- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Behaviorism. Basic names and stages презентация
Содержание
- 1. Behaviorism. Basic names and stages
- 2. BEHAVIORISM Is based on the proposition that
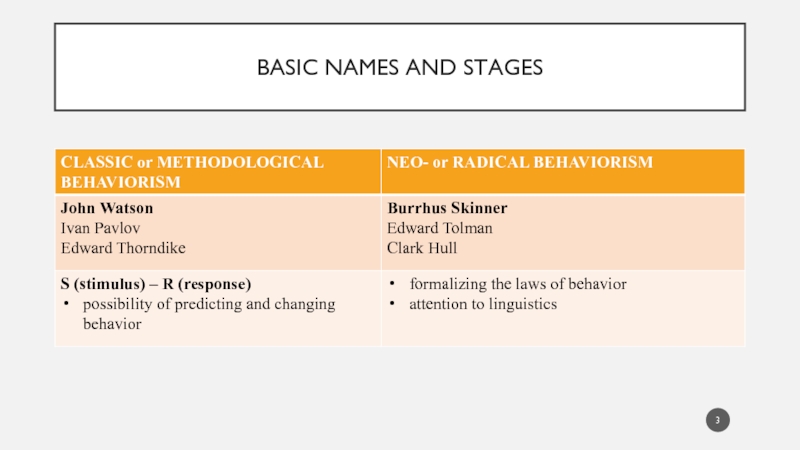
- 3. BASIC NAMES AND STAGES
- 4. VERBAL BEHAVIOR viewing a language from the
- 5. CHILD LANGUAGE ACQUISITION Main mechanisms: imitation, repetition,
- 6. DESCRIPTIVISM Leonard Bloomfield The central method: study
- 7. KEY TENETS Only the directly observed phenomena
- 8. THANK YOU FOR ATTENTION!
Слайд 2BEHAVIORISM
Is based on the proposition that behavior can be researched scientifically
without recourse to inner mental states
originated at the end of the 19th century in the US
analyzes human behavior
originated at the end of the 19th century in the US
analyzes human behavior
Слайд 4VERBAL BEHAVIOR
viewing a language from the position of an external observer;
studying Indian languages
speech ~ verbal behavior
B. F. Skinner: “Verbal behavior”, 1957
Thorndike’s reinforcement theory
speech ~ verbal behavior
B. F. Skinner: “Verbal behavior”, 1957
Thorndike’s reinforcement theory
Слайд 5CHILD LANGUAGE ACQUISITION
Main mechanisms: imitation, repetition, practice.
Success factors: quality and quantity
of heard language, regularity of the reinforcement.
Things to explain: mistakes, language creativity, understanding of the language structures.
Things to explain: mistakes, language creativity, understanding of the language structures.
Слайд 6DESCRIPTIVISM
Leonard Bloomfield
The central method: study of the distribution of linguistic units.
the
speaker's out-of-speech stimulus - their speech reaction –
the speech stimulus of the listener - the extra-verbal reaction of the listener
the speech stimulus of the listener - the extra-verbal reaction of the listener
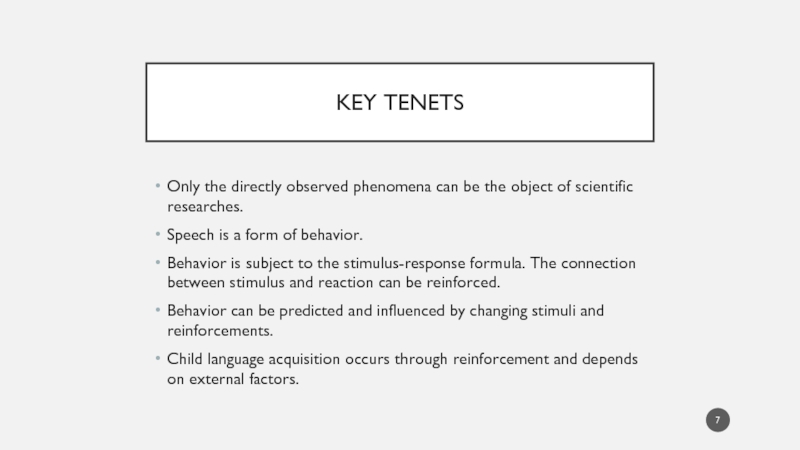
Слайд 7KEY TENETS
Only the directly observed phenomena can be the object of
scientific researches.
Speech is a form of behavior.
Behavior is subject to the stimulus-response formula. The connection between stimulus and reaction can be reinforced.
Behavior can be predicted and influenced by changing stimuli and reinforcements.
Child language acquisition occurs through reinforcement and depends on external factors.
Speech is a form of behavior.
Behavior is subject to the stimulus-response formula. The connection between stimulus and reaction can be reinforced.
Behavior can be predicted and influenced by changing stimuli and reinforcements.
Child language acquisition occurs through reinforcement and depends on external factors.