Why is hydrogen needed?
A modern commercially available car with a range of 400 km burns about 24 kg of petrol in a combustion engine or 8 kg of hydrogen.
For the electric car where hydrogen reacts with oxygen in a fuel cell by means the reaction
Н2 → 2Н+ + 2e-
O2 + 4H+ + 4e- → 2H2O,
is needed only 4 kg of hydrogen
What is the problem?
At the temperature 20oC and pressure 1 bar
4 kg of hydrogen occupied a volume of 45 m3.
What`s the way to squeeze 4 kg of hydrogen in a car?
2008 year
97% of transportation fuel comes from
crude oil
25% of global greenhouse emission are generated by cars
The number of cars - 750 millions
2050 year
The number of cars - 2.2 billions
Crude oil comes to an end
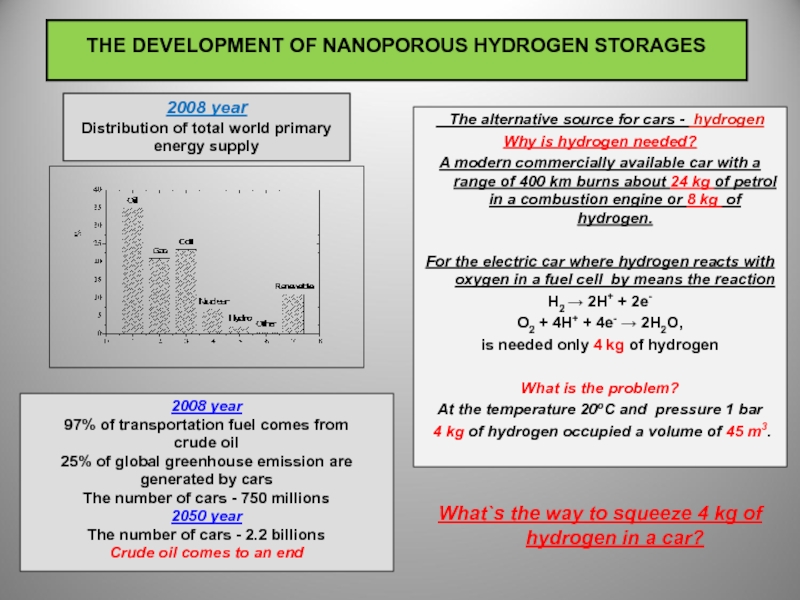
2008 year
Distribution of total world primary energy supply