- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
EBOLA презентация
Содержание
- 1. EBOLA
- 2. WHAT IS EBOLA VIRUS DISEASE (EVD)? The
- 3. chimpanzees, gorillas, fruit bats, monkeys HOW WAS
- 4. HOW DOES EBOLA SPREAD THROUGH HUMAN-TO-HUMAN
- 5. WHAT ARE THE SYMPTOMS OF EVD?
- 6. There is no approved vaccine or medicine
- 7. HOW DO WE STOP EBOLA FROM SPREADING?
- 8. What we need to know about EBOLA Sources: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs103/en/ http://www.vox.com/2014/10/9/6905347/too-afraid-to-ask-about-ebola-virus-outbreak-symptoms http://www.cdc.gov/vhf/ebola/resources/virus-ecology.html
- 9. The world's leading supplier of unique,
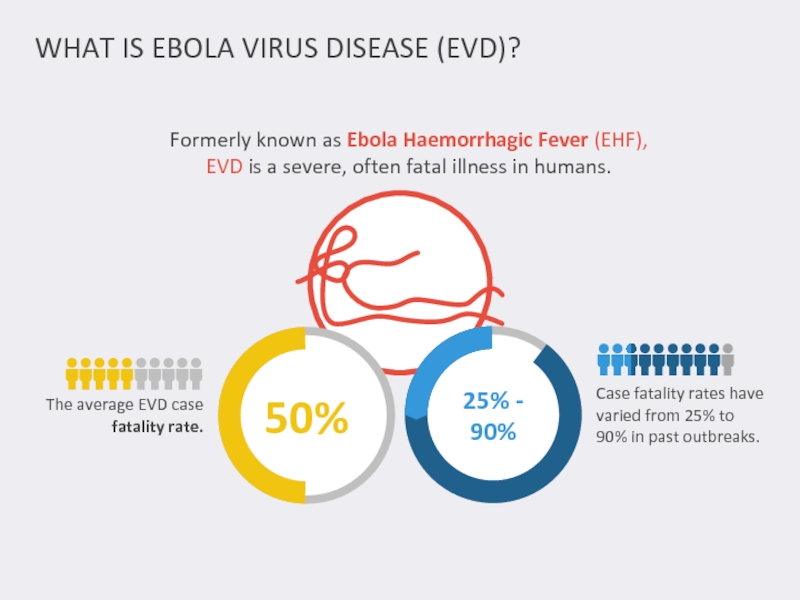
Слайд 2WHAT IS EBOLA VIRUS DISEASE (EVD)?
The average EVD case fatality rate.
Case
Formerly known as Ebola Haemorrhagic Fever (EHF), EVD is a severe, often fatal illness in humans.
Слайд 3chimpanzees, gorillas, fruit bats, monkeys
HOW WAS THE VIRUS ACQUIRED FROM ANIMALS?
Ebolavirus
It is thought that fruit bats of the Pteropodidae family are natural Ebola virus hosts.
Infected animals
Human beings
Слайд 4HOW DOES EBOLA SPREAD THROUGH
HUMAN-TO-HUMAN TRANSMISSION?
Direct contact through broken skin
Blood, vomit, sweat, saliva, urine, feces, and other body fluids
Слайд 5
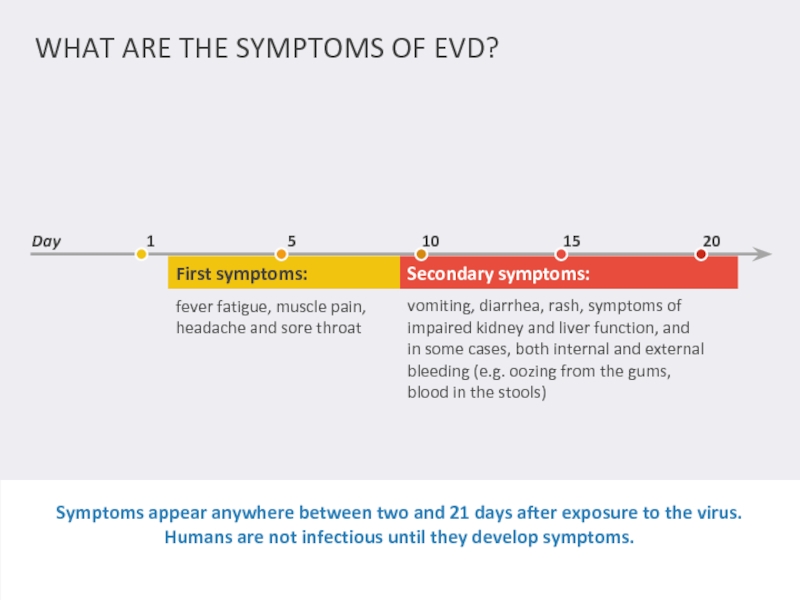
WHAT ARE THE SYMPTOMS OF EVD?
