Lecturer:
Assistant professor Antypenko Lyudmyla Mykolaivna
- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Сarbonyl compounds. Carboxylic acids. Lipids презентация
Содержание
- 1. Сarbonyl compounds. Carboxylic acids. Lipids
- 2. Plan Classification of aldehydes and ketones.
- 3. A carbonyl group is a group of
- 4. Classification Aldehydes, ketones aliphatic saturated unsaturated Aldehydes and ketones
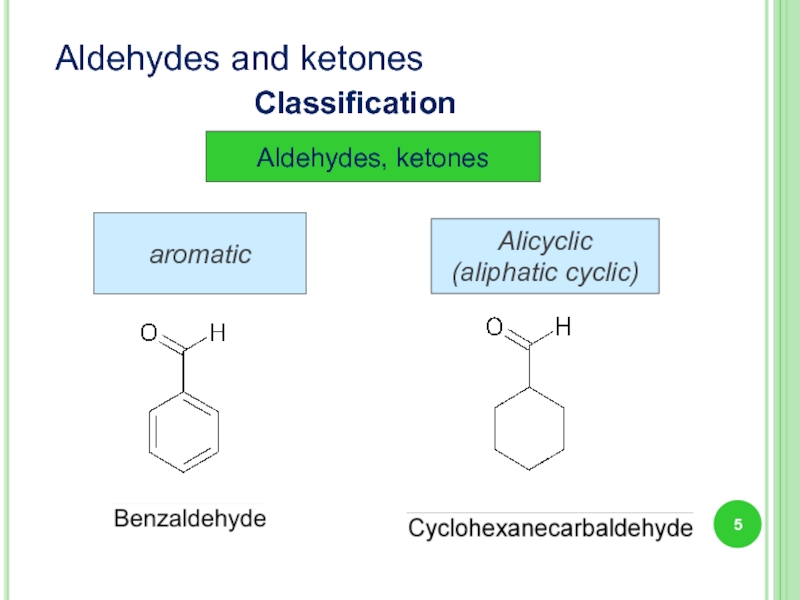
- 5. Aldehydes, ketones Alicyclic (aliphatic cyclic) aromatic Aldehydes and ketones Classification
- 6. Aldehydes. Nomenclature. Substitutive Trivial (Common name)
- 7. Aldehydes. Nomenclature. Substitutive Trivial (Common name)
- 8. Ketones. Nomenclature. Substitutive Trivial Radicalo-functional propan-2-one acetone dimethylketone
- 9. Preparation methods: 1. Alcohols oxidation:
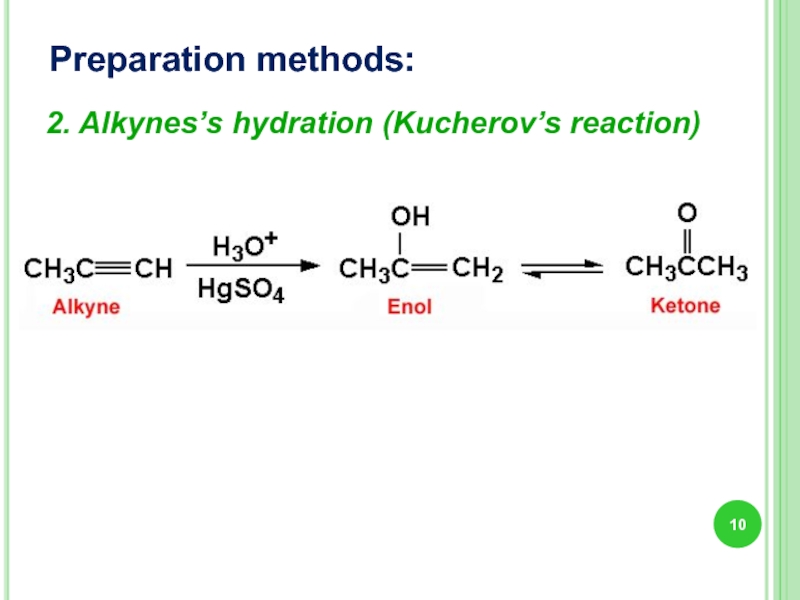
- 10. Preparation methods: 2. Alkynes’s hydration (Kucherov’s reaction)
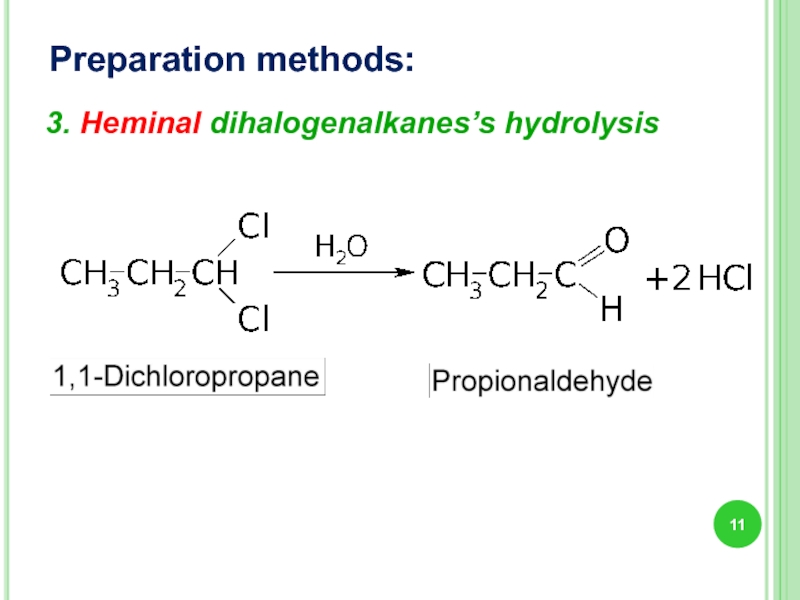
- 11. Preparation methods: 3. Heminal dihalogenalkanes’s hydrolysis
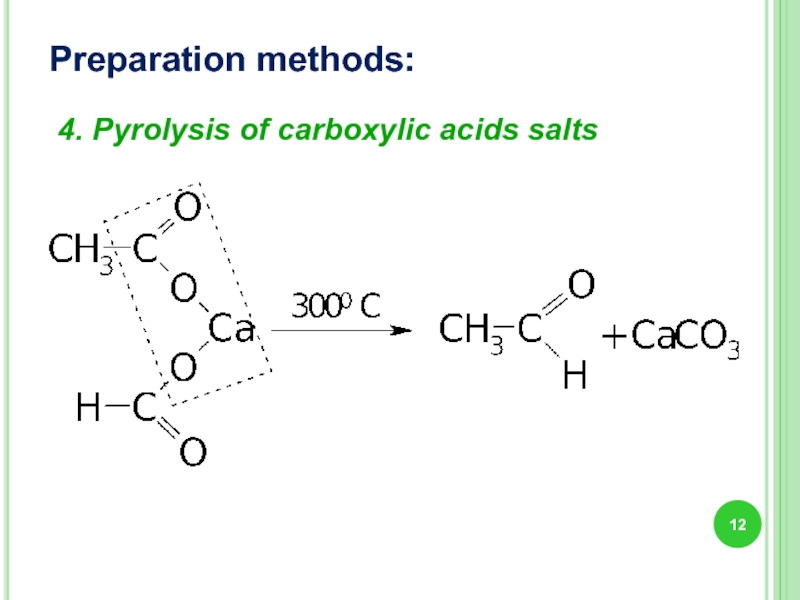
- 12. Preparation methods: 4. Pyrolysis of carboxylic acids salts
- 13. Structure and chemical properties
- 14. Chemical properties. Electrophilic center CH-acidic center
- 15. Characteristic reactions are:
- 16. Chemical properties. Tautomerism Eltekov
- 17. Nucleophilic addition (AN) 1. Addition of
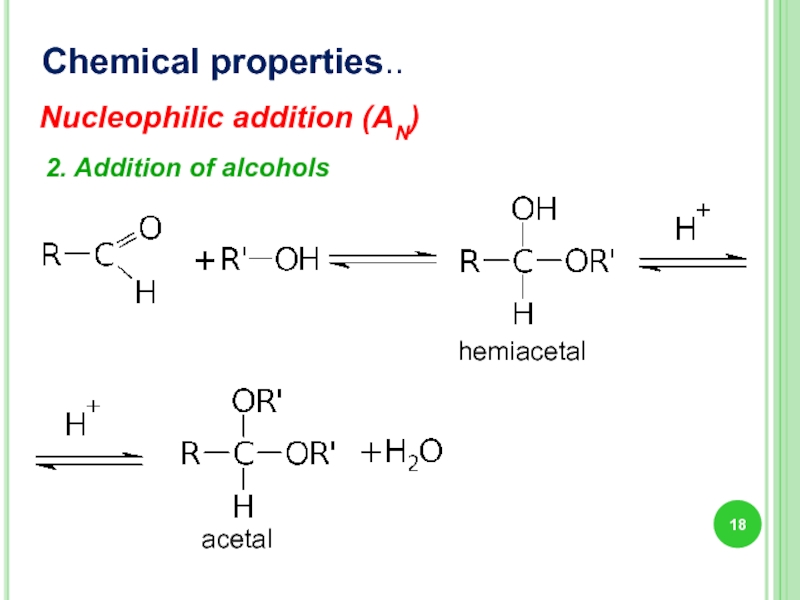
- 18. Chemical properties.. 2. Addition of alcohols Nucleophilic addition (AN) hemiacetal acetal
- 19. 1. Shiff bases formation Chemical properties. azomethins Addition – elimination reaction (AN-E)
- 20. Chemical properties. 2. With hydroxylamine aldoxime ketoxime Addition – elimination reaction (AN-E)
- 21. 3. With hydrazine derivatives Chemical properties. phenylhydrazine phenylhydrazone Addition – elimination reaction (AN-E)
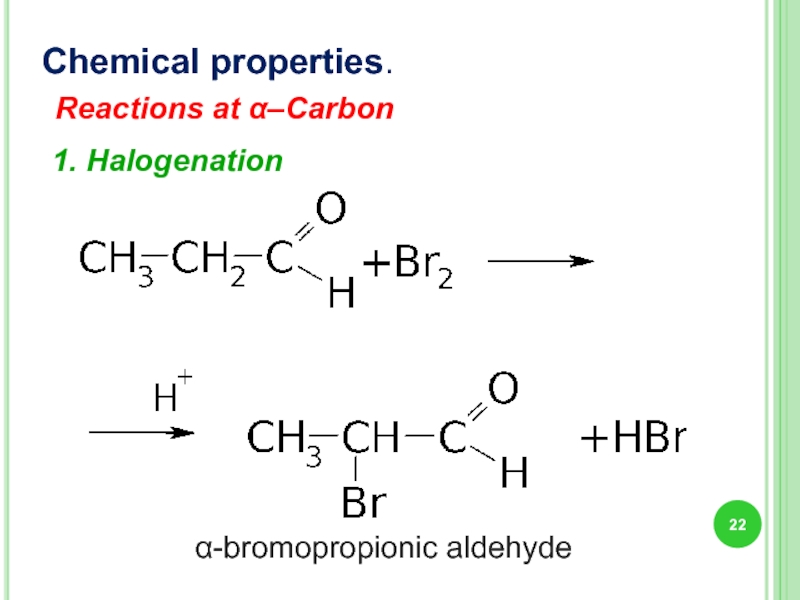
- 22. Chemical properties. Reactions at α–Carbon 1. Halogenation α-bromopropionic aldehyde
- 23. Chemical properties.. Reactions at α–Carbon 2.
