- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Pricing decisions. Pricing concepts. (Chapter 21) презентация
Содержание
- 1. Pricing decisions. Pricing concepts. (Chapter 21)
- 2. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights
- 3. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights
- 4. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights
- 5. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights
- 6. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights
- 7. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights
- 8. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights
- 9. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights
- 10. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights
- 11. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights
- 12. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights
- 13. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights
- 14. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights
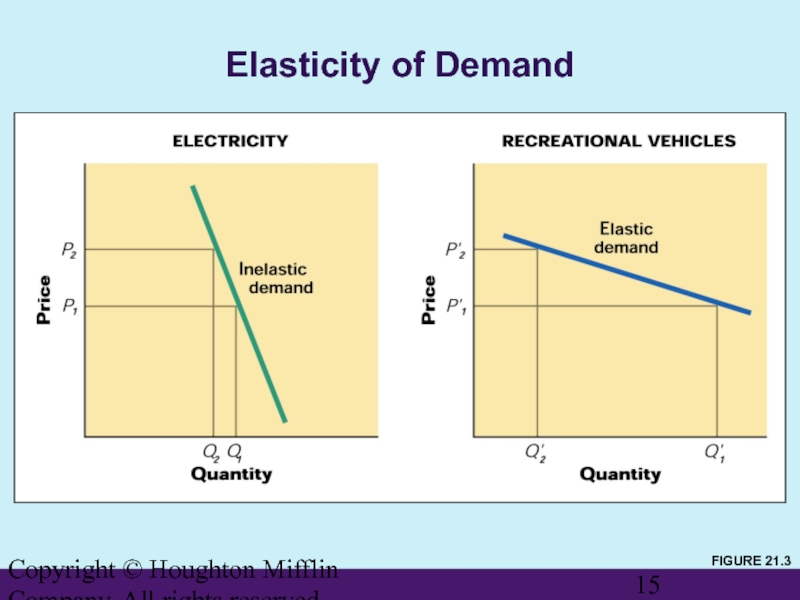
- 15. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. Elasticity of Demand FIGURE 21.3
- 16. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights
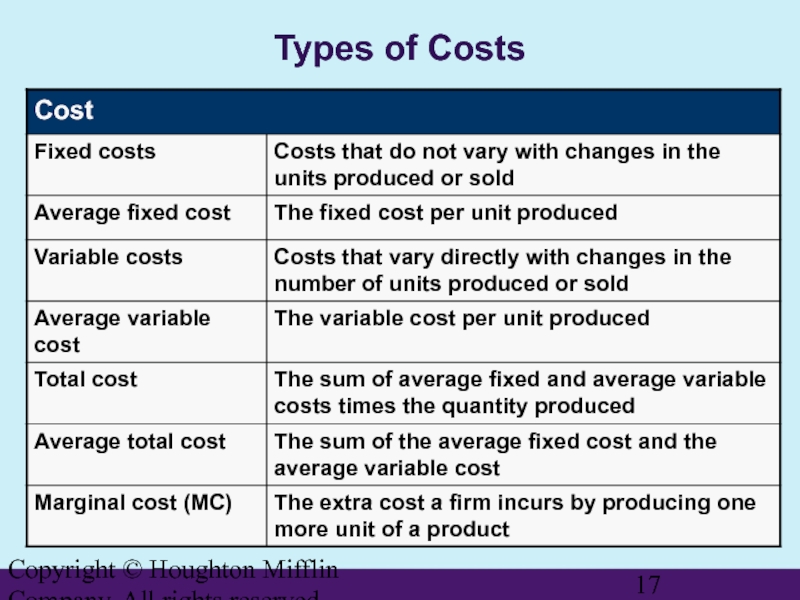
- 17. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. Types of Costs
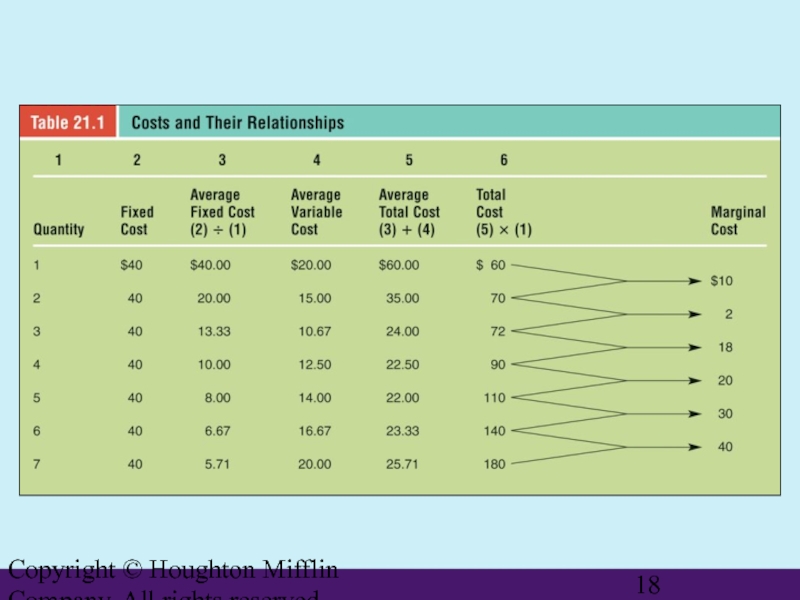
- 18. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
- 19. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights
- 20. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights
- 21. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights
- 22. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights
- 23. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. FIGURE 21.7 Determining the Breakeven Point
- 24. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. FIGURE 21.8 Factors That Affect Pricing Decisions
- 25. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights
- 26. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights
- 27. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights
- 28. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights
- 29. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights
- 30. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights
- 31. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
- 32. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights
- 33. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights
- 34. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights
- 35. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. Pricing for Business Markets Geographic Pricing (cont’d)
- 36. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights
- 37. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights
