- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
This course is concerned with making good economic decisions in engineering презентация
Содержание
- 1. This course is concerned with making good economic decisions in engineering
- 2. This course is concerned with making good
- 3. One of the important parts of economic
- 4. Physical output (products) Monetary income (profits) What Do Organizations Produce?
- 5. People’s services (labor) Materials and supplies
- 6. Most operating organizations’ costs can be
- 7. Most common direct costs: material &
- 8. Costs that cannot be traced directly
- 9. Standard Costs Representative costs per unit of
- 10. The costs of doing business (typically not
- 11. The cost or total amount of investment
- 12. Costs that remain constant: Don’t vary with
- 13. Costs that vary with activity level: E.g.,
- 14. This is simply total cost divided by
- 15. This is the cost change for
- 16. Let’s say: Fixed cost is $50, variable
- 17. Marginal cost: It is the correct
- 18. Average Versus Marginal Cost
- 19. Because is the change
- 20. Recurring are the costs that are
- 21. Opportunity cost is what you have
- 22. Sunk costs are costs that can’t be
- 23. This is the total cost for a
- 24. Accounting Method Engineering Method Statistical Method Cost-Estimating Methods
- 25. Based on historical data Costs are
- 26. Depends upon the knowledge of physical
- 27. Uses statistical tools (from simple graphs
- 28. PRICE DEMAND QUANTITY (OUTPUT) Price equals some
- 29. TR Total Revenue = p
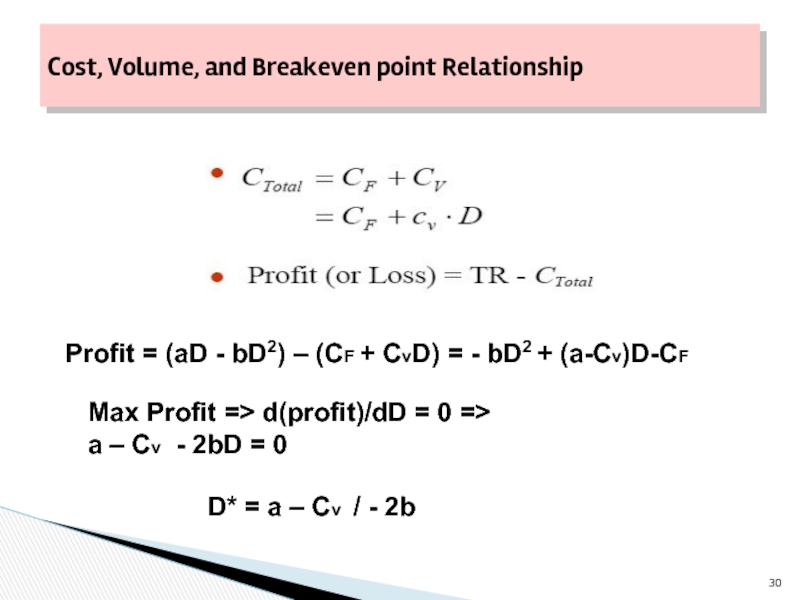
- 30. Cost, Volume, and Breakeven point Relationship Profit
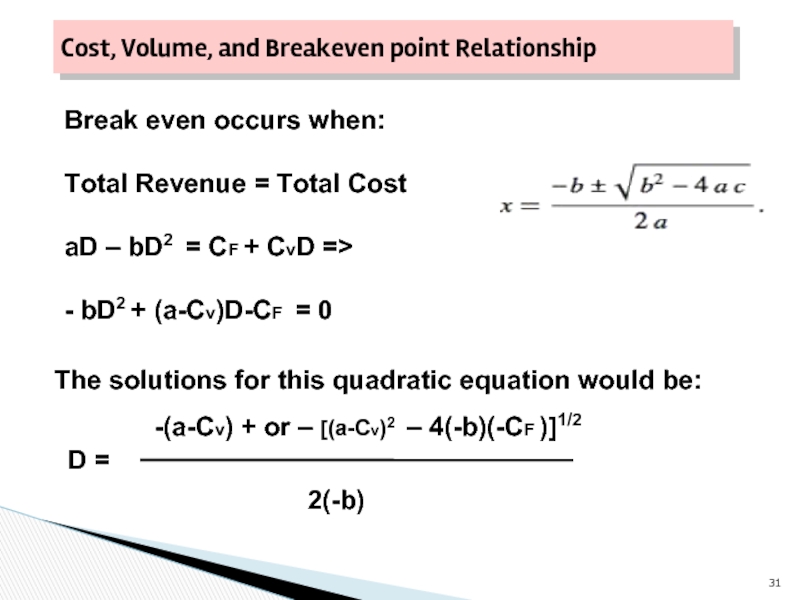
- 31. Cost, Volume, and Breakeven point Relationship Break
- 32. Cost, Volume, and Breakeven point Relationship Scenario 1: demand is a function of price.
- 33. PRICE DEMAND QUANTITY (OUTPUT) Price equals some
- 34. Cost / Revenue Quantity ( Output )
- 35. Example 2.6 A Company produces an electronic
- 36. Solution d(profit) / dD = a
- 37. Cost, Volume, and Breakeven point Relationship Scenario
- 38. Engineers must maintain a life-cycle (“cradle to
- 39. Determine optimal value for a certain alternative’s
- 40. Fixed cost(s) Cost(s) that vary directly with
- 41. Identify primary cost-driving design variable Write
- 42. When alternatives for accomplishing a
- 43. Total Cost in Material Selection In many
- 44. Make Versus Purchase (Outsourcing) Studies A company
- 45. Make Versus Purchase (Outsourcing) Studies Opportunity
- 46. Lumber put through the planer increases in
- 47. Solution
Слайд 1Cost Classification and Design Economics
Lecture 2; Chapter 2
AMERICAN UNIVERSITY OF
IE340-ENGINEERING ECONOMICS
SPRING SEMESTER, 2017
Слайд 2This course is concerned with making good economic decisions in engineering
These
Managers
Accountants
Etc.
You need to be able to communicate with these people, so you need a common language
Introduction
Слайд 3One of the important parts of economic decision is identification of
Several cost situations occur frequently
People have developed terms to describe these
You need to know these terms to
Understand what others are saying to you
Be able to persuade others that you know what you’re doing and therefore should be listened to
Introduction (cont.)
Слайд 5
People’s services (labor)
Materials and supplies
Raw materials used to make their final
Indirect materials (lubrication oil, etc.)
