- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Radiation safety training презентация
Содержание
- 1. Radiation safety training
- 2. Basic Radiation Theory and Fundamentals Sources of
- 4. Nucleus: Contains Protons (+1 charge)
- 5. Ionizing versus Non-Ionizing Radiation
- 6. Absorbed The rad (radiation
- 7. Key ‘Dose’ Terms Cont. 1 Sv =
- 8. Radioactivity: The spontaneous decomposition or disintegration of
- 9. Alpha Particle Massive; +2 charge Beta Particle
- 11. Compton Scatter
- 12. Common Sources of Ionizing Radiation Sources of
- 15. CyberKnife M6 Series TomoTherapy H
- 16. Biological Response to Ionizing Radiation – Key
- 17. Radiation Biology – Key Terms Somatic Effects:
- 18. Radiation Causes Ionizations of: ATOMS
- 19. Radiation Biology – Mechanisms DNA is the
- 20. Radiation Biology – Affects What can Happen
- 21. Radiation Biology – Factors Affecting Biological Response
- 22. Acute versus Chronic Exposures Chronic radiation exposures:
- 23. Radiation Risk Radiation Exposure Is Assumed to
- 25. The Principles of Radiological Protection Epidemiological Studies
- 26. Justification – No practice shall be
- 27. Epidemiology – the study of patterns, causes,
- 29. Epidemiological studies are performed and presented UNSCEAR
- 31. Unrestricted Area – Any area that is
- 32. The developing embryo/fetus, with rapidly dividing cells,
- 33. Member of the Public: means an individual
- 34. Radiation Protection Policies and Procedures
- 35. The most important policy to remember is
- 36. ALARA is an acronym for As Low
- 37. Reduce Exposures by Minimizing Time & Dose
- 38. Reduce Exposures by Maximizing Distance
- 39. Inverse Square Law - Example
- 40. Close the Jaws/MLC, Plug Beam, and Beam
- 41. Some areas require specific authorization or an
- 42. Emergency Buttons/Devices Warning Lights Note: Actuating
- 43. Operators must physically enter the test cell,
- 44. Personnel Monitoring Facility Monitoring Radiation Detectors Radiation Monitoring
- 45. Dosimetry Use is a Requirement for all
- 46. Test Cell/Bunker Commissioning and Routine Leakage Surveys
- 47. Radiation Leakage Surveys and Area Monitoring Gas
- 48. Briefly inspect the instrument for physical damage
- 49. Management Responsibilities Promote a positive radiation safety
- 50. Limit the radiation dose to involved persons
- 51. For more information, visit: http://sharepoint/Radiation Safety/ Procedures, forms, links, contact information, announcements, and more
- 52. Accuray is committed to maintaining a robust
