- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Elasticity and Its Application презентация
Содержание
- 1. Elasticity and Its Application
- 2. Elasticity . . . … is
- 3. Price Elasticity of Demand Price elasticity of
- 4. Determinants of Price Elasticity of Demand
- 5. Determinants of Price Elasticity of Demand
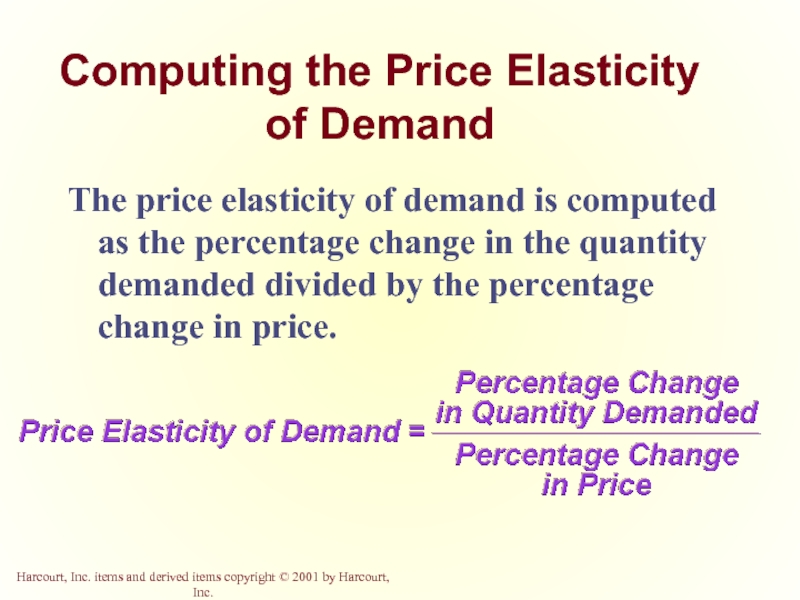
- 6. Computing the Price Elasticity of Demand The
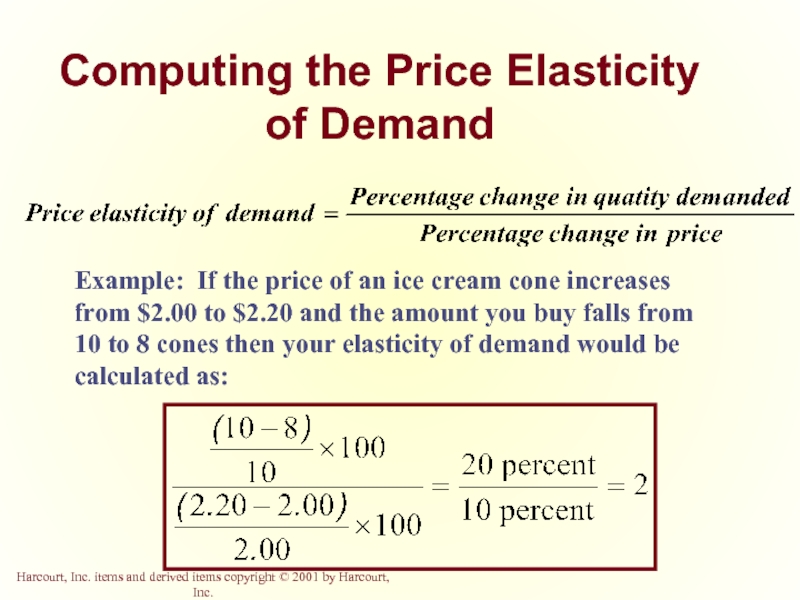
- 7. Computing the Price Elasticity of Demand Example:
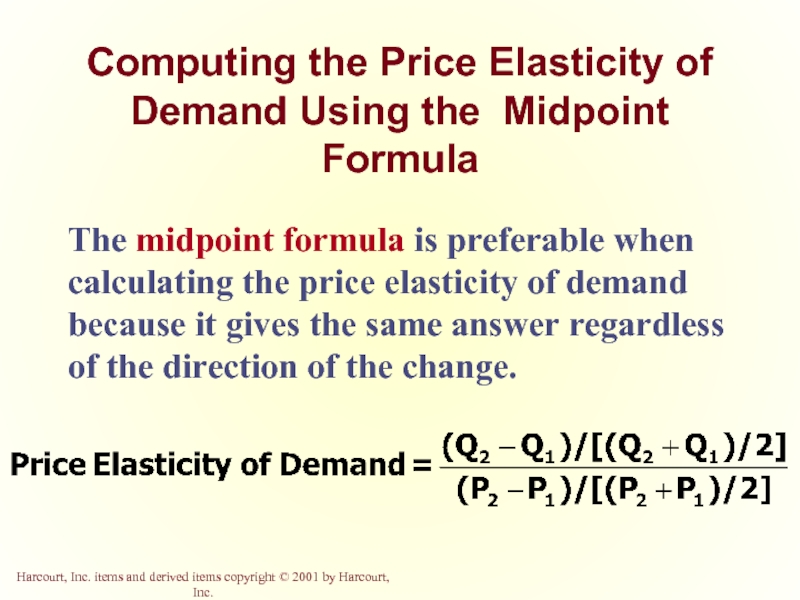
- 8. Computing the Price Elasticity of Demand Using
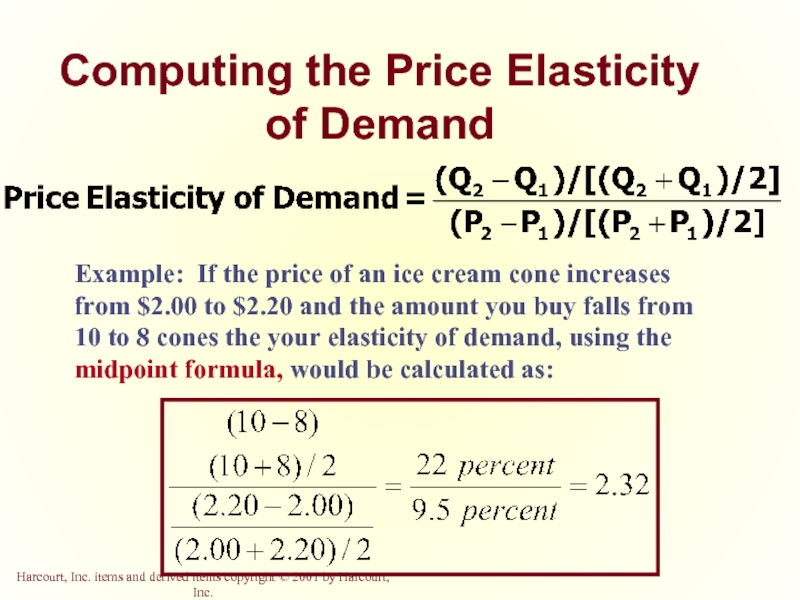
- 9. Computing the Price Elasticity of Demand Example:
- 10. Ranges of Elasticity Inelastic Demand Quantity demanded
- 11. Computing the Price Elasticity of Demand Demand
- 12. Ranges of Elasticity Perfectly Inelastic Quantity demanded
- 13. A Variety of Demand Curves Because the
- 14. Perfectly Inelastic Demand - Elasticity equals 0 Quantity Price 2. ...leaves the quantity demanded unchanged.
