- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Physics 1 for KMA презентация
Содержание
- 1. Physics 1 for KMA
- 2. Lecture 4 Rotation of rigid bodies.
- 3. Rotation of Rigid Bodies When a rigid
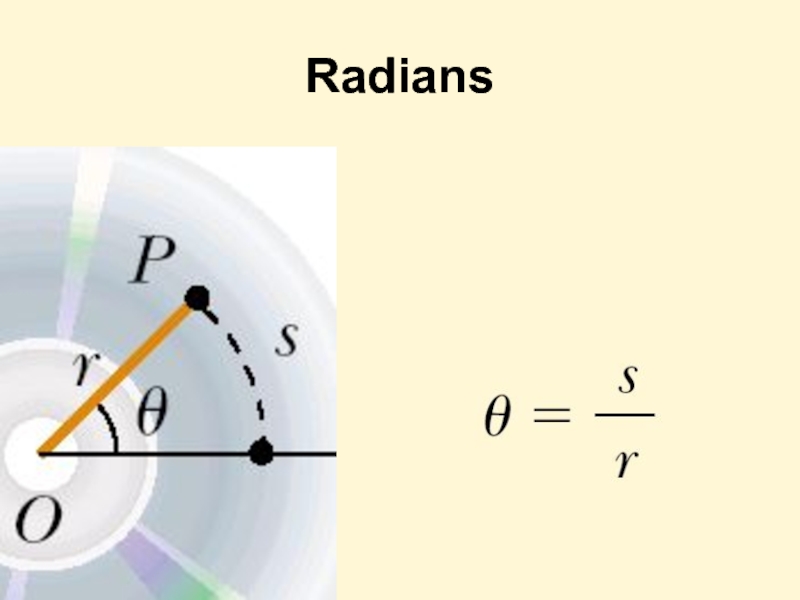
- 4. Radians
- 5. Angular kinematics Angular displacement: Instantaneous angular speed: Instantaneous angular acceleration:
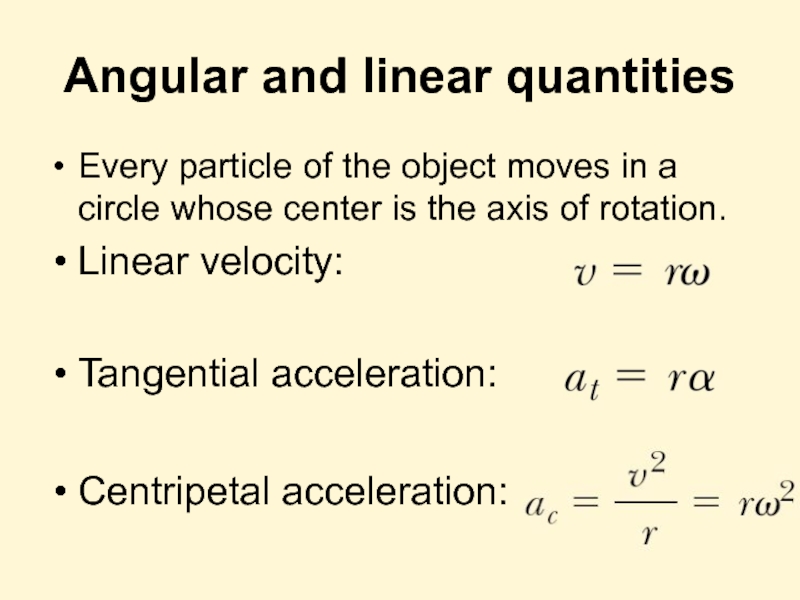
- 6. Angular and linear quantities Every particle of
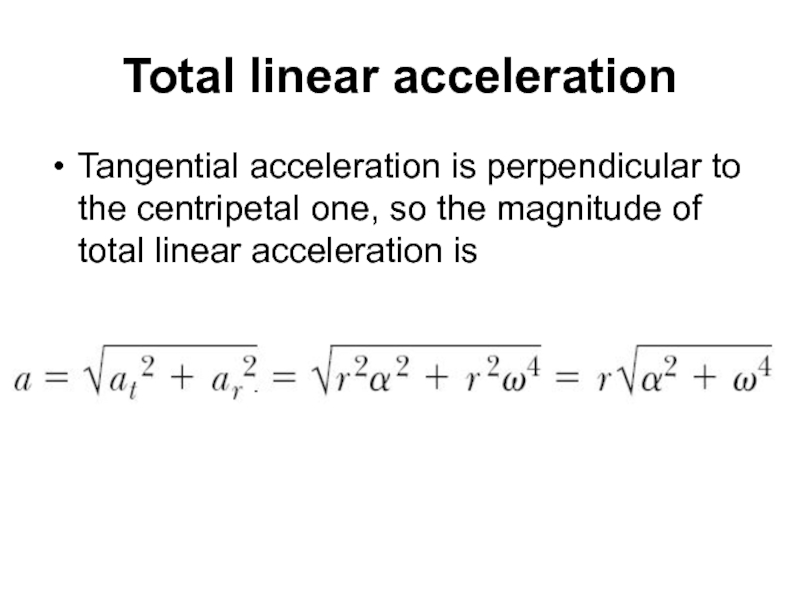
- 7. Total linear acceleration Tangential acceleration is perpendicular
- 8. Angular velocity Angular velocity is a vector.
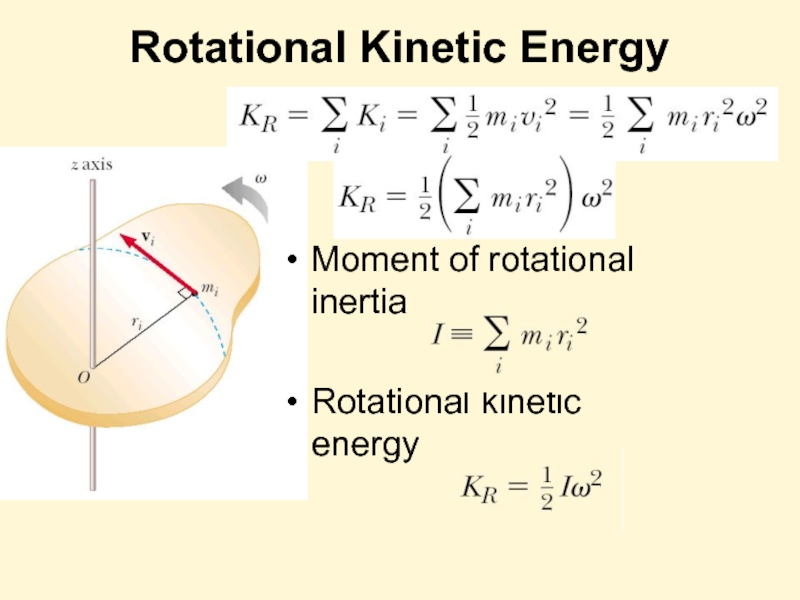
- 9. Rotational Kinetic Energy Moment of rotational inertia Rotational kinetic energy
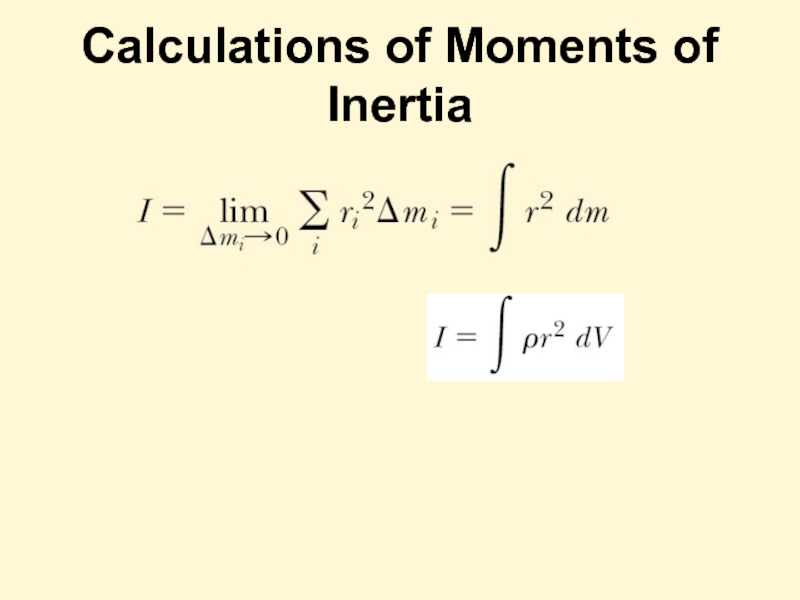
- 10. Calculations of Moments of Inertia
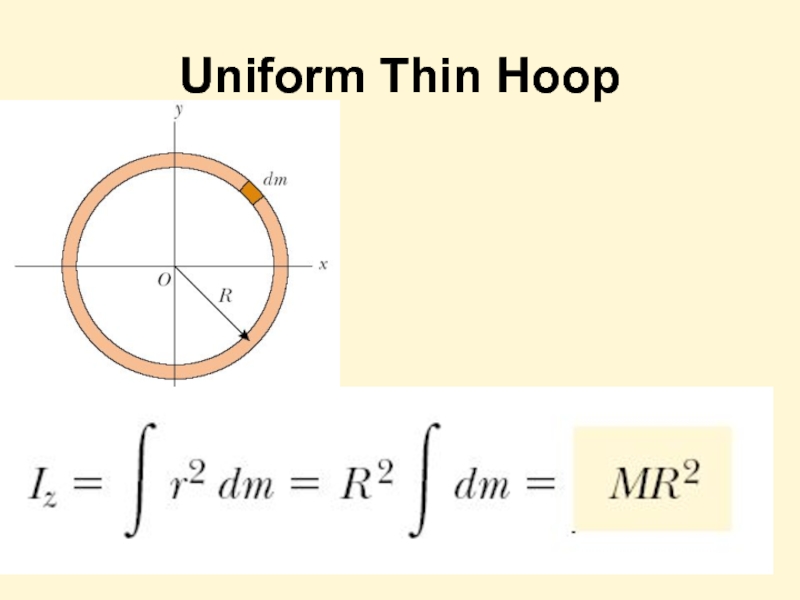
- 11. Uniform Thin Hoop
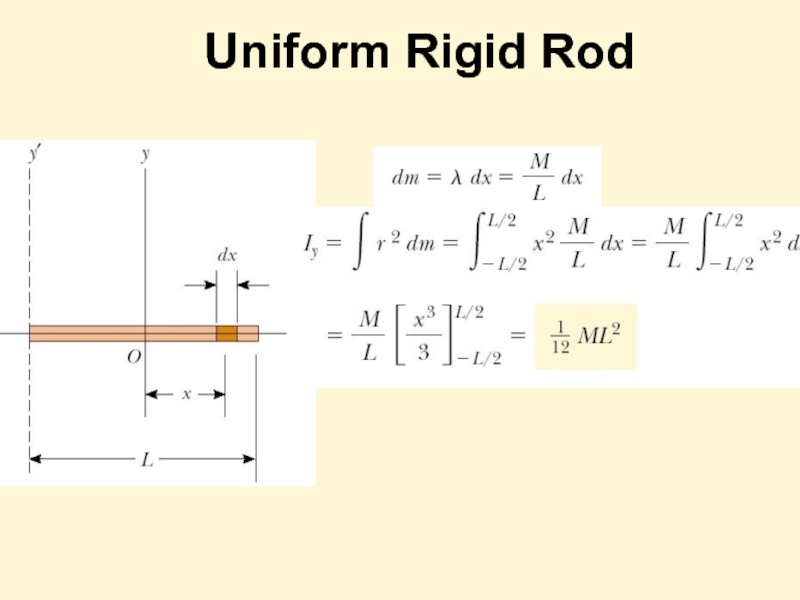
- 12. Uniform Rigid Rod
- 13. Uniform Solid Cylinder
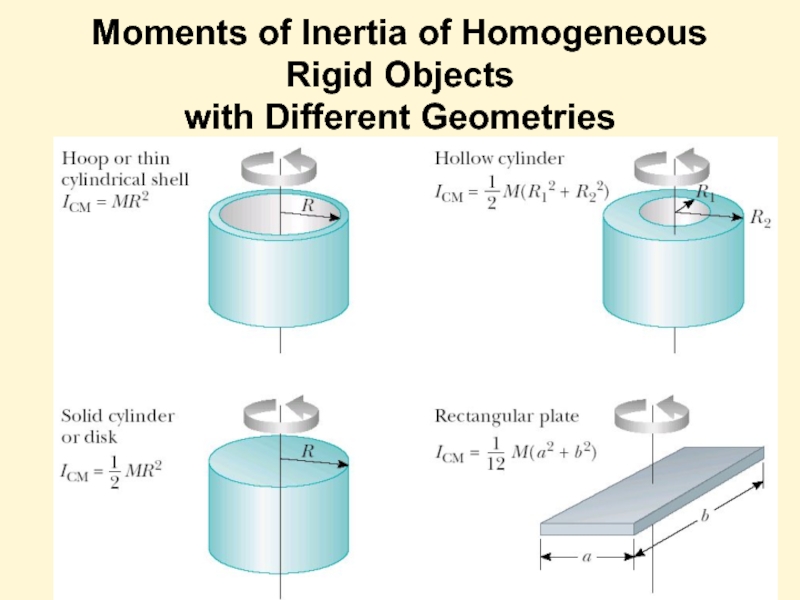
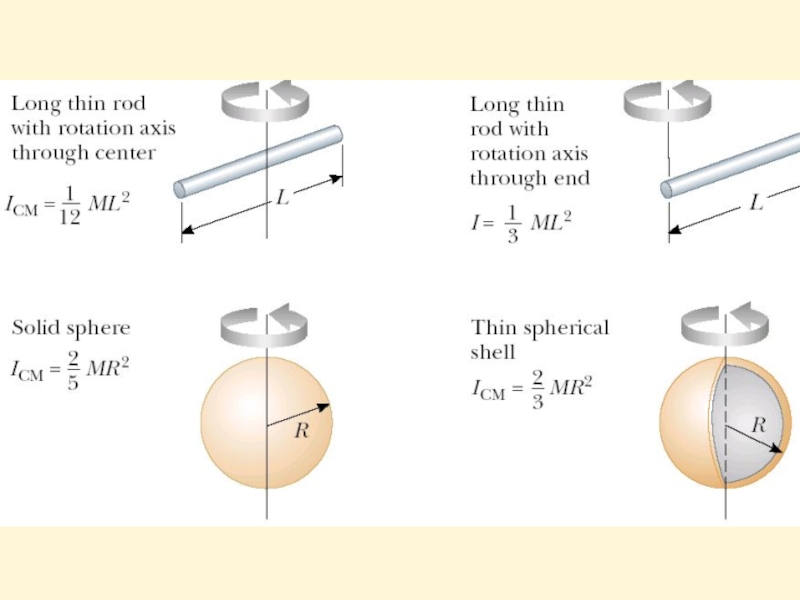
- 14. Moments of Inertia of Homogeneous Rigid Objects with Different Geometries
- 16. Parallel-axis theorem Suppose the moment of inertia
- 18. Torque When a force is exerted on
- 19. The force F has a greater
