- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Computer systems презентация
Содержание
- 1. Computer systems
- 2. Review Define volatile and none-volatile State what
- 3. Objectives Understand static electricity List reasons why
- 4. The movement and contact of the human
- 5. “Electro static discharge (ESD) is the transfer
- 6. Tribo-electrification Static electricity must build up a
- 7. ESD is more likely to exist in
- 8. ESD Symbols Fig 1 ESD Susceptibility
- 9. ESD protective devices A range of ESD
- 10. Working inside a computer When working on
- 11. Good uses of ESD ESD is used
- 12. Electrostatic discharge can cause damage to
- 13. Static Electricity Video Testing for Static
- 14. Follow the safety rules Be prepared:
- 15. This highly magnified picture shows the damage
- 16. Anti-static Wrist Strap Wrist straps safely remove
- 17. How do you know if its working?
- 18. Testing your wrist band Firstly check your
- 19. Motherboards The Main Printed Circuit Board Inside
- 20. Motherboard is… Multi-layered printed circuit board Copper
- 21. Think of a Motherboard as: Futuristic City
- 22. Motherboard MD Definition Research Activity MD Component
- 23. Basic Motherboard Chipset and Functions Different
- 24. Motherboard Determines: CPU type and speed Chipset
- 25. Form Factors Form factor means the size
- 26. What other features do modern Motherboards include?
