- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Earth Materials презентация
Содержание
- 1. Earth Materials
- 2. 3- Basic Building Blocks Atoms Nucleus contains
- 3. Basic Building Blocks Isotope – an atom
- 4. Basic Building Blocks 3-
- 5. 3- http://chemistry.about.com/library/pdfs/PeriodicTableMuted.pdf
- 6. Basic Building Blocks 3-
- 7. 3- Minerals Naturally occurring Inorganic 1 or
- 8. 3- Minerals 4,000+ minerals Each has
- 9. 3- Rock Forming Minerals Approximately 12 common
- 10. Rock Forming Minerals Minerals classified on type
- 11. 3- Rocks Aggregate or assemblage of one
- 12. 3- Igneous Rocks Form via cooling magma
- 13. 3- Weathering Breaking down of rocks Physical
- 14. 3- Physical Weathering
- 15. 3- Chemical Weathering
- 16. 3- Sedimentary Rocks Weathering results in sediment
- 17. Two Types of Sedimentary Rocks Detrital –
- 18. Sedimentary Rocks 3-
- 19. 3- Metamorphic Rocks Changes through heat and
- 20. Contact Metamorphism 3-
- 21. Regional Metamorphism 3-
- 22. Foliation 3- Figure 3.27, page 84
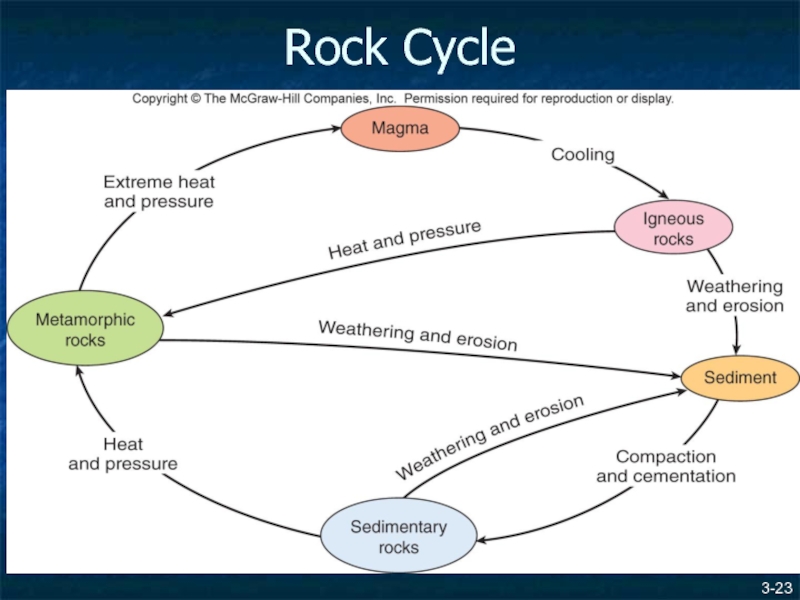
- 23. 3- Rock Cycle
- 24. 3- Rocks as Indicators of the Past Figure 3.30, page 87 Figure 3.31, page 88
- 25. Minerals 1A sulfur 2A native copper 3A
Слайд 23-
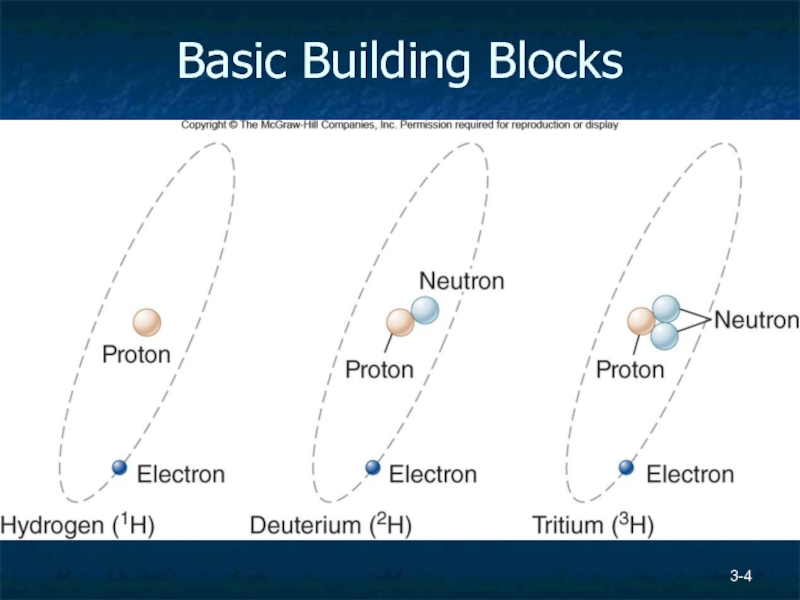
Basic Building Blocks
Atoms
Nucleus contains protons and neutrons
Electrons orbit the nucleus
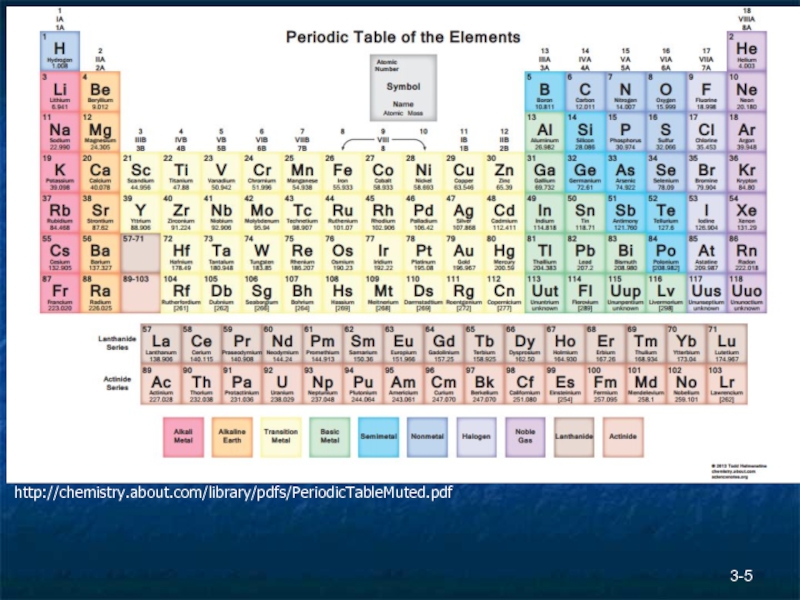
Elements
Atoms with
Hydrogen has one proton, Helium has two
Periodic Table of Elements
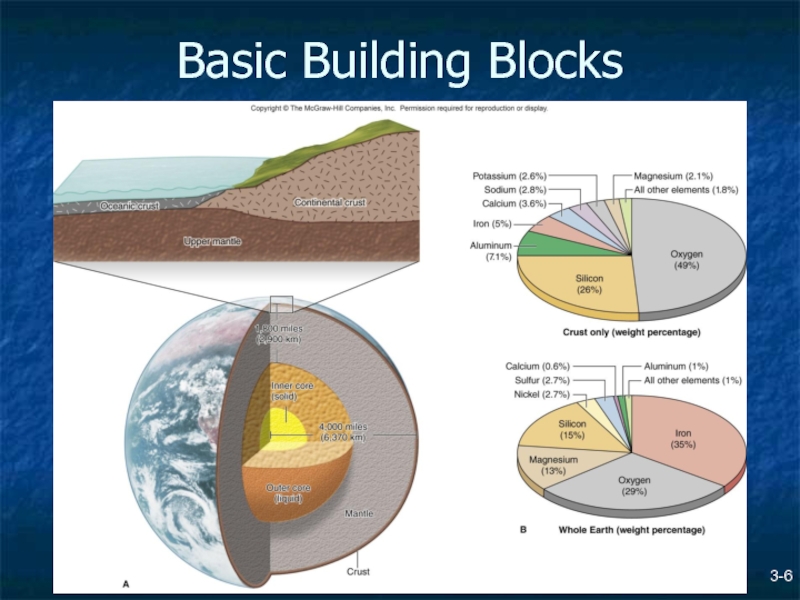
Слайд 3Basic Building Blocks
Isotope – an atom with varying number of neutrons,
Ion – atom has gained or loss and electron and is positively or negatively charged
Sodium Na+
Iron Fe 3+
Chlorine Cl-
Oxygen 02
3-
Слайд 73-
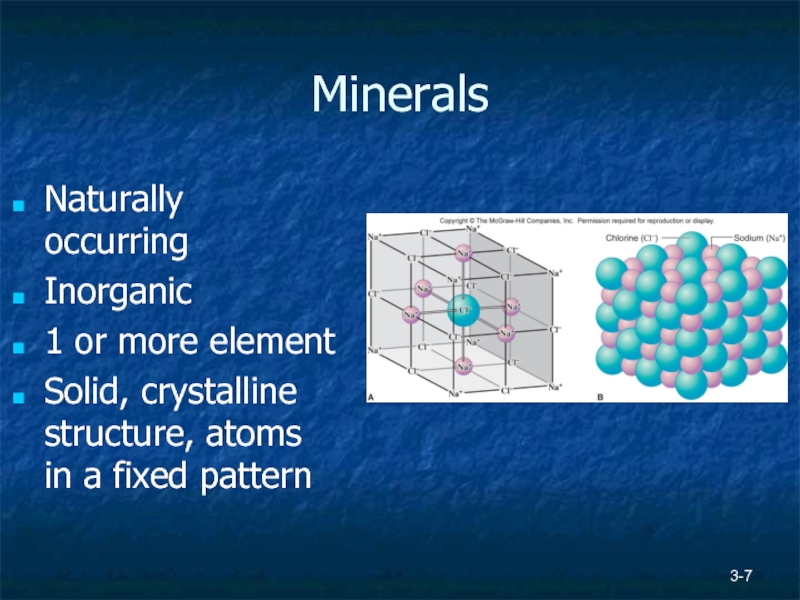
Minerals
Naturally occurring
Inorganic
1 or more element
Solid, crystalline structure, atoms in a fixed
Слайд 83-
Minerals
4,000+ minerals
Each has unique chemical and physical properties (for ex. -
Physical properties controlled by structure and composition
Building blocks of rocks
Слайд 93-
Rock Forming Minerals
Approximately 12 common minerals make up crust
Pyroxene and Amphibole
Feldspars – aluminum rich silicates
Clay minerals – result from weathering of silicates, broken down by rainwater
Quartz – almost pure silicon and oxygen
Calcite - limestone
Слайд 10Rock Forming Minerals
Minerals classified on type of negatively charged ion within
Sulfides contain sulfur bonded to positive Pb, Zn or Fe
Carbonates bonded to C and O
Oxides – negative charged O
Sulfates – negative charged SO4
Silicates – largest class, negatively charged Si and O4
Si and O make up 75% of crust by weight
3-
Слайд 113-
Rocks
Aggregate or assemblage of one or more types of minerals; many
Texture is studied, way mineral grains are arranged. Coarse, fine or mixed grains and shape of grain.
Formed when magma cools, minerals precipitate out of solution; grains can grow. Or exposure to heat/pressure.