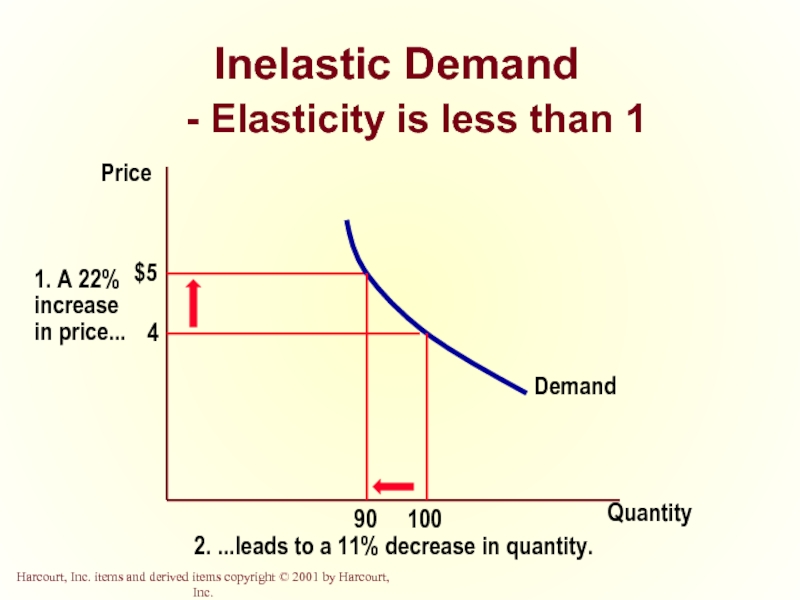
- 15. Inelastic Demand - Elasticity is less than 1 Quantity Price
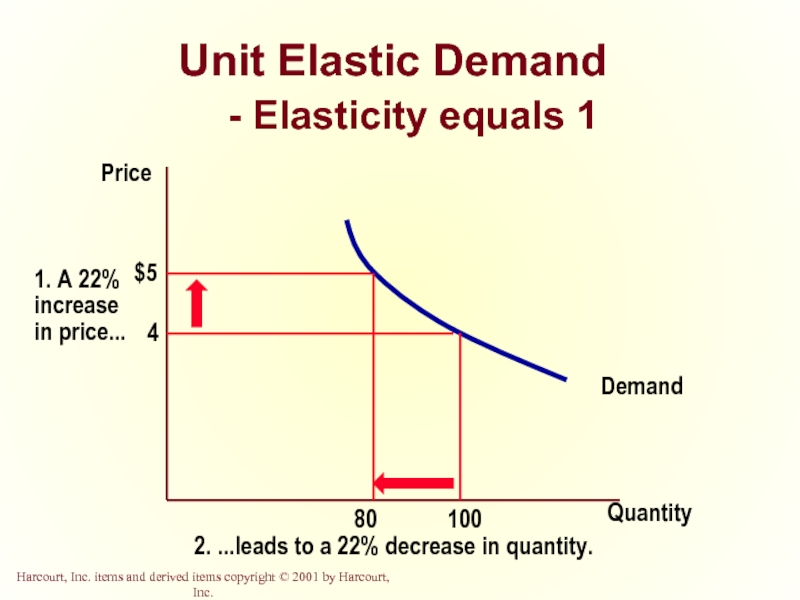
- 16. Unit Elastic Demand - Elasticity equals 1 Quantity Price
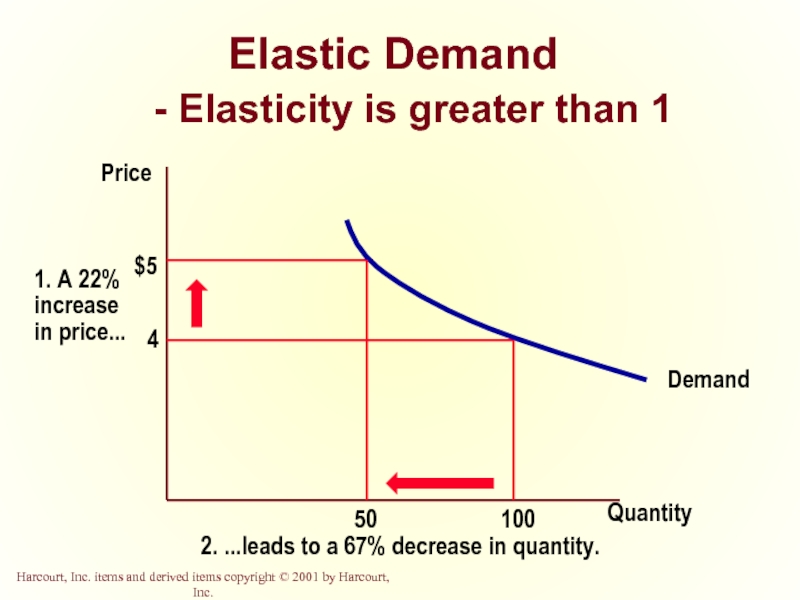
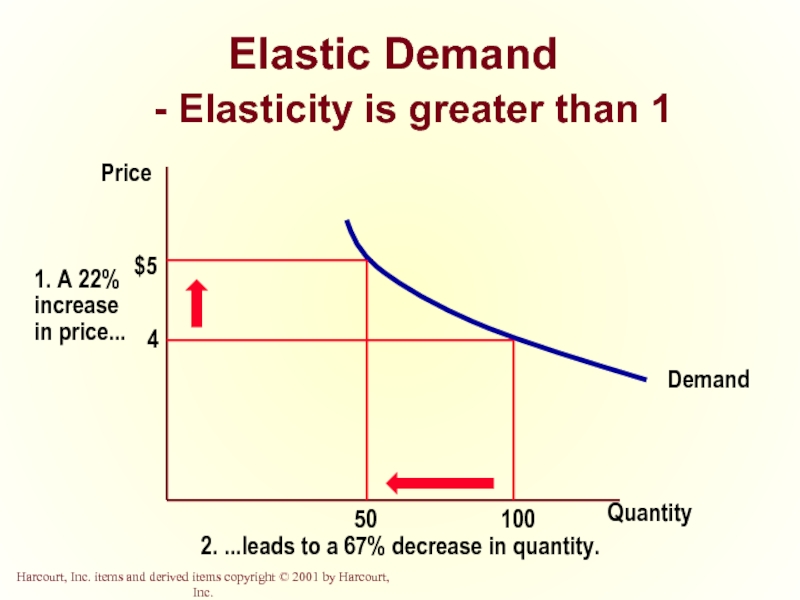
- 17. Elastic Demand - Elasticity is greater than 1 Quantity Price
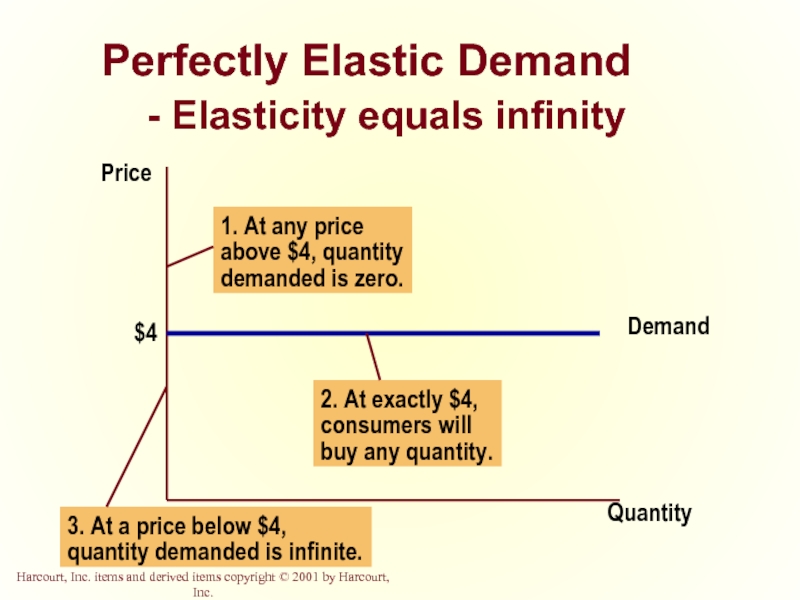
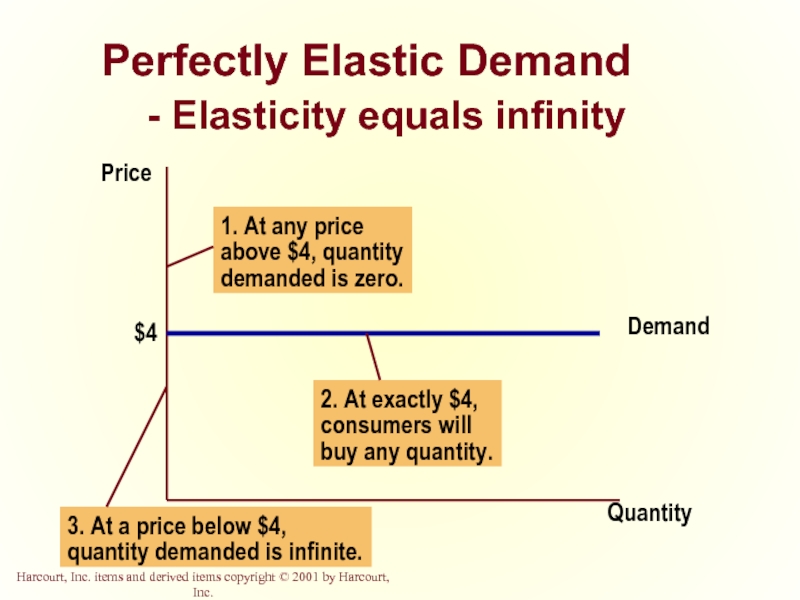
- 18. Perfectly Elastic Demand - Elasticity equals infinity Quantity Price
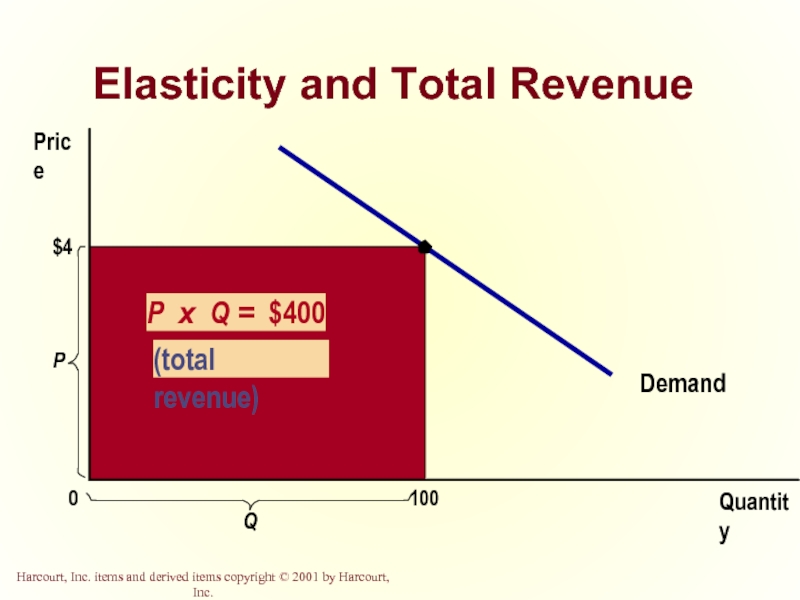
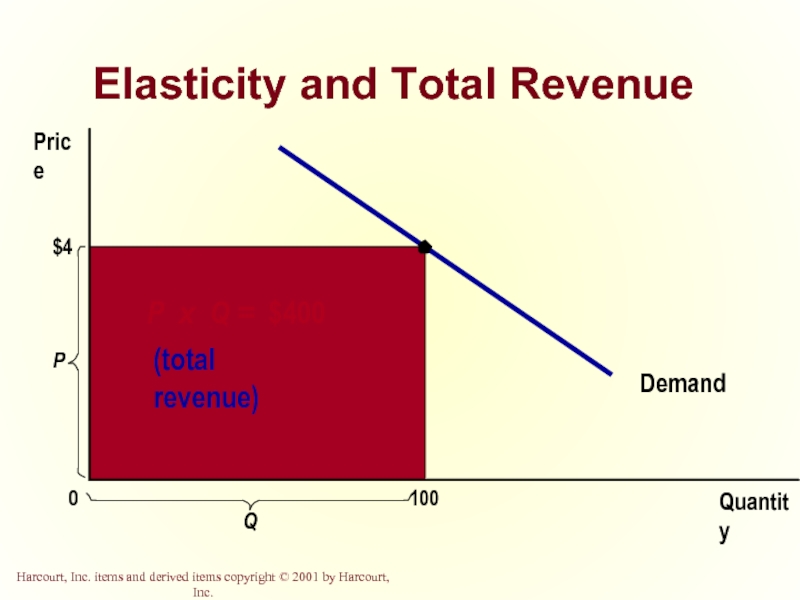
- 19. Elasticity and Total Revenue Total revenue is
- 20. $4 Demand Quantity P
- 21. Elasticity and Total Revenue With an inelastic
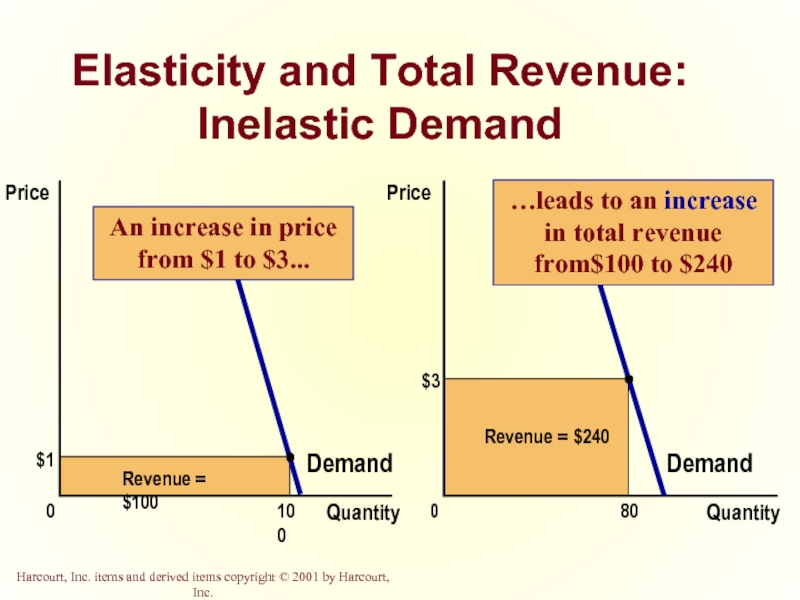