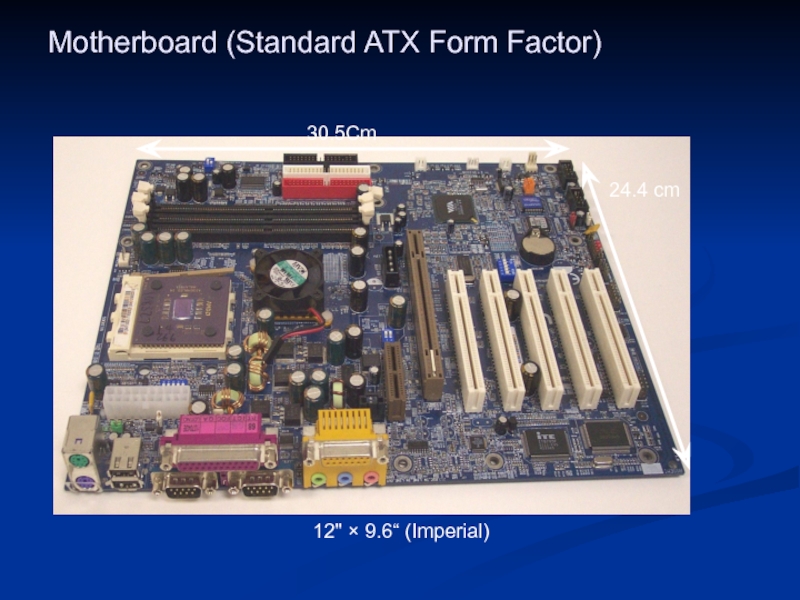
- 27. Motherboard (Standard ATX Form Factor) 12" × 9.6“ (Imperial) 30.5Cm 24.4 cm
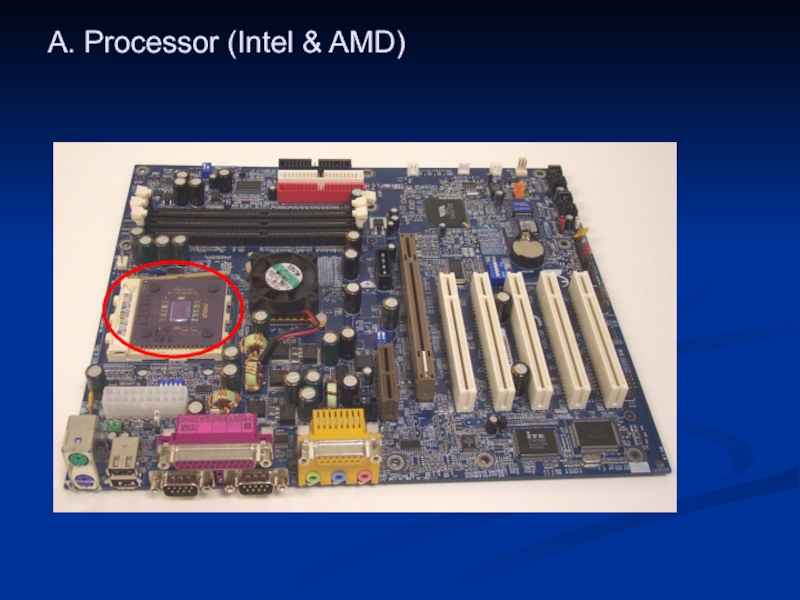
- 28. A. Processor (Intel & AMD)
- 29. B. North Bridge "North Bridge: The
- 30. I. South Bridge "South Bridge: The
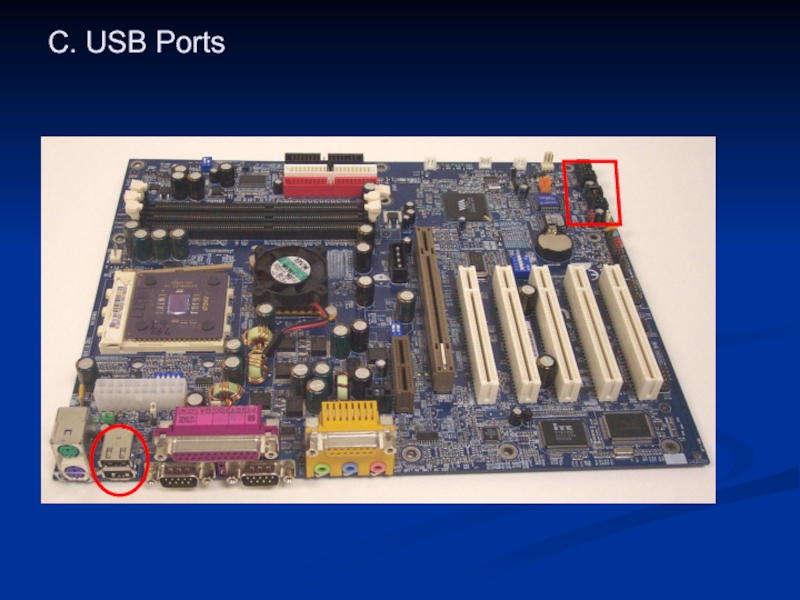
- 31. C. USB Ports
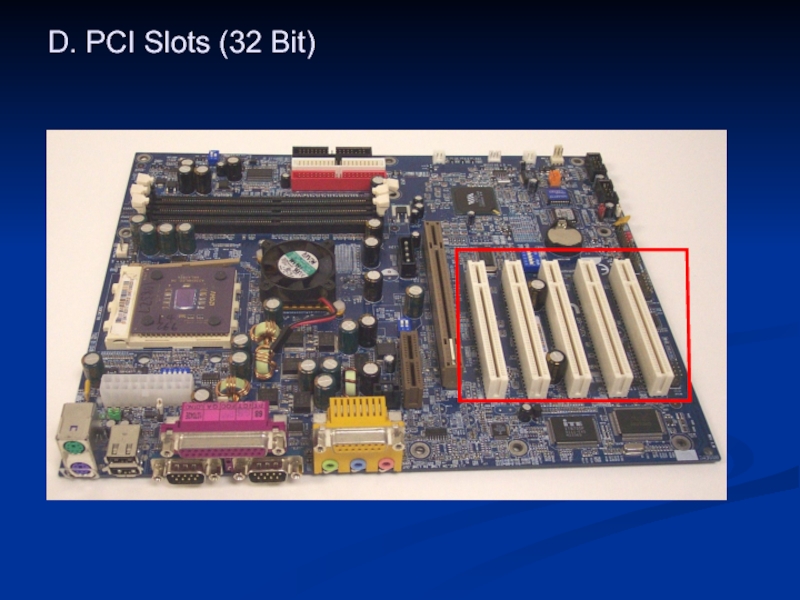
- 32. D. PCI Slots (32 Bit)
- 33. E. System BIOS (ROM) & CMOS
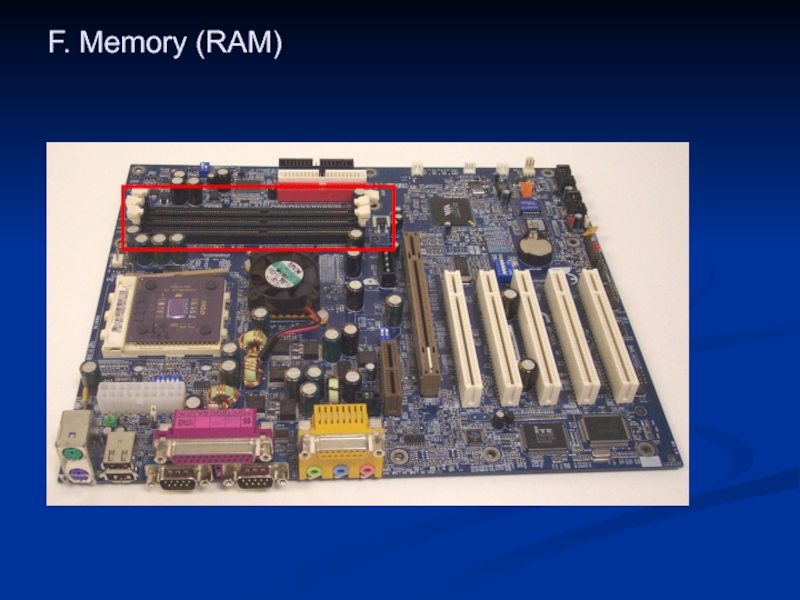
- 34. F. Memory (RAM)
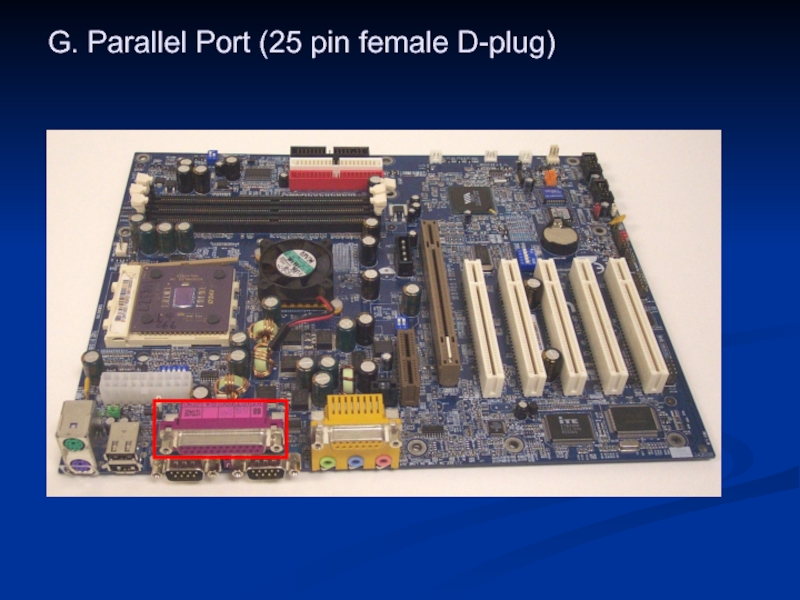
- 35. G. Parallel Port (25 pin female D-plug)
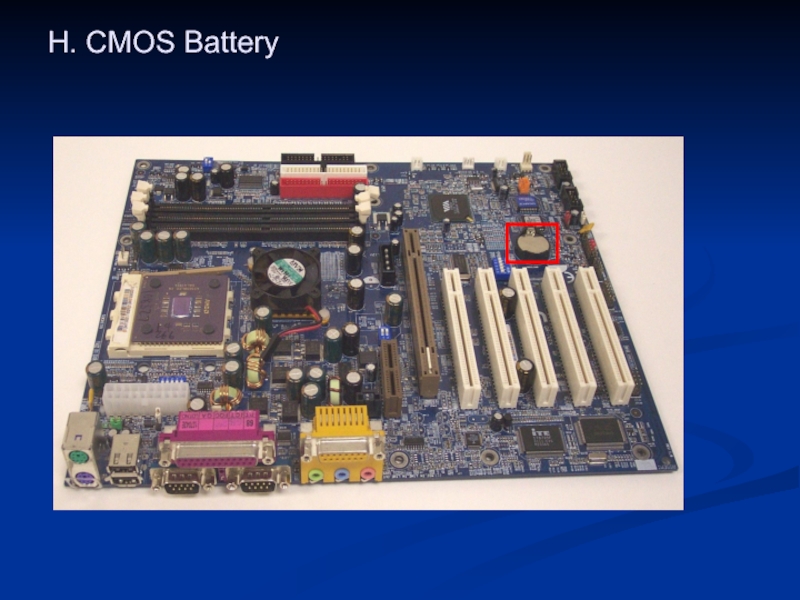
- 36. H. CMOS Battery
- 37. J. Power Connector (24 Pin Molex) P1
- 38. K. IDE Connections (4 channels, 2 per slot)
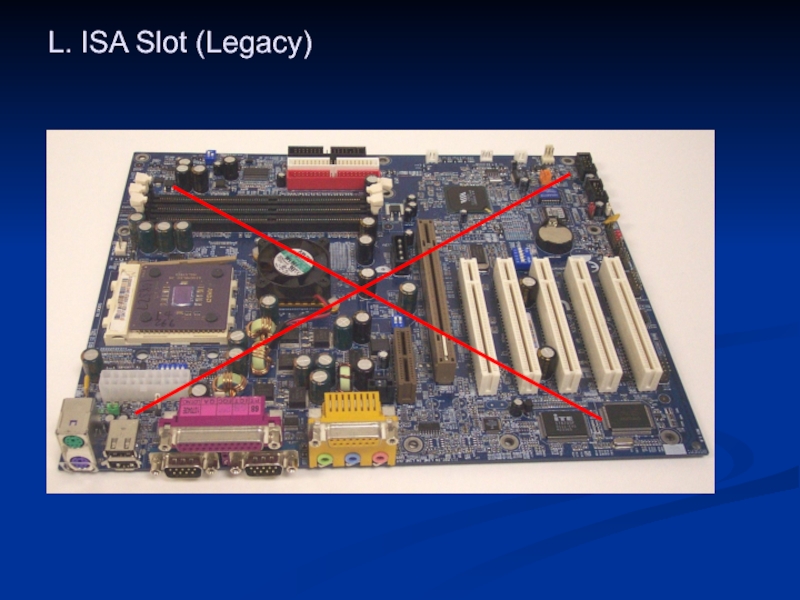
- 39. L. ISA Slot (Legacy)
- 40. M. Serial Ports
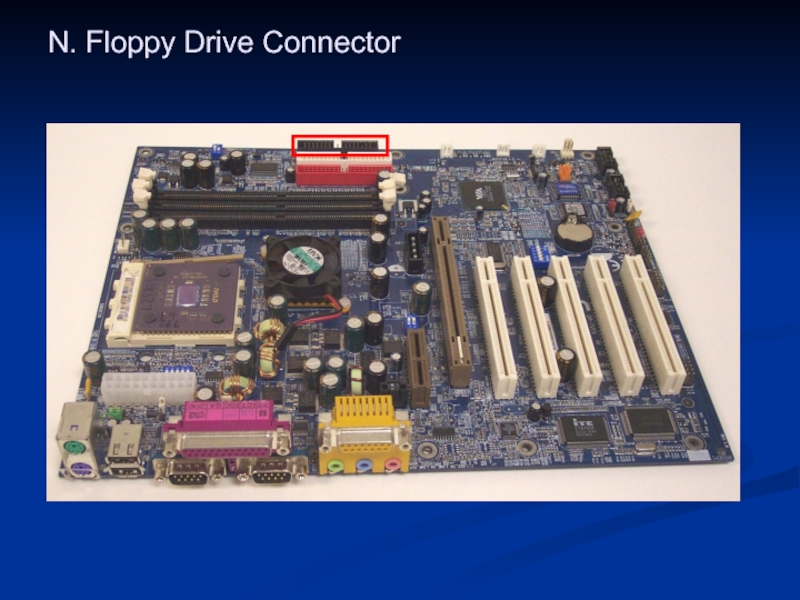
- 41. N. Floppy Drive Connector
- 42. O. PS/2 Connections for mouse/keyboard
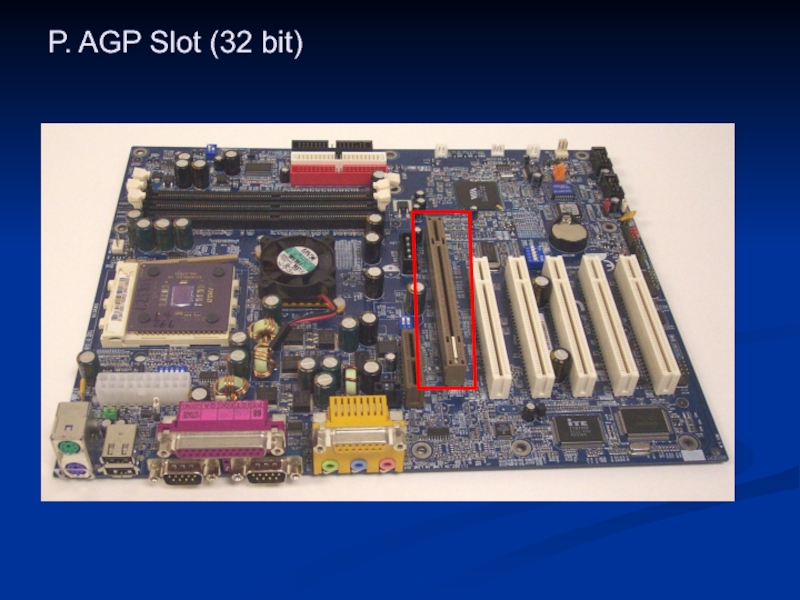
- 43. P. AGP Slot (32 bit)
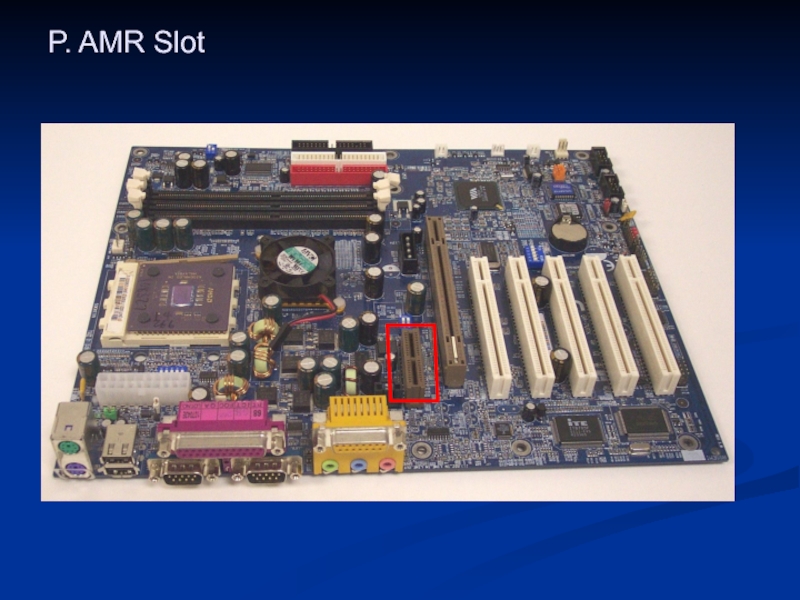
- 44. P. AMR Slot
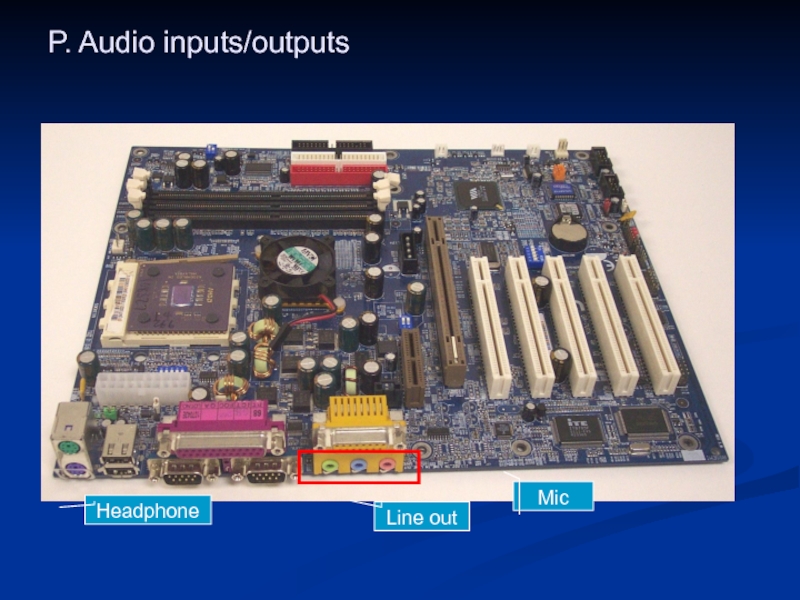
- 45. P. Audio inputs/outputs Mic Headphone Line out
- 46. P. VGA (15 Pin D-Plug Female)
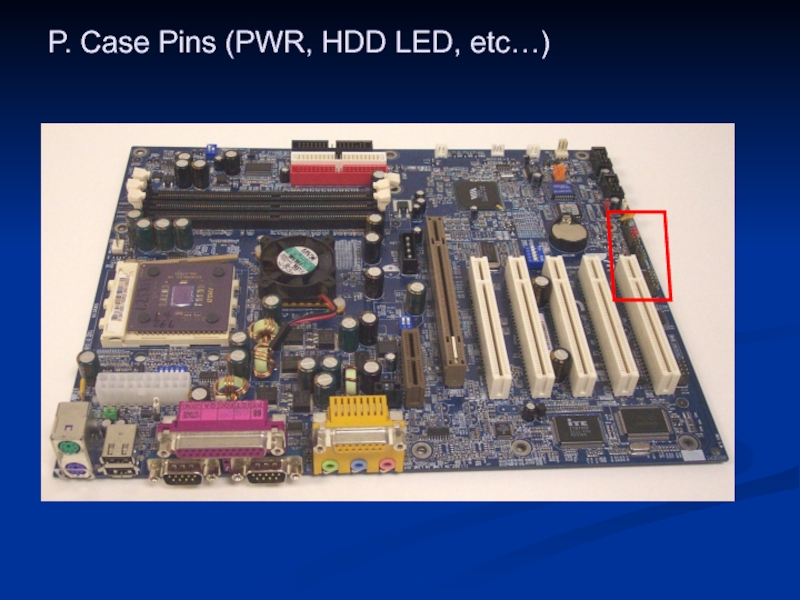
- 47. P. Case Pins (PWR, HDD LED, etc…)
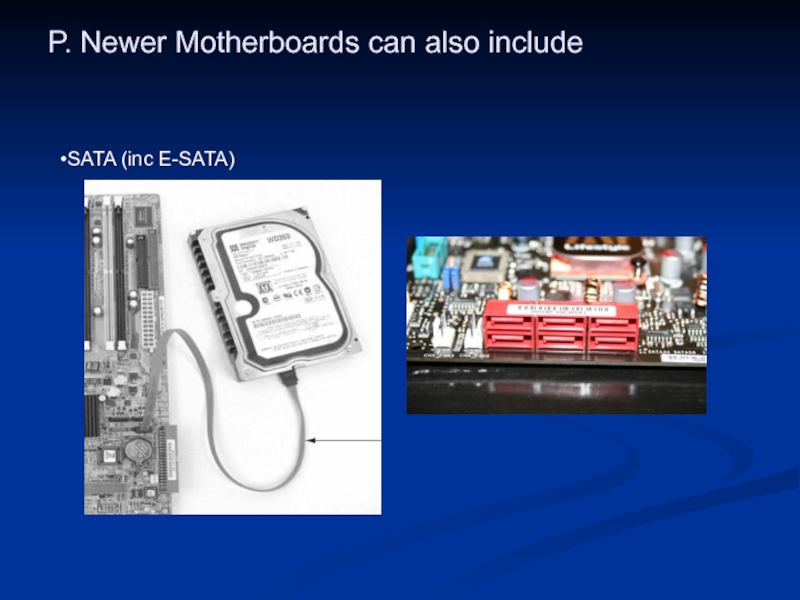
