- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Life-cycle phases from software project Мanagement by walker royce of IBM. (Chapter 5) презентация
Содержание
- 1. Life-cycle phases from software project Мanagement by walker royce of IBM. (Chapter 5)
- 2. Introduction On one hand, Do we
- 3. Introductory Statement: Walker Royce feels that we
- 4. Finer Granularity Further, we need a process
- 5. Engineering and Production Stages Royce claims to
- 6. Engineering and Production Stages He breaks all
- 7. Two Stages: Far Too Abstract BUT, he
- 8. Royce Claims that: These phases can be
- 9. Spiral Model - Overview Spiral Model is
- 10. Spiral Model Very much a Risks-Driven Approach
- 11. Previous Software Process Models An evolution of
- 12. Stagewise & Waterfall Born out of
- 13. Stagewise A development process of successive phases.
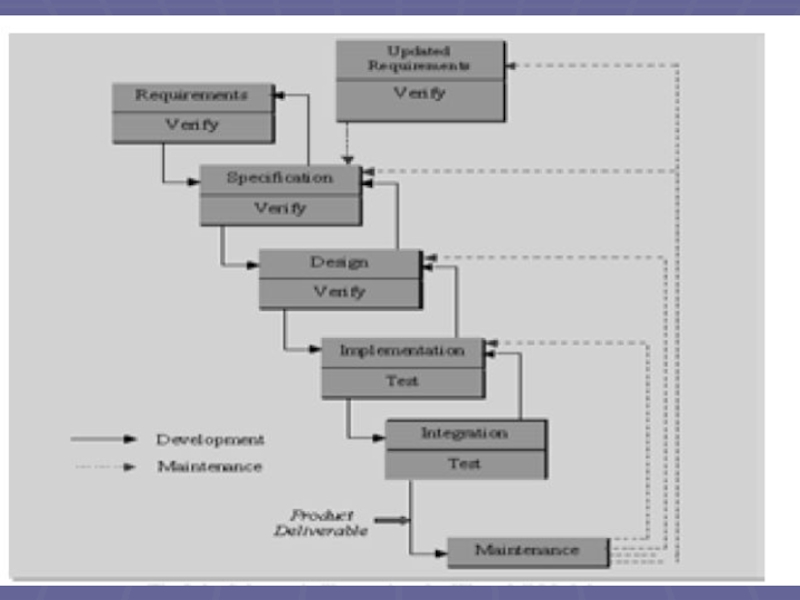
- 14. Waterfall Model Introduced: – Feedback loops across
- 16. Evolutionary Development Evolution of the system in
- 19. Spiral Model - Overview In the Spiral
- 20. Spiral Model - Overview Quadrants in a
- 21. Spiral Model - more May be several
- 22. R & D Stage
- 23. Back to our Process Model (RUP) Let’s
- 24. Inception Phase (1 of 3) Overriding Goal:
- 25. Inception Phase (2 of 3) Essential Activities
- 26. Inception Phase (3 of 3) Primary Evaluation
- 27. Elaboration Phase (1 of 5) Clearly the
- 28. Elaboration Phase (2 of 5) ? Primary
- 29. Elaboration Phase (3 of 5) Essential Activities
- 30. Elaboration Phase (4 of 5) Essential Activities
- 31. Elaboration Phase (5 of 5) Primary Evaluation
- 32. Construction Phase (1 of 5) Great mindset
- 33. Construction Phase (2 of 5) One very
- 34. Construction Phase (3 of 5) Primary Objectives
- 35. Construction Phase (4 of 5) Essential Activities
- 36. Construction Phase (5 of 5) Primary Evaluation
- 37. Transition Phase Recall end of phase
- 38. Transition Phase Phase concludes when the baseline
- 39. Transition Phase Transition is not uncomplicated May
- 40. Transition Phase Essential Activities “Synchronization and integration
- 41. Summary - Know These Recognize each phase
- 42. Summary (continued) – Know! Major Milestones (phase
- 43. Lessons Learned – Organizational Change Middle management
Слайд 1Chapter 5
Life-Cycle Phases
From
Software Project Management
By
Walker Royce (of IBM)
And Slides on
Слайд 2Introduction
On one hand,
Do we spend far too much time on
Do we delay actually doing the builds: the development baselines?
