- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
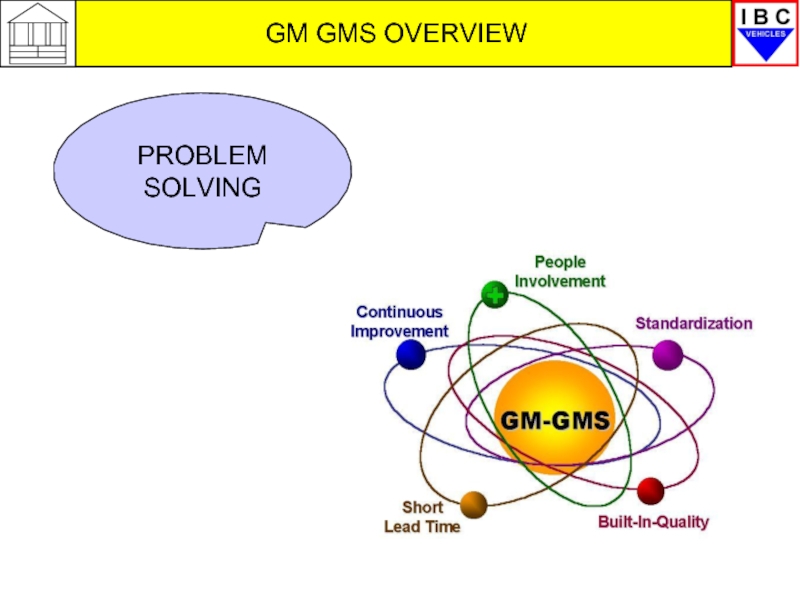
GM GMS overview problem solving презентация
Содержание
- 1. GM GMS overview problem solving
- 2. PROBLEM SOLVING IBC VEHICLES – STANDARD PROBLEM SOLVING PROCESS ‘7 Diamonds’
- 3. PROBLEM SOLVING What is 7 Diamonds?
- 4. Why do we need the 7 Diamonds
- 5. PROBLEM SOLVING Following the 7 Diamond process
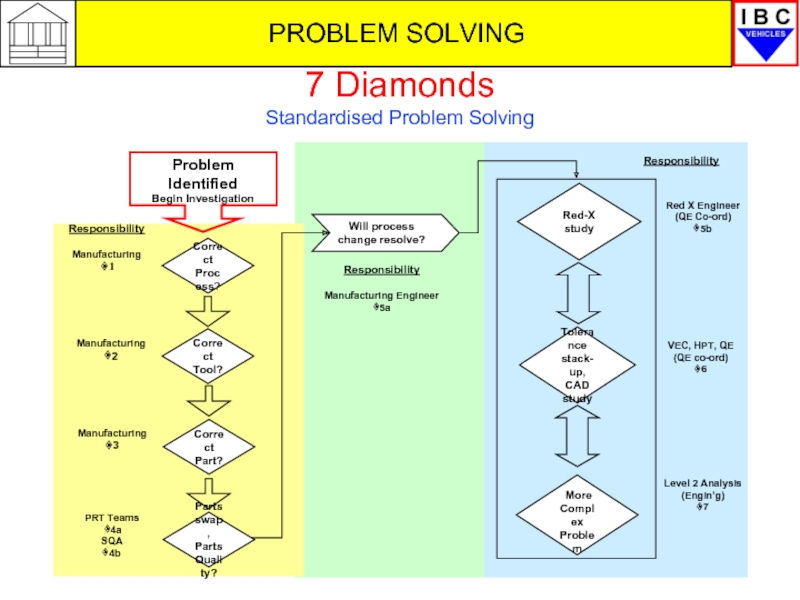
- 6. PROBLEM SOLVING 7 Diamonds Standardised Problem Solving
- 7. PROBLEM SOLVING Review
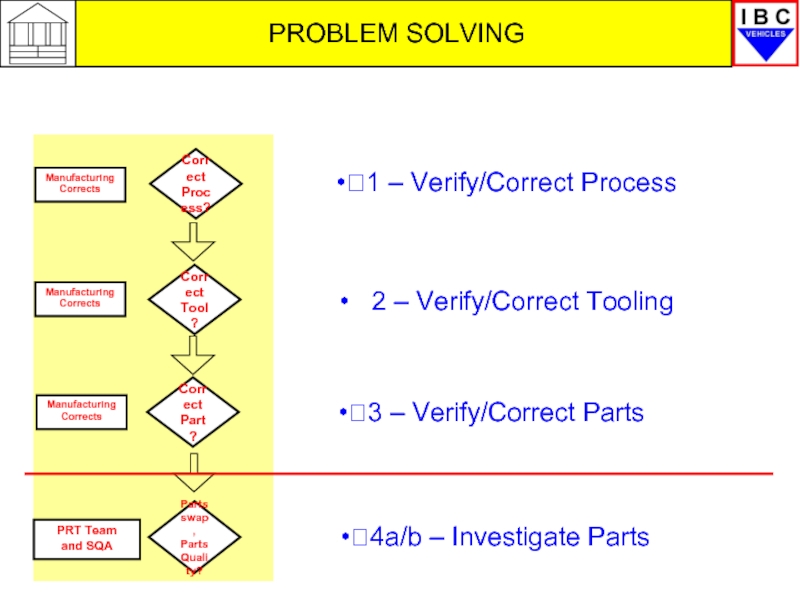
- 8. PROBLEM SOLVING Diamonds 1
- 9. PROBLEM SOLVING
- 10. PROBLEM SOLVING Diamonds 1-3 Review
- 11. PROBLEM SOLVING PCB – Problem Communication Brief
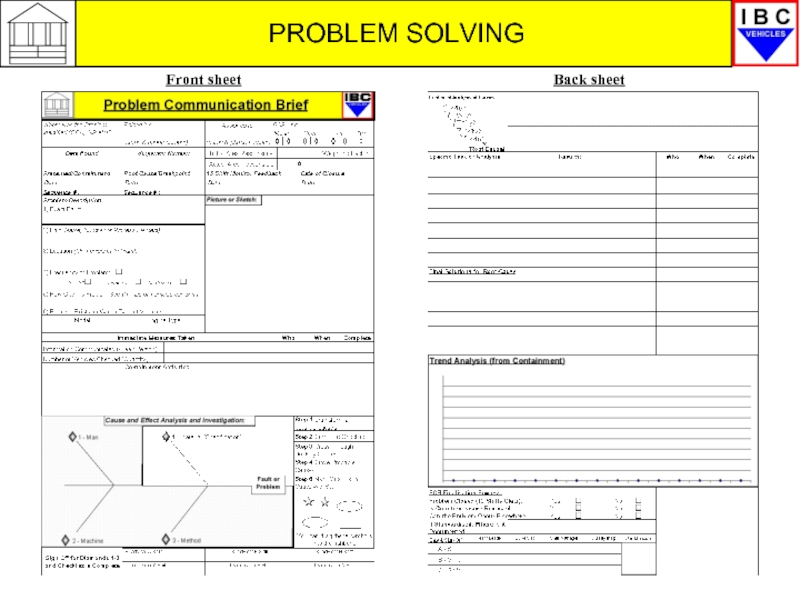
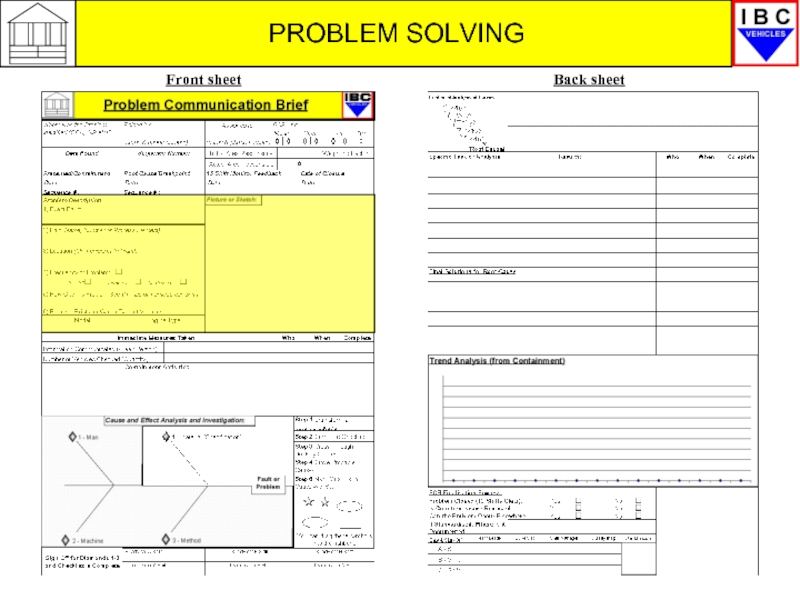
- 12. PROBLEM SOLVING Front sheet Back sheet
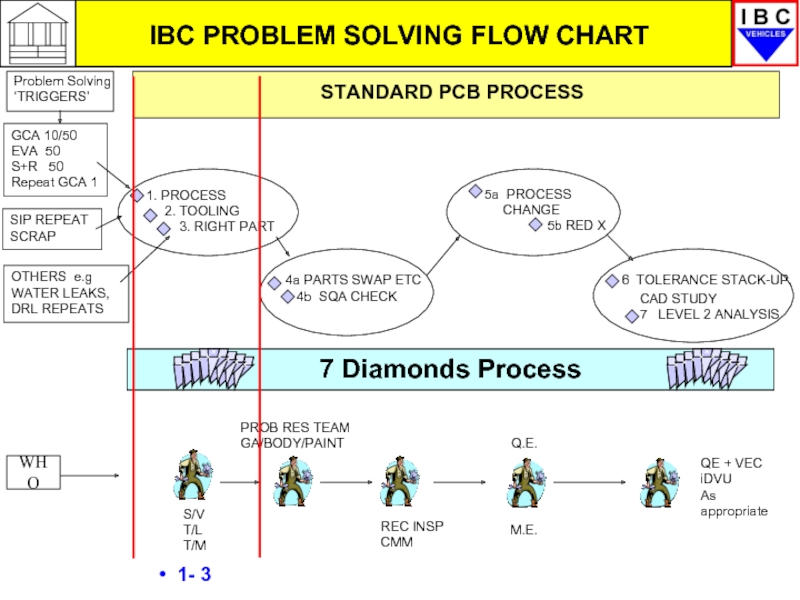
- 13. STANDARD PCB PROCESS IBC PROBLEM SOLVING FLOW CHART 1- 3
- 14. PROBLEM SOLVING Generating PCBs There are
- 15. PROBLEM SOLVING All PCBs are processed through
- 16. PROBLEM SOLVING All PCBs pertaining to any
- 17. PROBLEM SOLVING So how does the PCB
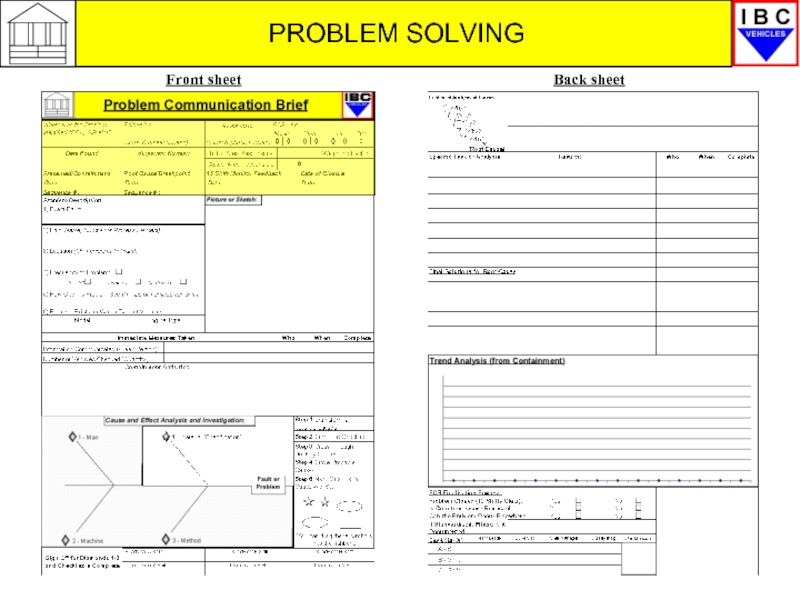
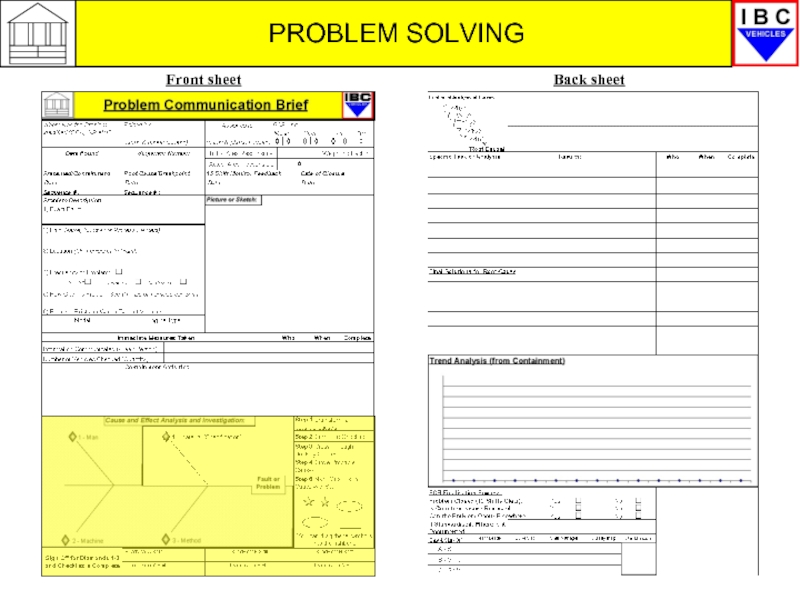
- 18. PROBLEM SOLVING Front sheet Back sheet
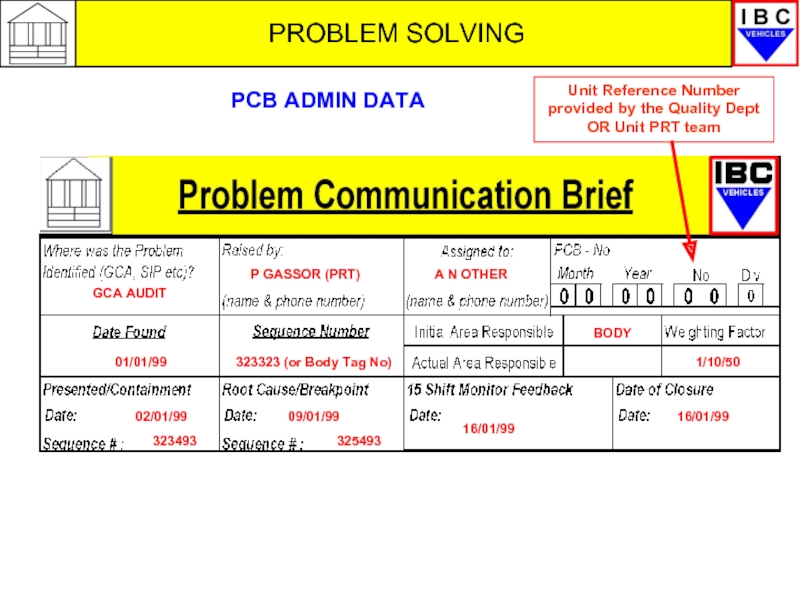
- 19. PROBLEM SOLVING GCA AUDIT P GASSOR (PRT)
- 20. PROBLEM SOLVING Front sheet Back sheet
- 21. PROBLEM SOLVING WELD NUT MISSING FROM LH
- 22. PROBLEM SOLVING Front sheet Back sheet
- 23. PROBLEM SOLVING ALL SUPVN, T/Ls, T/MS ON
- 24. PROBLEM SOLVING Front sheet Back sheet
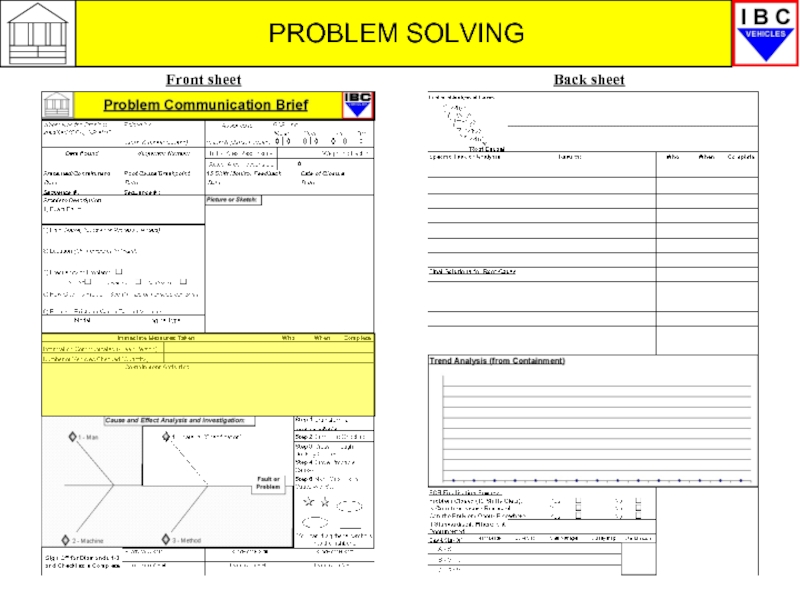
- 25. PROBLEM SOLVING BRAINSTORMING
