- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
History of the kazakhstan architecture презентация
Содержание
- 1. History of the kazakhstan architecture
- 2. Lecture 1. Ancient times 1.Main stages of
- 3. Main stages of Architecture development in Kazakhstan
- 4. Ancient times 1. PALEOLITH, NEOLITH (140 000-5000
- 5. Medieval times Period of Turkic khaganates
- 6. New and Newest times Soviet period (ХХ c.); Independence period (since 1990).
- 7. Geographical, cultural and historical regions – architectural
- 8. Paleolithic monuments (140,000-40,000 BC) The most
- 9. Paleolithic dwelling On the equal, protected from
- 10. Aydakharly cave (Ulytau mountains, Central Kazakhstan)
- 11. Neolithic monuments Types of Neolythic sites: Spring
- 12. Botay Settlement (3,000-2,000 BC) The Ayirtau district
- 13. Reconstruction of the Botay settlement dwelling
- 14. Settlements of Andronov culture (XVIII-XII c.
- 15. Atasu settlement (XV-XII c.BC) The area is
- 16. Atasu settlement’s plan
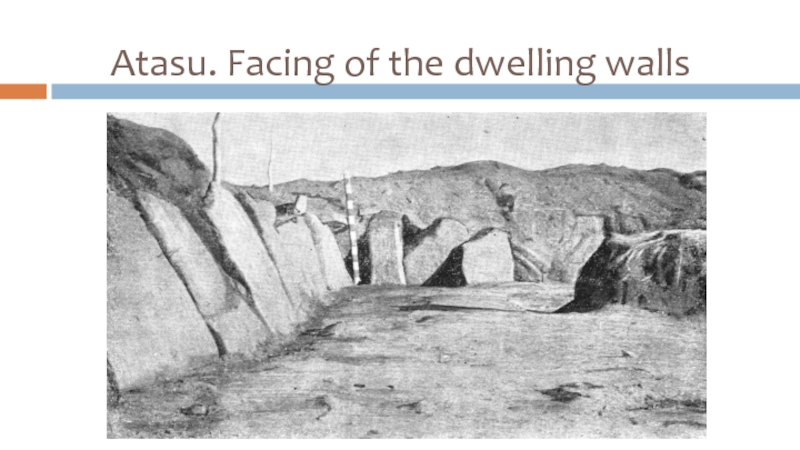
- 17. Atasu. Facing of the dwelling walls
- 18. Buguly settlement (XII-XI c.BC) about 50 hectares;
- 19. Buguly. Plans of single-chamber and multi-chamber dwellings
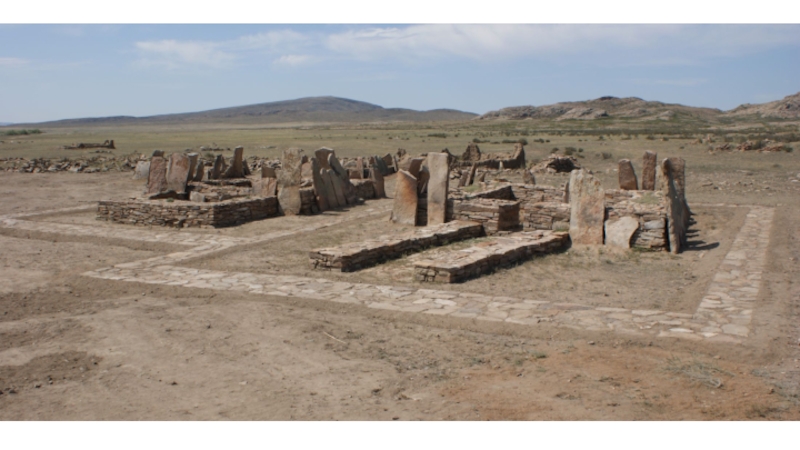
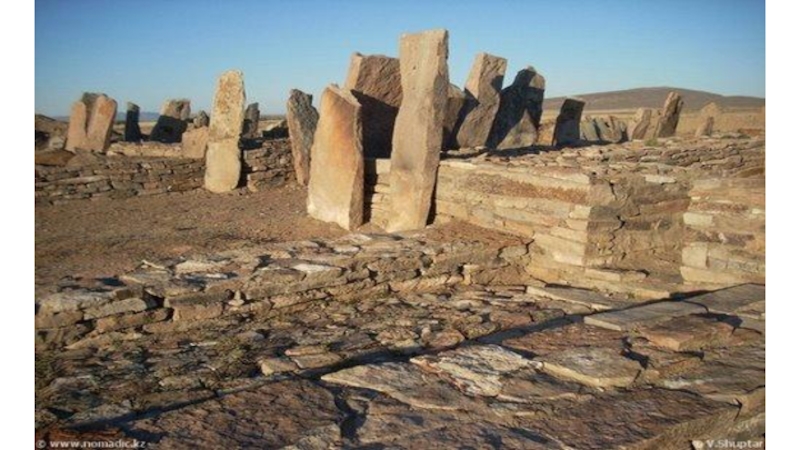
- 20. Memorial-and-cult constructions of the Begazy Tombs (X-VIII
- 25. Shagalaly settlement (Central Kazakhstan, XII-IX c.
