- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
History of Earth’s Climate презентация
Содержание
- 1. History of Earth’s Climate
- 2. History of Earth’s Climate Life appeared ~3.8
- 3. Earth’s Temperature The temperature of
- 4. Earth’s Temperature If amount of solar energy
- 5. Earth’s Temperature if the amount of solar
- 6. Earth’s Temperature If the amount of
- 7. Greenhouse Effect Sun
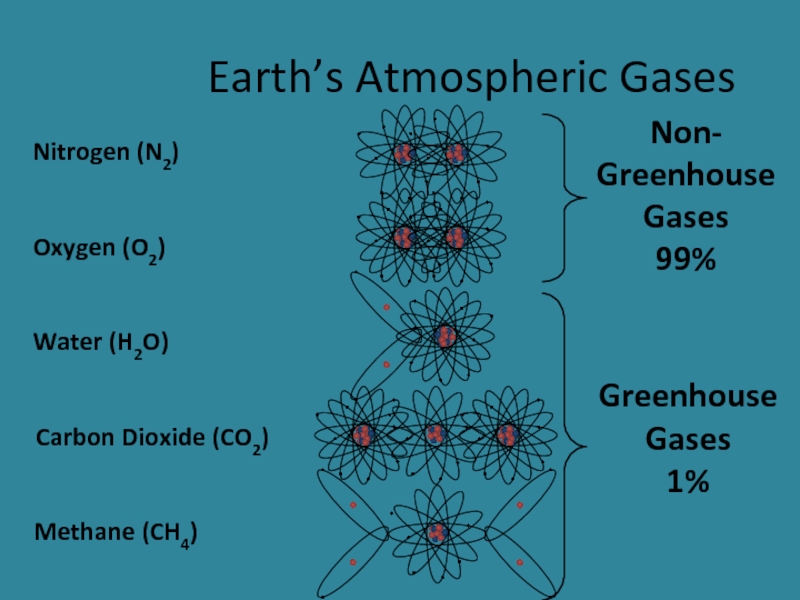
- 8. Earth’s Atmospheric Gases Non- Greenhouse Gases 99% Greenhouse Gases 1%
- 11. Recap and importance: The photochemical reactions produce
- 12. The Calvin cycle proceeds in three stages:
- 13. The affinity of Rubisco for CO2 is
- 14. Basics of foliage photosynthesis Any questions? Increasing
- 15. It is believed that photorespiration
- 16. Decarboxylation of malate (CO2 release) creates a
- 17. Crassulacean Acid Metabolism (CAM) Uses C4 pathways,
- 18. Efficiency in light
- 19. ISOTOPES AND LAND PLANT ECOLOGY C3 vs. C4 vs. CAM
- 20. Cool season grass most trees and shrubs
- 21. εp = δa - δf = εt
- 22. Ci, δi Inside leaf Ca,δa Ca,δa Cf,δf
- 23. Ci/Ca In C4, L is ~ 0.3,
- 24. Δ13C fraction-whole plant
- 25. δ13C varies with environment within C3 plants C3 plants
- 26. Quantum Yield (moles C fixed per photons
- 27. What happens when pCO2 changes? Ehleringer et
- 28. Quantum Yield (moles C fixed per photon
- 29. C3 versus C4 plants C3 plants are
- 30. 9/12/07
- 31. 9/12/07 Three modes of photosynthesis C3 pathway,
- 32. 9/12/07 Calvin Cycle
- 33. 9/12/07 Photorespiration depends on light
- 34. 9/12/07 Three modes of photosynthesis C4 pathway,
- 35. 9/12/07
- 36. 9/12/07 Three modes of photosynthesis C4 pathway