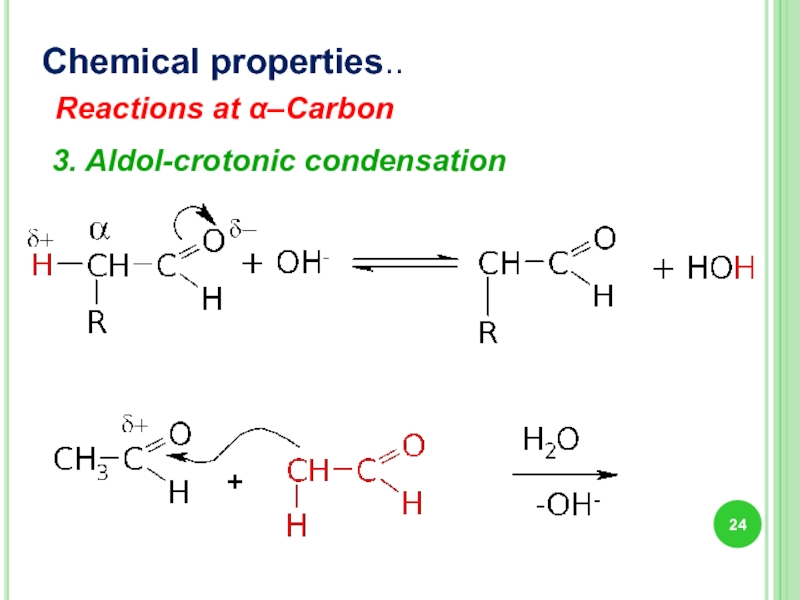
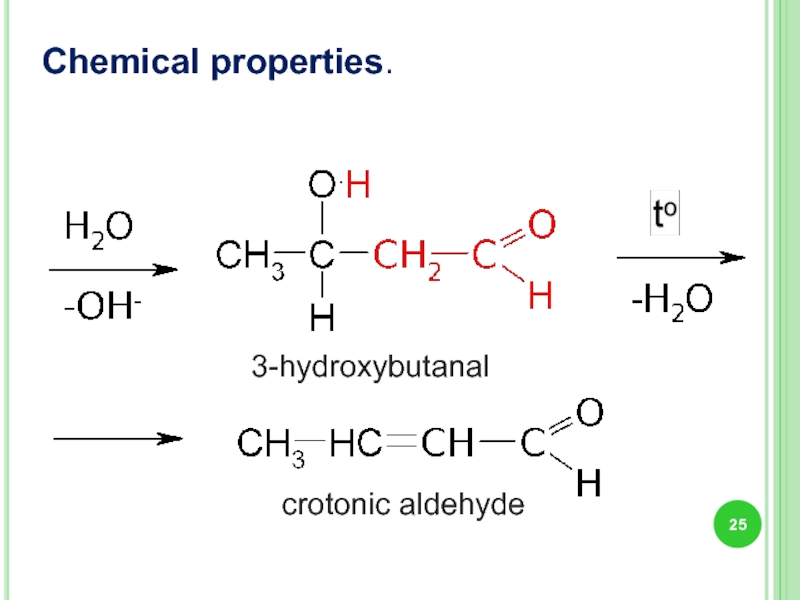
- 24. Chemical properties.. Reactions at α–Carbon 3. Aldol-crotonic condensation
- 25. Chemical properties. 3-hydroxybutanal crotonic aldehyde
- 26. Chemical properties. 4. Cannicaro reaction methanol potassium methylate
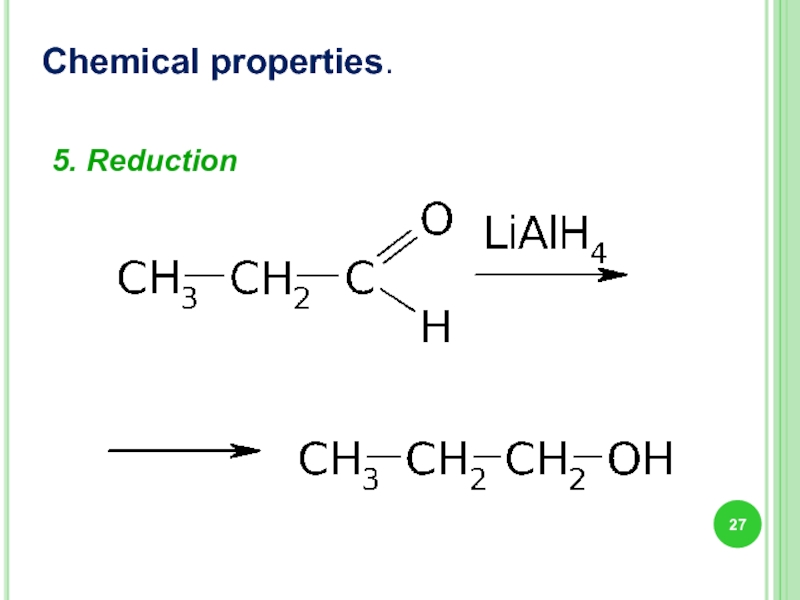
- 27. 5. Reduction Chemical properties.
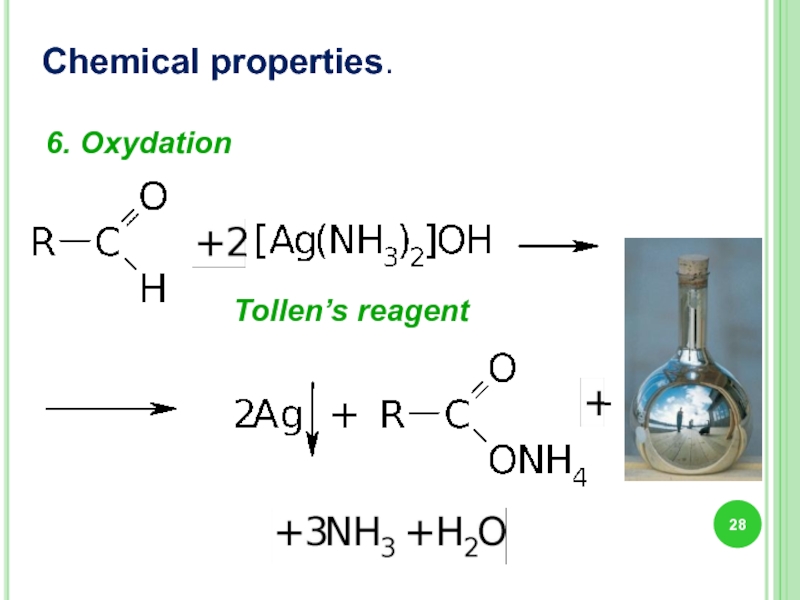
- 28. Chemical properties. 6. Oxydation Tollen’s reagent
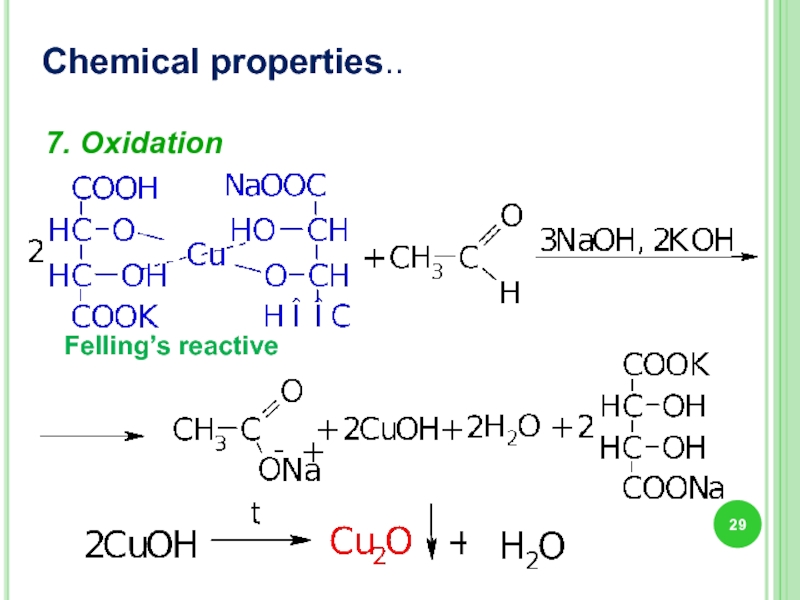
- 29. Chemical properties.. 7. Oxidation Felling’s reactive
- 30. Chemical properties.. The oxidation of ketones takes
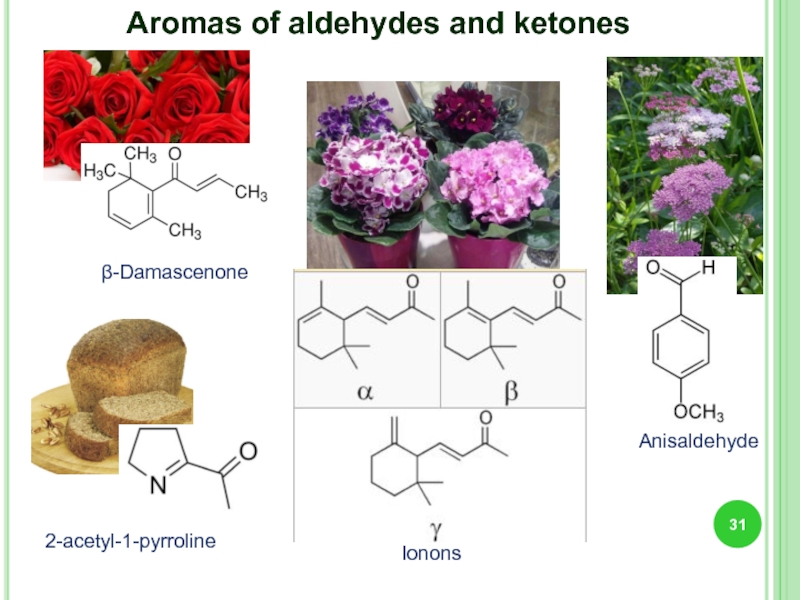
- 31. β-Damascenone Ionons Anisaldehyde 2-acetyl-1-pyrroline Aromas of aldehydes and ketones