- 26. PROBLEM SOLVING DIAMONDS 1,2,3 - PROBLEM
- 27. DIAMONDS 1-3 PROBLEM SOLVING TOOLS PROBLEM
- 28. PROBLEM SOLVING DIAMONDS 1-3 PROBLEM SOLVING
- 29. PROBLEM SOLVING Missed operation? Operator not
- 30. PROBLEM SOLVING
- 31. PROBLEM SOLVING
- 32. PROBLEM SOLVING (2) Correct Tool 1 Are
- 33. PROBLEM SOLVING
- 34. PROBLEM SOLVING This section of the check
- 35. PROBLEM SOLVING COMPLETING THE FISHBONE (1)
- 36. PROBLEM SOLVING Supervisor B
- 37. PROBLEM SOLVING Continued Analysis of
- 38. PROBLEM SOLVING (Root Cause): The ‘5 Whys’
- 39. PROBLEM SOLVING (Root Cause): Continued Analysis of
- 40. PROBLEM SOLVING Continued Analysis of
- 41. PROBLEM SOLVING Specific Task or Analysis: Results:
- 42. PROBLEM SOLVING Continued Analysis of
- 43. PROBLEM SOLVING Final Solutions for Root-Cause
- 44. PROBLEM SOLVING Continued Analysis of
- 45. PROBLEM SOLVING PCB Finalisation Process:
- 46. PROBLEM SOLVING PCB – Completion ONLY
- 47. GM GMS OVERVIEW SUSTAINABLE BUSINESS
Слайд 3PROBLEM SOLVING
What is 7 Diamonds?
Seven Diamonds is a standard 7
Confirmation of these items MUST be made by Manufacturing before Engineering can be involved in any further, more detailed investigations.
70% of all Quality and Build problems are caused
by non-standard operating or tooling not working or
not being used correctly!
Слайд 4Why do we need the 7 Diamonds process?
We need to apply
We fully UNDERSTAND all of the issues
We determine the RIGHTFUL OWNER/S of the problem
We ensure that corrective actions are EFFECTIVE
We actually SOLVE the problem.
Currently
We don’t always follow the same steps or directions.
Too often we attempt to solve problems without really understanding
them and all of the contributary factors.