Electric power and other energy inputs
Capital (money), which is used to pay for:
Land and buildings
Producer goods (e.g., tools, equipment)
Taxes
What Inputs Do They Use?
Слайд 6
Most operating organizations’ costs can be summarized under two headings
Direct costs
Overhead
Of these, overhead costs are often the most complicated and troublesome
Cost classification (direct and overhead)
Слайд 7
Most common direct costs: material & labor
These are costs that:
Can be
Can be conveniently allocated to a particular category (e.g. a product or service)
Examples:
Cost of steel used for making bolts
Salary of a nurse on cardiac surgery ward
Direct costs
Слайд 8
Costs that cannot be traced directly to a particular product/service, because
Examples:
Depreciation, taxes, insurance, maintenance; electricity; general repairs; common tools
Supervisors, engineers, and other administrative/clerical personnel
Can also include materials and labor for inspection, testing, etc.
Overhead (indirect) costs
Слайд 9Standard Costs
Representative costs per unit of output established before the good
They are developed from anticipated direct labor hours, materials, and overhead categories
Play an important role in cost control and other management functions
Comparing the actual cost with the standard cost
Estimating future manufacturing costs
Preparing bids on products or services requested by customers
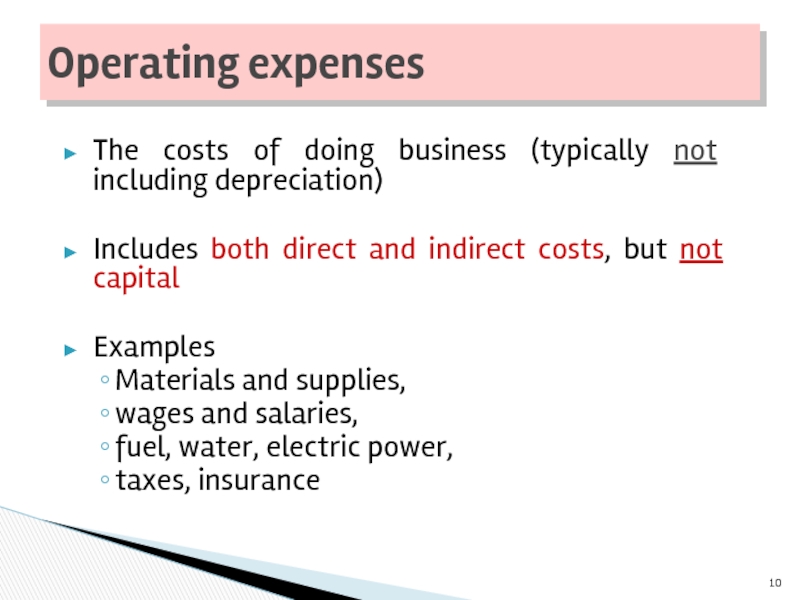
Слайд 10The costs of doing business (typically not including depreciation)