- 20. The force F1 tends to rotate the
- 21. Torque is not Force Torque is not
- 22. Rotational Dynamics Let’s add
- 23. Rotational analogue of Newton’s second law Quantity
- 24. Net External Torque The net external torque
- 25. Angular Momentum of a Rotating Rigid Object
- 26. Angular acceleration
- 27. The Law of Angular Momentum Conservation The
- 28. Change in
- 29. When a rotating skater pulls his hands towards his body he spins faster.
- 30. Three Laws of Conservation for an Isolated
- 31. Work-Kinetic Theory for Rotations Similarly to linear motion:
- 32. The net work done by external
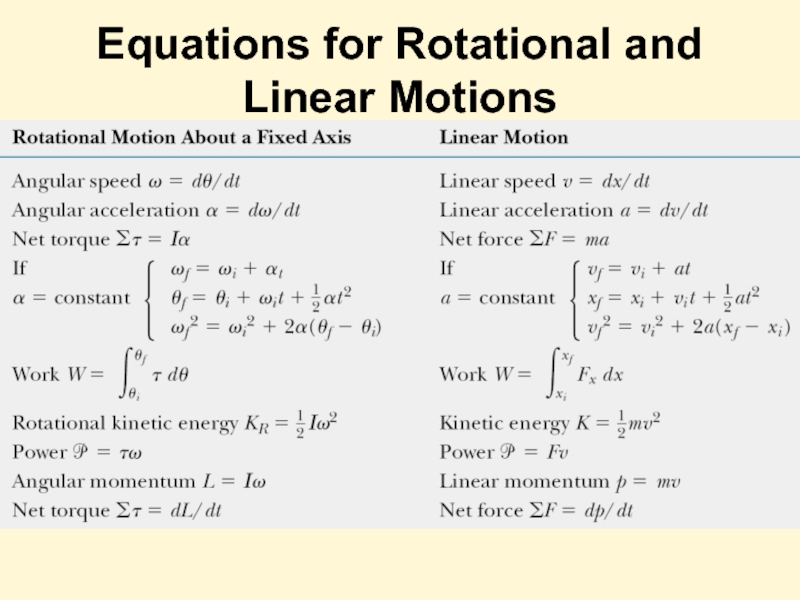
- 33. Equations for Rotational and Linear Motions
- 34. Gyroscope One typical type of gyroscope is
- 35. At high speeds, the gyroscope exhibits
- 36. If a gyroscope is tipped, the gimbals
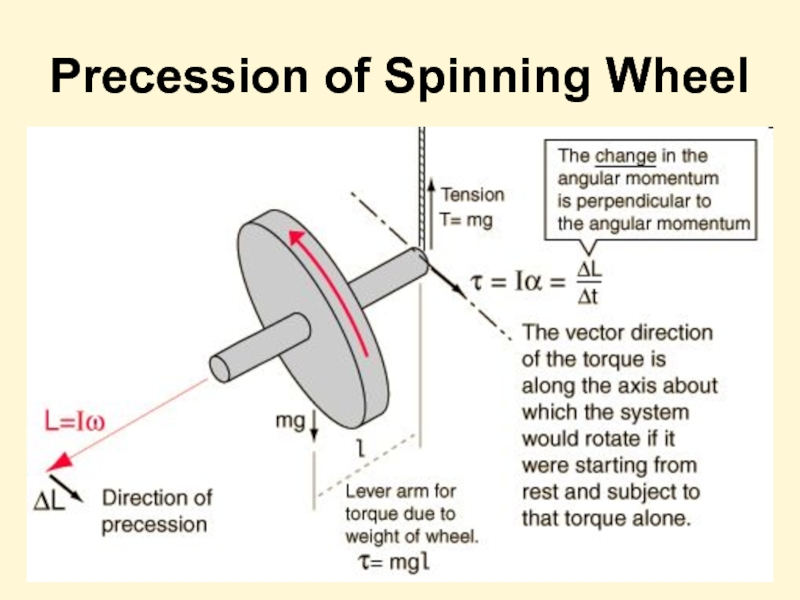
- 37. Precession of Spinning Wheel
- 38. Fluids and liquids
- 39. Relative density Relative density or specific gravity
- 41. Specific volume of a substance is the
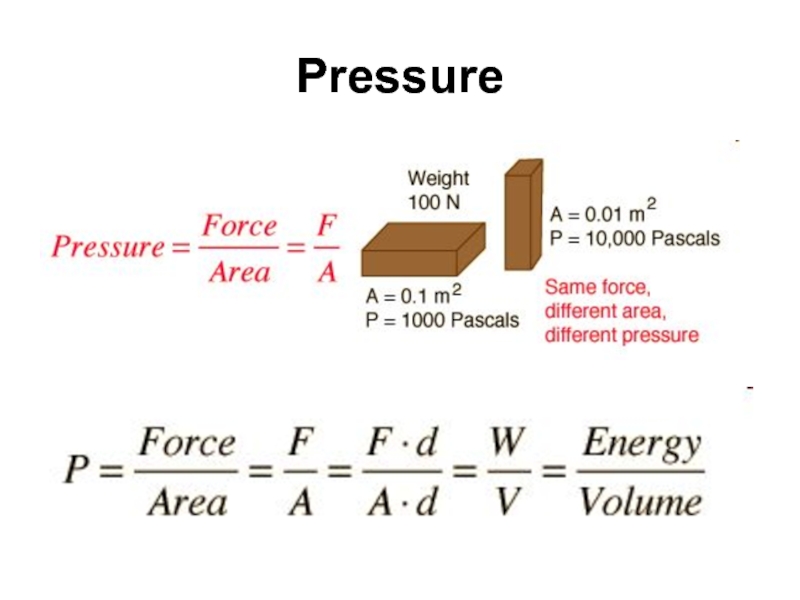
- 42. Pressure
- 43. Manometer The difference in fluid height in
- 44. Static Fluid Pressure Pstatic fluid = ρgh
- 45. Pressure Thrust Thrust is a total force
- 46. Atmospheric Pressure The surface of the earth