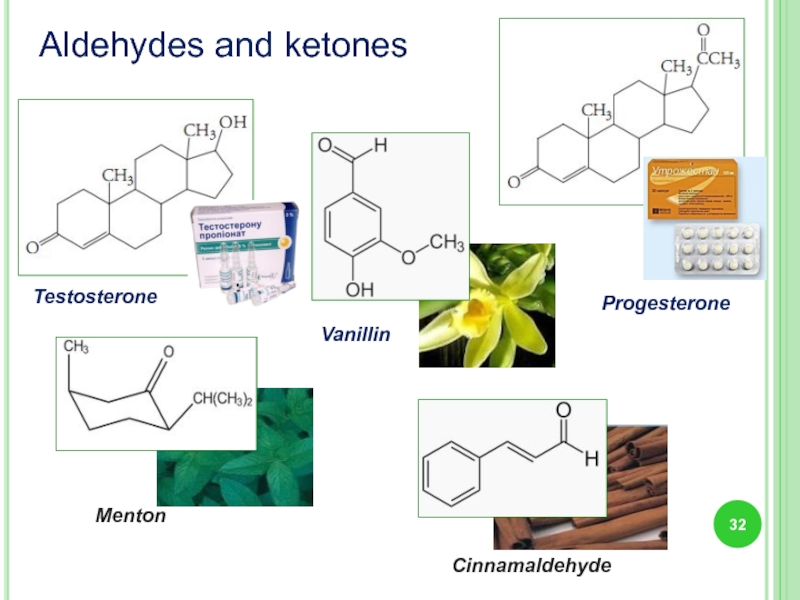
- 32. Aldehydes and ketones Testosterone Progesterone Menton Cinnamaldehyde Vanillin
- 33. Carboxylic acids - derivatives of hydrocarbons, containing
- 34. Carboxylic acid. Nomenclature. substitutive methanoic
- 35. Preparation methods: 1. Oxidation of primary alcohols
- 36. Preparation methods: 4. Hydrolysis of nitriles 5. Hydrocarbonylation of alkenes
- 37. Chemical properties • Reactions by acidic
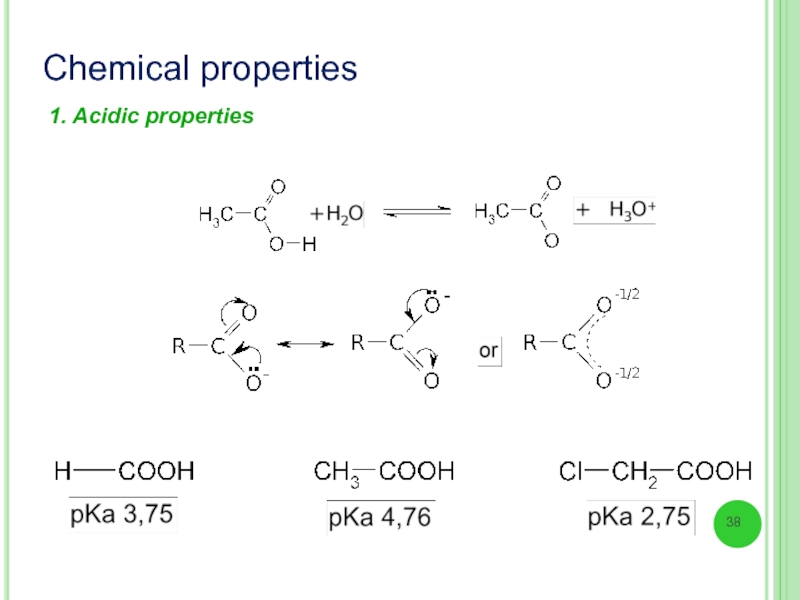
- 38. Chemical properties 1. Acidic properties
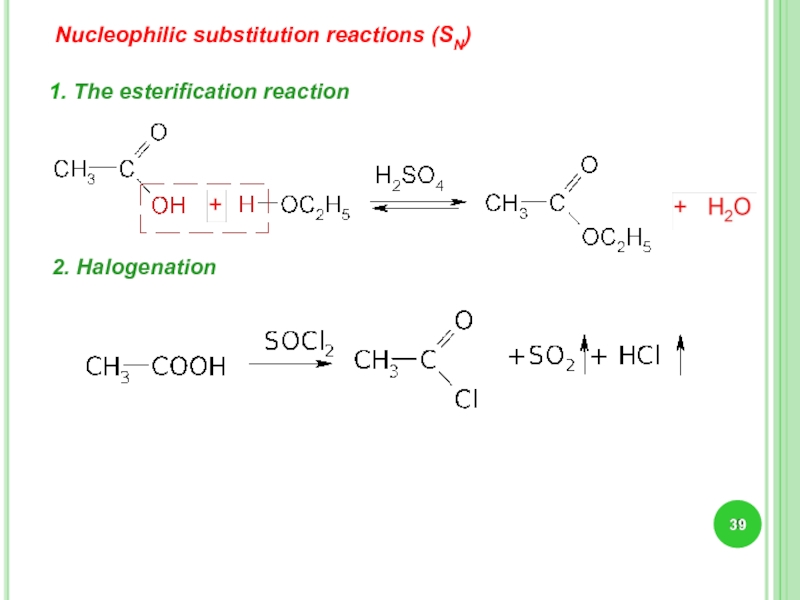
- 39. Nucleophilic substitution reactions (SN) 1. The esterification reaction 2. Halogenation
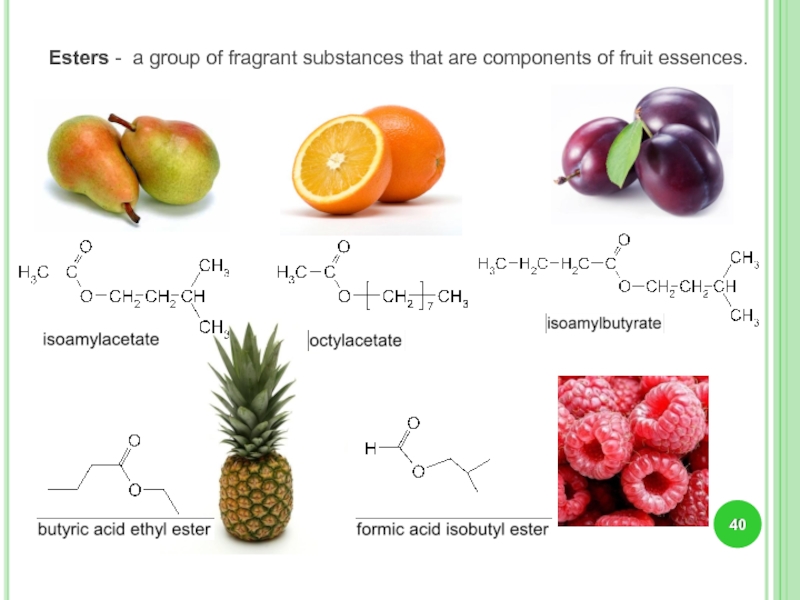
- 40. Esters - a group of fragrant substances that are components of fruit essences.
