- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Типы, переменные, управляющие инструкции. (Тема 2.1) презентация
Содержание
- 1. Типы, переменные, управляющие инструкции. (Тема 2.1)
- 3. Условные инструкции
- 4. Условная инструкция if if (condition)
- 5. Условная инструкция if public class IfDemo {
- 6. Условная инструкция if else if (condition)
- 7. Условная инструкция if else public class IfElseDemo
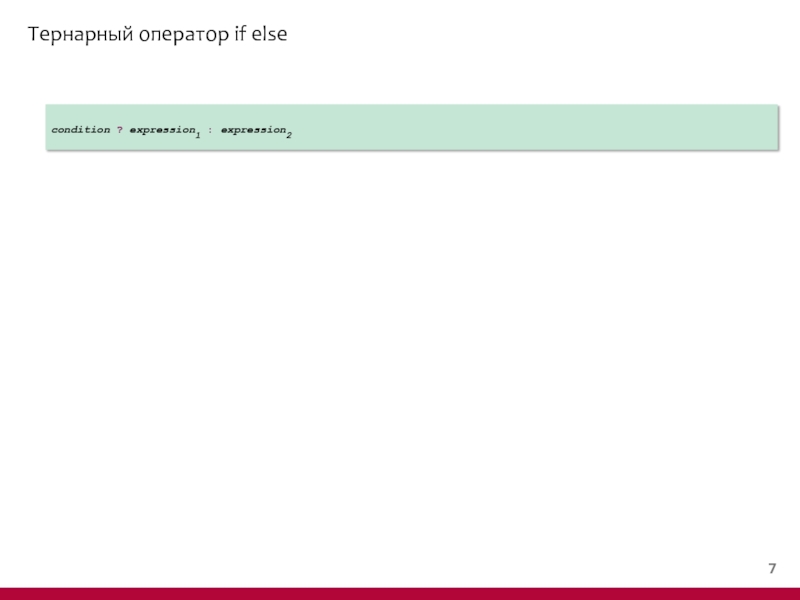
- 8. Тернарный оператор if else condition ? expression1 : expression2
- 9. Тернарный оператор if else public class TernaryDemo
- 10. Инструкция множественного выбора switch switch (expression)
- 11. Инструкция множественного выбора switch public class SwitchDemo
- 12. Циклы
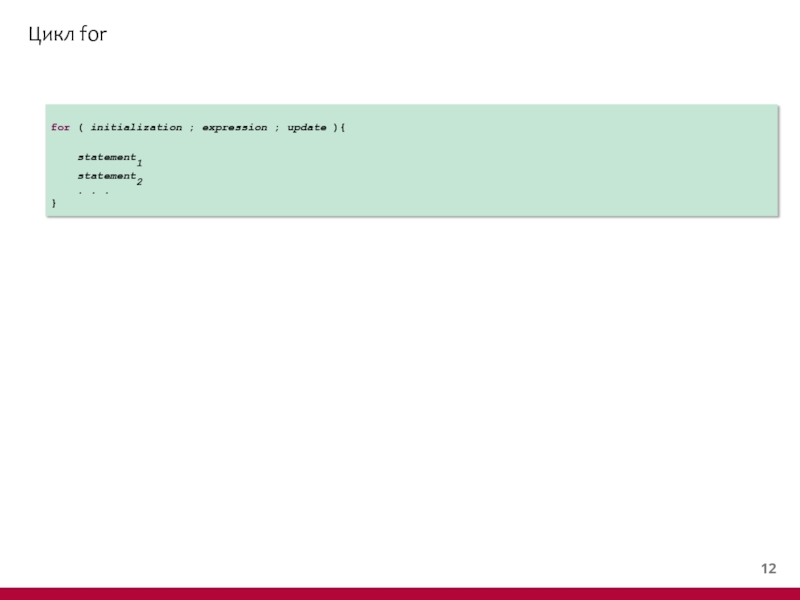
- 13. Цикл for for ( initialization ;
- 14. Цикл for public class ForDemo {
- 15. Цикл for Enter the number of
- 16. Цикл “for each” или “enhanced for”
- 17. Цикл “for each” или “enhanced for”
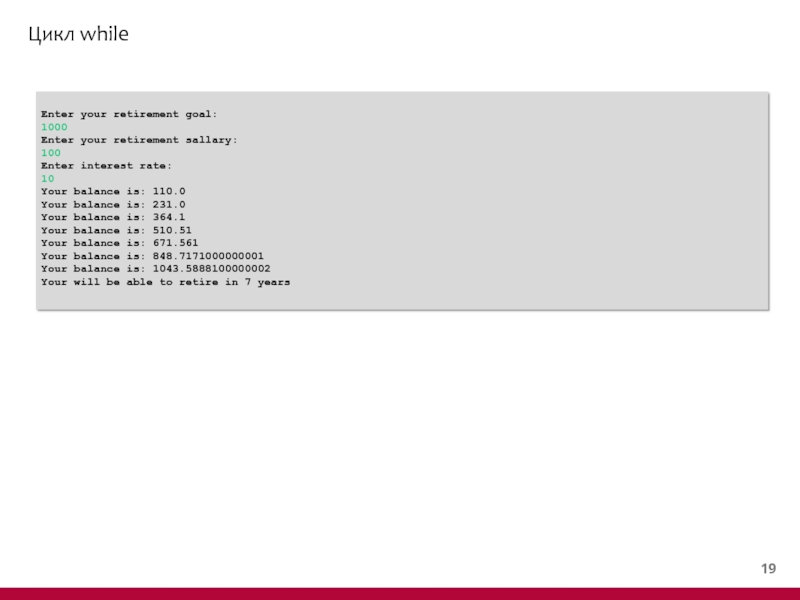
- 18. Цикл while while (condition) {
- 19. Цикл while public class WhileDemo {
- 20. Цикл while Enter your retirement goal:
- 21. Цикл do while do {
- 22. Цикл do while public class DoWhileDemo {
- 23. Цикл do while How much money
- 24. Инструкции перехода
- 25. Инструкция break { statement_sequence1
- 26. Инструкция break public class BreakDemo {
- 27. Инструкция continue { statement_sequence1
- 28. Инструкция continue public class ContinueDemo {
- 29. Инструкция return ... type method{
- 30. Инструкция return public class ReturnDemo {
Слайд 4Условная инструкция if
if (condition)
true-statement
if (condition) {
true-statement1
. . .
}
Слайд 5Условная инструкция if
public class IfDemo {
public static void main(String[]
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter your sales:");
double yourSales = in.nextDouble();
System.out.println("Enter your target:");
double target = in.nextDouble();
if (yourSales >= target) {
double bonus = 10 + 0.05 * (yourSales - target);
System.out.println("Your performance is Satifactory\n"
+ "Your bonus: " + bonus);
}
}
}
Enter your sales:
100
Enter your target:
50
Your performance is Satifactory
Your bonus: 12.5
Слайд 6Условная инструкция if else
if (condition) statement1 else statement2
if (condition) {
statement_sequence1
}
else {
statement_sequence2
}
Слайд 7Условная инструкция if else
public class IfElseDemo {
public static void
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter your sales:");
double yourSales = in.nextDouble();
System.out.println("Enter your target:");
double target = in.nextDouble();
String performance;
double bonus;
if (yourSales >= target) {
performance = "Satisfactory";
bonus = 10 + 0.05 * (yourSales - target);
} else {
performance = "Unsatisfactory";
bonus = 0;
}
System.out.println("Your performance is " + performance
+ "\nYour bonus: " + bonus);
}
}
Enter your sales:
100
Enter your target:
200
Your performance is Unsatisfactory
Your bonus: 0.0
Слайд 9Тернарный оператор if else
public class TernaryDemo {
public static void
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter your sales:");
double yourSales = in.nextDouble();
System.out.println("Enter your target:");
double target = in.nextDouble();