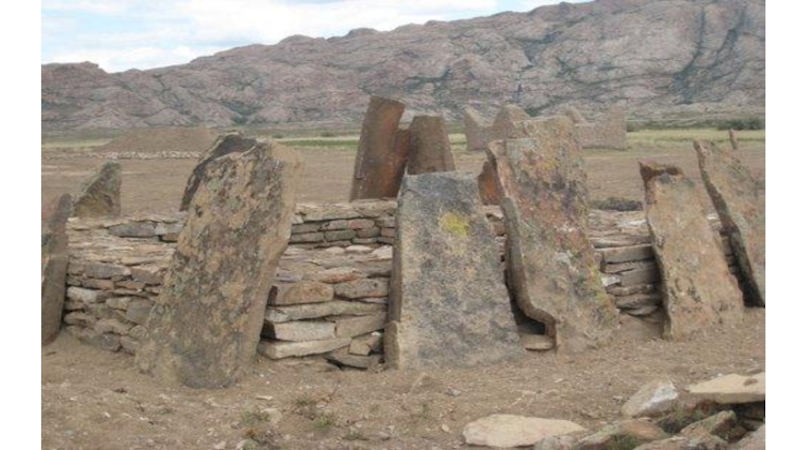
- 26. Memorial-and-cult constructions: Buguly Tomb (X-VIII c.
- 27. Megalithic structures Avenues of menhirs (the single:
- 28. Avenue of menhirs (Kanat-tas). Korpetay mountains (Karkaraly district, Karaganda region)
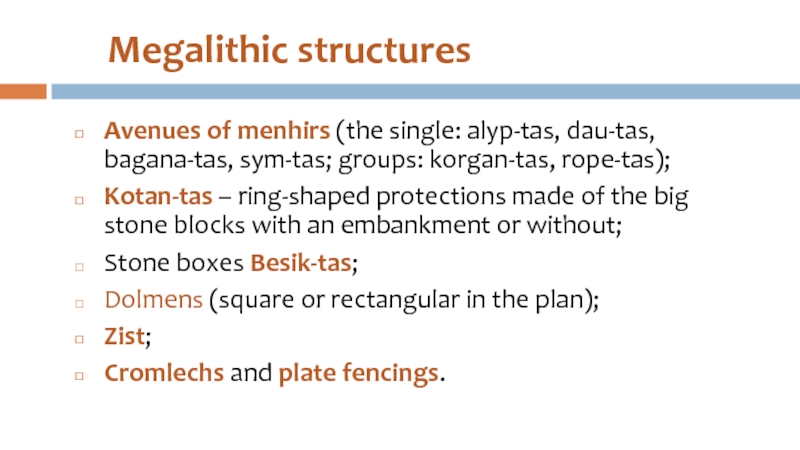
- 29. Plate fencings
- 31. The Dolmen. Sangru settlement
- 32. The Zist. Sangru settlement
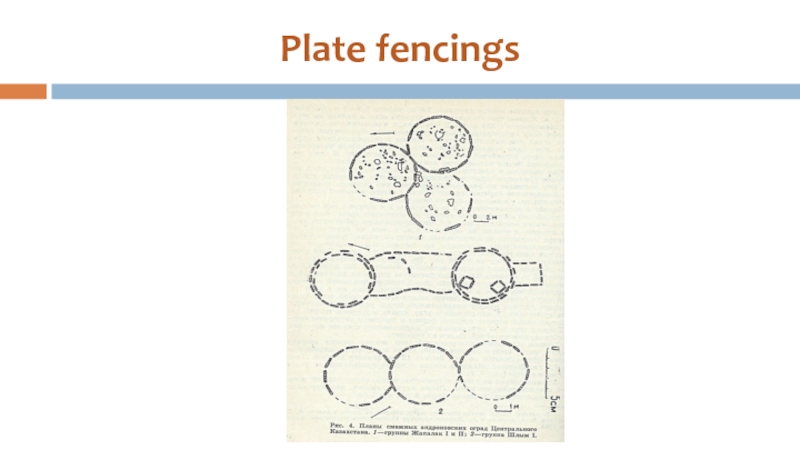
- 33. The Zist. Akchatau mountains
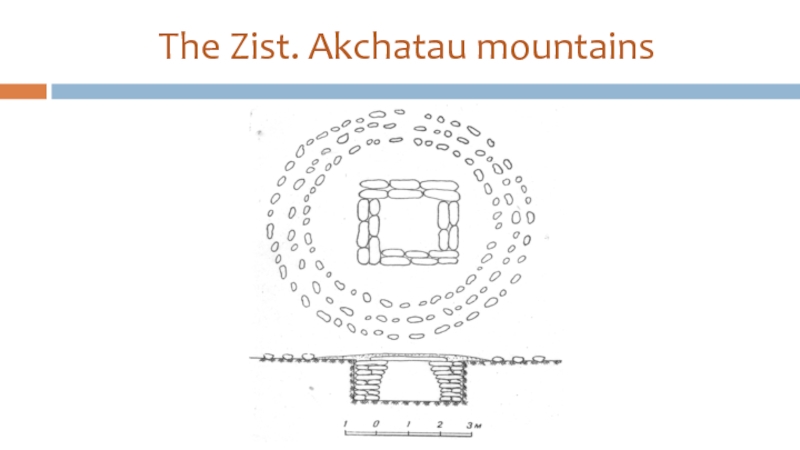
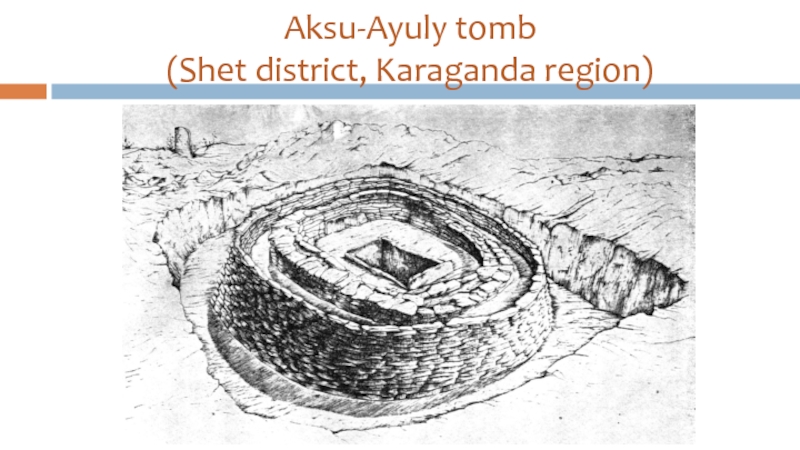
- 34. Aksu-Ayuly tomb (Shet district, Karaganda region)
- 35. Aksu-Ayuly tomb (XII-XI c.BC) It is covered
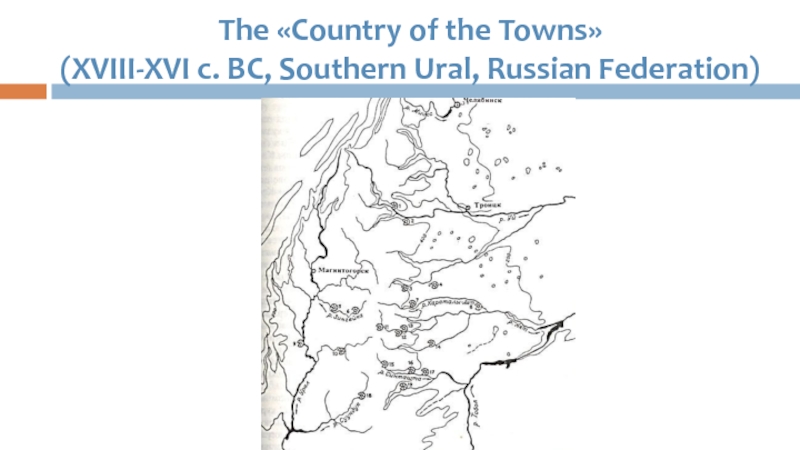
- 36. The «Country of the Towns» (XVIII-XVI c. BC, Southern Ural, Russian Federation)
- 37. The Arkaim settlement Has radial-and-ring plan Surrounded
- 38. The Toqsanbay settlement (3,000-2,000 BC, Beyneu district of Mangistau region)
- 39. The strengthened Toqsanbay settlement – proto-town
Слайд 2Lecture 1. Ancient times
1.Main stages of development of Kazakhstan material culture
2.
Geographical, cultural and historical regions of Kazakhstan
3. The most ancient monuments in the territory of Kazakhstan:
- sites and caves;
- settlements and dwellings;
- memorial and cult constructions;
- megaliths
3. The most ancient monuments in the territory of Kazakhstan:
- sites and caves;
- settlements and dwellings;
- memorial and cult constructions;
- megaliths
Слайд 3Main stages of Architecture development in Kazakhstan
1. Ancient times
(140 000 BC–
V c. BC);
2. Medieval
(VI – XIX c. AD)
3. New and Newest times
(XX-XXI c.)