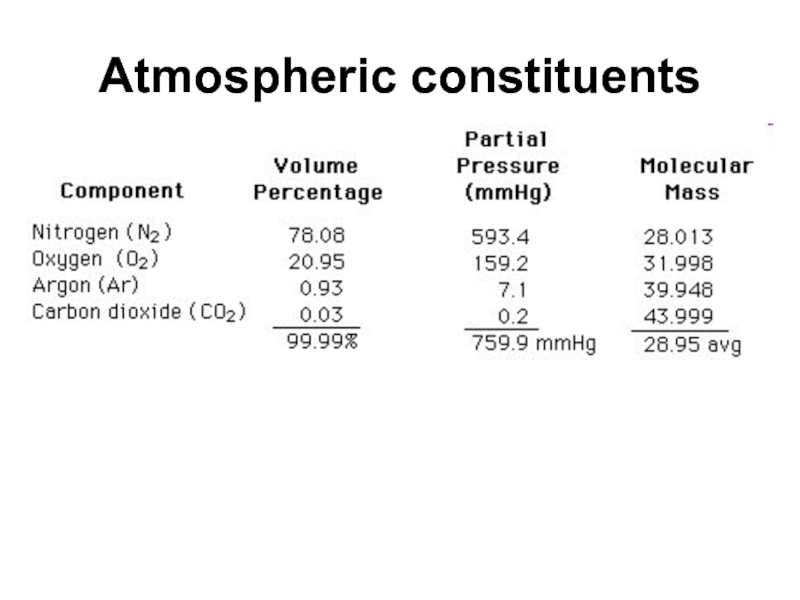
- 47. Atmospheric constituents
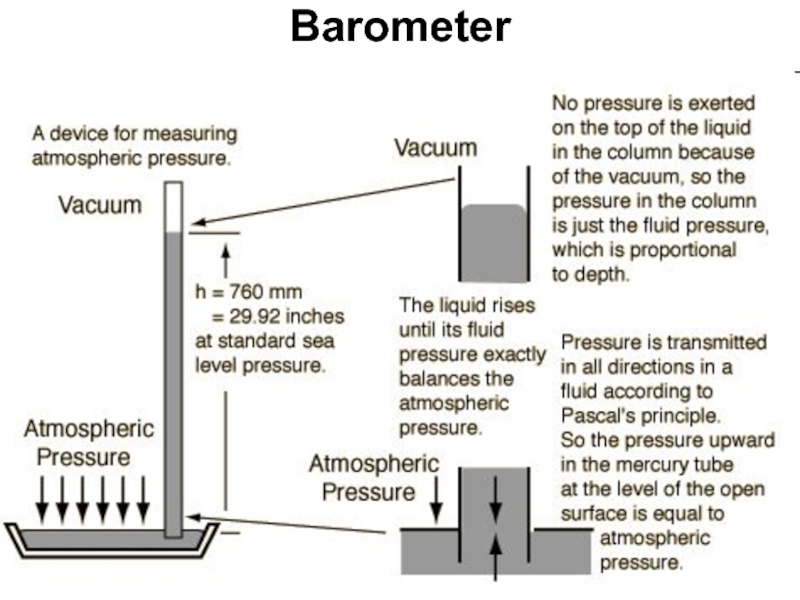
- 48. Barometer
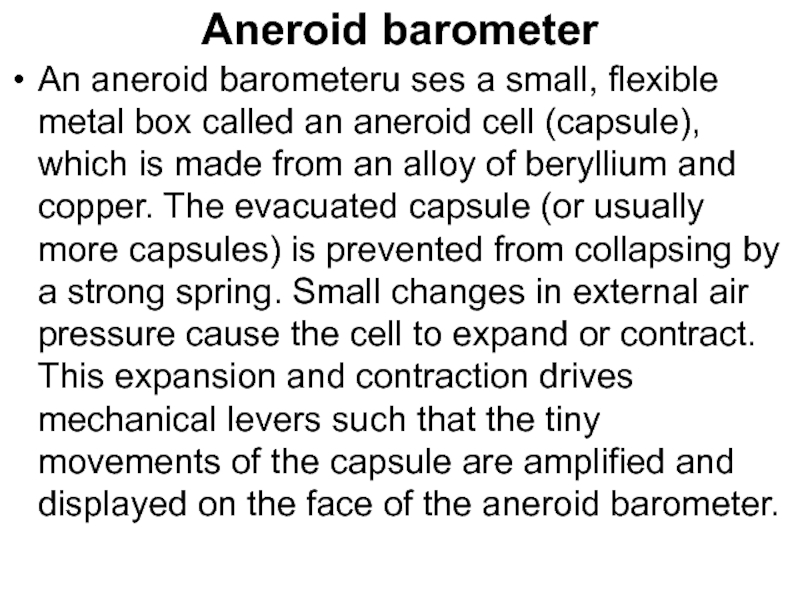
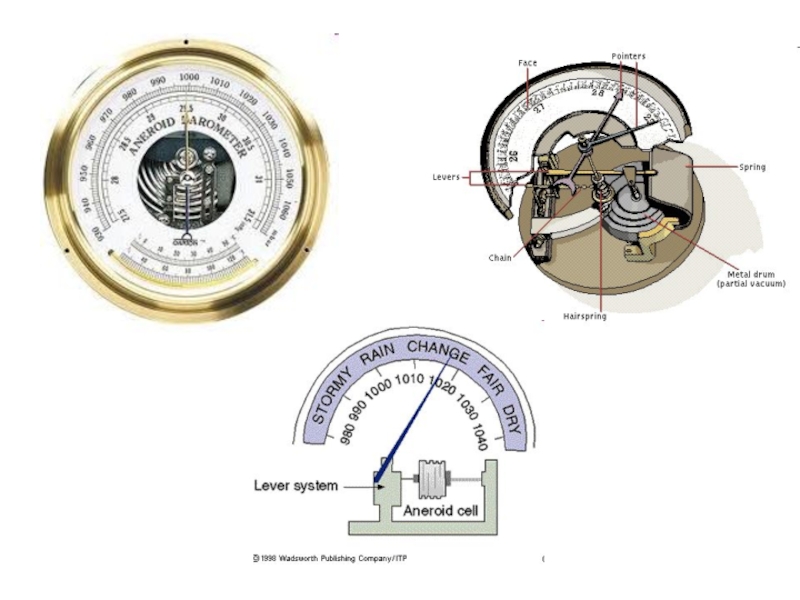
- 49. Aneroid barometer An aneroid barometeru ses a
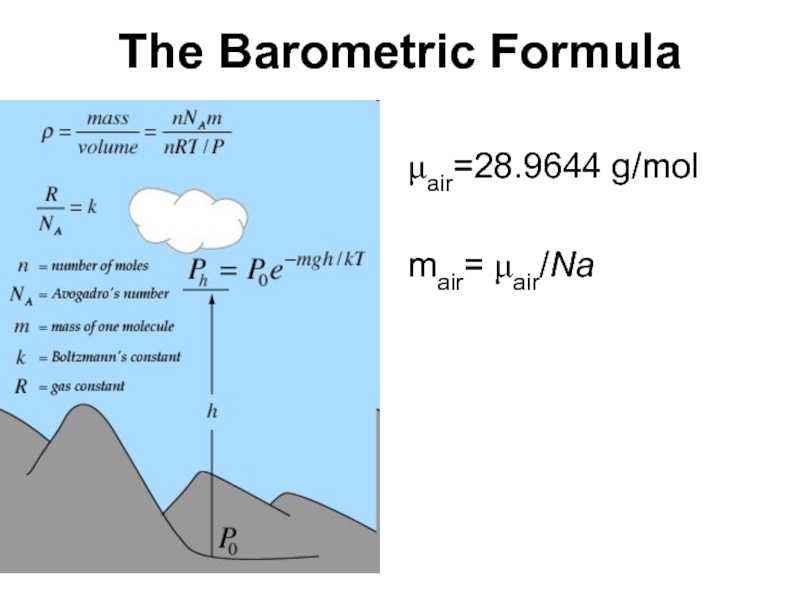
- 51. The Barometric Formula μair=28.9644 g/mol mair= μair/Na
- 52. Pascal's Principle Pressure exerted anywhere in a
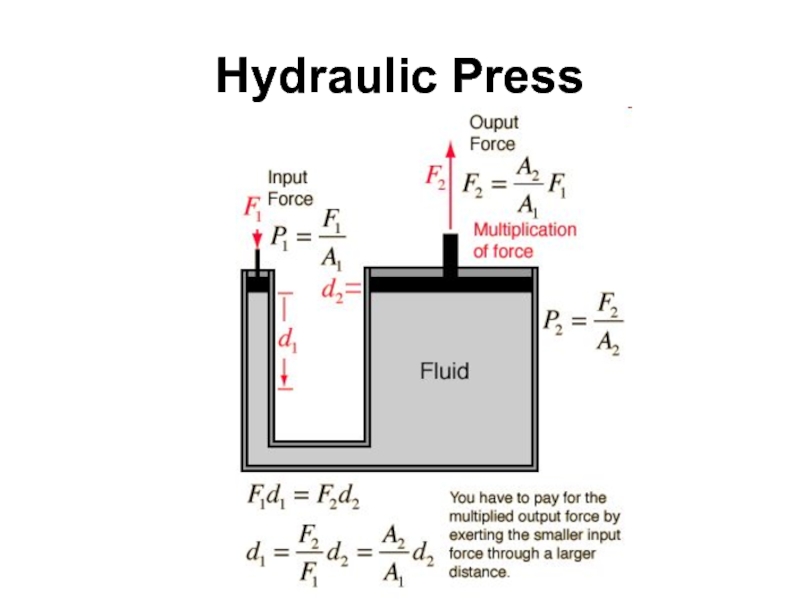
- 54. Hydraulic Press
- 55. Lift pump The lift pump, also known
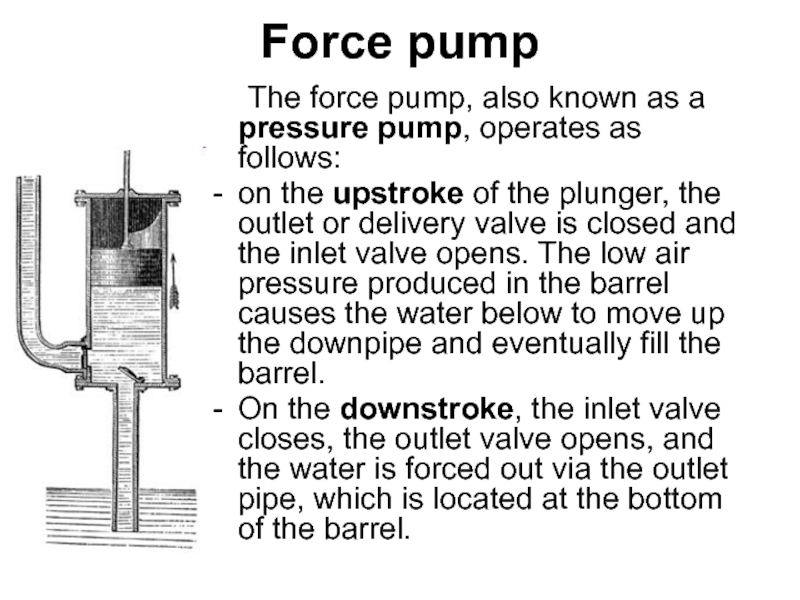
- 56. Force pump The force pump, also known
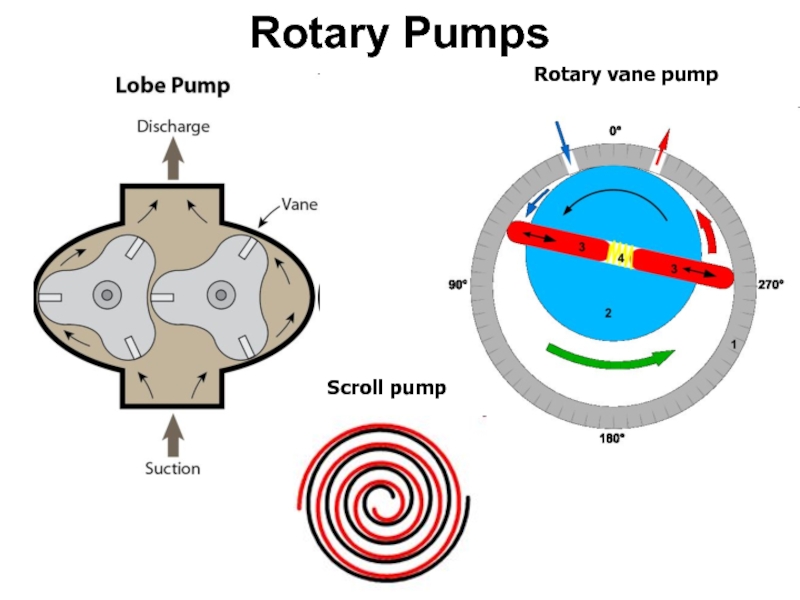
- 57. Rotary Pumps Rotary vane pump Scroll pump
- 58. Height limitation Total Dynamic Head (TDH) is
- 59. Total Dynamic Height TDH = Static Height
- 60. Viscosity The resistance to flow of a
- 61. Experimentally, under conditions of laminar flow,
- 63. Drag force due viscosity In a viscous
- 64. Effect of Temperature on Viscosity The
- 65. Liquid Damping Damping is an effect that
- 68. Buoyancy Buoyancy arises from the fact
- 69. Archimedes' Principle The buoyant force on a
- 70. Hydrometer A hydrometer is an
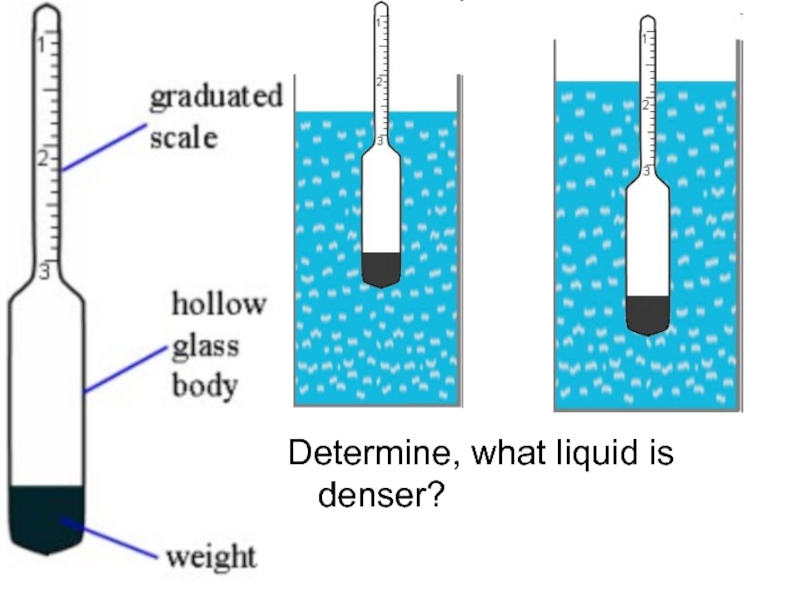
- 72. Determine, what liquid is denser?