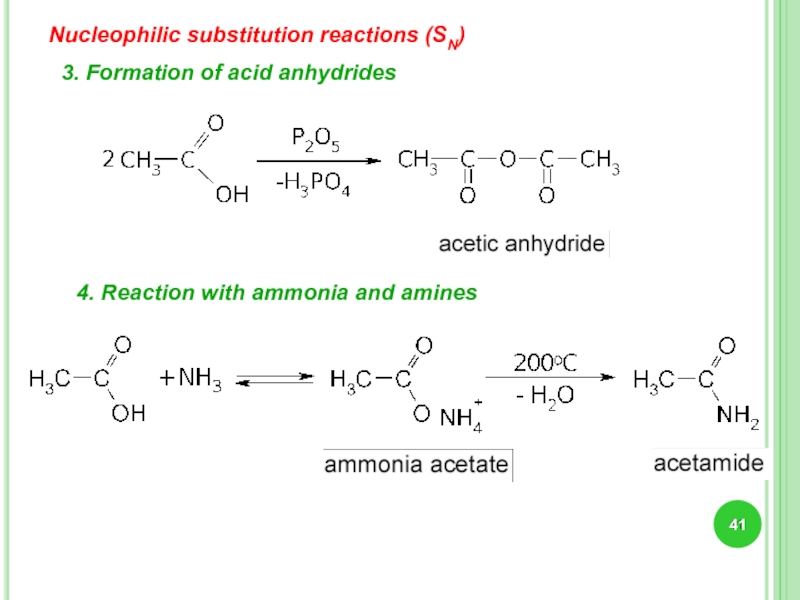
- 41. 3. Formation of acid
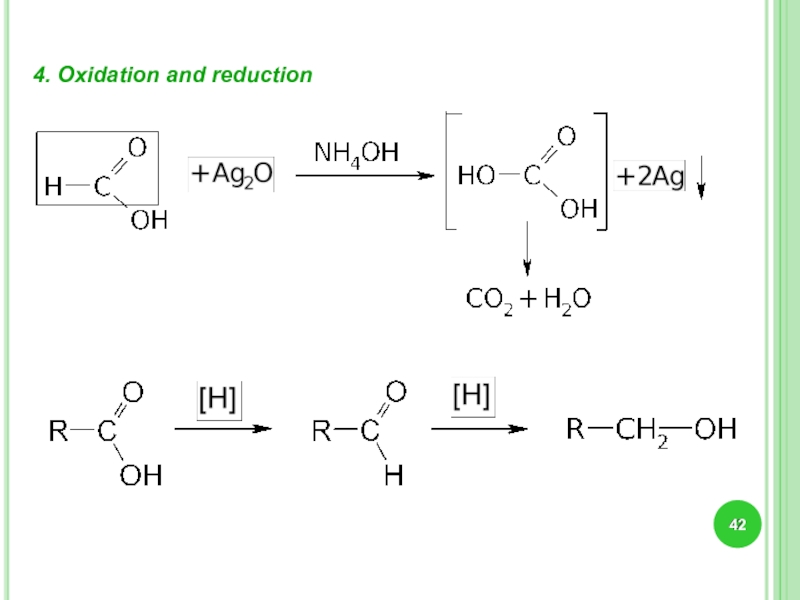
- 42. 4. Oxidation and reduction
- 43. Dicarboxylic acids Subsitutive ethandioic propandioic butandioic Trivial
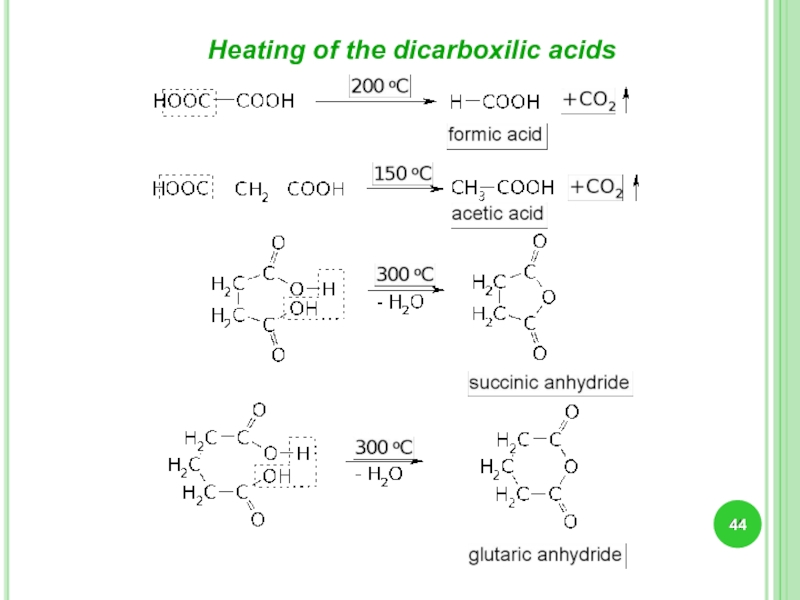
- 44. Heating of the dicarboxilic acids
- 45. Lipids (fats) - are esters, that are
- 46. Liquid vegetable oils contain mostly unsaturated acids
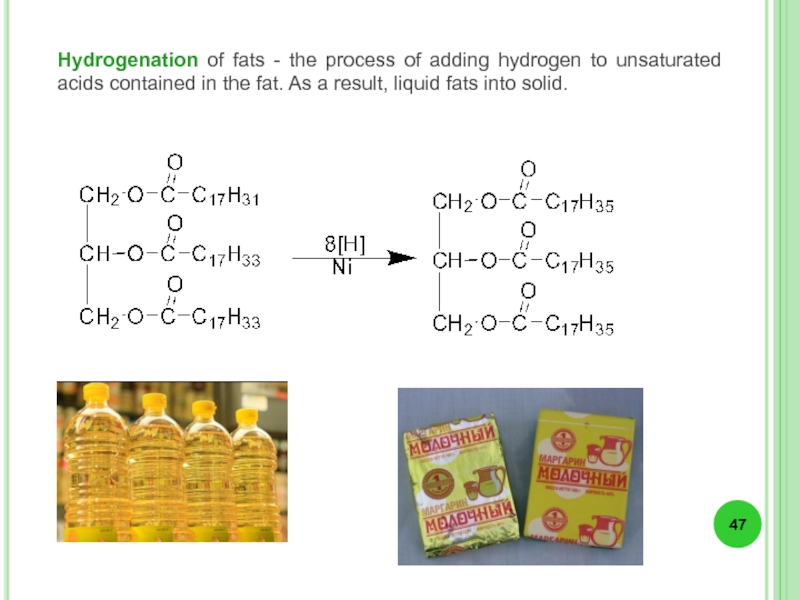
- 47. Hydrogenation of fats - the process of
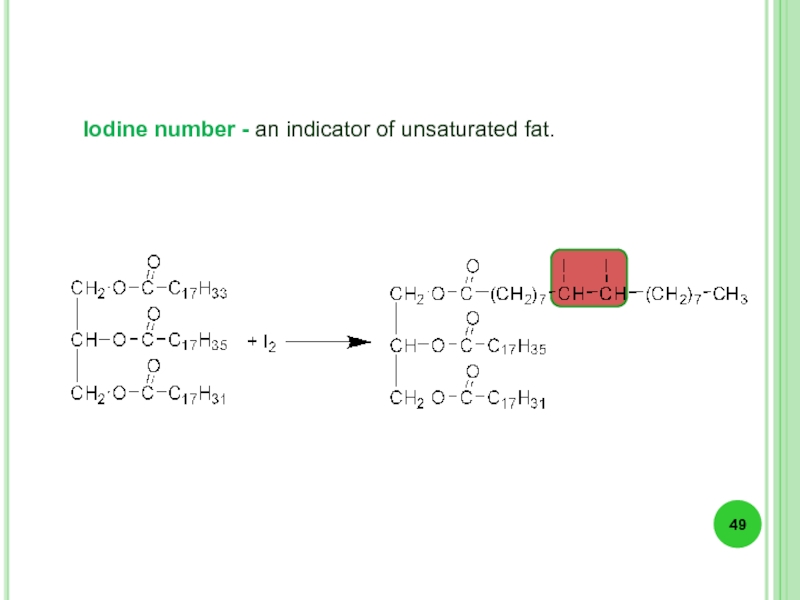
- 49. Iodine number - an indicator of unsaturated fat.
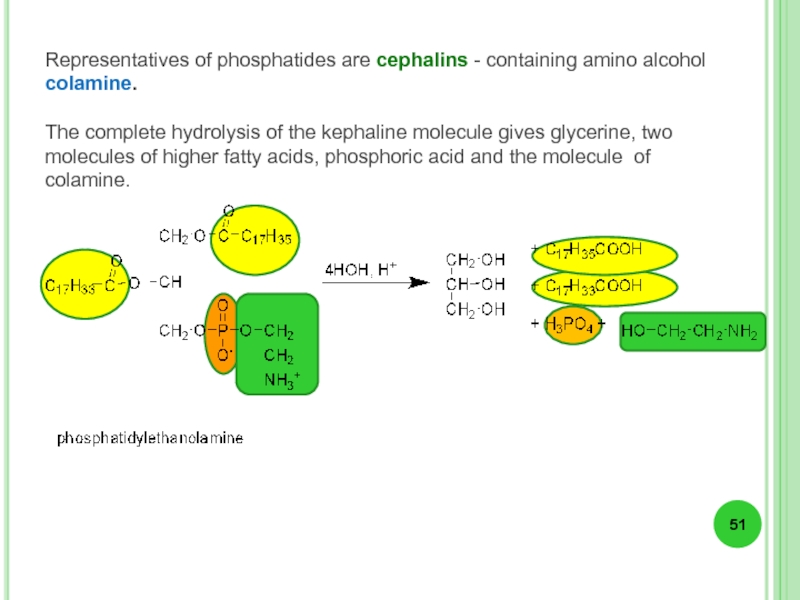
- 50. Phospholipids - lipids
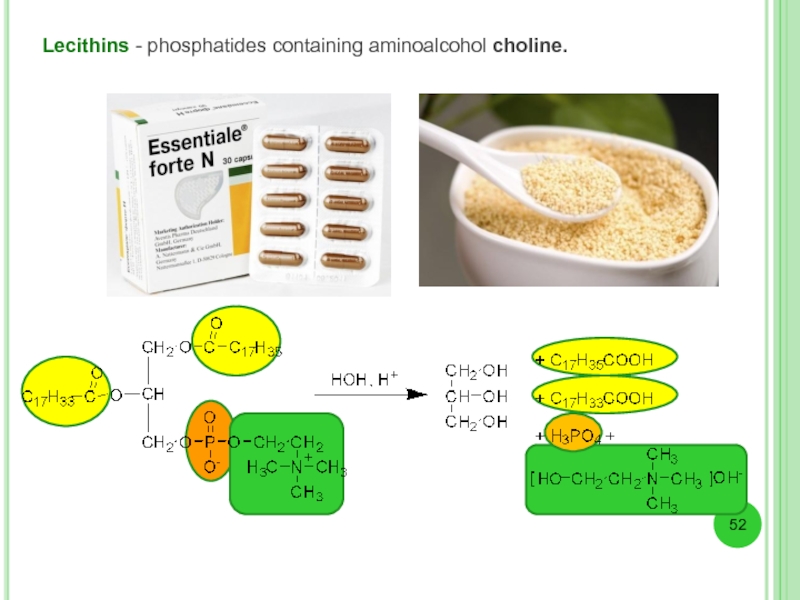
- 52. Lecithins - phosphatides containing aminoalcohol choline.
- 53. Thank You for Your attention!
Слайд 1LECTURE:
CARBONYL COMPOUNDS.
CARBOXYLIC ACIDS. LIPIDS.
MINISTRY OF PUBLIC HEALTH
ZAPOROZHYE STATE MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
DEPARTMENT
Слайд 2Plan
Classification of aldehydes
and ketones.
Nomenclature.
Preparation methods.
Chemical properties:
nucleophilic addition;
addition –
condensation;
at α-Carbon;
polymerisation;
oxydation and reduction
5. Aldehydes and ketones in
medicine .
Classification of carboxylic acids
Nomenclature.
Preparation methods.
