To Understand Society
To Understand Global Affairs
To Be an Informed Citizen
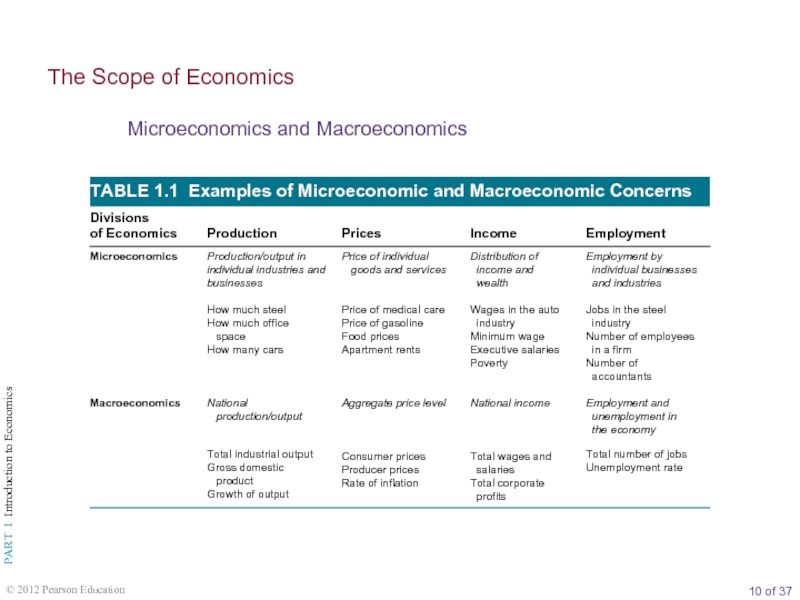
The Scope of Economics
Microeconomics and Macroeconomics
The Diverse Fields of Economics
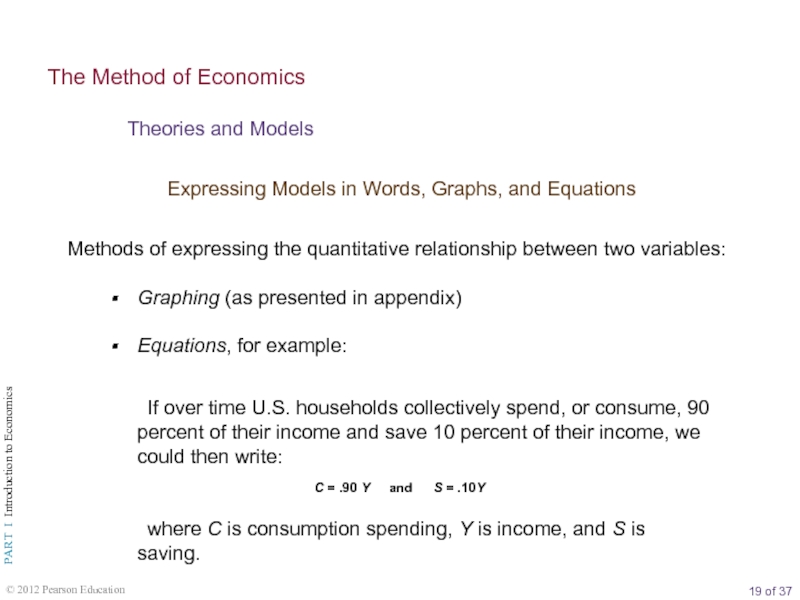
The Method of Economics
