- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Angular Basics презентация
Содержание
- 1. Angular Basics
- 2. Wiki
- 3. Angular CLI Install Node.js and npm: https://nodejs.org/en/download/
- 4. Angular
- 5. Project folder structure tsconfig.json – TypeScripts https://www.typescriptlang.org/docs/handbook/tsconfig-json.html
- 6. Project folder structure e2e – automated UI tests
- 7. NgModule main.ts – app entry point app.module.ts -
- 8. Component @Component({ selector: 'app-root', templateUrl: './app.component.html', styleUrls:
- 9. Data binding interpolation property binding event binding
- 10. Event binding Increment onIncrementClick() { this.visitors++; }
- 11. Two-way binding NgModel - a built-in directive
- 12. Binding syntax: An overview
- 13. Binding targets
- 14. Basic Routing import { RouterModule, Routes }
- 15. Build-in attribute directives: NgFor & NgIf NgFor
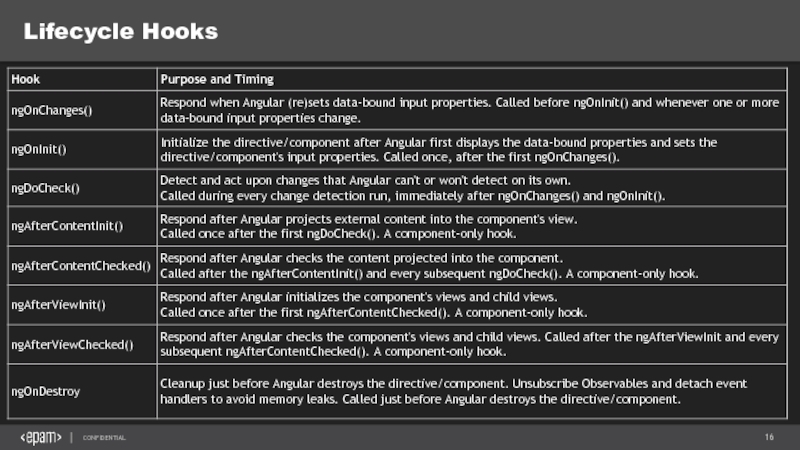
- 16. Lifecycle Hooks
- 17. Component Interaction: @Input decorator ng g c
- 18. Component Interaction: @Output decorator product.component.ts @Output() deleteRequest
- 19. Pipes ng g pipe price generate pipe:
- 20. Services ng g s products generate service:
- 21. Dependency Injection Angular has a Hierarchical Dependency Injection system.
- 22. Http getProducts(): Observable { return this.http.get('http://localhost:54145/api/products') .map(res
- 23. Http + AsyncPipe product-list.component.ts: products.service.ts: search(term: string):
- 24. Http + AsyncPipe this.products = this.searchTerms .debounceTime(300)
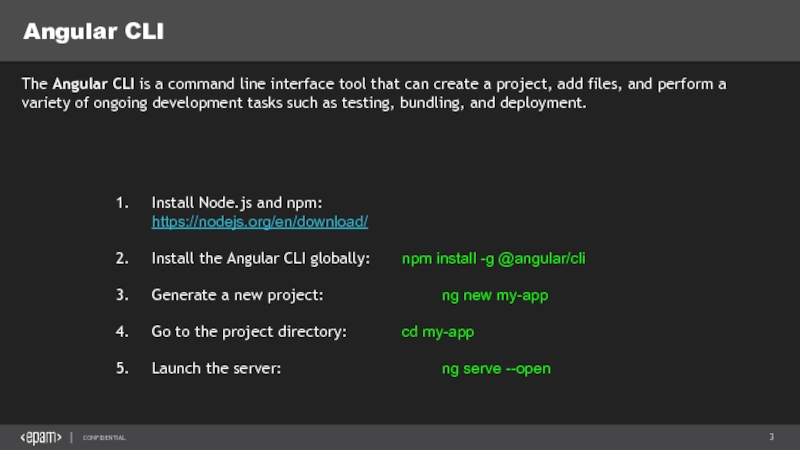
Слайд 3Angular CLI
Install Node.js and npm: https://nodejs.org/en/download/
Install the Angular CLI globally: npm install -g
Generate a new project: ng new my-app
Go to the project directory: cd my-app
Launch the server: ng serve --open
The Angular CLI is a command line interface tool that can create a project, add files, and perform a variety of ongoing development tasks such as testing, bundling, and deployment.
