- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Structuring. Transaction Framework презентация
Содержание
- 1. Structuring. Transaction Framework
- 2. Agenda Overview Perspective Creating
- 3. Overview Amsterdam Institute of Finance May, 2008
- 4. Transaction Framework Strategic Issues Do I
- 5. Transaction and Structuring Overview Accounting Tax
- 6. Structuring Environment Financial Preferences: Dilution Control
- 7. Different Menus Bull Market Menu Bear
- 8. Financing Approaches Left Hand Side Financing
- 9. Perspective Amsterdam Institute of Finance May, 2008
- 10. Capital Market Specific Factors Credit Specific
- 11. Acceptable leverage levels Interest Rate Amortization
- 12. Public Debt vs. Private Debt Relative Value
- 13. Amount of available cash flow Reliability
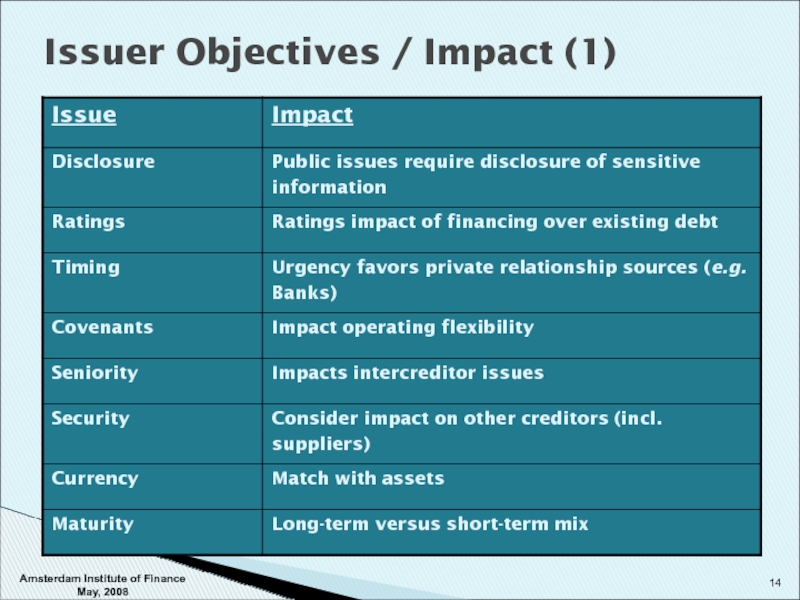
- 14. Issuer Objectives / Impact (1) Amsterdam Institute of Finance May, 2008
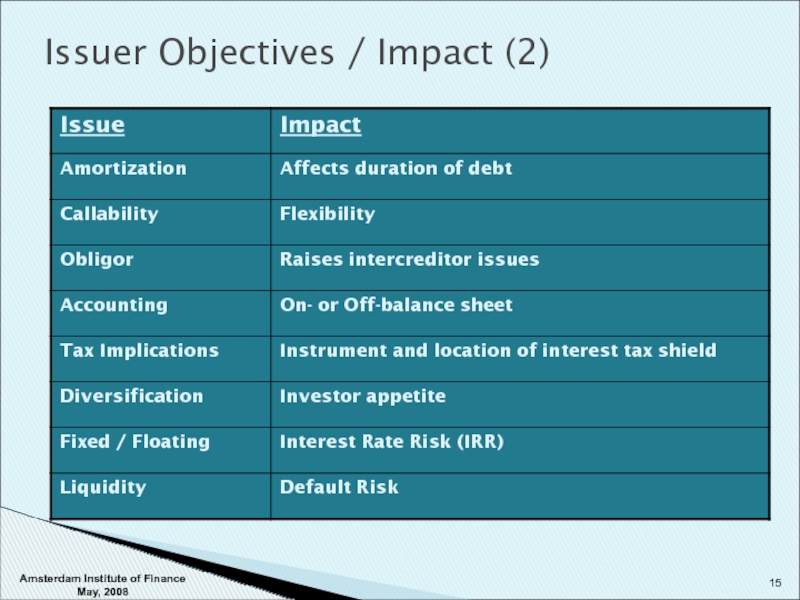
- 15. Issuer Objectives / Impact (2) Amsterdam Institute of Finance May, 2008
- 16. Critical Path & Decision Framework Financial Flexibility
- 17. Creating the Structure Amsterdam Institute of Finance May, 2008
- 18. Rule of Thumb Measures Balance Sheet Model
- 19. Deal Financial Arithmetic Amsterdam Institute of Finance May, 2008
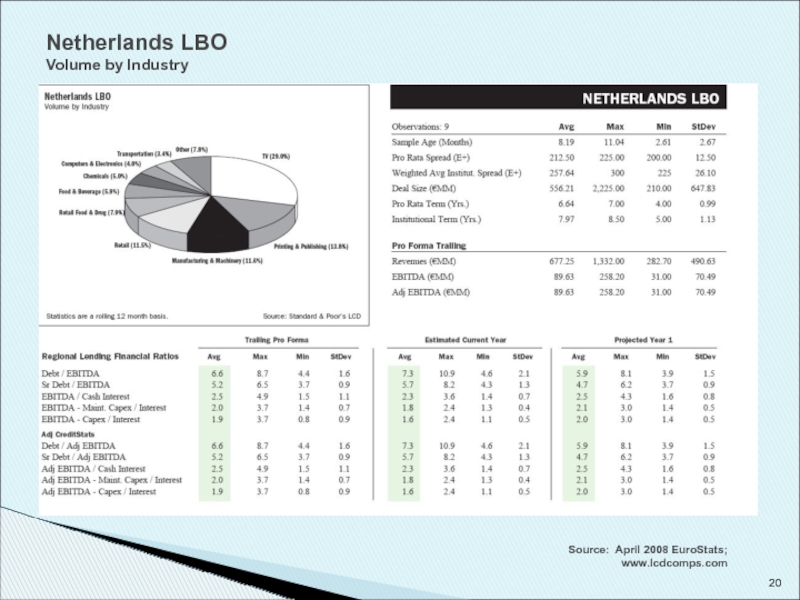
- 20. Netherlands LBO Volume by Industry Source: April 2008 EuroStats; www.lcdcomps.com
