- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Cascading Style Sheet (CSS) презентация
Содержание
- 1. Cascading Style Sheet (CSS)
- 2. When a browser reads a style
- 3. CSS Syntax A CSS rule-set consists of
- 4. For several elements First three heading levels have blue letters: h1,h2, h3{color: blue}
- 5. Inheritance In HTML document one element can
- 6. Class Selectors First, you single out specific
- 7. Id Selector Like a Class selector an
- 8. Color properties Colors in CSS are most
- 9. CSS Backgrounds The CSS background properties are
- 10. Text Alignment and Spacing
- 12. Alignment By default, all text on a
- 13. Spacing To adjust the spacing around any
- 14. Spacing All the margin properties can have
- 15. Margin-Shortland Property To shorten the code, it
- 16. CSS Padding Padding properties are used to
- 17. CSS Border properties The CSS border properties allow you
- 18. CSS border properties
- 19. Basic Fonts Using the CSS font properties,
- 20. Basic Fonts
- 21. Examples
- 22. Generic Family generic family - a group of
- 23. Font Size The font-size property sets the size of
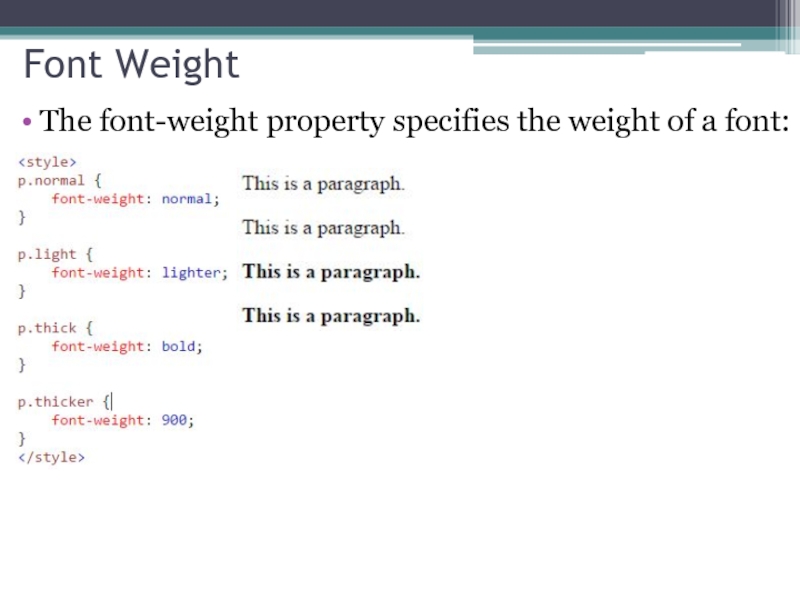
- 25. Font Weight The font-weight property specifies the weight of a font:
- 26. Font Style The font-style property is mostly used to
- 27. CSS line-height Property The line-height property specifies the line height.
- 28. Text-transform Property The text-transform property controls the capitalization of text.
- 29. List-style Property The list-style shorthand property sets all
- 30. Text-decoration Property The text-decoration property specifies the decoration added to text
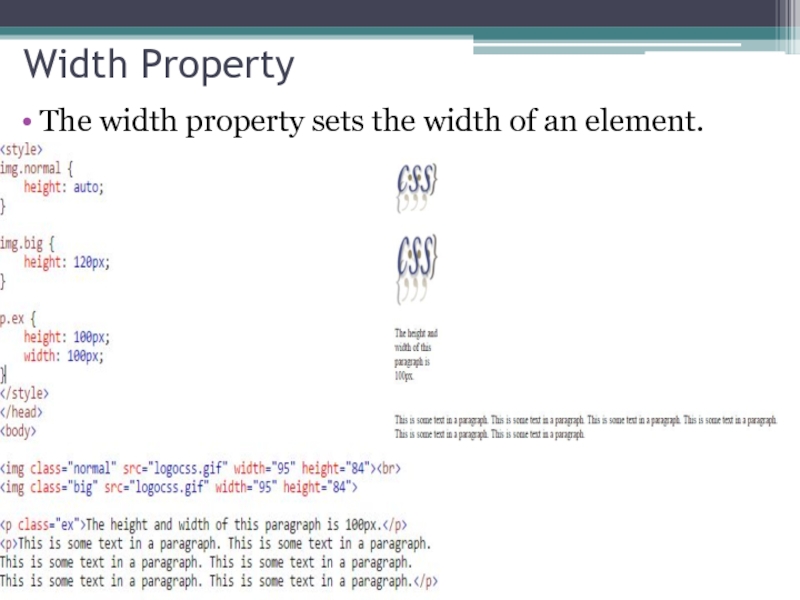
- 31. Width Property The width property sets the width of an element.