Chemical properties:
reactions by acidic О–Н;
nucleophilic substitution;
hydrogen at α-Carbon substitution;
oxidation and reduction.
5. Medical usage.
6. Esters. Structure and chemical properties.
7. Lipids. Structure and physico-chemical properties.
Part I
Part II
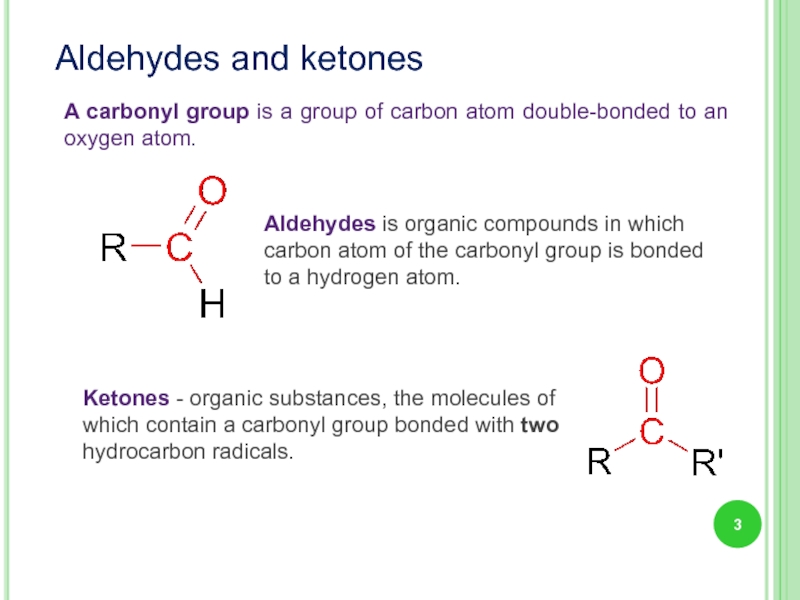
Слайд 3A carbonyl group is a group of carbon atom double-bonded to
Aldehydes and ketones
Aldehydes is organic compounds in which carbon atom of the carbonyl group is bonded to a hydrogen atom.
Ketones - organic substances, the molecules of which contain a carbonyl group bonded with two hydrocarbon radicals.
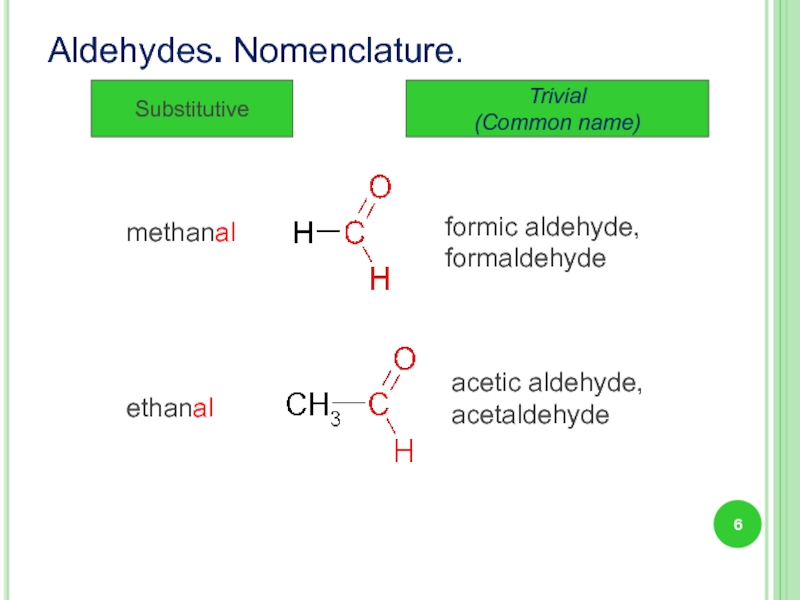
Слайд 6Aldehydes. Nomenclature.
Substitutive
Trivial
(Common name)
formic aldehyde,
formaldehyde
acetic aldehyde,
acetaldehyde
methanal
ethanal
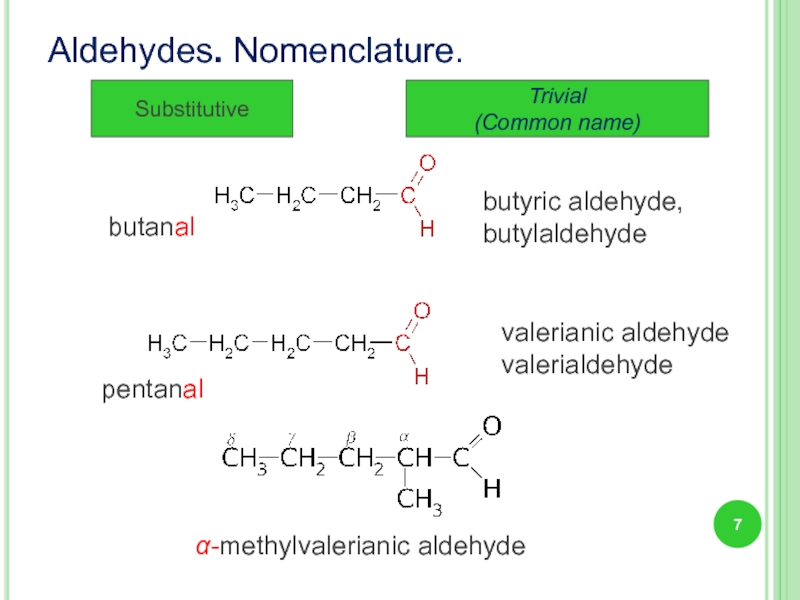
Слайд 7Aldehydes. Nomenclature.
Substitutive
Trivial
(Common name)
butyric aldehyde,
butylaldehyde
butanal
valerianic aldehyde
valerialdehyde
α-methylvalerianic aldehyde
pentanal
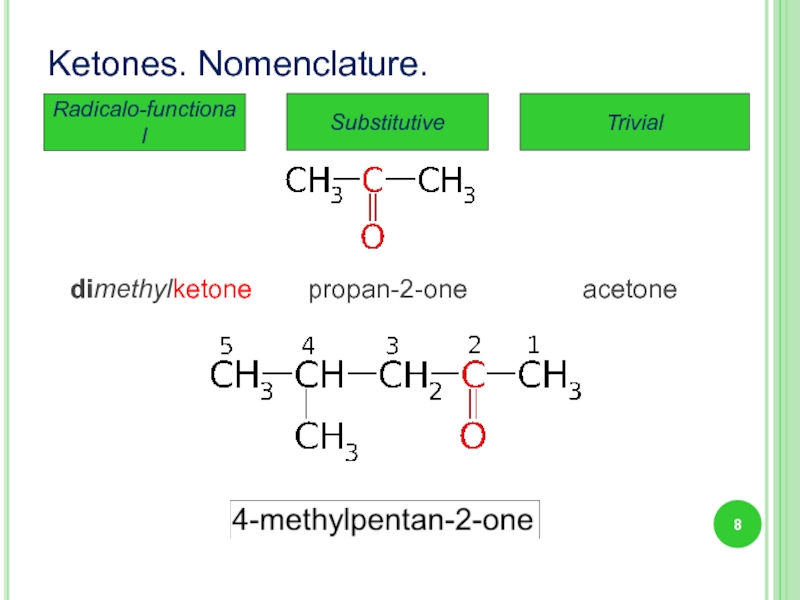
Слайд 8
Ketones. Nomenclature.
Substitutive
Trivial
Radicalo-functional
propan-2-one
acetone
dimethylketone
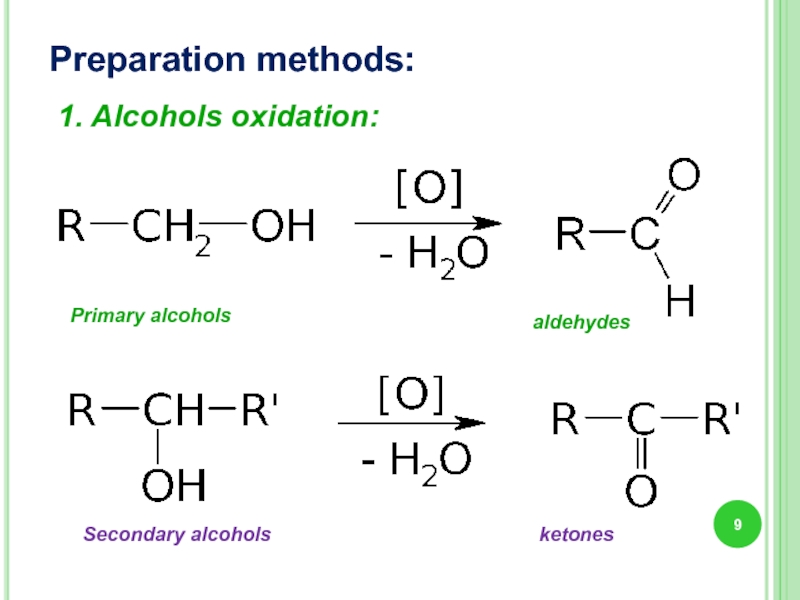
Слайд 9Preparation methods:
1. Alcohols oxidation:
Primary alcohols
Secondary alcohols
aldehydes
ketones
Слайд 13
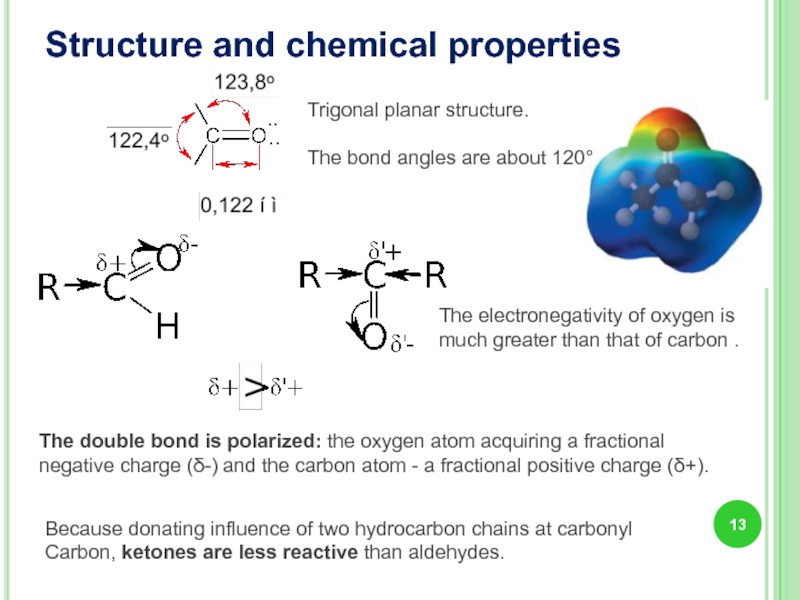
Structure and chemical properties
Trigonal planar structure.