- 38. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights
- 39. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights
Слайд 2Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
Objectives
To understand the nature
To identify the characteristics of price and nonprice competition
To explore demand curves and the price elasticity of demand
To examine the relationships among demand, costs, and profits
Слайд 3Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
Objectives (cont’d)
To describe key
To consider issues affecting the pricing of products for business markets
Слайд 4Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
Chapter Outline
The Nature of
Price and Nonprice Competition
Analysis of Demand
Demand, Cost, and Profit Relationships
Factors Affecting Pricing Decisions
Pricing for Business Markets
Слайд 5Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
The Nature of Price
Price
The
Barter
The trading of products; the oldest form of exchange
Terms Used to Describe Price
Tuition, premium, fine, fee, fare, toll, rent, commission, dues, deposit, tips, interest, taxes
Слайд 6Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
The Nature of Price
The Importance of Price to Marketers
The most readily changeable characteristic (under favorable circumstances) of a product.
It relates directly to generation of revenues and quantities sold.
A key component of the profit equation, having strong effect on the firm’s profitability.
Has symbolic value to customers—prestige pricing.
Слайд 7Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
Price and Nonprice Competition
Price
Emphasizing price and matching or beating competitors’ prices
An effective strategy in markets with standardized products
Lowest-cost competitor (seller) will be most profitable.
Allows marketers to respond quickly to competitors
Price wars can weaken competing organizations.
Слайд 8Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
Price and Nonprice Competition
Nonprice Competition
Emphasizing factors other than price to distinguish a product from competing brands
Distinctive product features
Service
Product quality
Promotion
Packaging
Слайд 9Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
Price and Nonprice Competition
Nonprice Competition (cont’d)
Advantage is in increasing brand’s unit sales without changing price.
Is effective when a product or service’s features are difficult to imitate by competitors and customers perceive their value
Builds customer loyalty by focusing on nonprice features
Слайд 10Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
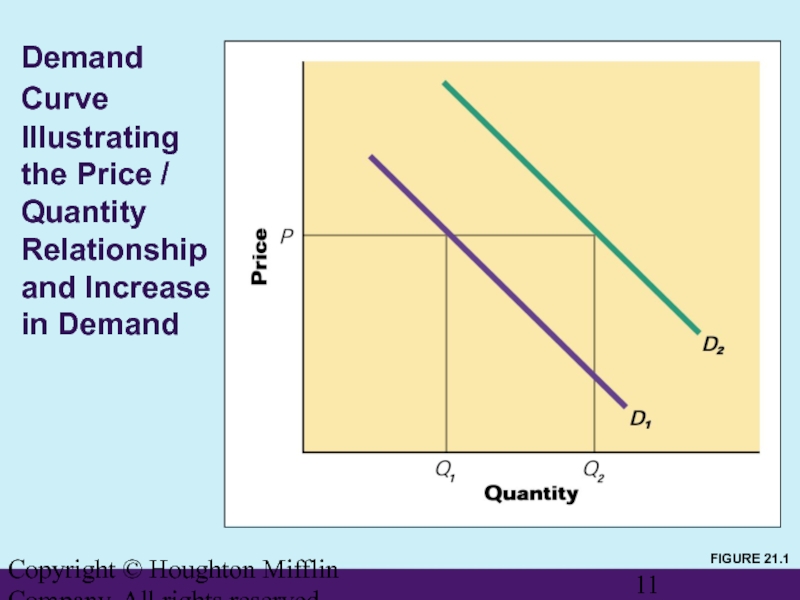
Analysis of Demand
The Demand
A graph of the quantity of products expected to be sold at various prices
Decreases in price create increases in quantities demanded.