- 53. Radiation Safety Exam Please email all questions and comments to: RSO@accuray.com
Слайд 1Radiation Safety Training
Required annually for all Accuray “Radiation Worker” personnel
Intended to provide the Knowledge, Skills and Abilities needed to work safely with radiation
Successful training completion involves:
Reading and Understanding SOP 027444 “Radiation Safety Program”
Scoring 80% or higher on the Exam
Please email all questions and comments to: RSO@accuray.com
Слайд 2Basic Radiation Theory and Fundamentals
Sources of Ionizing Radiation
Biological Effects and Risks
Radiation Protection Standards
Controlling Radiation Dose
Radiation Monitoring
Responsibilities for Radiation Protection
Emergency Response
Radiation Safety Training Exam
Training Topics
Слайд 3
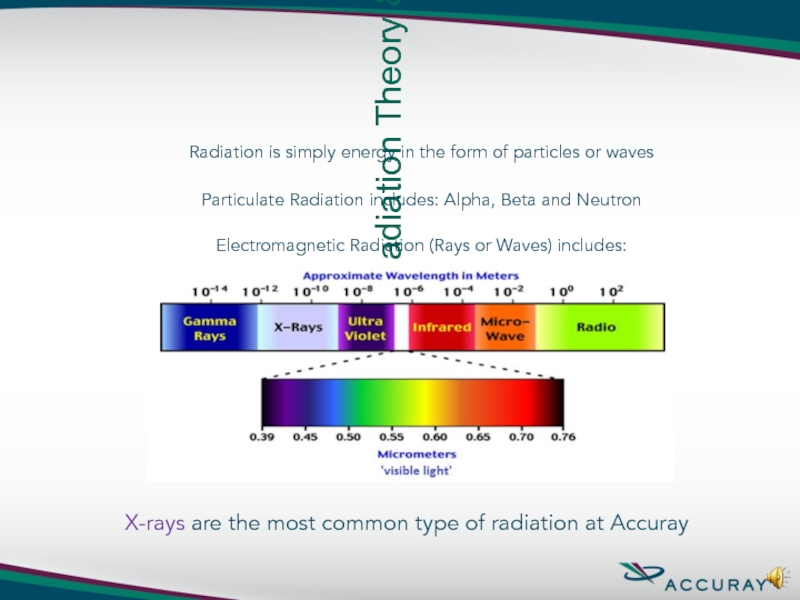
Basic Radiation Theory & Fundamentals
Radiation is simply energy in
Particulate Radiation includes: Alpha, Beta and Neutron Electromagnetic Radiation (Rays or Waves) includes:
X-rays are the most common type of radiation at Accuray
Слайд 4
Nucleus: Contains Protons (+1 charge)
and Neutrons (no charge)
Nuclear Diameter ~
Electrons: orbit the nucleus (-1 charge)
Atomic Diameter ~ 10-10 m More than 99.9% of the atomic mass and all the positive charge are in the nucleus ! Atomic vs. Nuclear Dimensions !
Atomic Structure
Слайд 5Ionizing versus Non-Ionizing Radiation
Ionizing Radiation: Means radiation with sufficient energy to liberate
The difference between ionizing and non-ionizing radiation is energy.
Слайд 6Absorbed The rad (radiation absorbed dose) is the
Dose ionizing radiation in a material. One rad equals 100 ergs per gram.
The SI unit of absorbed dose is the Gray. 1 Gy = 1 Joule/kg = 100 rad
Dose Takes into account the biological effectiveness, or quality, of different types of
Equivalent radiation. Dose Equivalent, measured in rems or Sieverts, is equal to the absorbed dose times a quality factor (Q).
Equivalent Takes into account the different probability of effects that occur with the same
Dose absorbed dose delivered by radiations with different weighting factors (WR).
The SI unit of Equivalent dose is the Sievert. 1 Sv = 100 rem
Exposure The unit of radiation exposure in air is the Roentgen (R). It is defined as that quantity of x-rays causing ionization in air equal to 2.58 x 10-4 coulombs per kilogram (C/kg).
Air Kerma Kinetic Energy Released per unit Mass of a small volume of air when it is irradiated by an x-ray beam. Kerma is measured in Gy.
Key ‘Dose’ Terms
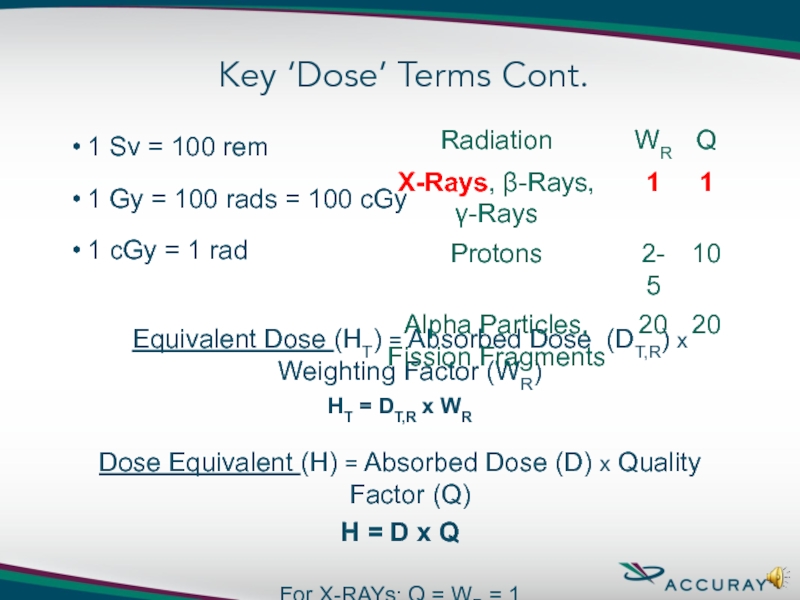
Слайд 7Key ‘Dose’ Terms Cont.