The bond angles are about 120°
Because
The double bond is polarized: the oxygen atom acquiring a fractional negative charge (δ-) and the carbon atom - a fractional positive charge (δ+).
The electronegativity of oxygen is much greater than that of carbon .
Слайд 15
Characteristic reactions are:
nucleophilic addition;
addition – elimination;
condensation;
at
polymerisation;
oxydation and reduction
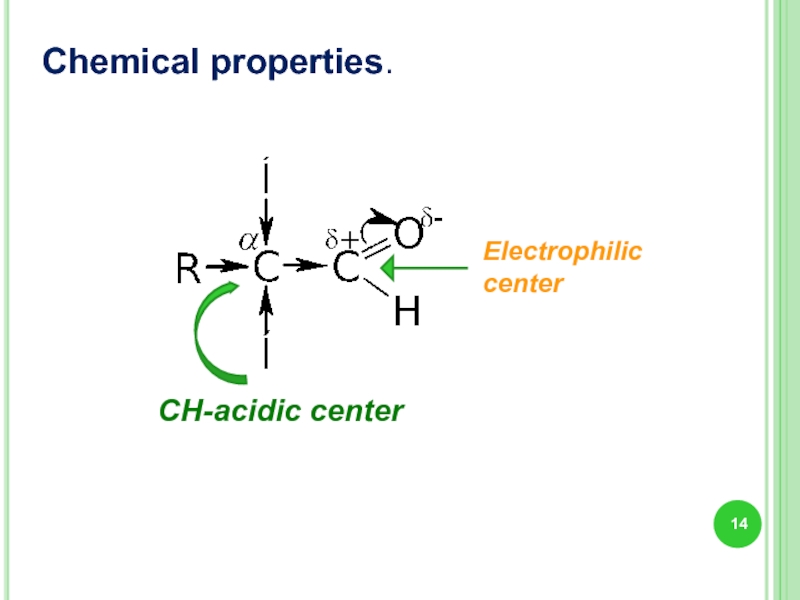
Chemical properties.
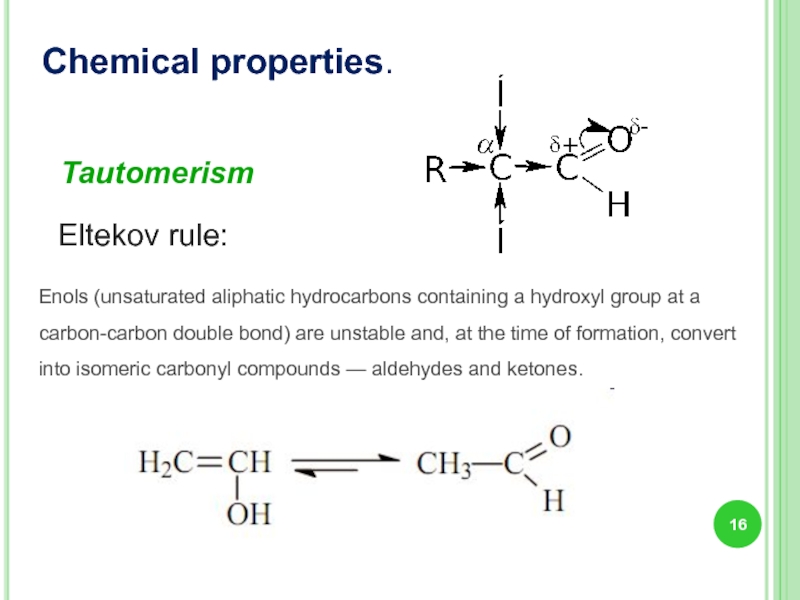
Слайд 16Chemical properties.
Tautomerism
Eltekov rule:
Enols (unsaturated aliphatic hydrocarbons containing a hydroxyl group
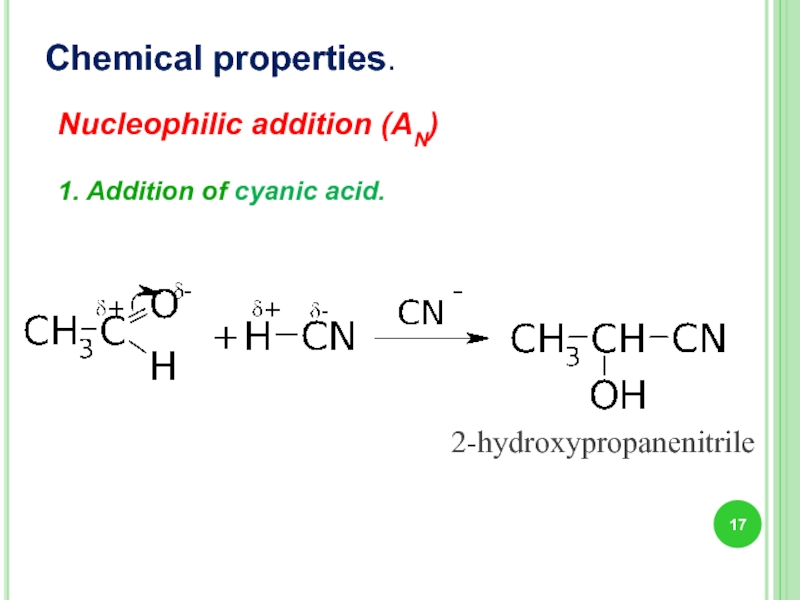
Слайд 17Nucleophilic addition (AN)
1. Addition of cyanic acid.
Chemical properties.
2-hydroxypropanenitrile
Слайд 19
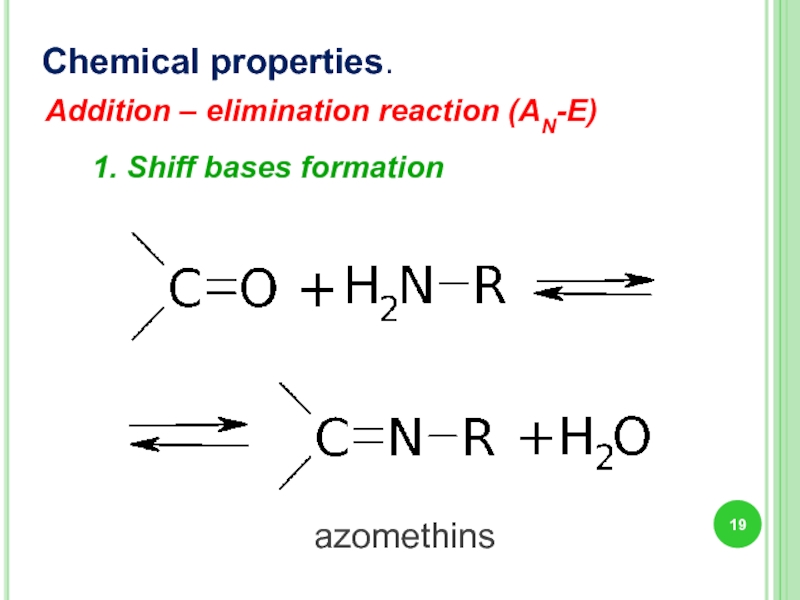
1. Shiff bases formation
Chemical properties.
azomethins
Addition – elimination reaction (AN-E)
Слайд 20
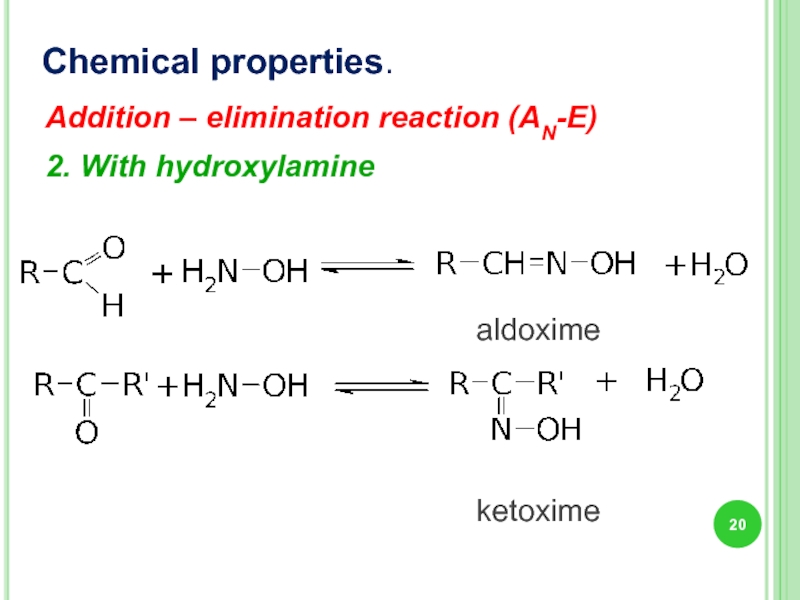
Chemical properties.