- 39. • There is a clear correlation between
Слайд 1History of Earth’s Climate
Earth formed ~4.6 billion years ago
Originally very hot
Sun’s
Liquid water present ~4.3 billion years
Слайд 2History of Earth’s Climate
Life appeared ~3.8 billion years ago
Photosynthesis began 3.5-2.5
Produced oxygen and removed carbon dioxide and methane (greenhouse gases)
Earth went through periods of cooling (“Snowball Earth”) and warming
Earth began cycles of glacial and interglacial periods ~3 million years ago
Слайд 3Earth’s Temperature
The temperature of the earth is directly related to the
Слайд 4Earth’s Temperature
If amount of solar energy absorbed by the earth is
Слайд 5Earth’s Temperature
if the amount of solar energy is greater than the
Слайд 6Earth’s Temperature
If the amount of solar energy is less than
Слайд 7Greenhouse Effect
Sun
To a certain degree, the earth acts like a
Слайд 11Recap and importance:
The photochemical reactions produce ATP and NADH at sites
The Dark Cycle (Calvin Cycle), or more descriptively, the carbon reactions of photosynthesis
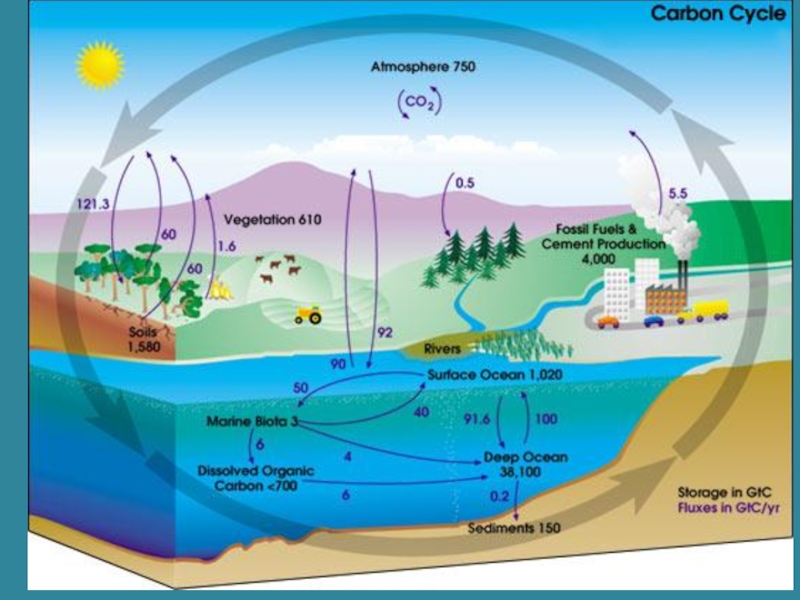
~200 billion tons of CO2 are converted to biomass each year
The enzyme ribulose biphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase, Rubisco, that incorporates CO2 is 40% of the protein in most leaves.
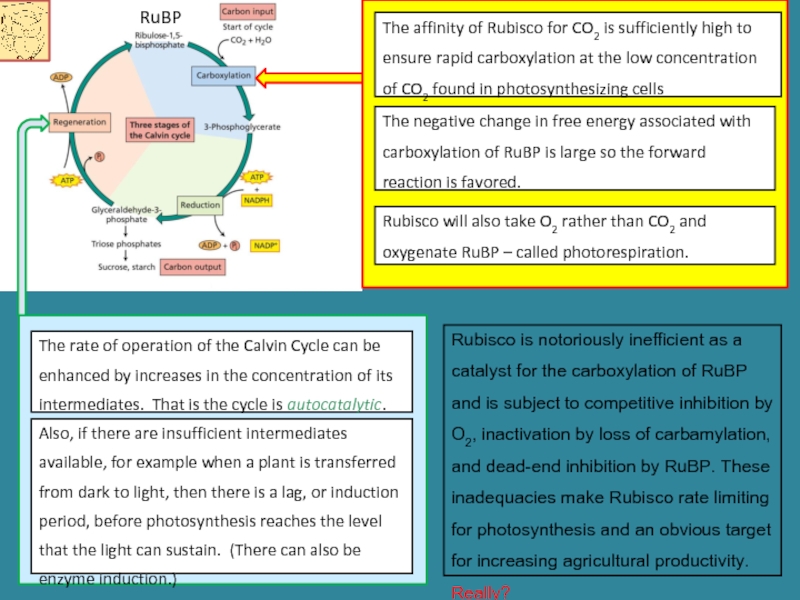
Слайд 12The Calvin cycle proceeds in three stages: carboxylation, reduction, and regeneration
Carboxylation
Reduction of 3-phosphoglycerate to form glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate which can be used in formation of carbon compounds that are translocated.
