- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Diesel engines презентация
Содержание
- 1. Diesel engines
- 2. A slow speed or medium speed
- 3. s V-engine and in-line engine In
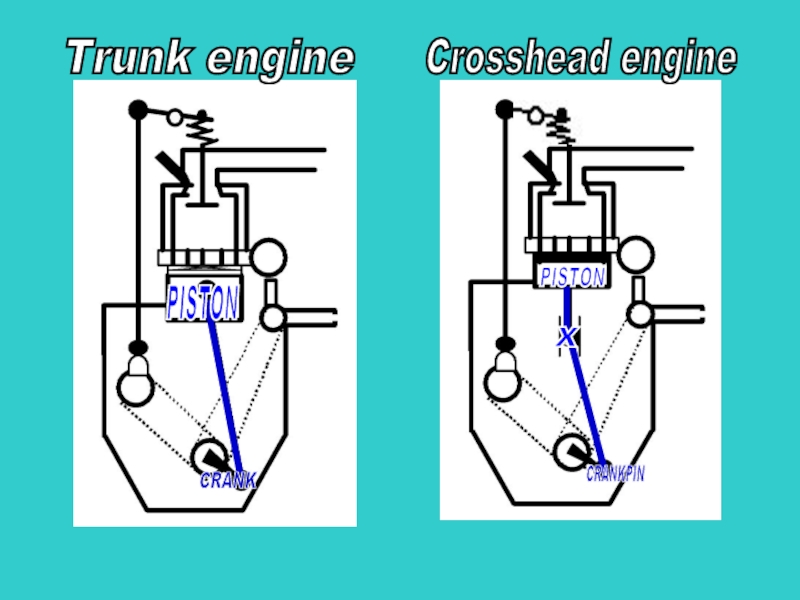
- 4. Trunk engine Crosshead engine PISTON
- 5. s 2-stroke crosshead engine
- 6. The cylinder is filled with air.
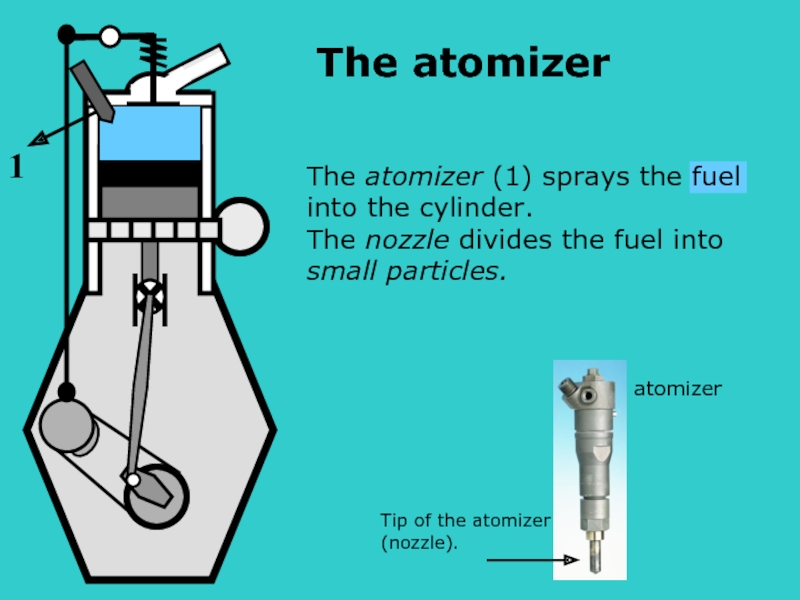
- 7. The atomizer (1) sprays the fuel
- 8. During the power stroke the
- 9. The piston makes a reciprocating motion. Piston The piston
- 10. 1 2 3 The crosshead
- 11. S 1 2 Crankshaft The crank (1)is connected to the crankshaft (2).
