- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Lecture 5. Memory accesses and memory management. Swapping. Main components of an operating system презентация
Содержание
- 1. Lecture 5. Memory accesses and memory management. Swapping. Main components of an operating system
- 2. Main Components Of An Operating System Process
- 3. In the early days of electronic computing, two different processor/memory architectures emerged:
- 4. Princeton Architecture (von Neumann architecture)
- 5. The principles of von Neumann." 1.
- 6. Harvard Architecture – Two separate memories. One
- 7. Which is better? Each architecture has
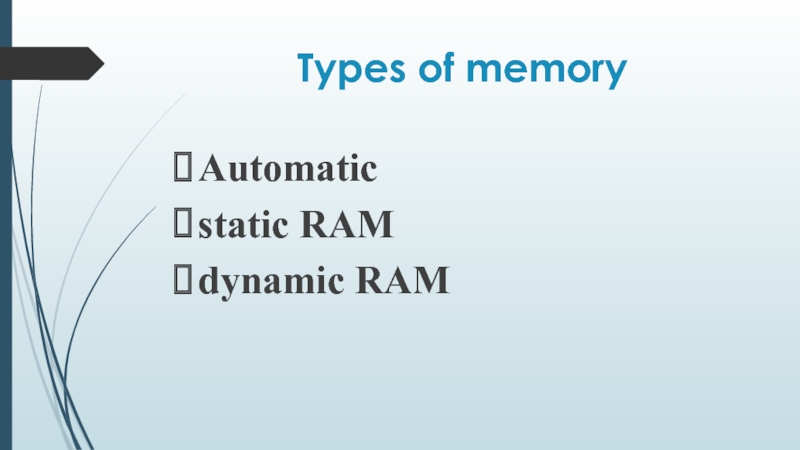
- 8. Types of memory Automatic static RAM dynamic RAM
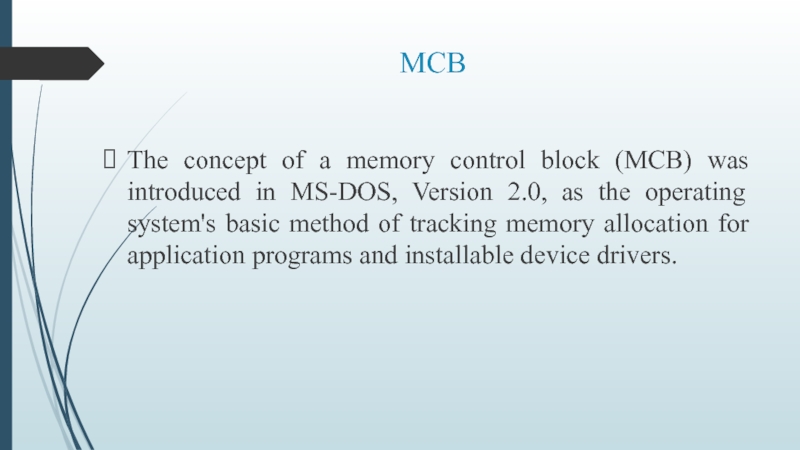
- 9. MCB The concept of a memory control
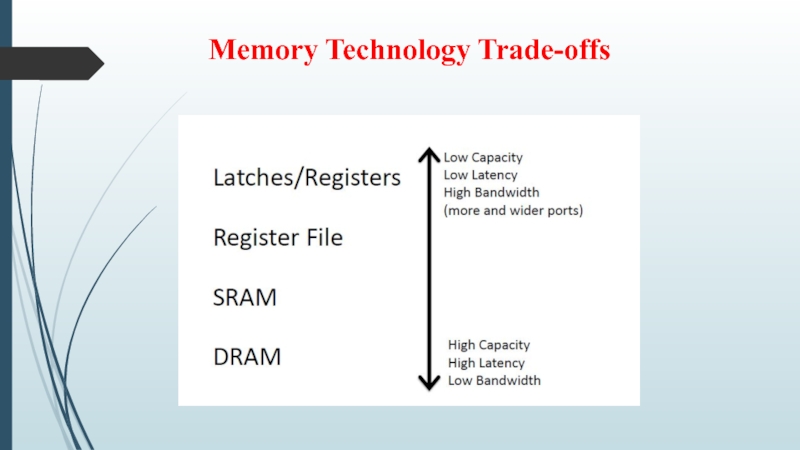
- 11. Memory Technology Trade-offs
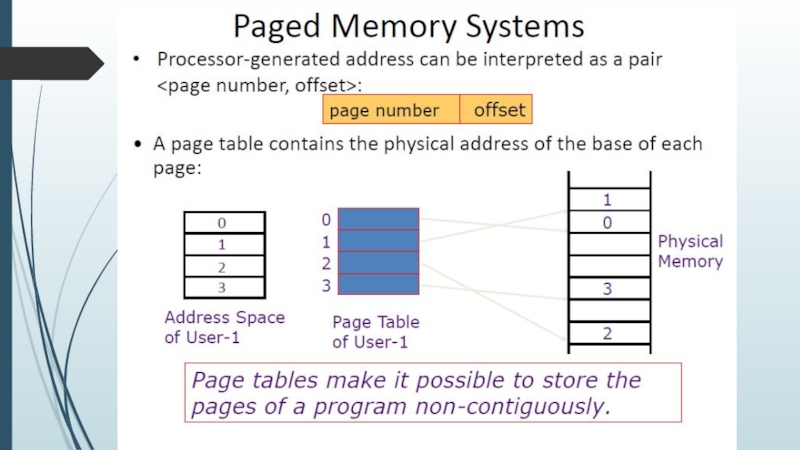
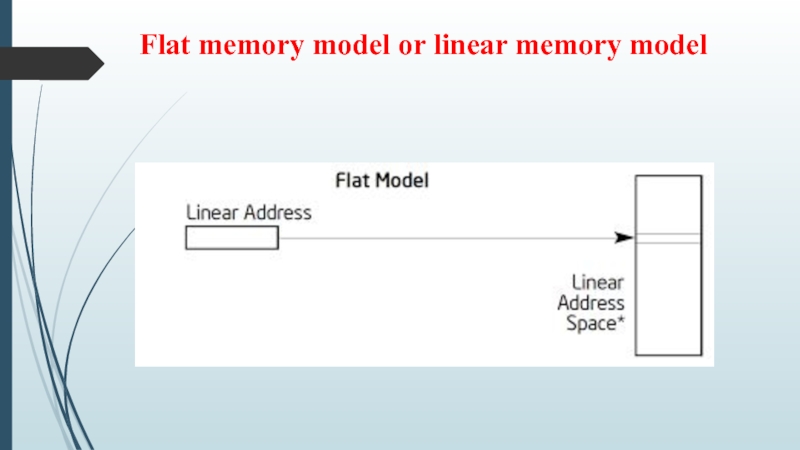
- 12. Flat memory model or linear memory model
- 15. ADDRESS Logical address is the address at
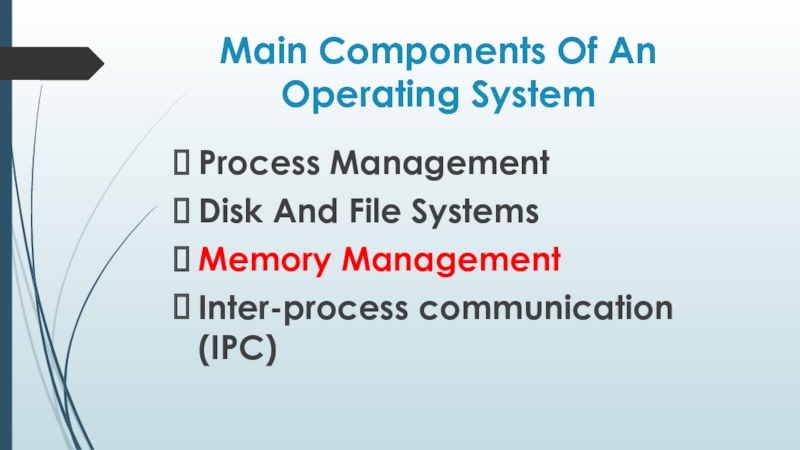
Слайд 2Main Components Of An Operating System
Process Management