Regeneration of the CO2 acceptor ribulose-1, 5-biphosphate from glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
Слайд 13The affinity of Rubisco for CO2 is sufficiently high to ensure
The negative change in free energy associated with carboxylation of RuBP is large so the forward reaction is favored.
RuBP
Rubisco will also take O2 rather than CO2 and oxygenate RuBP – called photorespiration.
The rate of operation of the Calvin Cycle can be enhanced by increases in the concentration of its intermediates. That is the cycle is autocatalytic.
Also, if there are insufficient intermediates available, for example when a plant is transferred from dark to light, then there is a lag, or induction period, before photosynthesis reaches the level that the light can sustain. (There can also be enzyme induction.)
Rubisco is notoriously inefficient as a catalyst for the carboxylation of RuBP and is subject to competitive inhibition by O2, inactivation by loss of carbamylation, and dead-end inhibition by RuBP. These inadequacies make Rubisco rate limiting for photosynthesis and an obvious target for increasing agricultural productivity. Really?
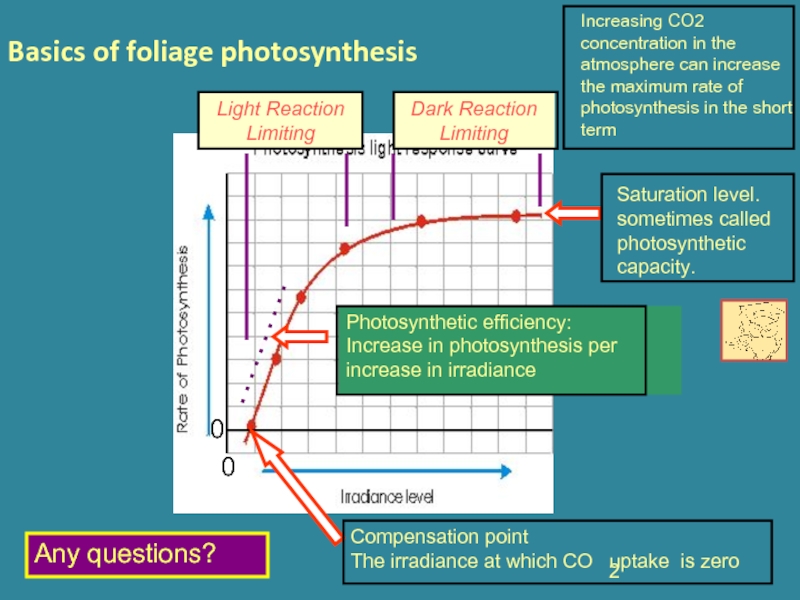
Слайд 14Basics of foliage photosynthesis
Any questions?
Increasing CO2 concentration in the atmosphere can
Слайд 15
It is believed that photorespiration in plants has increased over geologic
In the presence of higher O2 levels, photosynthesis rates are lower.
The inhibition of photosynthesis by O2 was first noticed by the German plant physiologist, Otto Warburg, in 1920, and called the "Warburg effect".