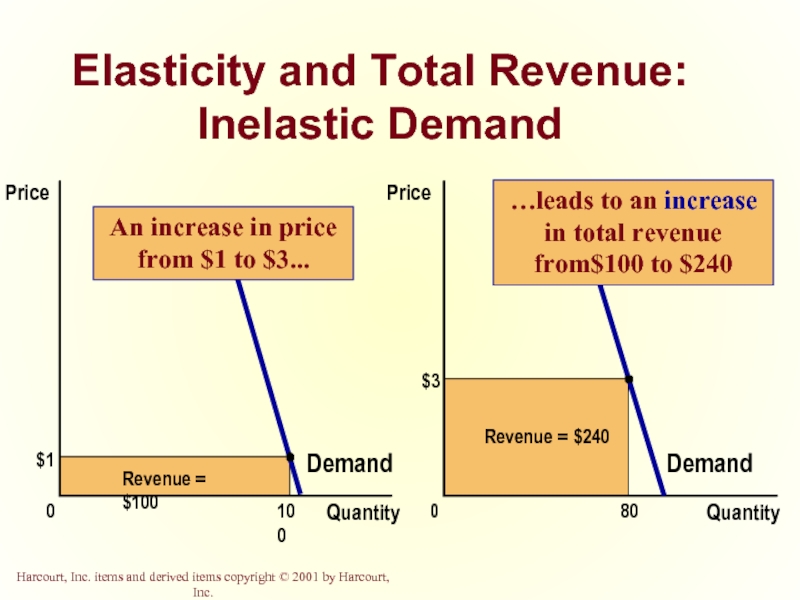
- 22. Elasticity and Total Revenue: Inelastic Demand
- 23. Elasticity and Total Revenue With an elastic
- 24. Elasticity and Total Revenue: Elastic Demand
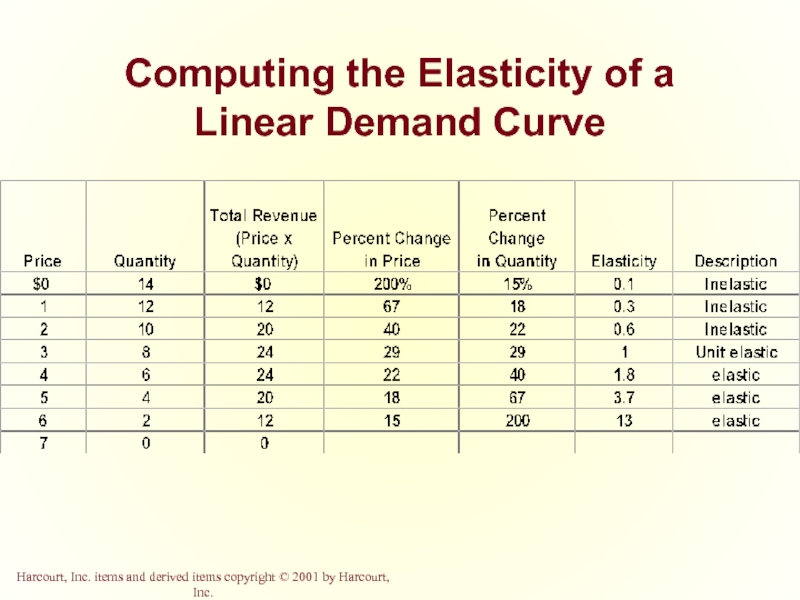
- 25. Computing the Elasticity of a Linear Demand Curve
- 26. Income Elasticity of Demand Income elasticity of
- 27. Computing Income Elasticity
- 28. Income Elasticity - Types of Goods -
- 29. Income Elasticity - Types of Goods -
- 30. Price Elasticity of Supply Price elasticity of
- 31. Ranges of Elasticity Perfectly Elastic ES =
- 32. Ranges of Elasticity Relatively Inelastic ES < 1 Perfectly Inelastic ES = 0
- 33. Perfectly Inelastic Supply - Elasticity equals 0 Quantity Price 2. ...leaves the quantity supplied unchanged.
