diverse in demographic trends - Japan , China, Singapore and Malaysia face an increasingly elderly population, however much of South East Asia still has very young demographics. There are therefore competing wellness challenges across the region and priorities vary from country to country.
This means more age related diseases and healthcare needs; needs which are currently largely ignored and in short supply.
Asia is focusing on its young, but it is the elderly which may prove to be a ticking time-bomb for the region. Healthcare companies have a potentially large role to play in providing for this growing need.
There is a huge lack of capacity in South East Asia for countries to treat and elderly health conditions such as dementia. This is combined with a lack of palliative care and suitable health support systems.
Image by garryknight
Слайд 25HIV/AIDS
According to the UNDP, Indonesia faces a threat of a major
HIV/AIDS has high prevalence levels in Jakarta and Bali (populous regions), but also serious concentrations in rural areas, usually in close proximity to mining areas. This is especially true of Papua.
According to a report by UNAIDS, the cumulative number of reported HIV infections in Indonesia has risen sharply from 7,195 in 2006 to 76,879 in 2011.
Some of the major issues include a lack of education and public awareness, and access and use of safe sex precautions (this is complicated by societal taboos and some conservative religious attitudes).
The Indonesian government is aware of the issue and has set up a National Strategy to combat the problem, with the goal that by 2014 eighty percent of key populations will be reached through effective preventive reduction programs.
Слайд 26HIV/AIDS
Although HIV/AIDS is a growing concern, countries such as Thailand –
Infection rates have been cut dramatically since 1991 and Thailand is one of the very first countries to have achieved the sixth Millennium Development goal, to begin to reverse the spread of HIV/AIDS by 2015, in advance of the target date.
Слайд 27Medical Tourism
Medical tourism is Big Business in Southeast Asia, especially for
Thailand has perhaps the most advanced medical tourism sector (with end-to-end solutions fully integrated with air travel; hotel accommodation for traveling families and airport greeting).
It is estimated Thai medical tourism increased from nearly 400,000 foreign patients, in 2007, to nearly 700,000 in 2012 worth a staggering $3.8 billion. That’s $3.8 billion in direct healthcare spending: the total economic impact may be three times that amount.
Another point of interest about the Thai health tourism sector is the wide range of countries from which it takes patients – Japan, Middle East, UK, USA and Australia are the big five – not just from its ASEAN neighbors.
Singapore is also a globally renowned medical tourism hub and also a center of excellence in oncology (which accounts for high revenue spend per patient): health tourism patients were worth over $800m in 2011 and nearly half from Indonesia.
Heath tourism is set to grow further still within the region, as better of patients from ASEAN travel to different countries for treatment, and the region’s growing medical prominence attracts more foreigners from developed markets.
Слайд 29INDONESIA
Small budgets and underinvestment have led to basic indeed poor provision
Basic primary healthcare provision is provided through an array of government social protection schemes. This does not cover the total population. This will change from 2014 with the introduction of a universal coverage scheme (discussed on next slide); this, however, will still only be basic cover.
Indonesia’s healthcare system is also decentralized (since 2001), which has led to varying degrees of quality and provision from region to region – Java has relatively good access to healthcare, but across the 17,000 islands, availability is patchy. ‘Puskesmas’ public health centers are the only available health services available in rural areas (if at all).
Healthcare spending is set to rise, due to an increase in state spending, and by encouraging the private sector to boost investments in health infrastructure via PPPs (Public-Private Partnerships). There has been a recent law change, increasing the allowed foreign ownership percentage of hospitals from 65% to 67%, also from Tier 1 major cities to across the country.
Key Facts
1,800 total hospitals
Only 5 hospitals internationally accredited; all 5 are private
0.3 doctors and 0.6 beds per 1,000 compared to neighbouring Malaysia 0.8 and 1.8 respectively. As a comparative, the OECD Average is 4.8 beds per 1,000 population and 3.2 doctors per 1,000 population
Major Hospital Groups
Lippo Group – Siloam Hospitals
Kalbe Group – RSMK Hospitals
Premier Group – RS Premier Hospitals
Health Issues
Increase in non-communicable diseases ((especially cardiovascular diseases)
Growing elderly population
Malaria and Dengue fever
Tuberculosis
Growing HIV/AIDs problem
Smoking related diseases
Слайд 30SJSN AND THE INTRODUCTION OF BPJS (A SEA CHANGE IN INDONESIAN
Indonesia currently has a basic level of healthcare provision, with half the population – i.e. 125m+ - lacking state health coverage or state or private health insurance.