By not identifying the real owner we do not arrive at the real root
cause and are left with permanent containments (extra work).
We often think we have cured a problem only for it to resurface at
a later date.
PROBLEM SOLVING
Слайд 5PROBLEM SOLVING
Following the 7 Diamond process allows us to break a
Verify the basics first:
is the standardised work process being used?
is the tooling standardised and correctly applied?
are the right parts being used?
Confirm the process (if we can make one right, why not all?)
Understand the impact of variation in the process
Is the process running out of control?
Is the process capable?
Can the process be changed to prevent the problem/defect?
ONLY when we have ensured these items can we;
Involve Engineering to apply more technical investigative methods
Слайд 7PROBLEM SOLVING
Review of Responsibilities
Diamonds 1-3 Production/Maintenance Supervisor & Team Leader/Team Members
Diamond 4b SQA
Diamond 5a Manufacturing Engineer
Diamond 5b-6 QE (Red-X, CAD, Tolerance Stack-up
Diamond 7 Product Engineering. Level 2 analysis
(QE co-ordination)
Слайд 8PROBLEM SOLVING
Diamonds 1 - 3
Diamonds 1 to 3 of the process
Production organisation is running the manufacturing process to design intent.
If the manufacturing process is NOT being managed to design intent, then it must be corrected and validated, before we can consider asking for Engineering assistance.
Engineering referral only occurs when the manufacturing process does meet design intent and the problem still exists.
Слайд 9PROBLEM SOLVING
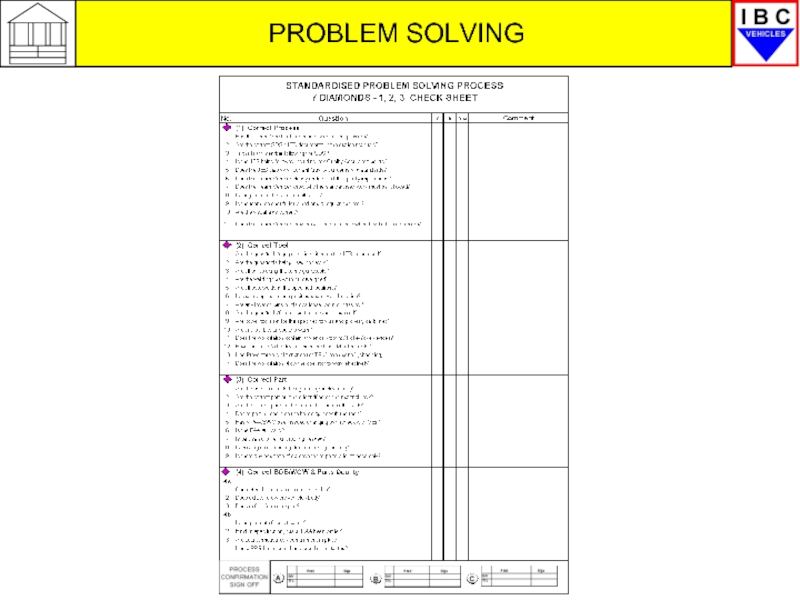
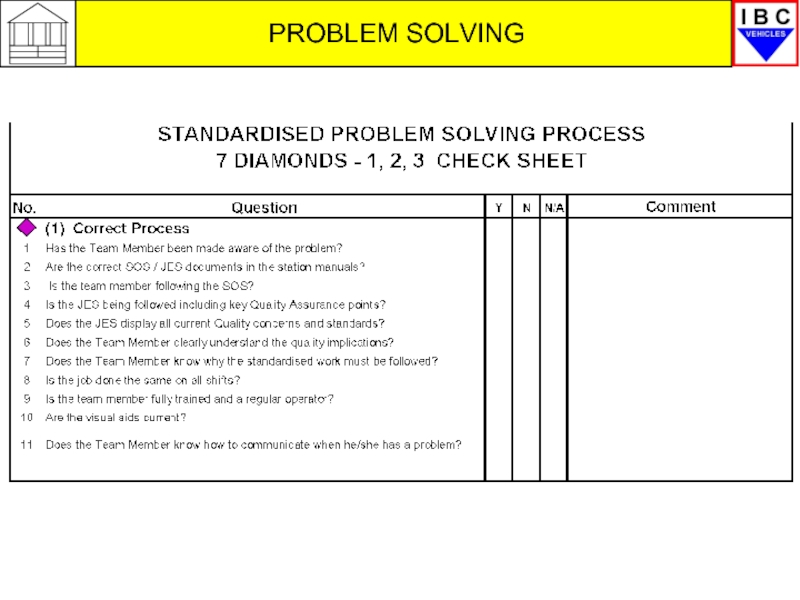
1 – Verify/Correct Process
Correct
Process?