1 Sv = 100 rem
1 Gy = 100
1 cGy = 1 rad
Equivalent Dose (HT) = Absorbed Dose (DT,R) x Weighting Factor (WR)
HT = DT,R x WR
Dose Equivalent (H) = Absorbed Dose (D) x Quality Factor (Q)
H = D x Q
For X-RAYs: Q = WR = 1
1cGy = 1 rad = 1 rem & 1 Gy = 1 Sv
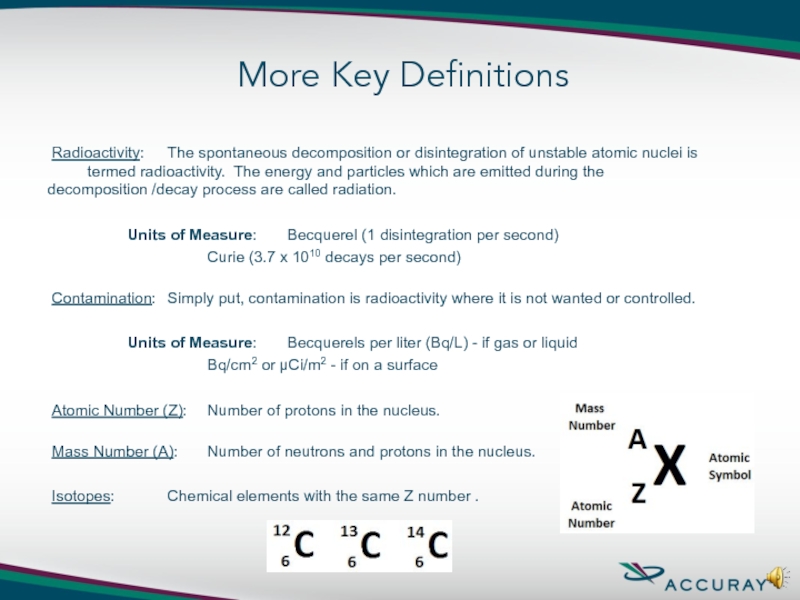
Слайд 8 Radioactivity: The spontaneous decomposition or disintegration of unstable atomic nuclei is
Units of Measure: Becquerel (1 disintegration per second)
Curie (3.7 x 1010 decays per second)
Contamination: Simply put, contamination is radioactivity where it is not wanted or controlled.
Units of Measure: Becquerels per liter (Bq/L) - if gas or liquid
Bq/cm2 or µCi/m2 - if on a surface
Atomic Number (Z): Number of protons in the nucleus.
Mass Number (A): Number of neutrons and protons in the nucleus.
Isotopes: Chemical elements with the same Z number .
