- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Foreign exchange market презентация
Содержание
- 1. Foreign exchange market
- 2. Foreign exchange market – the financial market
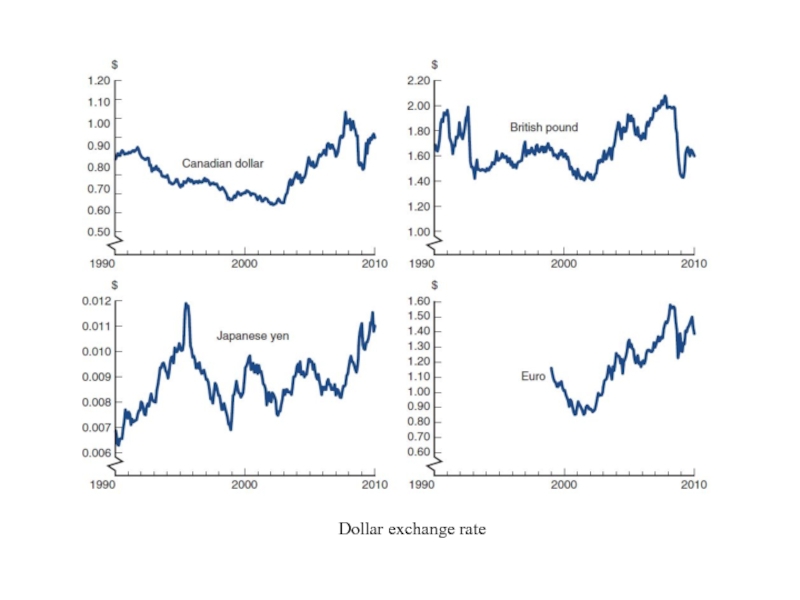
- 3. Dollar exchange rate
- 4. Law of One Price If two countries
- 5. Theory of Purchasing Power Parity The theory
- 6. Factors That Affect Exchange Rates in the
- 7. Equilibrium in the Foreign Exchange Market Equilibrium
- 8. Explaining Changes in Exchange Rates Shifts in
- 9. Factors That Change the Exchange Rate
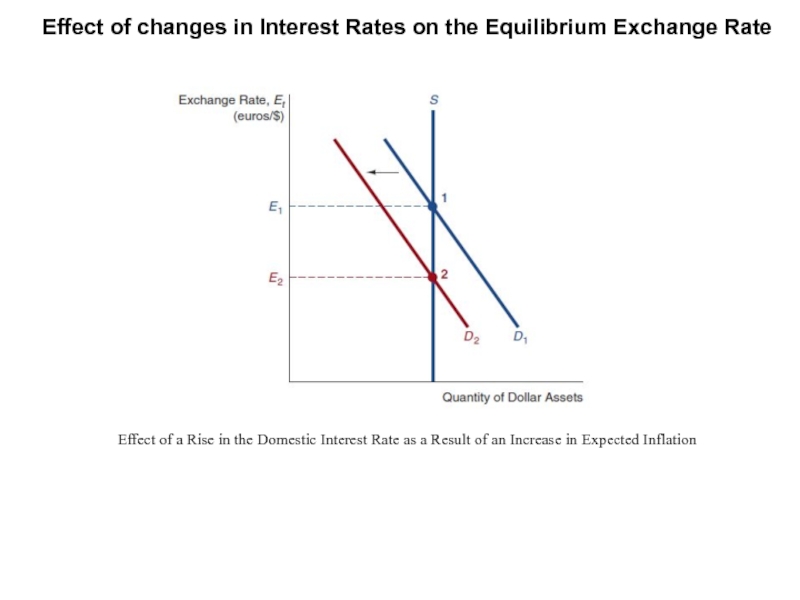
- 10. Effect of changes in Interest Rates on
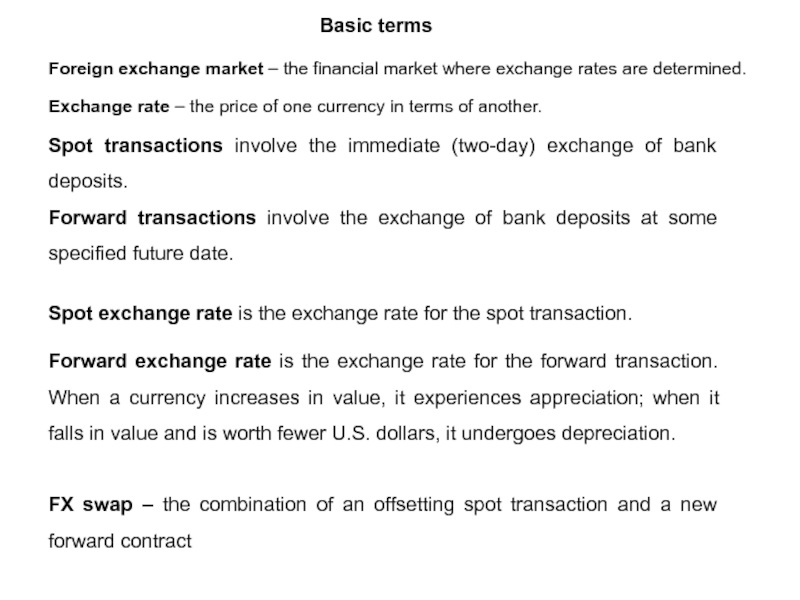
Слайд 2Foreign exchange market – the financial market where exchange rates are
Exchange rate – the price of one currency in terms of another.
Spot transactions involve the immediate (two-day) exchange of bank deposits.