Symptoms appear anywhere between two and
First symptoms:
Secondary symptoms:
fever fatigue, muscle pain, headache and sore throat
vomiting, diarrhea, rash, symptoms of impaired kidney and liver function, and in some cases, both internal and external bleeding (e.g. oozing from the gums, blood in the stools)
Day
1
5
10
15
20
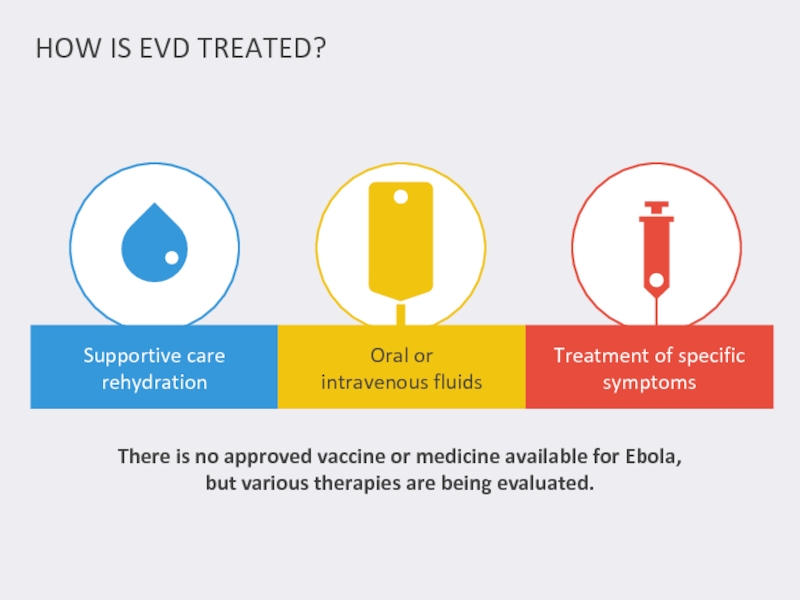
Слайд 6There is no approved vaccine or medicine available for Ebola,
but
HOW IS EVD TREATED?
Слайд 7HOW DO WE STOP EBOLA FROM SPREADING?
Wildlife-to-human transmission
Avoid eating raw meat
Handle animals with gloves and other protective clothing
Cook animal meat thoroughly before eating
Outbreak containment measures
Bury the dead safely and promptly
Identify people who may have been in contact with infected patients
Monitor the health of contacts for 21 days
Separate the healthy from the sick to prevent further spread
Maintain good hygiene and clean environment
Human-to-human transmission
Avoid contact with infected people
Use gloves and personal protective equipment when taking care of infected patients
Wash hands thoroughly after hospital visits
Слайд 8What we need to know about
EBOLA
Sources:
http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs103/en/
http://www.vox.com/2014/10/9/6905347/too-afraid-to-ask-about-ebola-virus-outbreak-symptoms
http://www.cdc.gov/vhf/ebola/resources/virus-ecology.html
Слайд 9
The world's leading supplier of unique, creative and effective PowerPoint templates.
contact:
pinterest: Slideshop
slideshare: slideshop.com
phone number: +1 602 559 4554