- 21. Purchase Price Minimum/Maximum Recapitalization Dividend Debt Refinancing
- 22. Revolver Tied to advance against current assets
- 23. Current Asset approach Use standard
- 24. Term Loans = Maximum Senior Debt -
- 25. Typical bank financings as structured as follows:
- 26. Long Term Debt = Max Total Debt
- 27. Subordination Senior lenders are concerned with
- 28. Contractual Subordination Holding Company Intermediate
- 29. Structural Subordination Holding Company Intermediate
- 30. Retranche Increase Pricing Lower Leverage Lower Purchase
- 31. Covenants Amsterdam Institute of Finance May, 2008
- 32. PURPOSE: maintain the original deal WHY
- 33. Categories Affirmative The maintenance, preservation and insurance
- 34. There are no standard covenants. They
- 35. First-lien leveraged loans covenant statistics: Average number
- 36. Amsterdam Institute of Finance May, 2008 Incidence
- 37. Amsterdam Institute of Finance May, 2008 Year
- 38. Amsterdam Institute of Finance May, 2008 Percent
- 39. Average Debt/EBITDA Covenant Level and Projected Ratio
- 40. Covenant Levels and Issues Covenants are negotiated
- 41. Translating Capital Structure and Debt Capacity into
- 42. Project Gear Amsterdam Institute of Finance May, 2008
- 43. Project Gear - Facts Potential deal
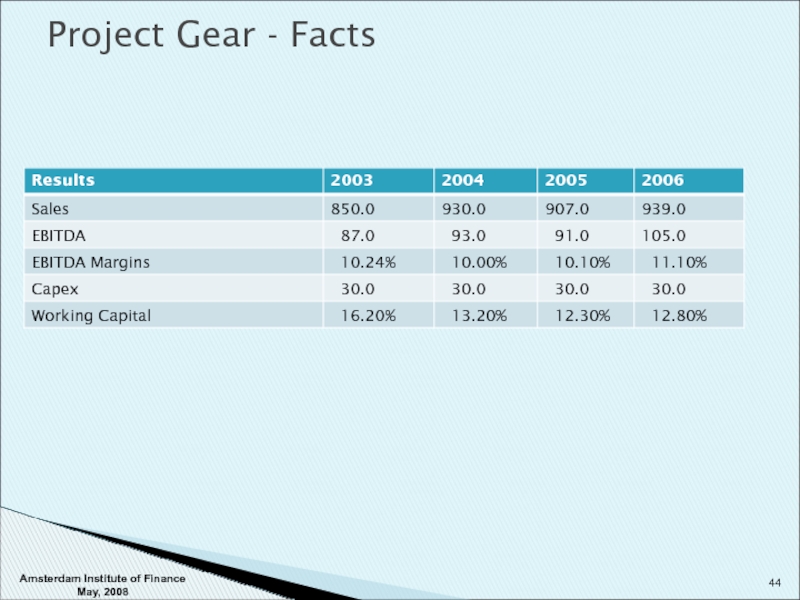
- 44. Project Gear - Facts Amsterdam Institute of Finance May, 2008
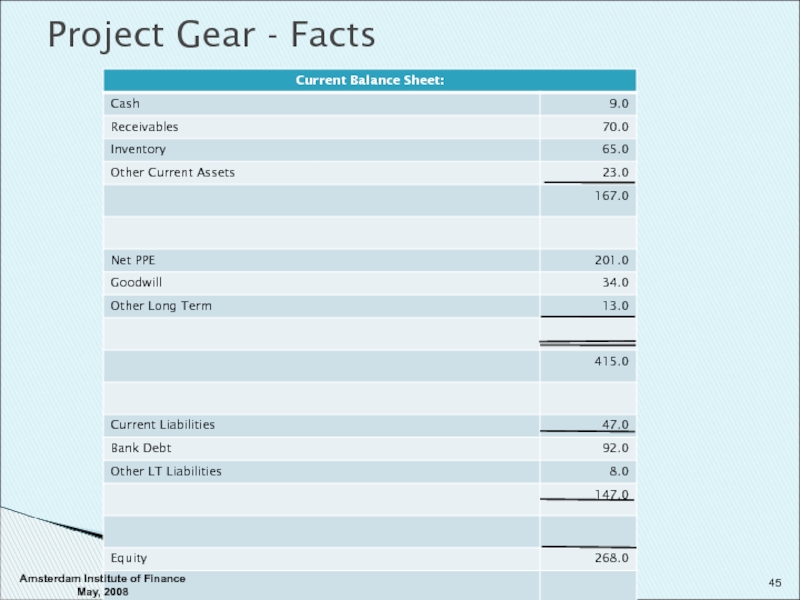
