- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
KS4 Earth's Structure презентация
Содержание
- 1. KS4 Earth's Structure
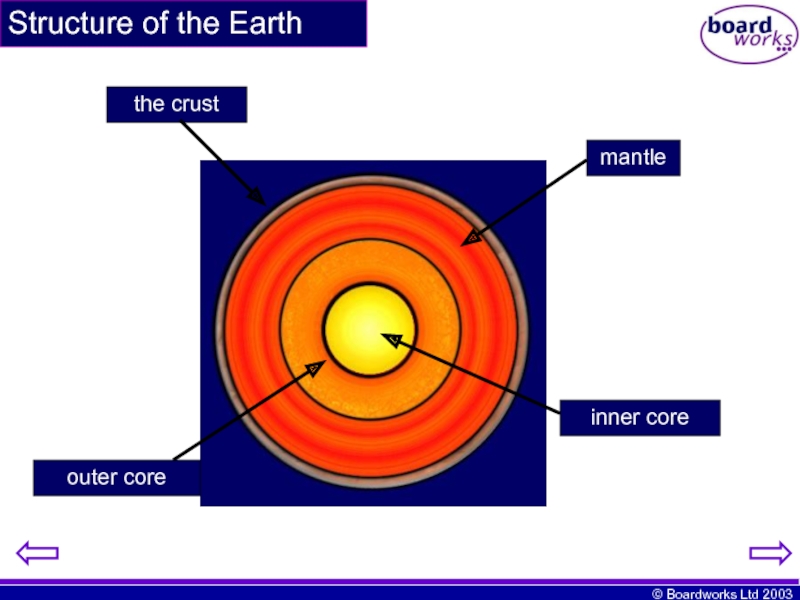
- 2. Structure of the Earth the crust mantle outer core inner core
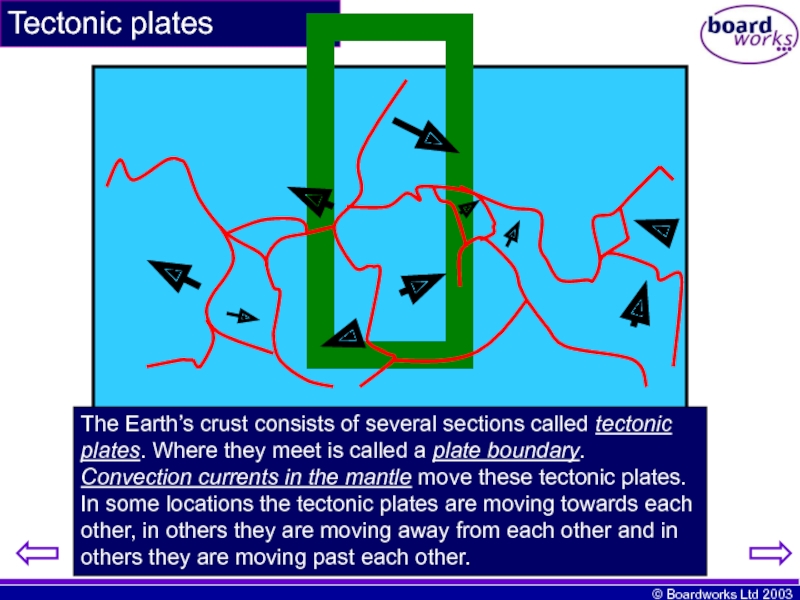
- 3. Tectonic plates The Earth’s crust consists
- 4. Plate boundaries 1 When two plates slide
- 5. Plate boundaries 1
- 6. Why do earthquakes happen?