Increased demand means larger quantities sold at the same price.
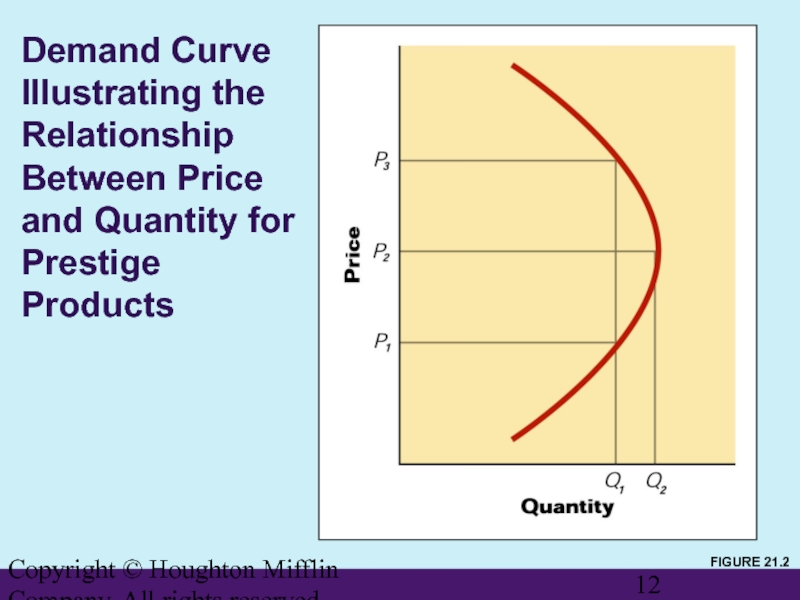
Prestige items sell best in higher price ranges.
Слайд 11Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
Demand Curve Illustrating the
FIGURE 21.1
Слайд 12Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
Demand Curve Illustrating the
FIGURE 21.2
Слайд 13Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
Analysis of Demand (cont’d)
Demand
Changes in buyers’ needs
Variations in the effectiveness of the marketing mix
The presence of substitutes
Dynamic environmental factors
Слайд 14Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
Analysis of Demand (cont’d)
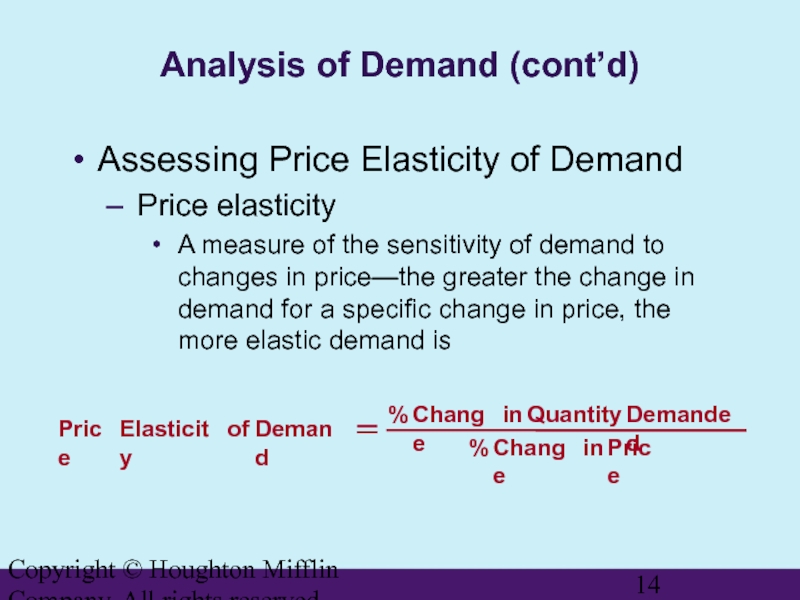
Assessing
Price elasticity