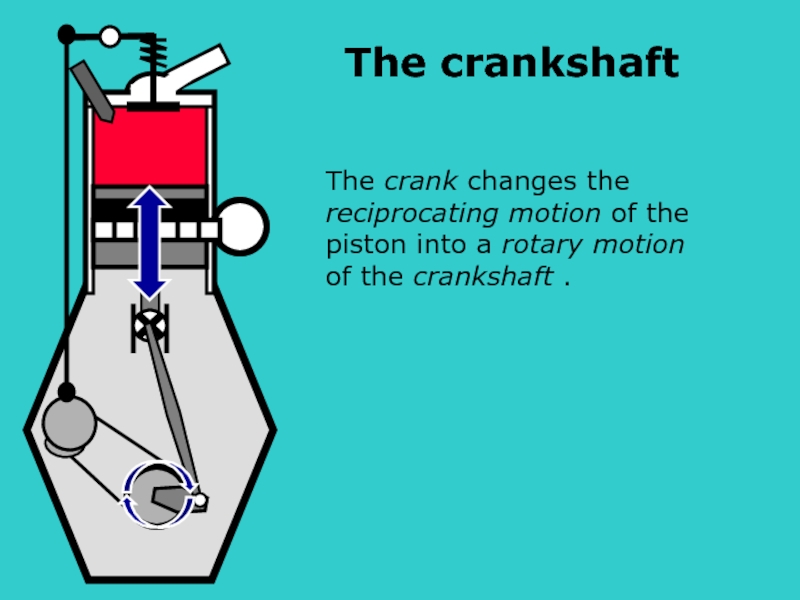
- 12. S The crank
- 13. S Gearwheels to drive the camshaft
- 14. S The campeak is fixed to the camshaft. campeak campeak The camshaft
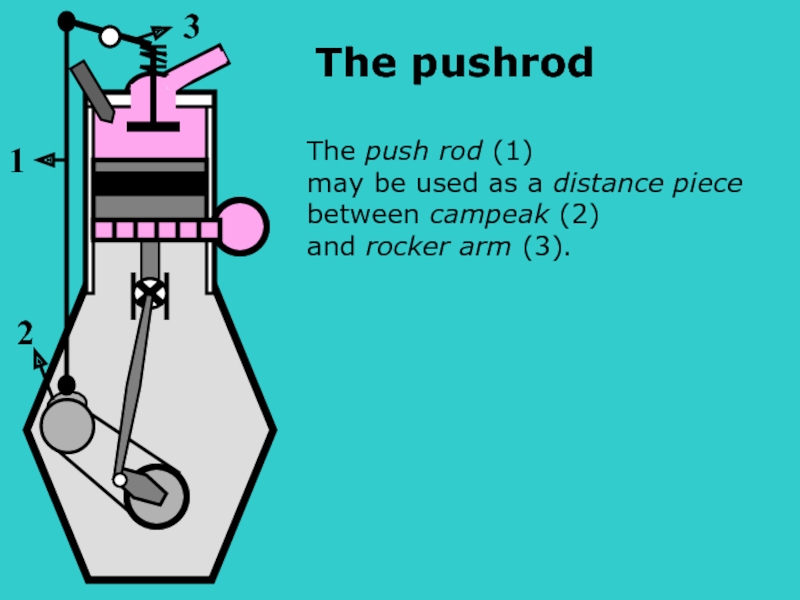
- 15. s The push rod (1) may
- 16. S The exhaust valve (1)
- 17. S The exhaust valve is
- 18. S The scavenging air
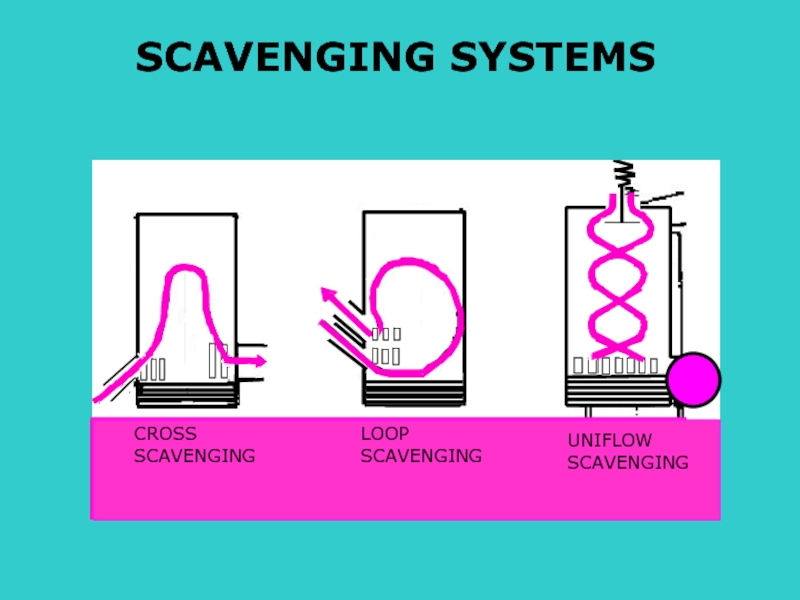
- 19. S CROSS SCAVENGING LOOP SCAVENGING UNIFLOW SCAVENGING
- 20. S The cylinder liner (1) and
- 21. A coolant (fresh water) is injected
- 22. s Cooling the piston: The
- 23. SO The piston rings (1)