Three types
Igneous
Sedimentary
Metamorphic
Слайд 123-
Igneous Rocks
Form via cooling magma
Intrusive cooled
Coarse grained
When magma breaches Earth’s
Extrusive cooled
Fine grained
Слайд 133-
Weathering
Breaking down of rocks
Physical weathering
Frost wedging
Plant roots
Crystal growth – minerals precipitate
Fluctuations in daily temperature
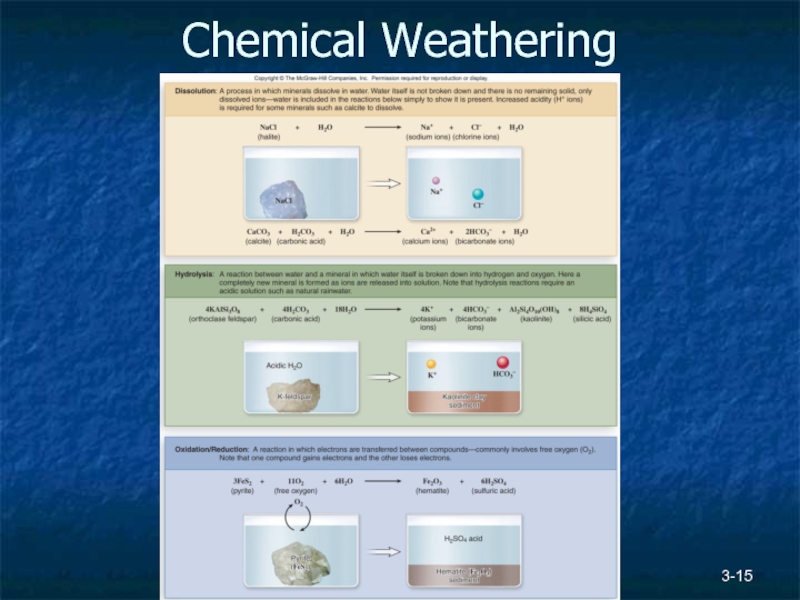
Chemical
Dissolution
Hydrolysis
Oxidation / reduction
Слайд 163-
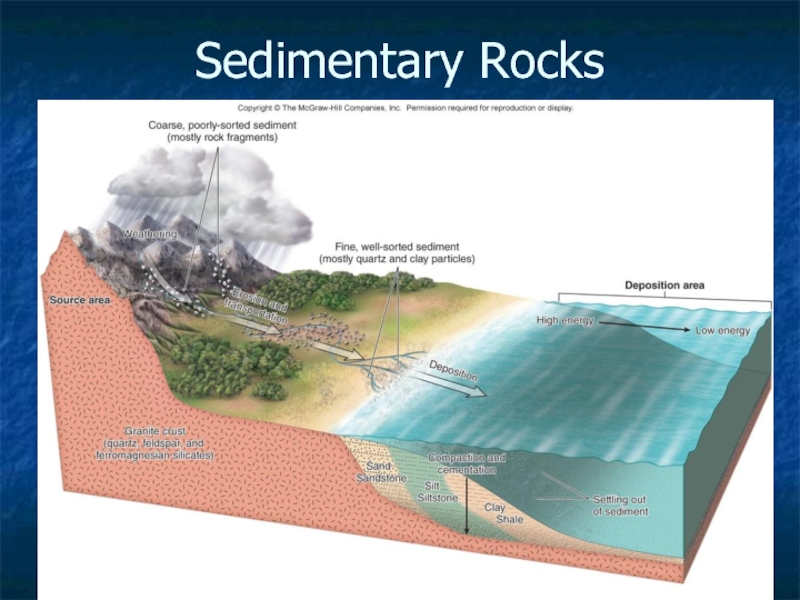
Sedimentary Rocks
Weathering results in sediment
Compacted and cemented sediment = sedimentary
Erosion – sediment and ions removed from given area.