A measure of the sensitivity of demand to changes in price—the greater the change in demand for a specific change in price, the more elastic demand is
Слайд 16Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
Demand, Cost, and Profit
Marginal Analysis
Examines what happens to a firm’s costs and revenues when product changes by one unit
Marginal Revenue
The change in total revenue resulting from the sale of an additional unit of product
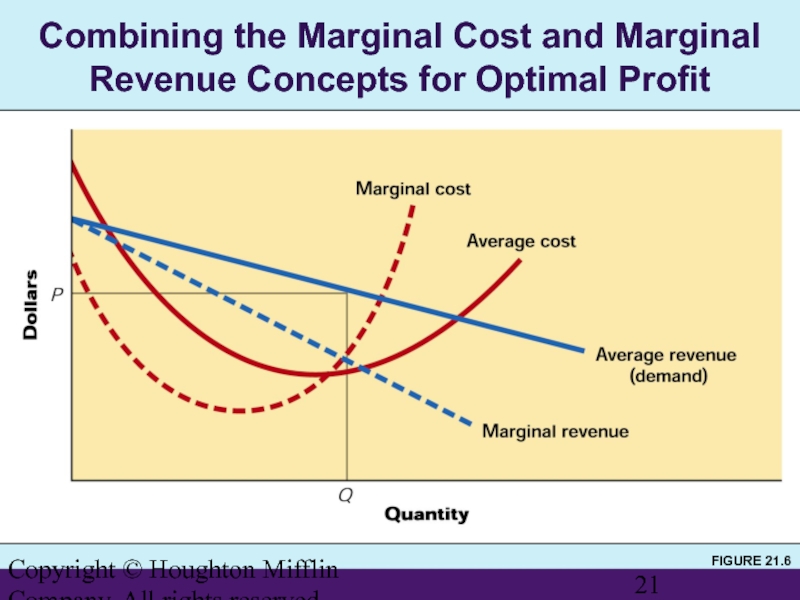
Profit is maximized where marginal costs (MC) are equal to marginal revenue (MR).
Слайд 19Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
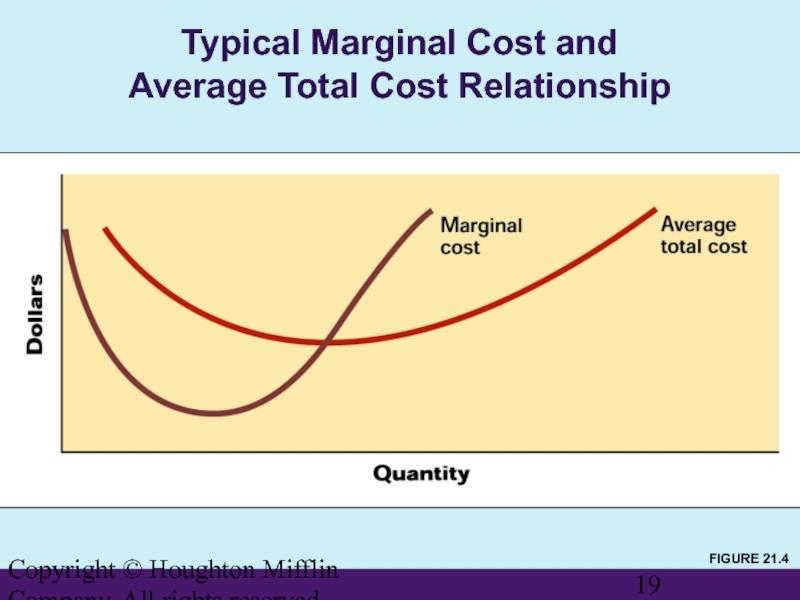
Typical Marginal Cost and
Average
FIGURE 21.4
Слайд 20Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
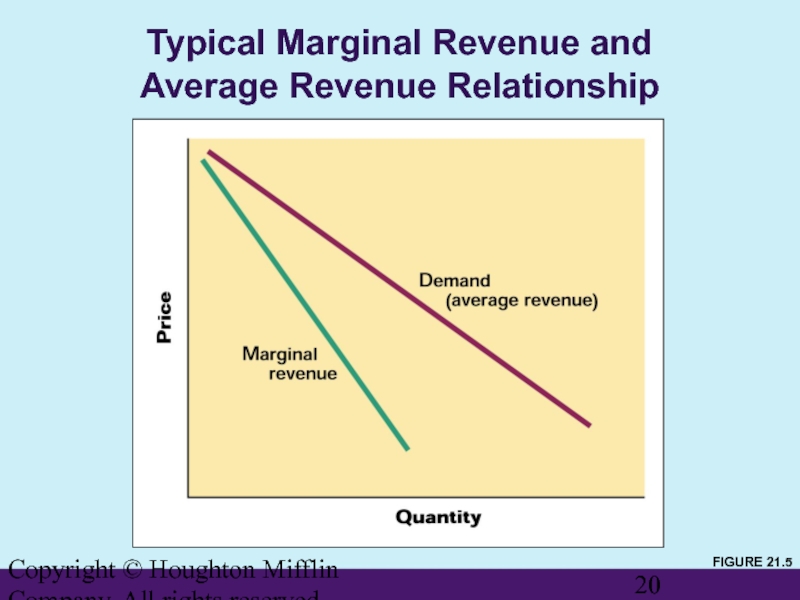