The government is set to introduce basic health health Insurance coverage called SJSN (Sistem Jaminan Sosial Nasional), where from 1st January 2014, it will provide 140 million Indonesians with health coverage implemented by the BPJS (Badan Penyelenggara Jaminan Sosial) state social security provider. Further, it aims to have truly universal coverage by 2019.
It will mainly provide for the poor and vulnerable, who are currently catered for under a number of other social protection programs.
SJSN is a move towards a more comprehensive and joined up approach to state cover and provision.
It is worth noting that with the 2014 elections fast approaching and a 2nd term ‘lame duck’ presidency, the government is content for high public spend levels, such as implementing the health scheme, without tackling politically sensitive and economically costly subsidies. The question remains: will the next government have the political will?
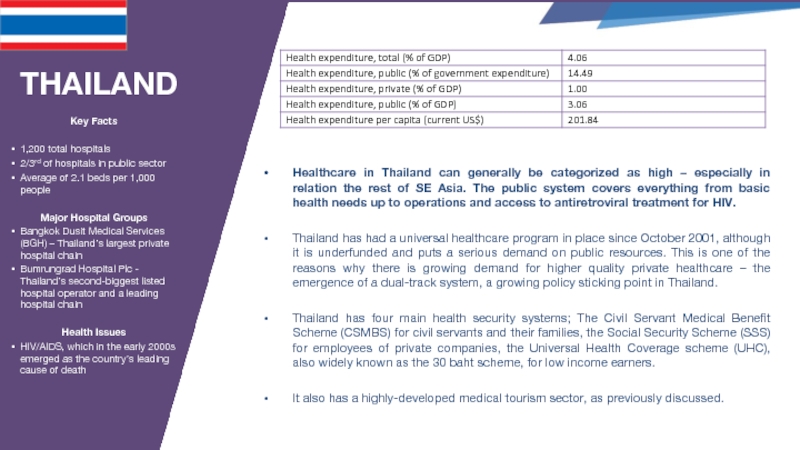
Слайд 31THAILAND
Healthcare in Thailand can generally be categorized as high – especially
Thailand has had a universal healthcare program in place since October 2001, although it is underfunded and puts a serious demand on public resources. This is one of the reasons why there is growing demand for higher quality private healthcare – the emergence of a dual-track system, a growing policy sticking point in Thailand.
Thailand has four main health security systems; The Civil Servant Medical Benefit Scheme (CSMBS) for civil servants and their families, the Social Security Scheme (SSS) for employees of private companies, the Universal Health Coverage scheme (UHC), also widely known as the 30 baht scheme, for low income earners.
It also has a highly-developed medical tourism sector, as previously discussed.
Key Facts
1,200 total hospitals
2/3rd of hospitals in public sector
Average of 2.1 beds per 1,000 people
Major Hospital Groups
Bangkok Dusit Medical Services (BGH) – Thailand’s largest private hospital chain
Bumrungrad Hospital Plc - Thailand’s second-biggest listed hospital operator and a leading hospital chain
Health Issues
HIV/AIDS, which in the early 2000s emerged as the country’s leading cause of death
Слайд 32THAILAND 2014 AND BEYOND
Despite its healthcare strength, Thailand's national health system
The ‘2011 World Health Statistics’ report by the World Health Organization stated that in Thailand there are just three physicians for every 10,000 patients, compared to 18.3 in Singapore, 9.4 in Malaysia, 11.5 in the Philippines and 12.2 in Vietnam. This may be exacerbated as the ASEAN Economic Community takes effect.
Ageing is also an issue. The population of Thailand is getting old. According to Viroj Tangcharoensathien, senior adviser of Thailand's International Health Policy Program, 11% of the Thai population is over 60 years of age and the trend is rising – more elderly healthcare provision is therefore needed. The proportion of older citizens in the total population is expected to reach 14% in 2015, 19.8% in 2025 and nearly 30% by 2050.
Слайд 33PHILIPPINES
The Filipino healthcare system can generally be considered to be of
In 2010, a major reform effort was made to achieve universal coverage, reduce payments and provide more comprehensive cover. Some still remain uncovered however; some rural areas only have basic primary healthcare.