- 48. P. Newer Motherboards can also include SATA (inc E-SATA)
- 49. P. Newer Motherboards can also include Passive Cooling
- 50. P. Newer Motherboards can also include Water cooled systems
- 51. P. Newer Motherboards can also include DDR3 (green slots)
- 52. Video Summary Form Factors Installing and configuring motherboards
- 53. Specialised Cards – Graphics Card What is
- 54. Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) A GPU is
- 55. Video BIOS This contains the basic program
- 56. Video Memory While a Video Card will
- 57. Outputs There are the connection systems which
- 58. Motherboard Interface It is the connection system
- 59. Cooling Device Video cards may use a
- 60. Power Demand Fast Video Cards consume a
- 61. Advantages of Graphics Cards Anti-Aliasing: This is
- 62. Without Graphics Card Distorted Edges.. No anti-Aliasing
- 63. With Graphics Card Smooth Motion Blur &
- 64. Objectives Plenary Understand static electricity List
- 65. Stretch & Challenge Download the Electrostatic Discharge
Слайд 2Review
Define volatile and none-volatile
State what components connect to the North and
Define what the PSU does?
What is the name of the PSU socket that connects to a Hard disk or Optical drive?
What is the PGA?
Слайд 3Objectives
Understand static electricity
List reasons why we take precautions from static electricity
State precautions we can use against static electricity