- 45. Project Gear - Facts Amsterdam Institute of Finance May, 2008
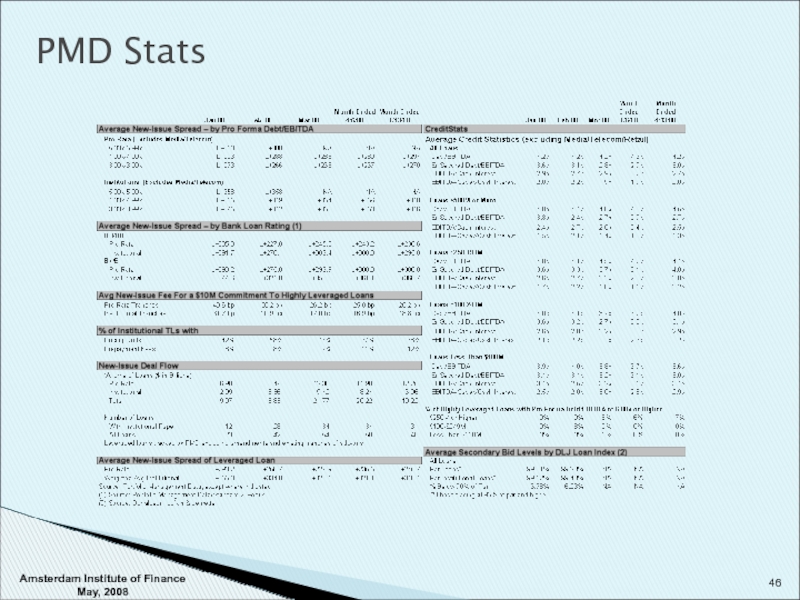
- 46. PMD Stats Amsterdam Institute of Finance May, 2008
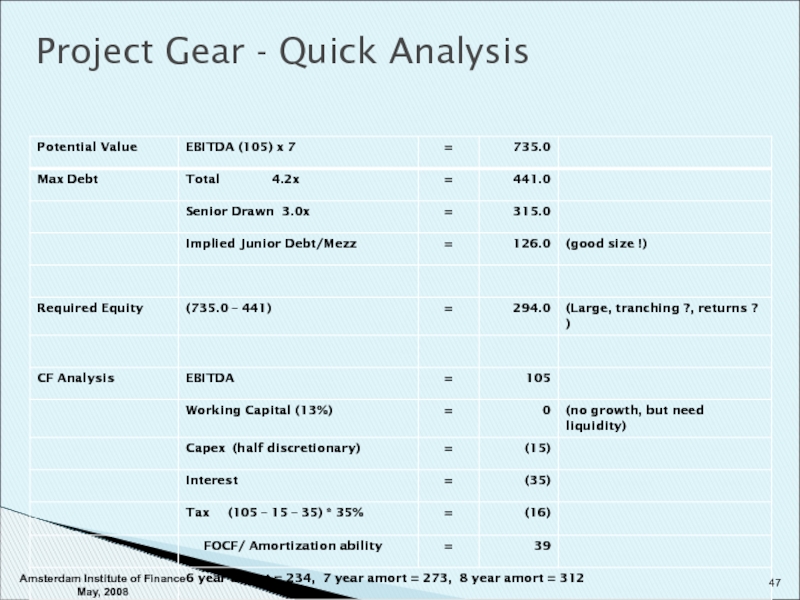
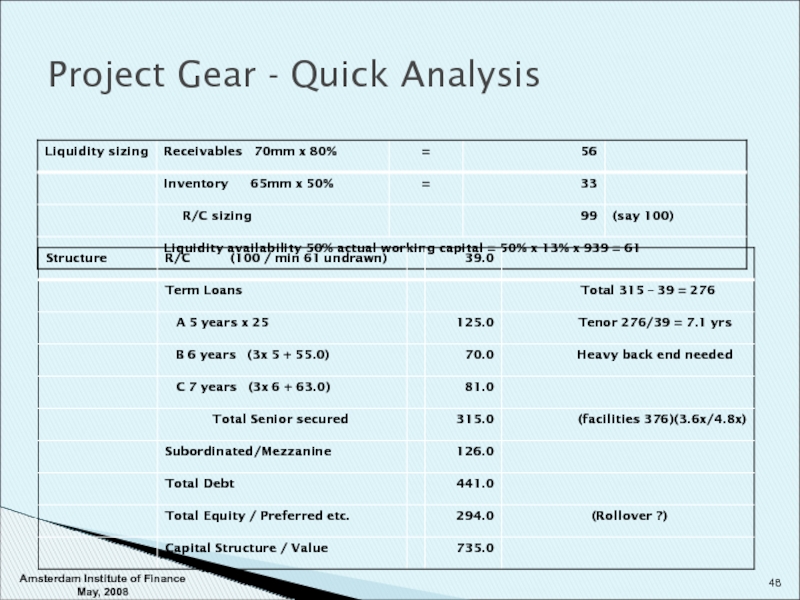
- 47. Project Gear - Quick Analysis Amsterdam Institute of Finance May, 2008
- 48. Project Gear - Quick Analysis Amsterdam Institute of Finance May, 2008
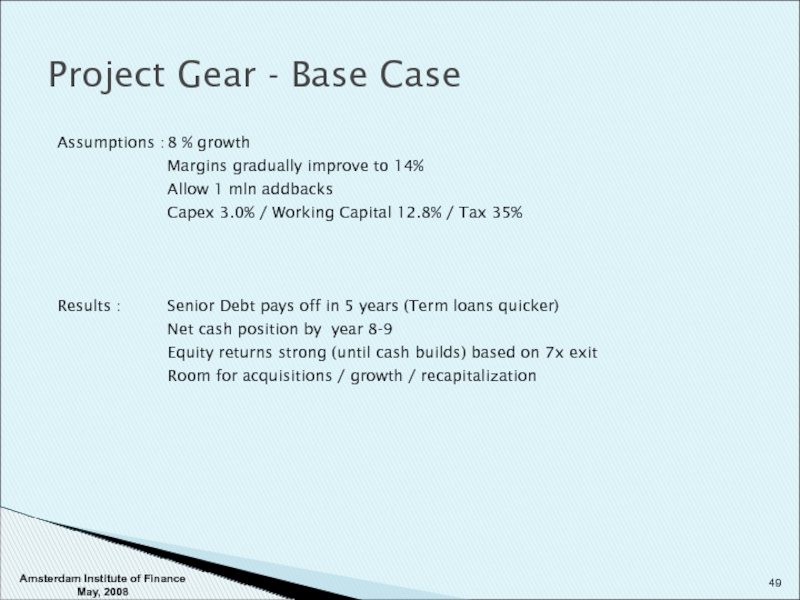
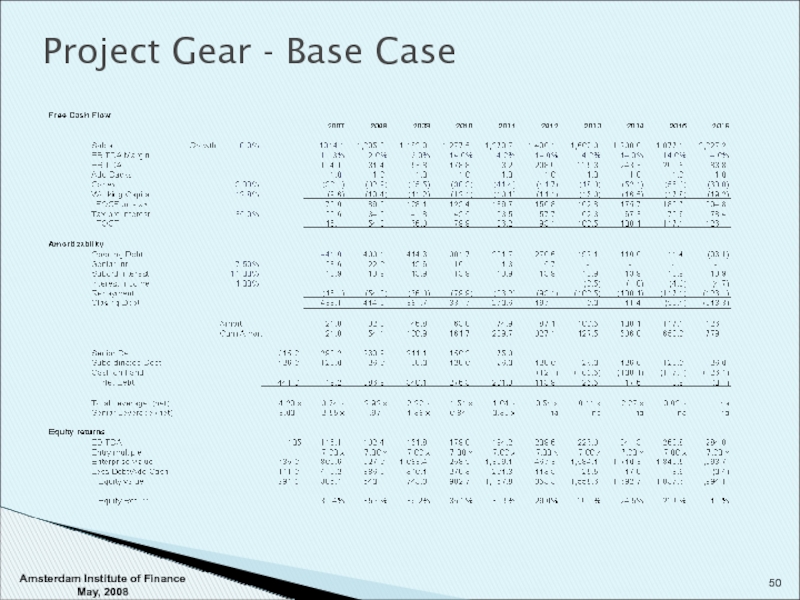
- 49. Project Gear - Base Case Assumptions : 8
- 50. Project Gear - Base Case Amsterdam Institute of Finance May, 2008
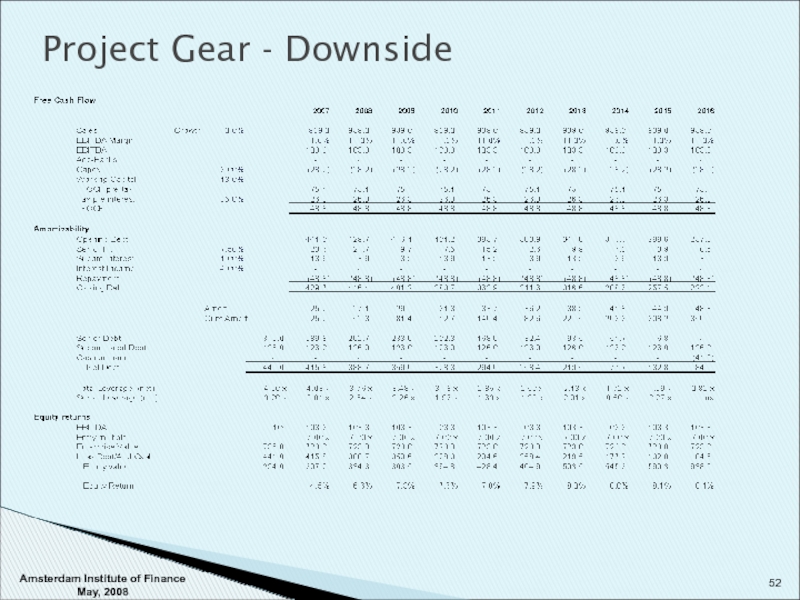
- 51. Project Gear - Downside Assumptions : 0%
- 52. Project Gear - Downside Amsterdam Institute of Finance May, 2008
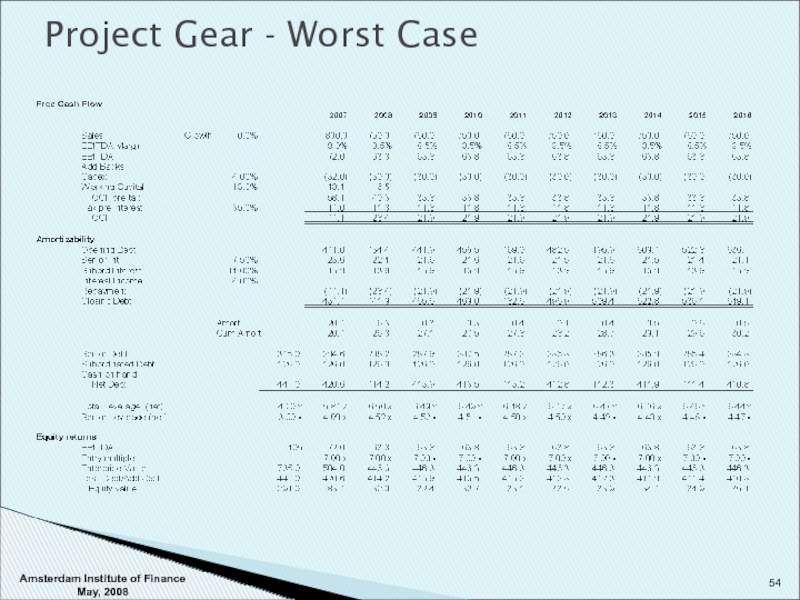
- 53. Project Gear - Worst Case Assumptons : 0%
- 54. Project Gear - Worst Case Amsterdam Institute of Finance May, 2008
- 55. Project Gear - Responses (How & When)
- 56. Disclosure This information has been prepared solely
Слайд 1Structuring
Joseph V. Rizzi
Amsterdam Institute of Finance
May, 2008
Copyright © Joe Rizzi, 2008
Слайд 2
Agenda
Overview
Perspective
Creating the structure
Covenants
Amsterdam Institute of Finance May, 2008
Слайд 4Transaction Framework
Strategic Issues
Do I make the acquisition?
Valuation
How much do
Financing
How do I pay?
Integration
Implementation of acquisition
Tactics
How do I make the offer?