More Key Definitions
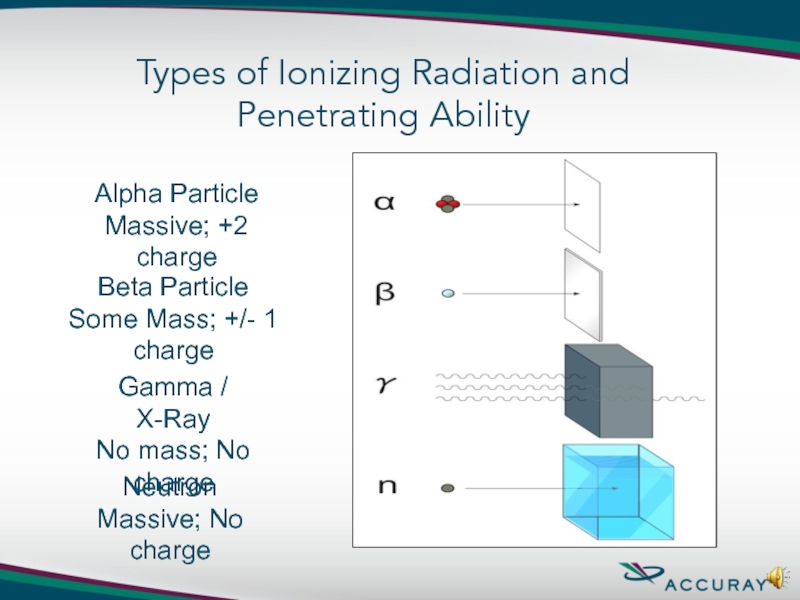
Слайд 9Alpha Particle
Massive; +2 charge
Beta Particle
Some Mass; +/- 1 charge
Gamma / X-Ray
No
Neutron
Massive; No charge
Types of Ionizing Radiation and Penetrating Ability
Слайд 10
Photodisintegration
Photoelectric Effect
X-Ray disappears => liberates an atomic electron
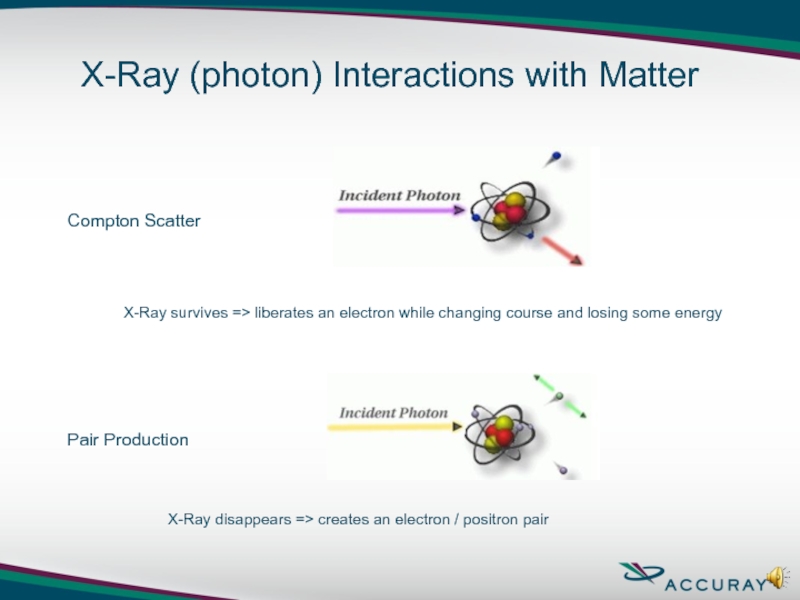
X-Ray (photon) Interactions with Matter
Слайд 11
Compton Scatter
X-Ray survives
Pair Production
X-Ray disappears => creates an electron / positron pair
X-Ray (photon) Interactions with Matter
Слайд 12Common Sources of Ionizing Radiation
Sources of Background Radiation Exposure
Natural Background
Medical Diagnosis
Manufactured/Industrial Sources
Sources of Occupational Radiation Exposure
Radiation Hazards in the Workplace
Radiation Sources
Слайд 15CyberKnife
M6 Series
TomoTherapy
H Series
Accuray radiation generating machines (RGMs) are capable
Слайд 16Biological Response to Ionizing Radiation – Key Terms
Somatic, Stochastic, Deterministic, Heritable
Radiation
Factors Affecting Biological Response
Total Dose, Dose Rate, Radiation Type & Energy
Area of the Body Irradiated, Cell Sensitivity, Individual Sensitivity
Radiation Risks
Quantifying Risks
The acceptability of Risks
Biological Effects and Risks of Exposure to Ionizing Radiation
Слайд 17Radiation Biology – Key Terms
Somatic Effects: biological effects that occur on
Deterministic Effects: definite threshold; the severity of effect increases with dose (Examples: cataracts; erythema; infertility)
Stochastic Effects: probabilistic in nature; existence of a threshold not clear; probability of occurrence increases with dose (Examples: cancer – DNA is the target of concern)
Heritable Effects: a physical mutation or trait that is passed on to offspring; these have never been observed in humans but are believed to be possible.