- 32. CSS height Property The height property sets the height
- 33. The CSS Box Model The CSS box
- 34. The CSS Box Model Content - The content
- 35. Example
- 36. The position Property The position property specifies the type
- 37. Position: Static HTML elements are positioned static
- 38. position: relative; An element with position: relative; is positioned
- 39. CSS clear Property The clear property specifies on which
- 40. Overflow Property The overflow property specifies what happens
- 41. Overflow property
- 42. z-index Property The z-index property specifies the stack
Слайд 2
When a browser reads a style sheet, it will format the
CSS is a language that describes the style of an HTML document.
CSS describes how HTML elements should be displayed.
How many ways to insert CSS?
Слайд 3CSS Syntax
A CSS rule-set consists of selector and a declaration block:
The
The declaration block contains one or more declarations separated by semicolons.
Each declaration includes a CSS property name and a value, separated by a colon.
A CSS declaration always ends with a semicolon, and declaration blocks are surrounded by curly braces
Слайд 5Inheritance
In HTML document one element can contain other elements.
Example: unordered list
can contain character formatting elements like: , , and elements contains the whole document.
Thanks to inheritance, when you apply formatting instructions to an element that contains other elements, that formatting rule applies to every one of those other elements.
For example, if you set a element to the font Verdana (as in the resume style sheet shown earlier), every element inside that element, including all the headings, paragraphs, lists, and so on, gets the Verdana font.
Слайд 6Class Selectors
First, you single out specific elements in your page by
You use the class name, precedes by a period (.)
h3.FancyTitle{
color: red;
font-weight: bolder;
}
Learning to Embodier
Слайд 7Id Selector
Like a Class selector an ID selector lets you format
In HTML:
In CSS: #Menu{
border-width: 2px;
boder-style:solid;
}
Слайд 8Color properties
Colors in CSS are most often specified by:
a valid color
an RGB value - like "rgb(255, 0, 0)"
a HEX value - like "#ff0000"
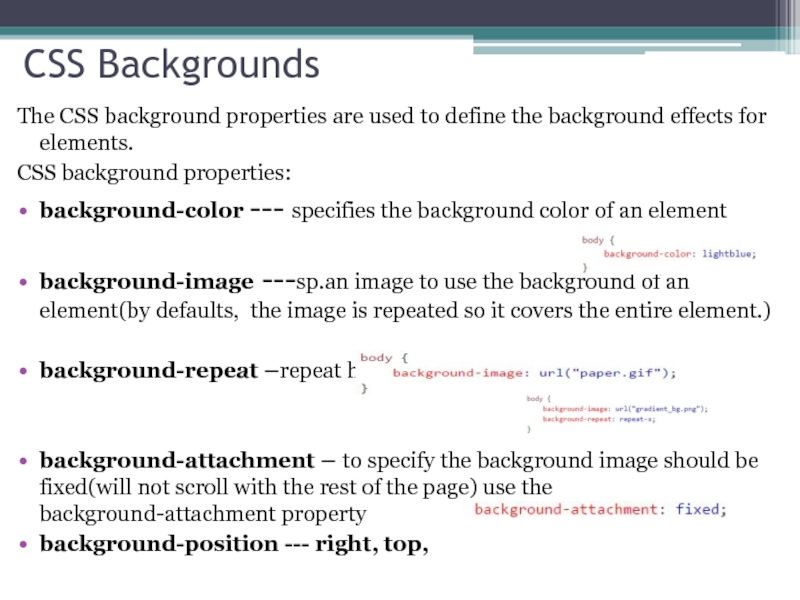
Слайд 9CSS Backgrounds
The CSS background properties are used to define the background
CSS background properties:
background-color --- specifies the background color of an element
background-image ---sp.an image to use the background of an element(by defaults, the image is repeated so it covers the entire element.)
