- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
ITIL Foundation and Overview. (Week 2) презентация
Содержание
- 1. ITIL Foundation and Overview. (Week 2)
- 2. Overview Processes (including Selected Process
- 3. Processes
- 4. Processes Structured set of activities
- 5. Process Control Process Owner Process Documentation
- 6. Selected Processes in SLC
- 7. SLC :: Service Design Purpose Converting
- 8. Processes in Service Design Availability Management
- 9. Service Level Management Service Level Agreement
- 10. Things you might find in an SLA
- 11. Types of SLA Service-based All customers
- 12. ITSCM IT Service Continuity Management
- 13. Information Security Management Confidentiality Making
- 14. SLC :: Service Transition Key Purpose
- 15. Knowledge Management Vital to enabling the
- 16. Data-Information-Knowledge-Wisdom Data Information - who, what
- 17. Service Asset and Configuration Managing these
- 18. Configuration Management System
- 19. Painting the Forth Bridge... A Baseline
- 20. Change Management Respond to customers changing
- 21. Change Types Normal Non-urgent, requires approval
- 22. Change Advisory Board Change Manager (VITAL) One
- 23. Release Management Release is a collection
- 24. Phased or Big Bang? Phased release
- 25. SLC :: Service Operation Maintenance
- 26. Processes in Service Operation Incident Management
- 27. Incident Management Deals with unplanned interruptions
- 28. Problem Management Aims to prevent problems
- 29. Access Management Right things for right
- 30. Service Desk Local, Central or Virtual
- 31. Functions & Roles
- 32. Functions Self contained subsets of an
- 33. Roles Collections of specific responsibilities and
- 34. Roles :: Service Owner Service Owner
- 35. Roles :: Service Owner :: Responsibilities
- 36. Roles :: Process Owner Process Owner
- 37. Roles :: Process Owner :: Responsibilities
- 38. Roles :: Service Manager Service Manager
- 39. Roles :: Product Manager Service Manager
- 40. Roles
- 41. ITIL Functions
- 42. ITIL Functions Service Desk Technical
- 43. Service Desk Provides a single point
- 44. Technical Management Charged with procurement, development,
- 45. Application Management Concerned with the end
- 46. IT Operations Management - I Deals
- 47. IT Operations Management - II Operational
- 48. The RACI Model
- 49. The RACI Model - I Ensures
- 50. The RACI Model - II
- 51. Technology and Automation
- 52. Technology and Automation - I Automation
- 53. Technology and Automation - II Automation of
- 54. Technology and Automation - III Service Management
Слайд 2Overview
Processes (including Selected Process of SLC)
Functions
ITIL Functions
The
RACI Model
Technology and Automation
Technology and Automation
Слайд 4Processes
Structured set of activities
Designed to achieve a specific objective
Four
basic characteristics
Transform inputs into outputs
Deliver results to specific customer or stakeholder
Measurable
Triggered by specific events
Transform inputs into outputs
Deliver results to specific customer or stakeholder
Measurable
Triggered by specific events
Слайд 5
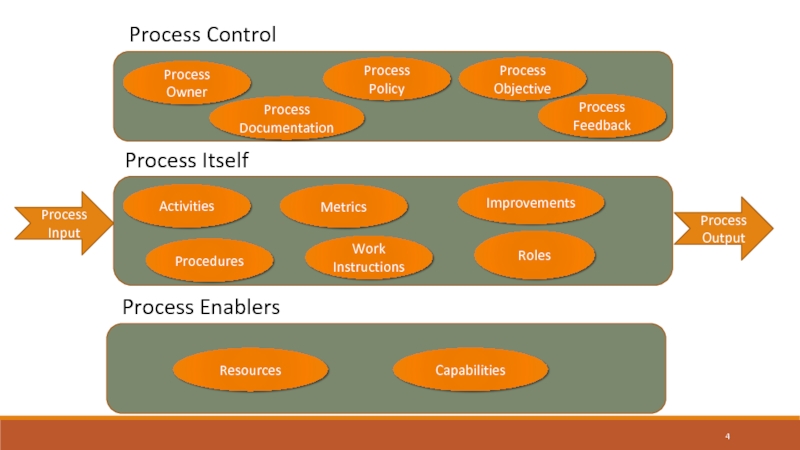
Process Control
Process Owner
Process Documentation
Process Policy
Process Objective
Process Feedback
Process Itself
Metrics
Procedures
Activities
Work
Instructions
Improvements
Roles
Process Input
Process Output
Process Enablers
Resources
Capabilities
Слайд 7SLC :: Service Design
Purpose
Converting the strategy into reality, through the
use of a consistent approach to the design and development of new service offerings
How are we going to provide it?
