- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
State-legal development of the United States in XVIII-XIX презентация
Содержание
- 1. State-legal development of the United States in XVIII-XIX
- 2. The struggle for independence and the causes
- 3. At the beginning of the 18th century.
- 4. Till the middle of the eighteenth century.
- 5. The causes of the revolution: The
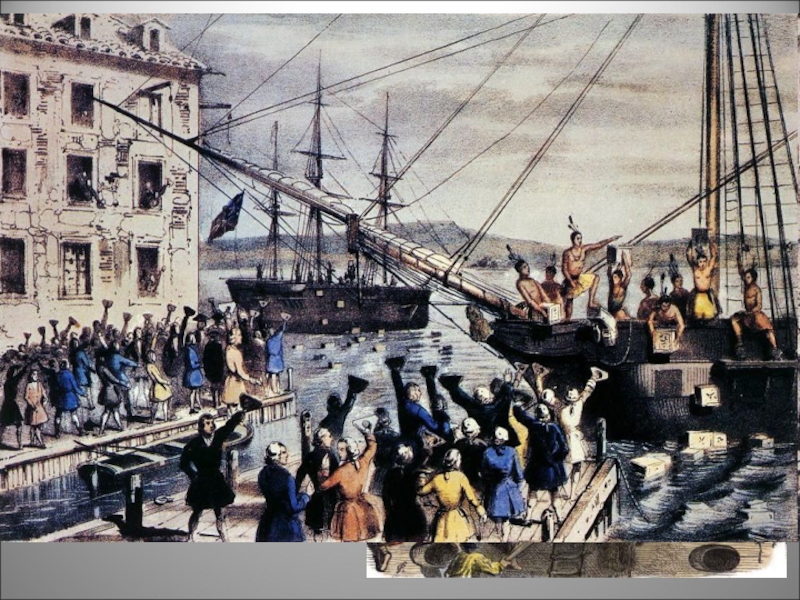
- 6. Бостонське чаювання— акція американських колоністів у
- 8. In may 1775, assembled the second
- 9. The second continental Congress in
- 10. George Washington— American statesman, the
- 12. Thomas Jefferson a member
- 13. The introductory part: that is the
- 14. Articles of Confederation The second continental
- 15. Articles of Confederation was created
- 16. Structure The principle of "one state has
- 17. The expenses of the Confederation shall be
- 18. But the Articles of Confederation
- 19. Constitution September 17, 1787, the Convention
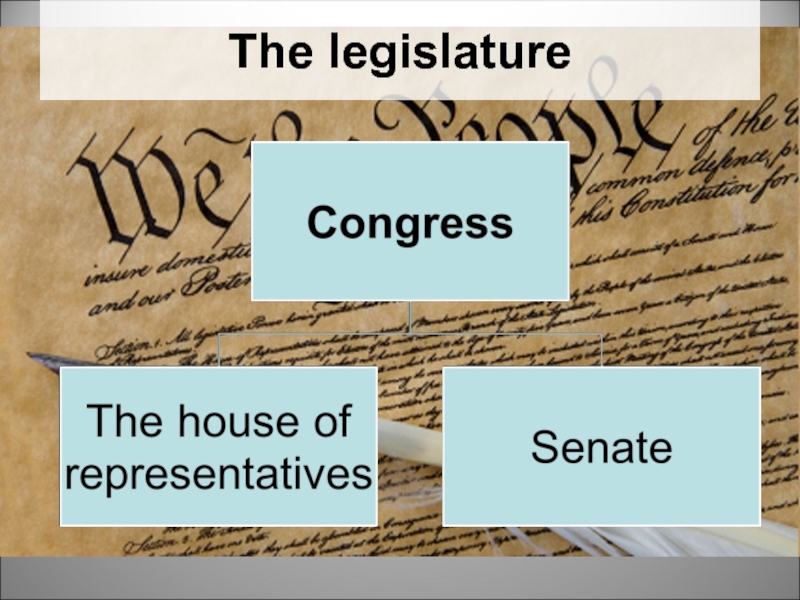
- 21. The legislature
- 22. The house of representatives Members were elected
- 23. Two senators were chosen from the state
- 24. The head of state and Executive is
- 26. The development of the law A feature
- 27. Civil law Federal legislation affected private law
- 28. Family law In the field of family
- 29. Thank you for your attention
Слайд 2The struggle for independence and the causes of the revolution
“Declaration of
“Articles of Confederation”
The US Constitution
The development of the law
Content
Слайд 3At the beginning of the 18th century. in the U.S., there
2) self-governing (Connecticut, Rhode island, Massachusetts
3) privately owned (Pennsylvania, Delaware, Maryland, etc.).