Manufacturing
Corrects
Correct
Tool?
Manufacturing
Corrects
Correct
Part?
Manufacturing
Corrects
Parts swap,
Parts Quality?
PRT Team
and SQA
3 – Verify/Correct Parts
4a/b – Investigate Parts
Слайд 10PROBLEM SOLVING
Diamonds 1-3 Review
Once a problem has been identified, the
must be to immediately step through diamonds 1-3.
Diamonds 1-3 are for evaluating the stability of the process.
If the process is being applied correctly, diamonds 4a and 4b
are applied to determine if the parts are to specification
Following steps 1,2 & 3 must become inherent in our problem
solving thought process.
Слайд 11PROBLEM SOLVING
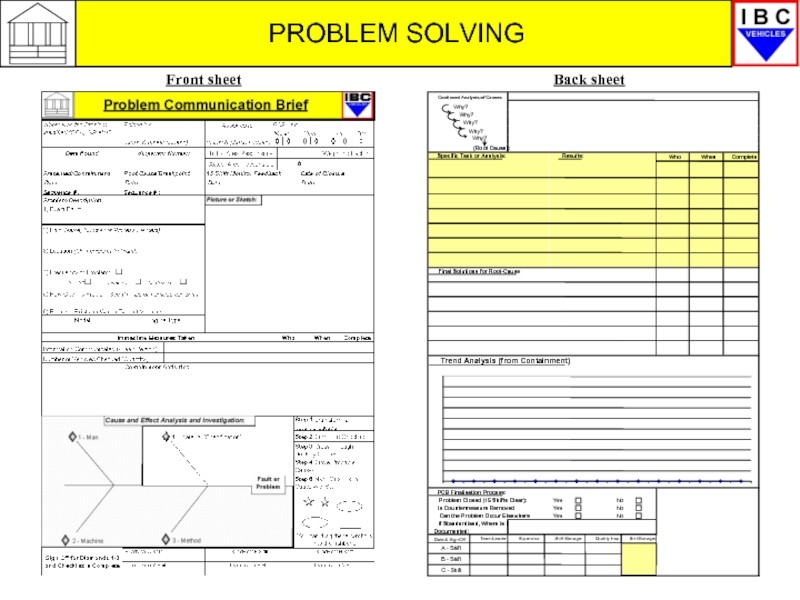
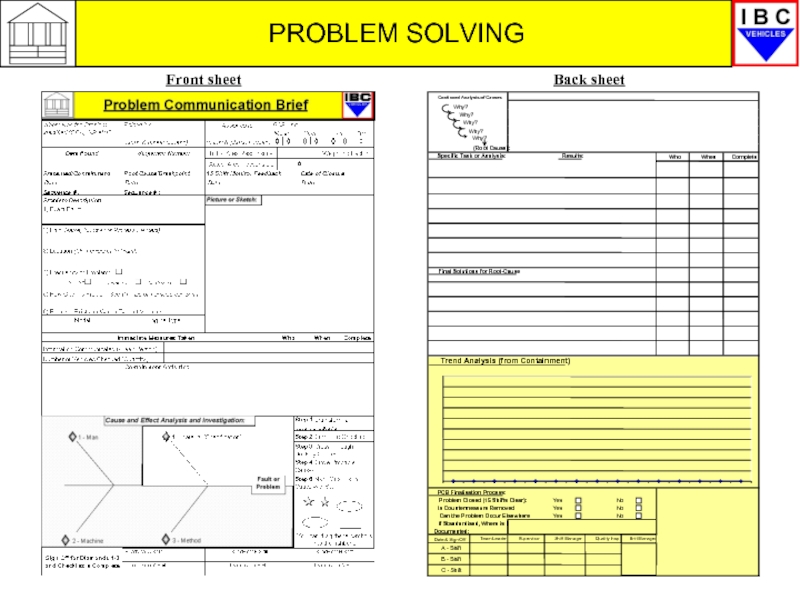
PCB – Problem Communication Brief
The PCB is a standard document
It ensures that everyone applies the same thought process towards understanding and resolving these problems.
As you will see the PCB is aligned to the 7 Diamonds process.
We will now look briefly at how the PCB works, remembering that the first 3 Diamonds are those you will be involved in.
Слайд 14PROBLEM SOLVING
Generating PCBs
There are a number of ‘trigger’ points which
(1) ‘Central’ PCBs
Issued by Plant QA for GCA Audit Factor 50, 10 and repetitive Factor 1.0 defects found on Audit vehicles. Repetitive defects found at the ‘Squeak and Rattle’ test, Water Test, C.A.T audit and Electrical Systems audit also generate PCBs.
(2) Local/Internal PCBs
These are issued by the Unit Manager through the Unit PRT Team for repetitive Quality defects, DRL repeats, BIW Audit defects and high cost or repeat Scrap parts and assemblies.
Слайд 15PROBLEM SOLVING
All PCBs are processed through the relevant Unit PRT Team
On completion all PCBs are returned to the PRT Team to update the tracking system and forward completed ‘central’ PCBs back to Plant QA.
PCB – Escalation to Diamond 4a
If after completing each stage of Diamond 1-3 on the PCB form the cause is not apparent or it is clear the problem belongs to another department the PCB is returned to the Unit PRT Team who will decide whether to refer the PCB elsewhere or progress the PCB to Diamonds 4a and/or 4b.
Слайд 16PROBLEM SOLVING
All PCBs pertaining to any particular area are tracked on
Here all OPEN PCBs are displayed and tracked for 15 shifts after the final counter measures have been implemented.
Supervisors and Team Leaders will discuss these issues and the current status with their Team members on a regular basis.
Слайд 17PROBLEM SOLVING
So how does the PCB work?