Very easy to do… Some feel in general that this is true…
On the other hand,
Do we jump into designs and coding, and hack the heck out of an application in attempts to get it to work?
Lots of people think we do this too….
Class discuss:
What do you do?
What do you think corporations think they do?
Слайд 3Introductory Statement:
Walker Royce feels that we need BALANCE between research and
Need some kind of balance between:
Concentrating on capturing and modeling functionality and
Building a robust product that has the performance, reliability, and scalability customers desire….
We are after a development life-cycle BALANCE…
Слайд 4Finer Granularity
Further, we need a process that supports this balance.
Need
? Need a process to help balance:
Planning, capturing, and modeling requirements and establishing a baseline architecture,
with
Continuous assessment, measuring risk, and testing to ensure progress and quality
with
Evolution and verification of the application’s functionality through series of customer demonstrations and ultimate validation.
Слайд 5Engineering and Production Stages
Royce claims to achieve the ROI for software
highest utilization of automated development tools and
use of component-based approaches to development.
He likens a desirable software process to a manufacturing process:
Слайд 6Engineering and Production Stages
He breaks all activities down into
Engineering and
Engineering work: This centers on risk reduction, prototyping, establishing architectural baseline, assessment, analysis, design, and planning…
Implies a smaller team up front.
Production work: programming and unit test, system and integration testing, demonstrations, assessment, base-lining (alpha, beta, …) configuration, and releases; operations
Note that production includes operations…
Слайд 7Two Stages: Far Too Abstract
BUT, he argues a life cycle of
So, he maps RUP Phases into these more comprehensive phases.
Enter: Engineering Phase = Inception and Elaboration
Enter: Production Phase = Construction and Transition
To wit:
Engineering, i.e., Inception and Elaboration, focuses on the concept (idea) of the application and its architectural components (analysis and preliminary design – perhaps a wee bit of detailed design)
Artifacts are established and base-lined; (Configurations…)
Production, i.e., Construction and Transition, focuses on programming, testing, releases and converting / establishing operational capabilities
Implies that artifacts from earlier stage (engineering) more difficult to change as activities more ‘downstream activities’ occur
Слайд 8Royce Claims that:
These phases can be mapped into the famous Spiral
developed by (Barry Boehm) (shall see ahead)
Now have:
Conventional Software Development Model (as represented by the Waterfall Model and its many variants;
OOSE approach (as represented by the RUP);
Spiral Model…Let’s discuss this important model…
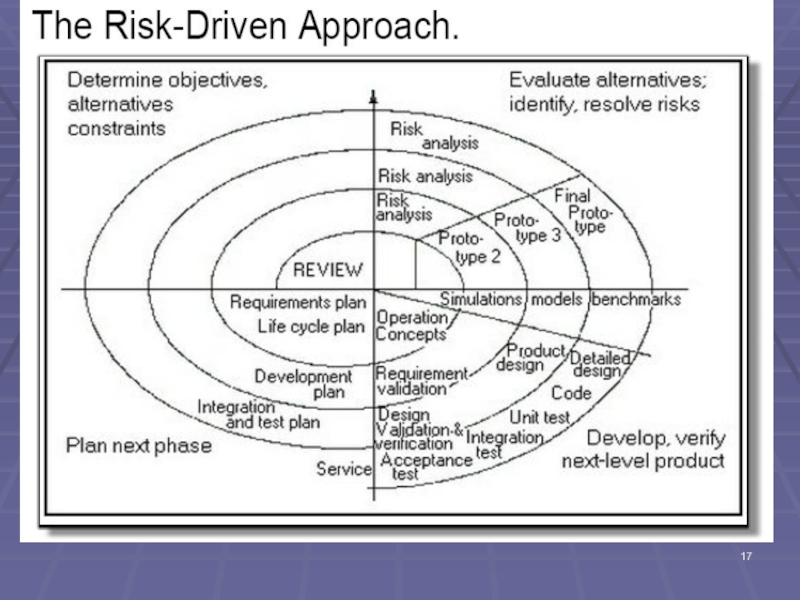
Слайд 9Spiral Model - Overview
Spiral Model is another incremental model.