2. Medieval
(VI – XIX c. AD)
3. New and Newest times
(XX-XXI c.)
Слайд 4Ancient times
1. PALEOLITH, NEOLITH
(140 000-5000 BC)
2. BRONZE ERA
(5000-1000 BC)
3. EARLY NOMADS
ERA
(VII c. BC – V c. AD)
(VII c. BC – V c. AD)
Слайд 5Medieval times
Period of Turkic khaganates (VI-IX centuries);
Karakhanid’s Era (X-XII centuries);
The
Mongolian period (XIII – 1st part of the XV century);
Period of the Kazakh khanates (2nd part of the XV-XVIII centuries);
Kazakhstan as a part of the Russian Empire (XIX – the head of the XX century);
Period of the Kazakh khanates (2nd part of the XV-XVIII centuries);
Kazakhstan as a part of the Russian Empire (XIX – the head of the XX century);
Слайд 7Geographical, cultural and historical regions – architectural schools of Kazakhstan
Central and
Northern Kazakhstan
Eastern Kazakhstan
Southern and Southeast Kazakhstan
Western Kazakhstan
Eastern Kazakhstan
Southern and Southeast Kazakhstan
Western Kazakhstan
Слайд 8Paleolithic monuments
(140,000-40,000 BC)
The most ancient workshop Zhetykonyr
Caves (Kazy-Kurt, Karatau, Bayan-Aul,
Karkaraly, Ulytau (Central Kazakhstan); Bukhtarma, New and Nikolsky caves (Eastern Kazakhstan)
Settlements Kanay (Eastern Kazakhstan), Kalkan (Southeast Kazakhstan).
Settlements Kanay (Eastern Kazakhstan), Kalkan (Southeast Kazakhstan).
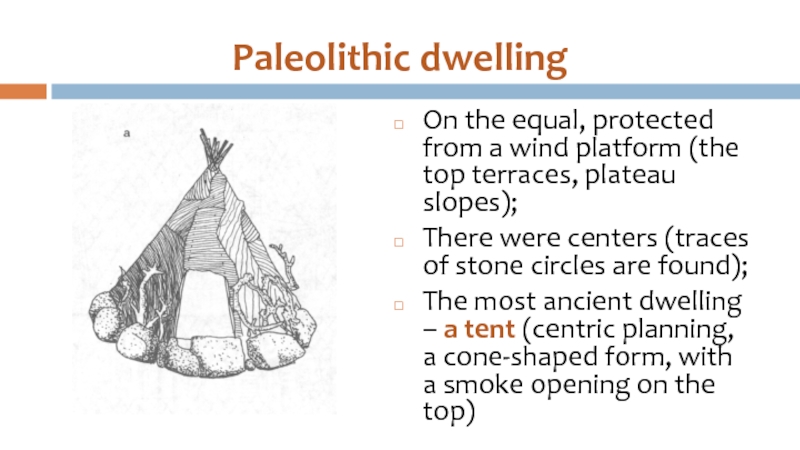
Слайд 9Paleolithic dwelling
On the equal, protected from a wind platform (the top
terraces, plateau slopes);
There were centers (traces of stone circles are found);
The most ancient dwelling – a tent (centric planning, a cone-shaped form, with a smoke opening on the top)
There were centers (traces of stone circles are found);
The most ancient dwelling – a tent (centric planning, a cone-shaped form, with a smoke opening on the top)
Слайд 11Neolithic monuments
Types of Neolythic sites:
Spring (Satchy-kyz, Eastern Kazakhstan region)
River (Makhandzhar, Nothern
Kazakhstan region)
Lake (Shatpakol, Atyrau Region)
Cave (Karaungur, Southern Kazakhstan region)
Lake (Shatpakol, Atyrau Region)
Cave (Karaungur, Southern Kazakhstan region)
Слайд 12Botay Settlement (3,000-2,000 BC)
The Ayirtau district of Nothern Kazakhstan region, the
area is 15 hectares;
About 250 dwellings are dug out;
Numerous remains of the cultivated horse are found
About 250 dwellings are dug out;
Numerous remains of the cultivated horse are found
Слайд 13Reconstruction of
the Botay settlement dwelling
The area is 30-70 sq.m,
height is 2,5 – 3,2 m;
Ditch of a polygonal or roundish form 60-80 cm high;
Walls from the clay lumps strengthened from two parties by bones of animals (thickness of 0,8-1,2 m, height of 0,6-1 m);
Ditch of a polygonal or roundish form 60-80 cm high;
Walls from the clay lumps strengthened from two parties by bones of animals (thickness of 0,8-1,2 m, height of 0,6-1 m);
Tent timbered overlapping with a light-and-smoke opening;
Clay plastering
Слайд 14Settlements of Andronov culture
(XVIII-XII c. BC)
Alekseev settlement (Kostanay region);
Sadchikov settlement
(Kostanay region);
Atasu settlement (Jana-Arka district of the Karaganda region);
Settlements of Buguly 1,2,3; Akbauyr, Shortandy-Bulak, Senkebay (Shet district of the Karaganda region);
Tagibay settlement (Bayan-Aul district).