How are we going to build it?
How are we going to test it?
How are we going to deploy it?
How are we going to provide it?
How are we going to build it?
How are we going to test it?
How are we going to deploy it?
Слайд 8Processes in Service Design
Availability Management
Capacity Management
ITSCM (disaster
recovery)
Supplier Management
Service Level Management
Information Security Management
Service Catalogue Management
Supplier Management
Service Level Management
Information Security Management
Service Catalogue Management
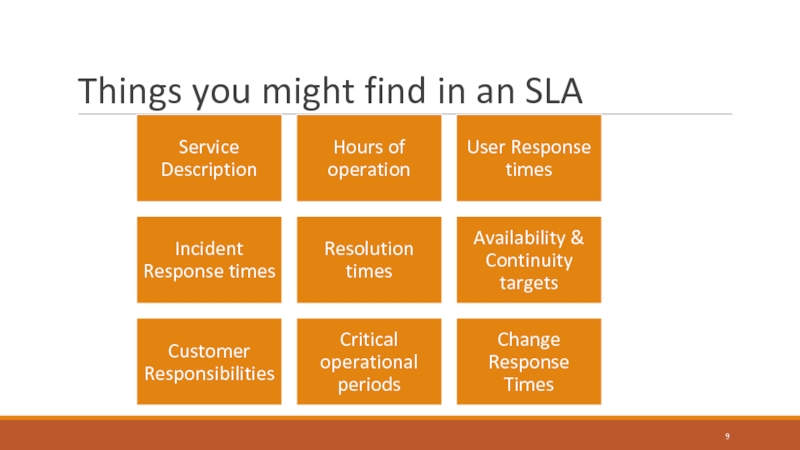
Слайд 9Service Level Management
Service Level Agreement
Operational Level Agreements
Internal
Underpinning Contracts
External Organisation
Supplier Management
Can
be an annex to a contract
Should be clear and fair and written in easy-to-understand, unambiguous language
Success of SLM (KPIs)
How many services have SLAs?
How does the number of breaches of SLA change over time (we hope it reduces!)?
Should be clear and fair and written in easy-to-understand, unambiguous language
Success of SLM (KPIs)
How many services have SLAs?
How does the number of breaches of SLA change over time (we hope it reduces!)?
Слайд 11Types of SLA
Service-based
All customers get same deal for same services
Customer-based
Different
customers get different deal (and different cost)
Multi-level
These involve corporate, customer and service levels and avoid repetition
Multi-level
These involve corporate, customer and service levels and avoid repetition
Слайд 12ITSCM
IT Service Continuity Management
Ensures resumption of services within agreed
timescale
Business Impact Analysis informs decisions about resources
E.g. Stock Exchange can’t afford 5 minutes downtime but 2 hours downtime probably wont badly affect a departmental accounts office or a college bursary
Business Impact Analysis informs decisions about resources
E.g. Stock Exchange can’t afford 5 minutes downtime but 2 hours downtime probably wont badly affect a departmental accounts office or a college bursary
Слайд 13Information Security Management
Confidentiality
Making sure only those authorised can see
data
Integrity
Making sure the data is accurate and not corrupted
Availability
Making sure data is supplied when it is requested
Integrity
Making sure the data is accurate and not corrupted
Availability
Making sure data is supplied when it is requested
Слайд 14SLC :: Service Transition
Key Purpose
To bridge both the gap
between projects and operations more effectively
Improve any changes that are going into live service
Build
Deployment
Testing
User acceptance
Bed-in
Improve any changes that are going into live service
Build
Deployment
Testing
User acceptance
Bed-in
Слайд 15Knowledge Management
Vital to enabling the right information to be provided
at the right place and the right time to the right person to enable informed decision
Stops data being locked away with individuals
Obvious organisational advantage
Stops data being locked away with individuals
Obvious organisational advantage
Слайд 16Data-Information-Knowledge-Wisdom
Data
Information
- who, what , where?
Knowledge
- How?
Wisdom
- Why?
Wisdom cannot be
assisted by technology it only comes with experience!