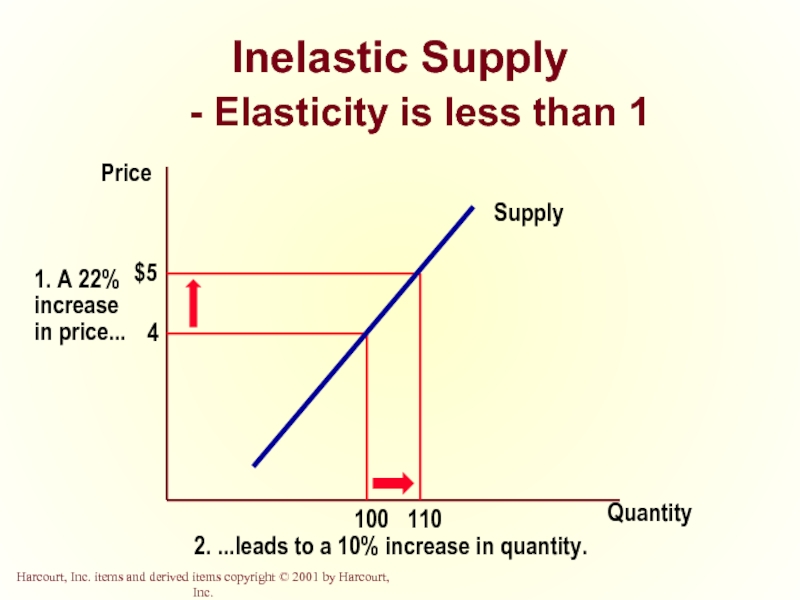
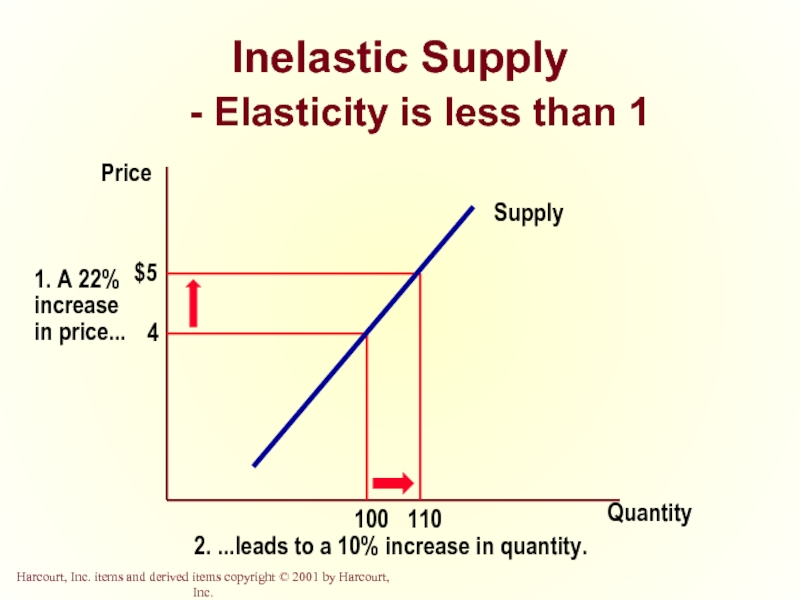
- 34. Inelastic Supply - Elasticity is less than 1 Quantity Price
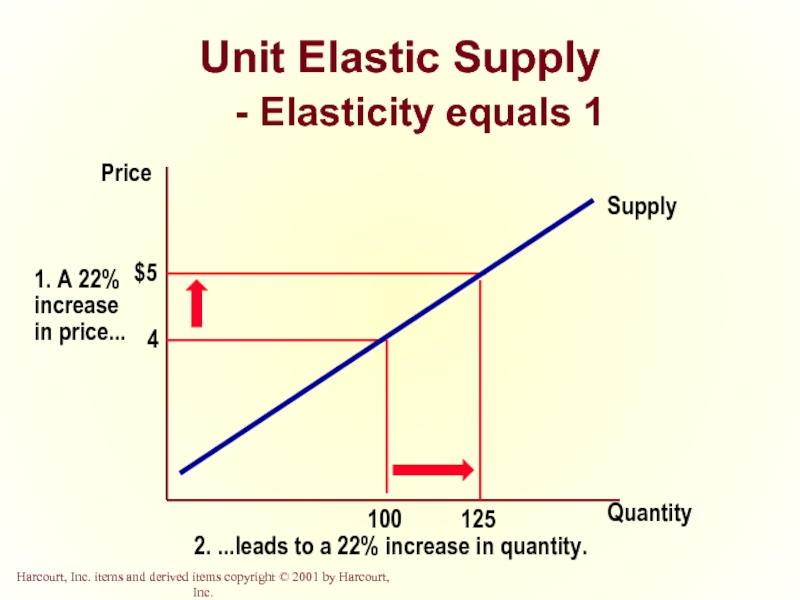
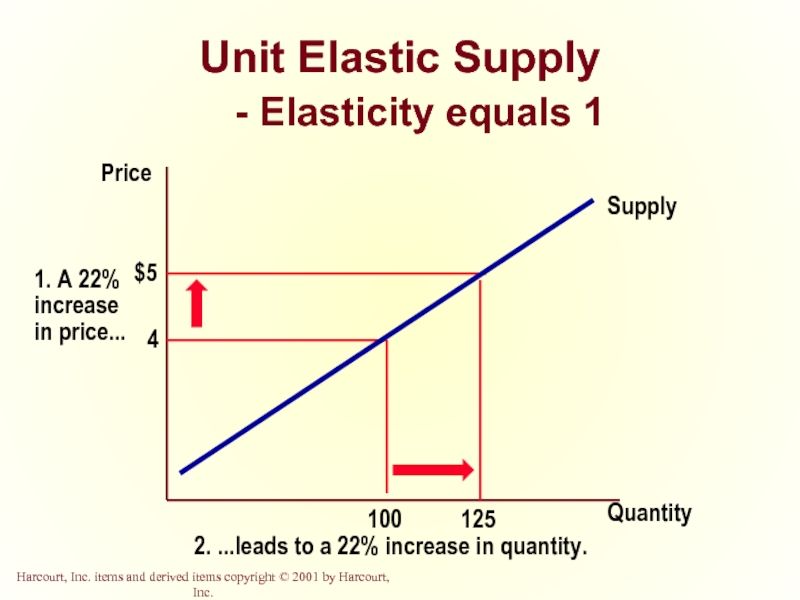
- 35. Unit Elastic Supply - Elasticity equals 1 Quantity Price
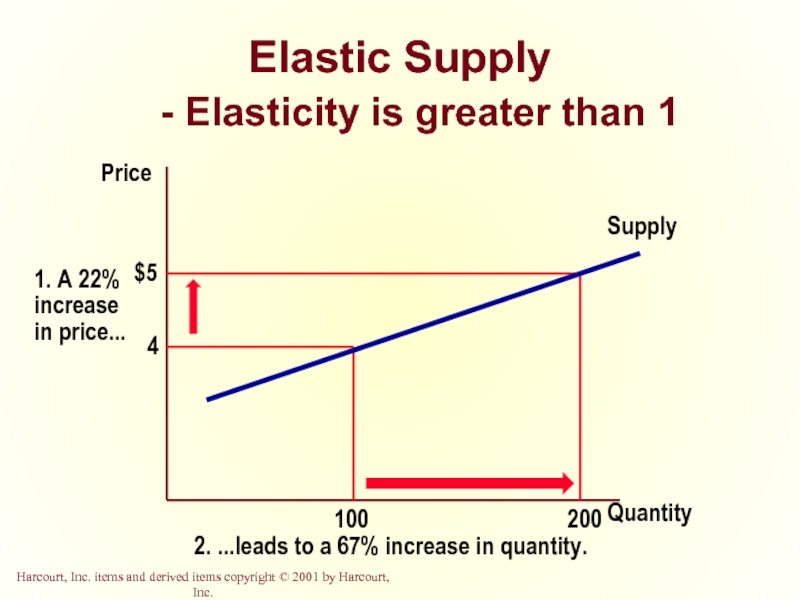
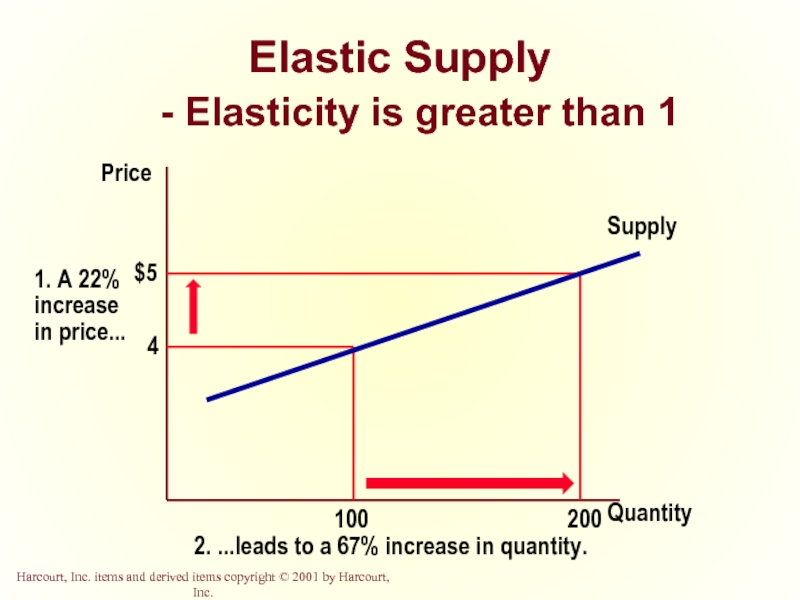
- 36. Elastic Supply - Elasticity is greater than 1 Quantity Price
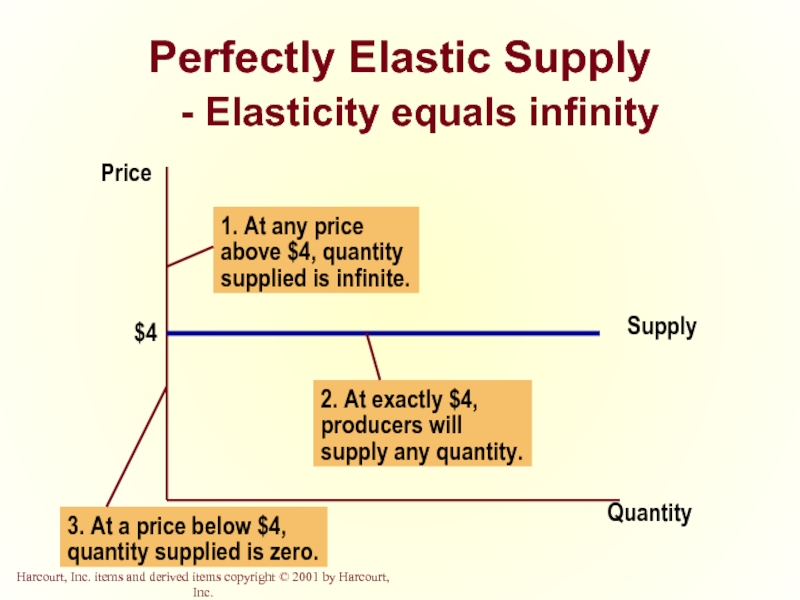
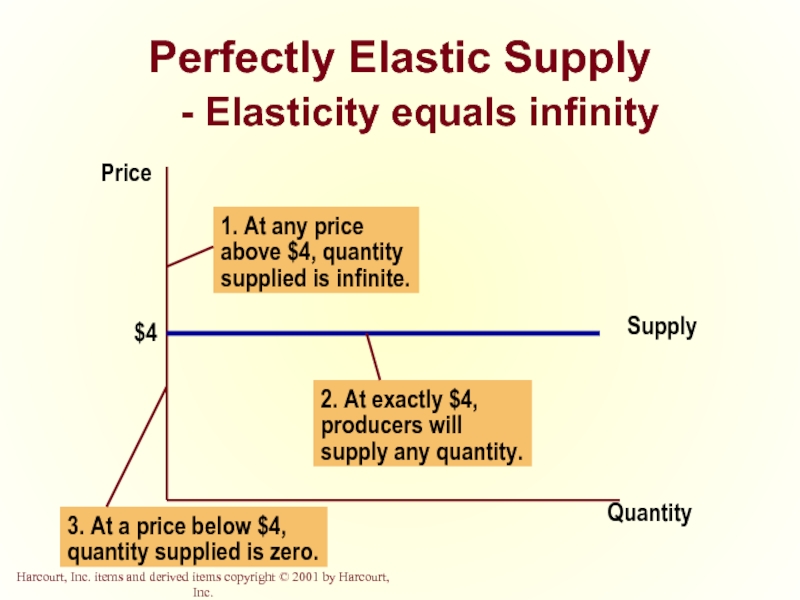
- 37. Perfectly Elastic Supply - Elasticity equals infinity Quantity Price
- 38. Determinants of Elasticity of Supply Ability
- 39. Computing the Price Elasticity of Supply The
- 40. Application of Elasticity Can good news for
- 41. Application of Elasticity Examine whether the supply
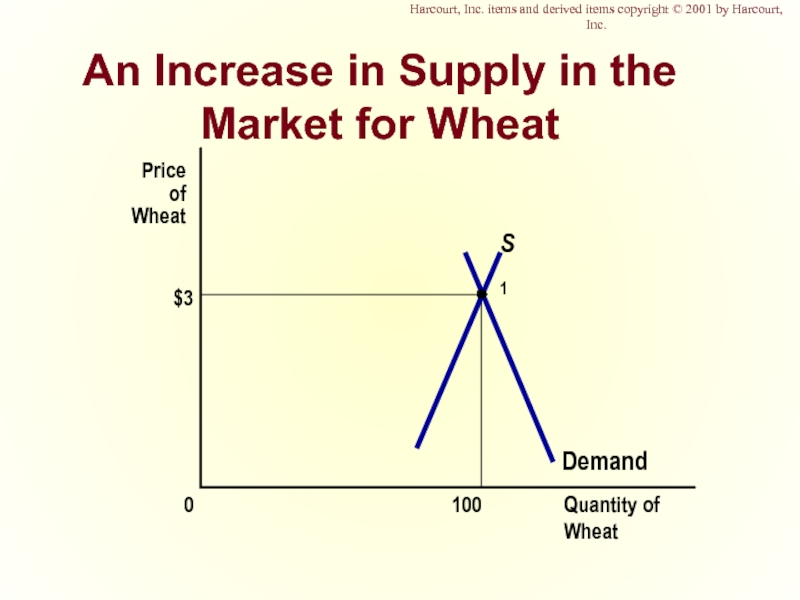
- 42. An Increase in Supply in the Market
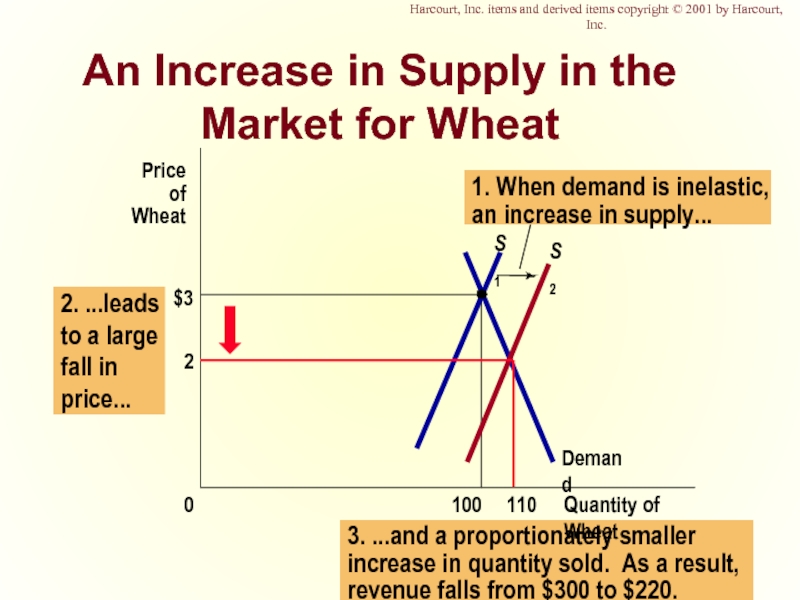
- 43. 3. ...and a proportionately smaller increase in
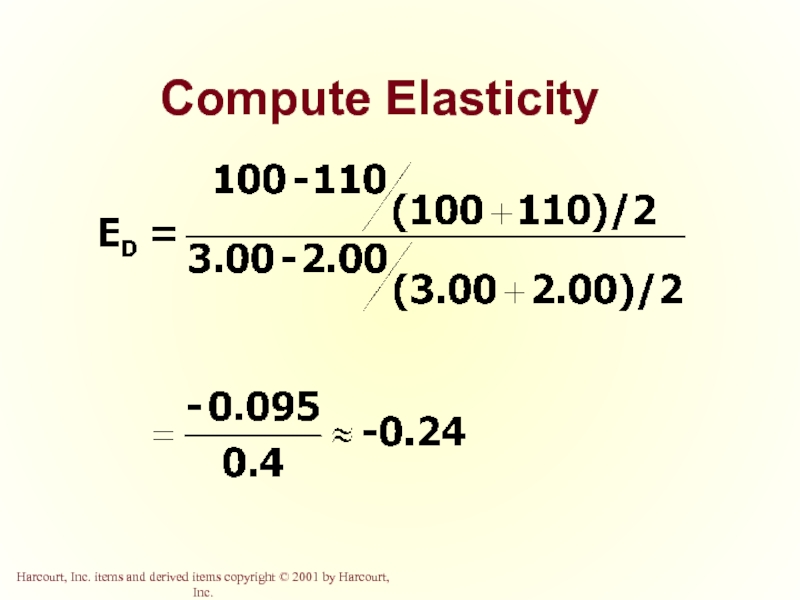
- 44. Compute Elasticity
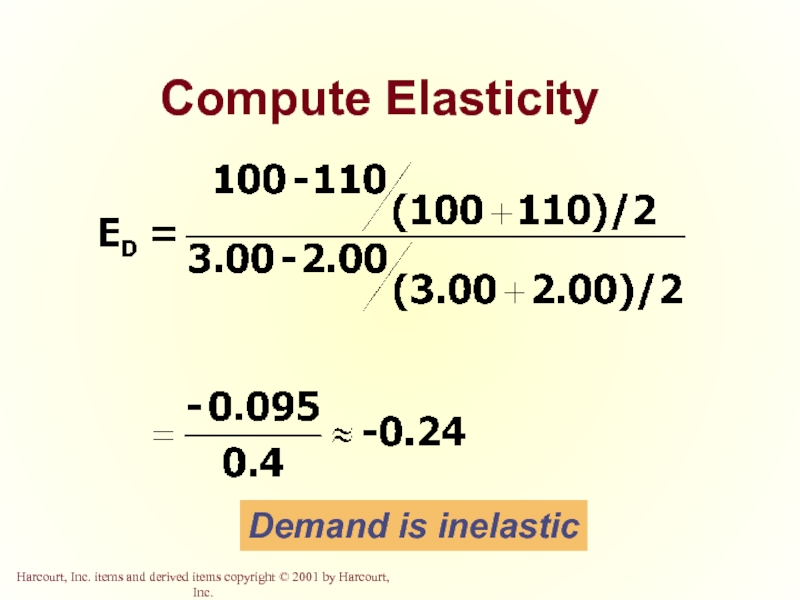
- 45. Compute Elasticity Demand is inelastic
- 46. Summary Price elasticity of demand measures how
- 47. Summary The price elasticity of supply measures
- 49. Computing the Price Elasticity of Demand
- 50. Perfectly Inelastic Demand - Elasticity equals 0
- 51. Inelastic Demand - Elasticity is less than 1
- 52. Unit Elastic Demand - Elasticity equals 1
- 53. Elastic Demand - Elasticity is greater than 1
- 54. Perfectly Elastic Demand - Elasticity equals infinity
- 55. Elasticity and Total Revenue
- 56. Elasticity and Total Revenue: Inelastic Demand
- 57. Elasticity and Total Revenue: Elastic Demand
- 58. Perfectly Inelastic Supply - Elasticity equals 0
- 59. Inelastic Supply - Elasticity is less than 1
- 60. Unit Elastic Supply - Elasticity equals 1
- 61. Elastic Supply - Elasticity is greater than 1
- 62. Perfectly Elastic Supply - Elasticity equals infinity
- 63. An Increase in Supply in the Market
- 64. An Increase in Supply in the Market
Слайд 1
Elasticity and Its Application
Chapter 5
Copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
All rights
Permissions Department, Harcourt College Publishers, 6277 Sea Harbor Drive, Orlando, Florida 32887-6777.
