- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Earth from a Larger Perspective презентация
Содержание
- 1. Earth from a Larger Perspective
- 2. We’re Affected by What’s in Space Wave
- 3. 2- The Solar System See figures on pages 38 and 39 of textbook.
- 4. 2- Our Sun an Average Star Hot
- 5. 2- The Planets Terrestrial planets Have rocky
- 6. 2- Pluto Demoted as a planet in
- 7. New Horizons Probe to Pluto Launched Jan.
- 8. New Horizons Probe to Pluto 2- https://blogs.nasa.gov/pluto/2016/08/04/pluto-what-a-journey/ http://www.nasa.gov/feature/one-year-later-new-horizons-top-10-discoveries-at-pluto Pluto Charon (moon)
- 9. 2- Comets and Asteroids Comets Small,
- 10. 2- The Moon Earth’s only satellite Gravity
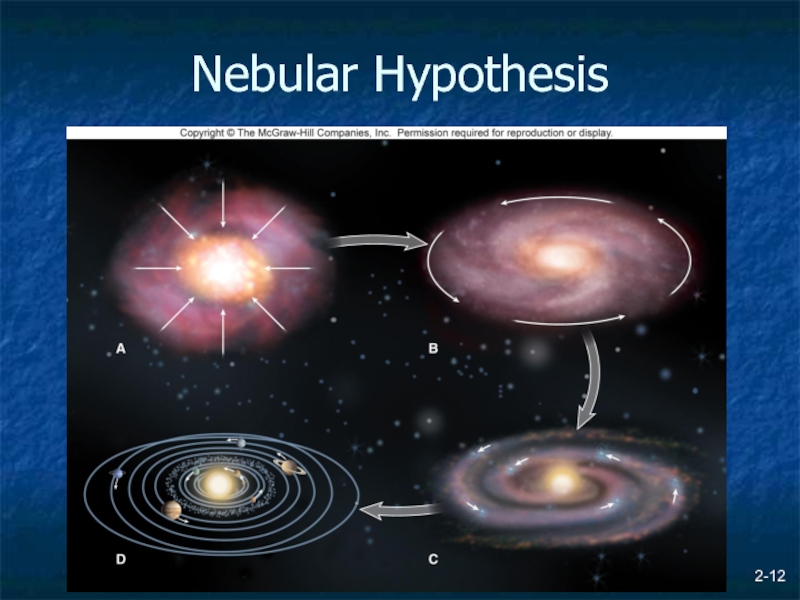
- 11. 2- Origin of the Solar System Nebular
- 12. 2- Nebular Hypothesis
- 13. 2- How Reliable is Nebular Hypothesis? Most
- 14. 2- Other Stars in the Universe Galaxy
- 15. Big Bang Theory Proposed in 1927 that
- 16. Other Stars in the Universe 2-
- 17. 2- Clockwise Rotating Galaxy Similar to The Milky Way
- 18. 2- Does Life Exist Beyond Earth? Life
- 19. 2- Possible Intelligent Life Rare Earth Hypothesis
- 20. 2- Solar System Hazards Electromagnetic radiation –
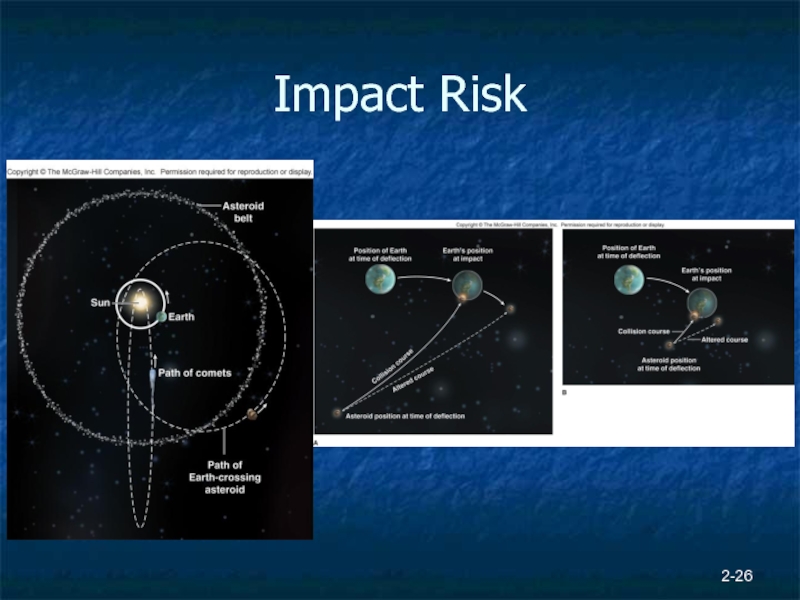
- 21. Solar System Hazards Asteroid and comet impacts
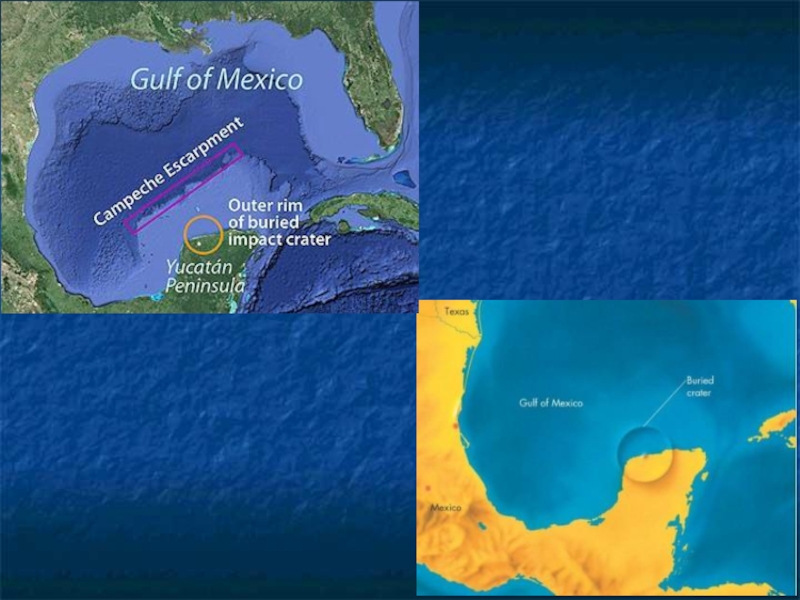
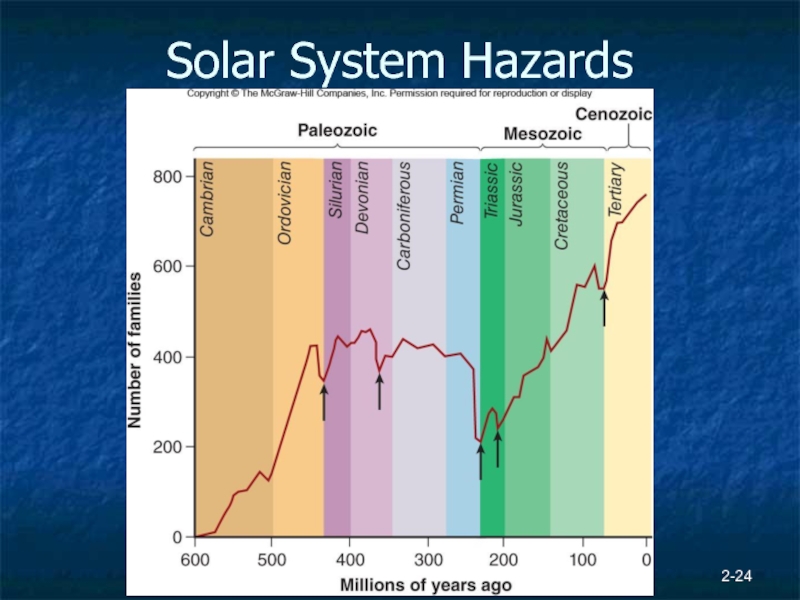
- 24. Solar System Hazards 2-
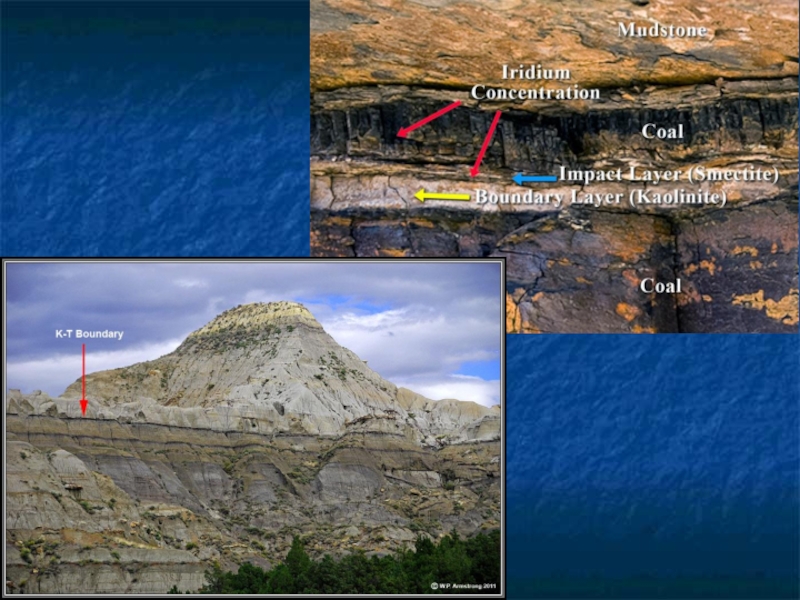
- 25. 2- Impacts Mesozoic/Cenozoic extinction event – KT boundary 65 mybp 1994 - impact on Jupiter
- 26. 2- Impact Risk
Слайд 2We’re Affected by What’s in Space
Wave energy from the sun drives
our climate
Moon’s gravity affects tides, ocean currents
Other planets’ gravity affects asteroids in Earth’s orbit
We have been and are hit by meteorites
Space and ground based telescopes
Moon’s gravity affects tides, ocean currents
Other planets’ gravity affects asteroids in Earth’s orbit
We have been and are hit by meteorites