Слайд 18Radiation Causes Ionizations of:
ATOMS
which may affect
MOLECULES
which may affect
CELLS
which
TISSUES
which may affect
ORGANS
which may affect
THE WHOLE BODY
Слайд 19Radiation Biology – Mechanisms
DNA is the Target of Concern
(Deoxyribonucleic acid [DNA]
Direct and Indirect Effects
DNA strand breaks (Direct Effect)
Water molecule dislocation (Indirect Effect)
Reactive species formation (Indirect Effect)
Radiation Causes Ionization and Excitation in Water (H+ OH- H20+ H20- H20* e- H202)
Слайд 20Radiation Biology – Affects
What can Happen after Direct or Indirect DNA
Detection and Repair
Cell Death
DNA Changes With No Negative Effects
DNA Changes With Deleterious Effects
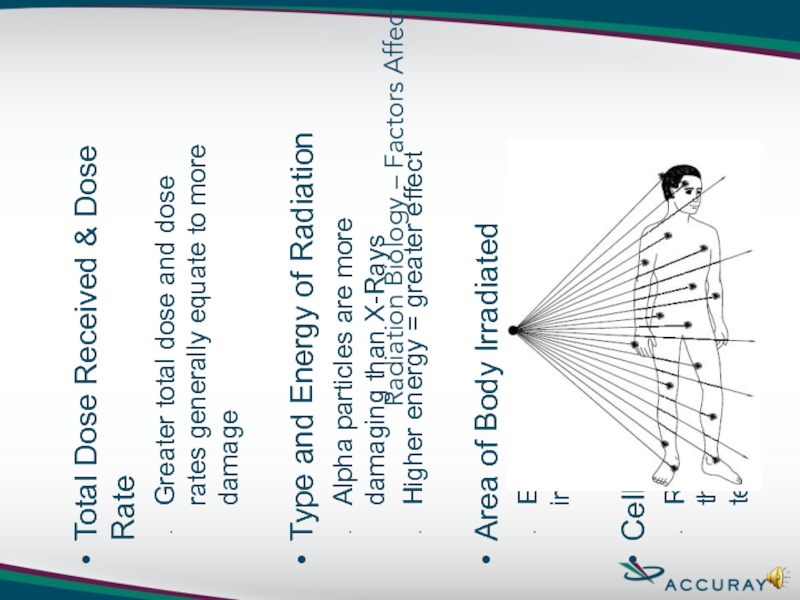
Слайд 21Radiation Biology – Factors Affecting Biological Response
Total Dose Received & Dose
Greater total dose and dose rates generally equate to more damage
Type and Energy of Radiation
Alpha particles are more damaging than X-Rays
Higher energy = greater effect
Area of Body Irradiated
Effects increase with area irradiated
Cell Sensitivity
Rapidly dividing cells and cells that have a long dividing future tend to be more sensitive
Individual Sensitivity
Each person responds differently
Слайд 22Acute versus Chronic Exposures
Chronic radiation exposures: low doses over long time
Acute radiation exposures: high doses over short time periods
The following effects are associated with acute, whole body exposures:
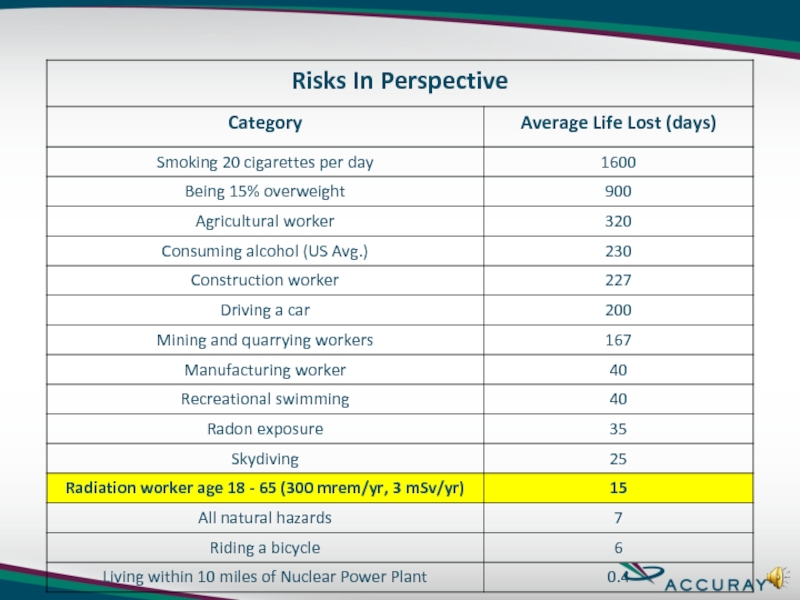
Слайд 23Radiation Risk
Radiation Exposure Is Assumed to Increase Cancer Risk
Approximately 35
Approximately 20% of all people will develop a fatal cancer in their lifetime – aside from radiation exposure.