Amsterdam Institute of Finance May, 2008
Слайд 5
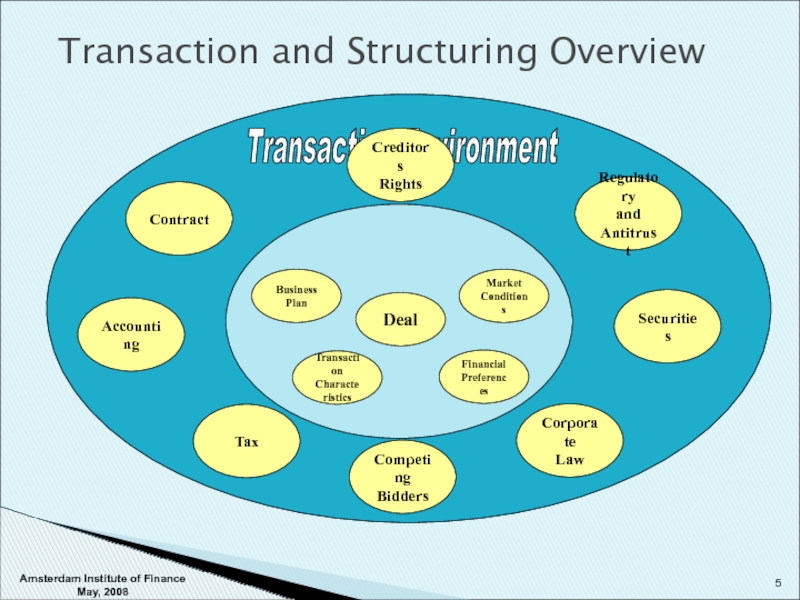
Transaction and Structuring Overview
Accounting
Tax
Corporate
Law
Securities
Regulatory
and Antitrust
Transaction Environment
Contract
Structuring Environment
Business
Plan
Transaction
Characteristics
Financial
Preferences
Market
Conditions
Deal
Competing
Bidders
Creditors
Rights
Amsterdam Institute
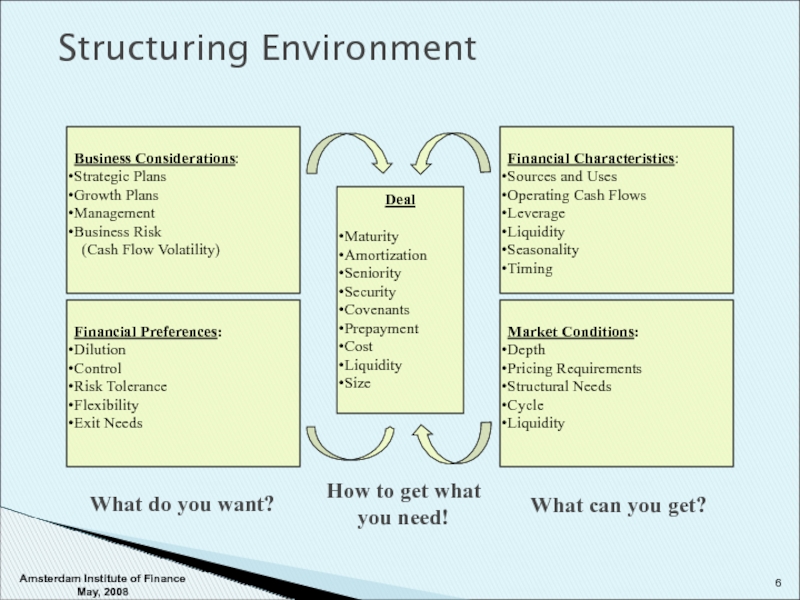
Слайд 6Structuring Environment
Financial Preferences:
Dilution
Control
Risk Tolerance
Flexibility
Exit Needs
Market Conditions:
Depth
Pricing Requirements
Structural Needs
Cycle
Liquidity
Business Considerations:
Strategic Plans
Growth Plans
Management
Business
(Cash Flow Volatility)
Financial Characteristics:
Sources and Uses
Operating Cash Flows
Leverage
Liquidity
Seasonality
Timing
Deal
Maturity
Amortization
Seniority
Security
Covenants
Prepayment
Cost
Liquidity
Size
What do you want?
How to get what
you need!
What can you get?
Amsterdam Institute of Finance May, 2008
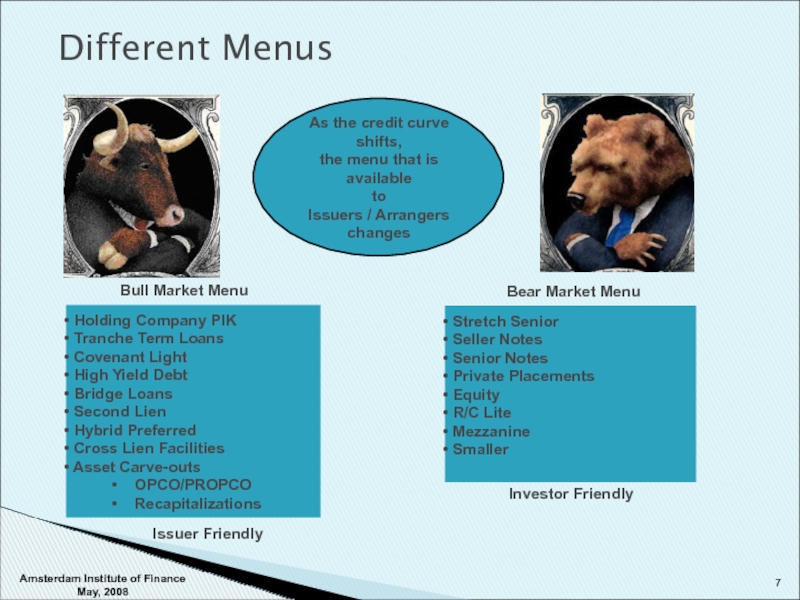
Слайд 7Different Menus
Bull Market Menu
Bear Market Menu
As the credit curve shifts,
the
to
Issuers / Arrangers
changes
Holding Company PIK
Tranche Term Loans
Covenant Light
High Yield Debt
Bridge Loans
Second Lien
Hybrid Preferred
Cross Lien Facilities
Asset Carve-outs
OPCO/PROPCO
Recapitalizations
Stretch Senior
Seller Notes
Senior Notes
Private Placements
Equity
R/C Lite
Mezzanine
Smaller
Issuer Friendly
Investor Friendly
Amsterdam Institute of Finance May, 2008
Слайд 8Financing Approaches
Left Hand Side Financing
Right Hand Side Financing
Based on the cash
Some examples include:
Asset Based Lending
Factoring
Leasing
Project Finance
Securitization
Based on the cash flow of the entire company.
Some examples include:
Bank Debt
Public Bonds
Mezzanine
Preferred Stock
Common Stock
Amsterdam Institute of Finance May, 2008
Слайд 10Capital Market Specific Factors
Credit Specific Factors
Customer Objectives
Valuation
Structuring Perspective
Amsterdam Institute of Finance
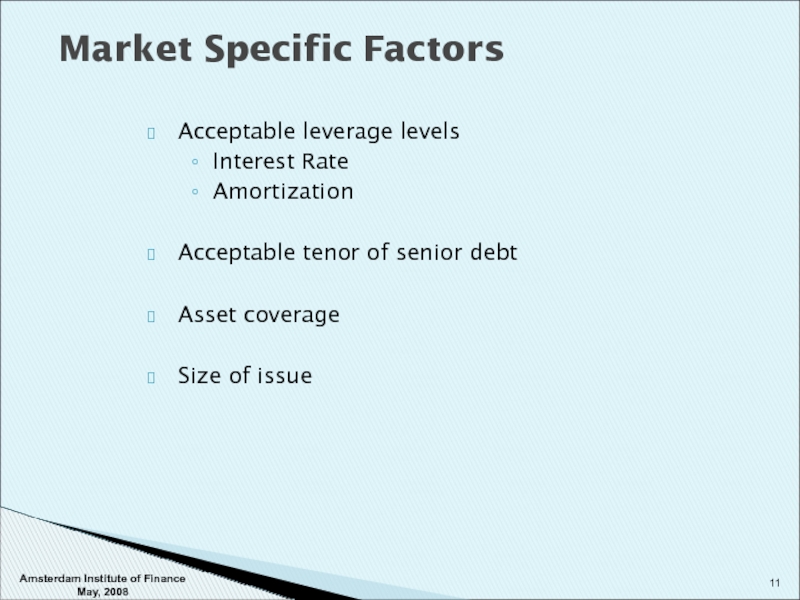
Слайд 11Acceptable leverage levels
Interest Rate
Amortization
Acceptable tenor of senior debt
Asset coverage
Size of issue
Market
Amsterdam Institute of Finance May, 2008
Слайд 12Public Debt vs. Private Debt
Relative Value Analysis
Domestic vs. International Issuance
Fixed vs.