Embraces (well known
prototyping,
iterative software development, and
risk assessment.
Model is graphed like a spiral.
Development can be halted at the end of any cycle…depending on evaluation of previous ‘cycle.’
IS ROI still looking good?
Are expended costs in line with anticipated costs – so far?
Have risks been mitigated?
Functionality delivered evolving properly via high priority requirements? And much more…..
Слайд 10Spiral Model
Very much a Risks-Driven Approach
Different idea of software development.
How
and the clients?
How does each step in the project affect
its overall development?
Not used in previous development models.
They were usually code-driven or document-driven.
Слайд 11Previous Software Process Models
An evolution of models
–Code & Fix
–Stagewise & Waterfall
–Evolutionary
–Others…
Code & Fix
• First, elementary model
• Write code now; fix it later
• No planning involved
• Problems:
– Code is poorly structured.
– The software developed was usually a poor match for users’ needs.
Слайд 12Stagewise & Waterfall
Born out of the shortsightedness of the Code
- need for a design phase, requirements phase,
and a testing phase.
First used to develop SAGE (Semi-Automated Ground Environment), an early warning system for the Cold War era.
Слайд 13Stagewise
A development process of successive phases.
– Phases included operational plan, operational
specs,
testing, assembly testing, shakedown, system
evaluation.
Underwent two refinements in 1970.
Now referred to as the Waterfall Model.
Слайд 14Waterfall Model
Introduced:
– Feedback loops across multiple stages: Validation and verification steps.
–
requirements and design.
• Difficulties exposed even as revisions were made to
the model.
– Required elaborated documents. (Document- driven; lengthy development cycles, etc.
– Led to pursuing stages of development in the wrong order
Слайд 16Evolutionary Development
Evolution of the system in directions based on experience.
Provides rapid
“I can’t tell you what I want, but I’ll know it when I see it.”
Flexible, yet uncertain approach.
Evolutionary Development Problems:
No formal design phase (same problem as Code & Fix).
One bad assumption – the unplanned paths “will” be compatible.
Hard-to-change code resulted.
Many problems when new software was incrementally replacing old software
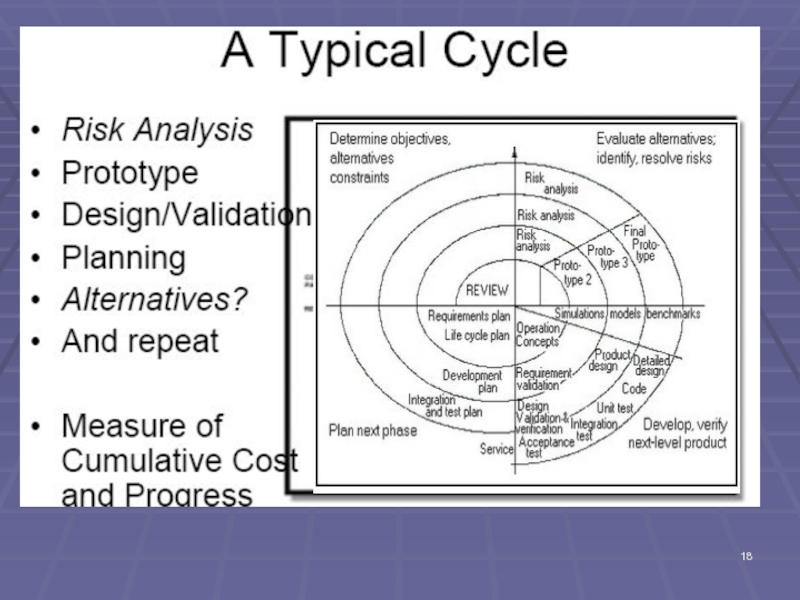
Слайд 19Spiral Model - Overview
In the Spiral Model, prototyping, evaluation, planning, and
But the basic notion of iteration is very firmly established.
For each ‘cycle’:
risk is assessed,
more design and development is undertaken,
the work products and evaluated, and
planning for the next cycle in the spiral is undertaken;
Iterate…..