Слайд 5Project folder structure
tsconfig.json – TypeScripts
https://www.typescriptlang.org/docs/handbook/tsconfig-json.html
package.json – npm
https://docs.npmjs.com/files/package.json
.angular-cli.json – Angular CLI configuration
https://github.com/angular/angular-cli/wiki/angular-cli
tslint.json - TSLint (TypeScript code
https://palantir.github.io/tslint/usage/tslint-json/
karma.conf.js – Karma test runner
…
Configuration files:
Слайд 6Project folder structure
e2e – automated UI tests (Selenium/Protractor)
src – our application sources
node_modules – npm
Folders:
Do not forget to save new npm modules in the package.json file!
How to install/uninstall new node module
Open CMD in the root folder and:
install all modules in package.json: npm install
install module globally: npm install module-name -g
install module locally: npm install module-name --save
install dev dependency: npm install module-name --save-dev
uninstall: npm uninstall module-name [-g|--save|--save-dev]
global modules are stored here: %appdata%/npm
Слайд 7NgModule
main.ts – app entry point
app.module.ts - main module
@NgModule({
declarations: [
AppComponent
],
imports: [
BrowserModule,
FormsModule,
HttpModule
],
providers: [],
bootstrap:
})
export class AppModule { }
Generate new module:
ng g module module_name
Слайд 8Component
@Component({
selector: 'app-root',
templateUrl: './app.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./app.component.css']
})
export class AppComponent {
title = 'app works!';
}
A component
index.html
app.component.html
{{title}}
The easiest way to display a component property is to bind the property name through interpolation. With interpolation, you put the property name in the view template, enclosed in double curly braces: {{title}}.
template expression:
Sum of 2 + 2 = {{2+2}}
you cannot use =. +=, -=, ++, --, new,
chaining expressions with ; or ,
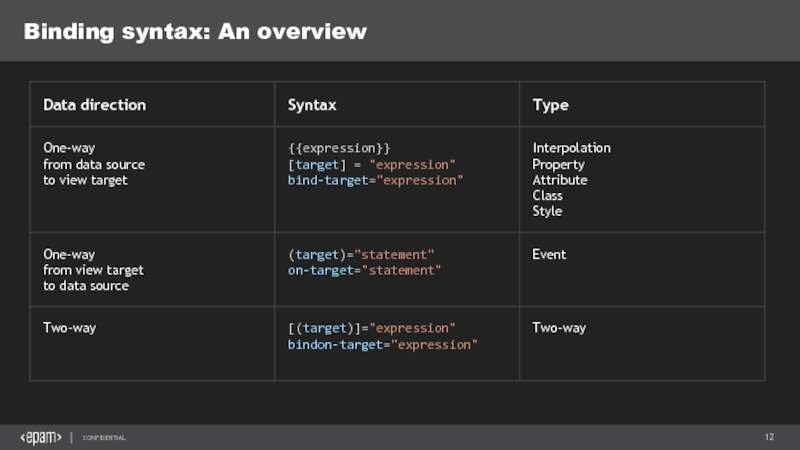
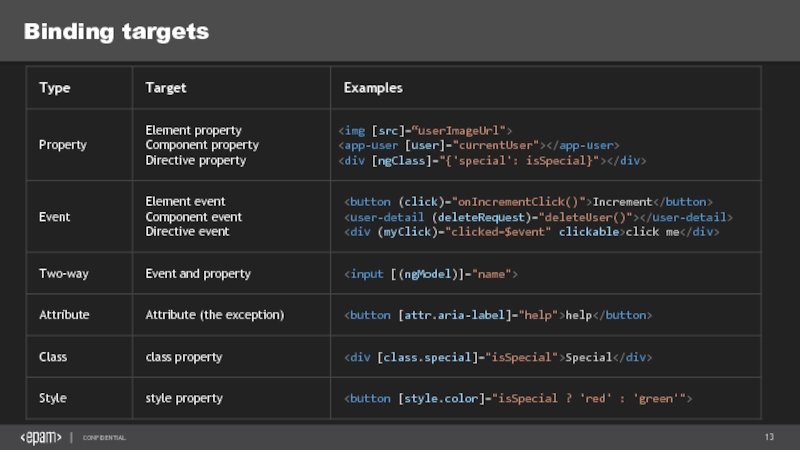
Слайд 9Data binding
interpolation
property binding
event binding
build-in directives
is the interpolated image.