Long vs. Short Term
Loans vs. Bonds
Structuring Issues
Amsterdam Institute of Finance May, 2008
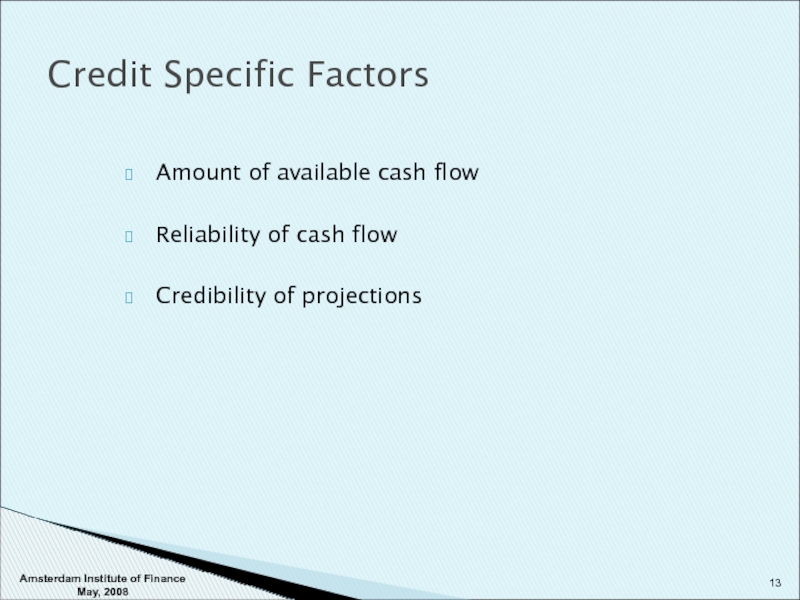
Слайд 13Amount of available cash flow
Reliability of cash flow
Credibility of projections
Credit Specific
Amsterdam Institute of Finance May, 2008
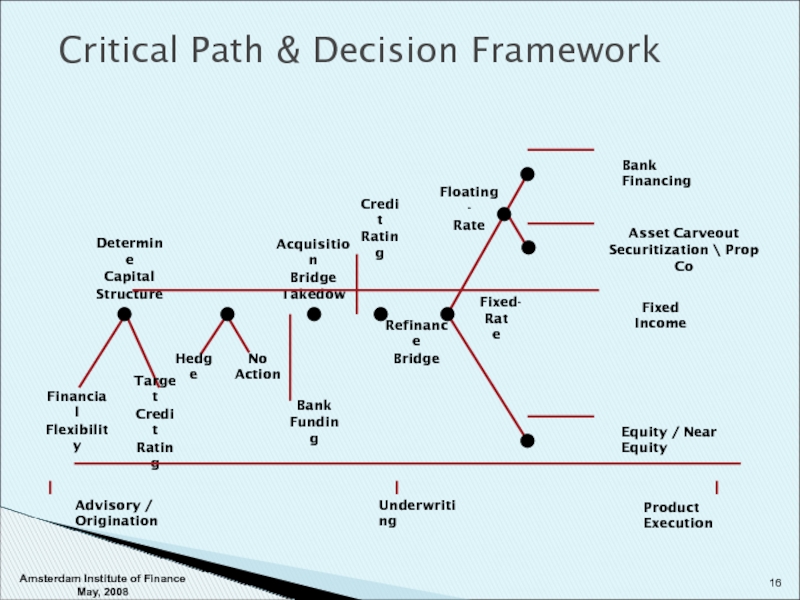
Слайд 16Critical Path & Decision Framework
Financial
Flexibility
Target
Credit
Rating
Determine
Capital
Structure
Hedge
No Action
Bank
Funding
Acquisition
Bridge
Takedown
Credit
Rating
Fixed Income
Asset Carveout
Securitization \
Bank Financing
Equity / Near Equity
Refinance
Bridge
Fixed-
Rate
Floating-
Rate
Advisory / Origination
Underwriting
Product Execution
Amsterdam Institute of Finance May, 2008
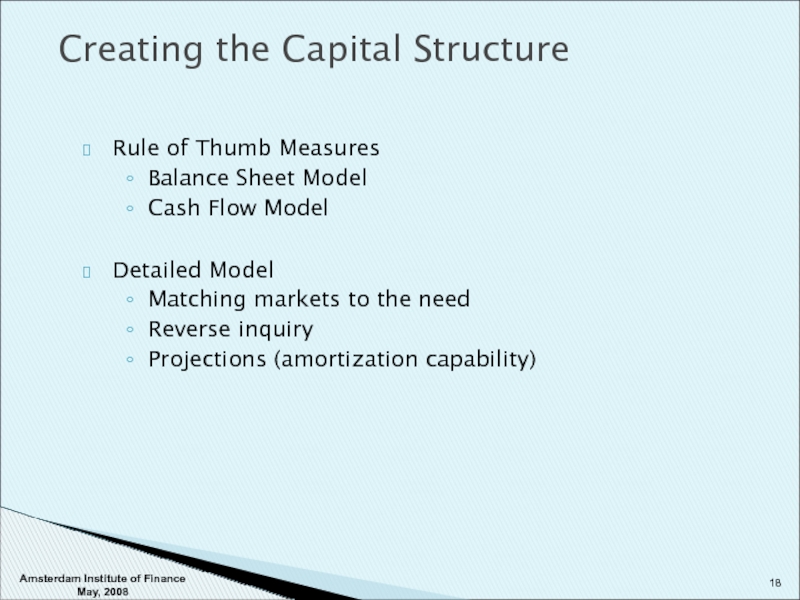
Слайд 18Rule of Thumb Measures
Balance Sheet Model
Cash Flow Model
Detailed Model
Matching markets to
Reverse inquiry
Projections (amortization capability)
Creating the Capital Structure
Amsterdam Institute of Finance May, 2008
Слайд 21Purchase Price
Minimum/Maximum
Recapitalization Dividend
Debt Refinancing
Callability
Premiums
Tax Issues
Expenses
Other Uses
Financing Need As a Starting Point
Amsterdam
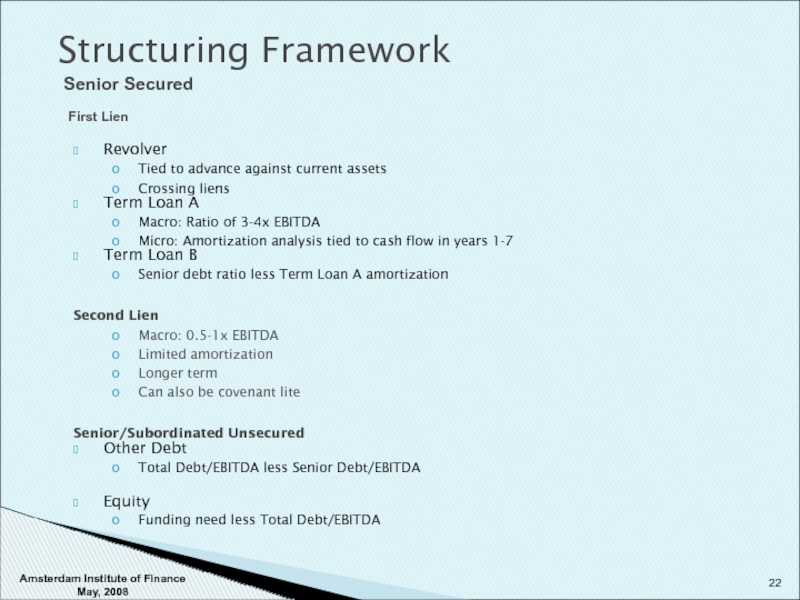
Слайд 22Revolver
Tied to advance against current assets
Crossing liens
Term Loan A
Macro: Ratio of
Micro: Amortization analysis tied to cash flow in years 1-7
Term Loan B
Senior debt ratio less Term Loan A amortization
Second Lien
Macro: 0.5-1x EBITDA
Limited amortization
Longer term
Can also be covenant lite
Senior/Subordinated Unsecured
Other Debt
Total Debt/EBITDA less Senior Debt/EBITDA
Equity
Funding need less Total Debt/EBITDA
Structuring Framework
Senior Secured
First Lien
Amsterdam Institute of Finance May, 2008
Слайд 23
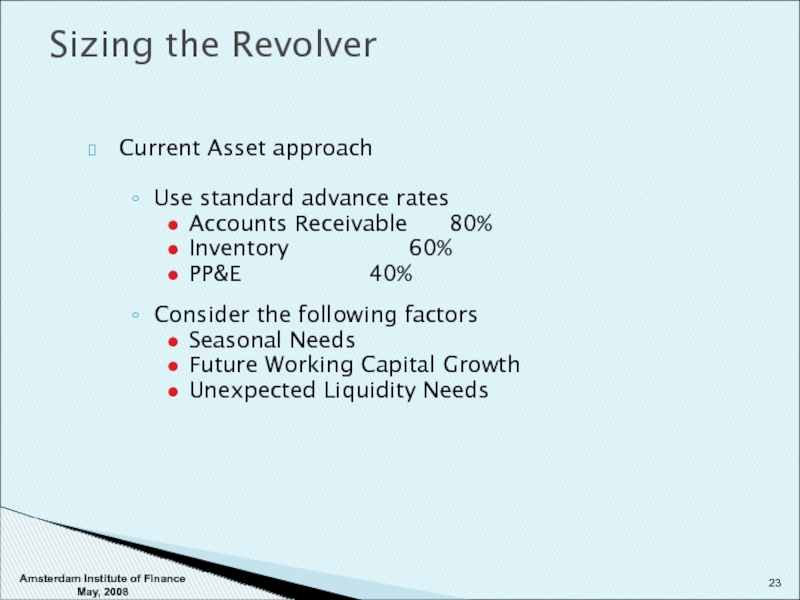
Current Asset approach
Use standard advance rates
Accounts Receivable 80%
Inventory 60%
PP&E 40%
Consider
Seasonal Needs
Future Working Capital Growth
Unexpected Liquidity Needs
Sizing the Revolver
Amsterdam Institute of Finance May, 2008
Слайд 24Term Loans = Maximum Senior Debt - Revolver
Focus is on Free
Market conditions also dictate the maximum tenor of the loan and the amount required to be amortized in the first five years
Acceptable asset coverage is also a consideration in determining the size of the term loans
Sizing the Term Loans
Amsterdam Institute of Finance May, 2008
Слайд 25Typical bank financings as structured as follows:
Revolving Credit
Term Loan A (amortising)
Term
Add-On Term Loans
Large unfunded revolvers are seldom used today due to the fact that it is capital unfriendly to banks and companies don’t like to pay for unused commitments.