Includes both
Examples
Materials and supplies,
wages and salaries,
fuel, water, electric power,
taxes, insurance
Operating expenses
Слайд 11The cost or total amount of investment required for getting an
Occurs only once for any given activity
Typically assumed to be paid in year 0
Typically used for capital (land, buildings, tools, equipment), not operating expenses
First Cost
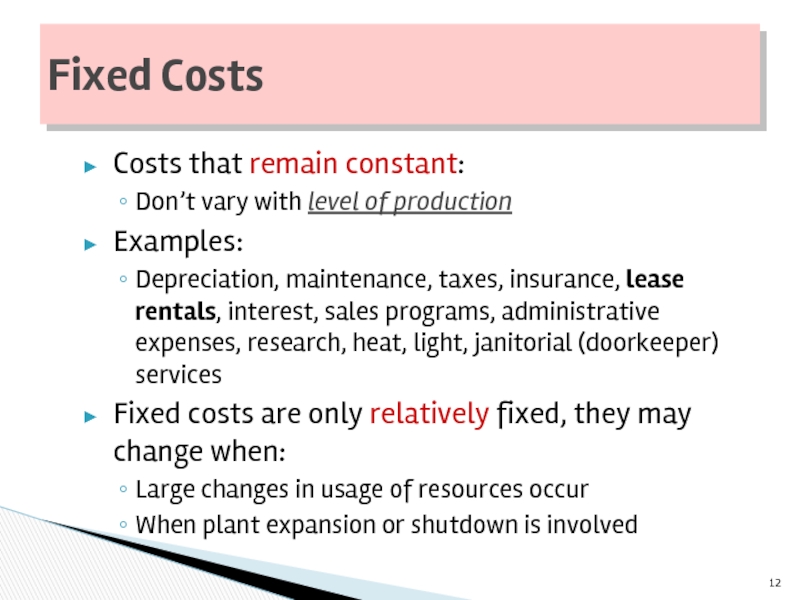
Слайд 12Costs that remain constant:
Don’t vary with level of production
Examples:
Depreciation, maintenance, taxes,
Fixed costs are only relatively fixed, they may change when:
Large changes in usage of resources occur
When plant expansion or shutdown is involved
Fixed Costs
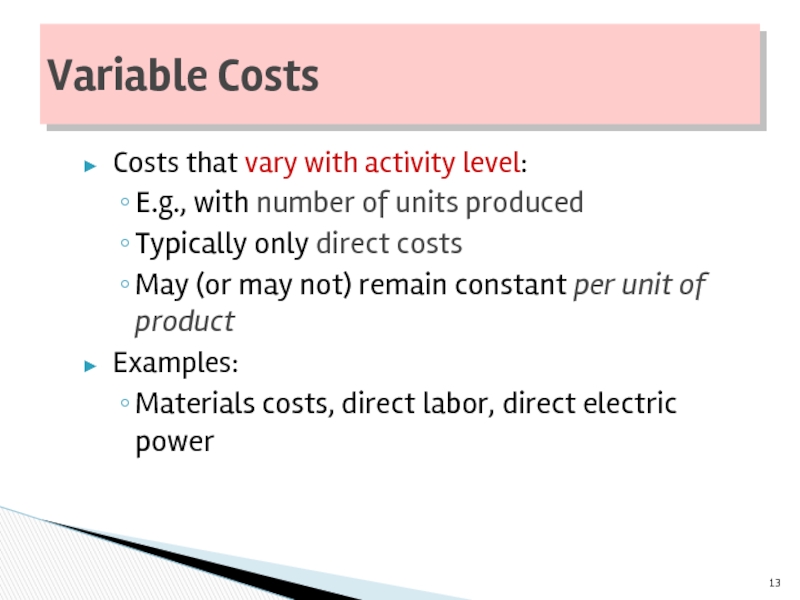
Слайд 13Costs that vary with activity level:
E.g., with number of units produced
Typically
May (or may not) remain constant per unit of product
Examples:
Materials costs, direct labor, direct electric power
Variable Costs
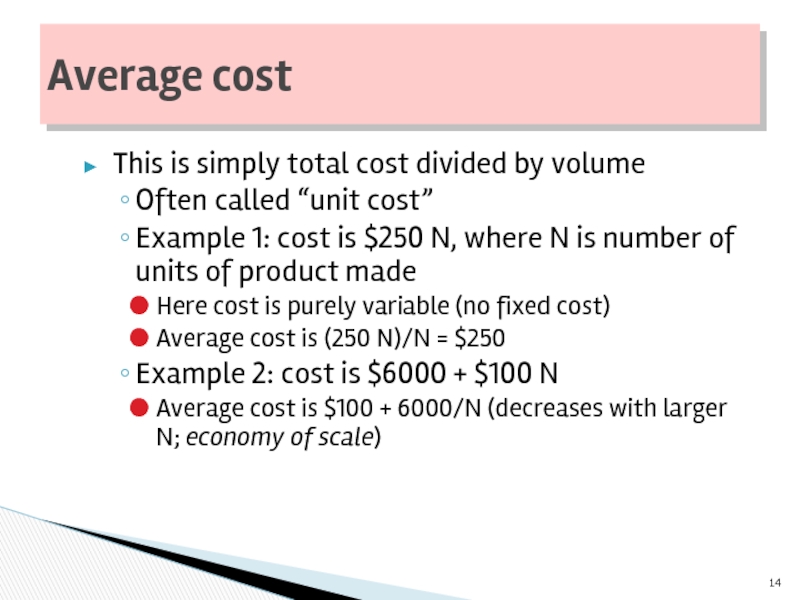
Слайд 14This is simply total cost divided by volume
Often called “unit cost”
Example
Here cost is purely variable (no fixed cost)
Average cost is (250 N)/N = $250
Example 2: cost is $6000 + $100 N
Average cost is $100 + 6000/N (decreases with larger N; economy of scale)
Average cost
Слайд 15
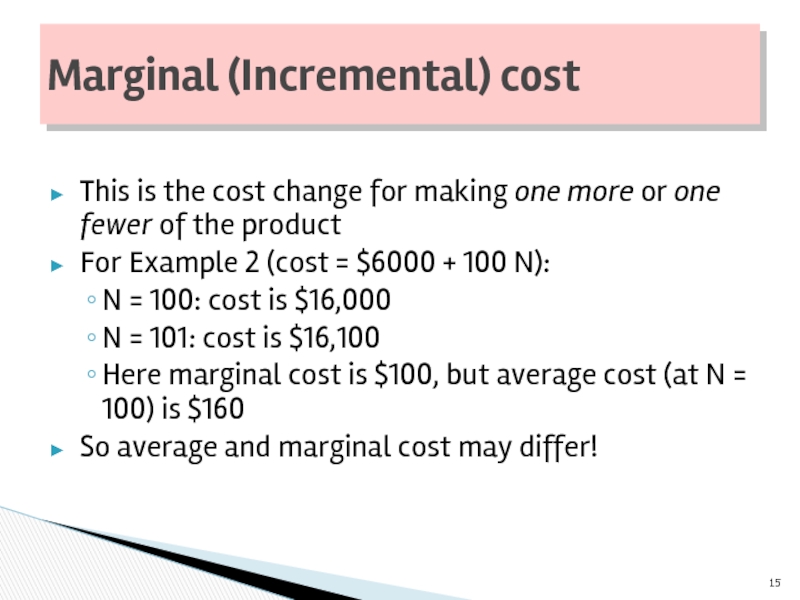
This is the cost change for making one more or one
For Example 2 (cost = $6000 + 100 N):
N = 100: cost is $16,000
N = 101: cost is $16,100