Forward transactions involve the exchange of bank deposits at some specified future date.
Spot exchange rate is the exchange rate for the spot transaction.
Forward exchange rate is the exchange rate for the forward transaction. When a currency increases in value, it experiences appreciation; when it falls in value and is worth fewer U.S. dollars, it undergoes depreciation.
FX swap – the combination of an offsetting spot transaction and a new forward contract
Basic terms
Слайд 4Law of One Price
If two countries produce an identical good, and
Example 1. Recently, the yen price of Japanese steel has increased by 10% (to 11,000 yen) relative to the dollar price of American steel (unchanged at $100).
By what amount must the dollar increase or decrease in value for the law of one price to hold true?
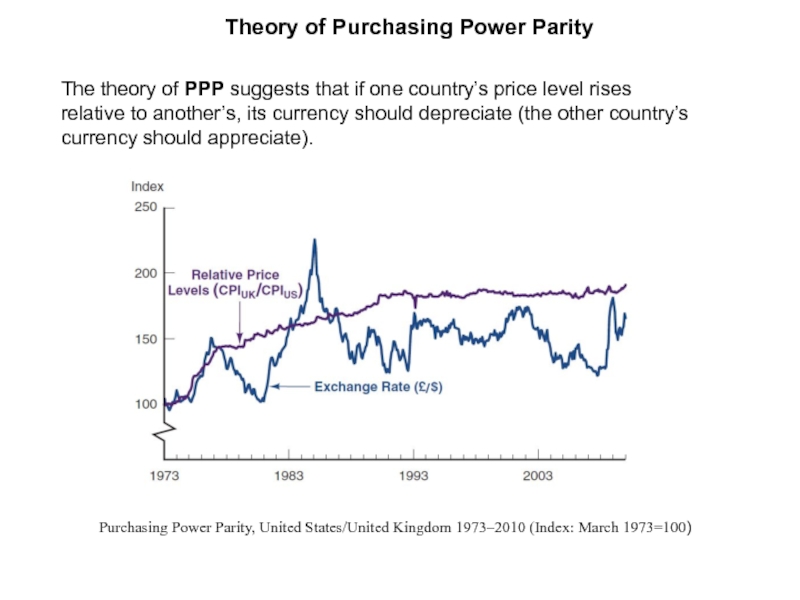
Слайд 5Theory of Purchasing Power Parity
The theory of PPP suggests that if