Test anti-static devices
Define the Motherboards role within a PC
State the role of a Graphics Card
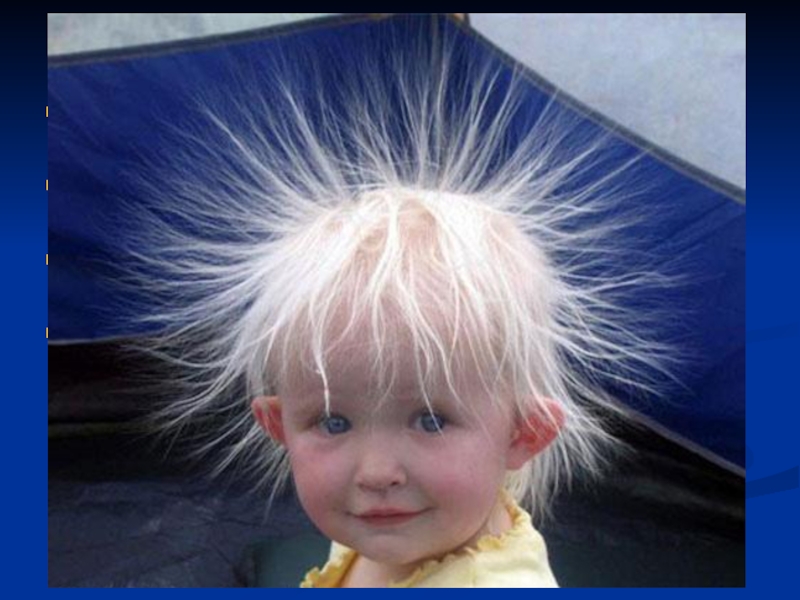
Слайд 4The movement and contact of the human body can accumulate energy
When an electric contact is established, electrostatic discharge (ESD) takes place in the form of a very brief flow of current
Although the discharge current is very small, the voltage could be in the region of few thousand volts
The human body can feel an ESD event if the voltage is more than 3000 volts
Electrostatic Charge
Слайд 5“Electro static discharge (ESD) is the transfer of an electrostatic charge
NEW VIDEO RESOURCE (BETTER)
Static Electricity: Snap, Crackle, Jump
VG
Слайд 6Tribo-electrification
Static electricity must build up a charge greater than 1000 V
Static Electricity is harmless to humans
We can withstand up to and including 10,000 V
Most CPUs, motherboards and associated circuitry normally operates at +/- 5 V
An electrical discharge of 10,000 V will blow almost all computer components
Слайд 7ESD is more likely to exist in work places which are
Electrical resistance is measured in Ohms
Electrostatic Charge
Слайд 8ESD Symbols
Fig 1 ESD Susceptibility
Fig 2 ESD Protective
Indicates that the device
Identifies items that provide ESD protection
Слайд 9ESD protective devices
A range of ESD protective devices are available to
Wrist Strap
Elasticised wristband with a metal pad which fits next to the skin
The cable runs to a ground connector which connects to a earth
Anti-Static Mat
Large rubber mat, runs to a ground connector which connects to earth
Usually you can connect your wrist band onto the mat
Anti-Static Bag
Used to transport and protect computer components
Newly purchased components are usually supplied in these bags
Any components not in the chassis of the computer must be kept in one of these bags
Слайд 10Working inside a computer
When working on the internals of a computer
Always connect yourself to an electrostatic wristband and ensure you are earthed
You should also do this when handling components outside of the computer and that are not even connected
Keep any ‘spare’ components that are not being used in electrostatic bags
Never wear a grounding strap when operating a monitor
The capacitors hold a huge charge, wearing the strap offers a shortcut – straight through you to the ground!
Слайд 11Good uses of ESD
ESD is used to apply toner to paper
ESD is used to clean up the air, removing pollen and dust to create a healthier environment
ESD is used to remove unwanted chemicals from output from Power Stations
Слайд 12 Electrostatic discharge can cause damage to integrated circuits such as
The damage caused by ESD may be instant failure.