- 7. Epicentre of an earthquake
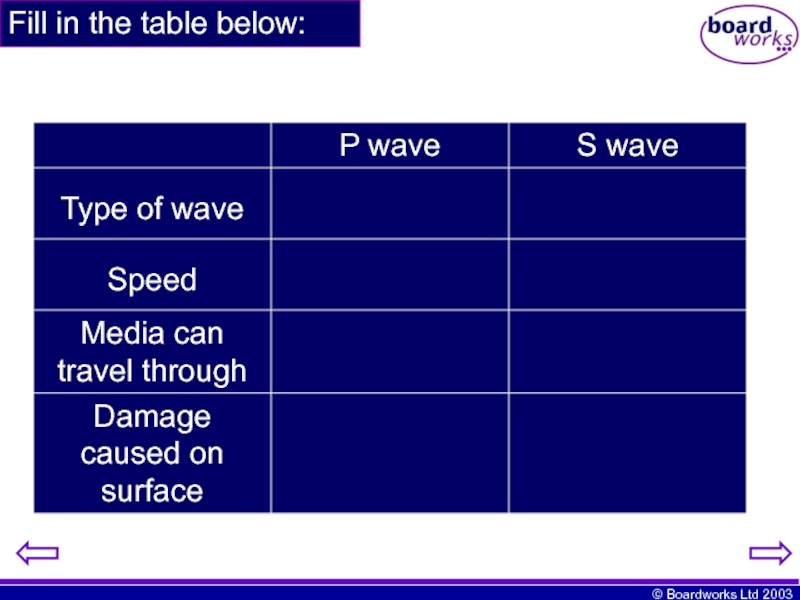
- 8. Primary and secondary waves During an earthquake
- 9. S-waves…… Shake
- 10. Seismic waves
- 11. Task 2 – Seismic waves Outer core
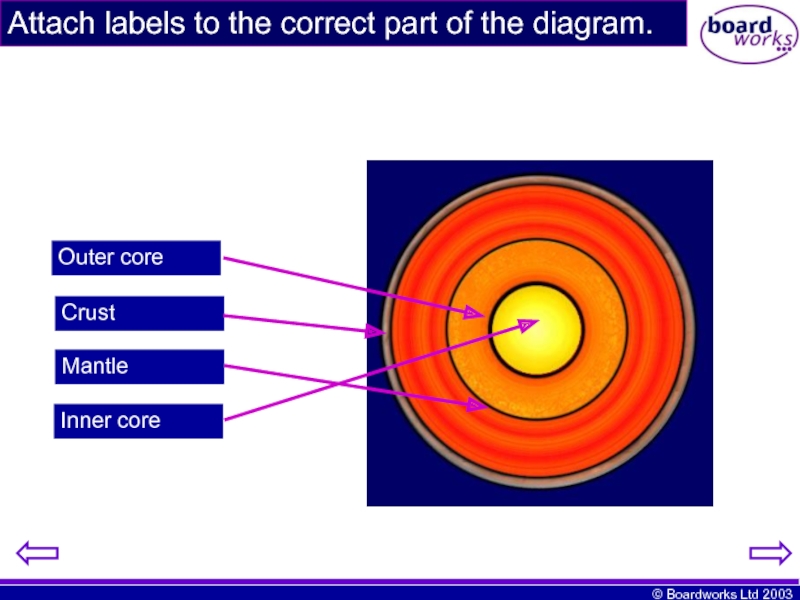
- 12. Outer core Crust Mantle Inner core Attach labels to the correct part of the diagram.
- 13. Task 3 – Tectonic plates Plate A
- 14. Match the word with the description: Epicentre
- 15. Fill in the table below:
- 16. Plate boundaries 2 What happens when
- 17. Plate boundaries 2
- 18. Convection current Convection current
- 19. Constructive Plate Boundary Plate boundaries 3
- 20. Match the word with the description: Subduction
- 21. Continental Drift It is thought that
- 22. Continental Drift
- 23. Evidence for continental drift theory: The shapes
Слайд 3Tectonic plates
The Earth’s crust consists of several sections called tectonic plates.
Слайд 4Plate boundaries 1
When two plates slide past each other, they don’t
This sudden movement of plates is called an earthquake and it can be very destructive.
Слайд 8Primary and secondary waves
During an earthquake the two types of wave
Primary or p-waves are the fastest. They are longitudinal in nature and when they hit the surface they make objects and buildings vibrate vertically. They can travel through solids and liquids.
Secondary or s-waves are the slowest. They are transverse in nature and when they hit the surface they make objects and buildings vibrate horizontally. They can only travel through solids.