Typical Marginal Revenue and
Average
FIGURE 21.5
Слайд 21Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
Combining the Marginal Cost
FIGURE 21.6
Слайд 22Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
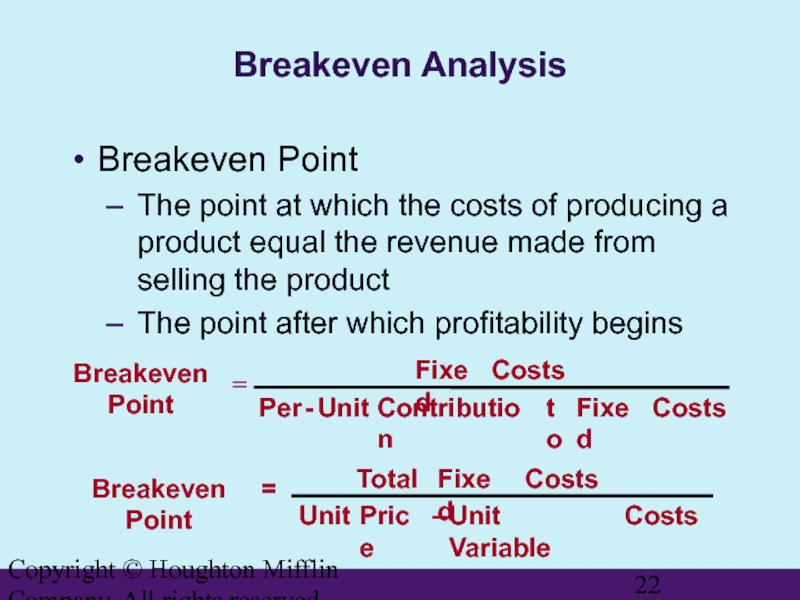
Breakeven Analysis
Breakeven Point
The
The point after which profitability begins
Слайд 23Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
FIGURE 21.7
Determining the Breakeven
Слайд 24Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
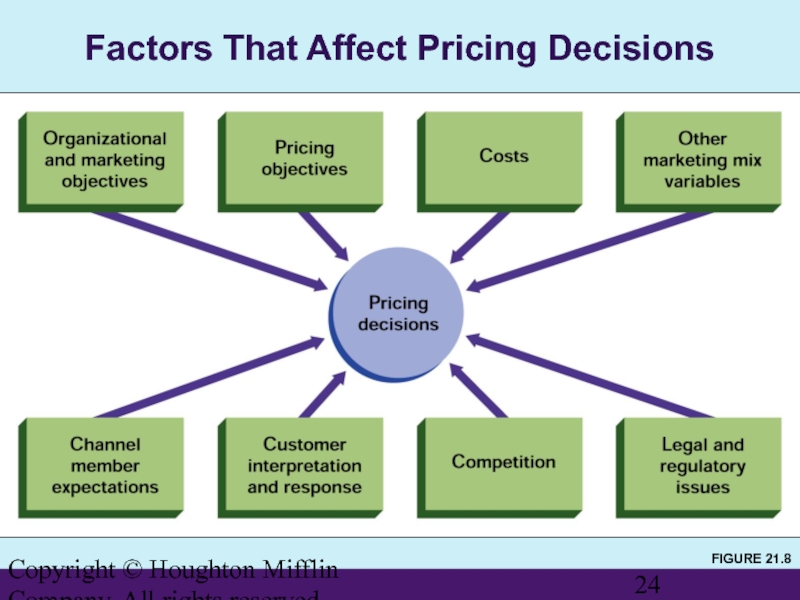
FIGURE 21.8
Factors That Affect
Слайд 25Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
Factors Affecting Pricing Decisions
Organizational
Prices should be set that are consistent with the organization’s goals and mission.