In the interest of keeping flexibility for the long term, additional indebtedness baskets should be negotiated upfront. This allows companies to access either the bank or bond markets under their existing credit agreements and saves the costs of having to refinance.
Amsterdam Institute of Finance May, 2008
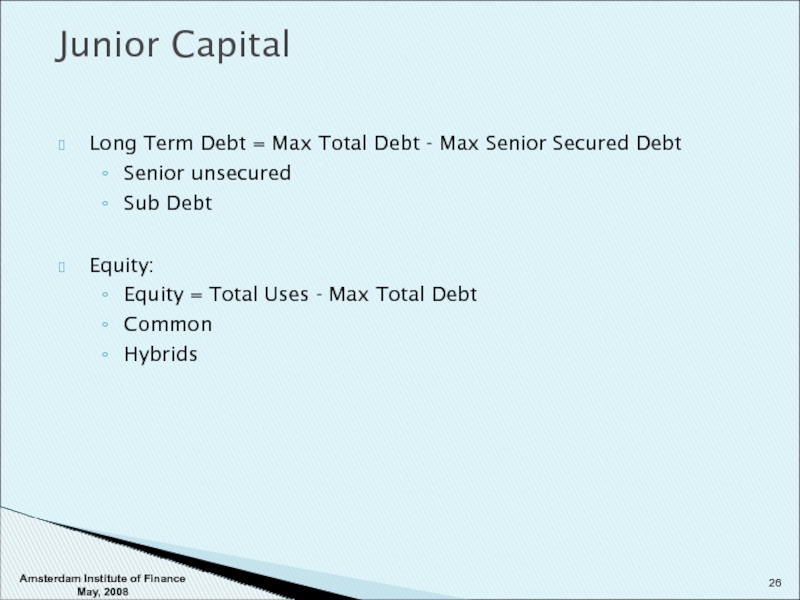
Слайд 26Long Term Debt = Max Total Debt - Max Senior Secured
Senior unsecured
Sub Debt
Equity:
Equity = Total Uses - Max Total Debt
Common
Hybrids
Junior Capital
Amsterdam Institute of Finance May, 2008
Слайд 27Subordination
Senior lenders are concerned with the implications of having high
EURO High Yield investors to date have not been as vocal as senior bank lenders, viewing the issue as one of pricing rather than principle.
All other things being equal, sophisticated investors will probably price structural subordination at 60-120 bps.
Amsterdam Institute of Finance May, 2008
Слайд 28
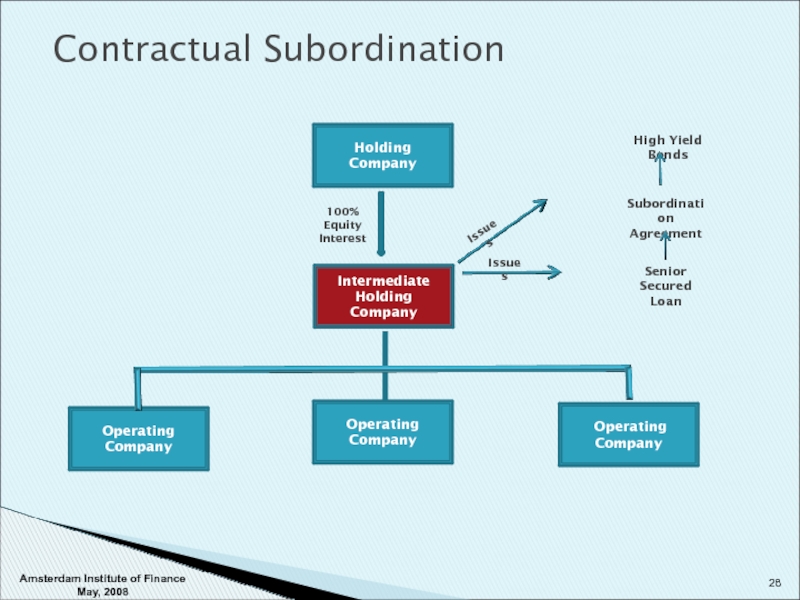
Contractual Subordination
Holding Company
Intermediate Holding Company
Operating Company
Operating Company
Operating
Company
100% Equity
Interest
Issues
Issues
High Yield Bonds
Subordination
Agreement
Senior
Loan
Amsterdam Institute of Finance May, 2008
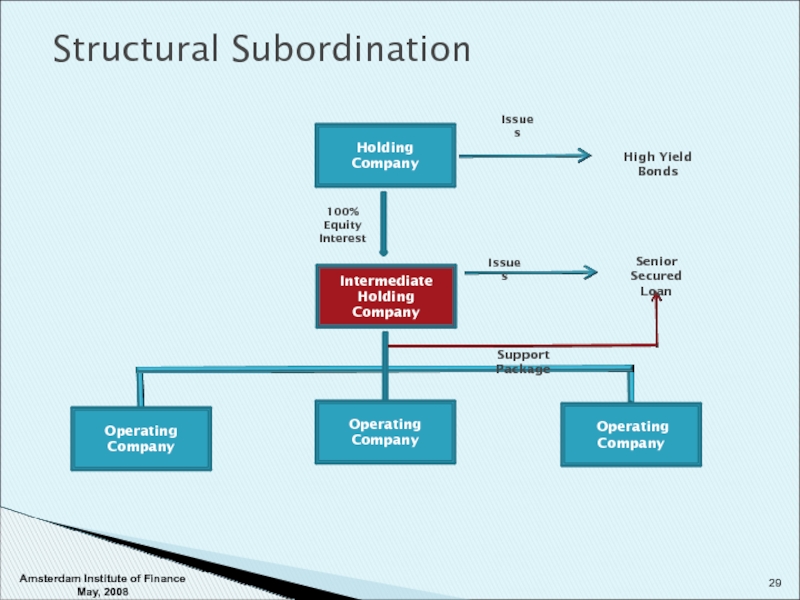
Слайд 29
Structural Subordination
Holding Company
Intermediate Holding Company
Operating Company
Operating Company
Operating
Company
100% Equity
Interest
Issues
Issues
High Yield Bonds
Support
Senior Secured
Loan
Amsterdam Institute of Finance May, 2008
Слайд 30Retranche
Increase Pricing
Lower Leverage
Lower Purchase Price
Seller Paper
Increase Equity
Senior Notes to cover Amortizing
Term Loan Carve-Out
Asset Sales
Second Lien
Debt covenants
Fixing Broken Deal
Amsterdam Institute of Finance May, 2008
Слайд 32PURPOSE: maintain the original deal
WHY
Agency problem due to asymmetric information
Adverse Selection
Moral
FOCUS
Asset Substitution
Cash Control
Payment and asset priority
Covenants - Fundamentals
Amsterdam Institute of Finance May, 2008
Слайд 33Categories
Affirmative
The maintenance, preservation and insurance of corporate assets and the compliance
Negative
Limit or prohibit the company from undertaking certain actions which would lower the overall credit quality or damage a potential secondary repayment source
Financial
Provide an early warning for deteriorating operating performance
Approach
Maintenance (Preserving the credit)
Incurrence (Maintaining relative priority of claim)
Covenants – Categories and Approach
Amsterdam Institute of Finance May, 2008
Слайд 34There are no standard covenants.