In total more than 60 settlements and 200 large burial grounds are revealed.
Atasu settlement (Jana-Arka district of the Karaganda region);
Settlements of Buguly 1,2,3; Akbauyr, Shortandy-Bulak, Senkebay (Shet district of the Karaganda region);
Tagibay settlement (Bayan-Aul district).
In total more than 60 settlements and 200 large burial grounds are revealed.
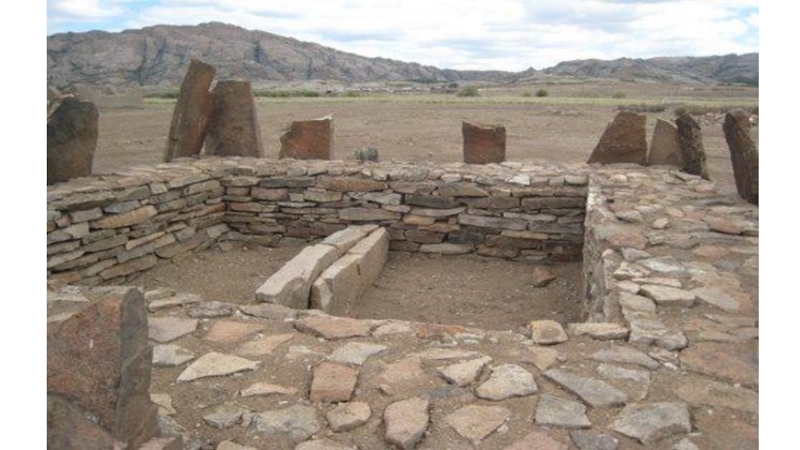
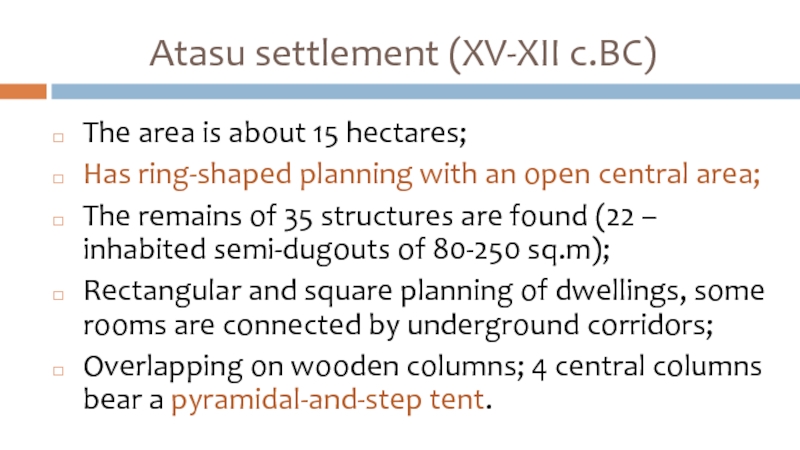
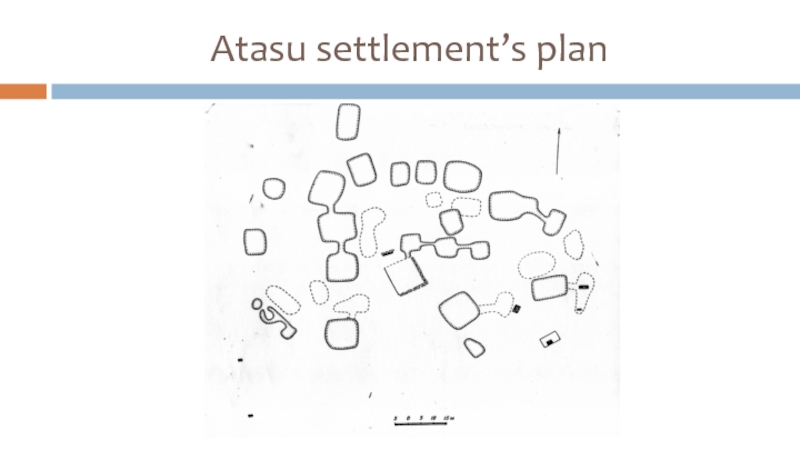
Слайд 15Atasu settlement (XV-XII c.BC)
The area is about 15 hectares;
Has ring-shaped planning
with an open central area;
The remains of 35 structures are found (22 – inhabited semi-dugouts of 80-250 sq.m);
Rectangular and square planning of dwellings, some rooms are connected by underground corridors;
Overlapping on wooden columns; 4 central columns bear a pyramidal-and-step tent.