Prices must be compatible with marketing objectives (e.g., setting premium prices to enhance a product’s quality image).
Types of Pricing Objectives
Setting prices low to increase market share
Using temporary price reductions to gain market share
Lowering prices to raise cash quickly
Слайд 26Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
Factors Affecting Pricing Decisions
Costs
Set a floor price—products must be sold above their costs if the firm is to remain in business.
Reducing costs increases productivity and profitability.
Using labor-saving technologies
Focusing on quality
Establishing efficient manufacturing processes
Other Marketing Mix Variables
Price/quality image of the product or brand
Selective or intensive product distribution
Product pricing used as a promotional tool
Слайд 27Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
Factors Affecting Pricing Decisions
Channel Member Expectations
To make a profit at least equivalent to the potential profit from handling a competitor’s brand
To earn a profit in line with the effort and resources the channel member expends on the product
To receive discounts for volume purchases and prompt payment
To be supported by the producer with training, advertising, sales promotion, and return policies
Слайд 28Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
Factors Affecting Pricing Decisions
Customers’ Interpretation and Response
What meaning does the product’s price have to the customer?
Does the customer respond to the price by moving closer to or farther away from making a purchase?
Internal reference price
A price developed in the buyer’s mind through experience with the product
External reference price
A comparison price provided by others
Слайд 29Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
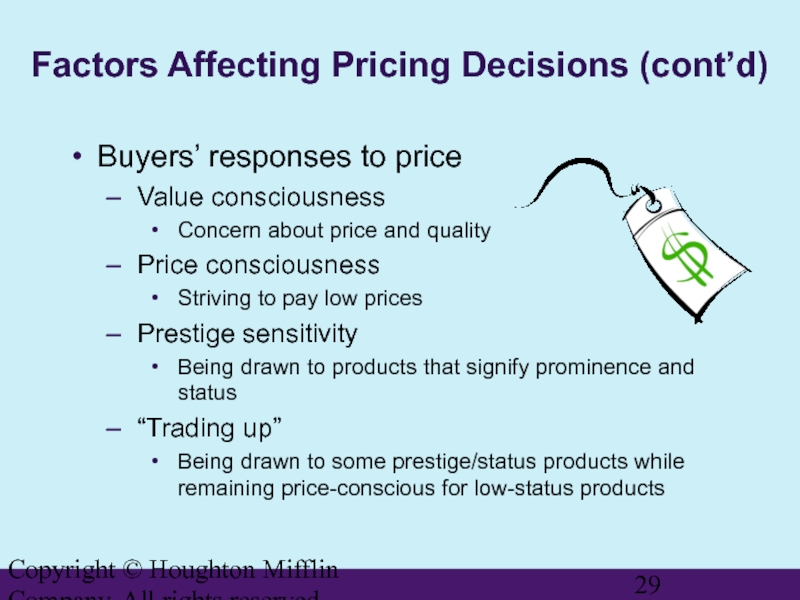
Factors Affecting Pricing Decisions
Buyers’ responses to price
Value consciousness
Concern about price and quality
Price consciousness
Striving to pay low prices
Prestige sensitivity
Being drawn to products that signify prominence and status
“Trading up”
Being drawn to some prestige/status products while remaining price-conscious for low-status products
Слайд 30Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
Factors Affecting Pricing Decisions
Competition
Pricing to match competitors’ prices
Judging competitors’ responses to adjusting prices
Changes in an industry’s market structure cause and create pricing opportunities.