Here marginal cost is $100, but average cost (at N = 100) is $160
So average and marginal cost may differ!
Marginal (Incremental) cost
Слайд 16Let’s say:
Fixed cost is $50, variable cost is $1 per unit
(Cost equation = $50 + $1 N)
If we make 10 units:
Total cost is $60
Average cost is total cost/number of units:
$60/10=$6 per unit
Marginal cost is the extra cost (additional cost) if we increase our production by 1 unit: $1 per unit
Marginal (incremental cost):
an example
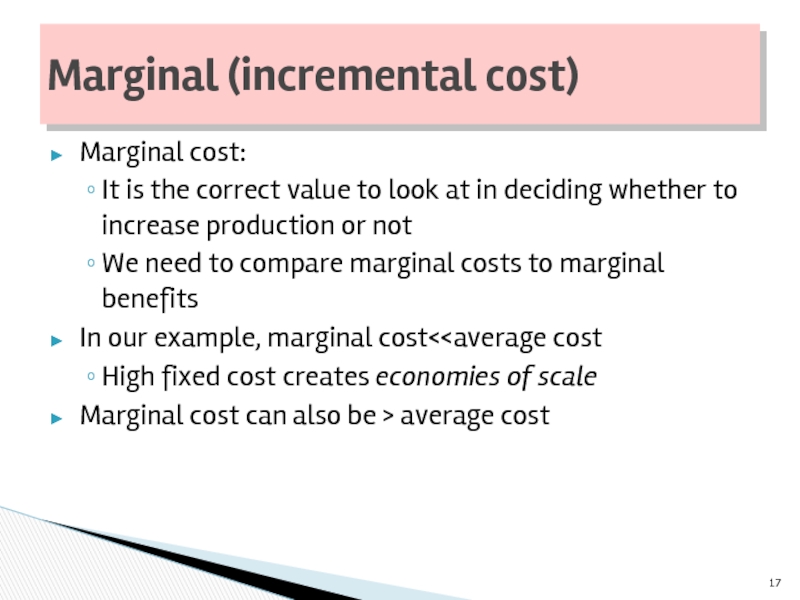
Слайд 17Marginal cost:
It is the correct value to look at in
We need to compare marginal costs to marginal benefits
In our example, marginal cost<
Marginal cost can also be > average cost
Marginal (incremental cost)
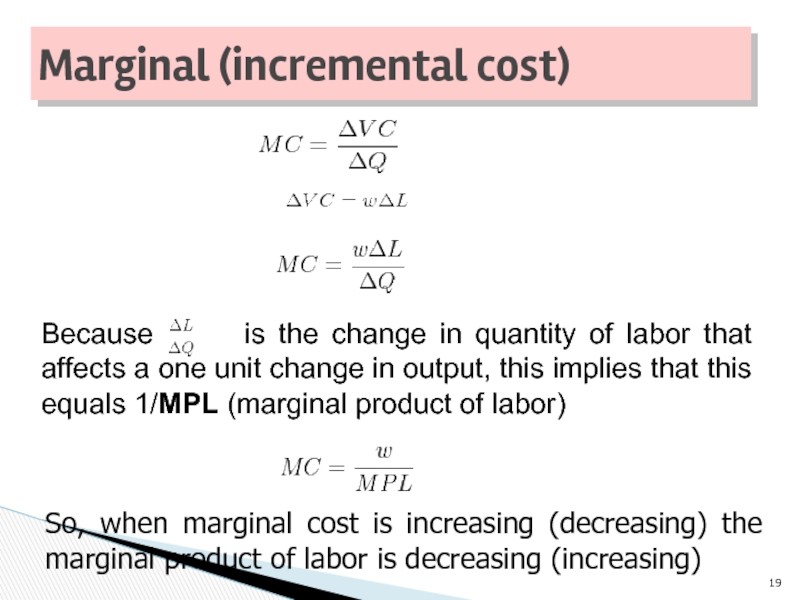
Слайд 19Because is the change in quantity of labor
So, when marginal cost is increasing (decreasing) the marginal product of labor is decreasing (increasing)
Marginal (incremental cost)
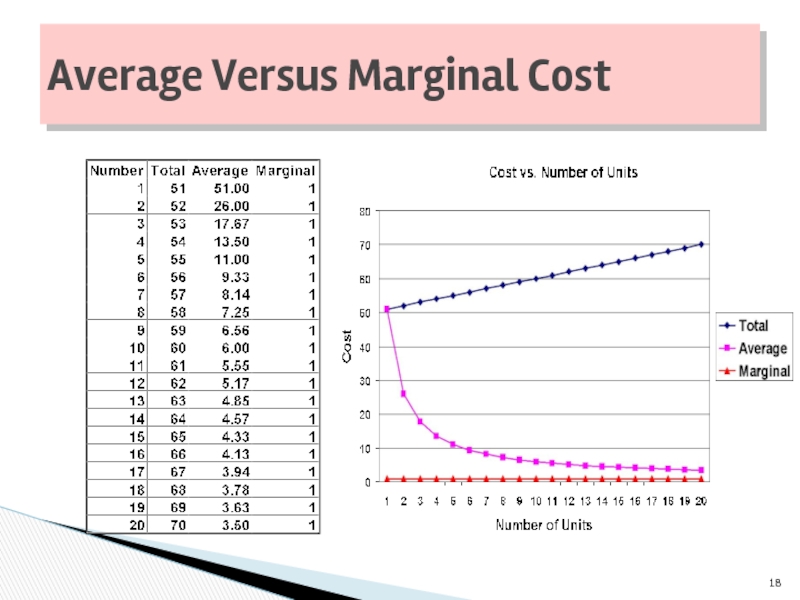
Слайд 20
Recurring are the costs that are repetitive
All variable costs are recurring,
A fixed cost can be recurring cost, e.g. Office space rental for architectural and engineering service
An example of a nonrecurring cost can be the cost of constructing a plant or purchasing a piece of land
Recurring and Nonrecurring Costs
Слайд 21
Opportunity cost is what you have to give up to get
Often expressed in dollar terms; but not always:
Opportunity cost of this lecture is 1 hour’s sleep, or more
Opportunity cost