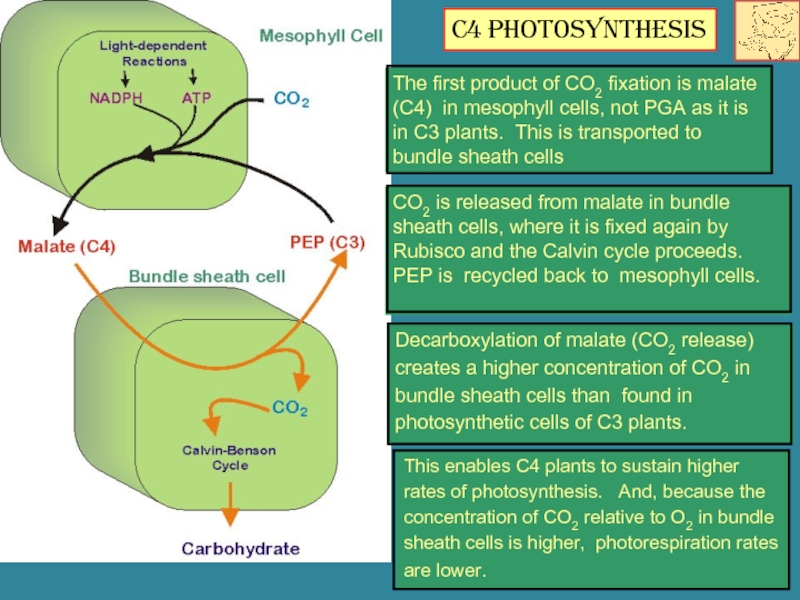
Слайд 16Decarboxylation of malate (CO2 release) creates a higher concentration of CO2
The first product of CO2 fixation is malate (C4) in mesophyll cells, not PGA as it is in C3 plants. This is transported to bundle sheath cells
CO2 is released from malate in bundle sheath cells, where it is fixed again by Rubisco and the Calvin cycle proceeds. PEP is recycled back to mesophyll cells.
This enables C4 plants to sustain higher rates of photosynthesis. And, because the concentration of CO2 relative to O2 in bundle sheath cells is higher, photorespiration rates are lower.
C4 Photosynthesis
Слайд 17Crassulacean Acid Metabolism (CAM)
Uses C4 pathways, but segregates CO2 assimilation and
CAM plants open their stomates at night. This conserves H2O. CO2 is assimilated into malic acid and stored in high concentrations in cell vacuoles
During the day, stomates close, and the stored malic acid is gradually recycled to release CO2 to the Calvin cycle
First discovered in succulents of the Crassulacea: e.g.,sedums
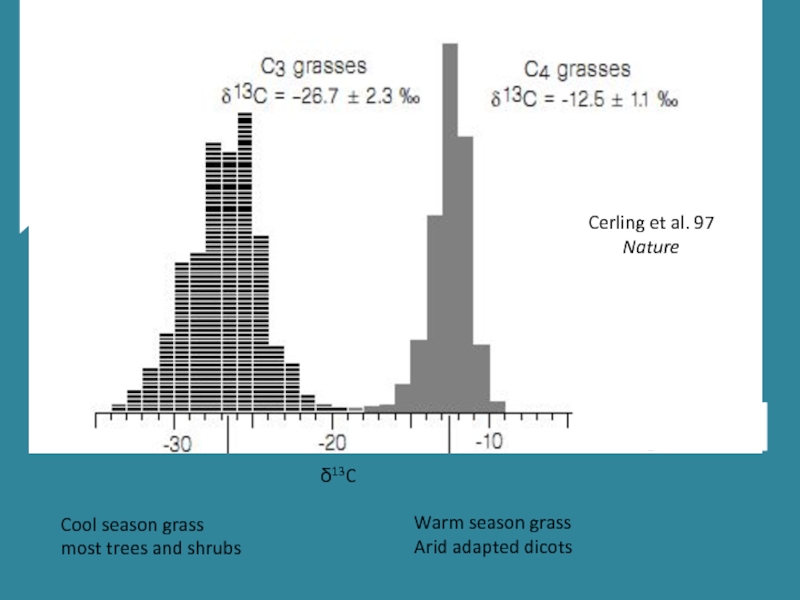
Слайд 20Cool season grass
most trees and shrubs
Warm season grass
Arid adapted dicots
Cerling et
Nature
δ13C
Слайд 21εp = δa - δf = εt + (Ci/Ca)(εf-εt)
When Ci ≈
When Ci << Ca (high rate of photosynthesis, closed stomata), then εp ≈ εt. Small fractionation, high plant δ13C values.