Legal and Regulatory Issues
Price controls intended to curb inflation
Controls that set/regulate prices for specific products
Regulations and laws to prohibit price fixing, and deceptive and discriminatory pricing
Слайд 32Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
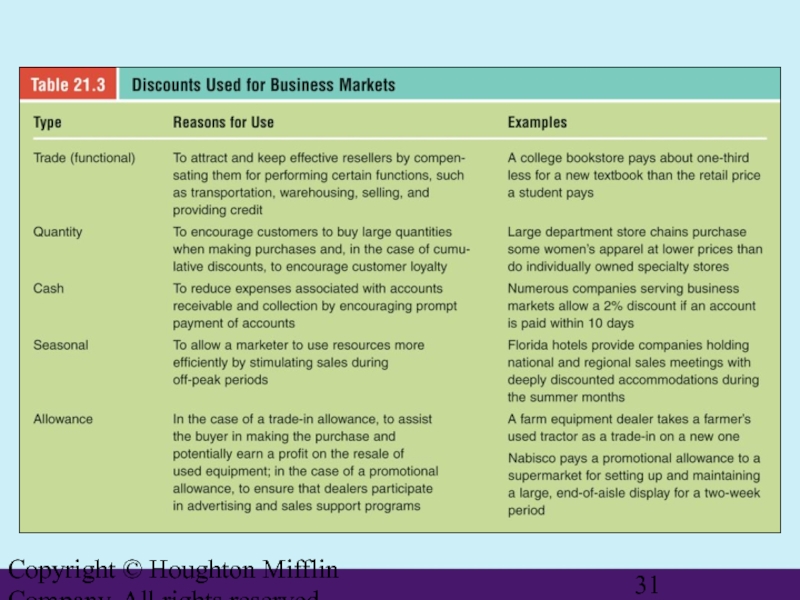
Price Discounting
Trade (Functional) Discounts
A
Quantity Discounts
Deductions from list price for purchasing large quantities
Cumulative Discounts
Quantity discounts aggregated over a stated period
Слайд 33Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
Price Discounting (cont’d)
Noncumulative Discounts
One-time
Cash Discount
A price reduction given to buyers for prompt payment or cash payment
Seasonal Discount
A price reduction given to buyers for purchasing goods or services out of season
Allowance
A concession in price to achieve a desired goal
Слайд 34Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
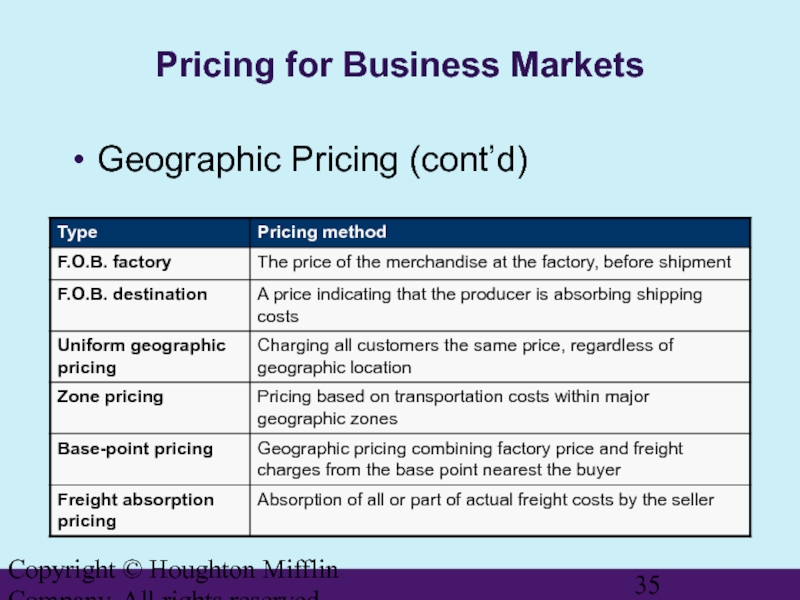
Pricing for Business Markets
Geographic
Reductions for transportation costs and other costs related to the physical distance between buyer and seller
Слайд 35Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
Pricing for Business Markets
Geographic
Слайд 36Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
Pricing for Business Markets
Transfer Pricing
The price of products that one organizational unit charges when selling to another unit in the same organization
Actual full cost
All fixed and variable costs divided by the number of units produced
Standard full cost
Pricing based on what it would cost to produce the goods at full plant capacity.
Cost plus investment
Full cost plus internal cost of assets used in production
Слайд 37Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
Pricing for Business Markets
Transfer Pricing (cont’d)
Market-based pricing
Market price less marketing and selling costs
Слайд 38Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
After reviewing this chapter
Understand the nature and importance of price.
Be aware of the characteristics of price and nonprice competition.
Be familiar with demand curves and the price elasticity of demand.
Be aware of the relationships among demand, costs, and profits.
Слайд 39Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
After reviewing this chapter
Be able to describe the key factors that may influence marketers’ pricing decisions.
Have considered the issues affecting the pricing of products for organizational markets.