The remains of 35 structures are found (22 – inhabited semi-dugouts of 80-250 sq.m);
Rectangular and square planning of dwellings, some rooms are connected by underground corridors;
Overlapping on wooden columns; 4 central columns bear a pyramidal-and-step tent.
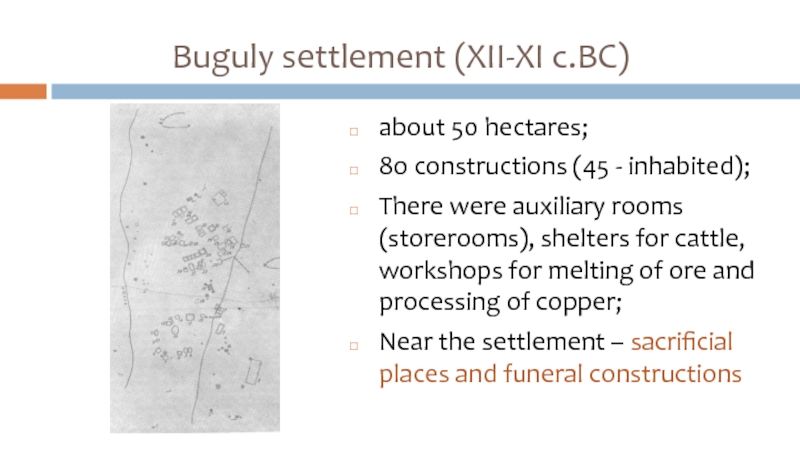
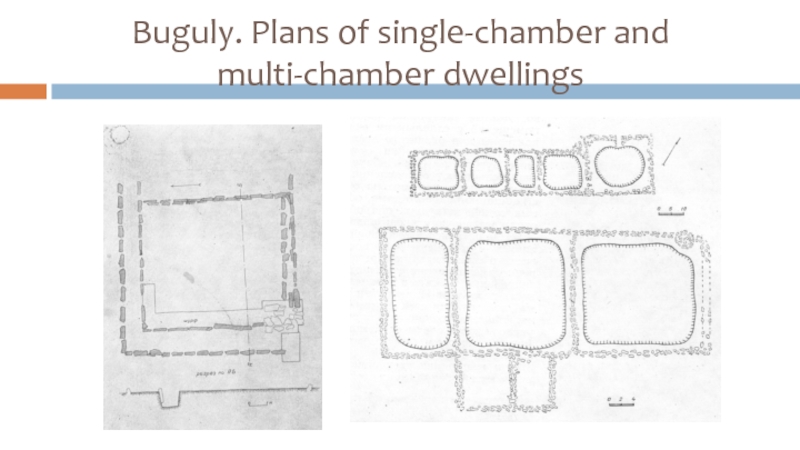
Слайд 18Buguly settlement (XII-XI c.BC)
about 50 hectares;
80 constructions (45 - inhabited);
There were
auxiliary rooms (storerooms), shelters for cattle, workshops for melting of ore and processing of copper;
Near the settlement – sacrificial places and funeral constructions
Near the settlement – sacrificial places and funeral constructions
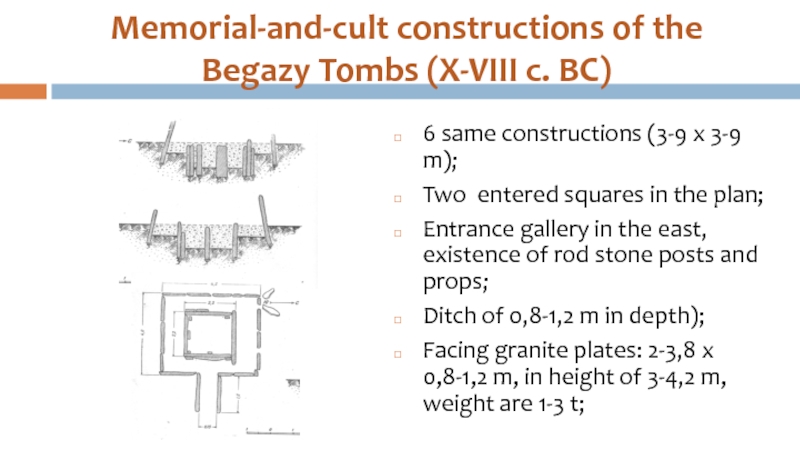
Слайд 20Memorial-and-cult constructions of the Begazy Tombs (X-VIII c. BC)
6 same constructions
(3-9 x 3-9 m);
Two entered squares in the plan;
Entrance gallery in the east, existence of rod stone posts and props;
Ditch of 0,8-1,2 m in depth);
Facing granite plates: 2-3,8 x 0,8-1,2 m, in height of 3-4,2 m, weight are 1-3 t;
Two entered squares in the plan;
Entrance gallery in the east, existence of rod stone posts and props;
Ditch of 0,8-1,2 m in depth);
Facing granite plates: 2-3,8 x 0,8-1,2 m, in height of 3-4,2 m, weight are 1-3 t;
Слайд 25Shagalaly settlement
(Central Kazakhstan, XII-IX c. BC)
Semi-dugouts up to 500 sq.m;