Слайд 22Sunk costs are costs that can’t be recovered
Not the same as
Sunk costs are generally irrelevant to decision
Example:
If a firm sinks $1 million on an enterprise software installation, that cost is "sunk" because it was a one-time thing and cannot be recovered once expended.
Room painting
Sunk Costs
Слайд 23This is the total cost for a system, machine, project, etc.
Major subdivisions:
Acquisition cost
Operation cost
Maintenance cost
Life-cycle cost
Слайд 25
Based on historical data
Costs are classified into fixed, variable and semivariable
simplicity
low cost
Disadvantages:
future might not be like the past
Accounting Method
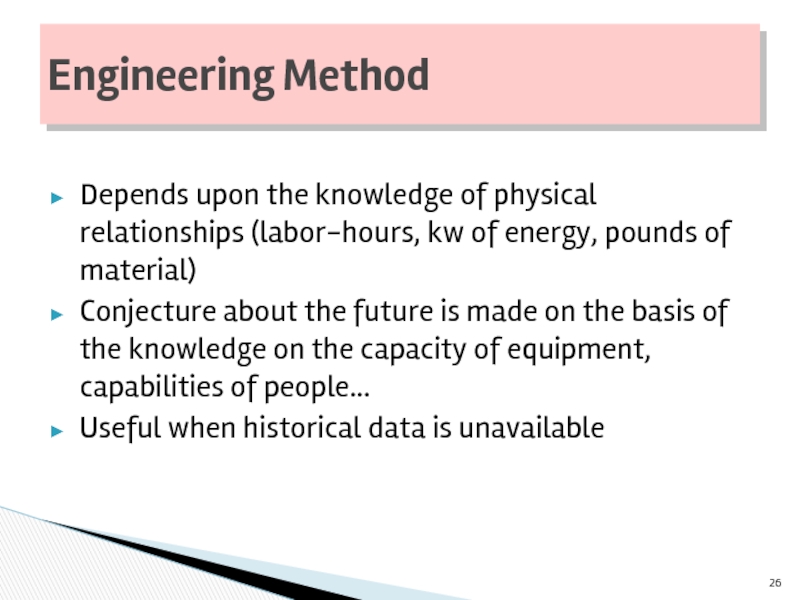
Слайд 26
Depends upon the knowledge of physical relationships (labor-hours, kw of energy,
Conjecture about the future is made on the basis of the knowledge on the capacity of equipment, capabilities of people…
Useful when historical data is unavailable
Engineering Method
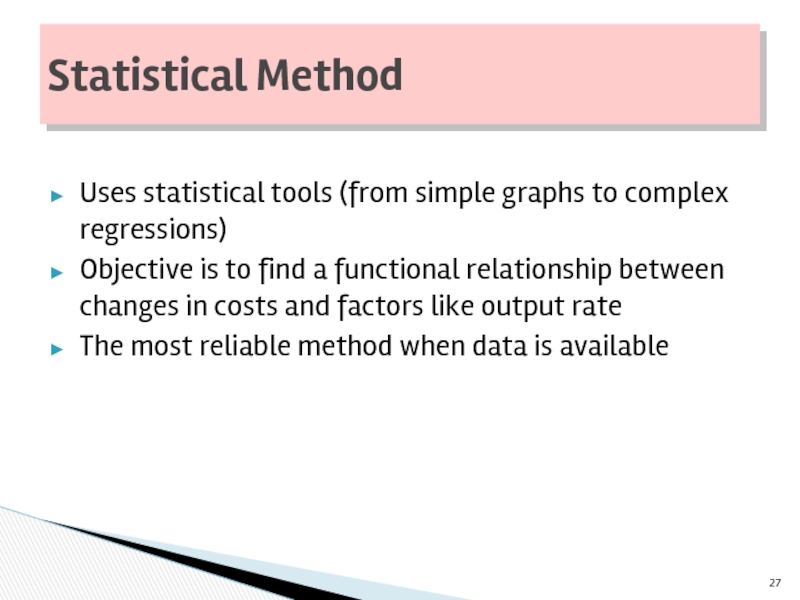
Слайд 27
Uses statistical tools (from simple graphs to complex regressions)
Objective is to
The most reliable method when data is available
Statistical Method
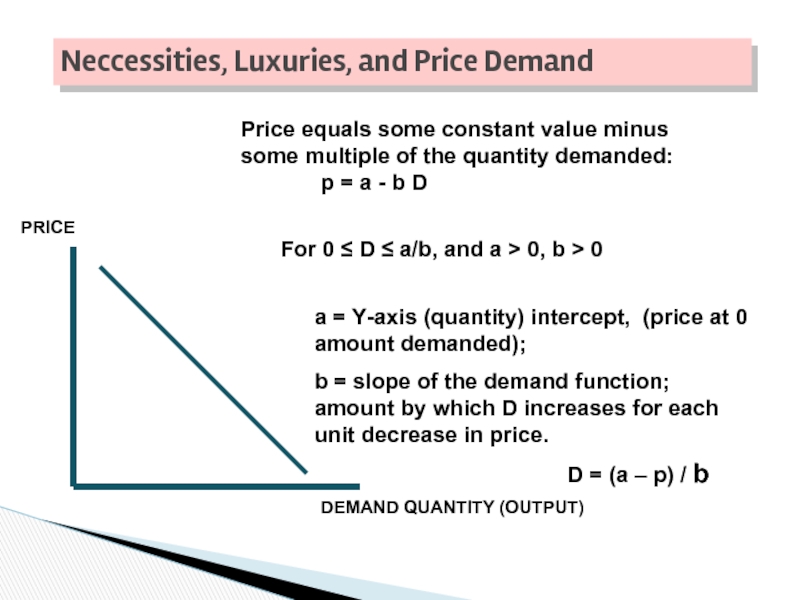
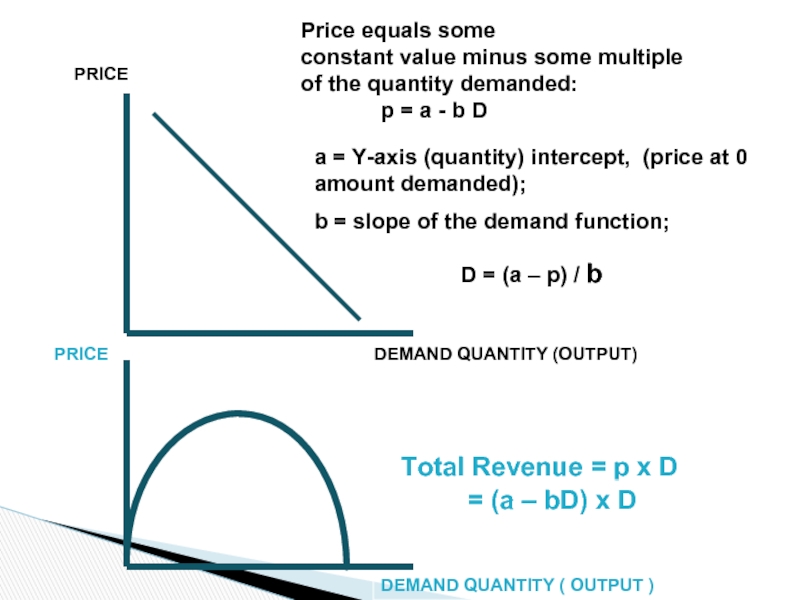
Слайд 28PRICE
DEMAND QUANTITY (OUTPUT)
Price equals some constant value minus some multiple of
p = a - b D
a = Y-axis (quantity) intercept, (price at 0 amount demanded);
b = slope of the demand function; amount by which D increases for each unit decrease in price.