Rock or sediment dissolved, picked up by wind or water, or abraded
Слайд 17Two Types of Sedimentary Rocks
Detrital – made of preexisting rock &
Material was deposited in low lying areas
Shale, sandstone
Table 3.2, page 80
Chemical – dissolved ions precipitate out of solution
Limestone, rock salt (halite)
Table 3.3, page 81
3-
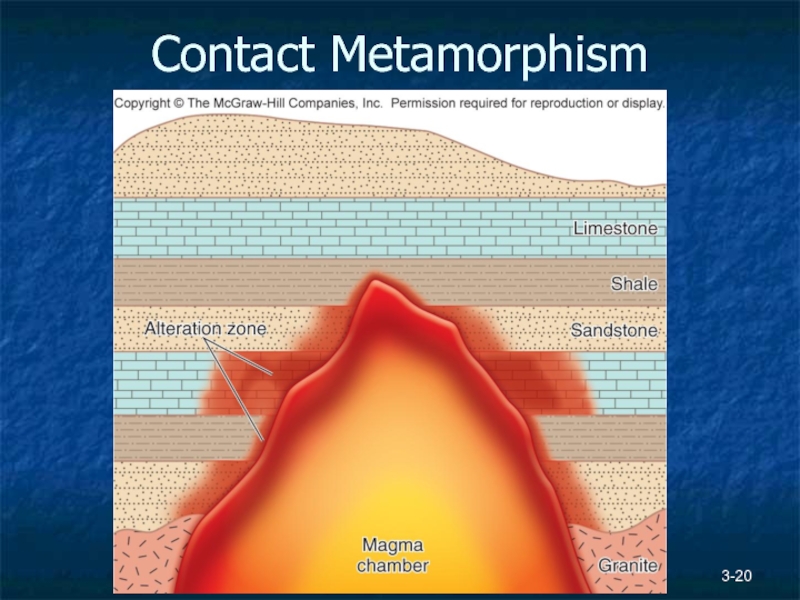
Слайд 193-
Metamorphic Rocks
Changes through heat and pressure, not enough to melt rock.
Contact metamorphism
Heat, low pressure
Nonfoliated texture, marble and quartzite
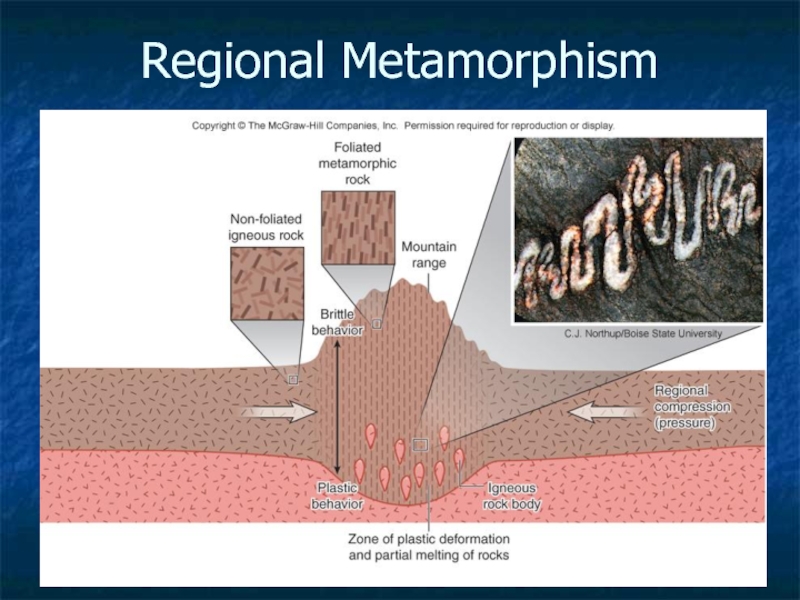
Regional metamorphism
heat, high pressure
Foliated texture due to pressure. Minerals reorient into parallel structure. Slate and gneiss.
Слайд 25Minerals
1A sulfur
2A native copper
3A graphite
4A galena (lead sulfide)
6A pyrite (fool’s
7A hematite
9A magnetite
11A halite
13A calcite
18A feldspar
20A quartz
21 A quartz
23 A mica, muscovite
Rocks
1B granite
2B granite, pegmatite
5B gabbro (oceanic crust)
8B basalt
12B obsidian
13B volcanic breccia
15B sandstone, siliceous
16B sandstone, arkose
17B shale
20B limestone, chalk
22B limestone, travertine
24B coal, bituminous
25B slate
30B quartzite
31B marble
32B anthracite coal
3-