- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Theme 13. Unemployment and inflation are both manifestations of economic instability презентация
Содержание
- 1. Theme 13. Unemployment and inflation are both manifestations of economic instability
- 2. 1. Essence and basic forms of unemployment
- 3. Unemployment - a condition in which the
- 5. Employment rate - the percentage of the
- 6. In modern conditions, employment status based on the following principles:
- 7. 2.The effect of unemployment rate on the value of GNP. The Law of Oaken
- 8. In cyclical unemployment production capacity is not
- 9. The main method of the state employment
- 10. The labor exchanges, which are:
- 11. 3.Inflation and its causes
- 12. The essence of inflation is that the
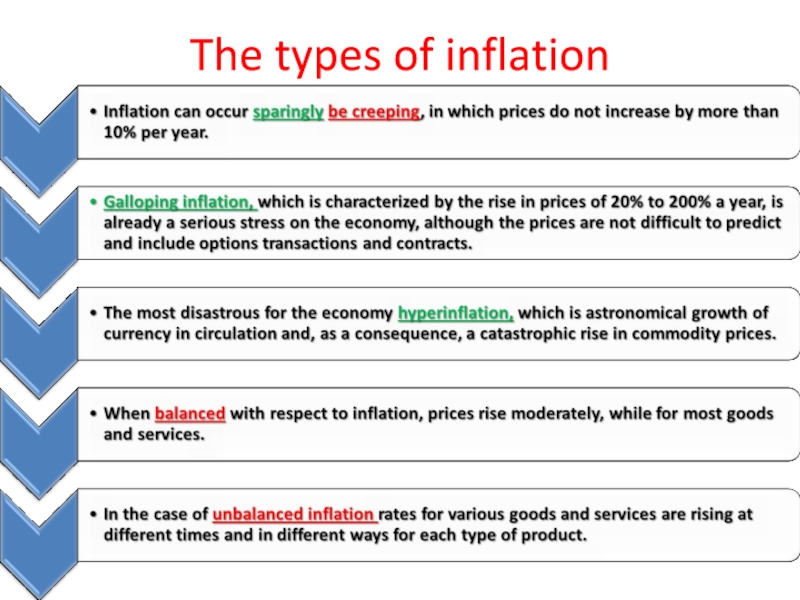
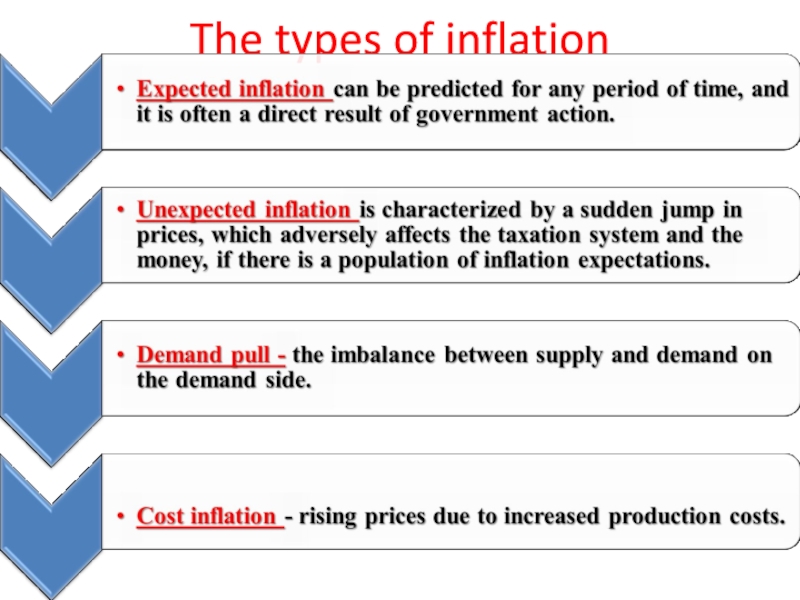
- 13. The types of inflation
- 14. The types of inflation
Слайд 3Unemployment - a condition in which the willing can not find
work at the regular rate of wages.
Unemployment rate - the percentage of the unemployed to the labor force, which does not include: students, pensioners, prisoners, and boys and girls up to 16 years.
The overall unemployment rate - the percentage of the unemployed to the total labor force, including those engaged in active military service.
Unemployment rate - the percentage of the unemployed to the labor force, which does not include: students, pensioners, prisoners, and boys and girls up to 16 years.
The overall unemployment rate - the percentage of the unemployed to the total labor force, including those engaged in active military service.
Слайд 5Employment rate - the percentage of the adult population employed that
are not on welfare, in shelters, nursing homes, etc.
Full employment does not mean complete absence of unemployment.
Natural rate of unemployment - a set of frictional and structural unemployment and the unemployment rate is associated with a stable economy, when the real national product is at the natural rate, and lacks both slowing and accelerating inflation or when the expected rate of inflation is equal to the actual level of inflation.
Full employment does not mean complete absence of unemployment.
Natural rate of unemployment - a set of frictional and structural unemployment and the unemployment rate is associated with a stable economy, when the real national product is at the natural rate, and lacks both slowing and accelerating inflation or when the expected rate of inflation is equal to the actual level of inflation.
Слайд 8In cyclical unemployment production capacity is not fully utilized and the
amount of GDP less than that which would be at full employment. The difference between potential output at full employment GDP and actually achieved in cyclical unemployment GDP is GDP gap.
The Law of Oaken expresses the relationship between the level of unemployment or lost in GDP. If the actual unemployment rate exceeds the natural rate of 1%, the gap in GDP of approximately 2.5%. This ratio (1:2.5) allows us to calculate the absolute loss associated with any level of unemployment.
The Law of Oaken expresses the relationship between the level of unemployment or lost in GDP. If the actual unemployment rate exceeds the natural rate of 1%, the gap in GDP of approximately 2.5%. This ratio (1:2.5) allows us to calculate the absolute loss associated with any level of unemployment.
Слайд 9The main method of the state employment policy are the programs
for the reduction of unemployment.
Слайд 12The essence of inflation is that the national currency depreciates in
relation to goods, services and foreign currency, preserving the stability of its purchasing power.