D = (a – p) / b
Neccessities, Luxuries, and Price Demand
For 0 ≤ D ≤ a/b, and a > 0, b > 0
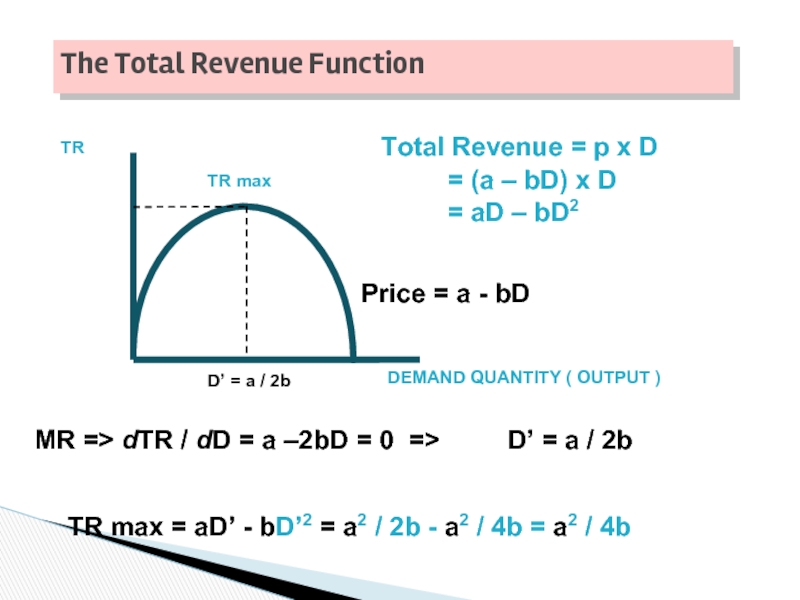
Слайд 29
TR
Total Revenue = p x D
DEMAND QUANTITY ( OUTPUT )
The Total
= (a – bD) x D
= aD – bD2
MR => dTR / dD = a –2bD = 0 =>
D’ = a / 2b
D’ = a / 2b
TR max
TR max = aD’ - bD’2 = a2 / 2b - a2 / 4b = a2 / 4b
Price = a - bD
Слайд 30Cost, Volume, and Breakeven point Relationship
Profit = (aD - bD2) –
Max Profit => d(profit)/dD = 0 =>
a – Cv - 2bD = 0
D* = a – Cv / - 2b
Слайд 31Cost, Volume, and Breakeven point Relationship
Break even occurs when:
Total Revenue =
aD – bD2 = CF + CvD =>
- bD2 + (a-Cv)D-CF = 0
The solutions for this quadratic equation would be:
-(a-Cv) + or – [(a-Cv)2 – 4(-b)(-CF )]1/2
D =
2(-b)
Слайд 33PRICE
DEMAND QUANTITY (OUTPUT)
Price equals some
constant value minus some multiple
of
p = a - b D
a = Y-axis (quantity) intercept, (price at 0 amount demanded);
b = slope of the demand function;
D = (a – p) / b
PRICE
Total Revenue = p x D
= (a – bD) x D
DEMAND QUANTITY ( OUTPUT )
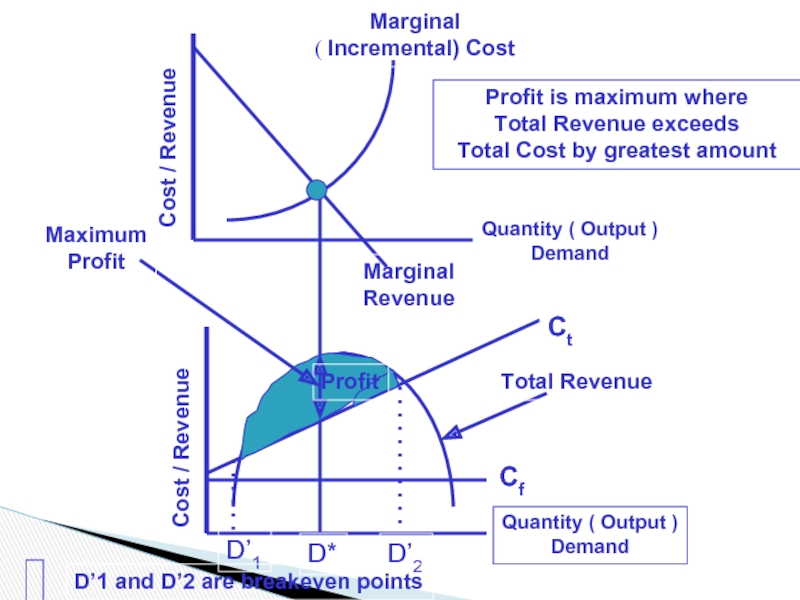
Слайд 34Cost / Revenue
Quantity ( Output )
Demand
Marginal
( Incremental) Cost
Cost / Revenue
Quantity
Demand
Cf
Ct
D’1
D’2
D*
Profit
Total Revenue
Maximum
Profit
Profit is maximum where
Total Revenue exceeds
Total Cost by greatest amount
D’1 and D’2 are breakeven points
Marginal
Revenue
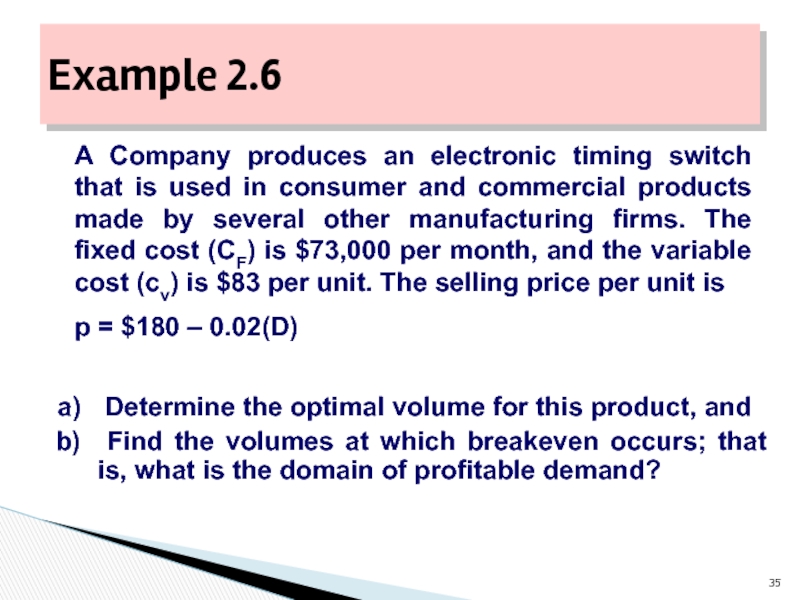
Слайд 35Example 2.6
A Company produces an electronic timing switch that is used
p = $180 – 0.02(D)
Determine the optimal volume for this product, and
Find the volumes at which breakeven occurs; that is, what is the domain of profitable demand?