They must be tailor fit for
The steps in structuring the covenants are:
Identify the risks (Business, Financial & Structural)
Select Covenants to monitor the risks
- Need to prioritize the risks to monitor because it will be impossible to monitor every risk
- The time and costs to monitor the covenants must be considered (i.e. sometimes one covenant can cover multiple risks)
Set Appropriate Levels
- Want the covenants to trigger a warning before any principal or interest payments become delinquent. Need to factor in any seasonal needs to the covenant levels.
Structuring Covenants
Amsterdam Institute of Finance May, 2008
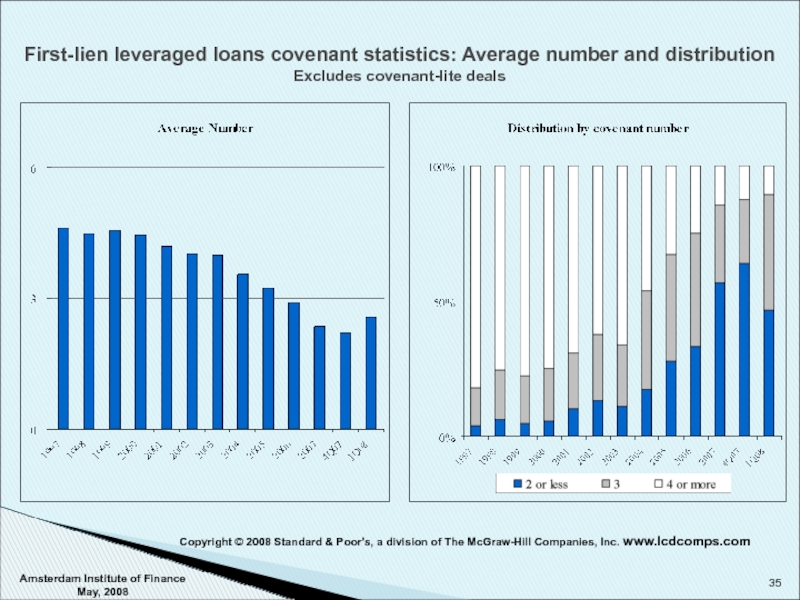
Слайд 35First-lien leveraged loans covenant statistics: Average number and distribution Excludes covenant-lite
Amsterdam Institute of Finance May, 2008
Copyright © 2008 Standard & Poor's, a division of The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. www.lcdcomps.com
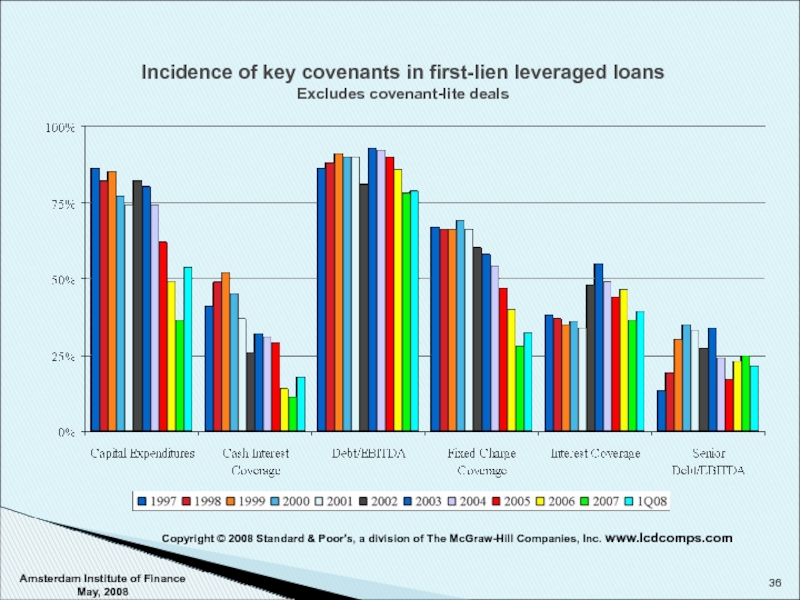
Слайд 36Amsterdam Institute of Finance May, 2008
Incidence of key covenants in first-lien
Copyright © 2008 Standard & Poor's, a division of The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. www.lcdcomps.com
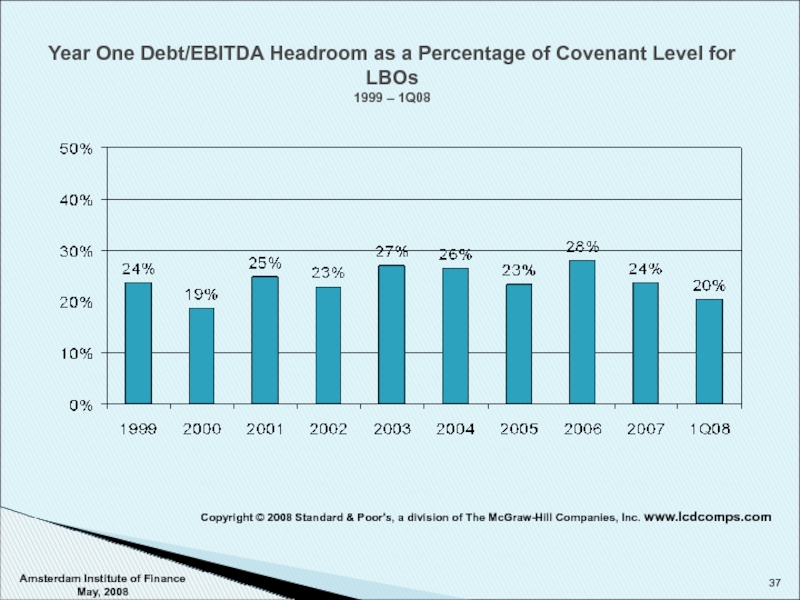
Слайд 37Amsterdam Institute of Finance May, 2008
Year One Debt/EBITDA Headroom as a
Copyright © 2008 Standard & Poor's, a division of The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. www.lcdcomps.com
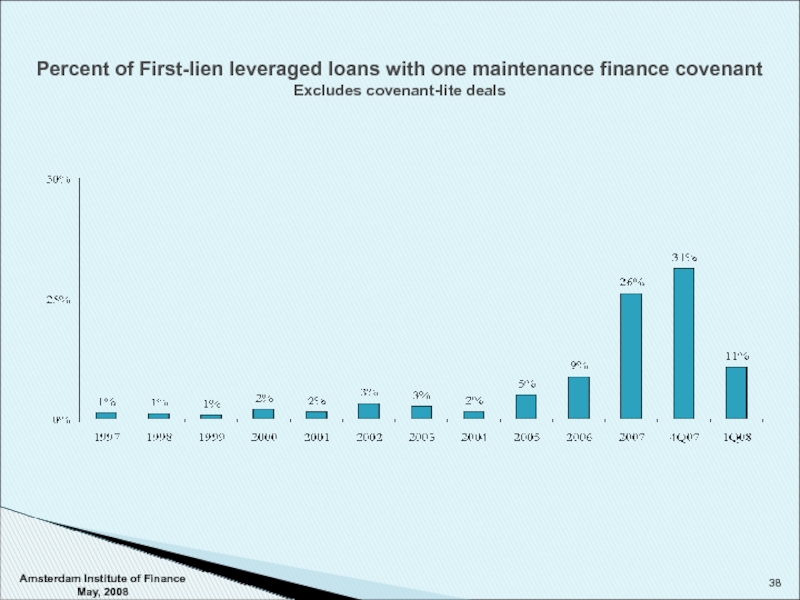
Слайд 38Amsterdam Institute of Finance May, 2008
Percent of First-lien leveraged loans with
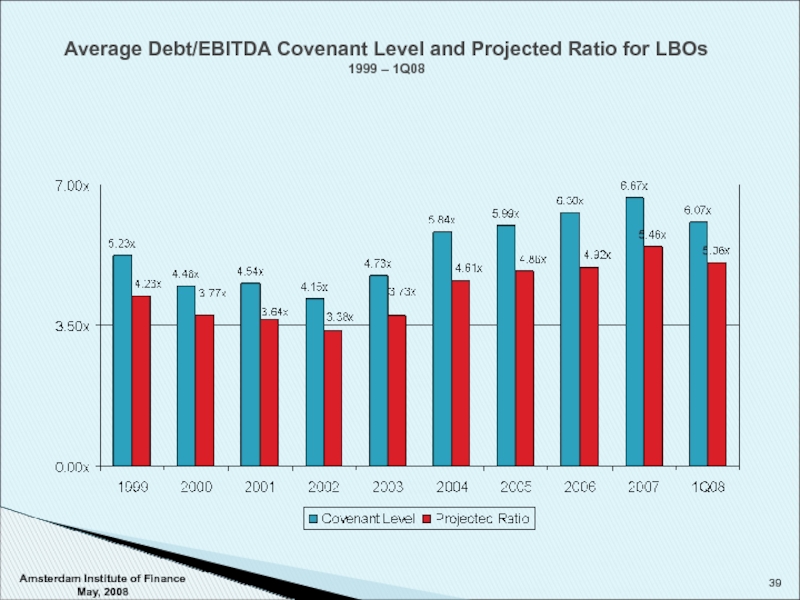
Слайд 39Average Debt/EBITDA Covenant Level and Projected Ratio for LBOs
1999 – 1Q08
Amsterdam
Слайд 40Covenant Levels and Issues
Covenants are negotiated between the lender and borrower.
Covenant
Other covenant issues include releases, voting rights and baskets.
Copyright © 2008 Standard & Poor's, a division of The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. www.lcdcomps.com
Amsterdam Institute of Finance May, 2008
Слайд 41Translating Capital Structure and Debt Capacity into a Detailed Financing Structure.
Conclusion
Amsterdam
Слайд 43Project Gear - Facts
Potential deal for a company in auction.