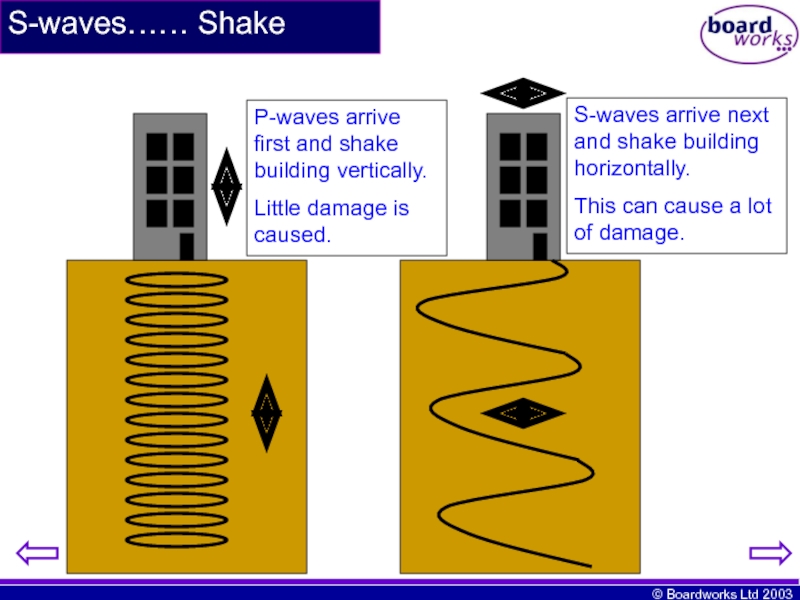
Слайд 9S-waves…… Shake
P-waves arrive first and shake building vertically.
Little damage is
S-waves arrive next and shake building horizontally.
This can cause a lot of damage.
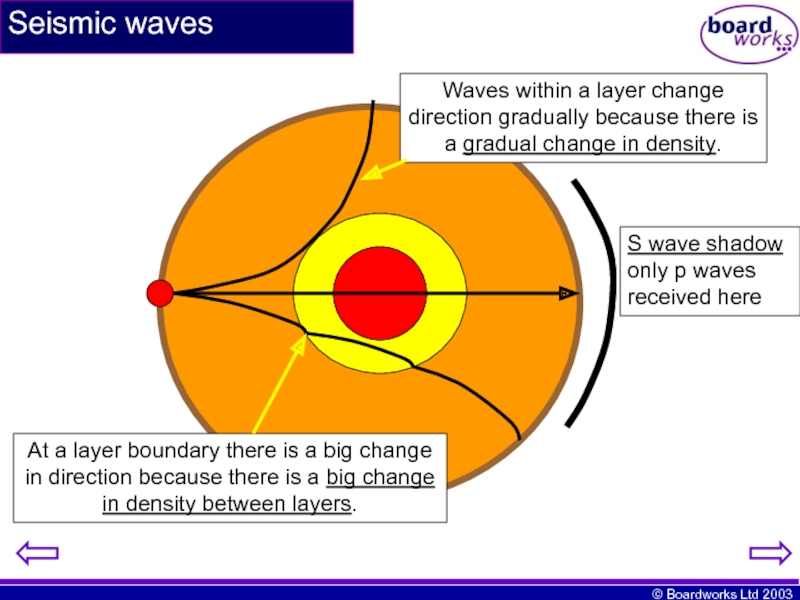
Слайд 10Seismic waves
Waves within a layer change direction gradually because there is
At a layer boundary there is a big change in direction because there is a big change in density between layers.