It is more likely to weaken the chip thus its lifespan, causing intermittent faults
Electro-Static Damage
Слайд 13Static Electricity Video
Testing for Static Electricity
Electrostatic Charge at a Petrol Station
Pauls
Слайд 14Follow the safety rules
Be prepared: have the right tools at
Obey the dress code: nothing dangling that will trap you
Wear your ESD wrist band
Before starting, turn off the PC and disconnect the AC power chord
Read the manual: do not do things from memory
Ground yourself by touching the chassis to discharge any static electricity that has accumulated in your body
Handle all parts gently, hold components by their edges
Remember that some components might be too hot to touch safely
Take your time and think carefully before acting
Слайд 15This highly magnified picture shows the damage that can be done
Слайд 16Anti-static Wrist Strap
Wrist straps safely remove static charge from individuals who
A coiled cord and clip is provided to allow connection to ground. The ground cord has a built-in 1MΩ resistor for user safety.
Слайд 17How do you know if its working?
Anti-static wrist straps can fail
Ground cords get stressed from prolonged use and can break open inside the insulation.
You can't see if your anti-static wrist strap is performing properly
They should be tested regularly.
Electronics professionals should test their wrist straps for proper function at least once per day
Слайд 18Testing your wrist band
Firstly check your multi-meter is working correctly by
Now remove the wristband from your antistatic band and holding one probe at each end test it
Does it give expected results, if not, why not?
Why is it important to carryout periodic testing of anti-static protection devices?
Don't worry it's only ESD
What not to do
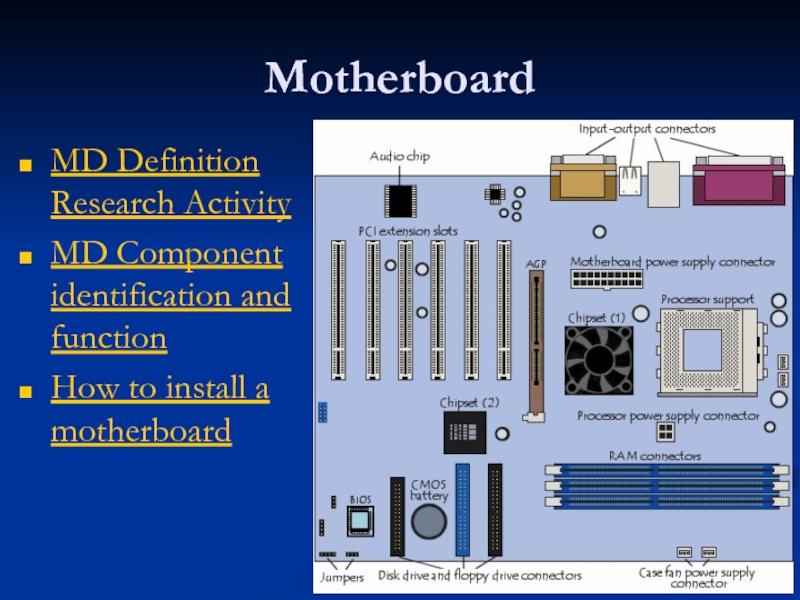
Слайд 19Motherboards
The Main Printed Circuit Board Inside The PC That Contains and
Слайд 20Motherboard is…
Multi-layered printed circuit board
Copper circuit paths called traces carry signals
Some layers carry data for input/output while other layers carry voltage and ground returns
Слайд 21Think of a Motherboard as:
Futuristic City with many modular plug-in buildings,
Multiple-lane highways of various widths transporting data between buildings
Data and power infrastructure for the entire computer
Слайд 22Motherboard
MD Definition Research Activity
MD Component identification and function
How to install a
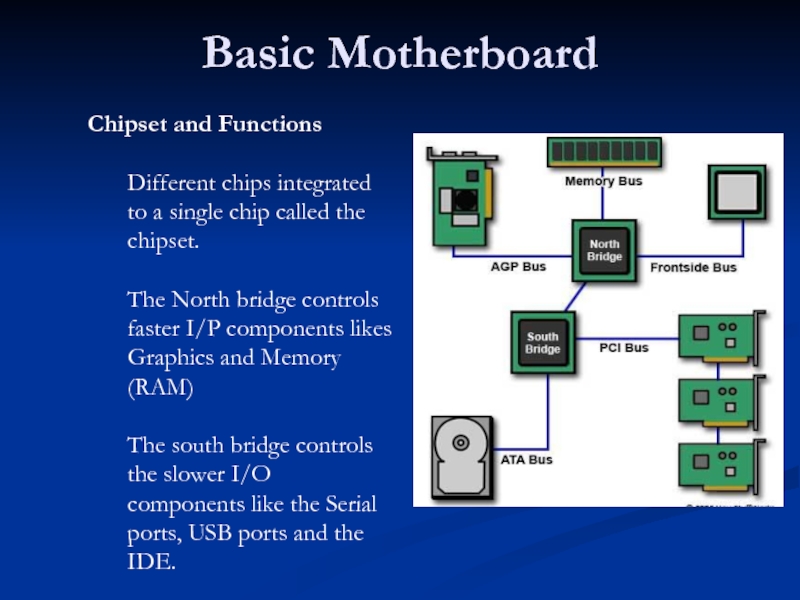
Слайд 23Basic Motherboard
Chipset and Functions
Different chips integrated to a single chip called
The North bridge controls faster I/P components likes Graphics and Memory (RAM)
The south bridge controls the slower I/O components like the Serial ports, USB ports and the IDE.
Слайд 24Motherboard Determines:
CPU type and speed
Chipset
Types & number of connection slots
Type of
Number of memory sockets and maximum memory
Type of case
ROM
Plug & Play compatibility
Type of keyboard
Слайд 25Form Factors
Form factor means the size and shape of the actual
3 most common Form Factor classifications:
Baby AT
ATX
Slimline NLX
Слайд 26What other features do modern Motherboards include?