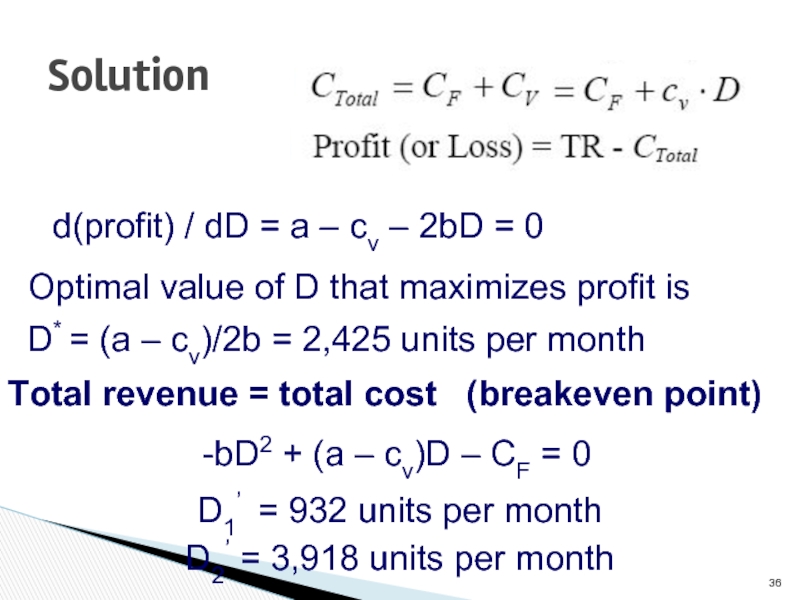
Слайд 36Solution
d(profit) / dD = a – cv – 2bD =
Optimal value of D that maximizes profit is
D* = (a – cv)/2b = 2,425 units per month
Total revenue = total cost (breakeven point)
-bD2 + (a – cv)D – CF = 0
D1’ = 932 units per month
D2’ = 3,918 units per month
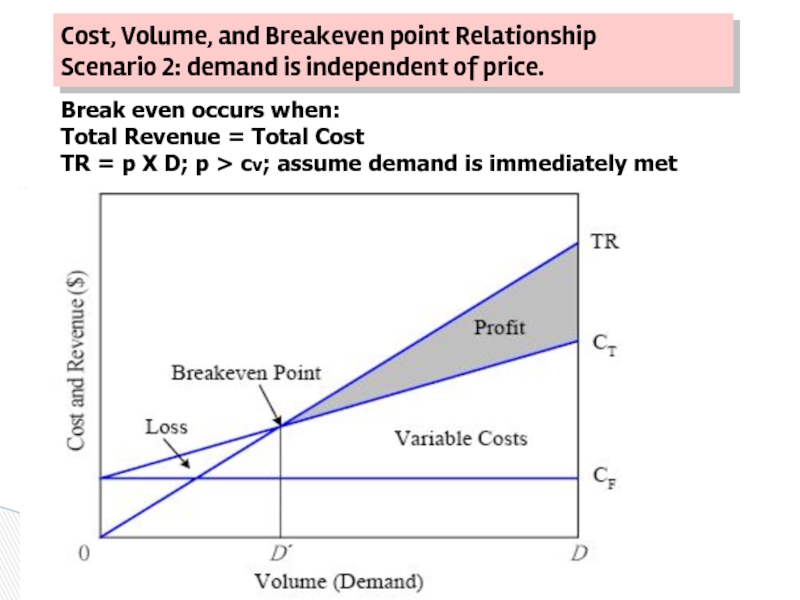
Слайд 37Cost, Volume, and Breakeven point Relationship Scenario 2: demand is independent of
Break even occurs when:
Total Revenue = Total Cost
TR = p X D; p > cv; assume demand is immediately met
Слайд 38Engineers must maintain a life-cycle (“cradle to
grave”) design perspective as they
Ensures engineers consider:
Initial investment costs
Operation and maintenance expenses
Other annual expenses in later years
Environmental and social consequences over design life
Cost driven design optimization
Design for the environment movement
This green-engineering approach has the following goals:
Prevention of waste
Improved materials selection
Reuse and recycling of resources
Слайд 39Determine optimal value for a certain alternative’s design variable
Example: what velocity
Select the best alternative, each with its own unique value for the design variable
Example: what insulation thickness is best for a home in Gyumri
Cost-driven Design Optimization Problem Tasks
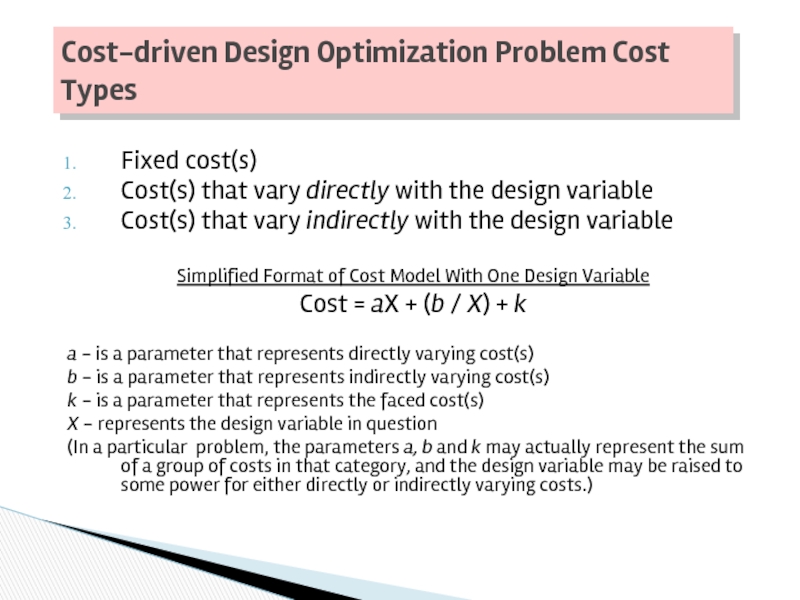
Слайд 40Fixed cost(s)
Cost(s) that vary directly with the design variable
Cost(s) that vary
Simplified Format of Cost Model With One Design Variable
Cost = aX + (b / X) + k
a - is a parameter that represents directly varying cost(s)
b - is a parameter that represents indirectly varying cost(s)
k - is a parameter that represents the faced cost(s)
X - represents the design variable in question
(In a particular problem, the parameters a, b and k may actually represent the sum of a group of costs in that category, and the design variable may be raised to some power for either directly or indirectly varying costs.)