Rectangular,
oval, 8-like plans;
The 8-like structure consists of two roundish rooms (D=10m), are connected by pass 2 m long, 1 m wide;
Roof on wooden columns;
In dwellings there were wells
The 8-like structure consists of two roundish rooms (D=10m), are connected by pass 2 m long, 1 m wide;
Roof on wooden columns;
In dwellings there were wells
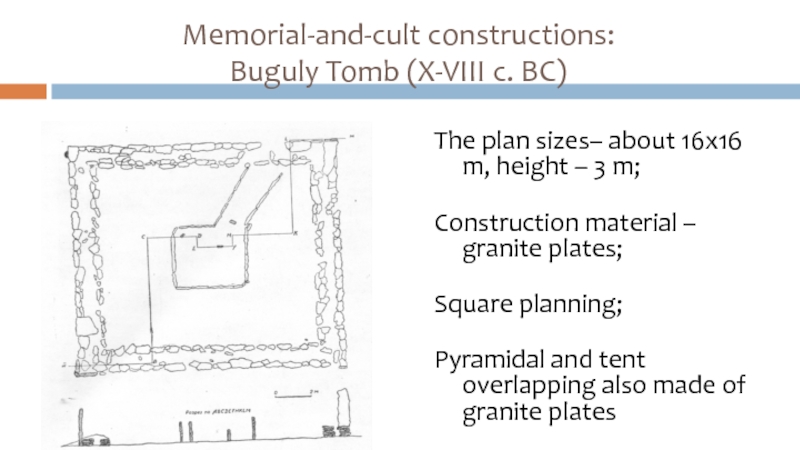
Слайд 26Memorial-and-cult constructions:
Buguly Tomb (X-VIII c. BC)
The plan sizes– about 16х16
m, height – 3 m;
Construction material – granite plates;
Square planning;
Pyramidal and tent overlapping also made of granite plates
Construction material – granite plates;
Square planning;
Pyramidal and tent overlapping also made of granite plates
Слайд 27Megalithic structures
Avenues of menhirs (the single: alyp-tas, dau-tas, bagana-tas, sym-tas; groups:
korgan-tas, rope-tas);
Kotan-tas – ring-shaped protections made of the big stone blocks with an embankment or without;
Stone boxes Besik-tas;
Dolmens (square or rectangular in the plan);
Zist;
Cromlechs and plate fencings.
Kotan-tas – ring-shaped protections made of the big stone blocks with an embankment or without;
Stone boxes Besik-tas;
Dolmens (square or rectangular in the plan);
Zist;
Cromlechs and plate fencings.
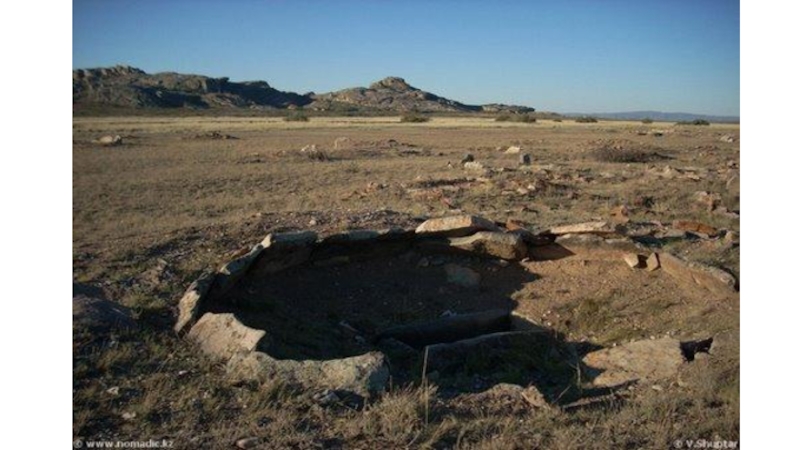
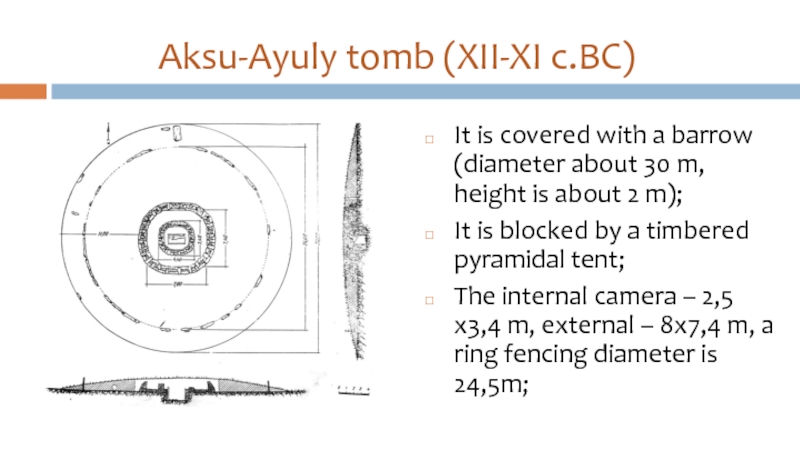