Слайд 22Ci, δi
Inside leaf
Ca,δa
Ca,δa
Cf,δf
φ1,δ1,εt
φ3,δ3,εt
φ2,δ2,εf
-12.4‰
-35‰
-27‰
Plant δ13C
(if δa = -8‰)
εp = εt =
εp = εf = +27‰
εf
0
0.5
1.0
Fraction C leaked (φ3/φ1 ∝ Ci/Ca)
δi
δf
δ1
εp = δa - δf = εt + (Ci/Ca)(εf-εt)
Слайд 23Ci/Ca
In C4, L is ~ 0.3, so εp is insensitive to
εp = εta+[εPEP-7.9+L(εf-εtw)-εta](Ci/Ca)
Under arid conditions, succulent CAM plants use PEP to fix CO2 to malate at night and then use RUBISCO for final C fixation during the daytime. The L value for this is typically higher than 0.38. Under more humid conditions, they will directly fix CO2 during the day using RUBISCO. As a consequence, they have higher, and more variable, εp values.
εp = 4.4+[-10.1+L(26.3)](Ci/Ca)
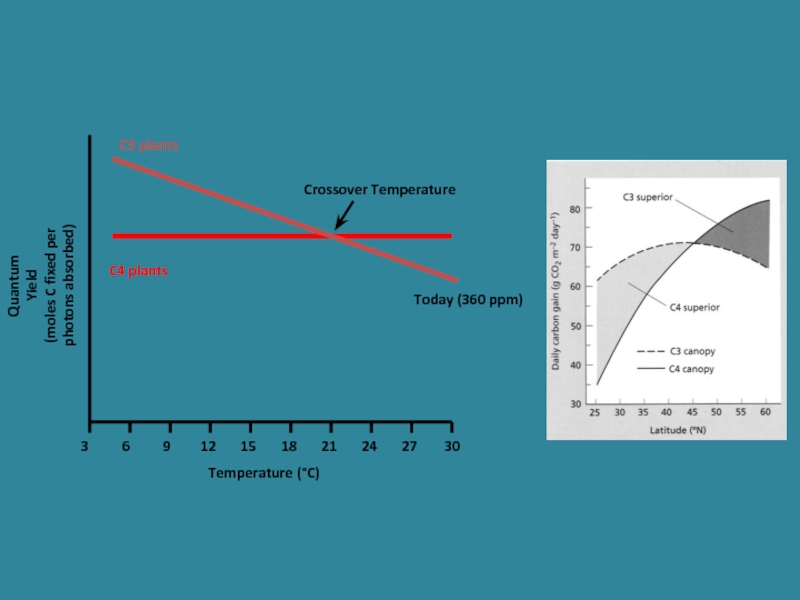
Слайд 26Quantum
Yield
(moles C fixed per
photons absorbed)
Temperature (°C)
3
6
9
12
15
18
21
24
27
30
C4 plants
C3 plants
Crossover Temperature
Today (360 ppm)
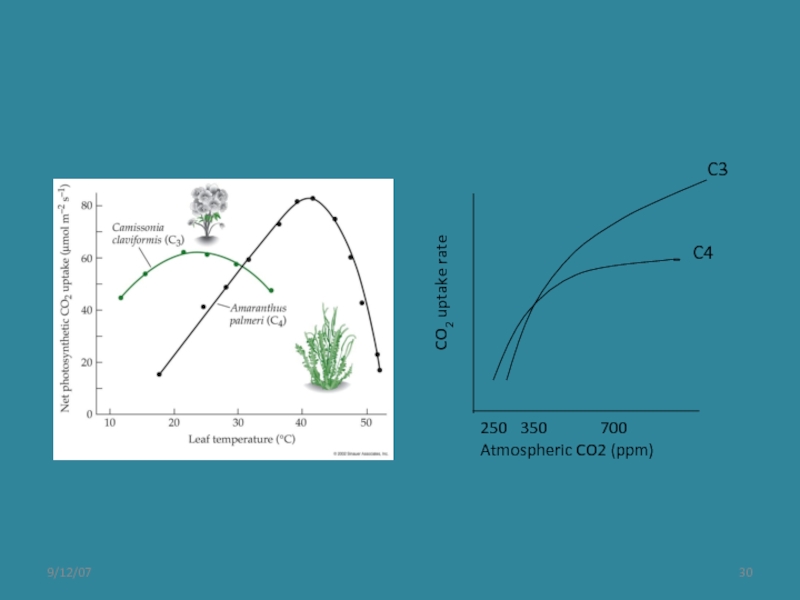
Слайд 27What happens when pCO2 changes?