Disk And File Systems
Memory Management
Inter-process
communication (IPC)
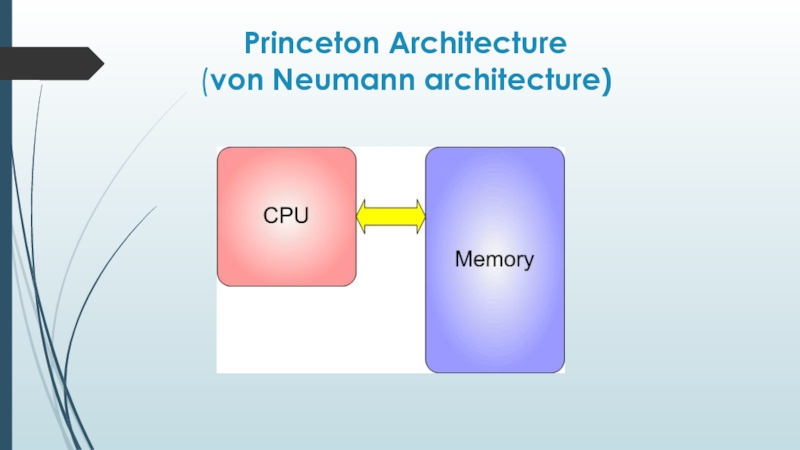
Слайд 3In the early days of electronic computing, two different processor/memory architectures
emerged:
Слайд 5The principles of von Neumann."
1. The principle of program control.
2. The
principle of one memory.
3. The principle of memory addressability.
3. The principle of memory addressability.
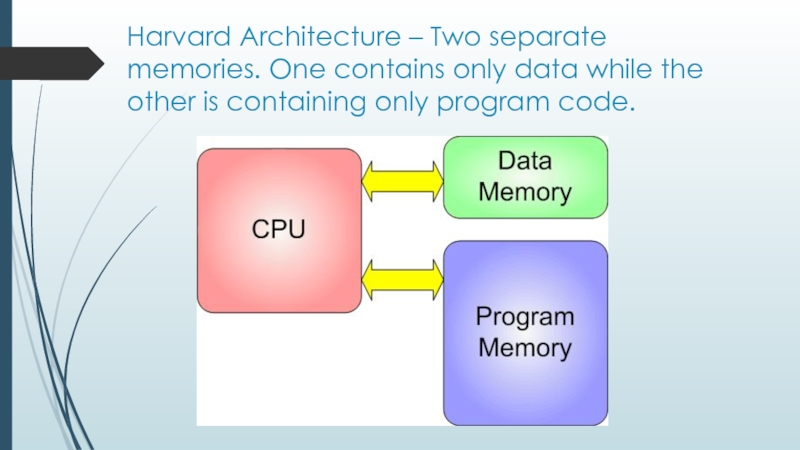
Слайд 6Harvard Architecture – Two separate memories. One contains only data while
the other is containing only program code.