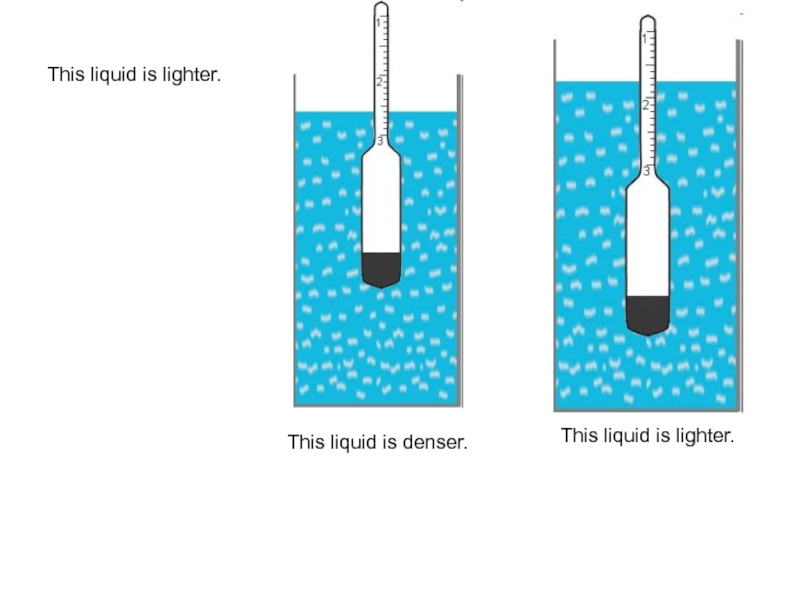
- 73. This liquid is lighter. This liquid is denser. This liquid is lighter.
- 74. Fluid Kinetic Energy The kinetic energy of
- 75. Fluid Potential Energy The potential energy of
- 76. Bernoulli Equation
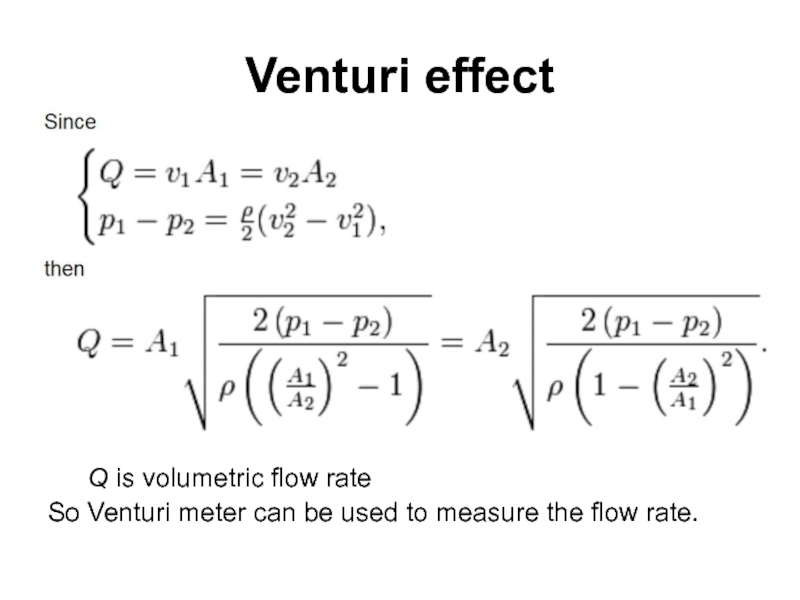
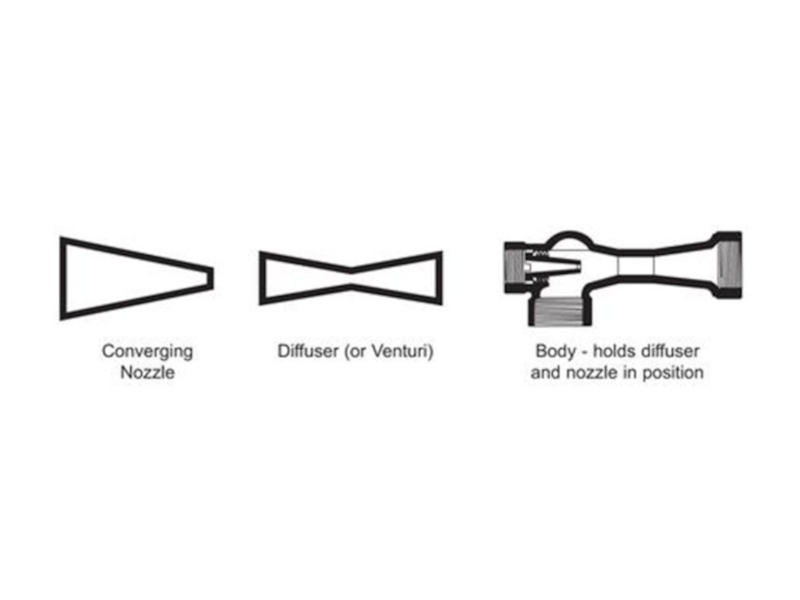
- 77. Venturi meter The Venturi effect is the
- 78. Venturi effect Q is volumetric flow rate
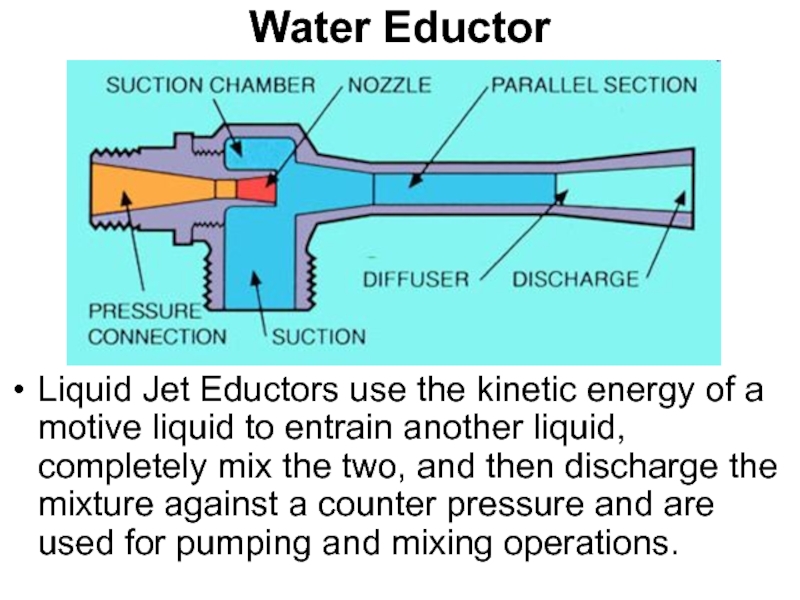
- 79. Water Eductor Liquid Jet Eductors use the
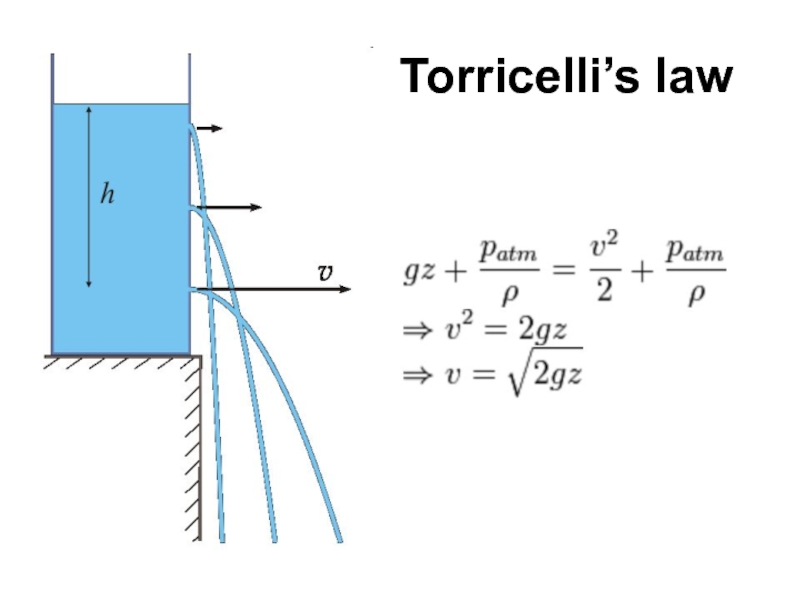
- 81. Torricelli’s law
Слайд 2Lecture 4
Rotation of rigid bodies.