Descriptive Economics and Economic Theory
Theories and Models
Economic Policy
An Invitation
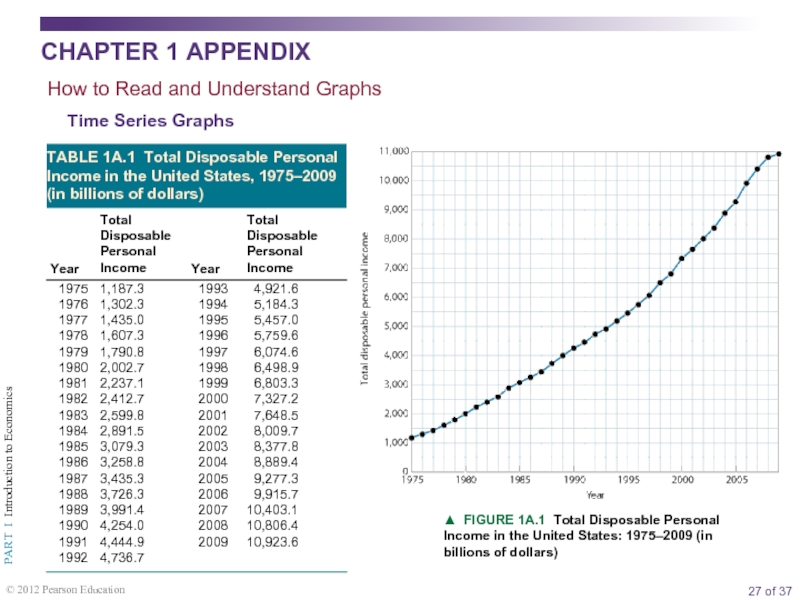
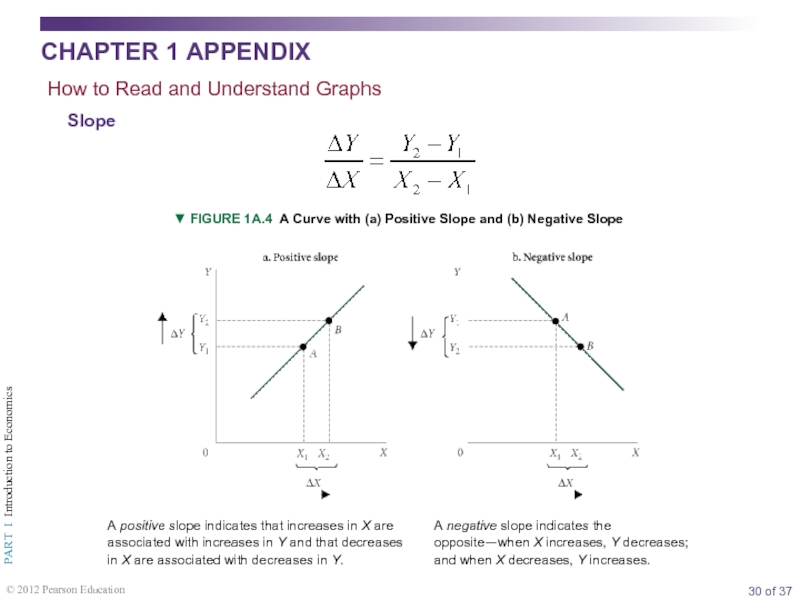
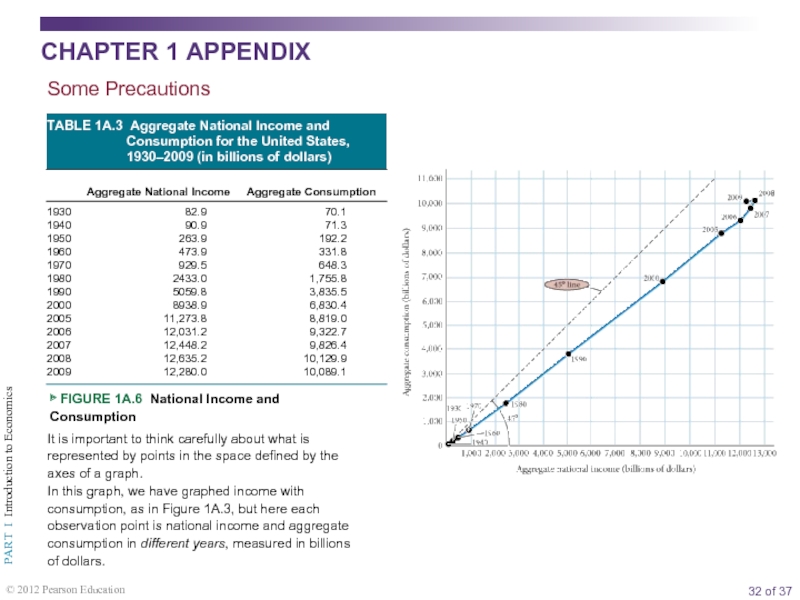
Appendix: How to Read and Understand Graphs