Space and ground based telescopes
2-
Слайд 42-
Our Sun an Average Star
Hot dense center surrounded by an outer,
less dense atmosphere
Nuclear fusion of hydrogen (H) and helium (He) caused by sun’s gravity produces wave energy. See Fig. 2.7 B, page 39.
Releases electromagnetic radiation – energy that travels in series of waves and is converted to heat when it reaches a planet
When H is used up, nuclear fusion continues producing heavier elements (C, Ni, Fe, O) until star goes supernova
Nuclear fusion of hydrogen (H) and helium (He) caused by sun’s gravity produces wave energy. See Fig. 2.7 B, page 39.
Releases electromagnetic radiation – energy that travels in series of waves and is converted to heat when it reaches a planet
When H is used up, nuclear fusion continues producing heavier elements (C, Ni, Fe, O) until star goes supernova
Слайд 52-
The Planets
Terrestrial planets
Have rocky surfaces
Small
Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars
Gas planets
Made up
of H and He, no solid surface
Large
Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune
Large
Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune
Слайд 62-
Pluto
Demoted as a planet in 2006 but has enough gravity to
maintain solar orbit
Rocky, cold and small, frozen water/methane
Very far away, last in solar system
Rocky, cold and small, frozen water/methane
Very far away, last in solar system
Слайд 7New Horizons Probe to Pluto
Launched Jan. 19, 2006
Arrived July 13, 2015
Pluto’s
largest moon named Charon
Variations in atmospheric pressure, may have liquids on surface
http://www.nasa.gov/feature/one-year-later-new-horizons-top-10-discoveries-at-pluto
Variations in atmospheric pressure, may have liquids on surface
http://www.nasa.gov/feature/one-year-later-new-horizons-top-10-discoveries-at-pluto
2-
Слайд 8New Horizons Probe to Pluto
2-
https://blogs.nasa.gov/pluto/2016/08/04/pluto-what-a-journey/
http://www.nasa.gov/feature/one-year-later-new-horizons-top-10-discoveries-at-pluto