The Philippines has a decentralized hospital system setting, wherein the Department of Health (DOH) serves as the governing agency for both local government units (LGUs) and the private sector providing services to communities and individuals.
The Philippines has a large private healthcare sector in which most expenditure is out-of-pocket, with the remainder being funded through insurance schemes.
Medical professionals are of a very high standard, training at the top universities in the country or outside, usually in the US. This has led to a number of Filipino health professionals being ‘poached’ by western countries – such as the UK – who have recruited Filipino nurses to fill shortfalls. Some areas in the Philippines are still understaffed.
Key Facts
1,921 total hospitals
Private sector hospitals 1,202
State hospitals are much larger than private and account fro 51% of the country’s 93,180 hospital beds
Health Issues
Heart disease
Слайд 34The private sector, which is much larger than the public sector
Although the private health sector is regulated by the DOH and the Philippine Health Insurance Corporation, health information generated by private providers is generally absent in the information system of the DOH.
Regulation of health science schools and universities is under the Commission on Higher Education, while the regulation of health professionals is carried out by the Professional Regulation Commission.
Some of the top private hospitals in the Philippines:
St. Luke's Medical Center
Makati Medical Center
Asian Hospital and Medical Center
University of Santo Tomas Hospital
The Medical City
PRIVATE HEALTH IN THE PHILIPPINES
Слайд 35MALAYSIA
Malaysia has a very high level of healthcare, from basic needs
The government is committed to universal coverage and public medical services are heavily subsidized. For the poor, healthcare is free. A majority of Malaysians have private insurance policies or pay out-of-pocket for private healthcare expenses. Through this ‘two-tier’ system the population has easy access to primary- and secondary-care facilities.
The government accounts for around 60% of total healthcare spending in Malaysia, but it is trying to reduce costs by advancing the private sector as an ever greater healthcare provider. Malaysia’s healthcare industry is valued at around US$8.4 billion. The government is pushing for spending on both public and private healthcare to rise to around 7% of GDP by 2020 in order for Malaysia to reach developed-country standards. This may be difficult to meet however, due to Malaysia’s fiscal consolidation and current budgetary constraints.
Private and public healthcare demand is set to grow due to an aging population, increased prosperity and greater consumer awareness of private healthcare services.
Key Facts
358 total hospitals
138 public hospitals
38,394 public hospital beds
2,880 public health clinics
220 private hospitals
6,589 private medical clinics
Major Hospital Groups
KPJ Healthcare Berhad
IHH Healthcare Berhad
Columbia Asia
Ramsey Sime Darby Health Care
Health Issues
Non-communicable diseases such as heart disease and type-2 diabetes
Dengue fever
Слайд 36VIETNAM
Healthcare in Vietnam can generally be described as good to basic
In 2010, 60% total coverage was achieved. Vietnam covers its population via a number of programs. One is the Vietnam Social Insurance Agency, for employees of state-owned enterprises and private companies. This is employee and employer contribution based – around 5% of salary. Vietnam also runs a Healthcare Fund for the Poor, with the aim of achieving universal coverage by 2014. Universal coverage, however, is unlikely due to poor health infrastructure, especially in rural areas, and complications involved in covering the informal sector.
The government carries around 30% of total expenditure on healthcare, with households making up the rest, increasingly via buying their own health insurance packages.
Most healthcare expenditure is now in the private sector, accounting for over 60% out of an expected total healthcare spend in Vietnam in 2014 of $6 billion, up from $3.5 billion in 2009.
There is a big push for private health sector involvement; this is driven by the need to upgrade services, lack of state finance, and a growing middle class. The Vietnamese government has implemented a number of laws from 2008 to 2011 to encourage growth and investment in the health sector. The government has encouraged private investment in the health sector, mostly due to Vietnam’s broader social mobilization policy in health; this has been backed by foreign investor tax breaks. The framework for private healthcare providers is therefore relatively good.