Cost-driven Design Optimization Problem Cost Types
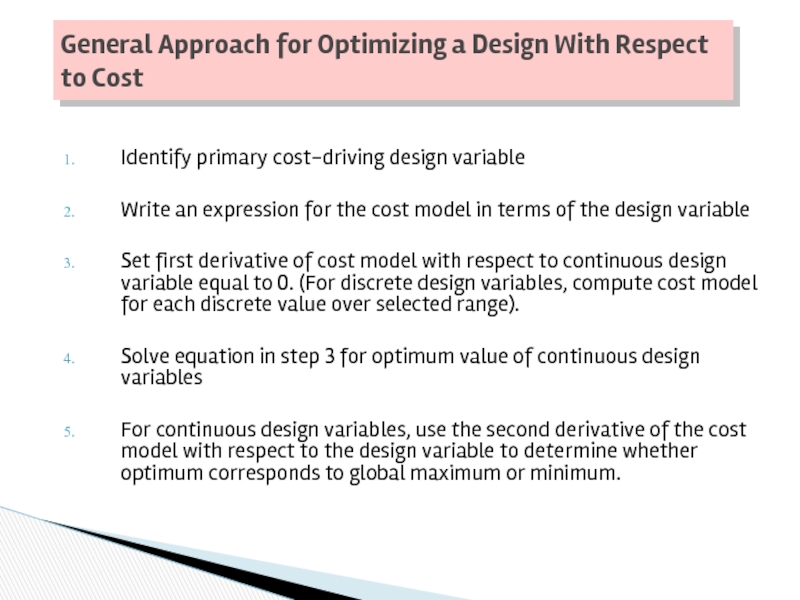
Слайд 41Identify primary cost-driving design variable
Write an expression for the cost model
Set first derivative of cost model with respect to continuous design variable equal to 0. (For discrete design variables, compute cost model for each discrete value over selected range).
Solve equation in step 3 for optimum value of continuous design variables
For continuous design variables, use the second derivative of the cost model with respect to the design variable to determine whether optimum corresponds to global maximum or minimum.
General Approach for Optimizing a Design With Respect to Cost
Слайд 42 When alternatives for accomplishing a task are compared for
Rules for Selecting Preferred Alternative
Rule 1 – When revenues and other economic benefits are present and vary among alternatives, choose alternative that maximizes overall profitability based on the number of defect-free units of output
Rule 2 – When revenues and economic benefits are not present or are constant among alternatives, consider only costs and select alternative that minimizes total cost per defect-free output
Present Economy Studies
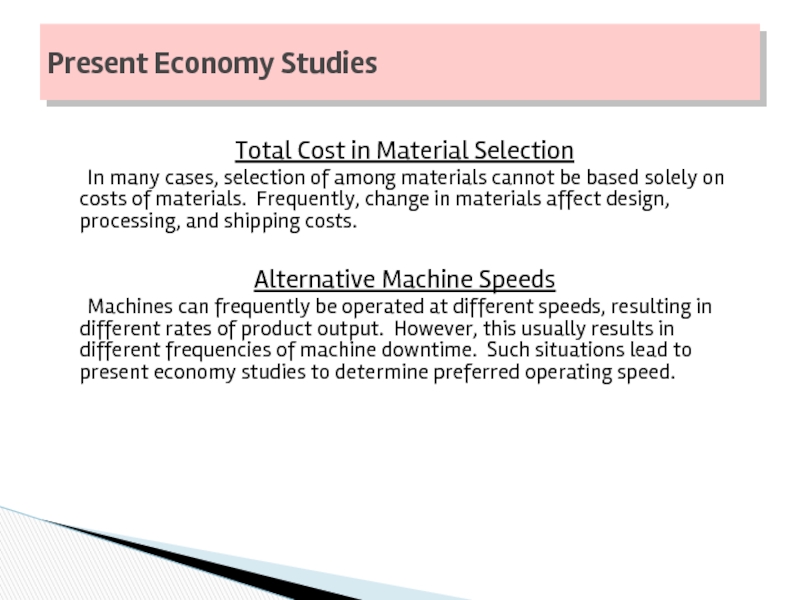
Слайд 43Total Cost in Material Selection
In many cases, selection of among materials
Alternative Machine Speeds
Machines can frequently be operated at different speeds, resulting in different rates of product output. However, this usually results in different frequencies of machine downtime. Such situations lead to present economy studies to determine preferred operating speed.
Present Economy Studies
Слайд 44Make Versus Purchase (Outsourcing) Studies
A company may choose to produce an
direct, indirect or overhead costs are incurred regardless of whether the item is purchased from an outside supplier, and
The incremental cost of producing the item in the short run is less than the supplier’s price.
The relevant short-run costs of the make versus purchase decisions are the incremental costs incurred and the opportunity costs of resources
Present Economy Studies
Слайд 45Make Versus Purchase (Outsourcing) Studies
Opportunity costs may become significant when in-house
In the long run, capital investments in additional manufacturing plant and capacity are often feasible alternatives to outsourcing.
Present Economy Studies
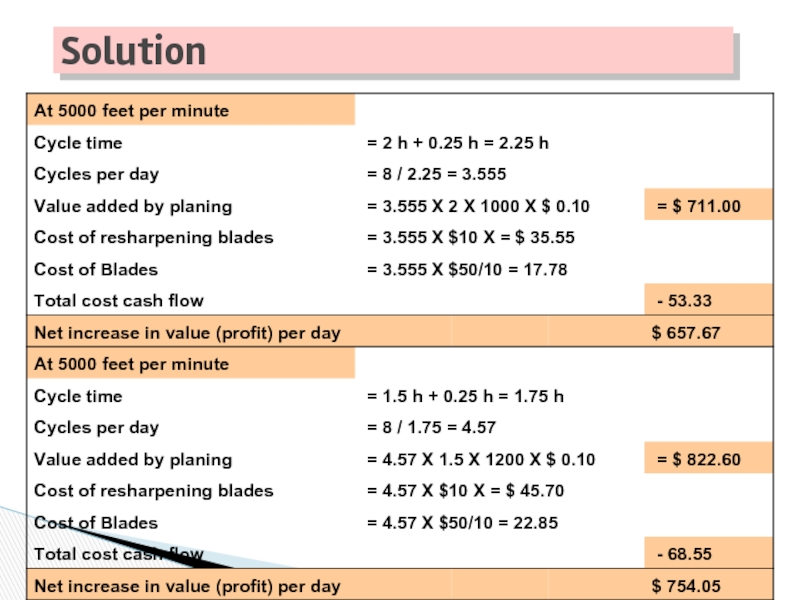
Слайд 46Lumber put through the planer increases in value by $0.10 per
At what speed should the planer be operated?
At what speed should it be operated when only one job requiring 6,000 board-feet of planing is considered.
Example 2.13 – Best Operating Speed