The struggle of the American colonies for independence
Слайд 4Till the middle of the eighteenth century. the colonies had a
Слайд 5 The causes of the revolution:
The selfish policy of the British
The enforced placement of growing contingents of British troops in the American colonies
England, impeding economic development of the colonies, took measures aimed at the cessation of their growth industry
the introduction of "stamp duty" - a new tax, which levied and shopping deals, and documents, and Newspapers , and ads
Слайд 6
Бостонське чаювання— акція американських колоністів у відповідь на дії Британського уряду,
Слайд 7
5
Слайд 8
In may 1775, assembled the second continental Congress, which, noting the
Слайд 9 The second continental Congress in terms of war, which
Слайд 10
George Washington— American statesman, the first President of the United States,
Слайд 11
In July 4,
The Declaration of independence
Слайд 12 Thomas Jefferson a member of the First American
Слайд 13
The introductory part:
that is the natural human aspiration to political independence
Preamble:
due
The main part:
a long list of "repeated harassment and usurpation" by the British government against the rights and freedoms of American colonists
mention the attempts of the colonists to attract the attention of the British authorities to set out issues
colonies are forced to discard their political connection with the British crown and become independent States
The Declaration of independence
Слайд 14Articles of Confederation
The second continental Congress in November 1777. adopts the
Слайд 15 Articles of Confederation was created in five pages and
Main provisions: The Name Of The Confederation Is "The United States Of America.
Proclaimed the sovereignty of States and guaranteed their powers in the part in which they are not transferred to the Confederation.
Set the goal of creating a Confederation, the States agree to help each other.
The freedom of movement of citizens of the States of the Confederation and the duty of States to extradite criminals.
Structure
Слайд 16Structure
The principle of "one state has one vote in Congress" and
International relations are the exclusive competence of the Confederation, the States may not have their own armed forces (except militia) and the Navy without the authorization of Congress.
The procedure of awarding military ranks during the war (the rank below Colonel assigned to the legislature of the States).
Слайд 17The expenses of the Confederation shall be paid from the fees
The powers of the Confederation: declare war, standardization of weights and measures (including cash handling), disputes between the States.
The Committee States, the authority of the acting government between sessions of Congress.
Establishes procedures for the acceptance of the new member (Canada (modern Quebec) is assumed by default, in other cases it requires the approval of nine States).Confirmation of the commitments made by the United States prior to the approval of the Articles of Confederation.
The procedure of changing of Articles - changes must be approved by all States.
Слайд 18 But the Articles of Confederation proved ineffective, and identified
The General budget of the Union did not exist There was no mechanism for the implementation of the resolutions of the Congress
Given this j. Washington called the Articles of Confederation “rope of sand”
Слайд 19Constitution
September 17, 1787, the Convention approved a draft Constitution
Consists
Written in the first person and begins with the words "We the people of the United States...".
The authors considered. Franklin, A. Hamilton, D. Madison
Слайд 20
The Principles Of The
Republican form of government
Federalism
The distribution of power among the three branches
Слайд 22The house of representatives
Members were elected for two years from each
Candidates were presented with the following requirements:
25 years
to be for 7 years a US citizen
- during the holding of elections to reside in the state from which elected
Слайд 23Two senators were chosen from the state for six years, at
Each Senator had one vote
A Senator could be a person who was 30 years old, for 9 years was a U.S. citizen at the time of the election lived in the state from which elected
The President of the Senate was Vice-President
The Senate
Слайд 24The head of state and Executive is the President
The President is
The President appointed Ministers, and was commander of the armed forces, carried out representative functions, - appointed members of the Supreme court
The President could be a person aged 35 years who was a U.S. citizen and lived in the United States at least 14 years
Executive power