Please note that in reality, the Spiral Model curve is actually skewed to the right, as the spirals do not ‘carve’ out equal ‘areas.
Area in each cycle is a determinant of effort and cost….
Слайд 20Spiral Model - Overview
Quadrants in a cycle:
Creation of a prototype
Risk is assessed and if acceptable,
Development activities then follow using the waterfall model
Specifications are created from the prototyping effort, Then Requirements, Analysis, Design, Implementation, … ensue
Review and release are undertaken…
Restart and iterate as above…
Planning for next iteration is undertaken – or not…
Iterate until application is developed fully and totally released to the clients.
Слайд 21Spiral Model - more
May be several cycles of prototyping…but as prototypes
Before a cycle ends, the review discusses experiences, assesses risk, and decision made whether or not to proceed.
Note: for each cycle, FIRST thing before embarking is to decide what are the major requirements to be handled.
Adjust the architecture and requirements and/or project plan as needed.
The Spiral forms the basis for entire life cycle of the product.
Thus, the Spiral Model continues the spiral process for Maintenance, and the model continues until the application is ultimately retired or replaced…
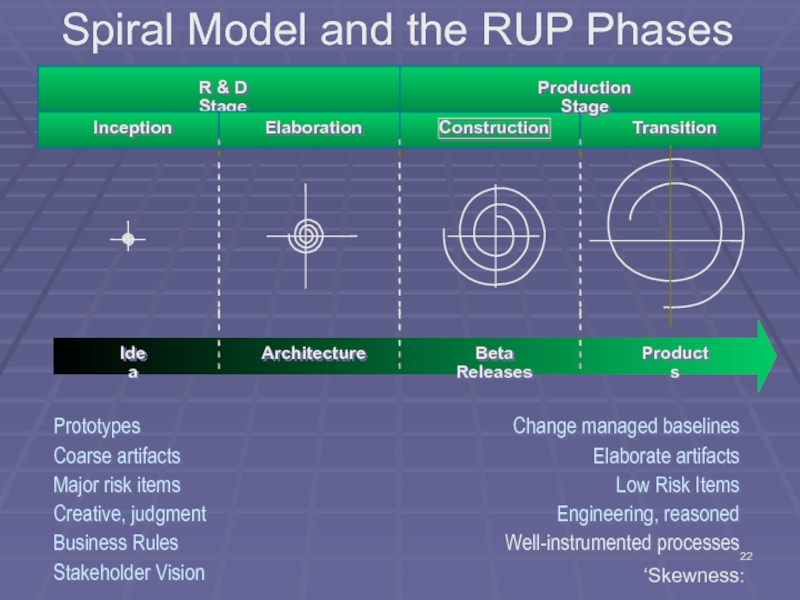
Слайд 22
R & D Stage
Inception
Elaboration
Construction
Transition
Production Stage
Idea
Architecture
Beta Releases
Products
Prototypes
Coarse artifacts
Major risk items
Creative, judgment
Business Rules
Stakeholder
Change managed baselines
Elaborate artifacts
Low Risk Items
Engineering, reasoned
Well-instrumented processes
‘Skewness:
Spiral Model and the RUP Phases
Слайд 23Back to our Process Model (RUP)
Let’s look more closely at the
Inception
Elaboration
Construction
Transition
Each phase has
primary objectives,
essential activities, and
primary evaluation criteria
to judge its success at milestone time.
?Since the process that is underpinning our management of software processes and personnel course is the RUP, it is imperative that we understand this management process, the RUP, as much as possible
Слайд 24Inception Phase (1 of 3)
Overriding Goal: achieve concurrence among stakeholders on
Primary Objectives: (by end of phase…)
Establish project software scope and boundary conditions
Includes operational concept, acceptance criteria, and a clear understanding of what is and what is not intended in the product
Identify critical use cases (core functionalities) of system and the primary scenarios that will drive the activities
Demonstrate at least one candidate architecture against some of the primary scenarios (walk through it…)
Estimate the cost and schedule for the entire project (including detailed estimates for the elaboration phase)
Estimate potential risks (sources of unpredictability)
Know These!