background-repeat –repeat horizontally or vertically
background-attachment – to specify the background image should be fixed(will not scroll with the rest of the page) use the background-attachment property
background-position --- right, top,
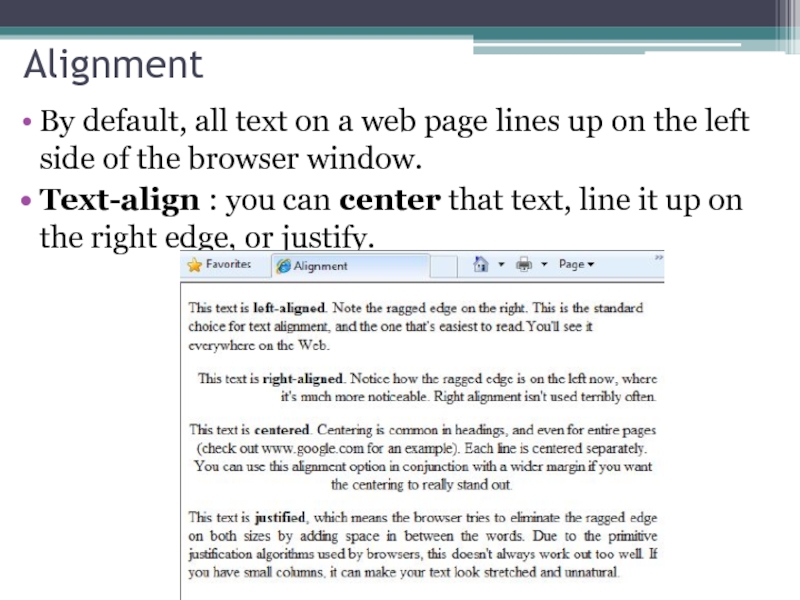
Слайд 12Alignment
By default, all text on a web page lines up on
Text-align : you can center that text, line it up on the right edge, or justify.
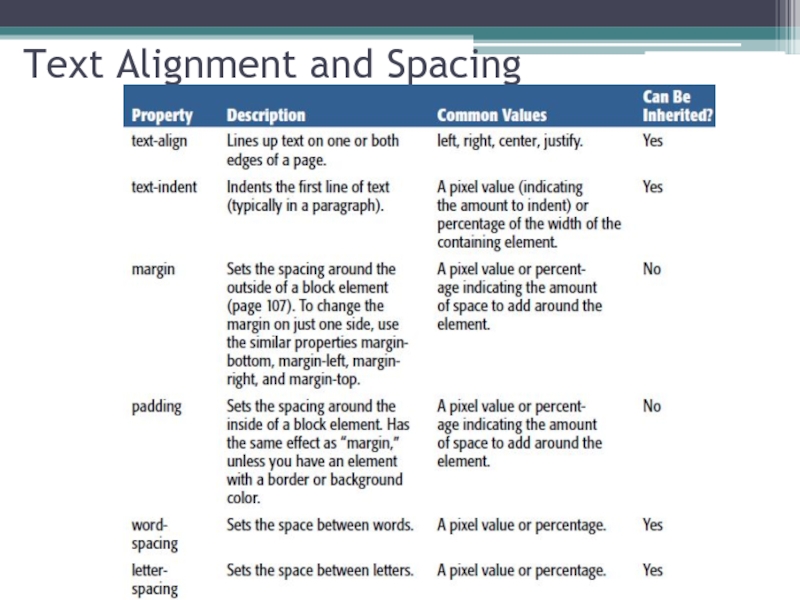
Слайд 13Spacing
To adjust the spacing around any element, use the margin property.
Set the size of the white space outside the border.
p{
margin: 8px;
}
For each side of an element:
margin-top
margin-right
margin-bottom
margin-left
Слайд 14Spacing
All the margin properties can have the following values:
auto - the
length - specifies a margin in px, pt, cm, etc.
% - specifies a margin in % of the width of the containing element
inherit - specifies that the margin should be inherited from the parent element
Слайд 15Margin-Shortland Property
To shorten the code, it is possible to specify all
margin-top
margin-right
margin-bottom
margin-left
p { margin: 100px 150px 100px 80px; }
auto value
The element will then take up the specified width, and the remaining space will be split equally between the left and right margins:
Слайд 16CSS Padding
Padding properties are used to generate space around content.