String performance = yourSales >= target ? "Satisfactory" : "Unsatisfactory";
double bonus = yourSales >= target ? 10 + 0.05 * (yourSales - target) : 0;
System.out.println("Your performance is " + performance
+ "\nYour bonus: " + bonus);
}
}
Enter your sales:
100
Enter your target:
50
Your performance is Satisfactory
Your bonus: 12.5
Слайд 10Инструкция множественного выбора switch
switch (expression) {
case value1:
break;
case value2:
statement_sequence2
break;
.
.
.
case valueN:
statement_sequenceN
break;
[default:
default_statement_sequence]
}
Слайд 11Инструкция множественного выбора switch
public class SwitchDemo {
public static void
System.out.println("Enter your grade:");
char grade = (char) System.in.read();
switch (grade) {
case 'A':
System.out.println("Excellent!");
break;
case 'B':
System.out.println("Well done");
break;
case 'C':
System.out.println("You need to improve your grade");
break;
default:
System.out.println("Invalid grade");
}
System.out.println("Your grade is " + grade);
}
}
Enter your grade:
B
Well done
Your grade is B
Слайд 14Цикл for
public class ForDemo {
public static void main(String[] args)
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter the number of years till retirement:");
int years = in.nextInt();
System.out.println("Enter your retirement payment:");
double payment = in.nextDouble();
System.out.println("Enter interest rate:");
double interestRate = in.nextDouble();
double balance = 0;
for(int y = 0; y < years ; y++) {
balance += payment;
double interest = balance * interestRate / 100;
balance += interest;
System.out.println("After year " + (y+1) + " your balance is: " + balance);
}
}
}
Слайд 15Цикл for
Enter the number of years till retirement:
10
Enter your retirement payment:
100
Enter
10
After year 1 your balance is: 110.0
After year 2 your balance is: 231.0
After year 3 your balance is: 364.1
After year 4 your balance is: 510.51
After year 5 your balance is: 671.561
After year 6 your balance is: 848.7171000000001
After year 7 your balance is: 1043.5888100000002
After year 8 your balance is: 1257.9476910000003
After year 9 your balance is: 1493.7424601000002
After year 10 your balance is: 1753.1167061100002
Слайд 16Цикл “for each” или “enhanced for”
for ( Type element :
statement1
statement2
. . .
}
Слайд 17Цикл “for each” или “enhanced for”
public class EnhancedDemo {
String[] fruitArray = { "Apple", "Grapes", "Mango", "Orange", "Melon", "Kiwi" };
for (String a : fruitArray) {
System.out.println(a);
}
}
}
Apple
Grapes
Mango
Orange
Melon
Kiwi
Слайд 19Цикл while
public class WhileDemo {
public static void main(String[] args)
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter your retirement goal:");
double goal = in.nextDouble();
System.out.println("Enter your retirement sallary:");
double payment = in.nextDouble();
System.out.println("Enter interest rate:");
double interestRate = in.nextDouble();
double balance = 0;
int years = 0;
while (balance < goal) {
balance += payment;
double interest = balance * interestRate / 100;
balance += interest;
System.out.println("Your balance is: " + balance);
years++;
}
System.out.println("Your will be able to retire in " + years + " years\n");
}
}
Слайд 20Цикл while
Enter your retirement goal:
1000
Enter your retirement sallary:
100
Enter interest rate:
10
Your balance
Your balance is: 231.0
Your balance is: 364.1
Your balance is: 510.51
Your balance is: 671.561
Your balance is: 848.7171000000001
Your balance is: 1043.5888100000002
Your will be able to retire in 7 years
Слайд 22Цикл do while
public class DoWhileDemo {
public static
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("How much money will you contribute every year? ");
double payment = in.nextDouble();
System.out.println("Interest rate in %: ");
double interestRate = in.nextDouble();
double balance = 0;
int year = 0;
String input;
do {
balance += payment;
double interest = balance * interestRate / 100;
balance += interest;
year++;
System.out.printf("After year %d, your balance is %,.2f%n", year, balance);
System.out.println("Ready to retire? (Y/N) ");
input = in.next();
} while (input.equals("N"));
}
}
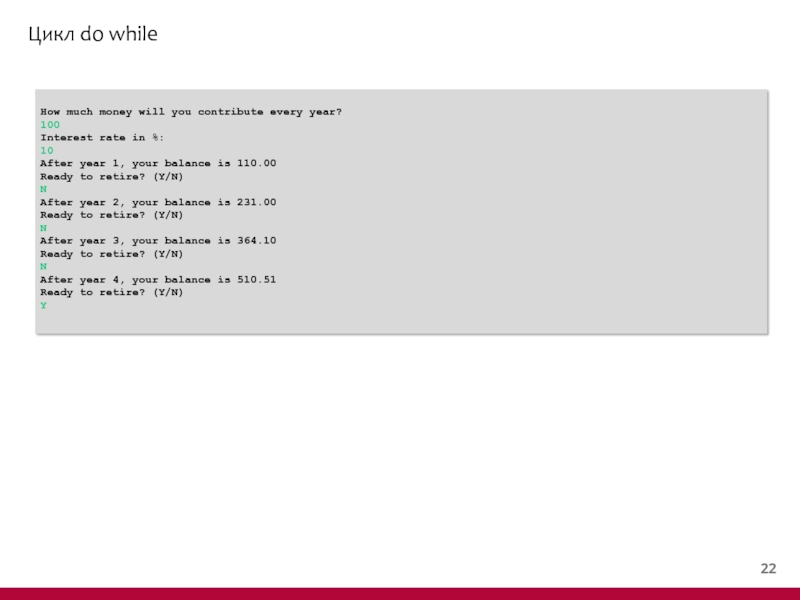
Слайд 23Цикл do while
How much money will you contribute every year?
100
Interest
10
After year 1, your balance is 110.00
Ready to retire? (Y/N)
N
After year 2, your balance is 231.00
Ready to retire? (Y/N)
N
After year 3, your balance is 364.10
Ready to retire? (Y/N)
N
After year 4, your balance is 510.51
Ready to retire? (Y/N)
Y
Слайд 25Инструкция break
{
statement_sequence1
...
if (condition) {
break;
}
...
statement_sequence3
}
Слайд 26Инструкция break
public class BreakDemo {
public static void main(String[] args)
String[] people = { "Tom", "Alice", "Bob", "John", "Harry", "Don", "Tony", "Carol" };
for (int i = 0; i < people.length; i++) {
System.out.println("Checking next person: " + people[i]);
if (people[i].equals("Don")) {
System.out.println("Found criminal Don");
break;
}
if (people[i].equals("John")) {
System.out.println("Found criminal John");
break;
}
}
}
}
Checking next person: Tom
Checking next person: Alice
Checking next person: Bob
Checking next person: John
Found criminal John
Слайд 27Инструкция continue
{
statement_sequence1
...
if (condition) {
continue;
}
...
statement_sequence3
}
Слайд 28Инструкция continue
public class ContinueDemo {
public static void main(String[] args)
String[] people = { "Tom", "Alice", "Bob", "John", "Harry", "Don", "Tony", "Carol" };
for (int i = 0; i < people.length; i++) {
if (people[i].equals("Don")) {
System.out.println("Found criminal Don");
continue;
}
if (people[i].equals("John")) {
System.out.println("Found criminal John");
continue;
}
System.out.println("Hello " + people[i] + " !");
}
}
}
Hello Tom !
Hello Alice !
Hello Bob !
Found criminal John
Hello Harry !
Found criminal Don
Hello Tony !
Hello Carol !
Слайд 29Инструкция return
... type method{
statement_sequence1
if (condition)
statement_sequence2
return [value];
}
statement_sequence3
}
Слайд 30Инструкция return
public class ReturnDemo {
public static void main(String[] args)
String[] names = { "Tom", "Alice", "Bob", "John", "Alex", "Don", "Carol" };
System.out.println(foundCriminal(names));
}
static String foundCriminal(String[] people) {
for (int i = 0; i < people.length; i++) {
if (people[i].equals("Don")) {
System.out.print("Found criminal ");
return "Don";
}
if (people[i].equals("John")) {
System.out.print("Found criminal ");
return "John";
}
}
return "";
}
}
Found criminal John