Purchasing Power Parity, United States/United Kingdom 1973–2010 (Index: March 1973=100)
Слайд 6Factors That Affect Exchange Rates in the Long Run
Relative Price
Trade Barriers
Preferences for Domestic Versus Foreign Goods
Productivity
If a factor increases the demand for domestic goods relative to foreign goods, the domestic currency will appreciate; if a factor decreases the relative demand for domestic goods, the domestic currency will depreciate
Summary Factors That Affect Exchange Rates in the Long Run
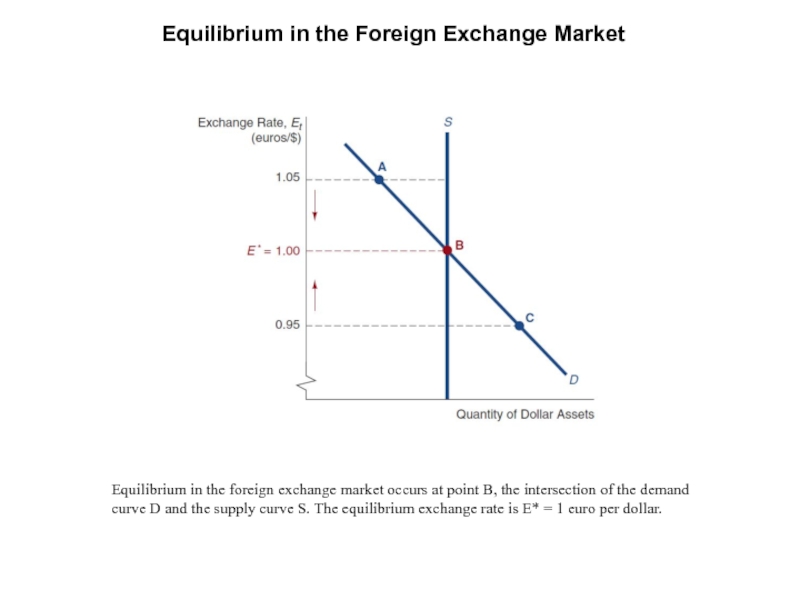
Слайд 7Equilibrium in the Foreign Exchange Market
Equilibrium in the foreign exchange market
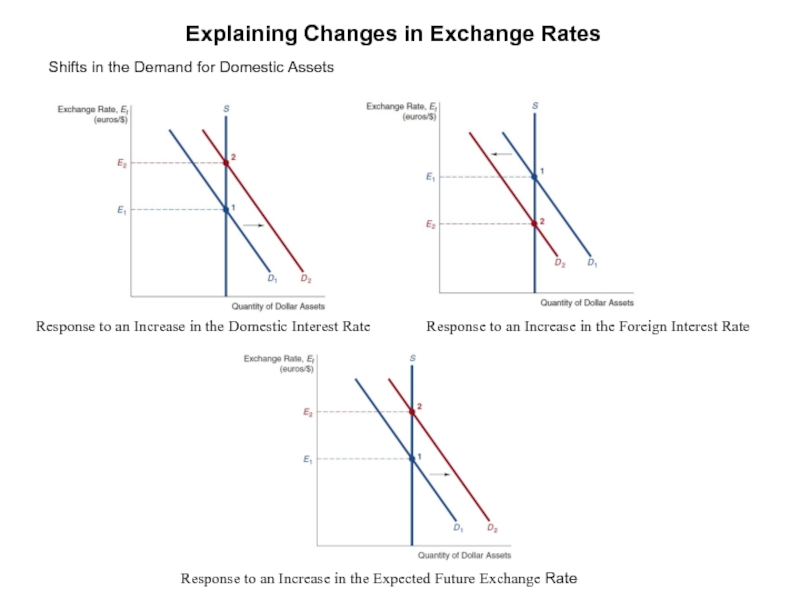
Слайд 8Explaining Changes in Exchange Rates
Shifts in the Demand for Domestic Assets
Response
Response to an Increase in the Foreign Interest Rate
Response to an Increase in the Expected Future Exchange Rate