S wave shadow only p waves received here
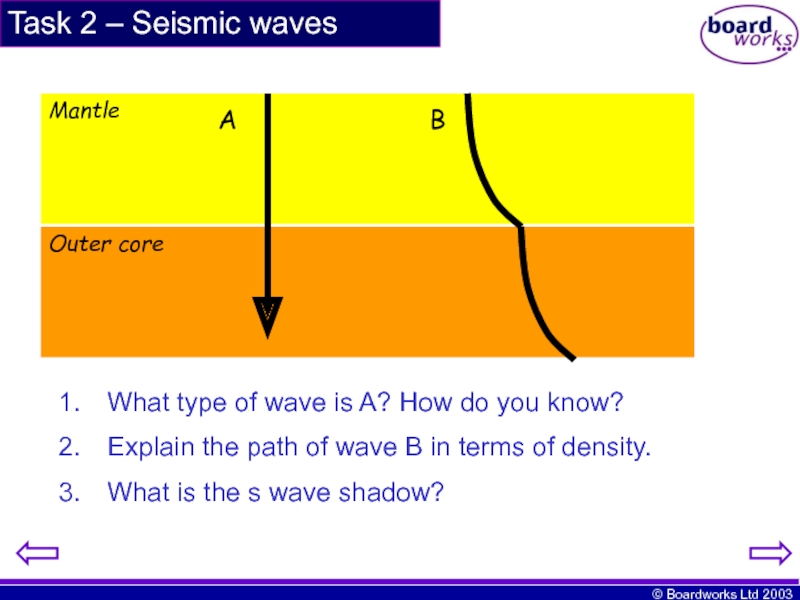
Слайд 11Task 2 – Seismic waves
Outer core
Mantle
A
B
What type of wave is A?
Explain the path of wave B in terms of density.
What is the s wave shadow?
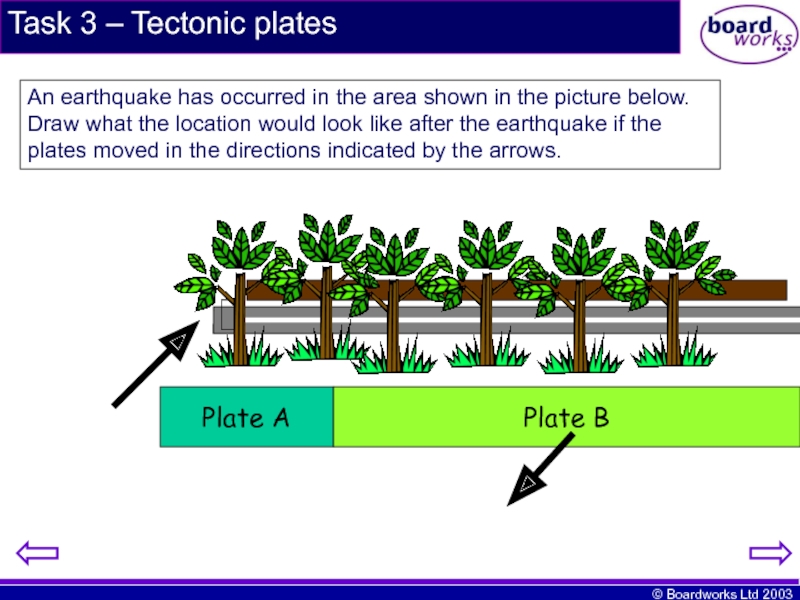
Слайд 13Task 3 – Tectonic plates
Plate A
Plate B
An earthquake has occurred in
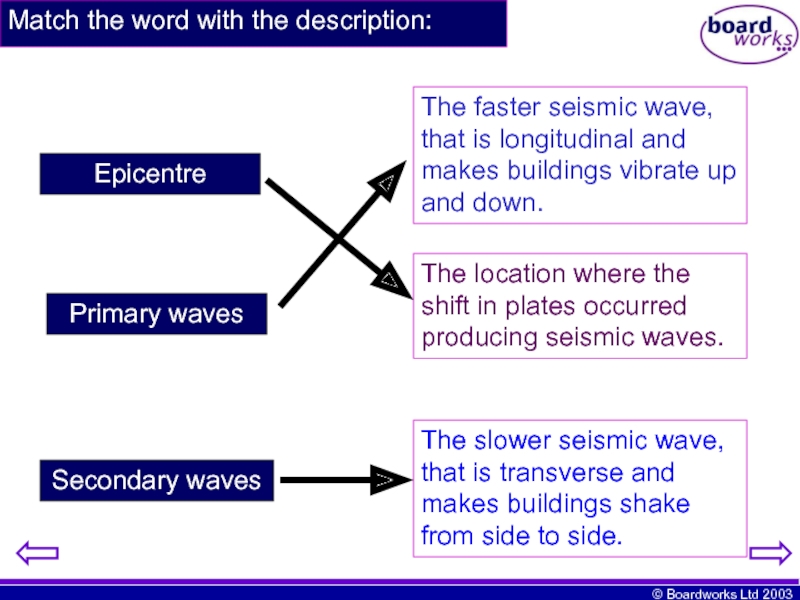
Слайд 14Match the word with the description:
Epicentre
Primary waves
Secondary waves
The faster seismic wave,
The location where the shift in plates occurred producing seismic waves.