Angular momentum and torque.
Properties of fluids.
Flotation.
Bernulli
Слайд 3Rotation of Rigid Bodies
When a rigid object is rotating about a
Слайд 5Angular kinematics
Angular displacement:
Instantaneous angular speed:
Instantaneous angular acceleration:
Слайд 6Angular and linear quantities
Every particle of the object moves in a
Linear velocity:
Tangential acceleration:
Centripetal acceleration:
Слайд 7Total linear acceleration
Tangential acceleration is perpendicular to the centripetal one, so
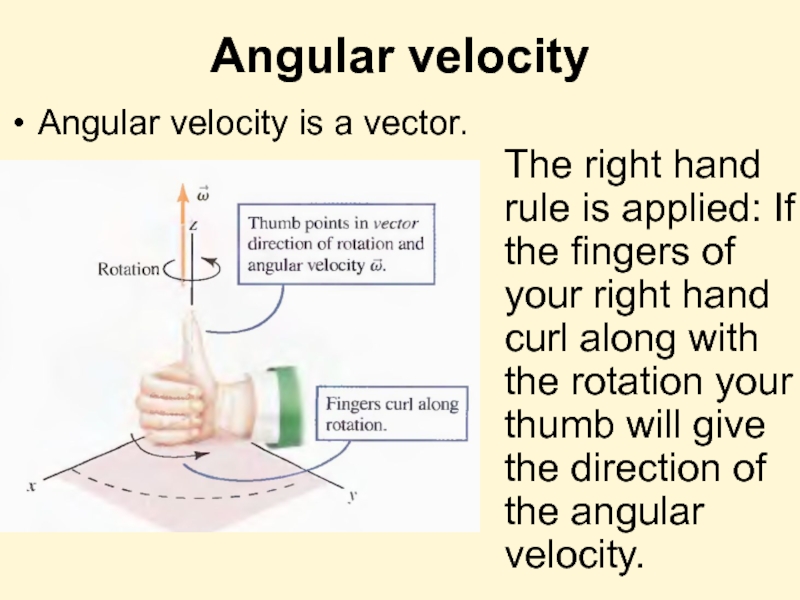
Слайд 8Angular velocity
Angular velocity is a vector.
The right hand
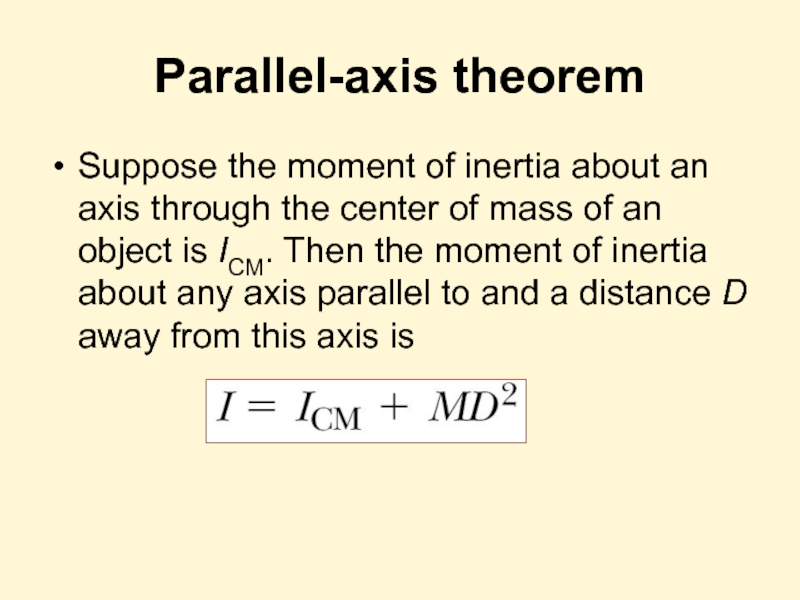
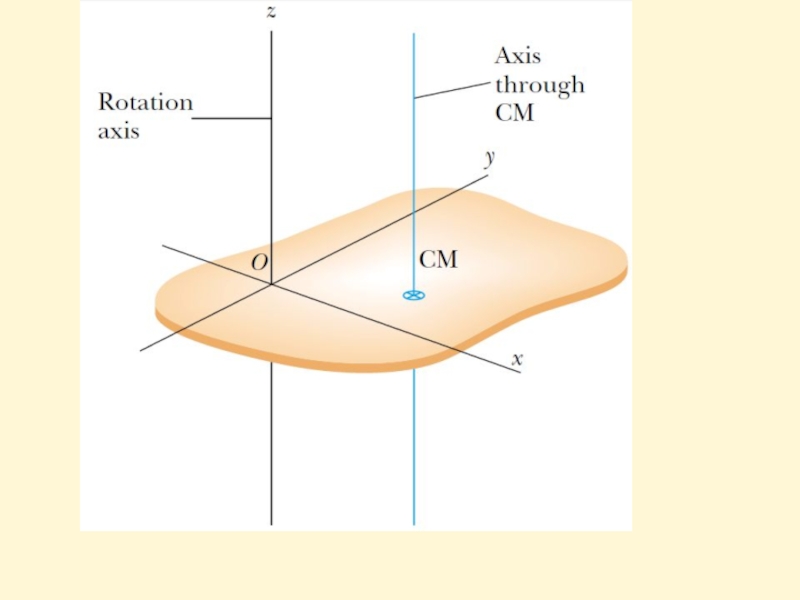
Слайд 16Parallel-axis theorem
Suppose the moment of inertia about an axis through the
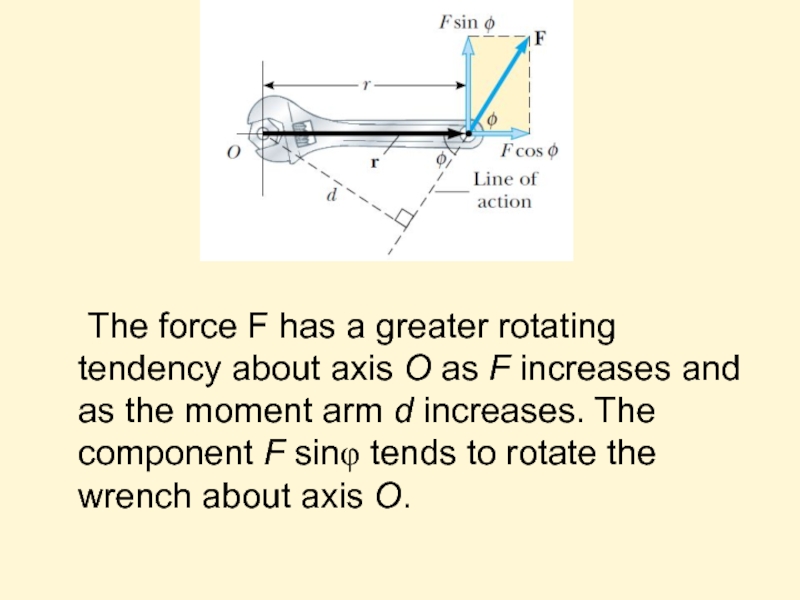
Слайд 18Torque
When a force is exerted on a rigid object pivoted about
Слайд 19
The force F has a greater rotating tendency about axis O
Слайд 20 The force F1 tends to rotate the object counterclockwise about O,
We use the convention that the sign of the torque resulting from a force is positive if the turning tendency of the force is counterclockwise and is negative if the turning tendency is clockwise. Then
The force F1 tends to rotate the object counterclockwise about O, and F2 tends to rotate it clockwise.
Слайд 21Torque is not Force
Torque is not Work
Torque should not be confused
Do not confuse torque and work, which have the same units but are very different concepts.
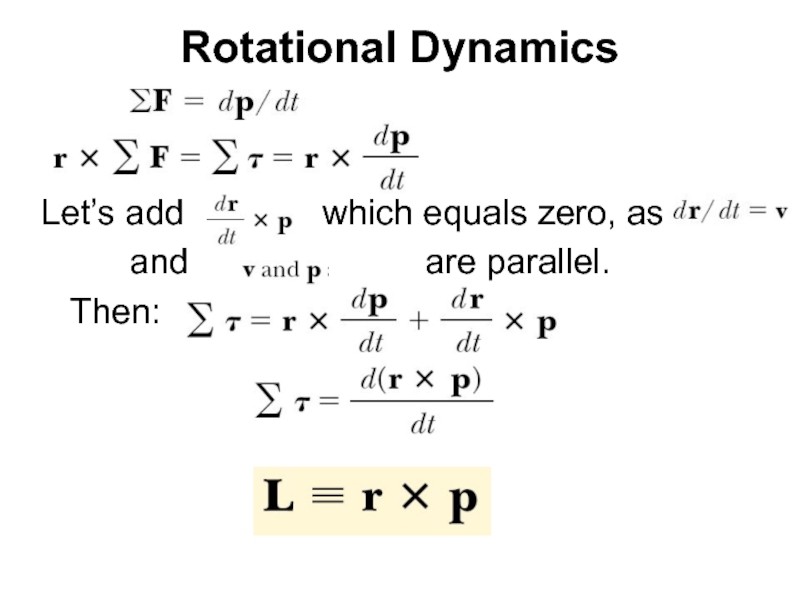
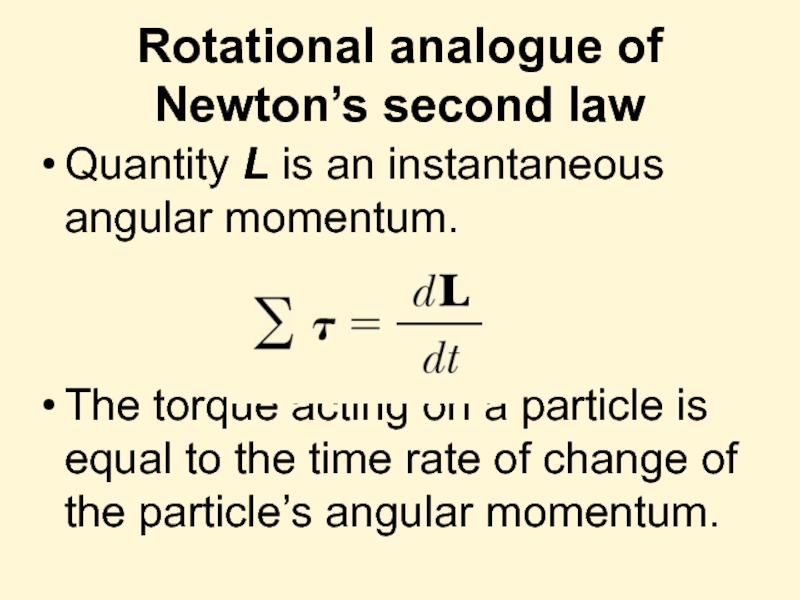
Слайд 23Rotational analogue of Newton’s second law
Quantity L is an instantaneous angular
The torque acting on a particle is equal to the time rate of change of the particle’s angular momentum.