Слайд 25Inception Phase (2 of 3)
Essential Activities
Develop Project Scope
Capture requirements and concept
Describes users’ view of the requirements
Repository contains information used to define problem space
Repository must contain information to capture acceptance criteria
Develop a Candidate Architecture and Demonstrate it
Repository contains enough information to demonstrate at least a single candidate architecture
This might be at a very high level, such as deployment level;
A general layered architecture may also be demonstrated.
But considerable Requirements have not yet been done and almost NO Analysis and Design have been undertaken.
Repository must include enough data to support make/buy decisions so that cost, schedule, resources can be ‘costed out.’
Planning and Preparing the Business Case
Risk management strategies, staffing, general iteration plans, cost/schedule/profitability tradeoffs are all evaluated.
Environmental (Infrastructure) support is defined.
ROI, market share, etc.
Слайд 26Inception Phase (3 of 3)
Primary Evaluation Criteria
Stakeholder concurrence on scope definition
Do critical use cases demonstrate that the requirements are understood?
Do we have credible estimates for cost/schedule/resources/risks/development?
Does the architectural prototype support previous items? (Does the prototype indicate that the scope of project is understood, and does the development group indicate prevalent understanding?)
Are actual expenditures verses planned expenditures acceptable? <
LCO Milestone…
Слайд 27Elaboration Phase (1 of 5)
Clearly the most important phase! Overriding goals
? At end of phase:
engineering is complete,
almost all use cases are designed (certainly all critical use cases and flows),
a prototype for gathering requirements and to demonstrate proof of concept is accommodated, and
an analysis model is constructed, and
a baseline executable architecture is established and demonstrated.
Risks have to have been addressed and strategies understood;
Business Rules have been subscribed to closely;
Cost and schedule are acceptable and predictable and updated, if necessary,
Stakeholder acceptance is achieved (the vision is realized in the artifacts), etc. and
We have stability…
? We want to graduate from a low-cost effort into a full-blown production process, where costs are maxed and personnel are on staff.
Слайд 28Elaboration Phase (2 of 5)
? Primary Objectives (at end of phase…)
Base-lining
Base-lining the Vision. It is now ‘solid’ and accommodated in the artifacts so far.
Base-lining a detailed plan for Construction
Demonstrating the baseline architecture such that it clearly supports the vision – at, of course, reasonable cost in reasonably time.
Слайд 29Elaboration Phase (3 of 5)
Essential Activities
Detail the Vision.
Ensure all have this
? Discuss: What does this mean to you??? Explain!
Detail the process (to come) and the infrastructure support.
Must be spelled out; the plans for each iteration in Construction (project management supporting discipline) and the anticipated assessment at the end of each iteration, the functionality accommodated by each iteration must be spelled out in general.
Detailed iteration planning (after first iteration or two) will come later. But overview planning is now!
? Discuss: What does this mean? Explain!
Слайд 30Elaboration Phase (4 of 5)
Essential Activities – continued
Build the Architecture…
Group classes
But you MUST integrate these into architectural units (layers, packages, subsystems, all with dependencies, well-defined interfaces, …)
Bounce your candidate architecture against your primary scenarios to trace that all functionality is accommodated by these artifacts.
May result in a number of design choices and changes in model elements (e.g. classes, responsibilities…)
May point out some requirements missing…
? Remember, requirements are singular; but there is not a single, perfect design.
Слайд 31Elaboration Phase (5 of 5)
Primary Evaluation Criteria
Remember, at the end of
Is the Vision solid? Stable?
Is the architecture stable? Demonstratable?
Execute example of addressing a high risk scenario?
Does the architecture indicated that all risk elements have been addressed/mitigated?
Have we looked carefully into Construction and established sufficient planning detail to project credibility in our estimates? (initial iteration – one or two – carefully planned?)
Do we have stakeholder buy-in that their vision can be accommodated if we proceed as plans indicate?
Are actual resource expenditures verses planned resource expenditures acceptable so far?
Achieve this Milestone! Press on – with concurrence.
Слайд 32Construction Phase (1 of 5)
Great mindset change: now interested in producing
iterate, iterate…, integrate/assess/plan as we go.