Слайд 35Aksu-Ayuly tomb (XII-XI c.BC)
It is covered with a barrow (diameter about
30 m, height is about 2 m);
It is blocked by a timbered pyramidal tent;
The internal camera – 2,5х3,4 m, external – 8х7,4 m, a ring fencing diameter is 24,5m;
It is blocked by a timbered pyramidal tent;
The internal camera – 2,5х3,4 m, external – 8х7,4 m, a ring fencing diameter is 24,5m;
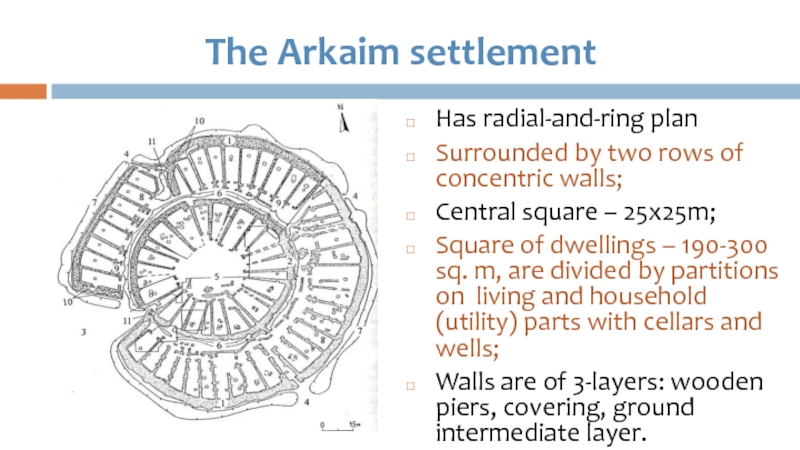
Слайд 37The Arkaim settlement
Has radial-and-ring plan
Surrounded by two rows of concentric walls;
Central
square – 25x25m;
Square of dwellings – 190-300 sq. m, are divided by partitions on living and household (utility) parts with cellars and wells;
Walls are of 3-layers: wooden piers, covering, ground intermediate layer.
Square of dwellings – 190-300 sq. m, are divided by partitions on living and household (utility) parts with cellars and wells;
Walls are of 3-layers: wooden piers, covering, ground intermediate layer.
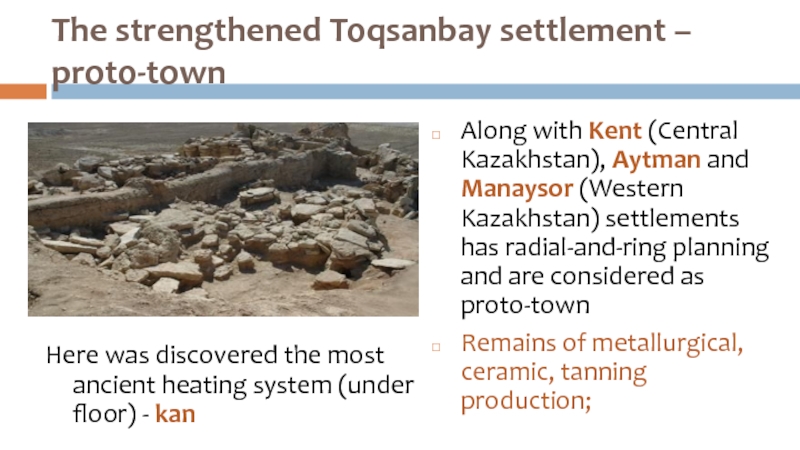
Слайд 39The strengthened Toqsanbay settlement –
proto-town
Along with Kent (Central Kazakhstan), Aytman
and Manaysor (Western Kazakhstan) settlements has radial-and-ring planning and are considered as proto-town
Remains of metallurgical, ceramic, tanning production;
Remains of metallurgical, ceramic, tanning production;
Here was discovered the most ancient heating system (under floor) - kan