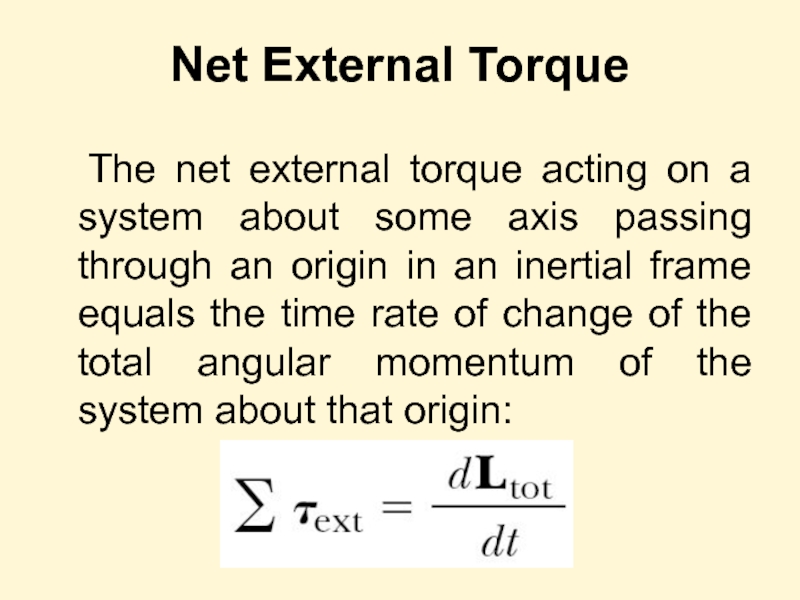
Слайд 24Net External Torque
The net external torque acting on a system about
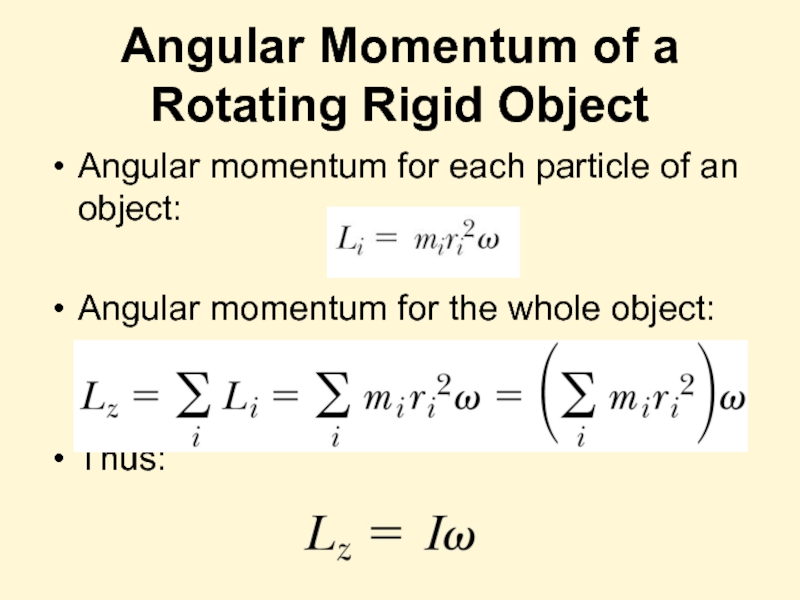
Слайд 25Angular Momentum of a Rotating Rigid Object
Angular momentum for each particle
Angular momentum for the whole object:
Thus:
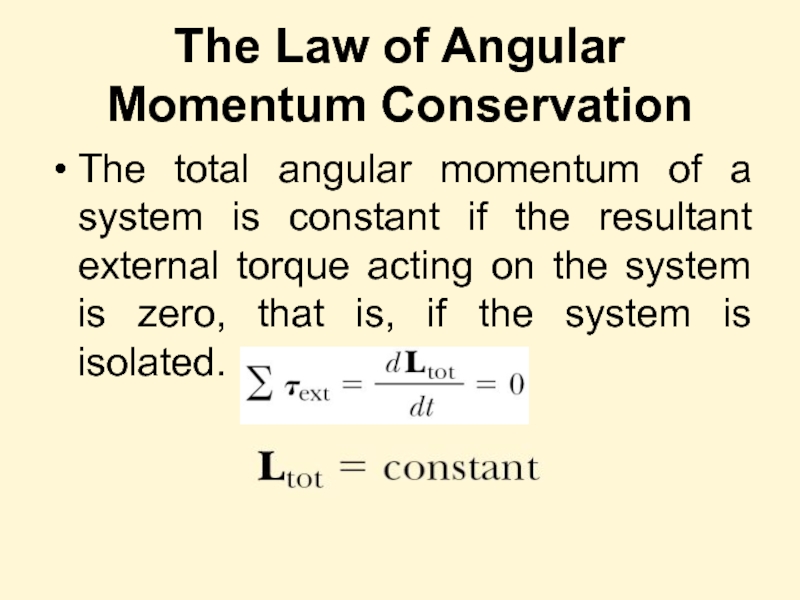
Слайд 27The Law of Angular Momentum Conservation
The total angular momentum of a
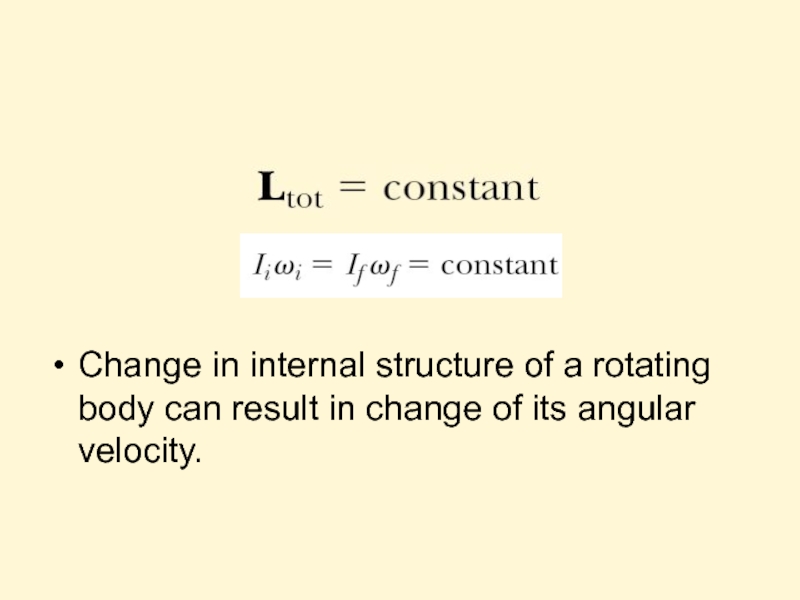
Слайд 28
Change in internal structure of a rotating body can result in
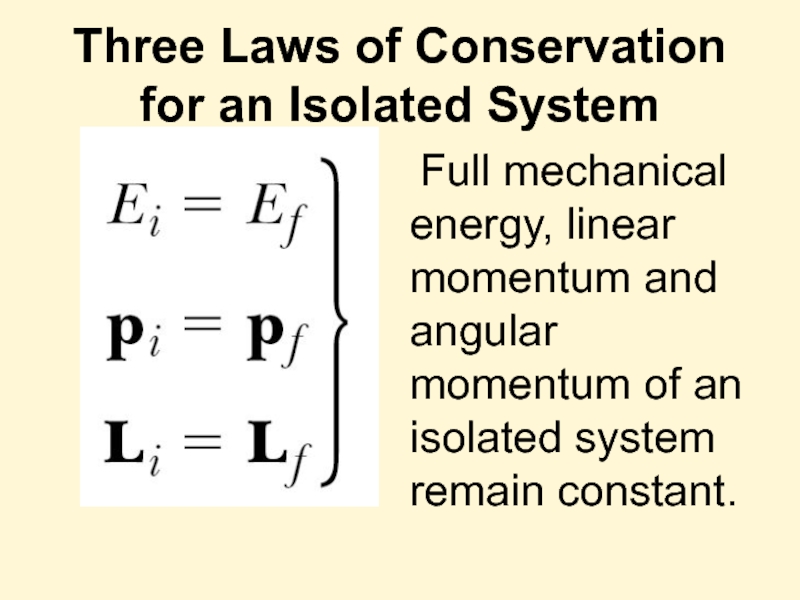
Слайд 30Three Laws of Conservation for an Isolated System
Full mechanical energy, linear
Слайд 32
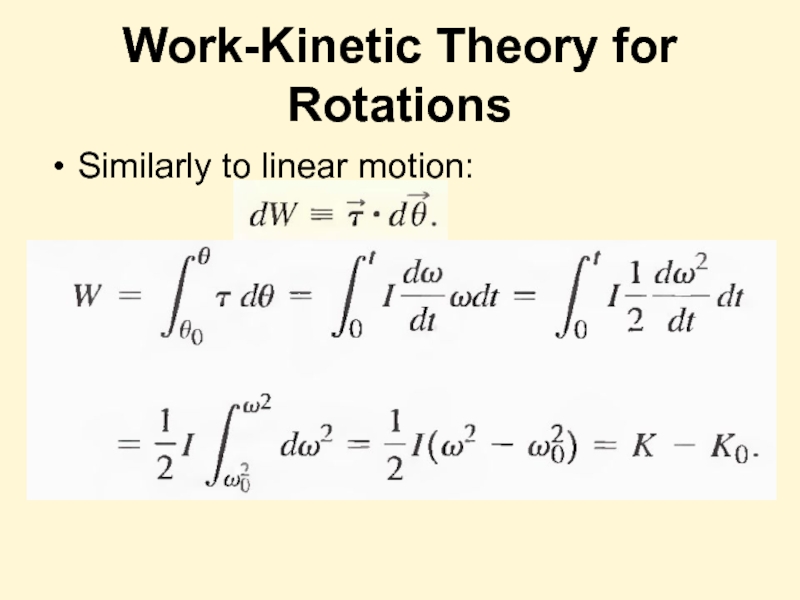
The net work done by external forces in rotating a symmetric
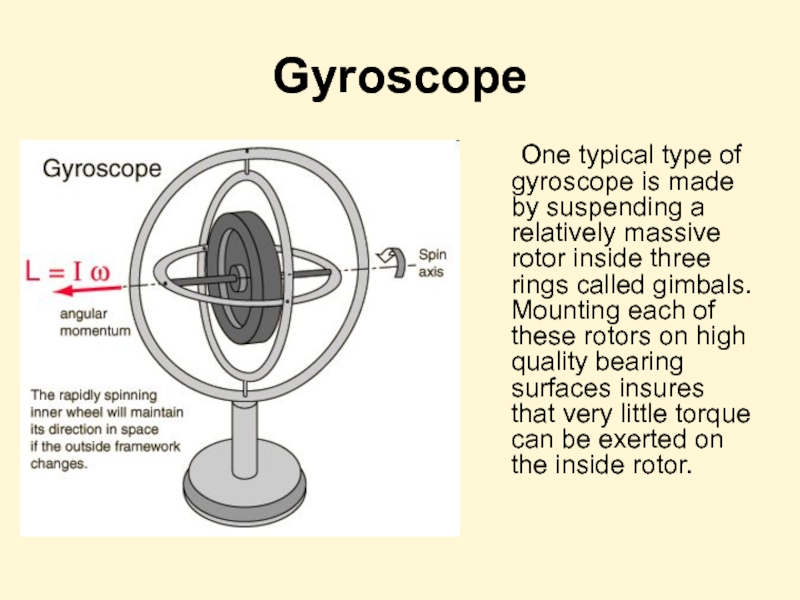
Слайд 34Gyroscope
One typical type of gyroscope is made by suspending a relatively
Слайд 35
At high speeds, the gyroscope exhibits extraordinary stability of balance and
Слайд 36 If a gyroscope is tipped, the gimbals will try to reorient
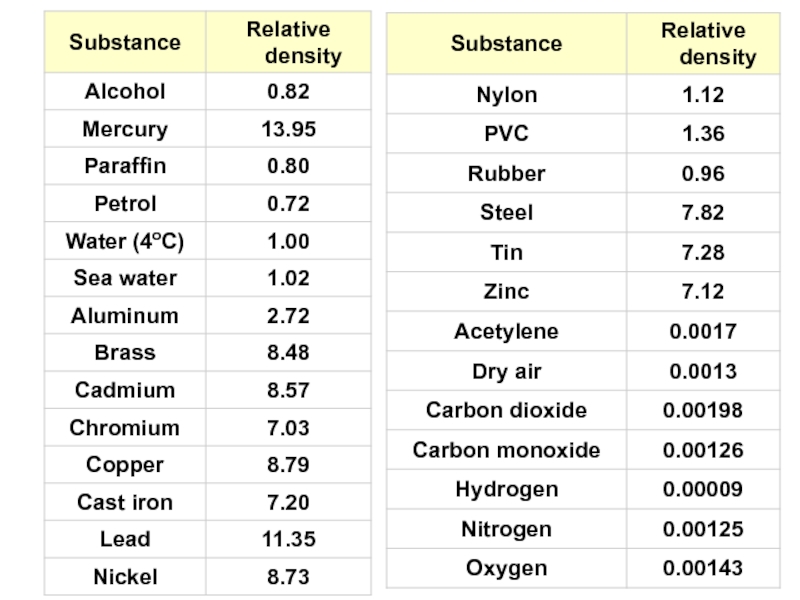
Слайд 39Relative density
Relative density or specific gravity is the ratio of the
If the reference material is water then a substance with a relative density (or specific gravity) less than 1 will float in water. For example, an ice cube, with a relative density of about 0.91, will float. A substance with a relative density greater than 1 will sink.
