- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
An Introduction to Cost Terms and Purposes презентация
Содержание
- 1. An Introduction to Cost Terms and Purposes
- 2. Basic Cost Terminology Cost – sacrificed resource
- 3. Basic Cost Terminology Cost Accumulation – a
- 4. Direct and Indirect Costs Direct Costs –
- 5. Cost Examples Direct Costs Parts Assembly line wages Indirect Costs Electricity Rent Property taxes
- 6. Factors Affecting Direct/Indirect Cost Classification Cost Materiality Availability of Information-gathering Technology Operational Design
- 7. Cost Behavior Variable Costs – changes in
- 8. Cost Behavior, continued Variable costs – are
- 9. Cost Behavior Summarized Total Dollars Cost per
- 10. Other Cost Concepts Cost Driver – a
- 11. A Cost Caveat Unit costs should be
- 12. Different Types of Firms Manufacturing-sector companies –
- 13. Types of Inventories Direct Materials – resources
- 14. Types of Product Costs Direct Materials Direct
- 15. Distinctions Between Costs Inventoriable Costs – product
- 16. Cost Flows The Cost of Goods Manufactured
- 17. Cost of Goods Manufactured Calculates the
- 18. Income Statement Figure carries forward from the
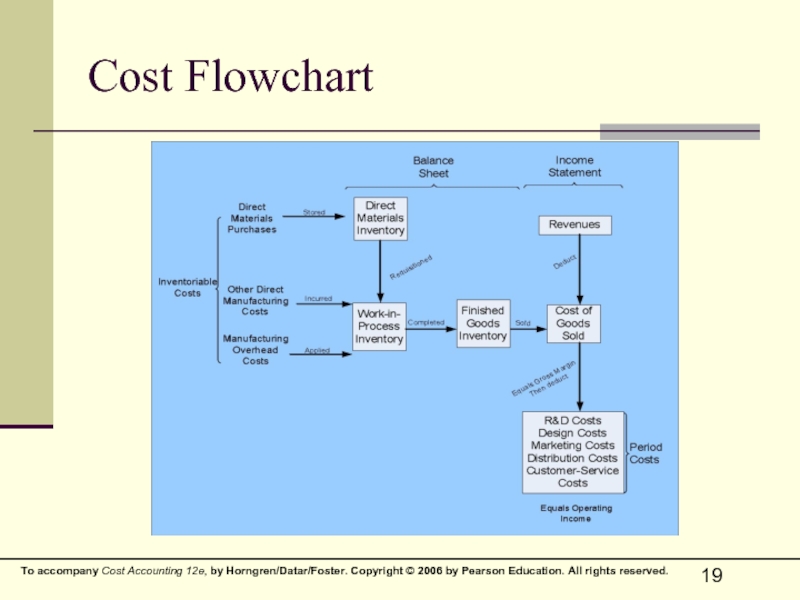
- 19. Cost Flowchart
- 20. Other Cost Considerations Prime cost is a
- 21. Different Definitions of Cost for Different Applications
- 22. Three Common Features of Cost Accounting and
Слайд 2Basic Cost Terminology
Cost – sacrificed resource to achieve a specific objective
Actual
Budgeted Cost – a predicted cost
Cost Object – anything of interest for which a cost is desired
Слайд 3Basic Cost Terminology
Cost Accumulation – a collection of cost data in
Cost Assignment – a general term that includes gathering accumulated costs to a cost object. This includes:
Tracing accumulated costs with a direct relationship to the cost object and
Allocating accumulated costs with an indirect relationship to a cost object
Слайд 4Direct and Indirect Costs
Direct Costs – can be conveniently and economically
Indirect Costs – cannot be conveniently or economically traced (tracked) to a cost object. Instead of being traced, these costs are allocated to a cost object in a rational and systematic manner
Слайд 6Factors Affecting Direct/Indirect Cost Classification
Cost Materiality
Availability of Information-gathering Technology
Operational Design
Слайд 7Cost Behavior
Variable Costs – changes in total in proportion to changes
Fixed Costs – remain unchanged in total regardless of changes in the related level of activity or volume
Costs are fixed or variable only with respect to a specific activity or a given time period
Слайд 8Cost Behavior, continued
Variable costs – are constant on a per-unit basis.