We will now look briefly
Слайд 19PROBLEM SOLVING
GCA AUDIT
P GASSOR (PRT)
A N OTHER
01/01/99
323323 (or Body Tag No)
1/10/50
09/01/99
16/01/99
16/01/99
325493
BODY
PCB
Слайд 21PROBLEM SOLVING
WELD NUT MISSING FROM LH SIDE LOAD DOOR
LH SIDE LOAD
LH SIDE LOAD DOOR LOCK LOCATION
AVE 2 PER WEEK (FROM STABS DATA)
ALL + LH S/L DOOR
N/A
PROBLEM DESCRIPTION/DATA
Слайд 23PROBLEM SOLVING
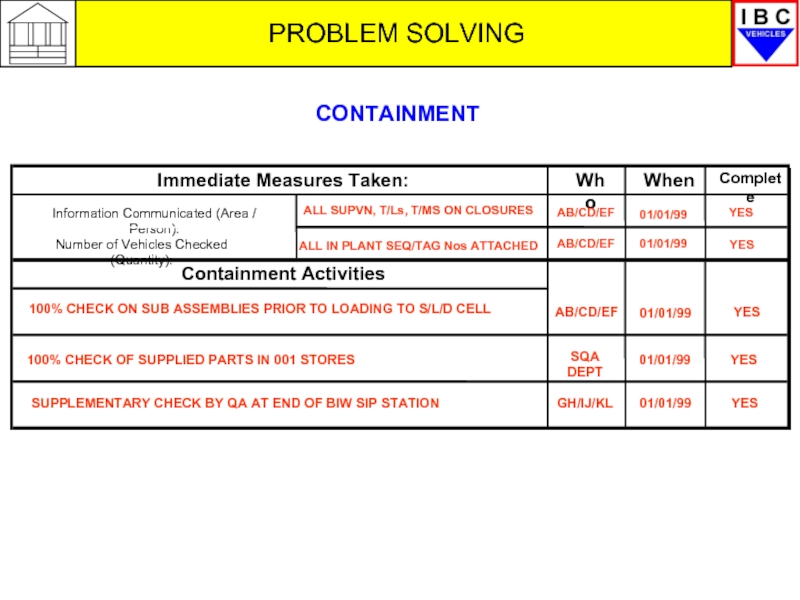
ALL SUPVN, T/Ls, T/MS ON CLOSURES
AB/CD/EF
01/01/99
YES
ALL IN PLANT SEQ/TAG Nos
AB/CD/EF
01/01/99
YES
100% CHECK ON SUB ASSEMBLIES PRIOR TO LOADING TO S/L/D CELL
100% CHECK OF SUPPLIED PARTS IN 001 STORES
SUPPLEMENTARY CHECK BY QA AT END OF BIW SIP STATION
AB/CD/EF
SQA DEPT
GH/IJ/KL
01/01/99
01/01/99
01/01/99
YES
YES
YES
CONTAINMENT
Слайд 26PROBLEM SOLVING
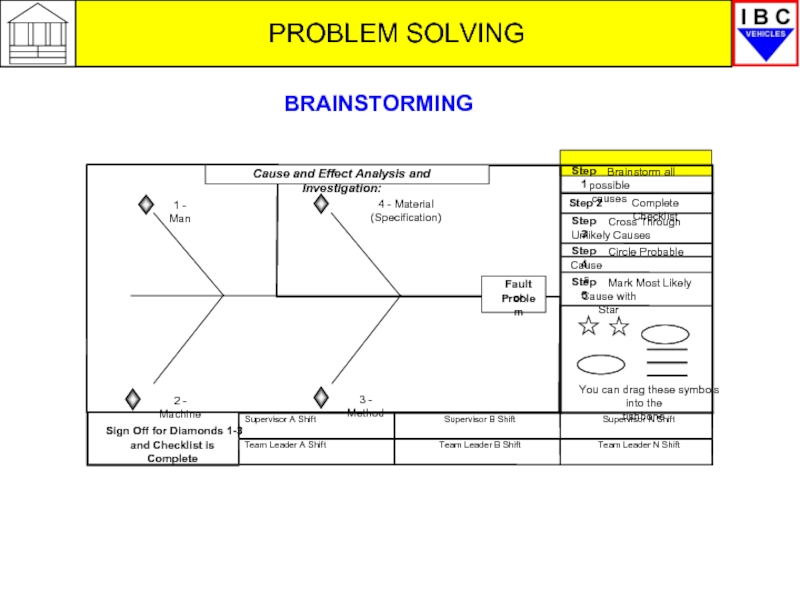
DIAMONDS 1,2,3 - PROBLEM SOLVING
When completing the
To generate the possible causes we use a simple but effective technique known as ‘brainstorming’ which is used to help create as many ideas in as short a time as possible.
BRAINSTORMING
Слайд 27 DIAMONDS 1-3 PROBLEM SOLVING TOOLS
PROBLEM SOLVING
HOW TO BRAINSTORM?
It is best
Ensure all group members are aware of the nature of the problem/defect e.g. missing part, damage, wrong part etc.
Next, ask each person to think of as many possible causes for the defect (however likely or unlikely they may seem).
Get each person to briefly explain their ideas and note down EVERY idea clearly on a flipchart/paper.
As a group discuss each idea and agree on the most likely causes.
Where possible ask group members to verify/investigate the most likely causes and suggest suitable countermeasures
Слайд 28PROBLEM SOLVING
DIAMONDS 1-3 PROBLEM SOLVING TOOLS
BRAINSTORMING – DO’s and
DO – record and discuss every idea – however extreme they may appear (quite often even the strangest ideas prove to contain some benefits)
DON’T – never dismiss or ridicule any ideas. This is likely to switch that person off and refrain from any further positive input.
DO – try to ensure that all ideas are fully understood – ask individuals to explain them and ask questions to ensure there are no misunderstandings.
DON’T – be influenced by any previous history of a particular problem or defect – always start with a blank sheet of paper!
DO – ensure whenever an idea is discarded, that the individual who came up with it fully understands why it will not be pursued.
Слайд 29
PROBLEM SOLVING
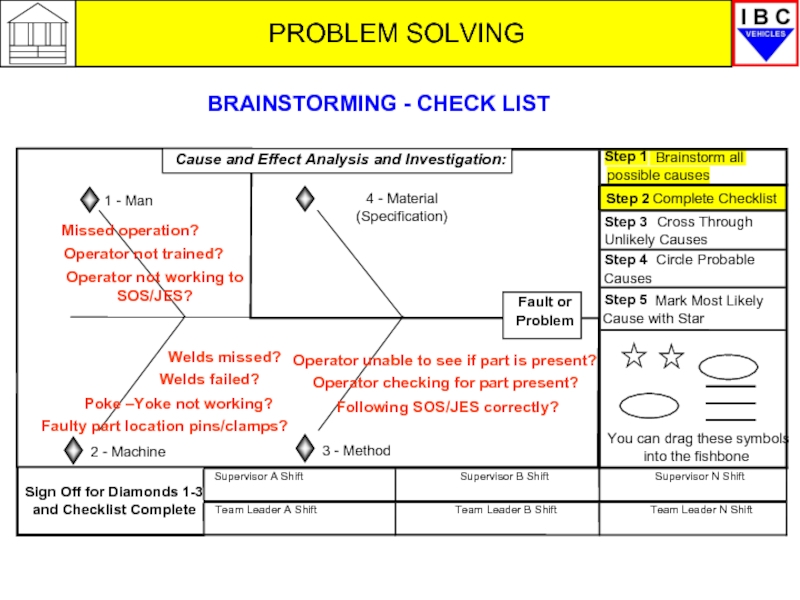
Missed operation?
Operator not trained?
Operator not working to SOS/JES?
Welds missed?
Welds failed?
Poke
Following SOS/JES correctly?
Operator checking for part present?
Operator unable to see if part is present?
Faulty part location pins/clamps?
BRAINSTORMING - CHECK LIST
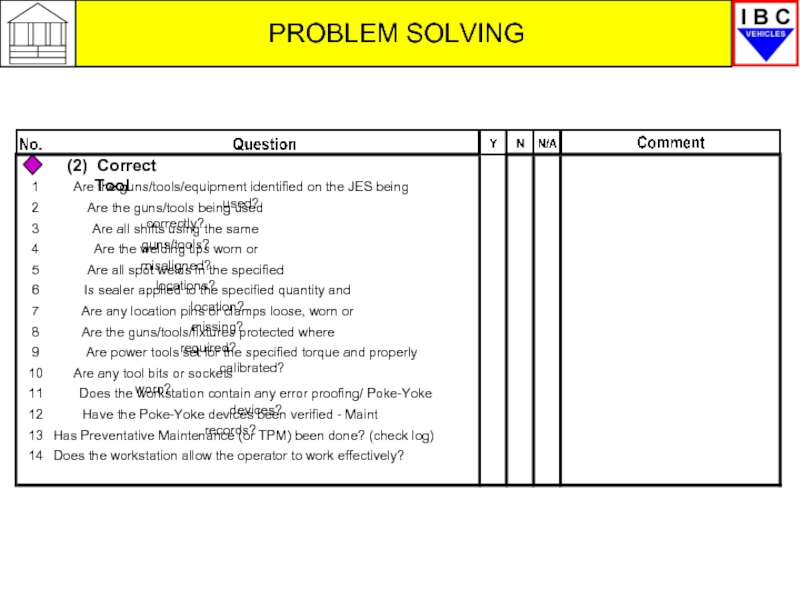
Слайд 32PROBLEM SOLVING
(2) Correct Tool
1
Are the guns/tools/equipment identified on the JES being
2
Are the guns/tools being used correctly?
3
Are all shifts using the same guns/tools?
4
Are the welding tips worn or misaligned?
5
Are all spot welds in the specified locations?
6
Is sealer applied to the specified quantity and location?
7
Are any location pins or clamps loose, worn or missing?
8
Are the guns/tools/fixtures protected where required?