Слайд 41Specific volume of a substance is the ratio of the substance's
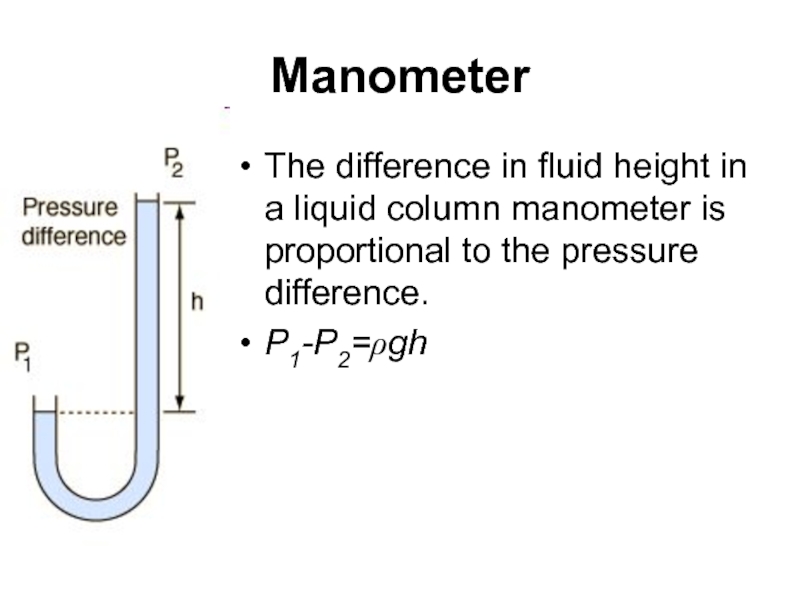
Слайд 43Manometer
The difference in fluid height in a liquid column manometer is
P1-P2=ρgh
Слайд 44Static Fluid Pressure
Pstatic fluid = ρgh where ρ = m/V =
g = gravitational acceleration
h = depth of fluid
The pressure exerted by a static fluid depends only upon the depth of the fluid, the density of the fluid, and the acceleration of gravity
Слайд 45Pressure Thrust
Thrust is a total force in a particular direction. The
F=P·A
Слайд 46Atmospheric Pressure
The surface of the earth is at the bottom of
1 atmosphere = 760 mmHg = 101.3 KPa
The bar is a unit of pressure defined as 100 kilopascals. It is about equal to the atmospheric pressure on Earth at sea level.
The unit mmHg is often called torr, particularly in vacuum applications: 760 mmHg = 760 torr
Слайд 49Aneroid barometer
An aneroid barometeru ses a small, flexible metal box called
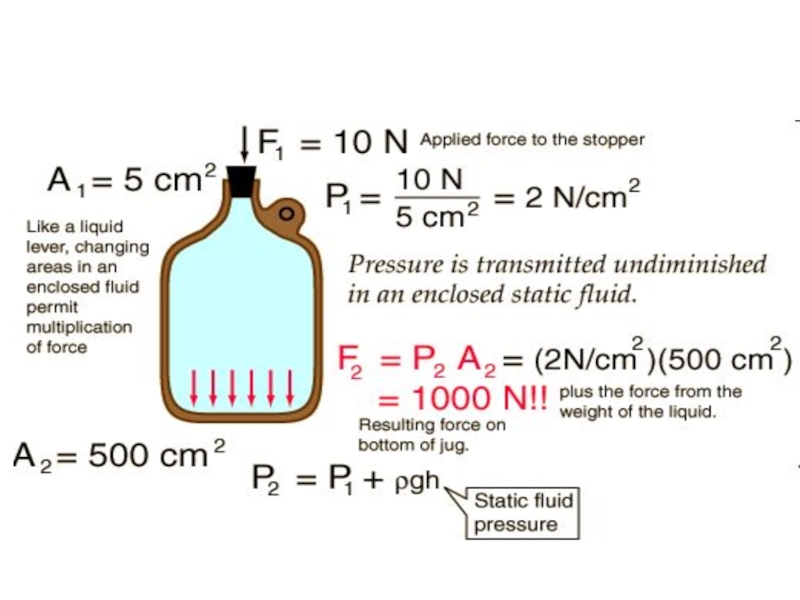
Слайд 52Pascal's Principle
Pressure exerted anywhere in a confined incompressible fluid is transmitted
Слайд 55Lift pump
The lift pump, also known as a suction pump, operates
on the upstroke of the plunger, the lower valve opens, the upper valve (situated on or in the plunger itself) is closed, and the low air pressure produced in the barrel allows atmospheric pressure on the surface of the water source, down below, to make the water move up the downpipe and eventually fill the barrel below the plunger.
On the downstroke, the lower valve closes, the upper one opens, and water is forced into the barrel above the upper valve. On the next upstroke, the water above the plunger is forced out of the spout, located at the top of the barrel, at the same time as the volume below the barrel fills up with water again.
Слайд 56Force pump
The force pump, also known as a pressure pump, operates
on the upstroke of the plunger, the outlet or delivery valve is closed and the inlet valve opens. The low air pressure produced in the barrel causes the water below to move up the downpipe and eventually fill the barrel.
On the downstroke, the inlet valve closes, the outlet valve opens, and the water is forced out via the outlet pipe, which is located at the bottom of the barrel.
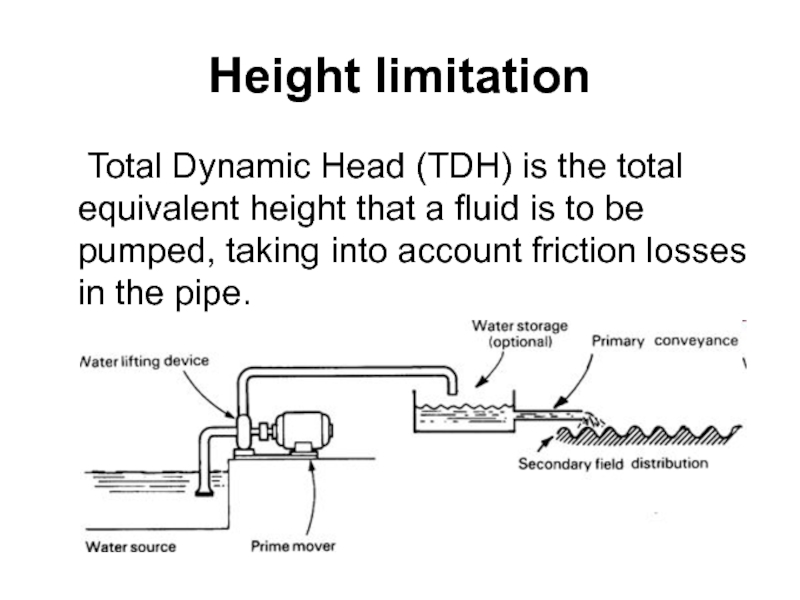
Слайд 58Height limitation
Total Dynamic Head (TDH) is the total equivalent height that
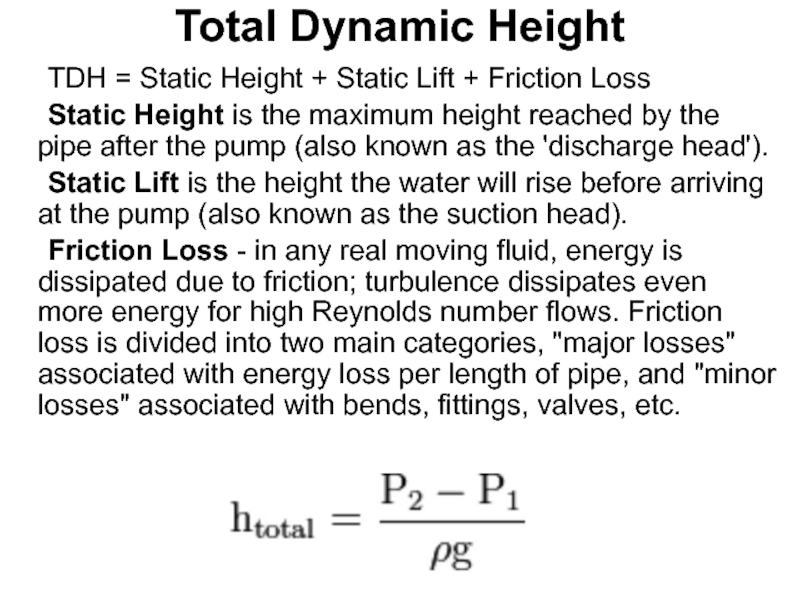
Слайд 59Total Dynamic Height
TDH = Static Height + Static Lift + Friction
Static Height is the maximum height reached by the pipe after the pump (also known as the 'discharge head').