Pluto
Charon (moon)
Слайд 92-
Comets and Asteroids
Comets
Small, 1-10 km in diameter
Rocky fragments in ice
and frozen gases
Tail caused by evaporating ice
Highly elliptical orbits
Asteroids
Small, mostly rock and metallic materials
Most from asteroid belt between Jupiter and Mars
Tail caused by evaporating ice
Highly elliptical orbits
Asteroids
Small, mostly rock and metallic materials
Most from asteroid belt between Jupiter and Mars
Слайд 102-
The Moon
Earth’s only satellite
Gravity controls tides and helps stabilize Earth’s “wobble”
Color
coding – reddish is older rocks and bluish represents younger rocks from lava flows
Слайд 112-
Origin of the Solar System
Nebular Hypothesis
Solar system formed from rotating cloud
of gas and dust (nebula)
Gases mainly hydrogen and helium
Disturbed by supernova, cloud contracted
Higher temperatures and pressures
Solid material formed, accretion due to gravity
Planetesimals + more accretion = Planets
Enough nuclear fusing w/ H and He that new star was born (our sun)
Gases mainly hydrogen and helium
Disturbed by supernova, cloud contracted
Higher temperatures and pressures
Solid material formed, accretion due to gravity
Planetesimals + more accretion = Planets
Enough nuclear fusing w/ H and He that new star was born (our sun)
Слайд 132-
How Reliable is Nebular Hypothesis?
Most bodies rotate and revolve counter-clockwise (Venus
is the exception)
All bodies in same plane with solar equator
Most craters occurred early in the solar system’s history
Accretion disks and planetary systems have been found around other stars
Radiometric dating
All bodies in same plane with solar equator
Most craters occurred early in the solar system’s history
Accretion disks and planetary systems have been found around other stars
Radiometric dating
Слайд 142-
Other Stars in the Universe
Galaxy – large groupings of stars
Our galaxy
is the Milky Way
Most bright points in the night sky are galaxies
The Big Bang Theory explains how the universe was formed from a central explosion