9
Are power tools set for the specified torque and properly calibrated?
10
Are any tool bits or sockets worn?
11
Does the workstation contain any error proofing/ Poke-Yoke devices?
12
Have the Poke-Yoke devices been verified - Maint records?
13
Has Preventative Maintenance (or TPM) been done? (check log)
14
Does the workstation allow the operator to work effectively?
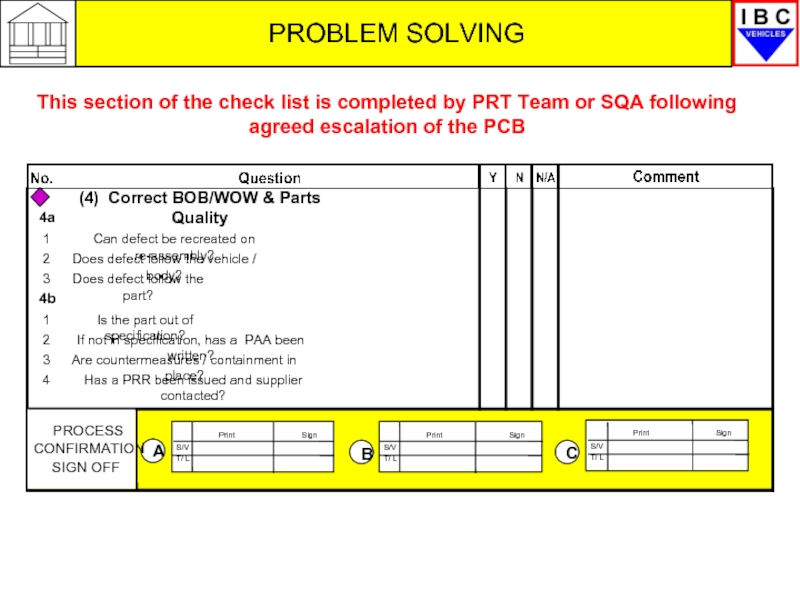
Слайд 34PROBLEM SOLVING
This section of the check list is completed by PRT
Слайд 36
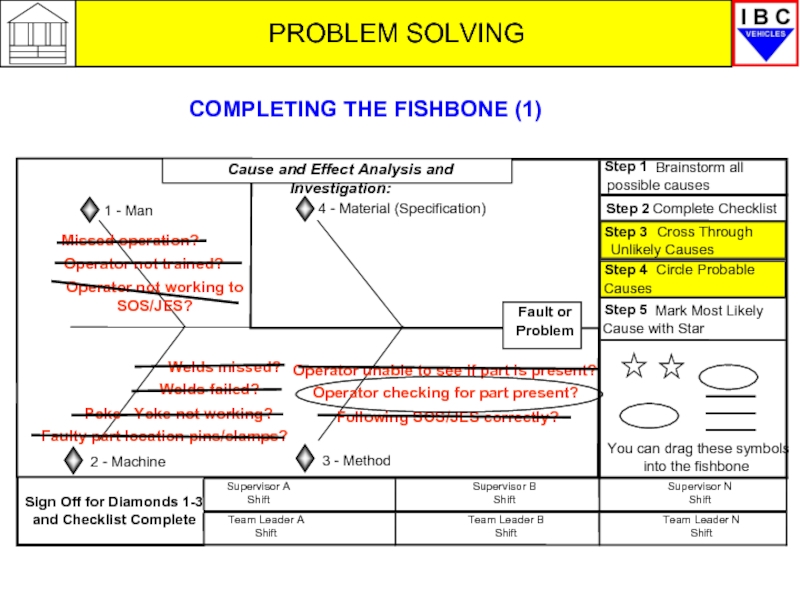
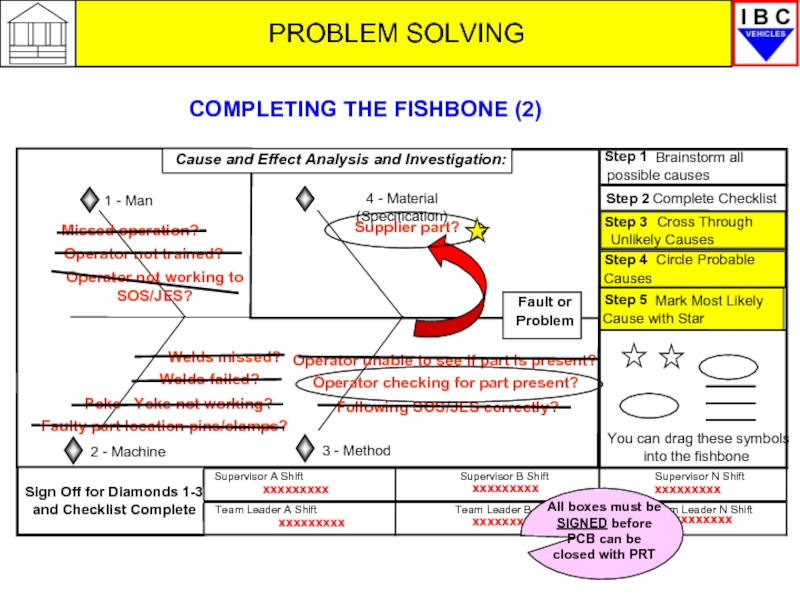
PROBLEM SOLVING
Supervisor B Shift
Team Leader B Shift
Supervisor N Shift
Team Leader N
You can drag these symbols
into the fishbone
Step 3
Cross Through
Unlikely Causes
Step 4
Circle Probable
Causes
Step 5
Mark Most Likely
Cause with Star
Team Leader A Shift
Supervisor A Shift
Step 1
Brainstorm all
possible causes
Step 2
Complete Checklist
Sign Off for Diamonds 1-3
and Checklist Complete
Fault or
Problem
1 - Man
4 - Material (Specification)
2 - Machine
3 - Method
Cause and Effect Analysis and Investigation:
Missed operation?
Operator not trained?
Operator not working to SOS/JES?
Welds missed?
Welds failed?
Poke –Yoke not working?
Following SOS/JES correctly?
Operator checking for part present?
Operator unable to see if part is present?
Faulty part location pins/clamps?
Supplier part?
COMPLETING THE FISHBONE (2)
Слайд 37
PROBLEM SOLVING
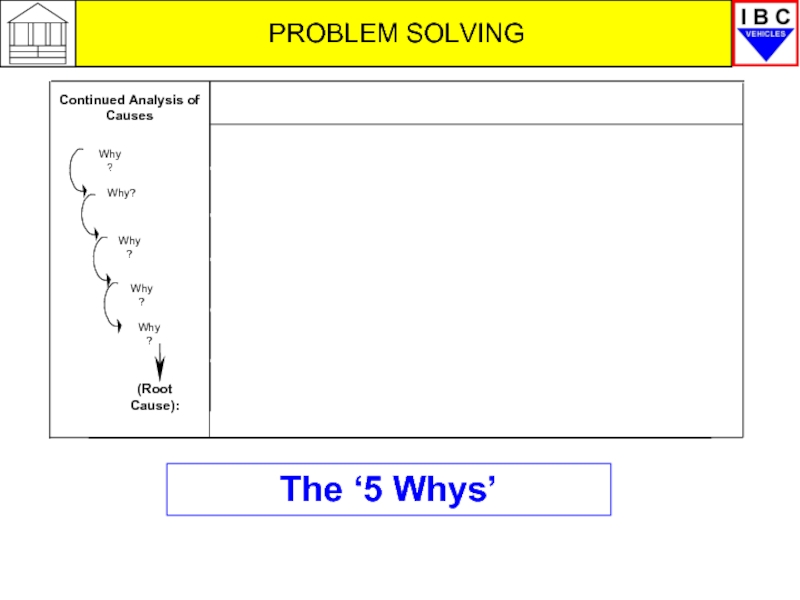
Continued Analysis of Causes
Specific Task or Analysis:
Results:
PCB Finalisation Process:
Yes
No
Is Countermeasure
Yes
No
Can the Problem Occur Elsewhere
Yes
No
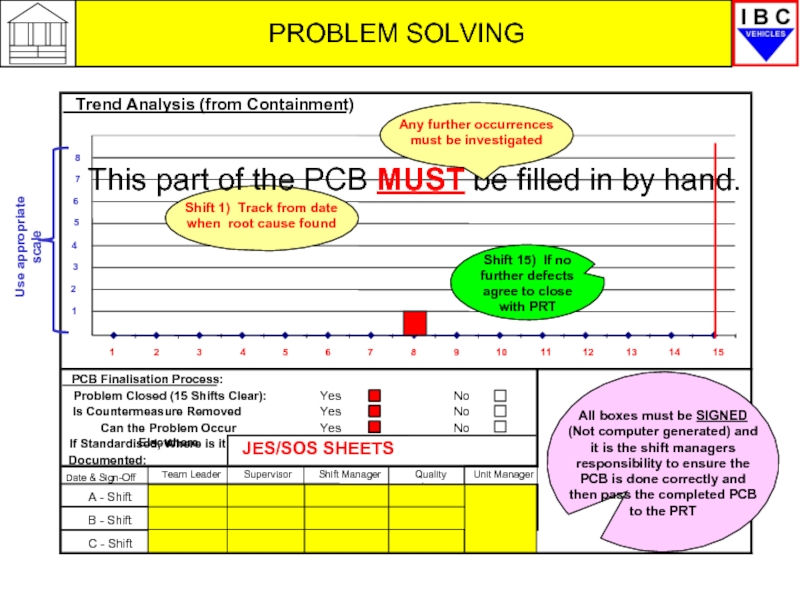
Trend Analysis (from Containment)
Problem Closed (15 Shifts Clear):
Final Solutions for Root-Cause
Complete
Who
When
(Root Cause):
If Standardised, Where is it
Documented:
Why?