In groups spend ten minutes
Consider what additional functionality they might include
List a minimum of three components you could share with the class
Слайд 29
B. North Bridge
"North Bridge: The Intel term for the main portion
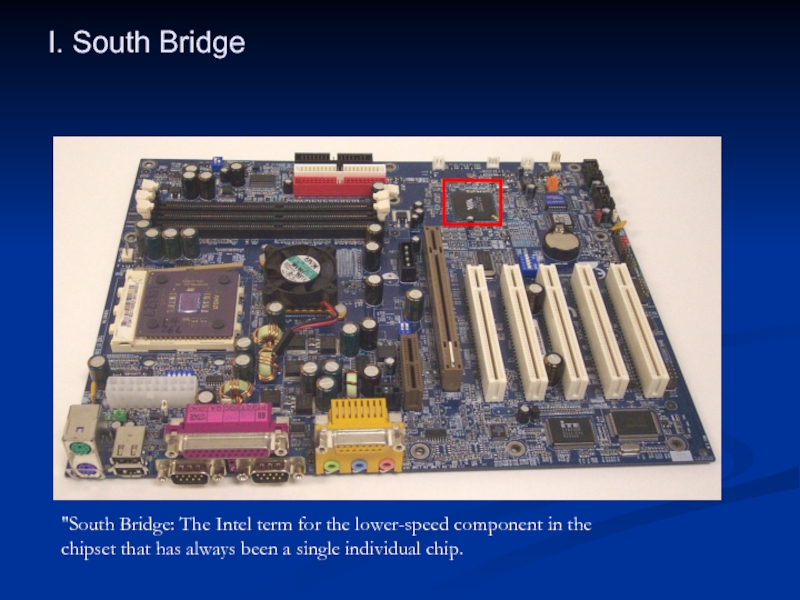
Слайд 30I. South Bridge
"South Bridge: The Intel term for the lower-speed component
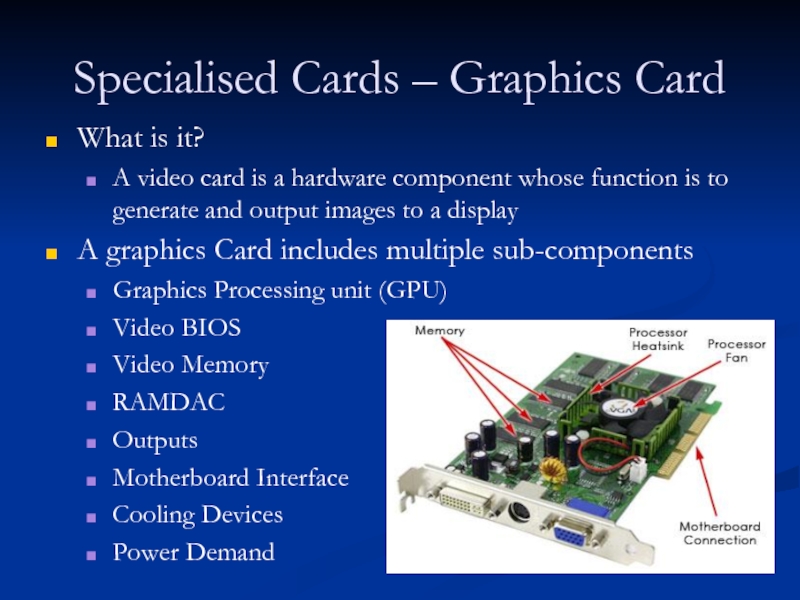
Слайд 53Specialised Cards – Graphics Card
What is it?
A video card is a
A graphics Card includes multiple sub-components
Graphics Processing unit (GPU)
Video BIOS
Video Memory
RAMDAC
Outputs
Motherboard Interface
Cooling Devices
Power Demand
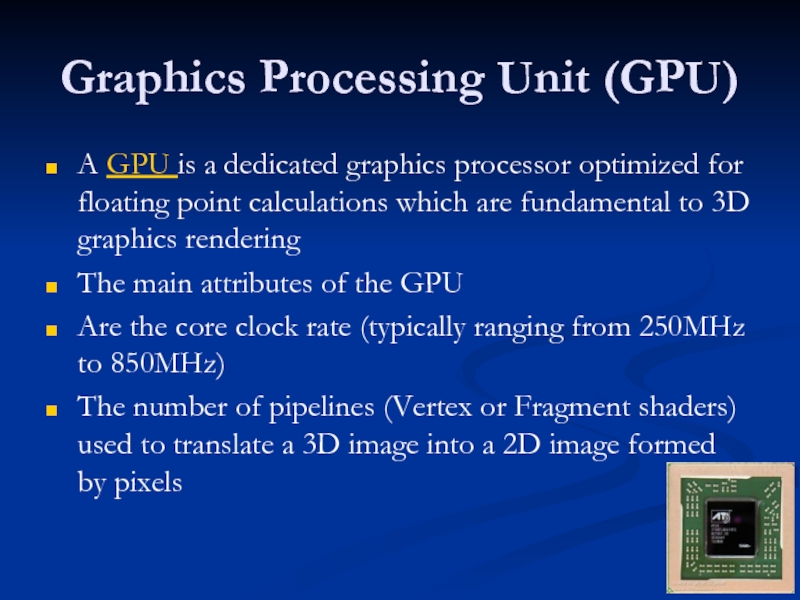
Слайд 54Graphics Processing Unit (GPU)
A GPU is a dedicated graphics processor optimized
The main attributes of the GPU
Are the core clock rate (typically ranging from 250MHz to 850MHz)
The number of pipelines (Vertex or Fragment shaders) used to translate a 3D image into a 2D image formed by pixels
Слайд 55Video BIOS
This contains the basic program that governs the video card’s
It contains information on the memory timing, operating speeds and voltages of the graphics processor and RAM and other information
It is sometimes possible to change the BIOS for higher performance although is this is typically only done by card over-clockers as it has the potential of damage to the card
Слайд 56Video Memory
While a Video Card will have its own video memory
The memory capacity of most modern video cards range from 128MB to 2GB
Since video memory needs to be accessed by the GPU it uses high speed memory
DDR, DDR2, GDDR3, GDDR4 & GDDR5
The memory clock rate in modern cards are generally between 400MHz and 2.4GHz
Слайд 57Outputs
There are the connection systems which connects the displays with the
Some different connection systems are as follows
Analogue-based standard adopted in the late 1980s designed for CRT displays, also called VGA connector
Digital-based standard for displays such as flat-panel displays and video projectors, these digital based DVI connectors are used for HDTV
HDMI is an advanced digital audio/video interconnector released in 2003 and is commonly used to connect Gaming Consoles and DVD players to a display
Display connectors