Fixed costs – change inversely with the level of production. As more units are produced, the same fixed cost is spread over more and more units, reducing the cost per unit
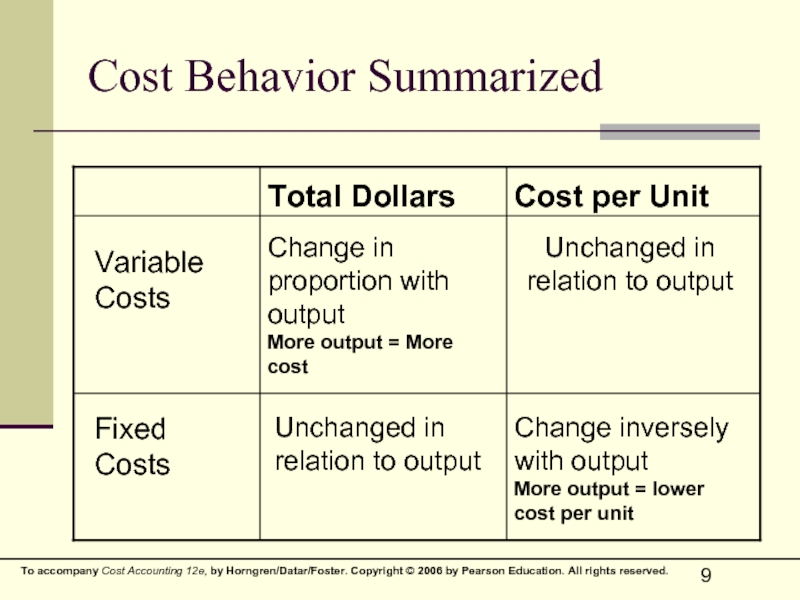
Слайд 9Cost Behavior Summarized
Total Dollars
Cost per Unit
Variable
Costs
Change in proportion with output
More
Unchanged in relation to output
Fixed
Costs
Unchanged in relation to output
Change inversely with output
More output = lower cost per unit
Слайд 10Other Cost Concepts
Cost Driver – a variable that causally affects costs
Relevant Range – the band of normal activity level (or volume) in which there is a specific relationship between the level of activity (or volume) and a given cost
For example, fixed costs are fixed only within the relevant range.
Слайд 11A Cost Caveat
Unit costs should be used cautiously. Since unit costs
Слайд 12Different Types of Firms
Manufacturing-sector companies – create and sell their own
Merchandising-sector companies – product resellers
Service-sector companies
Слайд 13Types of Inventories
Direct Materials – resources instock and available for use
Work-in-Process
Finished Goods – products completed and ready for sale
Слайд 14Types of Product Costs
Direct Materials
Direct Labor
Indirect Manufacturing – factory costs that
Слайд 15Distinctions Between Costs
Inventoriable Costs – product manufacturing costs. These costs are
Period Costs – have no future value and are expensed as incurred
Слайд 16Cost Flows
The Cost of Goods Manufactured and the Cost of Goods
Note the importance of inventory accounts in the following accounting reports, and in the cost flow chart
Слайд 17Cost of Goods Manufactured
Calculates the cost of Direct Materials Used
Accumulates the
Adjusts the current period manufacturing costs to account for units actually completed
Слайд 18Income Statement
Figure carries forward from the Schedule of Cost of Goods
Period Costs are expensed as incurred
Слайд 20Other Cost Considerations
Prime cost is a term referring to all direct
Conversion cost is a term referring to direct labor and factory overhead costs, collectively
Overtime labor costs are considered part of overhead
Слайд 21Different Definitions of Cost for Different Applications
Pricing and product-mix decisions –
Contracting with government agencies – very specific definitions of cost for “cost plus profit” contracts
Preparing external-use financial statements – GAAP-driven product costs only
Слайд 22Three Common Features of Cost Accounting and Cost Management
Calculating the cost
Obtaining information for planning and control, and performance evaluation
Analyzing the relevant information for making decisions