Why?
Why?
Why?
Why?
Date & Sign-Off
Team Leader
Supervisor
Shift Manager
Quality Insp
Unit Manager
A - Shift
B - Shift
C - Shift
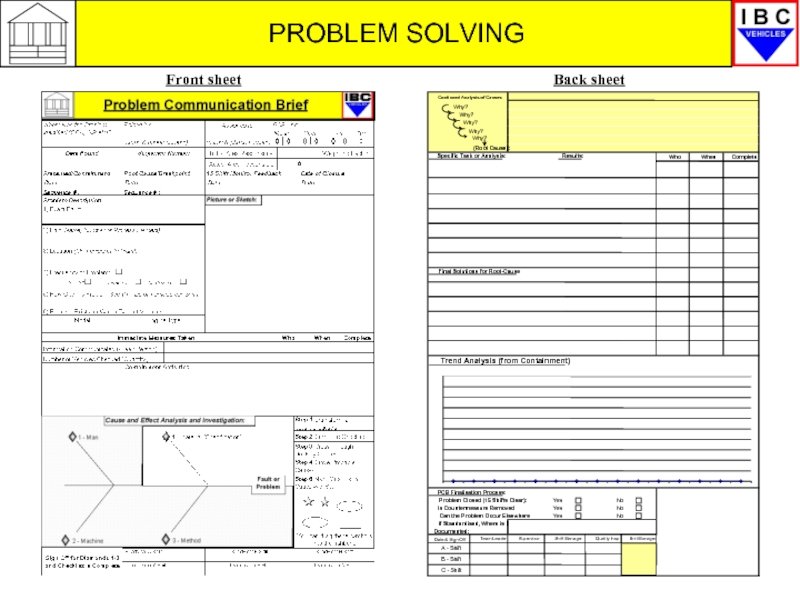
Front sheet
Back sheet
Слайд 39PROBLEM SOLVING
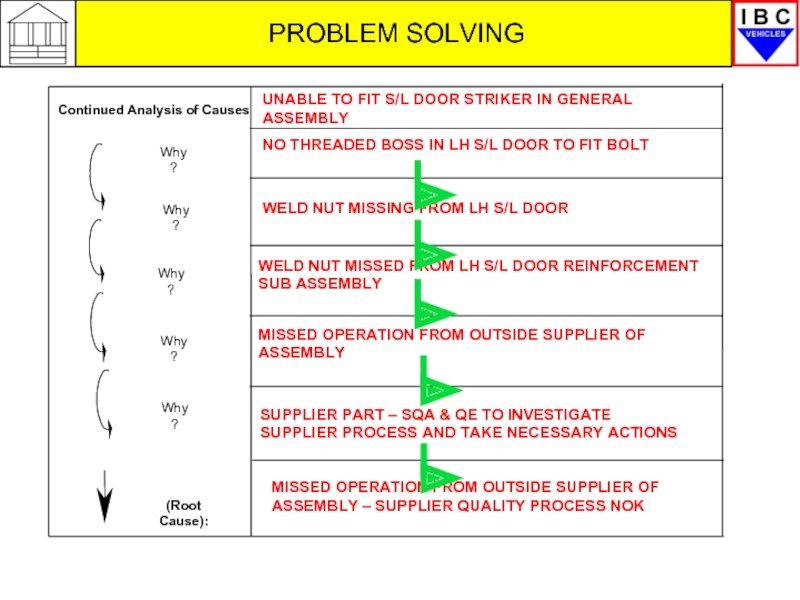
(Root Cause):
Continued Analysis of Causes
Why?
Why?
Why?
Why?
Why?
UNABLE TO FIT S/L DOOR STRIKER
NO THREADED BOSS IN LH S/L DOOR TO FIT BOLT
WELD NUT MISSING FROM LH S/L DOOR
WELD NUT MISSED FROM LH S/L DOOR REINFORCEMENT SUB ASSEMBLY
SUPPLIER PART – SQA & QE TO INVESTIGATE SUPPLIER PROCESS AND TAKE NECESSARY ACTIONS
MISSED OPERATION FROM OUTSIDE SUPPLIER OF ASSEMBLY
MISSED OPERATION FROM OUTSIDE SUPPLIER OF ASSEMBLY – SUPPLIER QUALITY PROCESS NOK
Слайд 40
PROBLEM SOLVING
Continued Analysis of Causes
Specific Task or Analysis:
Results:
PCB Finalisation Process:
Yes
No
Is Countermeasure
Yes
No
Can the Problem Occur Elsewhere
Yes
No
Trend Analysis (from Containment)
Problem Closed (15 Shifts Clear):
Final Solutions for Root-Cause
Complete
Who
When
(Root Cause):
If Standardised, Where is it
Documented:
Why?
Why?
Why?
Why?
Why?