The slower seismic wave, that is transverse and makes buildings shake from side to side.
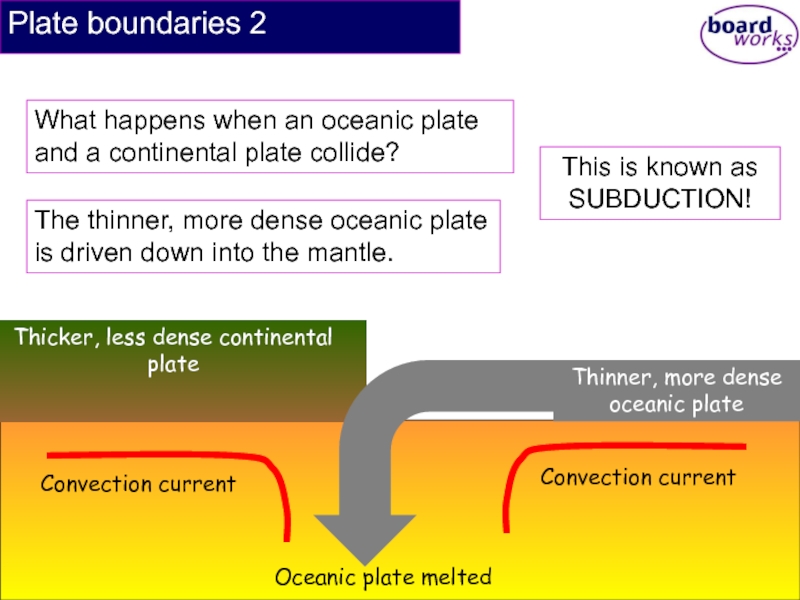
Слайд 16Plate boundaries 2
What happens when an oceanic plate and a continental
The thinner, more dense oceanic plate is driven down into the mantle.
Convection current
Convection current
Oceanic plate melted
This is known as SUBDUCTION!
Thicker, less dense continental plate
Thinner, more dense oceanic plate
Слайд 18
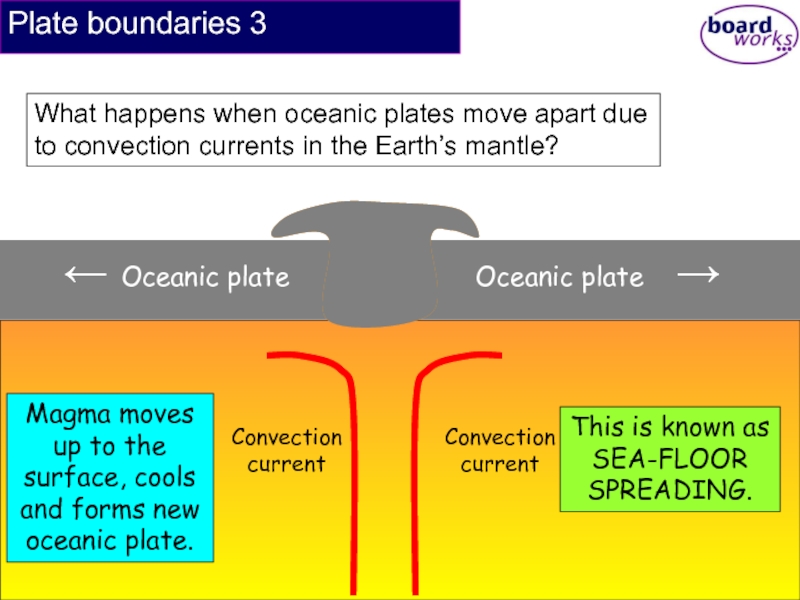
Convection current
Convection current
← Oceanic plate
What happens when oceanic plates move apart due to convection currents in the Earth’s mantle?