If 10,000 people all received 1,000 mrem, (1 rem), (10 mSv) of radiation exposure, we would expect 5 or 6 to die from radiation related cancer and 2,000 to die from all other cancer sources.
Risk of developing a fatal cancer from radiation exposure:
5.5 x 10-4 per rem or 5.5 x 10-2 per Sv
Слайд 25The Principles of Radiological Protection
Epidemiological Studies
Dose Response Models
National / International Recommendations
Occupational Limits
Facility Control Levels
Protection of the Embryo/Fetus
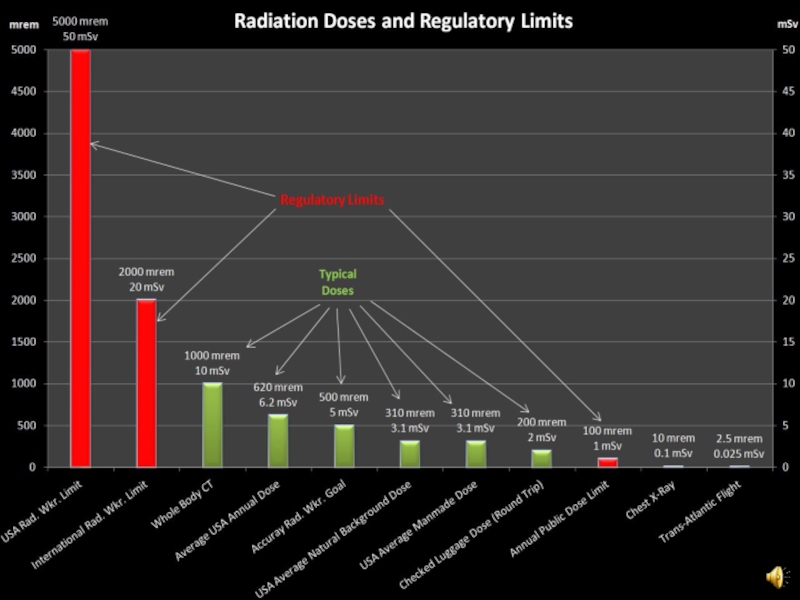
Protection of the General Public (100 mrem; 1 mSv)
Radiation Protection Standards
Слайд 26
Justification – No practice shall be adopted unless its introduction produces
Optimization – All exposures shall be kept ALARA, economic and social factors being taken into account.
Limitation – Individual exposures shall not exceed the limits.
The Principles of Radiation Protection
Слайд 27Epidemiology – the study of patterns, causes, and effects of health
UNSCEAR - United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation
Sources of Human Population Radiation Epidemiological Data
Atomic Bomb Survivors
Radiotherapy Patients
Occupational
Radium Dial Painters, Miners (Radon Exposure), Radiologists, Nuclear Workers
Environment
Chernobyl Accident, Weapons Test Fallout, Natural Background
Epidemiological Studies
Слайд 29Epidemiological studies are performed and presented
UNSCEAR
World Health Organization
National and International agencies
International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA)
International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP)
National Council on Radiological Protection and Measurements (NCRP)
Country, State and Local Laws
Exposure Limits and Guidance Documents
National / International Recommendations & Law
Слайд 31Unrestricted Area – Any area that is not controlled for the
Controlled Areas – Access is controlled for radiation protection purposes (includes areas adjacent to mega voltage enclosures)
Restricted Areas – Access is prevented or limited for the purpose of protecting individuals from undue risks from radiation exposure (includes inside test cells / bunkers when radiation is being generated
Facility Control Levels
Слайд 32The developing embryo/fetus, with rapidly dividing cells, is sensitive to many
The embryo/fetus is most susceptible to developing adverse health effects if exposed during the time period 8-15 weeks after conception.