Date & Sign-Off
Team Leader
Supervisor
Shift Manager
Quality Insp
Unit Manager
A - Shift
B - Shift
C - Shift
Front sheet
Back sheet
Слайд 41PROBLEM SOLVING
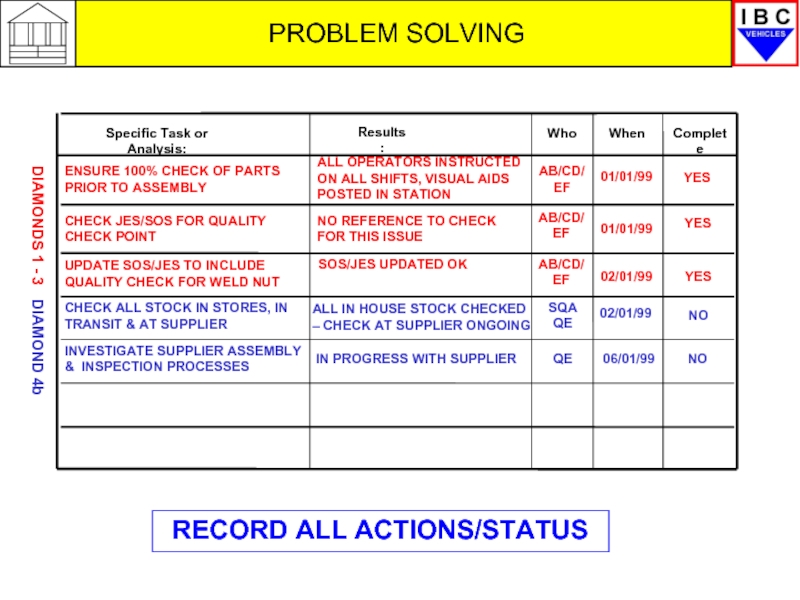
Specific Task or Analysis:
Results:
Complete
Who
When
ENSURE 100% CHECK OF PARTS PRIOR TO
CHECK JES/SOS FOR QUALITY CHECK POINT
UPDATE SOS/JES TO INCLUDE QUALITY CHECK FOR WELD NUT
CHECK ALL STOCK IN STORES, IN TRANSIT & AT SUPPLIER
INVESTIGATE SUPPLIER ASSEMBLY & INSPECTION PROCESSES
ALL OPERATORS INSTRUCTED ON ALL SHIFTS, VISUAL AIDS POSTED IN STATION
AB/CD/EF
01/01/99
YES
NO REFERENCE TO CHECK FOR THIS ISSUE
AB/CD/EF
01/01/99
YES
SOS/JES UPDATED OK
AB/CD/EF
02/01/99
YES
ALL IN HOUSE STOCK CHECKED – CHECK AT SUPPLIER ONGOING
SQA QE
02/01/99
NO
IN PROGRESS WITH SUPPLIER
QE
06/01/99
NO
DIAMONDS 1 - 3
DIAMOND 4b
RECORD ALL ACTIONS/STATUS
Слайд 42
PROBLEM SOLVING
Continued Analysis of Causes
Specific Task or Analysis:
Results:
PCB Finalisation Process:
Yes
No
Is Countermeasure
Yes
No
Can the Problem Occur Elsewhere
Yes
No
Trend Analysis (from Containment)
Problem Closed (15 Shifts Clear):
Final Solutions for Root-Cause
Complete
Who
When
(Root Cause):
If Standardised, Where is it
Documented:
Why?
Why?
Why?
Why?
Why?
Date & Sign-Off
Team Leader
Supervisor
Shift Manager
Quality Insp
Unit Manager
A - Shift
B - Shift
C - Shift
Front sheet
Back sheet
Слайд 43PROBLEM SOLVING
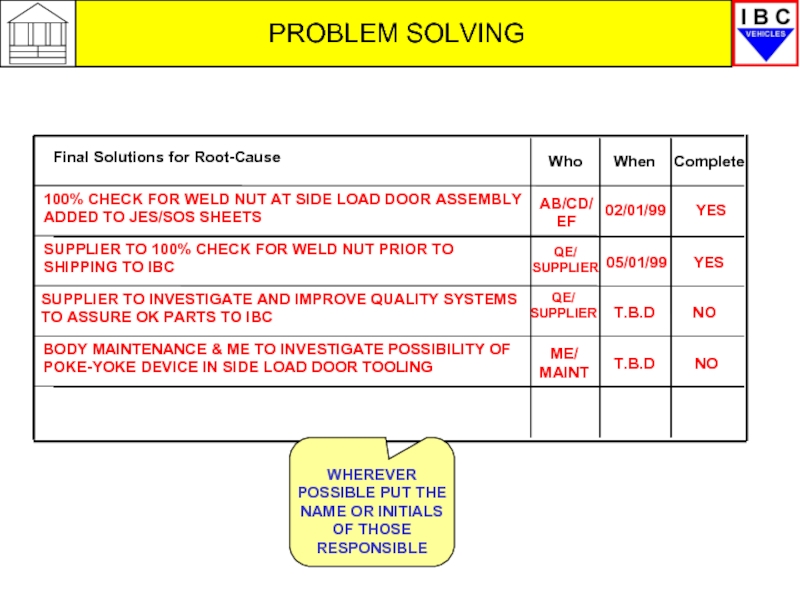
Final Solutions for Root-Cause
100% CHECK FOR WELD NUT AT SIDE
SUPPLIER TO 100% CHECK FOR WELD NUT PRIOR TO SHIPPING TO IBC
BODY MAINTENANCE & ME TO INVESTIGATE POSSIBILITY OF POKE-YOKE DEVICE IN SIDE LOAD DOOR TOOLING
Who
When
Complete
AB/CD/ EF
QE/ SUPPLIER
ME/ MAINT
02/01/99
05/01/99
T.B.D
YES
YES
NO
SUPPLIER TO INVESTIGATE AND IMPROVE QUALITY SYSTEMS TO ASSURE OK PARTS TO IBC
QE/ SUPPLIER
T.B.D
NO
Слайд 44
PROBLEM SOLVING
Continued Analysis of Causes
Specific Task or Analysis:
Results:
PCB Finalisation Process:
Yes
No
Is Countermeasure
Yes
No
Can the Problem Occur Elsewhere
Yes
No
Trend Analysis (from Containment)
Problem Closed (15 Shifts Clear):
Final Solutions for Root-Cause
Complete
Who
When
(Root Cause):
If Standardised, Where is it
Documented:
Why?
Why?
Why?
Why?
Why?
Date & Sign-Off
Team Leader
Supervisor
Shift Manager
Quality Insp
Unit Manager
A - Shift
B - Shift
C - Shift
Front sheet
Back sheet
Слайд 45
PROBLEM SOLVING
PCB Finalisation Process:
Yes
No
Is Countermeasure Removed
Yes
No
Can the Problem Occur Elsewhere
Yes
No
Trend Analysis
Problem Closed (15 Shifts Clear):
If Standardised, Where is it
Documented:
Date & Sign-Off
Team Leader
Supervisor
Shift Manager
Quality Insp
Unit Manager
A - Shift
B - Shift
C - Shift
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
Use appropriate scale
JES/SOS SHEETS
This part of the PCB MUST be filled in by hand.
Слайд 46PROBLEM SOLVING
PCB – Completion
ONLY after the PCB has been signed off
If the issuing body (e.g. Plant QA, Unit PRT Team etc.) agree that a problem has been clear for 15 shifts following the introduction of suitable counter-measures, then the PCB can be closed.
On completion and closure all PCBs will be archived by the PRT Team and the tracking system updated. External PCBs will be forwarded to the relevant locations by the PRT Team.
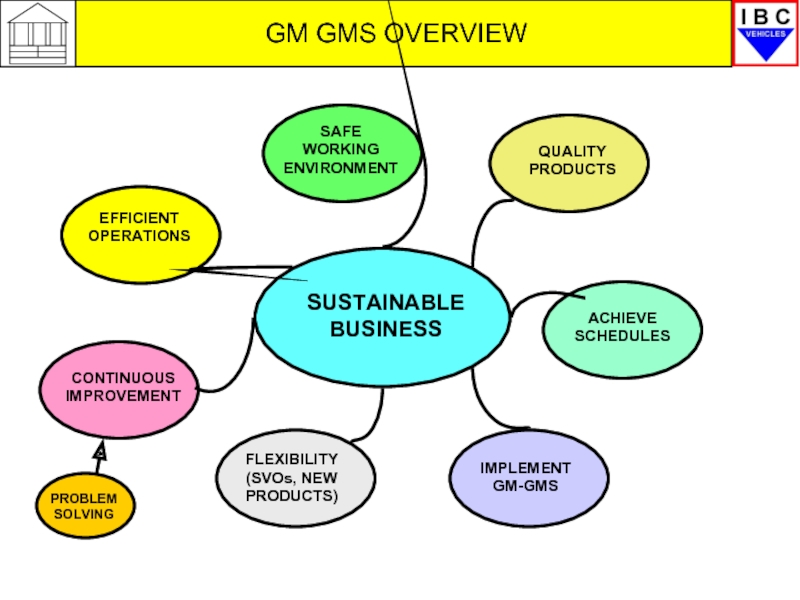
Слайд 47GM GMS OVERVIEW
SUSTAINABLE BUSINESS
QUALITY PRODUCTS
SAFE WORKING ENVIRONMENT
EFFICIENT OPERATIONS
ACHIEVE SCHEDULES
IMPLEMENT GM-GMS
CONTINUOUS IMPROVEMENT
FLEXIBILITY
PROBLEM SOLVING