The padding
padding-top
padding-right
padding-bottom
padding-left
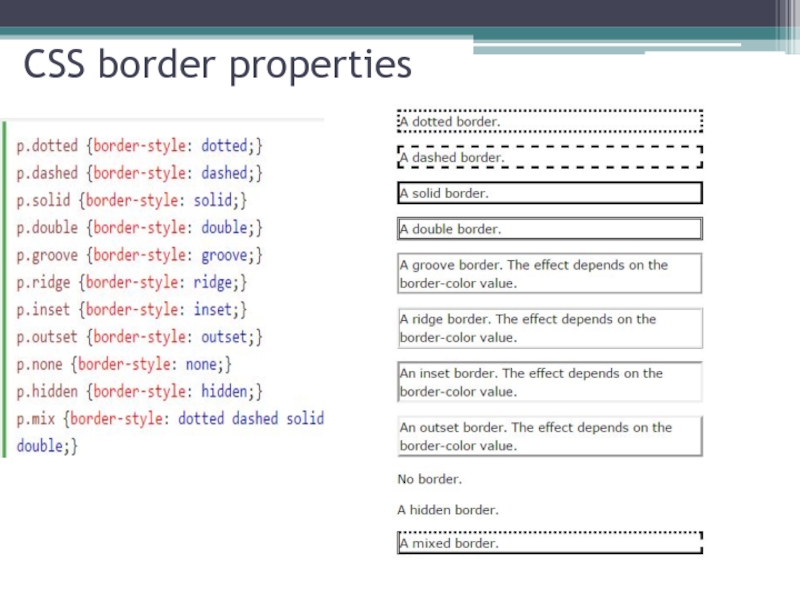
Слайд 17CSS Border properties
The CSS border properties allow you to specify the style, width,
Border Style – specifies what kind of border to display.
Слайд 19Basic Fonts
Using the CSS font properties, you can choose a font
setting), and font size
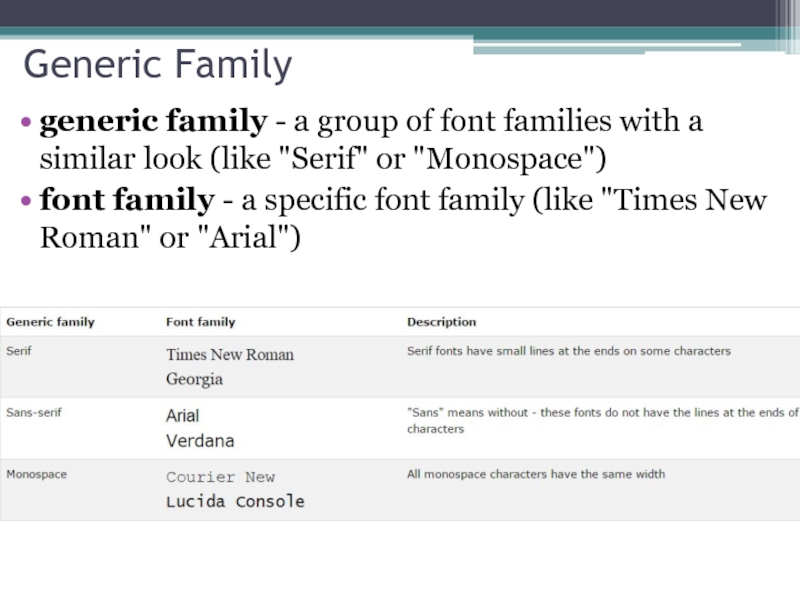
Слайд 22Generic Family
generic family - a group of font families with a similar
font family - a specific font family (like "Times New Roman" or "Arial")
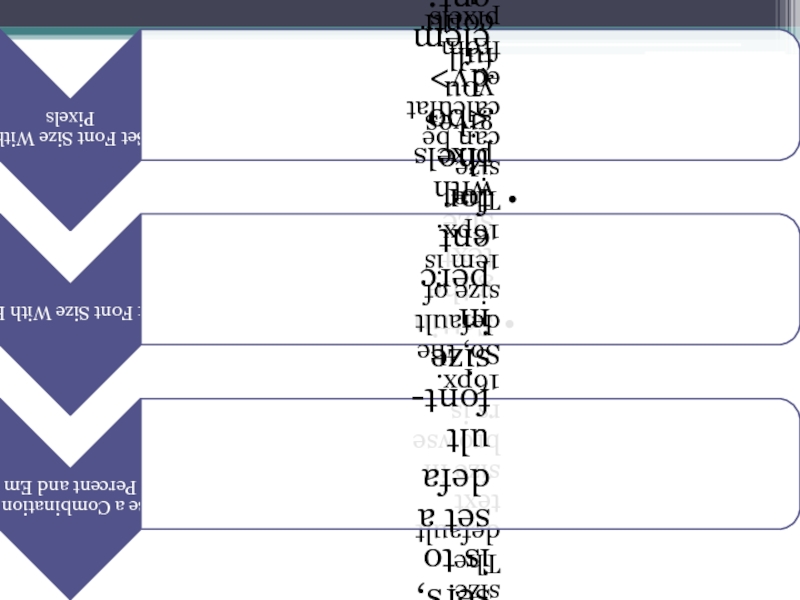
Слайд 23Font Size
The font-size property sets the size of the text.