Слайд 2Elasticity . . .
… is a measure of how much
… allows us to analyze supply and demand with greater precision.
Слайд 3Price Elasticity of Demand
Price elasticity of demand is the percentage change
It is a measure of how much the quantity demanded of a good responds to a change in the price of that good.
Слайд 4Determinants of
Price Elasticity of Demand
Necessities versus Luxuries
Availability of Close Substitutes
Definition
Time Horizon
Слайд 5Determinants of
Price Elasticity of Demand
Demand tends to be more elastic
if the good is a luxury.
the longer the time period.
the larger the number of close substitutes.
the more narrowly defined the market.
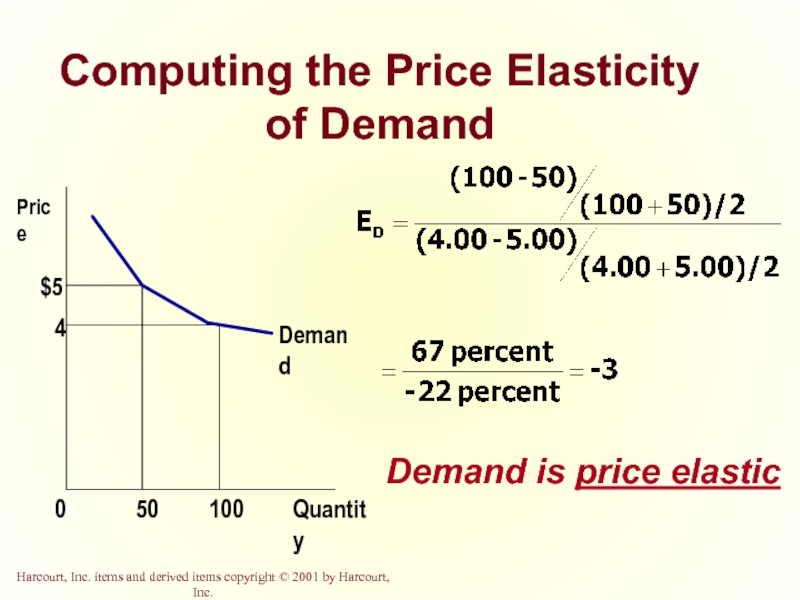
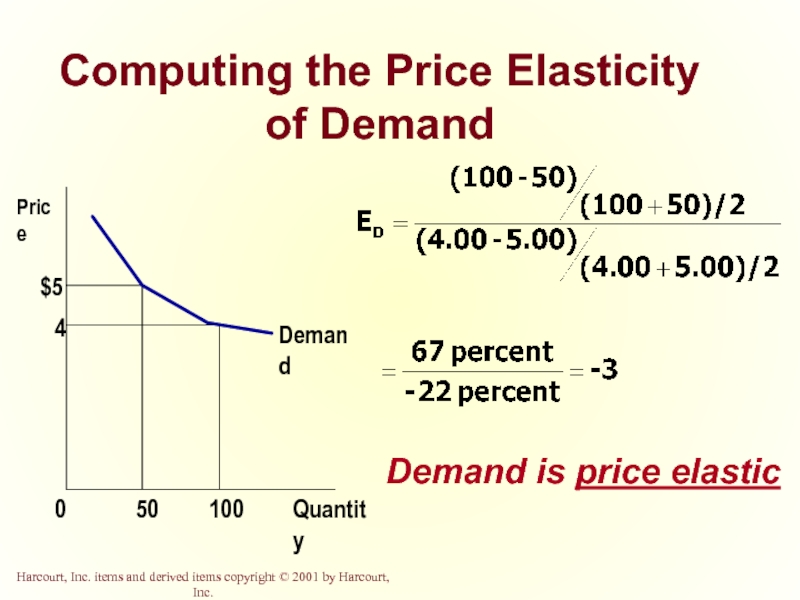
Слайд 6Computing the Price Elasticity of Demand
The price elasticity of demand is
Слайд 7Computing the Price Elasticity of Demand
Example: If the price of an
Слайд 8Computing the Price Elasticity of Demand Using the Midpoint Formula
The midpoint
Слайд 9Computing the Price Elasticity of Demand
Example: If the price of an
Слайд 10Ranges of Elasticity
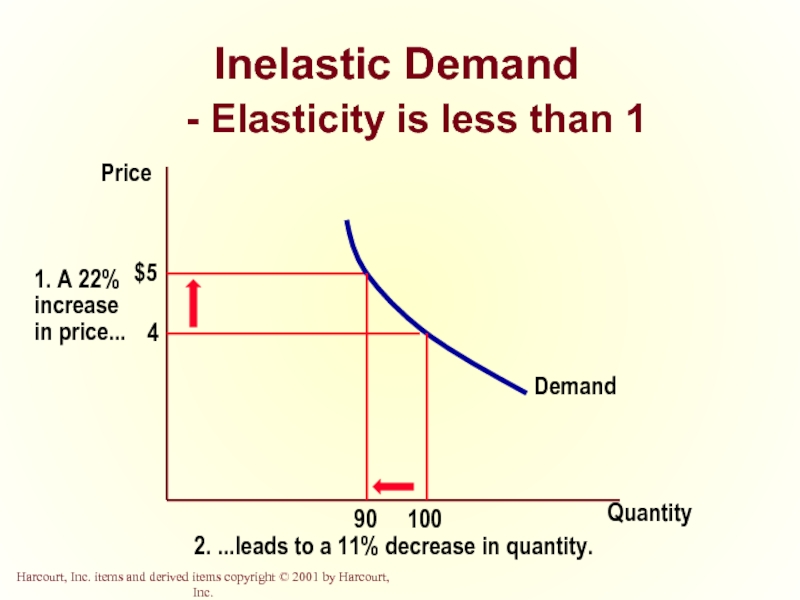
Inelastic Demand
Quantity demanded does not respond strongly to price
Price elasticity of demand is less than one.
Elastic Demand
Quantity demanded responds strongly to changes in price.
Price elasticity of demand is greater than one.