Magma moves up to the surface, cools and forms new oceanic plate.
This is known as SEA-FLOOR SPREADING.
Plate boundaries 3
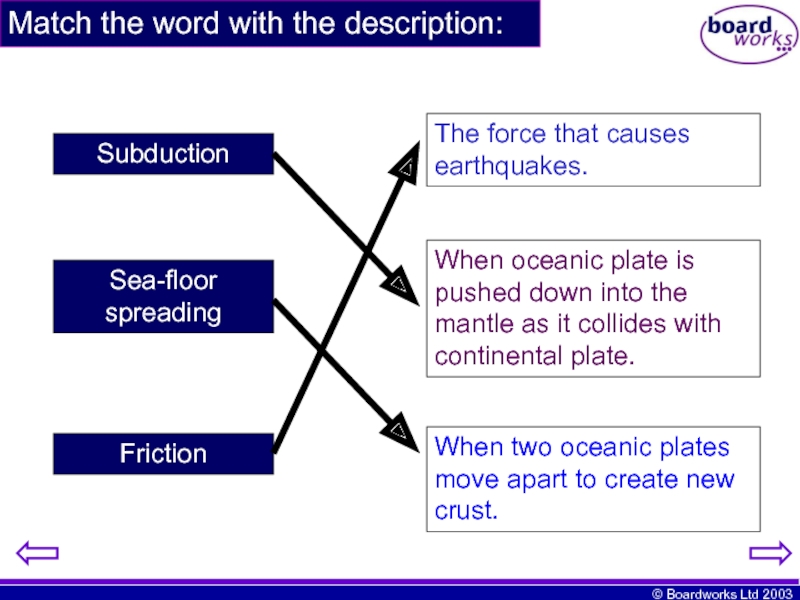
Слайд 20Match the word with the description:
Subduction
Sea-floor spreading
Friction
The force that causes earthquakes.
When
When two oceanic plates move apart to create new crust.
Слайд 21
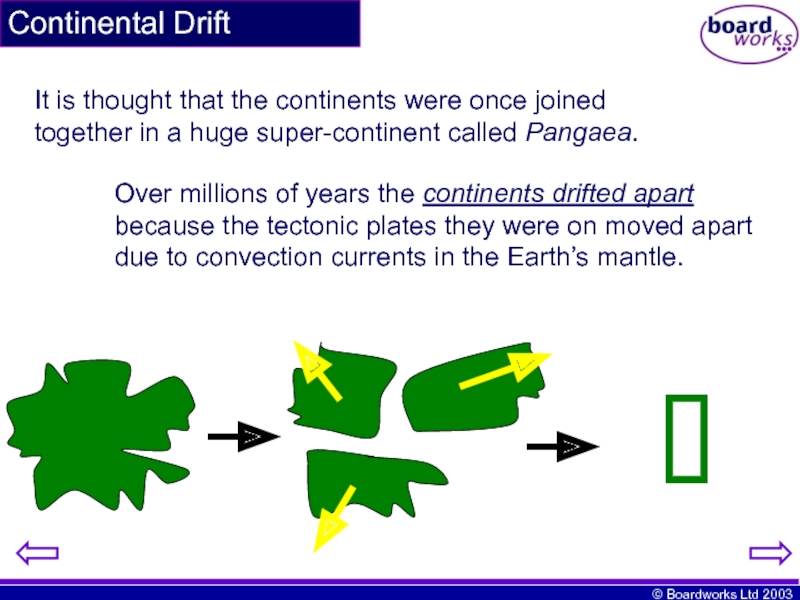
Continental Drift
It is thought that the continents were once joined together
Over millions of years the continents drifted apart because the tectonic plates they were on moved apart due to convection currents in the Earth’s mantle.
Слайд 23Evidence for continental drift theory:
The shapes of the continents fit like
The rock strata on separated continents are identical.
The fossil records on separated continents are identical.
Continent A
Continent B