Ehleringer et al. 1997 Oecologia
C3 decreases in
Слайд 28Quantum
Yield
(moles C fixed per
photon absorbed)
Temperature (°C)
3
6
9
12
15
18
21
24
27
30
C4 plants
C3 plants
Crossover Temperature
Today (360 ppm)
Слайд 29C3 versus C4 plants
C3 plants are favoured in environments where water
C4 plants are favoured in environments where water is limiting and light and temperatures are high (tropical / subtropical habitats)
Слайд 319/12/07
Three modes of photosynthesis
C3 pathway, aka Calvin cycle, most common.
Ribulose
Phosphoglyceric acid (PGA) is 3-C sugar formed during CO2 uptake.
Photorespiration makes photosynthesis less efficient but also protects cells from excess light energy.
At high CO2:O2 ratios, Rubisco is more efficient, thus C3 plants respond more to elevated CO2 than do C4 plants
Most trees, shrubs, cool-season grasses
Слайд 339/12/07
Photorespiration
depends on light
“wastes” CO2
protects against light damage
Слайд 349/12/07
Three modes of photosynthesis
C4 pathway, aka Hatch-Slack, has additional enzyme, PEP
Oxaloacetate (OAA) is 4-C sugar formed during CO2 uptake.
Rubisco concentrated in bundle sheath cells, where OAA delivers CO2.
Photorespiration limited because CO2:O2 is much higher inside bundle sheath cells than in C3’s.
Less Rubisco needed for psn means higher N-use efficiency.
Слайд 369/12/07
Three modes of photosynthesis
C4 pathway
Higher T optimum and light saturation.
High water use efficiency (C gained per H2O lost) because stomates can be partly closed.
Lower response to elevated CO2
Cost of C4: additional ATP is needed for PEP cycle, which may limit C4 growth at low light levels
2000 species in 18 families; half of all grass (Poaceae) species (warm-season grasses)
Слайд 39• There is a clear correlation between the amount of anthropogenic
• Atmospheric oxygen is declining proportionately to CO2 increase and fossil fuel combustion.
• For the last half century, the CO2 airborne fraction (AF) parameter remained consistent and averaged at 0.55 (the AF parameter is the ratio of the increase in atmospheric CO2 concentration to fossil fuel-derived CO2 emissions). AF has been introduced to assess short- and long-term changes in the atmospheric carbon content; in particular, AF of 0.55 indicates that the oceans and terrestrial ecosystems have cumulatively removed about 45 % of anthropogenic CO2 from the atmosphere over the last half century [6].
• The isotopic signature of fossil fuels (e.g., the lack of 14C and the depleted level of 13C carbon isotopes) is detected in atmospheric CO2.
• There exists an interhemispheric gradient in the atmospheric CO2 concentrations in the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. In particular, the predominance of fossil-derived CO2 emissions in more industrially developed Northern Hemisphere (compared to the Southern Hemisphere) causes the occurrence of the atmospheric CO2 gradient in the amount of about 0.5 ppm per GtC per year [6].
• There have been dramatic changes in RFCO2 values over the last decades. For example, during 1995–2005, the RFCO2 increased by about 0.28 W/m2 (or about 20 % increase), which represents the largest increase in RFCO2 for any decade since the beginning of the industrial era. RFCO2 in 2005 was estimated at RFCO2=1.66±0.17 W/m2 (corresponding to the atmospheric CO2 concentration of 379±0.65 ppm), which is the largest RF among all major forcing factors (The concept of radiative forcing (RF))
• The data show that the changes in the land use greatly contributed to the RFCO2 value in the amount of about 0.4 W/m2 (since the beginning of the industrial era). This implies that the remaining three quarters of RFCO2 can be attributed to burning fossil fuels, cement manufacturing, and other industrial CO2 emitters [6].