2. With hydroxylamine
aldoxime
ketoxime
Addition – elimination reaction (AN-E)
Слайд 21
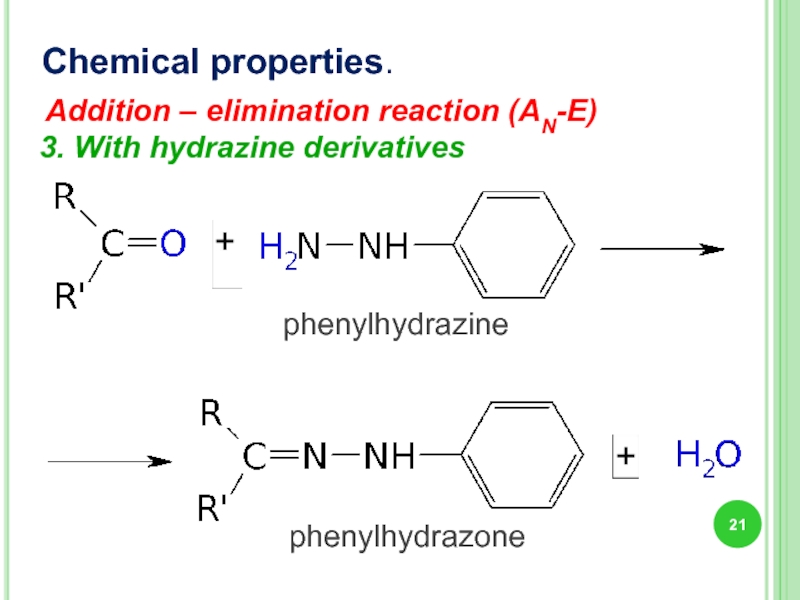
3. With hydrazine derivatives
Chemical properties.
phenylhydrazine
phenylhydrazone
Addition – elimination reaction (AN-E)
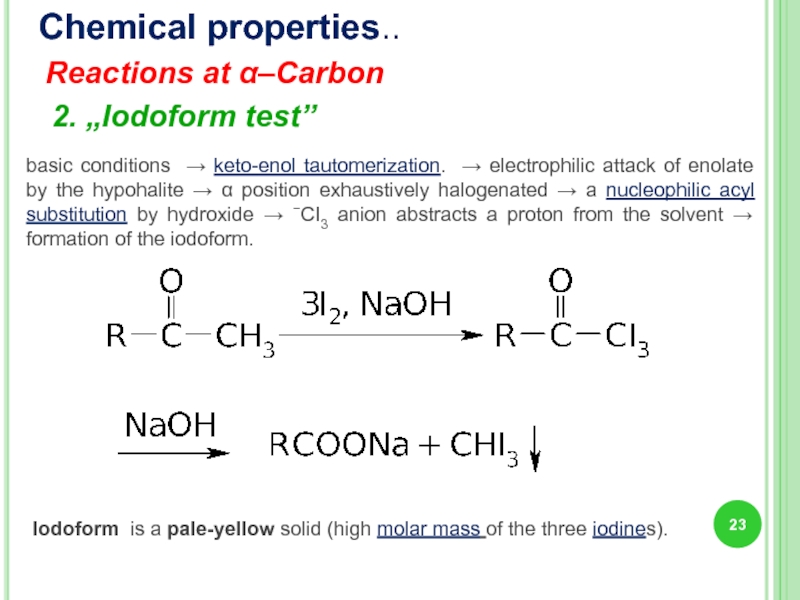
Слайд 23Chemical properties..
Reactions at α–Carbon
2. „Iodoform test”
Iodoform is a pale-yellow solid
basic conditions → keto-enol tautomerization. → electrophilic attack of enolate by the hypohalite → α position exhaustively halogenated → a nucleophilic acyl substitution by hydroxide → −CI3 anion abstracts a proton from the solvent → formation of the iodoform.
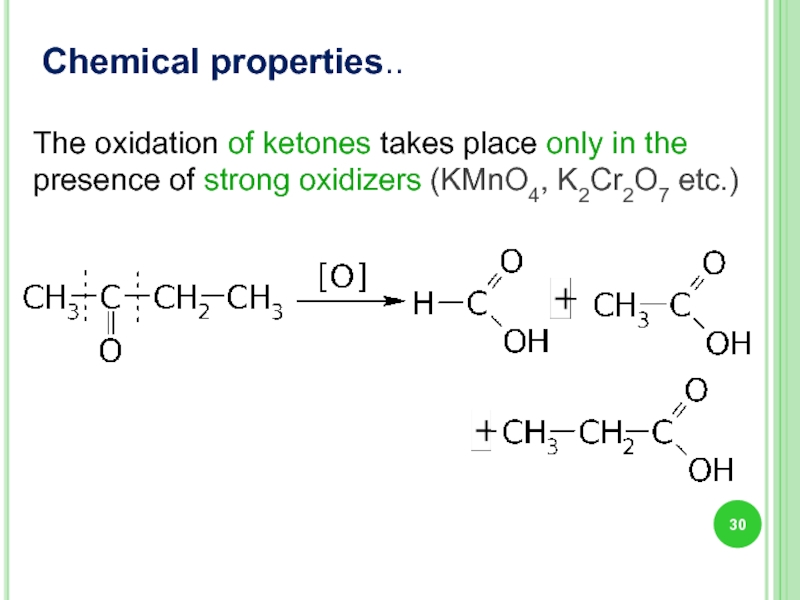
Слайд 30Chemical properties..
The oxidation of ketones takes place only in the presence
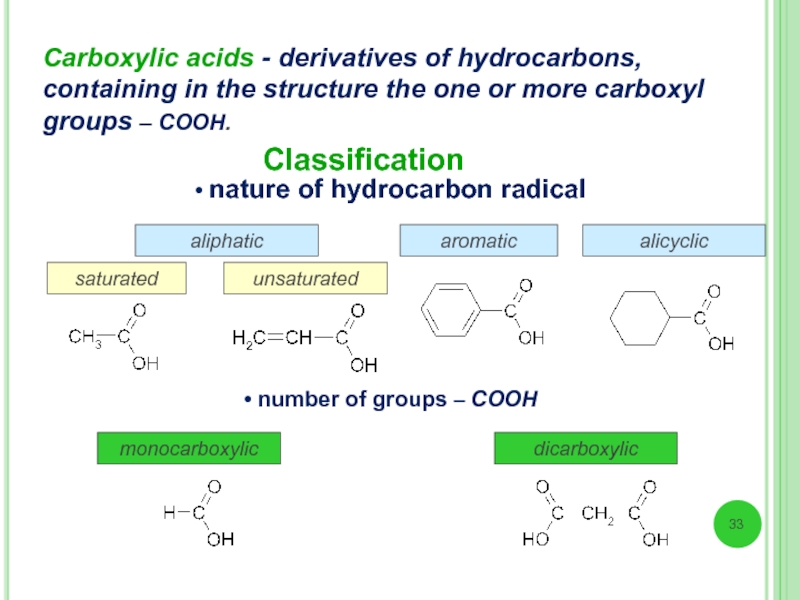
Слайд 33Carboxylic acids - derivatives of hydrocarbons, containing in the structure the
Classification
aliphatic
alicyclic
aromatic
saturated
unsaturated
• nature of hydrocarbon radical
• number of groups – СООН
monocarboxylic
dicarboxylic
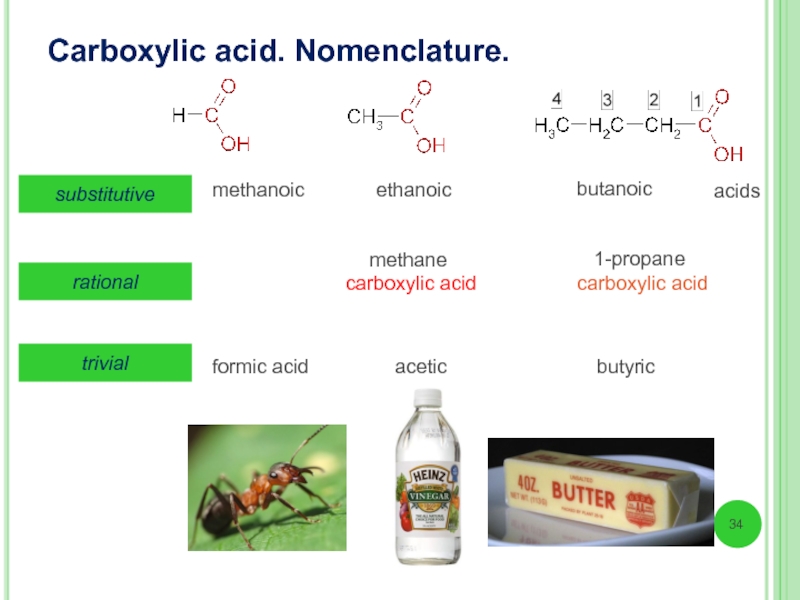
Слайд 34Carboxylic acid. Nomenclature.
substitutive
methanoic
ethanoic
butanoic
methane
carboxylic acid
1-propane
carboxylic acid
formic acid
acetic
butyric
trivial
rational
acids
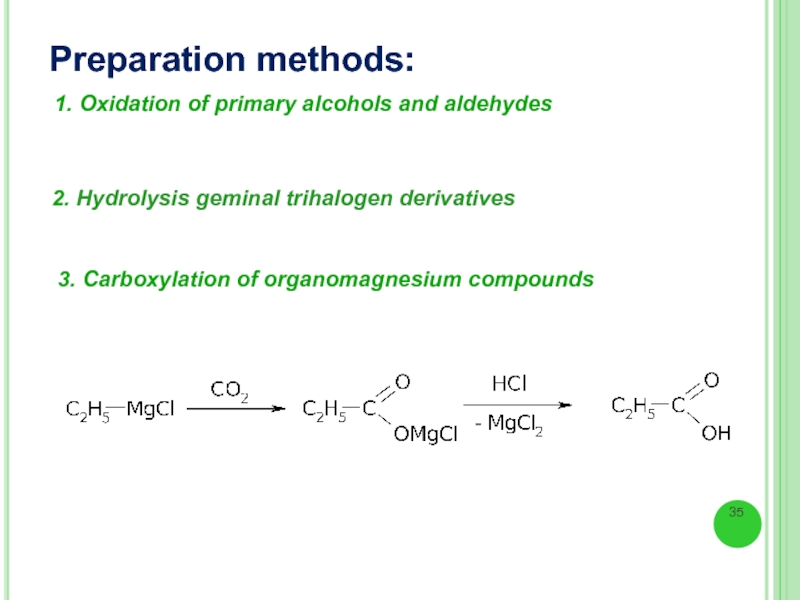
Слайд 35Preparation methods:
1. Oxidation of primary alcohols and aldehydes
2. Hydrolysis geminal trihalogen
3. Carboxylation of organomagnesium compounds
Слайд 37
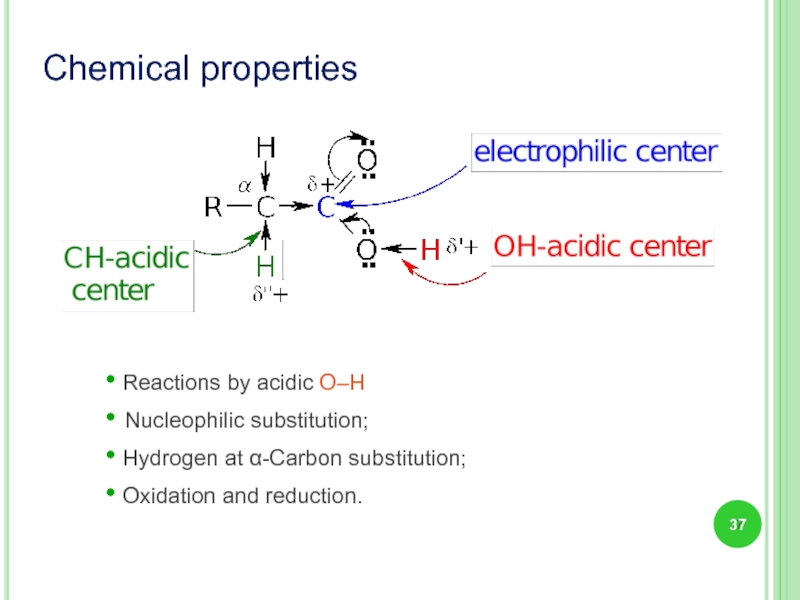
Chemical properties
• Reactions by acidic О–Н
• Nucleophilic substitution;
• Hydrogen at α-Carbon
• Oxidation and reduction.