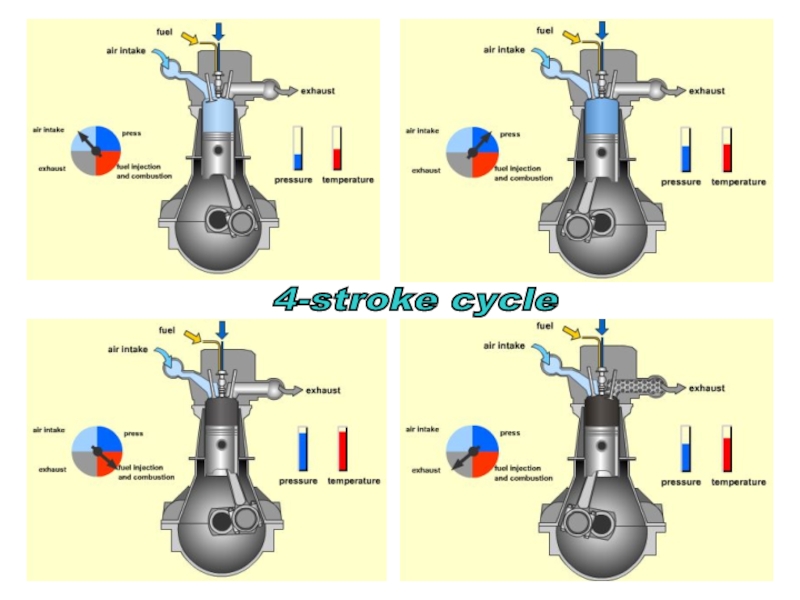
- 24. s 4-stroke cycle
- 25. S During the air induction stroke (or
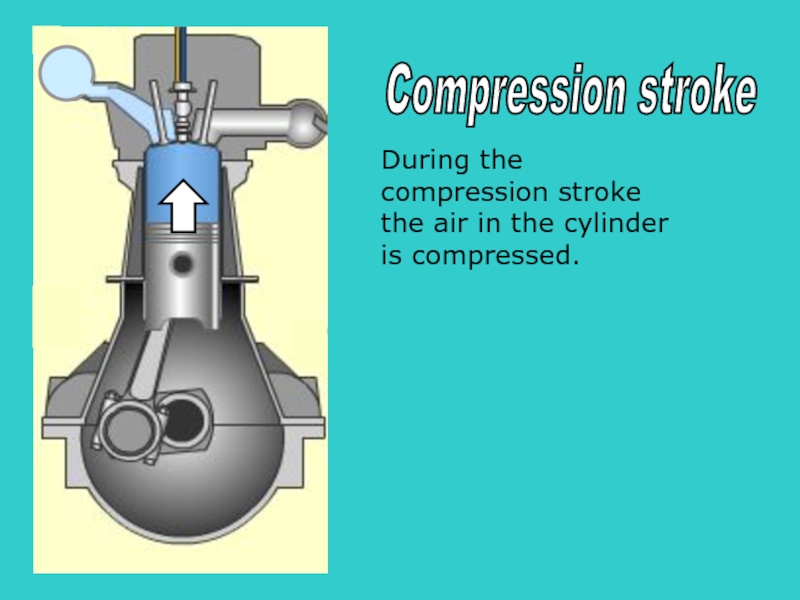
- 26. S During the compression stroke the air
- 27. S During the power
- 28. S During the exhaust stroke
Слайд 2
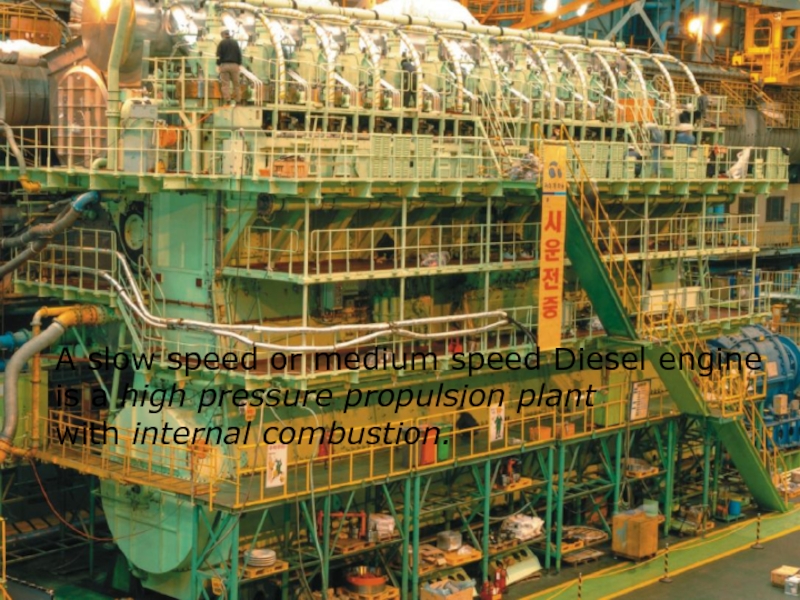
A slow speed or medium speed Diesel engine
is a high
with internal combustion.
Слайд 3s
V-engine and in-line engine
In a V-engine the cylinders are placed
V-engine
In-line
engine
Слайд 6
The cylinder is filled with air.
S
During the compression stroke the air
cylinder
Слайд 7
The atomizer (1) sprays the fuel into the cylinder.
1
atomizer
Tip of the atomizer
(nozzle).
The atomizer
Слайд 8 During the power stroke the fuel is injected and
1
2
The power stroke
Слайд 10
1
2
3
The crosshead (1) serves as a hinging connection between piston
Crosshead guides and
crosshead guide shoes (4)
absorb the forces onto
the crosshead when the piston goes down.
4
The crosshead
Слайд 12 S
The crank changes the
reciprocating motion of the
of the crankshaft .
The crankshaft
Слайд 15s
The push rod (1)
may be used as a distance piece
between campeak
and rocker arm (3).