{{title}}
Interpolation is a special syntax that Angular converts into a property binding
HTML attribute vs. DOM property
You deal with DOM properties!
For attribute binding use:
One-Two
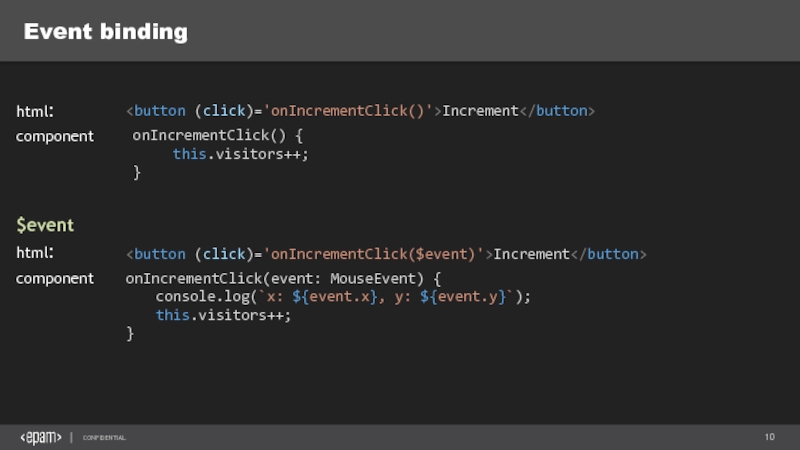
Слайд 10Event binding
Increment
onIncrementClick() {
this.visitors++;
}
html:
component
onIncrementClick(event: MouseEvent) {
console.log(`x: ${event.x}, y: ${event.y}`);
this.visitors++;
}
$event
html:
component
Increment
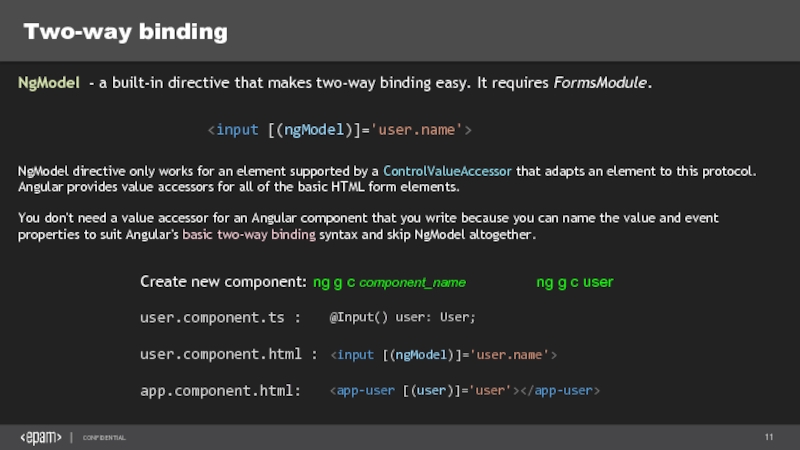
Слайд 11Two-way binding
NgModel - a built-in directive that makes two-way binding easy.
NgModel directive only works for an element supported by a ControlValueAccessor that adapts an element to this protocol. Angular provides value accessors for all of the basic HTML form elements.
You don't need a value accessor for an Angular component that you write because you can name the value and event properties to suit Angular's basic two-way binding syntax and skip NgModel altogether.