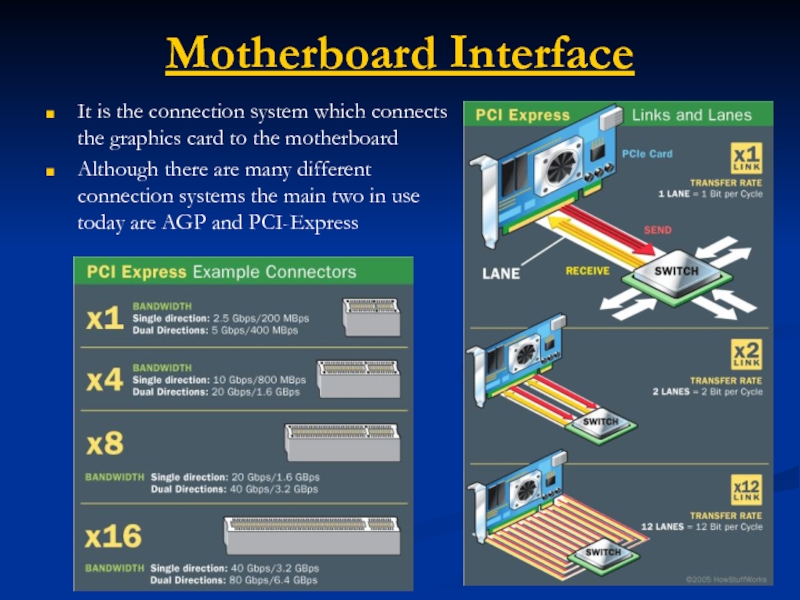
Слайд 58Motherboard Interface
It is the connection system which connects the graphics card
Although there are many different connection systems the main two in use today are AGP and PCI-Express
The graphics card's hardware directly affects its speed. These are the hardware specifications that most affect the card's speed and the units in which they are measured:
GPU clock speed (MHz)
Size of the memory bus (bits)
Amount of available memory (MB)
Memory clock rate (MHz)
Memory bandwidth (GB/s)
RAMDAC speed (MHz)
Слайд 59Cooling Device
Video cards may use a lot of electricity which is
If the heat isn’t dissipated, the video card could overheat and get damaged
Cooling devices are incorporated to transfer the heat elsewhere
Слайд 60Power Demand
Fast Video Cards consume a great deal of power
Power demands
Most connection systems that can be used to connect a graphics card supply no more than 75watts to power a graphics card
For recent graphics cards that require more than this level of power can connect to a direct PSU power source
8 pin (150W) power source
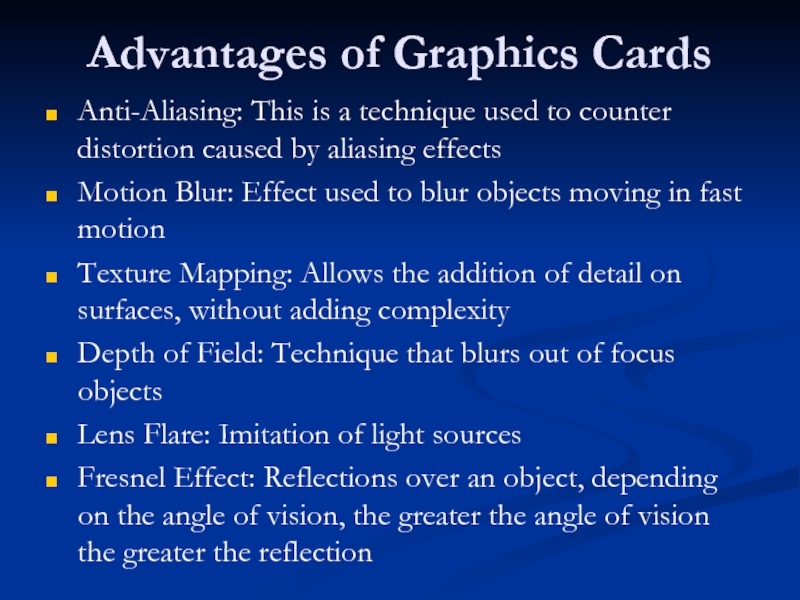
Слайд 61Advantages of Graphics Cards
Anti-Aliasing: This is a technique used to counter
Motion Blur: Effect used to blur objects moving in fast motion
Texture Mapping: Allows the addition of detail on surfaces, without adding complexity
Depth of Field: Technique that blurs out of focus objects
Lens Flare: Imitation of light sources
Fresnel Effect: Reflections over an object, depending on the angle of vision, the greater the angle of vision the greater the reflection
Слайд 62Without Graphics Card
Distorted Edges.. No anti-Aliasing
No reflection detail (No Fresnel Effect)
Poor
Poor Motion Blur & Depth of Field
Слайд 63With Graphics Card
Smooth Motion Blur & Depth of field
Better level of
Car Reflection Detail turned on. Fresnel Effect
Edge smoothened by Anti Aliasing
Слайд 64Objectives Plenary
Understand static electricity
List reasons why we take precautions from
State precautions we can use against static electricity
Test anti-static devices
Define the Motherboards role within a PC
State the role of a Graphics Card
Слайд 65Stretch & Challenge
Download the Electrostatic Discharge Exam and see what answers
ESD Quiz