1
3
2
The pushrod
Слайд 16S
The exhaust valve (1)
is actuated (opened) by the
rocking lever
2
1
The exhaust valve
Слайд 18S
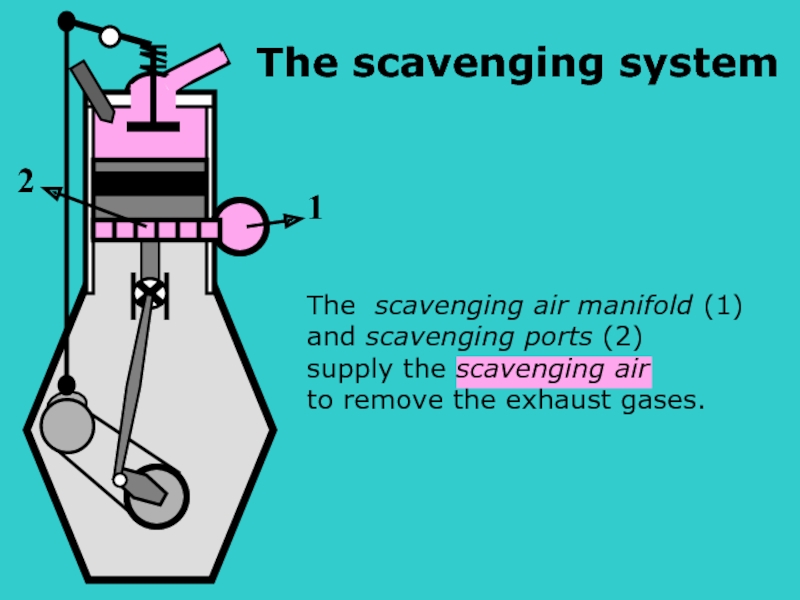
The scavenging air manifold (1)
and scavenging ports (2)
supply the scavenging air
to
1
2
The scavenging system
Слайд 20S
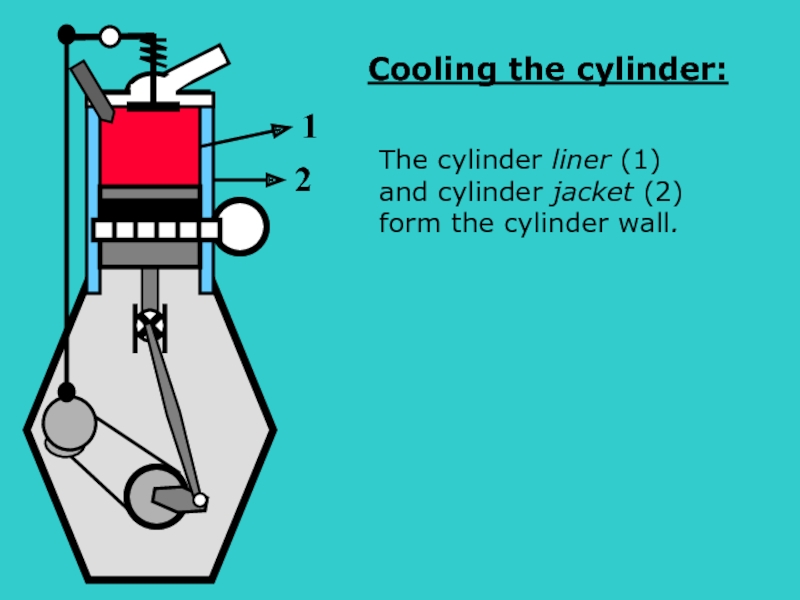
The cylinder liner (1)
and cylinder jacket (2)
form the cylinder wall.
1
2
Cooling the
Слайд 21
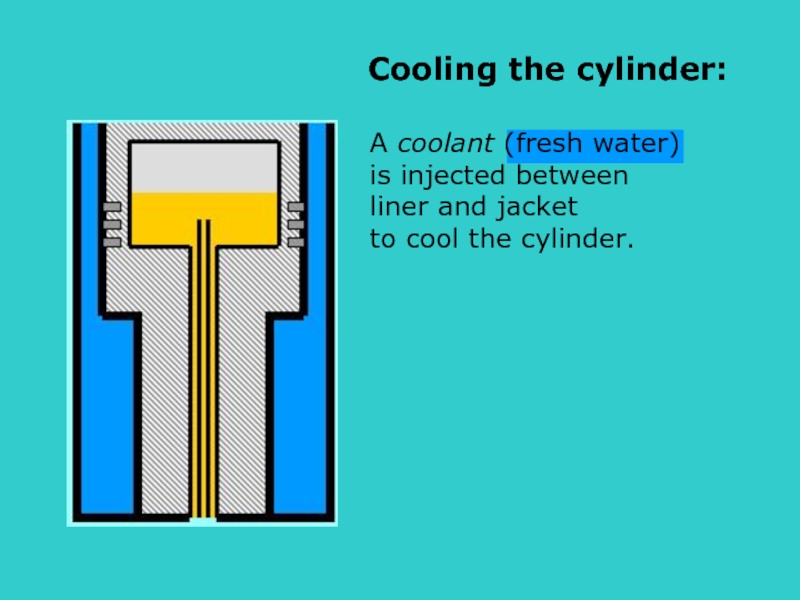
A coolant (fresh water)
is injected between
liner and jacket
to cool the cylinder.
s
Cooling
Слайд 22s
Cooling the piston:
The advantages of oil as
a coolant are:
. it
. it purifies;
. it forms a seal;
. it lubricates;
. it is anti-corrosive;
. it has a higher resistance
to heat.