Key Facts
1,063 total hospitals
137 private hospitals
152,000 hospital beds
State hospitals are much larger than private and account fro 51% of the country’s 93,180 hospital beds
Health Issues
Developing country ailments including rabies, malaria, dengue fever
Tuberculosis
Слайд 37SINGAPORE
Despite the relatively low level of spending on healthcare in Singapore,
Singapore operates a universal healthcare system through compulsory insurance, subsidies and price limitations. No medical service is free, despite public insurance schemes and subsides. This is designed to ration the use of services. Around 70-80% of Singaporeans obtain their medical care within the public health system via the three major public healthcare finance schemes; Medisave, Medishield and Medifund. Private healthcare demand is still high however, via private insurance schemes.
Overall, the ‘Healthcare 2020 Masterplan’ aims to add 4,100 hospital beds by 2020, including 1,900 community hospital beds, mainly to cater to the aging population. The government also plans to build four new acute hospitals between 2020 and 2030.
In 2014, MediShield will be renamed MediShield Life, the age ceiling (previously 90 years) will be removed and the compulsory fund will cover all Singaporeans, including those with pre-existing illnesses. The government has also introduced the Pioneer Generation Package, which will pay for healthcare bills for those in the late 60s and older. For low-income families, the qualifying age floor of 40 years will be removed from the Community Health Assist Scheme (CHAS) so that children in these families can also receive subsidized outpatient medical treatments. Subsidies for lower and middle-income patients at specialist outpatient clinics will also be increased.
Key Facts
25 total hospitals
10,756 hospital beds
15 public hospitals
10 private hospitals
Health Issues
‘Developed country’ ailments such as cancer, cardiovascular diseases and strokes; these account for 60% of all deaths
Слайд 38BRUNEI
Brunei has a very good public health care system, in which
A handful of hospitals are supported by health clinics around the country. These facilities are of a high level and provide good treatment for all standard medical needs. Health facilities are very good and a large number of health professionals and doctors receive their training in the UK, North America, New Zealand and Australia; until recently all medical training took place overseas as there were no medical training establishments in the country.
The government also funds overseas specialist treatment, usually in Singapore and Malaysia, as part of the paternalist, absolute monarchy ‘social compact with the people’.
Key Facts
6 total hospitals
4 public hospitals
2 private hospitals
17 heath centers
Health Issues
Ageing population
Lifestyle related health problems such as inactivity and smoking
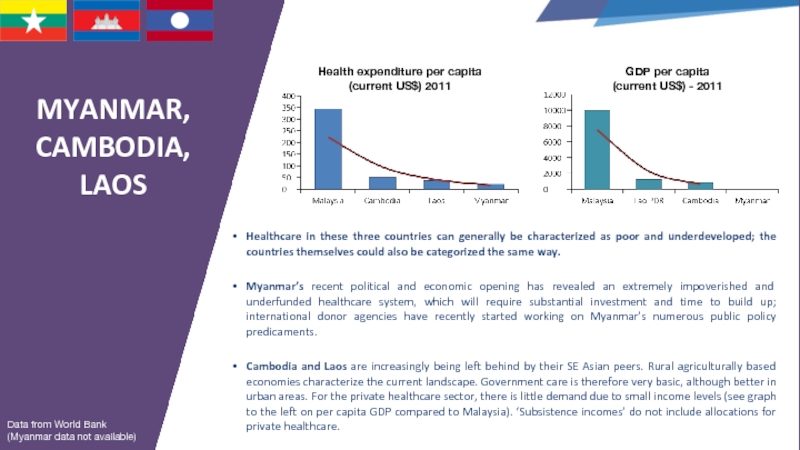
Слайд 39MYANMAR, CAMBODIA, LAOS
Healthcare in these three countries can generally be characterized
Myanmar’s recent political and economic opening has revealed an extremely impoverished and underfunded healthcare system, which will require substantial investment and time to build up; international donor agencies have recently started working on Myanmar’s numerous public policy predicaments.
Cambodia and Laos are increasingly being left behind by their SE Asian peers. Rural agriculturally based economies characterize the current landscape. Government care is therefore very basic, although better in urban areas. For the private healthcare sector, there is little demand due to small income levels (see graph to the left on per capita GDP compared to Malaysia). ‘Subsistence incomes’ do not include allocations for private healthcare.