Static Lift is the height the water will rise before arriving at the pump (also known as the suction head).
Friction Loss - in any real moving fluid, energy is dissipated due to friction; turbulence dissipates even more energy for high Reynolds number flows. Friction loss is divided into two main categories, "major losses" associated with energy loss per length of pipe, and "minor losses" associated with bends, fittings, valves, etc.
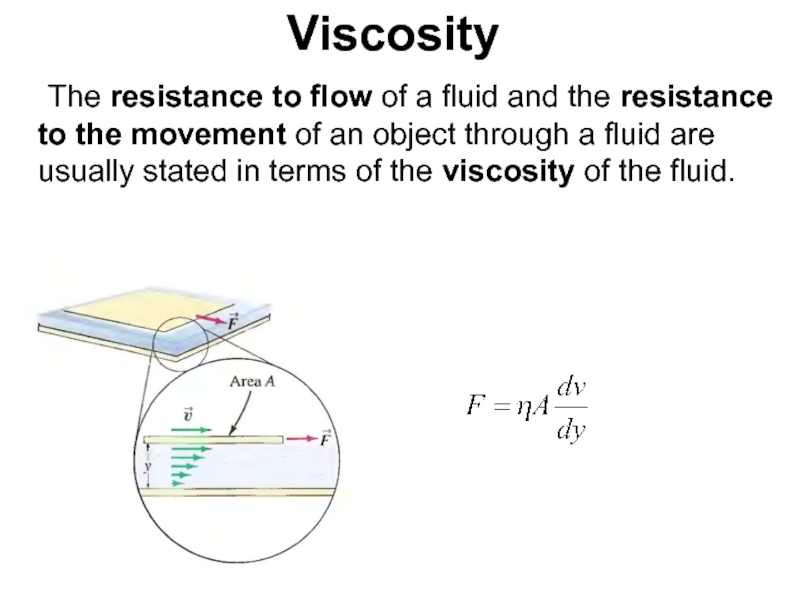
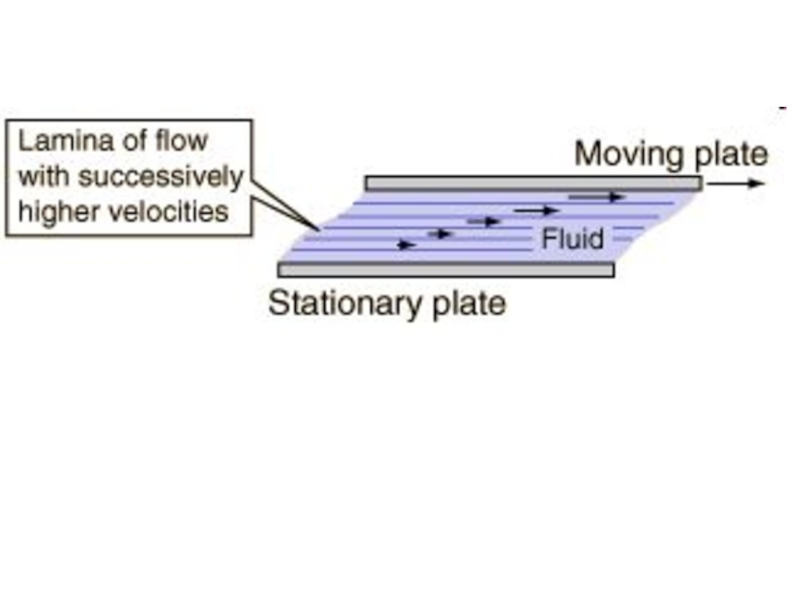
Слайд 60Viscosity
The resistance to flow of a fluid and the resistance to
Слайд 61
Experimentally, under conditions of laminar flow, the force required to move
Слайд 63Drag force due viscosity
In a viscous fluid, a boundary layer is
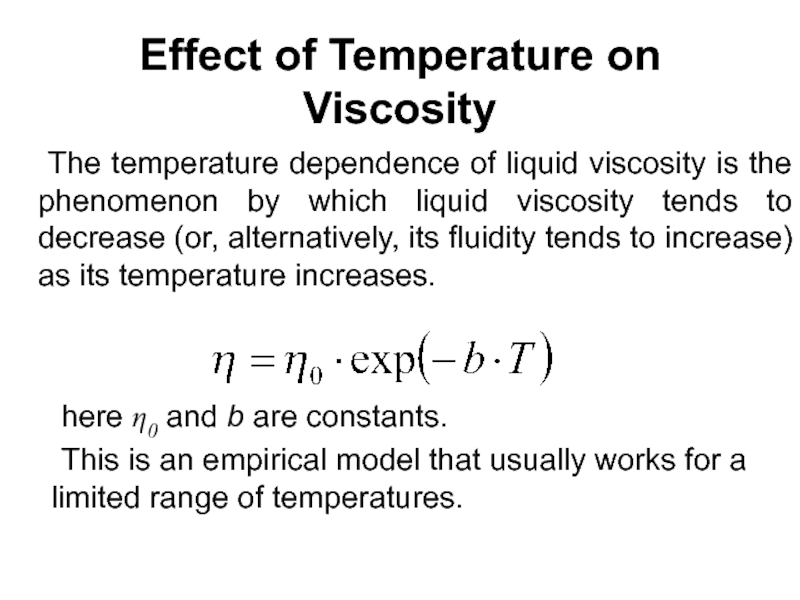
Слайд 64Effect of Temperature on Viscosity
The temperature dependence of liquid viscosity
here η0 and b are constants.
This is an empirical model that usually works for a limited range of temperatures.
Слайд 65Liquid Damping
Damping is an effect that reduces the amplitude of oscillations
Fluid viscous damping is a way to add energy dissipation to the lateral system of a building structure. A fluid viscous damper dissipates energy by pushing fluid through an orifice, producing a damping pressure which creates a force. These damping forces are 90 degrees out of phase with the displacement driven forces in the structure. This means that the damping force does not significantly increase the seismic loads for a comparable degree of structural deformation.
Слайд 68Buoyancy
Buoyancy arises from the fact that fluid pressure increases with depth
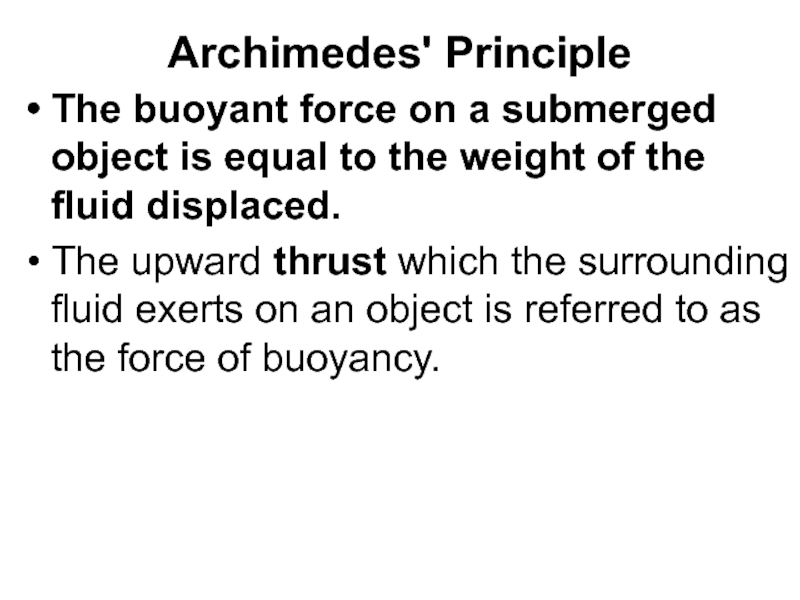
Слайд 69Archimedes' Principle
The buoyant force on a submerged object is equal to
The upward thrust which the surrounding fluid exerts on an object is referred to as the force of buoyancy.
Слайд 70Hydrometer
A hydrometer is an instrument used to measure the specific
A hydrometer is usually made of glass and consists of a cylindrical stem and a bulb weighted with mercury or lead shot to make it float upright. The liquid to be tested is poured into a tall container, often a graduated cylinder, and the hydrometer is gently lowered into the liquid until it floats freely. The point at which the surface of the liquid touches the stem of the hydrometer is noted. Hydrometers usually contain a scale inside the stem, so that the specific gravity can be read directly. A variety of scales exist, and are used depending on the context.
Hydrometers may be calibrated for different uses, such as a lactometer for measuring the density (creaminess) of milk, a saccharometer for measuring the density of sugar in a liquid, or an alcoholometer for measuring higher levels of alcohol in spirits.
Слайд 74Fluid Kinetic Energy
The kinetic energy of a moving fluid is more
Слайд 75Fluid Potential Energy
The potential energy of a moving fluid is more
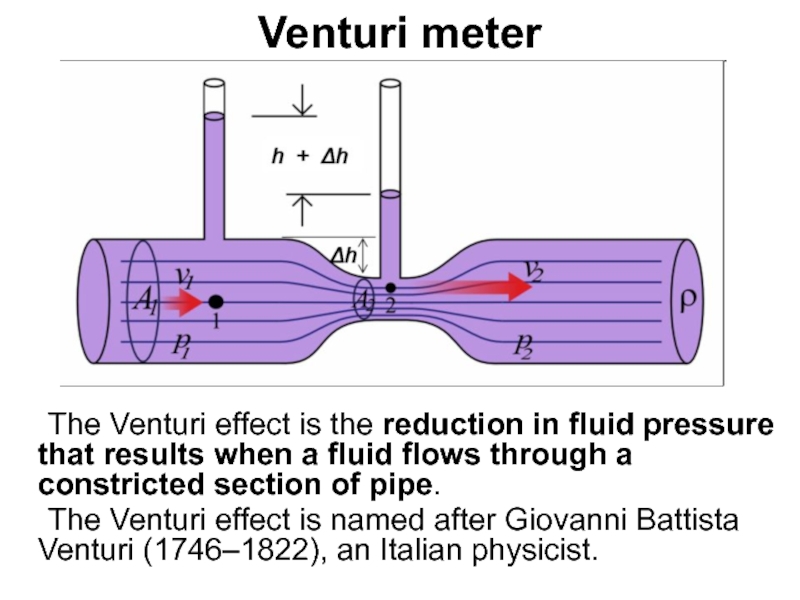
Слайд 77Venturi meter
The Venturi effect is the reduction in fluid pressure that
The Venturi effect is named after Giovanni Battista Venturi (1746–1822), an Italian physicist.