The piston is cooled by oil.
Слайд 23 SO
The piston rings (1)
form a seal around the cylinder
1
Piston rings
Piston rings
Слайд 25S
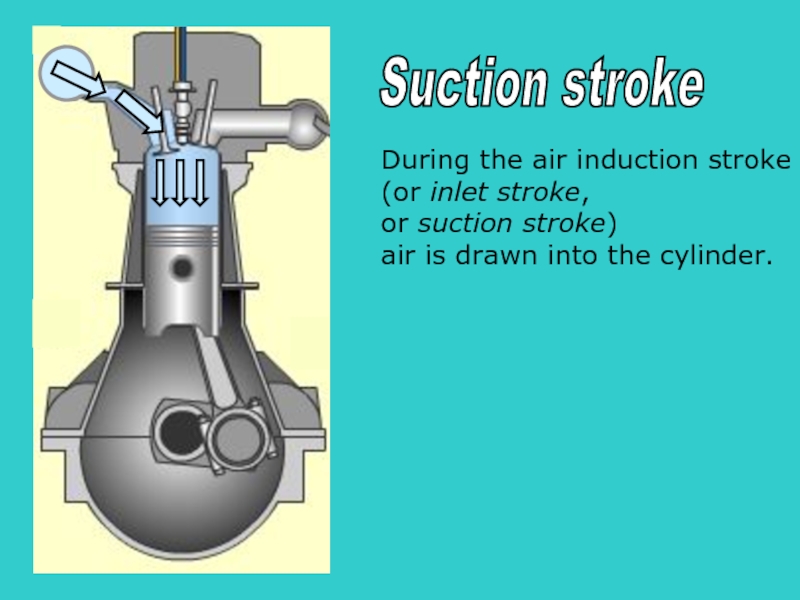
During the air induction stroke
(or inlet stroke,
or suction stroke)
air is
Suction stroke
Слайд 28S
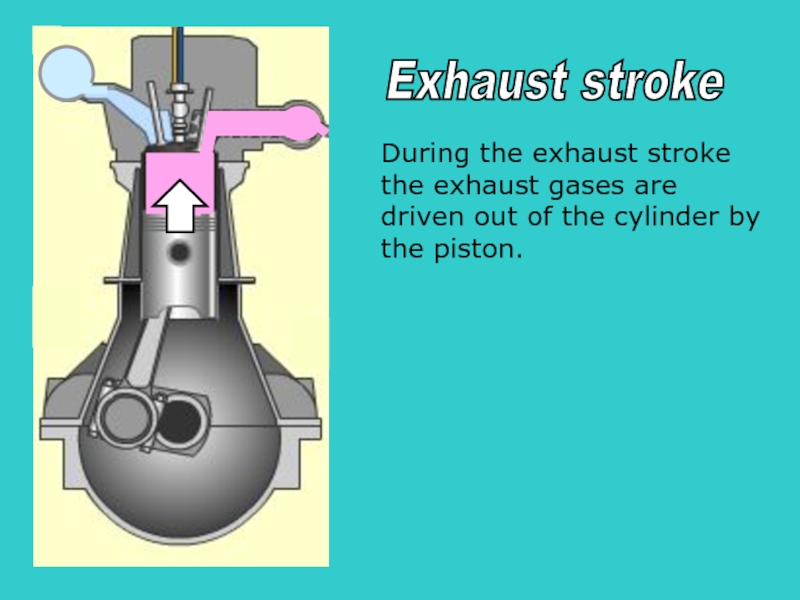
During the exhaust stroke
the exhaust gases are
driven out of the cylinder
the piston.
Exhaust stroke