Create new component: ng g c component_name
ng g c user
user.component.ts :
@Input() user: User;
app.component.html:
user.component.html :
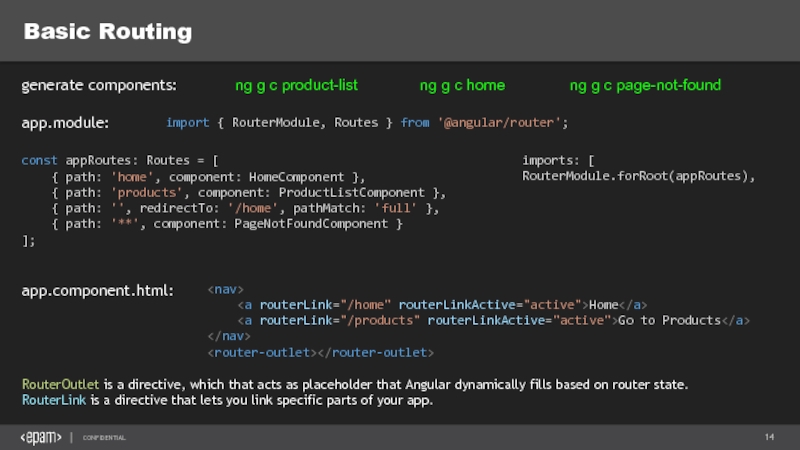
Слайд 14Basic Routing
import { RouterModule, Routes } from '@angular/router';
ng g c product-list
generate
app.module:
imports: [
RouterModule.forRoot(appRoutes),
ng g c home
app.component.html:
const appRoutes: Routes = [
{ path: 'home', component: HomeComponent },
{ path: 'products', component: ProductListComponent },
{ path: '', redirectTo: '/home', pathMatch: 'full' },
{ path: '**', component: PageNotFoundComponent }
];
ng g c page-not-found
RouterOutlet is a directive, which that acts as placeholder that Angular dynamically fills based on router state.
RouterLink is a directive that lets you link specific parts of your app.
Слайд 15Build-in attribute directives: NgFor & NgIf
NgFor is a repeater directive —
{{product.name}}
Take each product in the products array, store it in the local product looping variable, and make it available to the templated HTML for each iteration.
{{product.name}}- Best Seller!
{{product.name}}- Best Seller!
isBestSeller(product) {
return product.name === 'produc B';
}
NgIf is a directive that allows to add or remove an element from the DOM
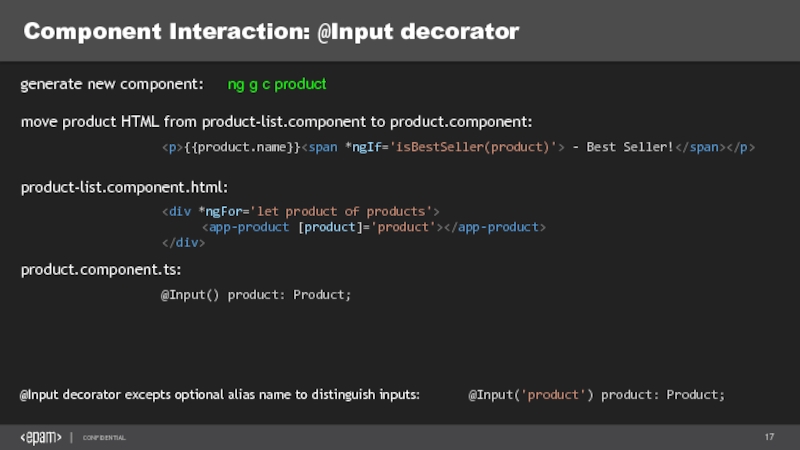
Слайд 17Component Interaction: @Input decorator
ng g c product
generate new component:
move product HTML
{{product.name}} - Best Seller!