Service Knowledge Information Management System is crucial to retaining this extremely valuable information
Service Knowledge Information Management System is crucial to retaining this extremely valuable information
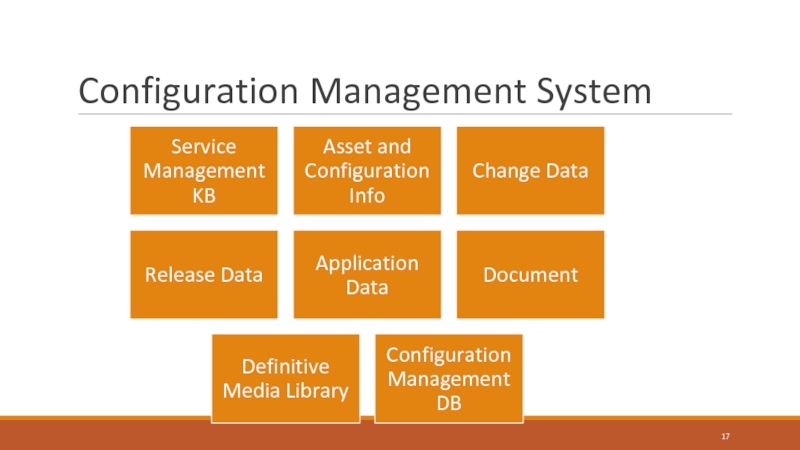
Слайд 17Service Asset and Configuration
Managing these properly is key
Provides Logical
Model of Infrastructure and Accurate Configuration information
Controls assets
Minimised costs
Enables proper change and release management
Speeds incident and problem resolution
Controls assets
Minimised costs
Enables proper change and release management
Speeds incident and problem resolution
Слайд 19Painting the Forth Bridge...
A Baseline is a “last known good
configuration”
But the CMS will always be a “work in progress” and probably always out of date. But still worth having
Current configuration will always be the most recent baseline plus any implemented approved changes
But the CMS will always be a “work in progress” and probably always out of date. But still worth having
Current configuration will always be the most recent baseline plus any implemented approved changes
Слайд 20Change Management
Respond to customers changing business requirements
Respond to business
and IT requests for change that will align the services with the business needs
Roles
Change Manager
Change Authority
Change Advisory Board (CAB)
Emergency CAB (ECAB)
80% of service interruption is caused by operator error or poor change control (Gartner)
Roles
Change Manager
Change Authority
Change Advisory Board (CAB)
Emergency CAB (ECAB)
80% of service interruption is caused by operator error or poor change control (Gartner)
Слайд 21Change Types
Normal
Non-urgent, requires approval
Standard
Non-urgent, follows established path, no approval
needed
Emergency
Requires approval but too urgent for normal procedure
Emergency
Requires approval but too urgent for normal procedure
Слайд 22Change Advisory Board
Change Manager (VITAL)
One or more of
Customer/User
User Manager
Developer/Maintainer
Expert/Consultant
Contractor
CAB considers the
7 Rs
Who RAISED?, REASON, RETURN, RISKS, RESOURCES, RESPONSIBLE, RELATIONSHIPS to other changes
Who RAISED?, REASON, RETURN, RISKS, RESOURCES, RESPONSIBLE, RELATIONSHIPS to other changes
Слайд 23Release Management
Release is a collection of authorised and tested changes
ready for deployment
A rollout introduces a release into the live environment
Full Release
e.g. Office 2007
Delta (partial) release
e.g. Windows Update
Package
e.g. Windows Service Pack
A rollout introduces a release into the live environment
Full Release
e.g. Office 2007
Delta (partial) release
e.g. Windows Update
Package
e.g. Windows Service Pack
Слайд 24Phased or Big Bang?