Private automotive
Our client, financial sponsor (RCC) looking to bid on the transaction.
May use this transaction as a platform.
Valuation range is 6x-8x EBITDA (or 63mm-84mm). A number of bidders.
The sponsor has a successful buyout fund (returns exceed 25% p.a.)
Avoidable private company expenses net of other adjustments are a maximum of 1 mm per annum.
Contracts/Relationships with OEMs should preserve sales and markets provide future achievable 5% growth. Could be as high as 10%.
Currently sales/assets mostly within Europe, in major economies.
Opportunities for growth through acquisition.
Amsterdam Institute of Finance May, 2008
Слайд 49Project Gear - Base Case
Assumptions : 8 % growth
Margins gradually improve to
Allow 1 mln addbacks
Capex 3.0% / Working Capital 12.8% / Tax 35%
Results : Senior Debt pays off in 5 years (Term loans quicker)
Net cash position by year 8-9
Equity returns strong (until cash builds) based on 7x exit
Room for acquisitions / growth / recapitalization
Amsterdam Institute of Finance May, 2008
Слайд 51Project Gear - Downside
Assumptions : 0% growth
Margins flat (slight decline) to 11%
Do
Capex 3.0% / Working Capital 13% / Tax 35%
Results : Senior Debt pays off slowly but still within 7-8 years
Term loan amortization still met
Equity returns weak
Limited room for acquisitions / growth / recapitalization
Amsterdam Institute of Finance May, 2008
Слайд 53Project Gear - Worst Case
Assumptons : 0% growth AND LBO/other causes lead
(loss of >10% of sales in year one follow by >5% in year 2 because of
inability to respond)
Margins decline to 9% and then 8.5%
Do not allow 1 mln addbacks
Capex 4% (committed on lower sales / respond to issues)
Working Capital 13% / Tax 35%
Results : Senior Debt (increases / no liquidity by yr 2-3)
Never in net cash position
Equity returns gone - Need for new equity !
No flexibility
Amsterdam Institute of Finance May, 2008
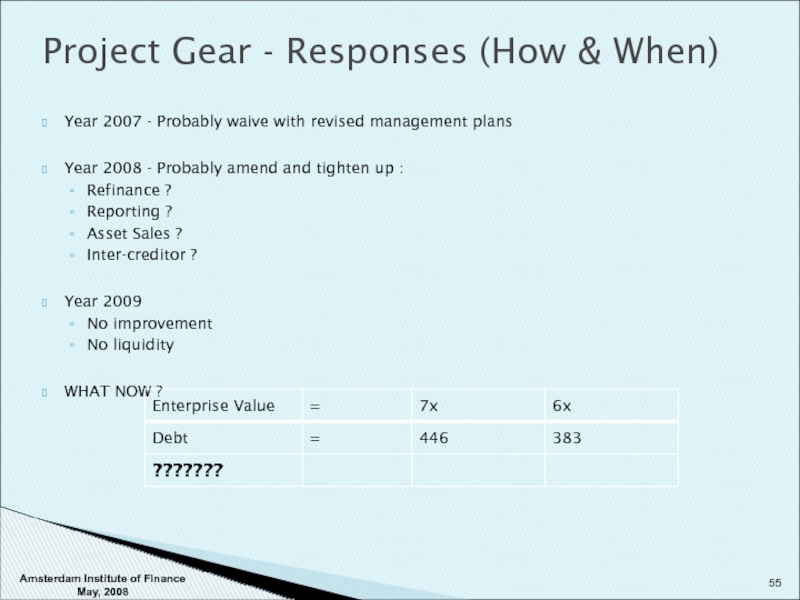
Слайд 55Project Gear - Responses (How & When)
Year 2007 - Probably waive
Year 2008 - Probably amend and tighten up :
Refinance ?
Reporting ?
Asset Sales ?
Inter-creditor ?
Year 2009
No improvement
No liquidity
WHAT NOW ?
Amsterdam Institute of Finance May, 2008