Declaration of Pregnancy
Additional safety precautions are available to declared pregnant workers
The declaration must be submitted (in writing) to the RSO
Detailed training material and information will be made available
A historical dose assessment and job analysis will be performed
Temporary changes to job duties will be considered
A fetal dosimeter will be issued
Protection of the Embryo/Fetus
Слайд 33 Member of the Public: means an individual who is not a
The strict exposure limit to a member of the public is:
100 mrem/yr (1 mSv/yr)
Members of the public are not allowed unescorted access to test cell or bunker areas.
Protection of the General Public
Слайд 34
Radiation Protection
Policies and Procedures
The ALARA Concept (Time, Distance and
Signs, Labels, and Postings
Access Controls
Controlling Radiation Dose
Слайд 35The most important policy to remember is … never be inside
SOP 027444 is the main Radiation Safety Program Procedure
* Personnel Dosimetry Request Form * Lost, Damaged, or Exposed Personnel Dosimetry Form * Declaration of Pregnancy Form * Declaration of Worker Status Form * Engineering and Administrative Controls Checklist * Request and Authorization for Radiation Exposure History Form * Notification of Nuclear Energy Worker Status
There are many other country and site specific requirements such as: Canada Specific Training (for Canadian Citizens); UK Local Radiation Rules; Radiation Safety in Europe – Belgium; Radiation Protection Organization (German); and many others.
Radiation Protection Policies & Procedures
Слайд 36ALARA is an acronym for As Low As Reasonably Achievable.
Since it
Time – whenever practical, minimize the time spent near sources of radiation and minimize the output from RGMs.
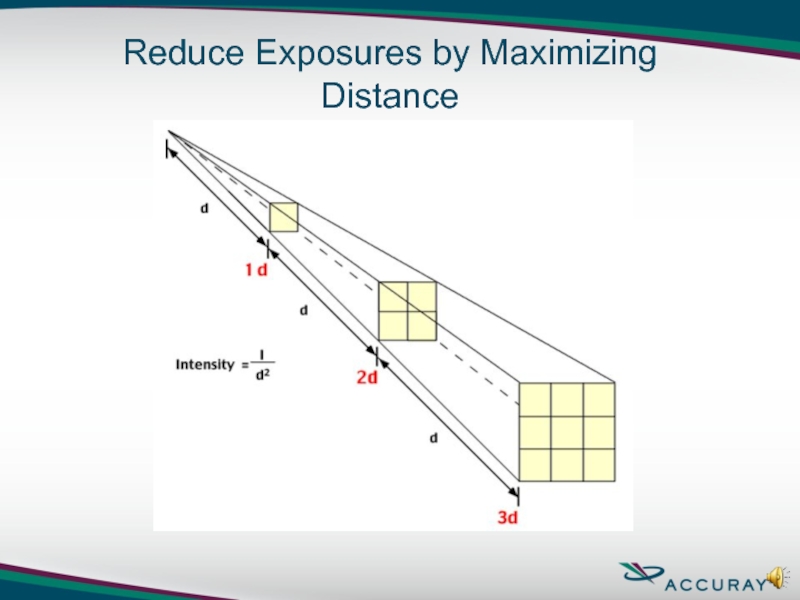
Distance – to the extent practical, maximize the distance between personnel and radiation sources.
Shielding – incorporate attenuating barriers between radiation sources and personnel whenever practical.