Слайд 41
3. Formation of acid anhydrides
4. Reaction with ammonia and amines
Nucleophilic substitution
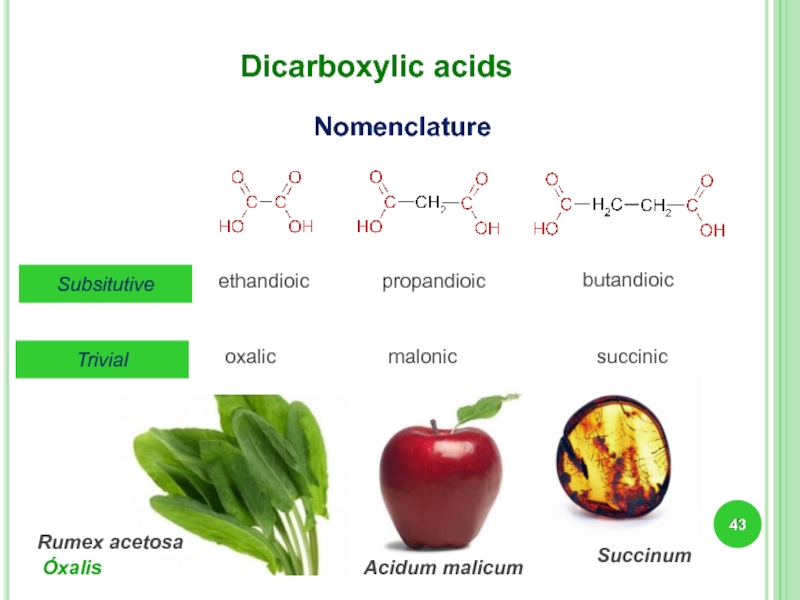
Слайд 43Dicarboxylic acids
Subsitutive
ethandioic
propandioic
butandioic
Trivial
Nomenclature
malonic
succinic
oxalic
Rumex acetosa
Óxalis
Succinum
Acidum malicum
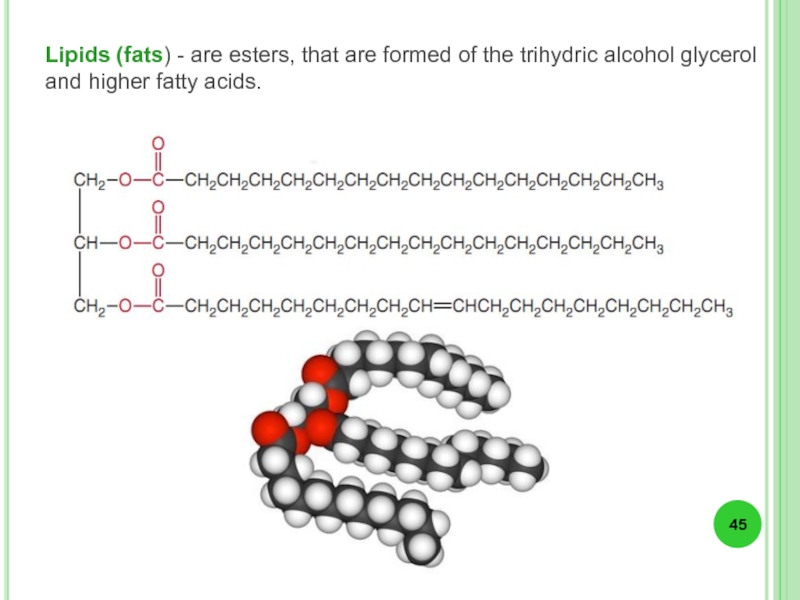
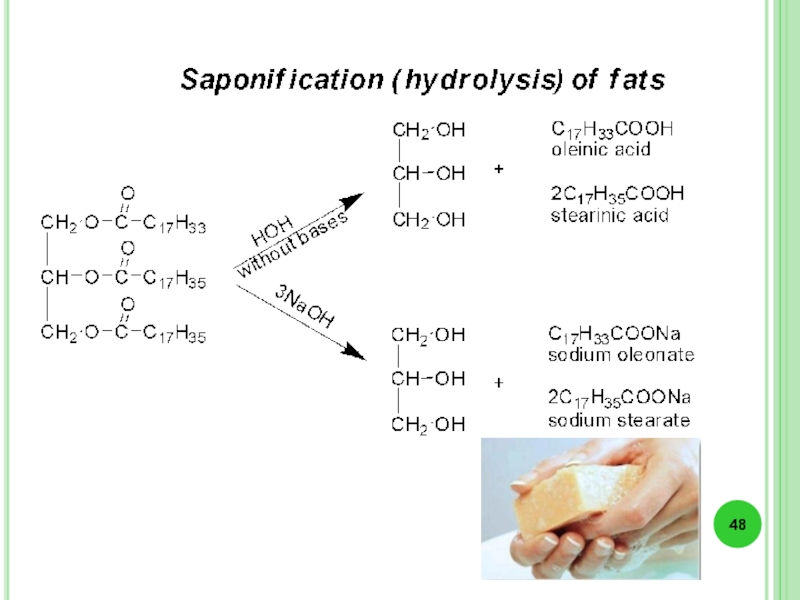
Слайд 45Lipids (fats) - are esters, that are formed of the trihydric
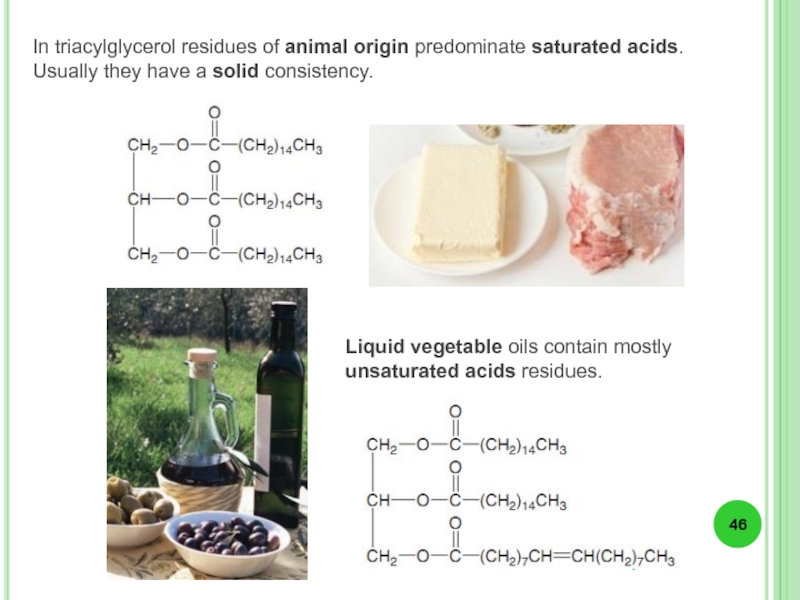
Слайд 46Liquid vegetable oils contain mostly unsaturated acids residues.
In triacylglycerol residues of
Слайд 47Hydrogenation of fats - the process of adding hydrogen to unsaturated
Слайд 50
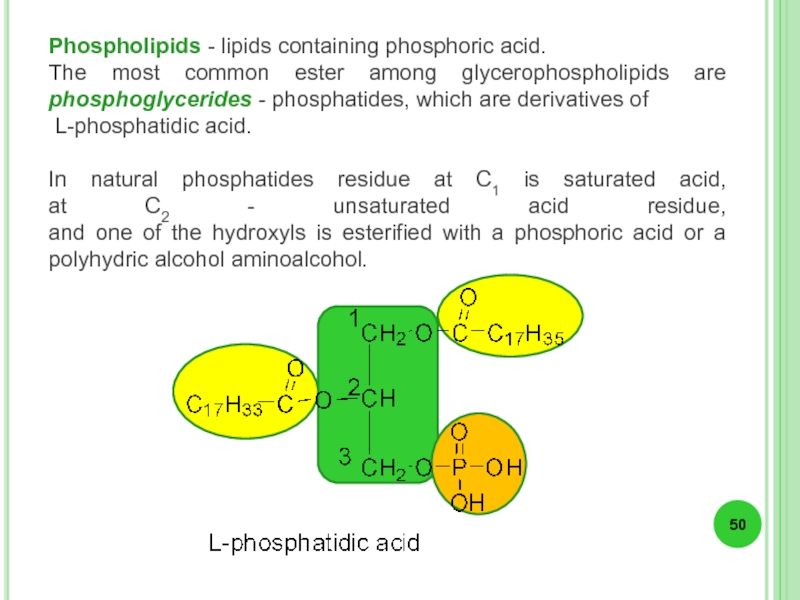
Phospholipids - lipids containing phosphoric acid.
The most common ester among glycerophospholipids
L-phosphatidic acid.
In natural phosphatides residue at C1 is saturated acid, at C2 - unsaturated acid residue, and one of the hydroxyls is esterified with a phosphoric acid or a polyhydric alcohol aminoalcohol.