- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Decision tree. Risk planning and value презентация
Содержание
- 1. Decision tree. Risk planning and value
- 2. A decision tree is a graphical method
- 3. Building the decision tree begins with the
- 5. 4 Because of every decision depends on
- 6. The decision tree analysis
- 7. Risk planning and price of risk
- 8. For the risk it is characteristic that
- 9. In-house risk Concerns possible losses that firms
- 10. If the number of accidents within the
- 11. Determination of the possibility of such damages
- 12. Therefore, banks regularly write off bad loans,
- 13. Occurs if the number of observations within
- 14. When considering a lot of firms, the
- 15. Examples of such risks are fire,
- 16. floods,
- 17. storms and other natural disasters
- 18. The burden of forecasting passed on insurance
- 19. The likelihood of loss cannot be set
- 20. Insurance company predicts cumulative risk of all
- 21. Insurance premium becomes part of the cost structure of the insured company
- 22. The insurance company must decide what premium
- 23. The manager, trying to avoid risk, should
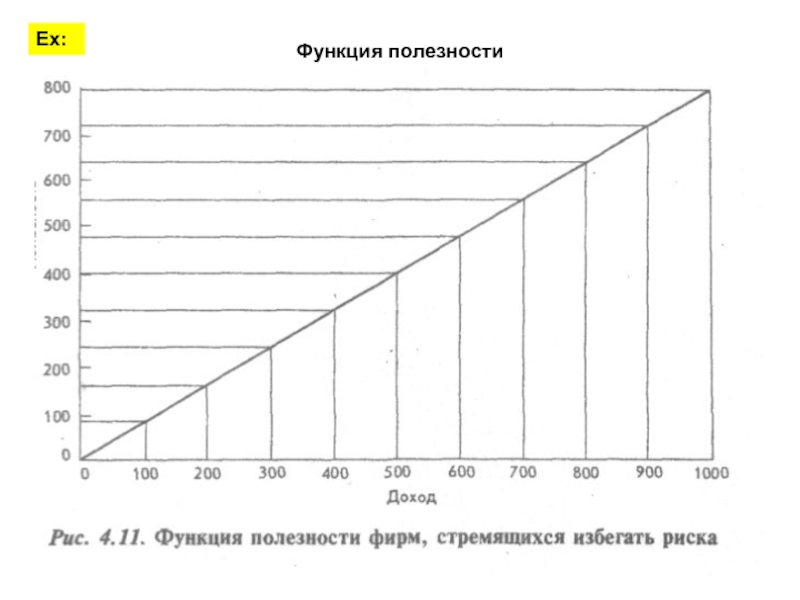
- 24. Функция полезности Ех:
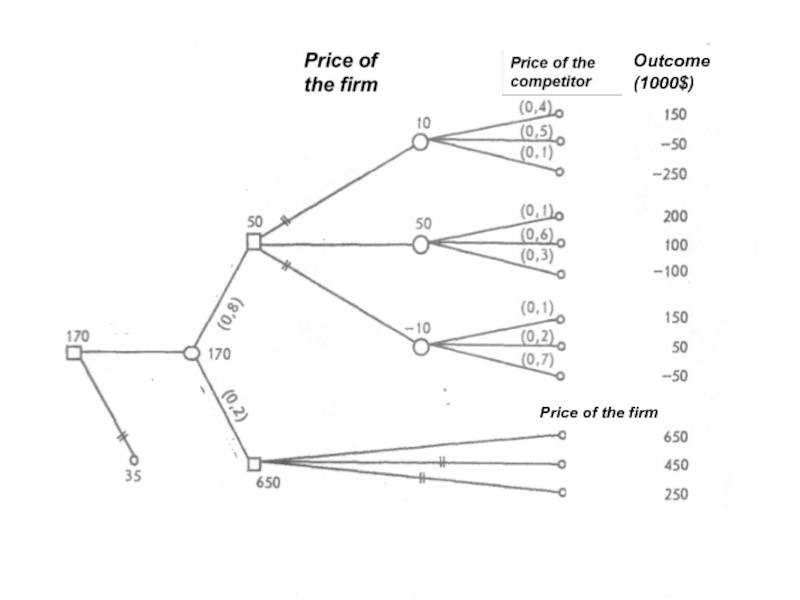
Слайд 2A decision tree is a graphical method that shows the sequence
2
Слайд 3Building the decision tree begins with the earliest decisions and moves
3