GDP per capita
(current US$) - 2011
Data from World Bank
(Myanmar data not available)
Health expenditure per capita
(current US$) 2011
Слайд 413,784,644,400
43%
57%
Total Asian Population
Rural
Urban
1,033,688,491
Internet Users
27%
Internet Penetration
3,110,235,171
Mobile Subscribers
82%
Mobile Penetration
ACROSS ASIA
Слайд 42Digital health is growing
in South East Asia – like the
eHealth, telehealth, mHealth, social health
THE APPLICATION OF DIGITAL HEALTH
Слайд 43Telehealth Systems
Therapeutic & Diagnostic Medical Devices
Remote Monitoring Devices
Mobile Health Applications
Secured Wireless
Medication Monitoring Equipment
Mobile Health Devices
Medical Robotics
Personal Health Records
Communications Networks
Gaming for Health
ePrescriptions
Patient communities
Information websites
SOME EXAMPLES
Слайд 44INDONESIA
IT and digital technologies are already being used widely in Indonesia
So far in terms of IT integrated systems, these are limited, usually to one hospital or one hospital unit, if at all. They are also all found in high-end private hospitals. Potential is ripe!
Digital technologies though are widely used; according to Edelman Indonesia’s ‘Healthcare Professionals Survey 2013 ’, 4 out of 5 physicians in Jakarta trawl the internet for work-related information. Digital is already used in helping doctors with limited means and services to make diagnoses.
Dokter Gratis (Free Doctor)
An App for consultation (iOS, Android)
Developed by Warung Kreasi and handled by Medika Consulting group
At the moment there are 12 general practitioners to respond to all the chats every day. Working in shifts, it’s claimed that a doctor has the capacity to handle about 1,000 chats per day. The app has so far been downloaded 130,000 times with around 500 chats happening each day
SOCIAL AND DIGITAL
Some widely used digital apps…
Dokita (Dokter Kita – ‘Our Doctor’)
An (Android) app service of Dokita.co, one of the products/ideas by Aibilities;
Patients are able to:
Consult
Submit prescriptions
Purchase medicine & medical items
Aibilities is a startup company focusing on health issues
DIGITAL HOSPITAL TAKEUP
Our preliminary research shows that digital hospital and healthcare system take up is low. According to our contacts in the Ministry of Heath, patient-centric e-records have been implemented in a limited number of cases. In the small number of hospitals that they have, such as Cipto Mangunkusumo Hospital (RSCM), there is still limited awareness and understanding. The Ministry says there is plenty of scope for improvement.
Most hospitals are still using internal based information systems (HIS), and there are no major digital providers. The only major firm is AdMedika, who provide a Hospital Information System (Hisys); the firm is a subsidiary from Telkom Indonesia.
Слайд 45PHILIPPINES
The digital landscape in the Philippines is changing fast. At present,
Seeing the necessity of digital health strategy, Philippine healthcare initiatives are now finding its rightful place in the digital space. The government together with the private sector is pushing forward the digitalization of Healthcare information and accessibility for the benefit of the Filipinos.
DIGITAL HOSPITAL TAKEUP
Government and Private Sector Initiatives
Digital Healthcare Week 2013 Conference and Exhibition is a one-stop-shop where policy-makers, senior executives from healthcare providers, care providers, clinicians, nurses, healthcare IT professionals and technologies companies can come together for a week of collaboration, sharing and learning for improving the quality of care and accessibility to healthcare for patients.
Full Information: PHIE Workshop
Private Sector Partnerships
Last July 2013, Smart Communications, Inc. subsidiary Voyager Innovations, Inc. collaborated with Asian Hospital and Medical Center to develop a digital health system that will improve coordination between patients and their healthcare providers.
Full Information: Smart subsidiary partners with Asian Hospital for mobile health project
Слайд 46THAILAND
Successive Thai governments have aimed to turn the country into a
Patient e-records and integrated IT systems are currently not widely used, with traditional administration remaining the primary system for keeping patient records.
DIGITAL HOSPITAL TAKEUP
There is one example of digital and IT systems beginning to be integrated into healthcare. A Thai IT company has developed its own innovative application, Tele Diang, which could ease problems associated with the country’s shortage of radiologists by offering a pioneering tele-radiologist service.
The solution allows radiologists to access the system from other hospitals or even from home via the internet and view the images and send back their interpretations.
This has so far been adopted by at least 20 hospitals nationwide, including Praram 9 Hospital and Vejthani Hospital in Bangkok, Srisawan Hospital in Nakhon Sawan province and other provincial hospitals.