![Условная инструкция ifpublic class IfDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner in](/img/tmb/6/505615/ed455c70c23fd647a9950efe3c1ccb9d-800x.jpg)

![Условная инструкция if elsepublic class IfElseDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner](/img/tmb/6/505615/6ef8dda757f8fa760c8ef2cd28b316b5-800x.jpg)
![Тернарный оператор if elsepublic class TernaryDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner](/img/tmb/6/505615/8c2e0f94095d8d0ea04e3f52dc147bf1-800x.jpg)

![Инструкция множественного выбора switchpublic class SwitchDemo { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {](/img/tmb/6/505615/48e84b6097ada699451a0d895f6190ff-800x.jpg)

![Цикл forpublic class ForDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner in =](/img/tmb/6/505615/899bb0d4d3b3da67a2ec42b90b422439-800x.jpg)


![Цикл “for each” или “enhanced for” public class EnhancedDemo { public static void main(String[] args)](/img/tmb/6/505615/ed52182daf35ba25bedb939abcefdadc-800x.jpg)

![Цикл whilepublic class WhileDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner in =](/img/tmb/6/505615/c84ffffc38c2b3fc16c4d2c6029b5e2b-800x.jpg)

![Цикл do whilepublic class DoWhileDemo { public static void main(String[] args) {](/img/tmb/6/505615/99807991f82aafacd9291d78e7e3e83f-800x.jpg)


![Инструкция breakpublic class BreakDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { String[] people =](/img/tmb/6/505615/8f7e622a363b8c562d33aa50b4376107-800x.jpg)

![Инструкция continuepublic class ContinueDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { String[] people](/img/tmb/6/505615/661ae13179b24e32fe56991b9224c878-800x.jpg)
![Инструкция return... type method{ statement_sequence1 if (condition) { statement_sequence2 return [value];](/img/tmb/6/505615/c37380483a48c2ea0b88f0969b66d7b3-800x.jpg)
![Инструкция returnpublic class ReturnDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { String[] names =](/img/tmb/6/505615/460d540f4d7d0d94ea526d68df51f5ba-800x.jpg)