Being able to manage
Always use the proper HTML tags, like
- for headings and
for paragraphs.
The font-size value can be an absolute, or relative size.
Слайд 26Font Style
The font-style property is mostly used to specify italic text.
This property has
normal - The text is shown normally
italic - The text is shown in italics
oblique - The text is "leaning" (oblique is very similar to italic, but less supported)
Слайд 29List-style Property
The list-style shorthand property sets all the list properties in one
The properties that can be set, are (in order): list-style-type, list-style-position, list-style-image.
If one of the values above are missing, e.g. "list-style:circle inside;", the default value for the missing property will be inserted, if any.
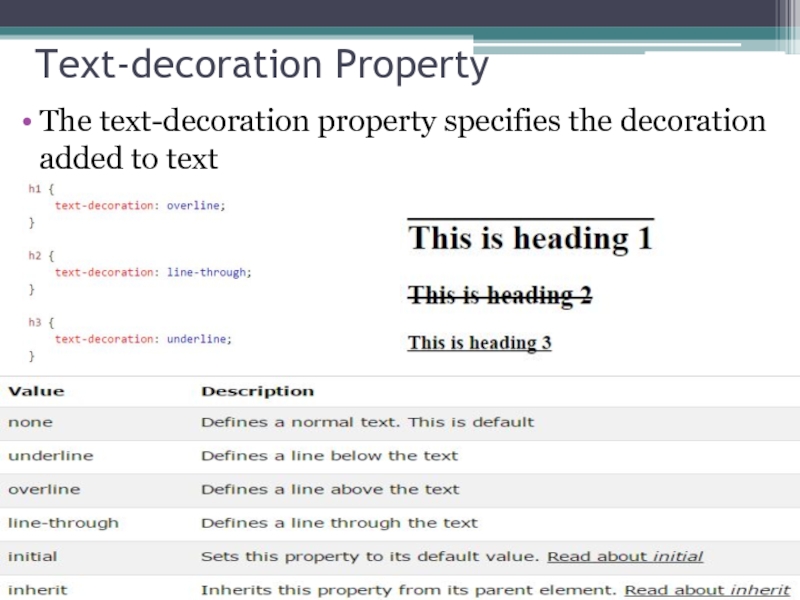
Слайд 30 Text-decoration Property
The text-decoration property specifies the decoration added to text
Слайд 32CSS height Property
The height property sets the height of an element.
Note: The height property
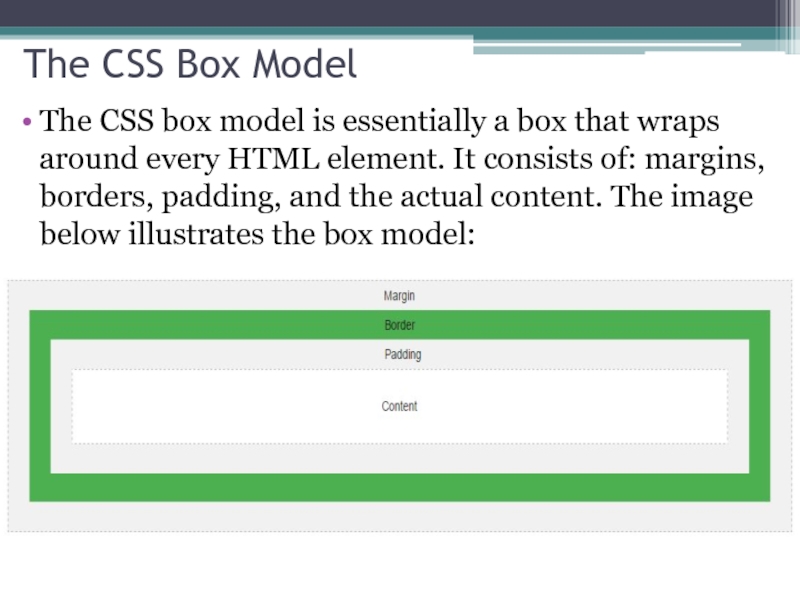
Слайд 33The CSS Box Model
The CSS box model is essentially a box