Слайд 47MALAYSIA
For digital healthcare providers, big opportunities; from 2010-2014 the government is
However…
This is a very ambitious national initiative and has failed to get large-scale traction due to a lack of knowledge and execution capabilities.
DIGITAL HOSPITAL TAKEUP
With the slow nation-wide take up of digital healthcare, hospitals in both the public and private sector have been installing their own system networks – on a case by case, individual hospital by individual hospital basis.
There is definitely demand for technology and integrated systems, but no grand joined up strategy at present, such as in the UK.
Слайд 48VIETNAM
In Vietnam, digital healthcare is so far mainly convened to
Predominantly, e-health applications are so far used to support the management and administration of health services, reduce arbitrary work pressure for staff of health facilities, and improve the quality of Information.
DIGITAL HOSPITAL TAKEUP
In hospitals, the term e-health is understood so far as a software system for the purpose of public health, mainly free software, provided by the state.
Current examples include
Medisoft (by MOH): the standard software for all hospital statistic medical reports
Healthnet
Goodsoft
E-Health (by IBOSS Vietnam)
The introduction of ‘Telemedicine’ has recently been picked up, and some systems are used in tele-consultation, tele-surgery assistance, tele-imaging, and tele-cardiology. This has proved very popular with medical professionals and patients.
Слайд 49BRUNEI
The Government of Brunei aims to have a single electronic health
It has signed an agreement to develop the Brunei Healthcare Information System (Bru-HIMS), a nationwide project to digitise patient care documents and provide electronic medical records.
iSoft and Ishajaya Technology have been commissioned to build the framework of the digital healthcare system that will provide access to patient data, identity management, process automation for administrative and clinical departments, workflow design and resource scheduling.
DIGITAL HOSPITAL TAKEUP
Brunei was the first country in the region to have telemedical facilities that allow patients to access stroke specialists in Germany without stepping out of Southeast Asia.
Telemedicine has helped connect Jerudong Park Medical Centre (JPMC) doctors and patients with specialists from overseas through satellite technology, video conferencing and data transfer through phones and the Internet, a strategy that will put it closer to its bid to lure medical tourists.
Telemedicine has also helped connect doctors and nurses of Neuroscience Stroke Rehabilitation Centre (NRSC) with Krakenhaus Nordwest Hospital in Frankfurt, Germany through a protected data line to allow for assessment, interpretation, and reporting of MR-I and CT imaging.
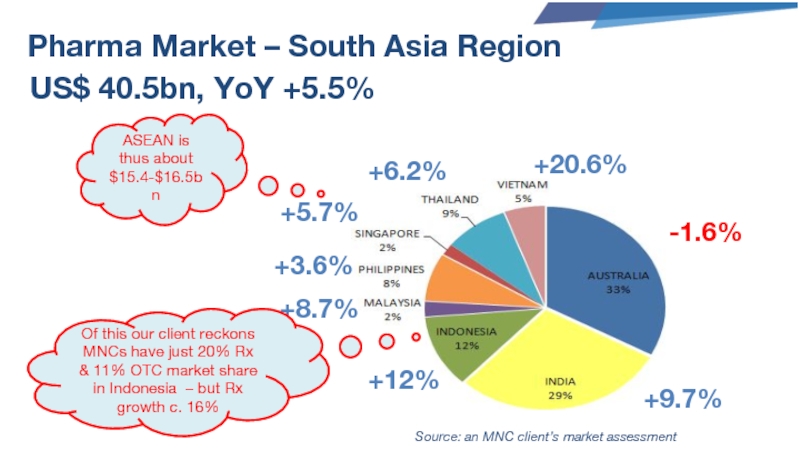
Слайд 51Pharma Market – South Asia Region
US$ 40.5bn, YoY +5.5%
-1.6%
+9.7%
+12%
+8.7%
+3.6%
+5.7%
+6.2%
+20.6%
ASEAN is thus
Source: an MNC client’s market assessment
Of this our client reckons MNCs have just 20% Rx & 11% OTC market share in Indonesia – but Rx growth c. 16%
Слайд 52Drugs Spend And Market Size
Source: World Health Organization
Thailand is key for
Malaysia is also big spending– mostly private, despite its small market size.
Vietnam is mostly private spend, despite large state healthcare provision.
The Philippines is almost entirely private spend.
Indonesia’s market potential is huge – biggest economy and population in the region with solid growth rates – but from a low base.