Phased release is less painful but more
work
Deploy can be manual or automatic
Automatic can be push or pull
Release Manager will produce a release policy
Release MUST be tested and NOT by the developer or the change instigator
Deploy can be manual or automatic
Automatic can be push or pull
Release Manager will produce a release policy
Release MUST be tested and NOT by the developer or the change instigator
Слайд 25SLC :: Service Operation
Maintenance
Management
Realises Strategic Objectives and is
where the Value is seen
Слайд 26Processes in Service Operation
Incident Management
Problem Management
Event Management
Request
Fulfilment
Access Management
Access Management
Слайд 27Incident Management
Deals with unplanned interruptions to IT Services or reductions
in their quality
Failure of a configuration item that has not impacted a service is also an incident (e.g. Disk in RAID failure)
Reported by:
Users
Technical Staff
Monitoring Tools
Failure of a configuration item that has not impacted a service is also an incident (e.g. Disk in RAID failure)
Reported by:
Users
Technical Staff
Monitoring Tools
Слайд 28Problem Management
Aims to prevent problems and resulting incidents
Minimises impact
of unavoidable incidents
Eliminates recurring incidents
Proactive Problem Management
Identifies areas of potential weakness
Identifies workarounds
Reactive Problem Management
Indentifies underlying causes of incidents
Identifies changes to prevent recurrence
Eliminates recurring incidents
Proactive Problem Management
Identifies areas of potential weakness
Identifies workarounds
Reactive Problem Management
Indentifies underlying causes of incidents
Identifies changes to prevent recurrence
Слайд 29Access Management
Right things for right users at right time
Concepts
Access
Identity
(Authentication, AuthN)
Rights (Authorisation, AuthZ)
Service Group
Directory
Rights (Authorisation, AuthZ)
Service Group
Directory
Слайд 30Service Desk
Local, Central or Virtual
Examples?
Single point of contact
Skills for operators
Customer Focus
Articulate
Interpersonal Skills (patient!)
Understand Business
Methodical/Analytical
Technical knowledge
Multi-lingual
Service desk often seen as the bottom of the pile
Bust most visible to customers so important to get right!
Customer Focus
Articulate
Interpersonal Skills (patient!)
Understand Business
Methodical/Analytical
Technical knowledge
Multi-lingual
Service desk often seen as the bottom of the pile
Bust most visible to customers so important to get right!
Слайд 32Functions
Self contained subsets of an organization
Intended to accomplish
specific tasks
Takes the form of a team or group of people and the tools being used
Add structure and stability to organizations
Supported by budget and reporting structures
Takes the form of a team or group of people and the tools being used
Add structure and stability to organizations
Supported by budget and reporting structures
Слайд 33Roles
Collections of specific responsibilities and privileges
Held by individuals or
teams
Standard roles include;
Service Owner
Process Owner
Service Manager
Product Manager
Standard roles include;
Service Owner
Process Owner
Service Manager
Product Manager
Слайд 34Roles :: Service Owner
Service Owner
Accountable for the overall design,
performance, integration, improvement, and management of a single service
responsible for continual improvement and management of change affecting Services under their care
Example
The owner of the Payroll Service
responsible for continual improvement and management of change affecting Services under their care
Example
The owner of the Payroll Service
Слайд 35Roles :: Service Owner :: Responsibilities
To act as prime Customer
contact for all Service related enquiries and issues
To ensure that the ongoing Service delivery and support meet agreed Customer requirements
To identify opportunities for Service Improvements, discuss with the customer and to initiate changes for improvements if appropriate.
To liaise with the appropriate Process Owners throughout the Service Management lifecycle
To solicit required data, statistics and reports for analysis and to facilitate effective Service monitoring and performance
To ensure that the ongoing Service delivery and support meet agreed Customer requirements
To identify opportunities for Service Improvements, discuss with the customer and to initiate changes for improvements if appropriate.
To liaise with the appropriate Process Owners throughout the Service Management lifecycle
To solicit required data, statistics and reports for analysis and to facilitate effective Service monitoring and performance
Слайд 36Roles :: Process Owner
Process Owner
Accountable for the overall design, performance,
integration, improvement, and management of a single process
Example
The owner for the Availability Management Process
Example
The owner for the Availability Management Process
Слайд 37Roles :: Process Owner :: Responsibilities
Assisting with process design
Documenting the process
Make sure the process is being performed as documented
Making sure process meetings it aims
Monitoring and improving the process over time
Make sure the process is being performed as documented
Making sure process meetings it aims
Monitoring and improving the process over time
Слайд 38Roles :: Service Manager
Service Manager
Accountable for the development, performance, and
improvement of all services in the environment
Слайд 39Roles :: Product Manager
Service Manager
Accountable for development, performance, and improvement
of a group of related services
Слайд 42ITIL Functions
Service Desk
Technical Management
Application Management
IT Operations Management
Слайд 43Service Desk
Provides a single point of contact
Between users and
IT
Processes inbound incidents, service requests, change requests, etc.
Owns and executes incident management process
Acts as a hub for all communications internal to IT Service Provider
Processes inbound incidents, service requests, change requests, etc.
Owns and executes incident management process
Acts as a hub for all communications internal to IT Service Provider
Слайд 44Technical Management
Charged with procurement, development, and management of the technical
skill sets and resources
Required to support the infrastructure and the ITSM effort
Primary task is to ensure…
Service Provider has the right skill sets available to deliver the offered services!