No longer ‘engineering;’ rather, production!!!
Need to manage resources, control operations to optimize costs, schedules, and quality.
Emphasis on the development of intellectual property shifts to the reality of usable products.
Слайд 33Construction Phase (2 of 5)
One very nice attribute in Construction:
Parallel development
Based
Accelerates delivery of deployable releases
Downside: complicates project management and synchronization of teams, integration, and workflow.
Architecture will drive this
A good architecture will support parallel development
Emphasized during Elaboration – planning for Construction.
Слайд 34Construction Phase (3 of 5)
Primary Objectives
? Develop the system rapidly but
Take advantage of the process, versioning, reviews, assessment, etc. to minimize costs due to needless rework and scrap.
Develop alpha, beta, ‘or what have you’ releases for Transition phase.
Слайд 35Construction Phase (4 of 5)
Essential Activities
Manage resources; control development (via plans,
Perform unit testing (component testing) against requirements (verification)
Assess releases against acceptance criteria cited in vision. (validation)
V&V …Discuss….
Слайд 36Construction Phase (5 of 5)
Primary Evaluation Criteria (at end)
Milestone is ‘Initial
Is the product reliable enough for deployment?
Does not mean everything must be perfect…Showstoppers?
Does it fail frequently??
Is product ‘stable’ enough for deployment?
Pending changes are okay
But are we getting change requests a-plenty?
Are defects being identified rapidly ‘as we speak?’
How significant are the changes??
Is the stakeholder community ready to transition?
Are actual expenditures reasonably close to planned expenditures?
Слайд 37Transition Phase
Recall end of phase milestone: product release to user
Implies product is stable, has high quality, has accompanying user documentation (on-site or web-based training…), customer support is ‘ready’, etc...
Phase ‘could’ include any of these…
Beta testing to validate new system against expectations
Beta testing in parallel with legacy system to be replaced
Installation
Conversion of operational data bases
Training users, maintenance team, customer support…
Слайд 38Transition Phase
Phase concludes when the baseline realizes the original vision and
Might be end of project development or starting point for next cycle, or starting point for next version of deployable version...
Might be forwarding ‘whole shooting match’ over to
the maintenance group or
third party for future work…
Слайд 39Transition Phase
Transition is not uncomplicated
May involve several iterations including
Beta1, beta2, …
Custom software?
Conversion software?
Development of user documentation,
User training, especially in initial use of product
Web-X; on developer’s site; on client’s site.
Who pays for what? How does this work? Millions!!!
Usability problems and tuning,
(Un)solicited feedback, and more….
Слайд 40Transition Phase
Essential Activities
“Synchronization and integration of concurrent construction increments into consistent
?Installation / Conversion
Cut over (complete switch to new application)
Run in parallel, or
Phased…
Assessment against vision and acceptance criteria.
Evaluation Criteria
Is user satisfied?
Are actual expenditures reasonably close to planned expenditures?
Слайд 41Summary - Know These
Recognize each phase has one or more iterations
Phases
Iterations within phases have minor milestones.
Each have deliverable(s) and undergoes assessment against criteria
Each iteration entails a sequence of activities that culminate in a minor milestones or major milestones (if iteration ends phase)
Scope and results of iterations are captured via artifacts produced.
Слайд 42Summary (continued) – Know!
Major Milestones (phase end):
Approved by stakeholders
Map to
Minor milestones (iteration end):
Approved internally and
Realized by artifacts / new versions of artifacts in repository;
internal synchronization,
internal assessment,
Additional planning take place…
‘Executable’ releases (not necessary deployable…)
Слайд 43Lessons Learned – Organizational Change
Middle management is where the war is
Championed by respected leaders who own the plan and execution.
Project Management: Can be immense pressures from above (Sr. Management) and different sets of problems/issues from below (actual developers)
ROI on first implementation
Disruption costs must be absorbable in the benefit
Implemented on business critical project
This is where the A-players are
Success breeds success – (like the NFL)
First increment needs to be ambitious, but realistic
Results drive incentives
Such as: milestone demonstrations, release timeliness, release content, etc
Not: processes, methods, expended energy, reuse, audits, meetings, subjective assessments, document production,…