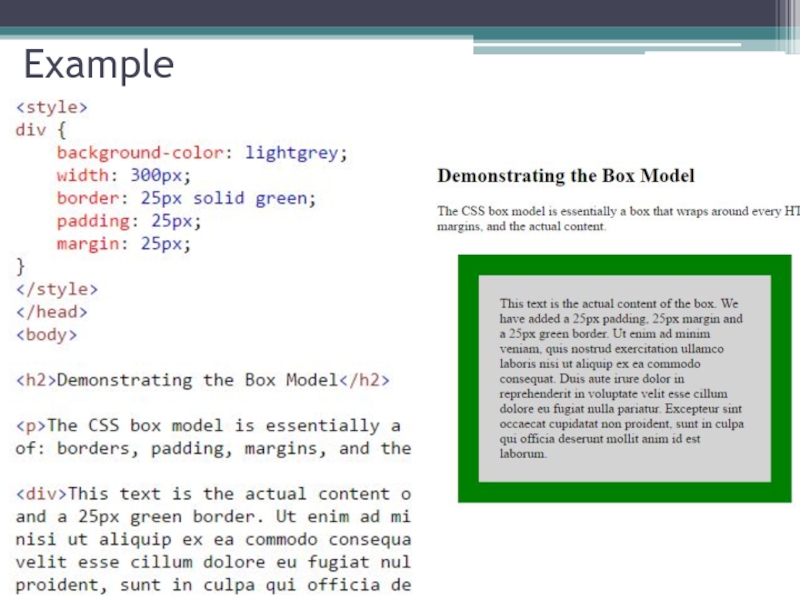
Слайд 34The CSS Box Model
Content - The content of the box, where text
Padding - Clears an area around the content. The padding is transparent
Border - A border that goes around the padding and content
Margin - Clears an area outside the border. The margin is transparent
Слайд 36The position Property
The position property specifies the type of positioning method used for
There are 4 different position values:
Слайд 37Position: Static
HTML elements are positioned static by default.
Static positioned elements are
Слайд 38position: relative;
An element with position: relative; is positioned relative to its normal position.
Setting
Слайд 39CSS clear Property
The clear property specifies on which sides of an element floating
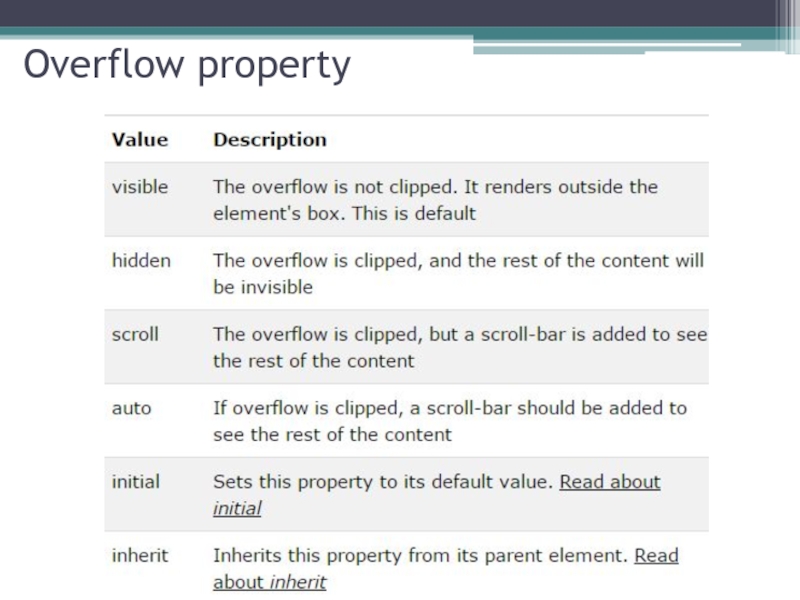
Слайд 40Overflow Property
The overflow property specifies what happens if content overflows an element's
This property specifies whether to clip content or to add scrollbars when an element's content is too big to fit in a specified area.
Note: The overflow property only works for block elements with a specified height.