Seeks and represents different specialized teams or functions within an IT organization
Networking, Security, Storage, Database, Servers, etc.
Required to support the infrastructure and the ITSM effort
Primary task is to ensure…
Service Provider has the right skill sets available to deliver the offered services!
Seeks and represents different specialized teams or functions within an IT organization
Networking, Security, Storage, Database, Servers, etc.
Слайд 45Application Management
Concerned with the end to end management of applications
Seeks specialized skills sets required to support organization’s applications.
Executes and is supported by different ITIL core processes
Executes and is supported by different ITIL core processes
Слайд 46IT Operations Management - I
Deals with the day to day
maintenance of the IT infrastructure and facilities
Divided into two sub-functions
Operations Control
Facilities Management
Divided into two sub-functions
Operations Control
Facilities Management
Слайд 47IT Operations Management - II
Operational Control
Involves regular maintenance cycles associated
with infrastructure management
Console management, Backup and restore operations, Media management, Batch job execution
Facilities Management
Involves maintenance of the facilities housing IT operations
Looks after HVAC, Fire suppression, Facilities access, Power, etc.
Console management, Backup and restore operations, Media management, Batch job execution
Facilities Management
Involves maintenance of the facilities housing IT operations
Looks after HVAC, Fire suppression, Facilities access, Power, etc.
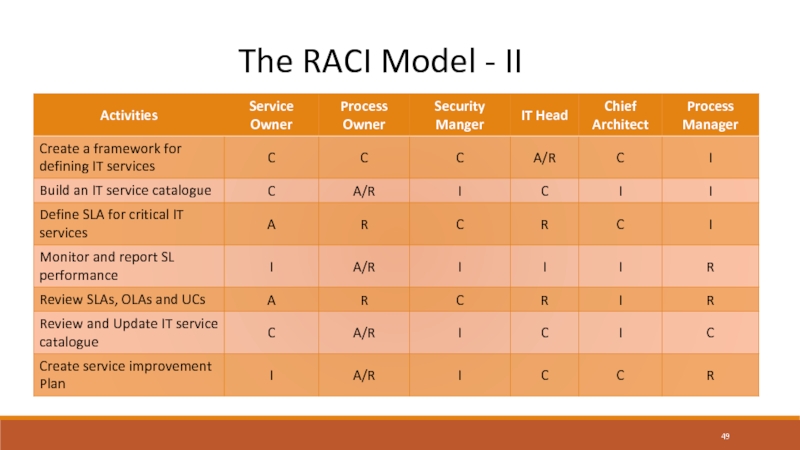
Слайд 49The RACI Model - I
Ensures that roles are appropriately filled
in processes
R = Responsible
Execute or perform the task
A = Accountable
Own the task and answerable for outcomes
C = Consulted
Review and provide advice and authorization for the task
I = Informed
Receive updates as the task progresses
R = Responsible
Execute or perform the task
A = Accountable
Own the task and answerable for outcomes
C = Consulted
Review and provide advice and authorization for the task
I = Informed
Receive updates as the task progresses
Слайд 52Technology and Automation - I
Automation (Tools) are extremely useful to
improve utility and warranty of services:
Real time and historical data for analysis
Correlation of data from multiple devices
Service Impact analysis for prioritization
Service Performance optimization
Real time and historical data for analysis
Correlation of data from multiple devices
Service Impact analysis for prioritization
Service Performance optimization
Слайд 53Technology and Automation - II
Automation of service processes helps improve the
quality of service, reduce costs and reduce risks by reducing complexity and uncertainty, and by efficiently resolving trade-offs.
Some of the areas where service management can benefit from automation
Design and modeling
Service catalogue
Pattern recognition and analysis
Classification, prioritization and routing
Detection and monitoring
Optimization.
Some of the areas where service management can benefit from automation
Design and modeling
Service catalogue
Pattern recognition and analysis
Classification, prioritization and routing
Detection and monitoring
Optimization.
Слайд 54Technology and Automation - III
Service Management Tools functionality include;
Self Help
Workflow or Process Engine
Integrated CMS
Discovery/Deployment technology
Remote Control
Diagnostic scripts & utilities
Reporting & Dashboards
Integrated CMS
Discovery/Deployment technology
Remote Control
Diagnostic scripts & utilities
Reporting & Dashboards