Слайд 54
Because of every decision depends on the assessment of the events
Слайд 6
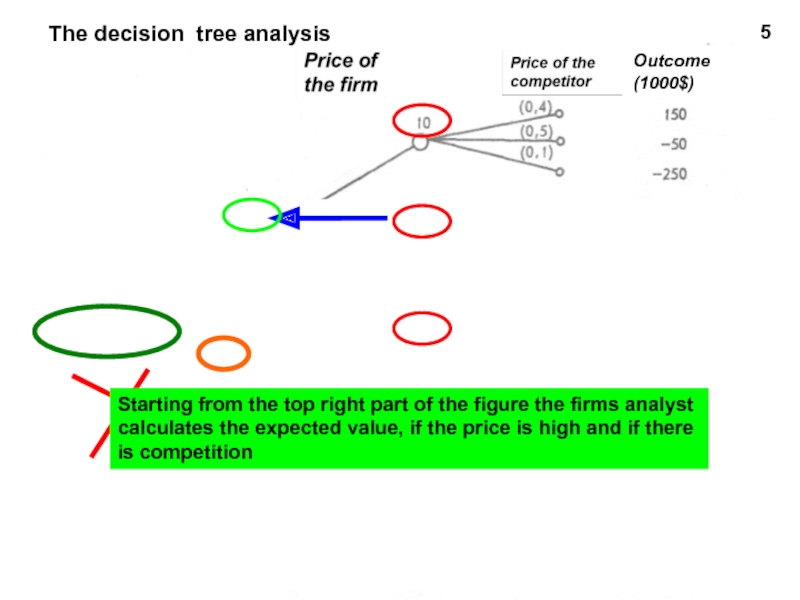
The decision tree analysis
5
Starting from the top right part of the
Слайд 8For the risk it is characteristic that the probability of outcomes
Potential profit and loss can be included in the cost structure of the firm
9
Слайд 9In-house risk
Concerns possible losses that firms prefer to include in the
10
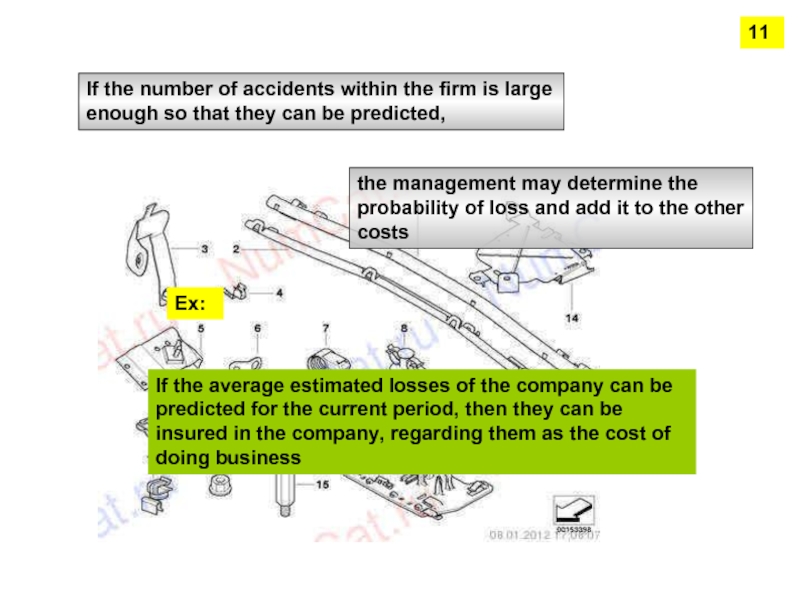
Слайд 10If the number of accidents within the firm is large enough
the management may determine the probability of loss and add it to the other costs
Ех:
If the average estimated losses of the company can be predicted for the current period, then they can be insured in the company, regarding them as the cost of doing business
11
Слайд 11Determination of the possibility of such damages can be part of
Слайд 12Therefore, banks regularly write off bad loans, and the usual practice
Слайд 13Occurs if the number of observations within one company is not
Intercompany risk
Слайд 14When considering a lot of firms, the number of observations becomes
Слайд 18The burden of forecasting passed on insurance companies
The insurance companies have
Since the heads of companies are not able to predict such damage to their firms
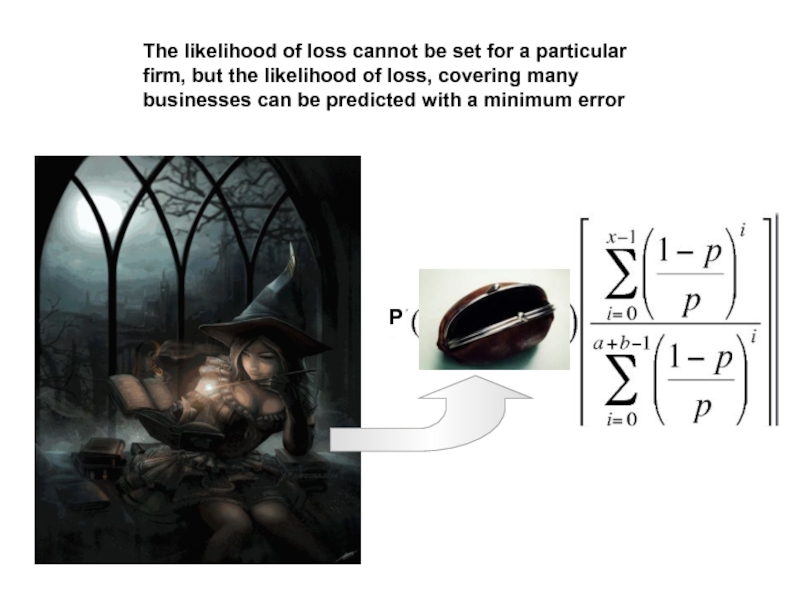
Слайд 19The likelihood of loss cannot be set for a particular firm,
Р