product-list.component.html:
product.component.ts:
@Input() product: Product;
@Input decorator excepts optional alias name to distinguish inputs:
@Input('product') product: Product;
Слайд 18Component Interaction: @Output decorator
product.component.ts
@Output() deleteRequest = new EventEmitter();
onDeleteClick() {
this.deleteRequest.emit(this.product);
}
product.component.html
Delete
product-list.component.ts
onProductDelete(product: Product)
console.log(`delete request: product name - ${product.name}`);
}
product-list.component.html
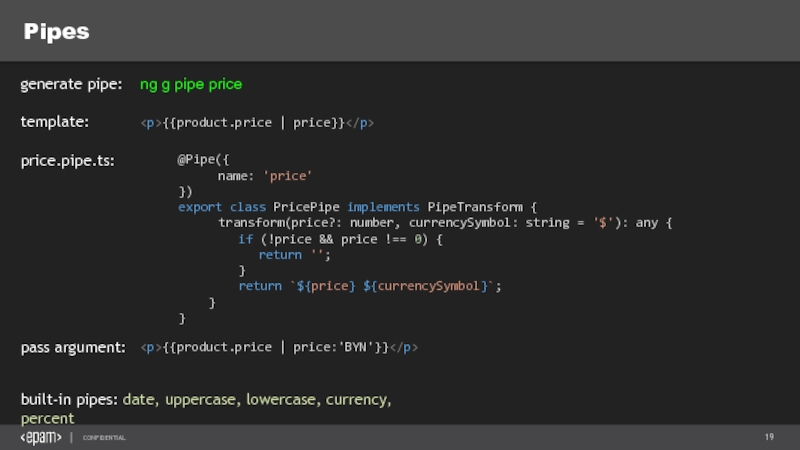
Слайд 19Pipes
ng g pipe price
generate pipe:
built-in pipes: date, uppercase, lowercase, currency, percent
template:
{{product.price
@Pipe({
name: 'price'
})
export class PricePipe implements PipeTransform {
transform(price?: number, currencySymbol: string = '$'): any {
if (!price && price !== 0) {
return '';
}
return `${price} ${currencySymbol}`;
}
}
price.pipe.ts:
{{product.price | price:'BYN'}}
pass argument:
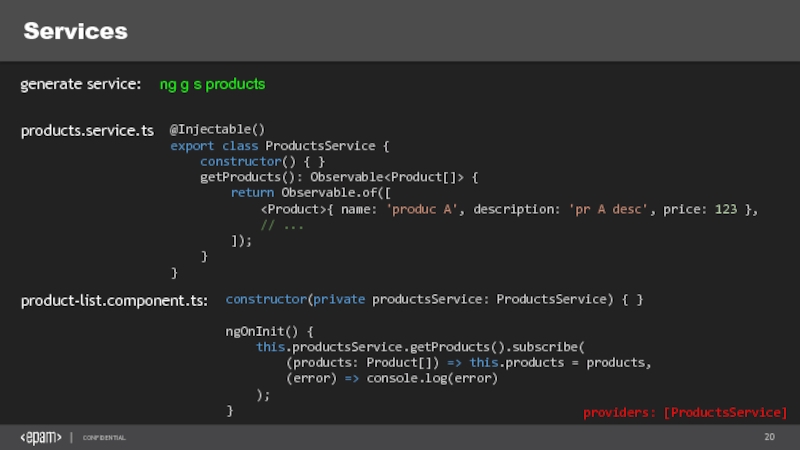
Слайд 20Services
ng g s products
generate service:
products.service.ts
@Injectable()
export class ProductsService {
constructor() { }
getProducts(): Observable
return Observable.of([
// ...
]);
}
}
product-list.component.ts:
constructor(private productsService: ProductsService) { }
ngOnInit() {
this.productsService.getProducts().subscribe(
(products: Product[]) => this.products = products,
(error) => console.log(error)
);
}
providers: [ProductsService]
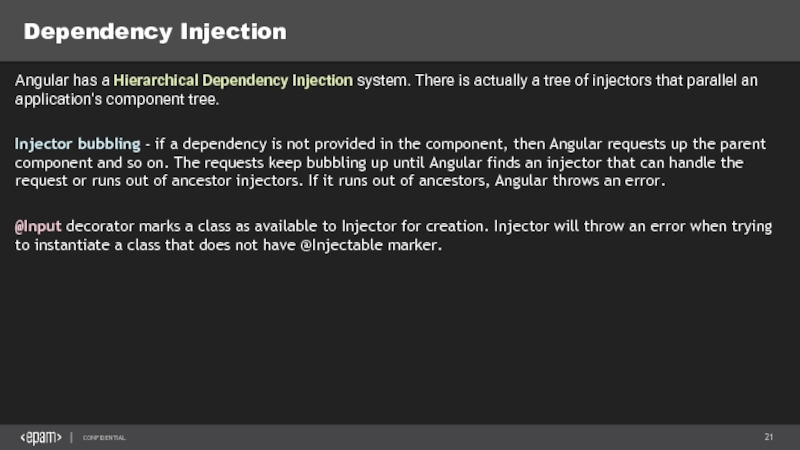
Слайд 21Dependency Injection
Angular has a Hierarchical Dependency Injection system. There is actually a tree
Injector bubbling - if a dependency is not provided in the component, then Angular requests up the parent component and so on. The requests keep bubbling up until Angular finds an injector that can handle the request or runs out of ancestor injectors. If it runs out of ancestors, Angular throws an error.