The ALARA Concept
Слайд 37Reduce Exposures by Minimizing Time & Dose Rate
Dose = Dose Rate
500 mrem = 10 mrem/hr x 50 hrs
Or
1000 cGy/min x 10 min = 10,000 cGy !!!
Слайд 40Close the Jaws/MLC, Plug Beam, and Beam Down Whenever Possible/Practical
Reduce Exposures
Слайд 41Some areas require specific authorization or an escort prior to entry.
Radiation ‘Trefoil’ Symbols
Foreground and background colors may vary
Caution Signs
Radiation Hazard Communication
Слайд 42Emergency Buttons/Devices
Warning
Lights
Note: Actuating an Emergency Button/Device, or opening the main
Engineering Safety Controls
Слайд 43Operators must physically enter the test cell, bunker or shielded enclosure
Once the test cell is cleared and the door closed, access must be continually monitored, otherwise the cell must be re-cleared prior to the next Beam-On.
Personnel who need access to an enclosure must get permission from the operator prior to entry.
It is absolutely forbidden to generate radiation while persons are within an Accuray shielded enclosure.
It is prohibited to enter a cell in which a radiation device is in use.
Access Controls - Mandatory
Слайд 45Dosimetry Use is a Requirement for all Radiation Workers
Basic Dosimetry Use
Keep away from non-occupational radiation sources such as:
Airport checked luggage scans
Medical and dental imaging
Prevent the dosimeter from receiving excessive exposure to heat, sunlight or moisture
Promptly exchange at regular intervals (usually every three months)
Notify radiation safety personnel when a dosimeter is lost, damaged or accidentally exposed
Personnel Monitoring
Слайд 46 Test Cell/Bunker Commissioning
and Routine Leakage Surveys
Facility Monitoring
Continuous Area Monitoring
Слайд 47Radiation Leakage Surveys and Area Monitoring
Gas Filled Detectors –Ionization Chambers
Benefits –
Potential Problems - recombination, dead time, pile up, RF & magnetic field interference
Radiation Detectors
Слайд 48Briefly inspect the instrument for physical damage or excessive wear.
Ensure the
Power on the instrument and perform a battery check.
Note the natural background radiation level and fluctuations in instrument response.
Always lead with the detector, maximizing your distance from radiation sources.
Think ALARA and caution is warranted as exposure rates approach or exceed: 10 mR/hr; 100 µSv/hr
Use of Survey Instruments
Damaged or ‘out of calibration’ instruments cannot
be used and must be taken out of service.
Слайд 49Management Responsibilities
Promote a positive radiation safety culture and ensure adequate resources
Radiation Safety Organization Responsibilities
Ensure protection of persons, the environment and property
Ensure regulatory compliance and advise on technical issues
Individuals’ Responsibilities
Adhere to all radiation worker requirements, postings, and controls
Demonstrate responsibility and accountability through an informed, disciplined and cautious attitude toward radiation
Individuals’ Rights
Stay informed of all risks and associated controls prior to performing radiation work duties
Have access to personal dose records
Responsibilities for Radiation Protection
Слайд 50Limit the radiation dose to involved persons … the first action
If radioactive materials are involved, limit the spread of contamination.
Seek assistance from experienced radiation safety professionals. Contact the Accuray RSO and local Radiation Safety Personnel.
Evacuate the immediate area of the incident.
Control entry to the scene of the accident.
Indentify and isolate persons who may have received significant radiation exposures.
Record all details of the event chronologically.
Emergency Response
Слайд 51For more information, visit: http://sharepoint/Radiation Safety/
Procedures, forms, links, contact information, announcements,
Слайд 52Accuray is committed to maintaining a robust radiation safety program. As
Non-Radiation Workers are expected to receive truly negligible exposures: less than 1% of the natural background and typically below the limits of routine detection.
Everyone is encouraged to play an active role regarding radiation safety - think ALARA.













![Radiation Biology – MechanismsDNA is the Target of Concern (Deoxyribonucleic acid [DNA] encodes the genetic instructions](/img/tmb/5/413462/65bd276b8c5d6e2ffbca5e49066ae2ce-800x.jpg)