Слайд 12Ranges of Elasticity
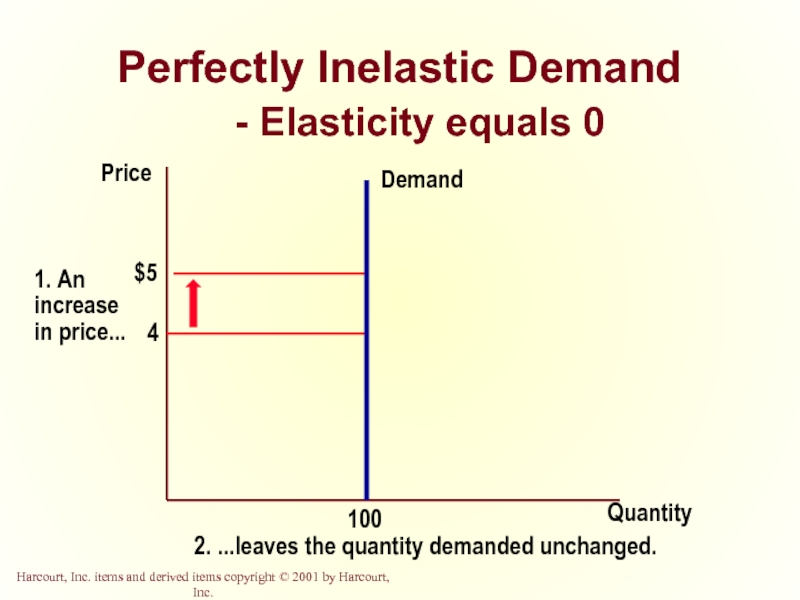
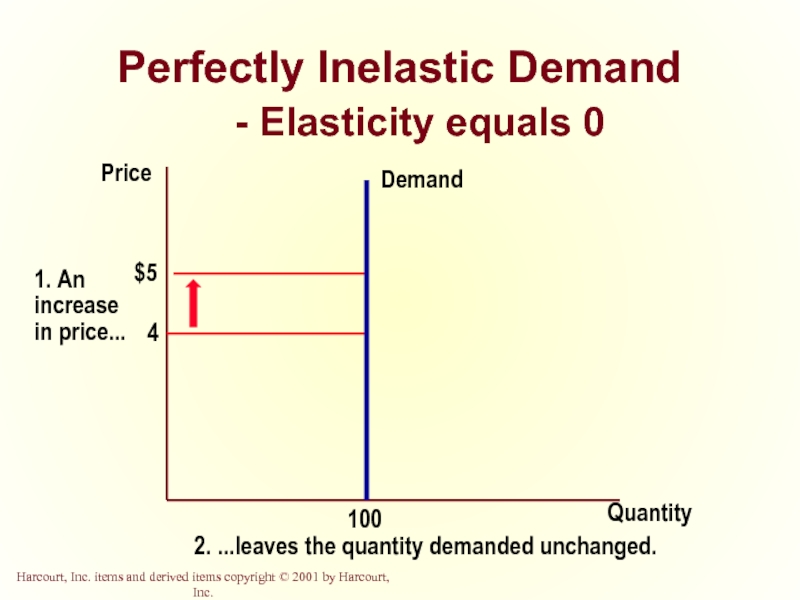
Perfectly Inelastic
Quantity demanded does not respond to price changes.
Perfectly
Quantity demanded changes infinitely with any change in price.
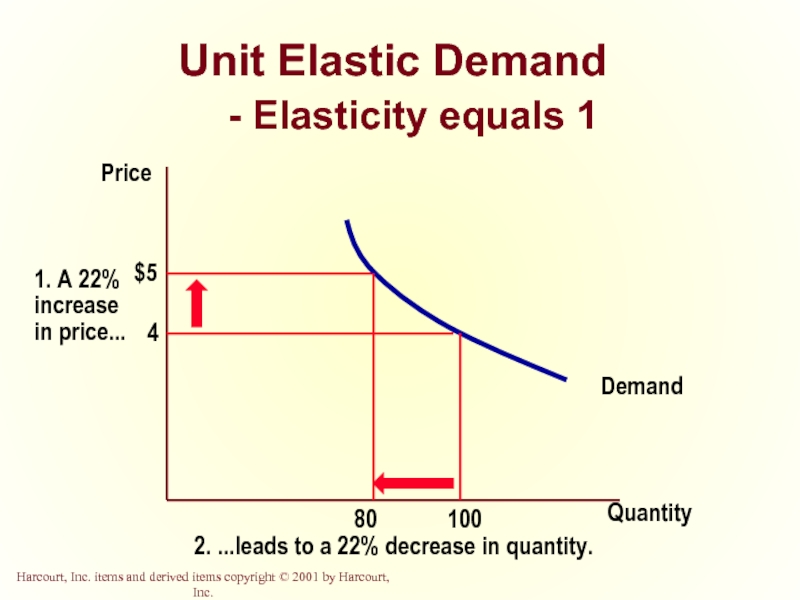
Unit Elastic
Quantity demanded changes by the same percentage as the price.
Слайд 13A Variety of Demand Curves
Because the price elasticity of demand measures
Слайд 14Perfectly Inelastic Demand
- Elasticity equals 0
Quantity
Price
2. ...leaves the quantity demanded unchanged.
Слайд 19Elasticity and Total Revenue
Total revenue is the amount paid by buyers
Computed as the price of the good times the quantity sold.
TR = P x Q
Слайд 21Elasticity and Total Revenue
With an inelastic demand curve, an increase in
Слайд 22Elasticity and Total Revenue: Inelastic Demand
$3
Quantity
0
Price
80
Revenue = $240
Demand
$1
Demand
Quantity
0
Revenue = $100
100
An increase in price from $1 to $3...
…leads to an increase in total revenue from$100 to $240
Слайд 23Elasticity and Total Revenue
With an elastic demand curve, an increase in
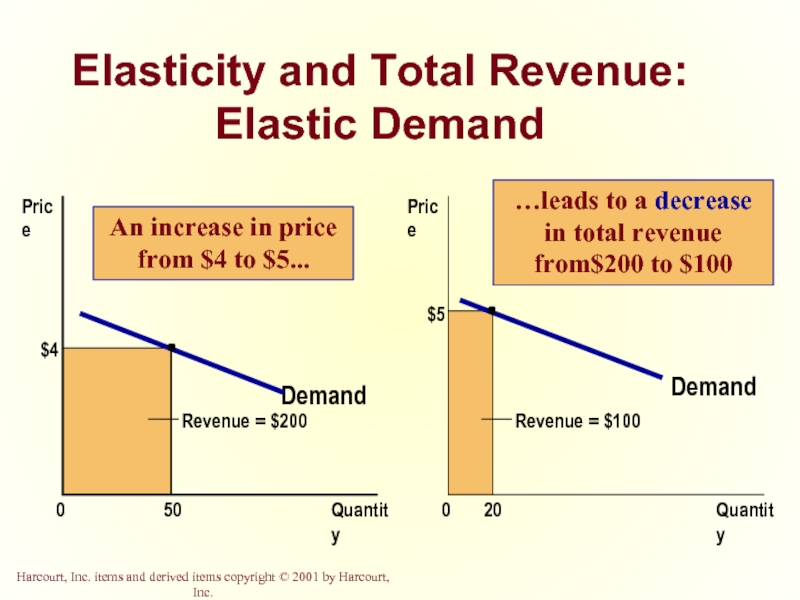
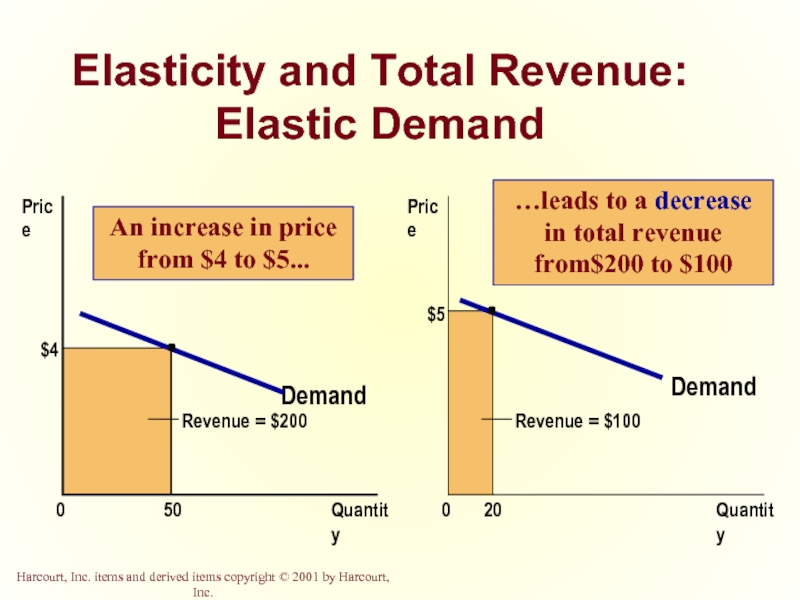
Слайд 24Elasticity and Total Revenue: Elastic Demand
Demand
Quantity
0
Price
$4
50
Demand
Quantity
0
Price
Revenue = $100
$5
20
An increase in
…leads to a decrease in total revenue from$200 to $100
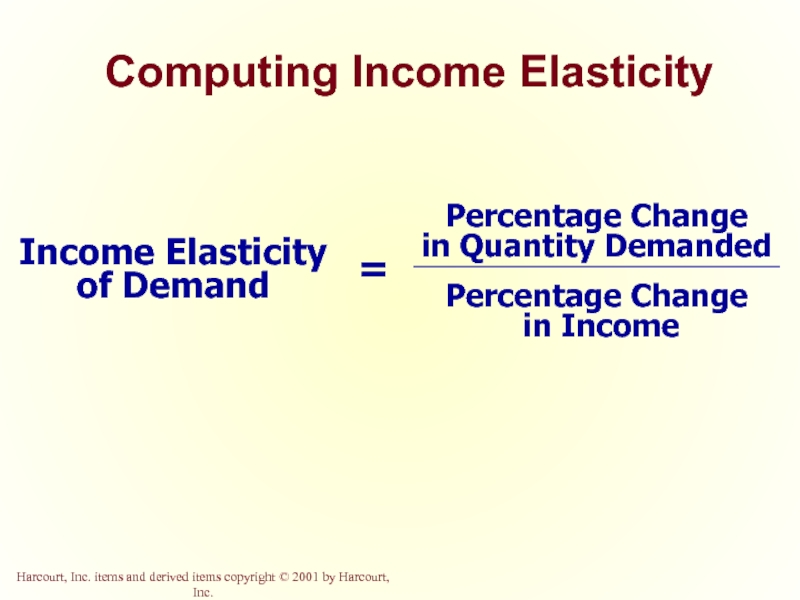
Слайд 26Income Elasticity of Demand
Income elasticity of demand measures how much the
It is computed as the percentage change in the quantity demanded divided by the percentage change in income.