Most bright points in the night sky are galaxies
The Big Bang Theory explains how the universe was formed from a central explosion
Слайд 15Big Bang Theory
Proposed in 1927 that all matter had once existed
in a single point
1929 Edwin Hubble proved all galaxies are moving away from each other
Measurements from Hubble and Spitzer space telescopes
Cosmic radiation coming from all of deep space not a single source
1929 Edwin Hubble proved all galaxies are moving away from each other
Measurements from Hubble and Spitzer space telescopes
Cosmic radiation coming from all of deep space not a single source
2-
Слайд 182-
Does Life Exist Beyond Earth?
Life on Earth
Earth is 4.6 billion years
old
Life started in extreme conditions
Extremophile bacteria
Need liquid water
Orbit in habitable zone
Distance from sun or star that liquid water can exist
Life started in extreme conditions
Extremophile bacteria
Need liquid water
Orbit in habitable zone
Distance from sun or star that liquid water can exist
Слайд 192-
Possible Intelligent Life
Rare Earth Hypothesis
Energy output of sun fairly stable
Earth’s processes
help regulate CO2
Jupiter ‘catches’ asteroids and comets
Moon has reduced wobble of Earth’s axis
Jupiter ‘catches’ asteroids and comets
Moon has reduced wobble of Earth’s axis
Слайд 202-
Solar System Hazards
Electromagnetic radiation – damages living cell tissue
UV radiation and
the ozone layer
Chlorine and fluorine based gases (CFCs) deplete O3
1987 Montreal Protocol – nations agree to phase out use of CFCs
Gamma ray burst from exploding stars destroys O3
Chlorine and fluorine based gases (CFCs) deplete O3
1987 Montreal Protocol – nations agree to phase out use of CFCs
Gamma ray burst from exploding stars destroys O3
Слайд 21Solar System Hazards
Asteroid and comet impacts
About 175 impact sites discovered on
Earth
214 million year impact site due to asteroid >3 miles in diameter
214 million year impact site due to asteroid >3 miles in diameter
2-