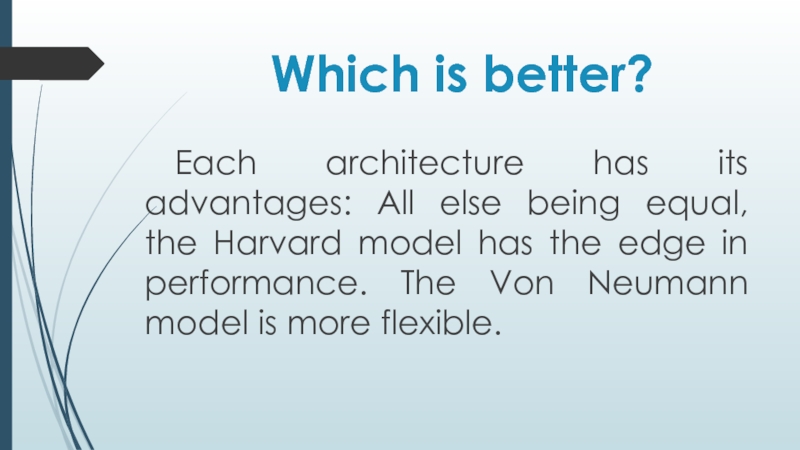
Слайд 7Which is better?
Each architecture has its advantages: All else being equal,
the Harvard model has the edge in performance. The Von Neumann model is more flexible.
Слайд 9MCB
The concept of a memory control block (MCB) was introduced in
MS-DOS, Version 2.0, as the operating system's basic method of tracking memory allocation for application programs and installable device drivers.
Слайд 15ADDRESS
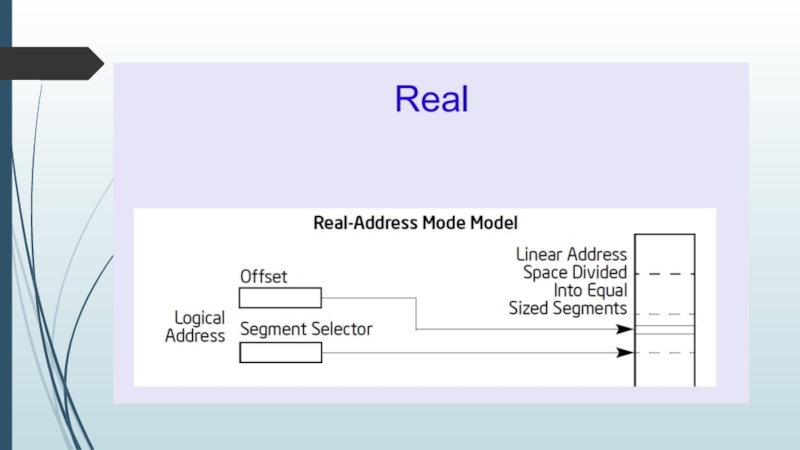
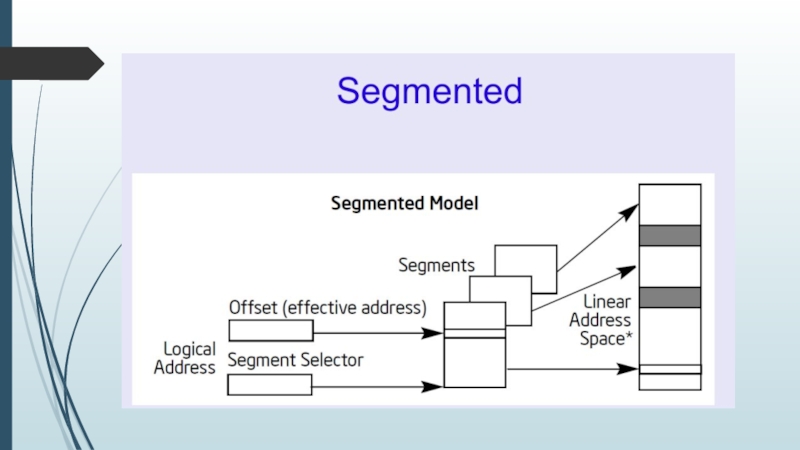
Logical address is the address at which an item (memory cell,
storage element, network host) appears to reside from the perspective of an executing application program. (selector, offset)
Linear address (also known as virtual address): are calculated from virtual addresses by segment translation.
In computing, a physical address (also real address, or binary address), is the end result of all the transformations of other types of addresses
Linear address (also known as virtual address): are calculated from virtual addresses by segment translation.
In computing, a physical address (also real address, or binary address), is the end result of all the transformations of other types of addresses