@Input decorator marks a class as available to Injector for creation. Injector will throw an error when trying to instantiate a class that does not have @Injectable marker.
Слайд 22Http
getProducts(): Observable {
return this.http.get('http://localhost:54145/api/products')
.map(res => res.json() as Product[]);
}
ngOnInit() {
this.productsService.getProducts().subscribe(
(products: Product[]) =>
(error) => console.log(error)
);
}
product-list.component.ts:
products.service.ts:
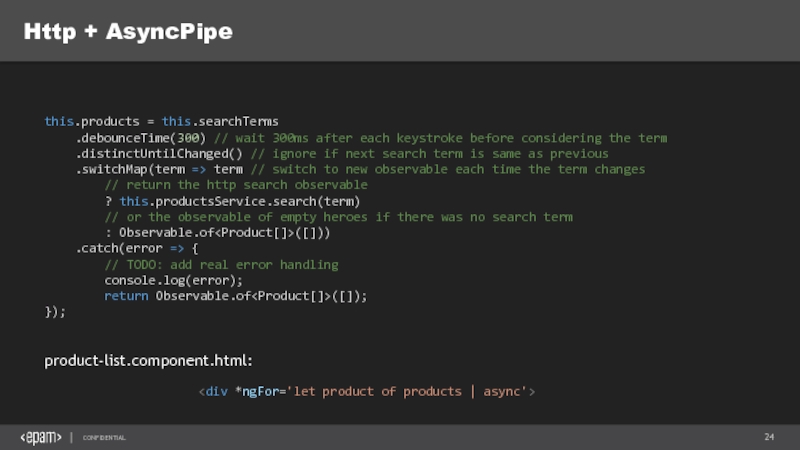
Слайд 23Http + AsyncPipe
product-list.component.ts:
products.service.ts:
search(term: string): Observable {
return this.http
.post(`http://localhost:54145/api/products`, { name: term })
.map(response
}
products: Observable
private searchTerms = new Subject
// push a search term into the observable stream.
search(term: string): void {
this.searchTerms.next(term);
}
Слайд 24Http + AsyncPipe
this.products = this.searchTerms
.debounceTime(300) // wait 300ms after each keystroke
.distinctUntilChanged() // ignore if next search term is same as previous
.switchMap(term => term // switch to new observable each time the term changes
// return the http search observable
? this.productsService.search(term)
// or the observable of empty heroes if there was no search term
: Observable.of
.catch(error => {
// TODO: add real error handling
console.log(error);
return Observable.of
});
product-list.component.html:
Обратная связь
Если не удалось найти и скачать презентацию, Вы можете заказать его на нашем сайте. Мы постараемся найти нужный Вам материал и отправим по электронной почте. Не стесняйтесь обращаться к нам, если у вас возникли вопросы или пожелания:
Email: Нажмите что бы посмотреть




![NgModulemain.ts – app entry pointapp.module.ts - main module @NgModule({declarations: [ AppComponent],imports: [BrowserModule,FormsModule,HttpModule],providers: [],bootstrap: [AppComponent]})export class AppModule {](/img/tmb/3/211954/1d158e8b83d0ccef2057a3dfcfcd8bcb-800x.jpg)
![Component@Component({selector: 'app-root',templateUrl: './app.component.html',styleUrls: ['./app.component.css']})export class AppComponent { title = 'app works!';}A component controls a patch of](/img/tmb/3/211954/22d1fd7ff6835c02bbaf05f673b88429-800x.jpg)



![HttpgetProducts(): Observable {return this.http.get('http://localhost:54145/api/products').map(res => res.json() as Product[]);}ngOnInit() {this.productsService.getProducts().subscribe((products: Product[]) => this.products = products,(error) => console.log(error));}product-list.component.ts:products.service.ts:](/img/tmb/3/211954/daa3e785ace2f50dcfd4679f74cbf242-800x.jpg)
![Http + AsyncPipeproduct-list.component.ts:products.service.ts:search(term: string): Observable {return this.http.post(`http://localhost:54145/api/products`, { name: term }).map(response => response.json() as Product[]);}products:](/img/tmb/3/211954/03ad03e1a733ce0a9cf8caccea65ba03-800x.jpg)