Слайд 28Income Elasticity
- Types of Goods -
Normal Goods
Inferior Goods
Higher income raises the
Слайд 29Income Elasticity
- Types of Goods -
Goods consumers regard as necessities tend
Goods consumers regard as luxuries tend to be income elastic. Examples include sports cars, furs, and expensive foods.
Слайд 30Price Elasticity of Supply
Price elasticity of supply is the percentage change
It is a measure of how much the quantity supplied of a good responds to a change in the price of that good.
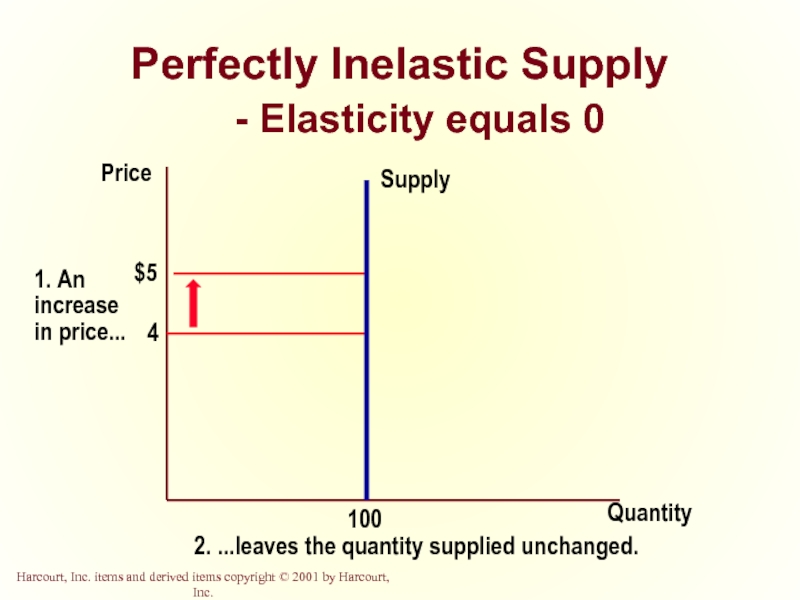
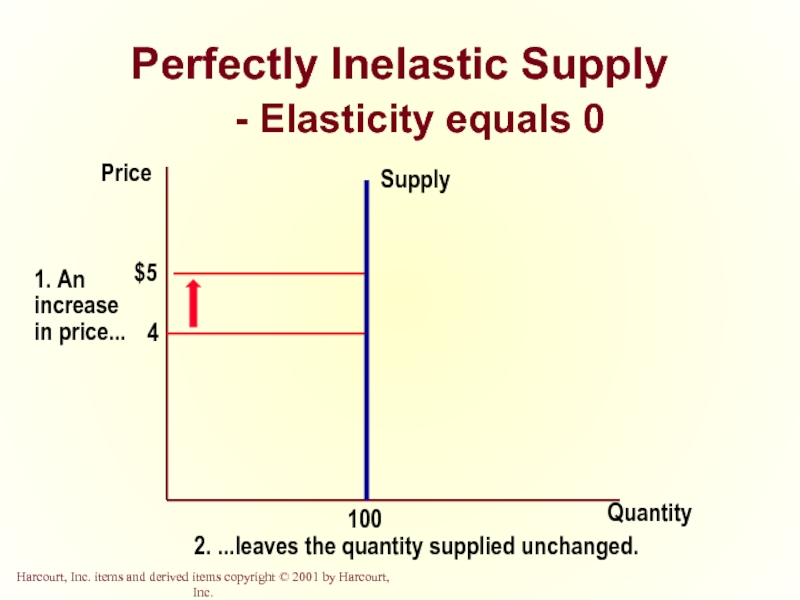
Слайд 33Perfectly Inelastic Supply
- Elasticity equals 0
Quantity
Price
2. ...leaves the quantity supplied unchanged.
Слайд 38Determinants of
Elasticity of Supply
Ability of sellers to change the amount
Beach-front land is inelastic.
Books, cars, or manufactured goods are elastic.
Time period.
Supply is more elastic in the long run.
Слайд 39Computing the Price Elasticity of Supply
The price elasticity of supply is
Слайд 40Application of Elasticity
Can good news for farming be bad news for
What happens to wheat farmers and the market for wheat when university agronomists discover a new wheat hybrid that is more productive than existing varieties?
Слайд 41Application of Elasticity
Examine whether the supply or demand curve shifts.
Determine the
Use the supply-and-demand diagram to see how the market equilibrium changes.
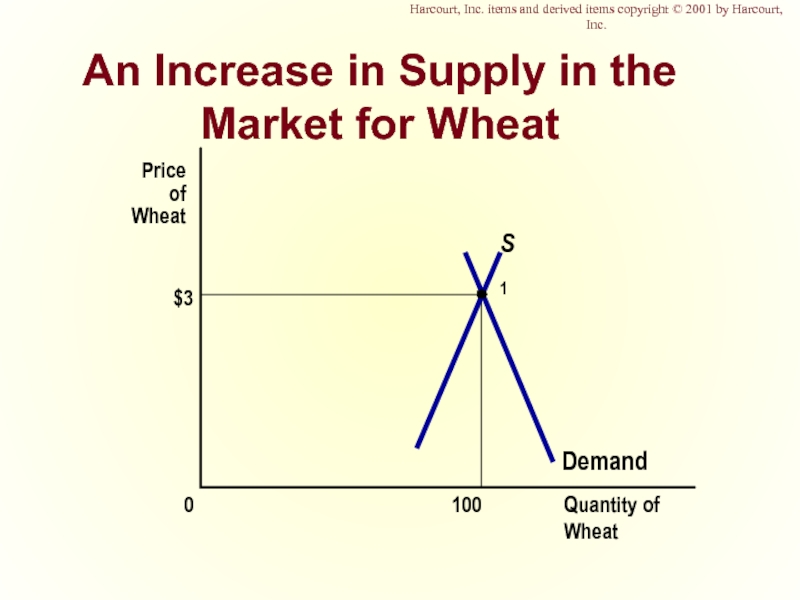
Слайд 42An Increase in Supply in the Market for Wheat
$3
Quantity of Wheat
100
0
Price
Wheat
Demand
S1
Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
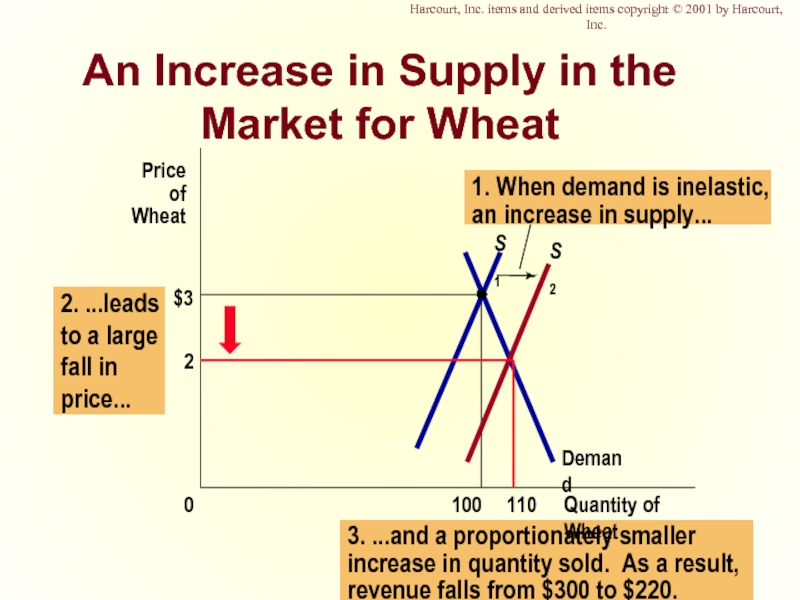
Слайд 433. ...and a proportionately smaller
increase in quantity sold. As a result,
revenue
An Increase in Supply in the Market for Wheat
$3
Quantity of Wheat
100
0
Price of
Wheat
1. When demand is inelastic,
an increase in supply...
Demand
S1
S2
2
110
2. ...leads
to a large
fall in
price...
Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcourt, Inc.
Слайд 46Summary
Price elasticity of demand measures how much the quantity demanded responds
If a demand curve is elastic, total revenue falls when the price rises.
If it is inelastic, total revenue rises as the price rises.
Слайд 47Summary
The price elasticity of supply measures how much the quantity supplied
In most markets, supply is more elastic in the long run than in the short run.